Water Erosion Response to Rainfall Type on Typical Land Use Slopes in the Red Soil Region of Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
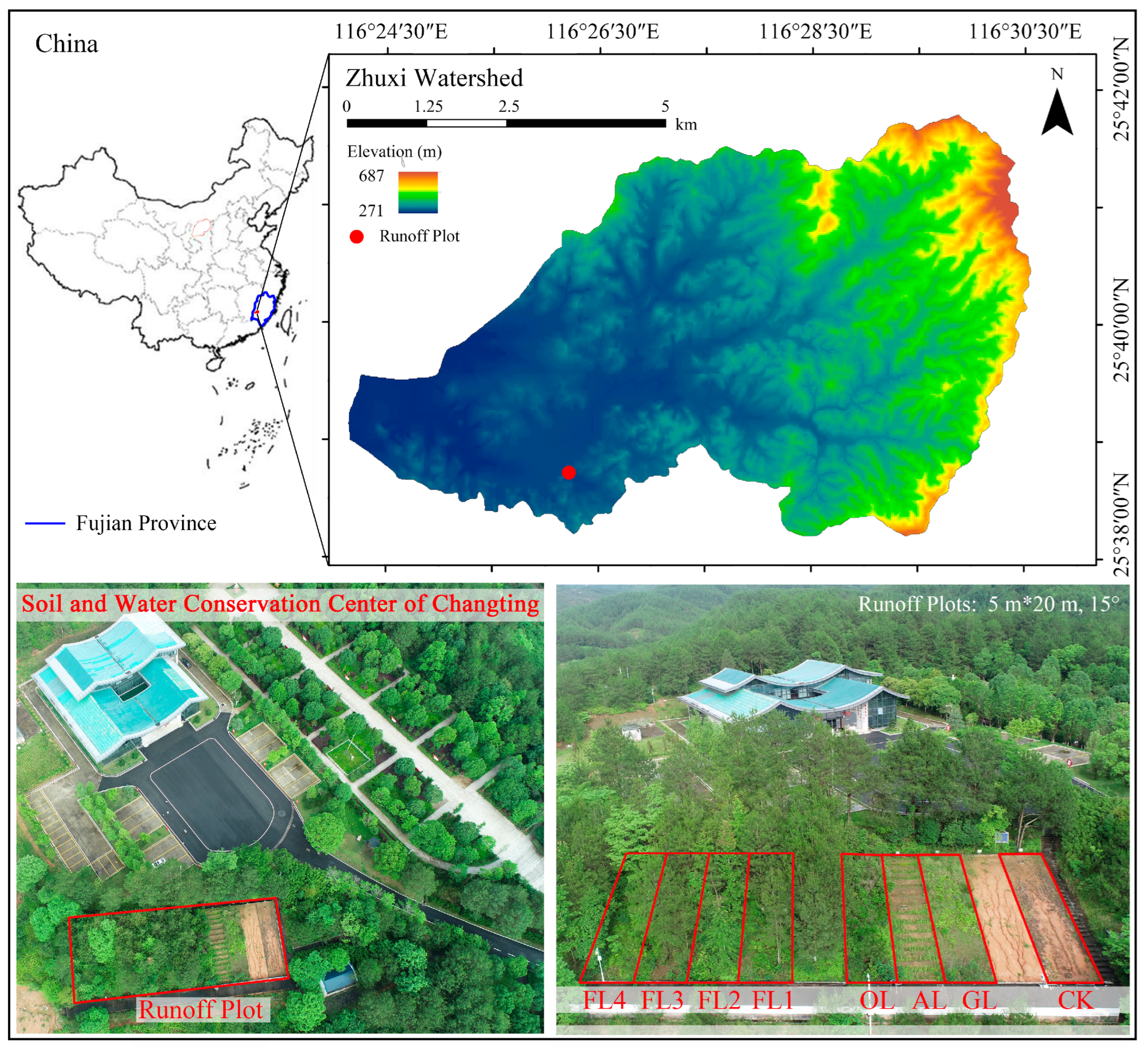
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Plots
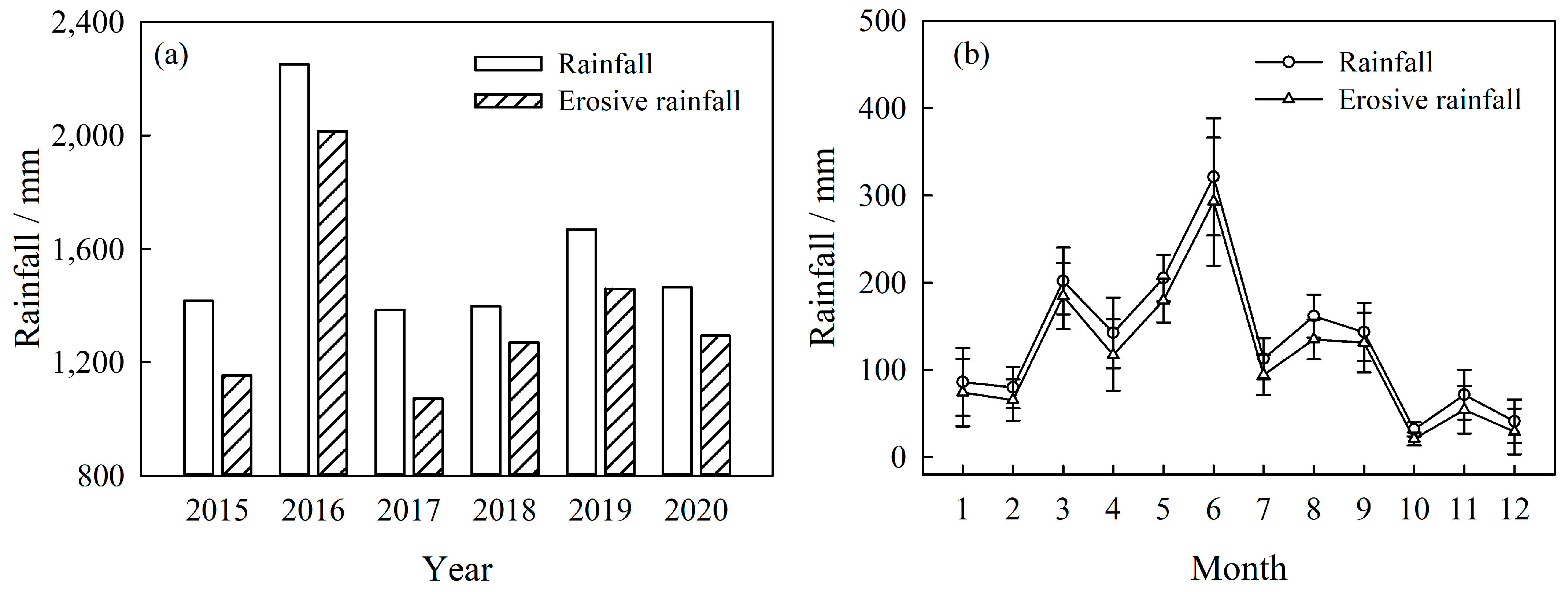
2.2. Rainfall, Runoff, and Soil Erosion Measurements
2.3. Rainfall Threshold of Runoff and Soil Erosion Generation
2.4. Rainfall Classification
2.5. The Ratio between Runoff and Soil Erosion Reduction
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
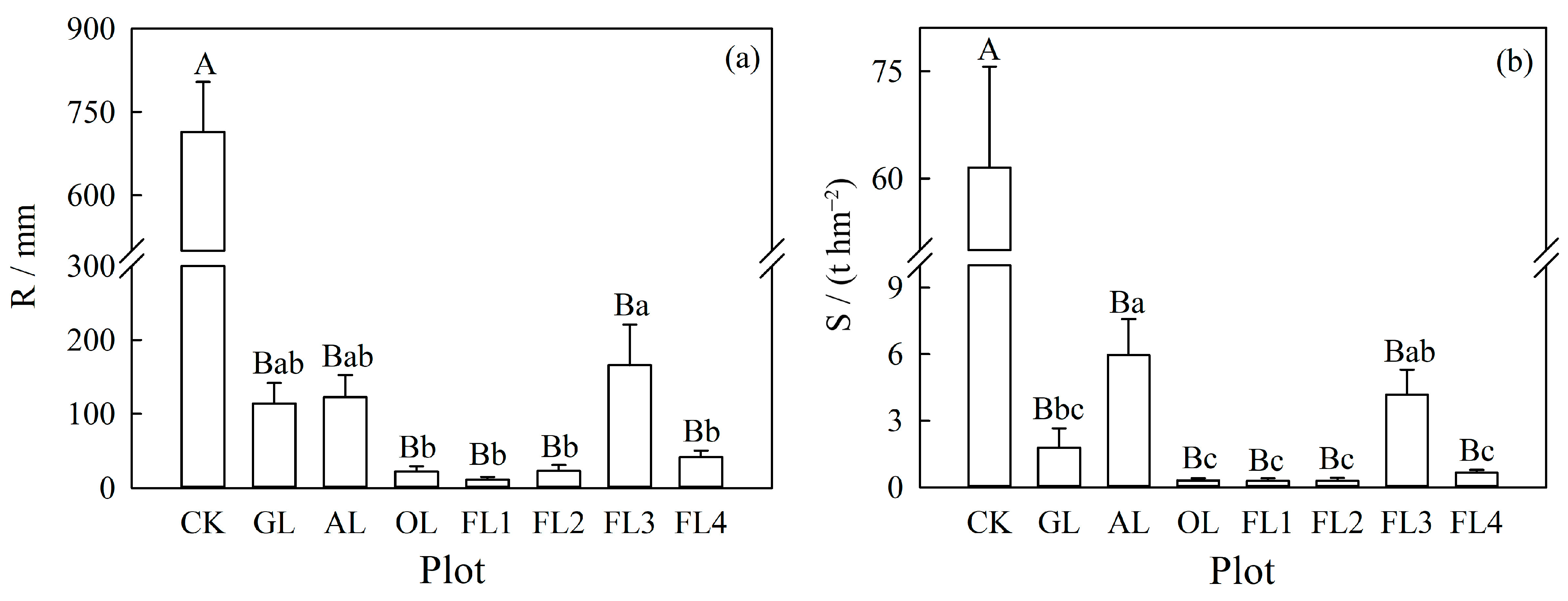
3.1. Runoff and Soil Erosion of Different Land Uses
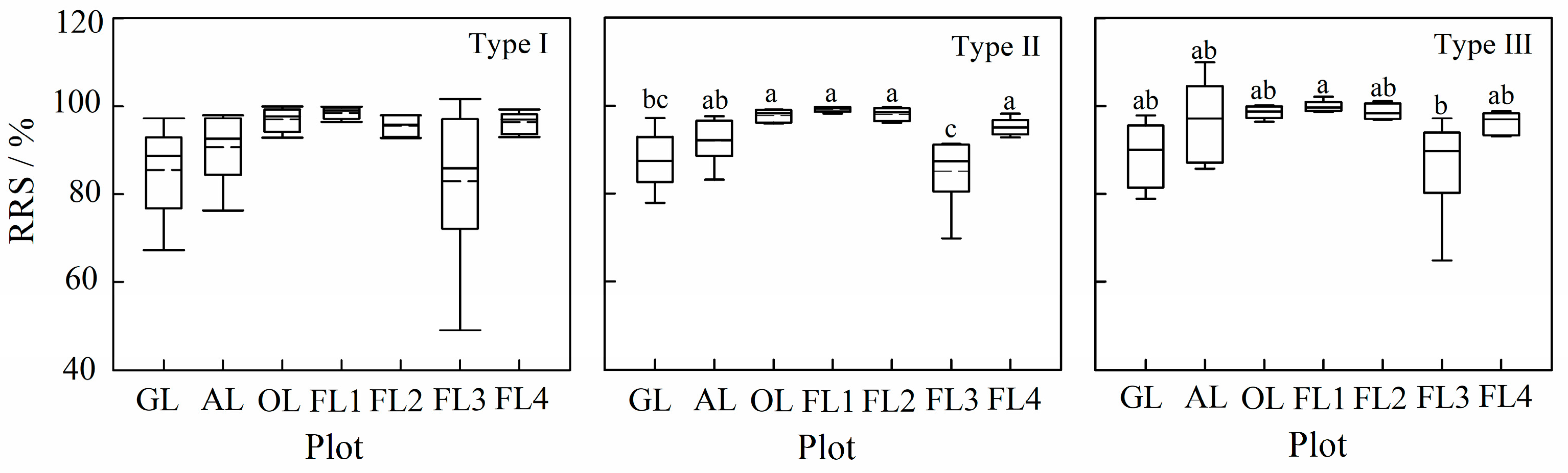
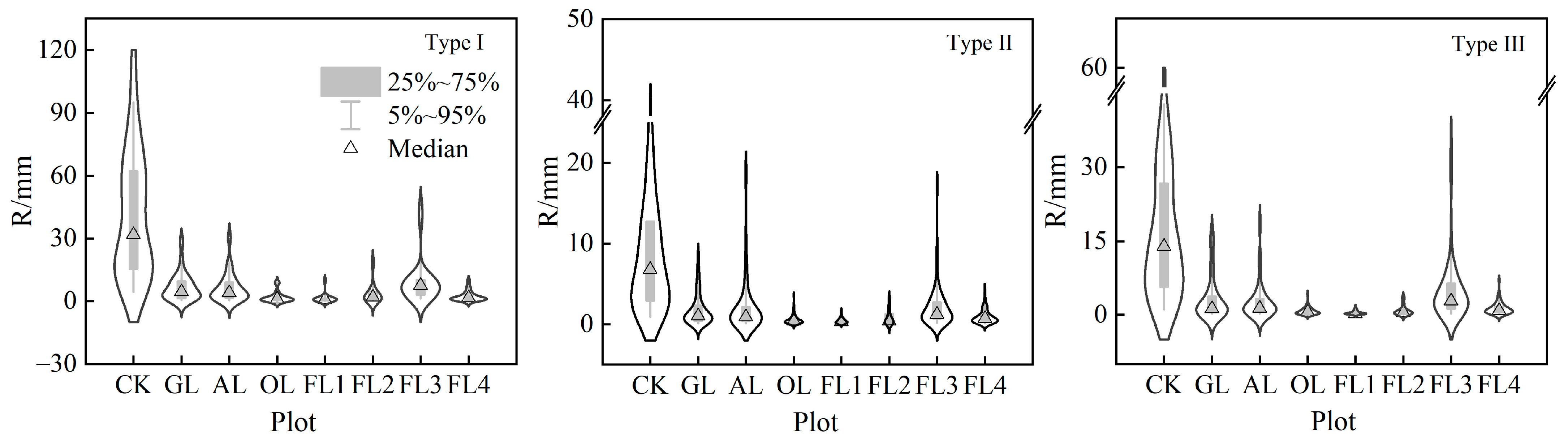
3.2. Variation of Runoff and Soil Erosion among Rainfall Types
3.2.1. Rainfall Types
3.2.2. Runoff and Soil Erosion
3.3. Relationship between Runoff and Soil Erosion for Different Land Uses
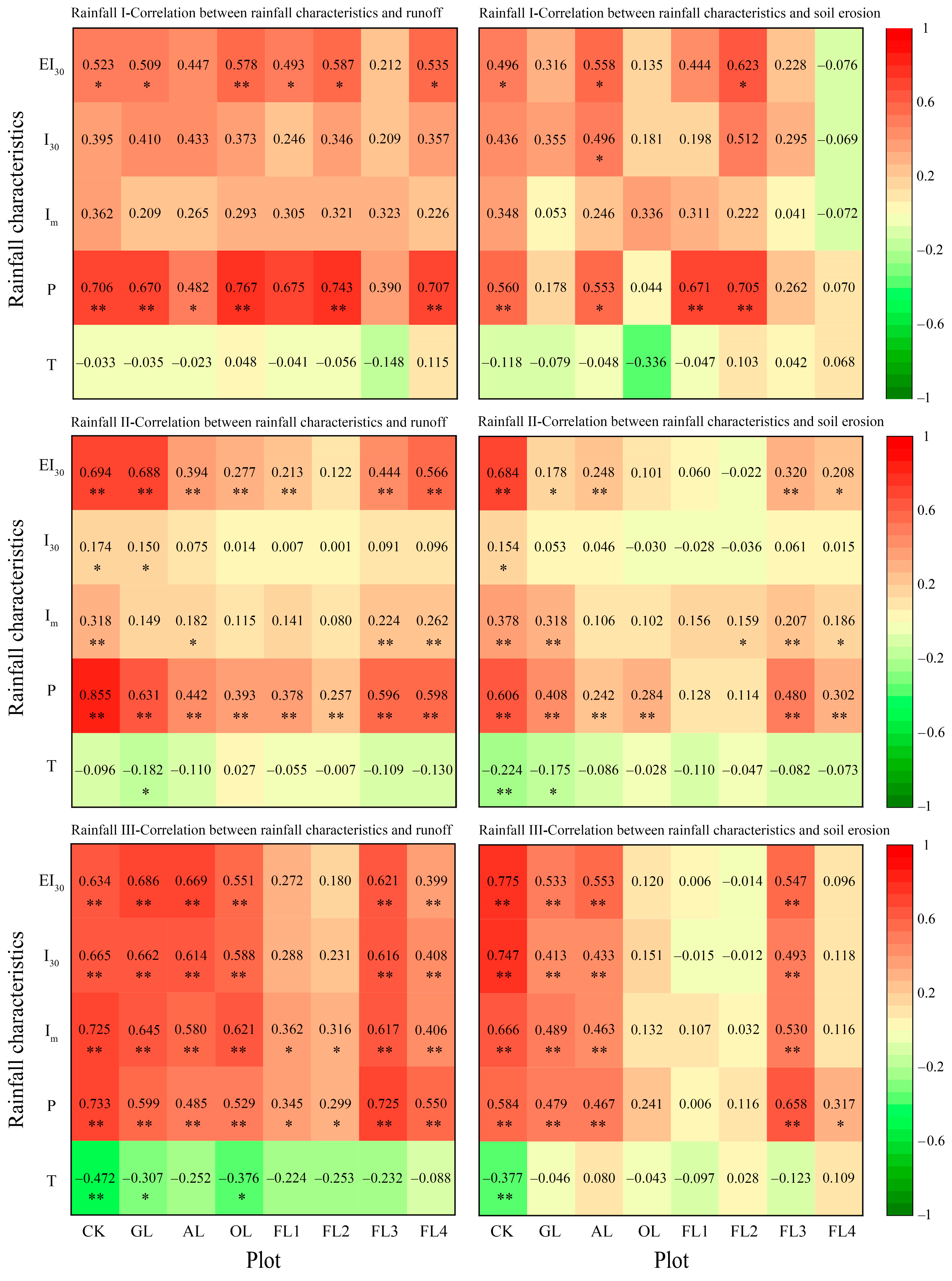
3.4. Effects of Rainfall and Land Use on Runoff and Soil Erosion
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Land Use on Runoff and Soil Erosion
4.2. Effects of Rainfall Type on Runoff and Soil Erosion
4.3. Combination Effects of Land Use and Rainfall on Runoff and Soil Erosion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Beguería, S.; Nadal-Romero, E.N.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Lana-Renault, N.; Yasmina Sanjuán, Y. A meta-analysis of soil erosion rates across the world. Geomorphology 2015, 239, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, Y.J.; Tang, C.J.; Shi, Z.H.; Yang, J. Efficacy of orchard terrace measures to minimize water erosion caused by extreme rainfall in the hilly region of China: Long-term continuous in situ observations. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 278, 111537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrière, N.; Locatelli, B.; Laumonier, Y.; Freycon, V.; Bemoux, M. Soil erosion in the humid tropics: A systematic quantitative review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, H.B.; Li, Z.W.; Liu, C.; Ning, K.; Tang, C.J. How effective are soil and water conservation measures (SWCMs) in reducing soil and water losses in the red soil hilly region of China? A meta-analysis of field plot data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Soil conservation and ecosystem services. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014, 2, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.D. Effects of terracing practices on water erosion control in China: A meta-analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.Z.; Zhang, G.H.; Wang, H.X.; Yang, H.Y.; Zhang, B.J.; Wang, L.L. Effectiveness of typical plant communities in controlling runoff and soil erosion on steep gully slopes on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavinia, M.; Saleh, F.N.; Asadi, H. Effects of rainfall patterns on runoff and rainfall-induced erosion. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, J.P.; Ni, C.S.; Wang, S.; Xie, D.T. Effect of natural rainfall on the migration characteristics of runoff and sediment on purple soil sloping cropland during different planting stages. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 3064–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, W.S.; Seitz, S.; Oliveira, L.F.C.; Carvalho, D.F. Duration and intensity of rainfall events with the same erosivity change sediment yield and runoff rates. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.L.; Han, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. Assessment of Erosion Characteristics in Purple and Yellow Soils Using Simulated Rainfall Experiments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Liang, Y.; Gao, G.Y.; Dunkerley, D.; Fu, B.J. Quantifying the effects of rainfall intensity fluctuation on runoff and soil loss: From indicators to models. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.D.; Fu, B.J.; Huang, Z.L.; Wu, D.P.; Gui, L.D. The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.P.; Abla, M.; Lü, D.; Yan, R.; Ren, Q.F.; Ren, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, W.H.; Lin, P.F.; et al. Effects of vegetation and rainfall types on surface runoff and soil erosion on steep slopes on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 170, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wei, W.; Pan, D.L. Effects of rainfall and terracing-vegetation combinations on water erosion in a loess hilly area, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.Y.; Yu, X.X.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, L.H.; Zheng, W.G.; Yang, Y.H.; Tang, Z.X. Effects of soil and water conservation management and rainfall types on runoff and soil loss for a sloping area in North China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2117–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, A.A.; Wright, D.B.; Stewart, R.D.; LoBue, A.C. The role of rainfall temporal and spatial averaging in seasonal simulations of the terrestrial water balance. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2531–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.S.; Guo, S.L.; Qian, S.N.; Wang, Z.L.; Lai, C.G.; Li, J.; Liu, P. Long-range precipitation forecast based on multipole and preceding fluctuations of sea surface temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 8024–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Wang, S.S.; Huang, J.P.; He, Y.L.; Ren, Y. The precipitation-recycling process enhanced extreme precipitation in Xinjiang, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.H.; Zhang, K.L. Interaction effects of rainfall and soil factors on runoff, erosion, and their predictions in different geographic regions. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, S.J. Effects of land use, land cover and rainfall regimes on the surface runoff and soil loss on karst slopes in southwest China. Catena 2012, 90, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.W.; Xiao, H.B.; Ke, N.; Tang, C.J. Effects of land use and land cover on soil erosion control in southern China: Implications from a systematic quantitative review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 282, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.Z.; Zhao, X.; Liang, S.L.; Zhao, J.C.; Xu, P.P.; Wu, D.H. Quantitatively Assessing and Attributing Land Use and Land Cover Changes on China’s Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Gao, G.Y.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Wu, X.; Fu, B.J. The effects of vegetation on runoff and soil loss: Multidimensional structure analysis and scale characteristics. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, H.B.; Li, Z.W.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.Y.; Wang, L.X.; Tang, C.J. Threshold effects of vegetation coverage on soil erosion control in small watersheds of the red soil hilly region in China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 132, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.Q.; Sun, R.H.; Chen, L.D. A global comparison of soil erosion associated with land use and climate type. Geoderma 2019, 343, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.C.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Zhao, D. Modeling vegetation coverage and soil erosion in the Loess Plateau Area of China. Ecol. Model. 2006, 198, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, C.Q.; Yang, J.Y.; Yue, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.Z. Analysis of spatiotemporal heterogeneity and influencing factors of soil erosion in a typical erosion zone of the southern red soil region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Zha, X.; Bai, Y.H.; Wang, L.Y. Evaluation of soil erosion vulnerability on the basis of exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity: A case study in the Zhuxi watershed, Changting, Fujian Province, Southern China. Catena 2019, 177, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis, 2nd ed.; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Jiao, J.Y.; Dang, W.Q.; Cao, W. The Thresholds of Sediment-Generating Rainfall from Hillslope to Watershed Scales in the Loess Plateau, China. Water 2019, 11, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A. Practical thresholds for separating erosive and non-erosive storms. Trans. ASABE 2002, 45, 1843–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, C.J.; Chen, L.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, L.Y. Effects of rainfall patterns and land cover on the subsurface flow generation of sloping Ferralsols in southern China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 0182706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Lü, Y.H.; Fu, B.J.; Comber, A.J.; Harris, P. Quantifying the effect of ecological restoration on runoff and sediment yields: A meta-analysis for the Loess Plateau of China. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2017, 41, 753–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Wang, Z.G.; Dong, Y.F.; Yang, Z.Q.; Govers, G. How soil erosion and runoff are related to land use, topography and annual precipitation: Insights from a meta-analysis of erosion plots in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Song, J.X.; Wang, Y.R.; Deng, W.J.; Liu, Y.F. Effects of land use on slope runoff and soil loss in the Loess Plateau of China: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.D.; Deng, J.C.; Gu, C.J.; Mu, X.M.; Gao, P.; Gao, J.J. Effect of shrub-grass vegetation coverage and slop gradient on runoff and sediment yield under simulated rainfall. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Franch-Pardo, I.; Úbeda, X.; Novara, A.; López-Vicente, M.; Popović, Z.; Pulido, M. The role of plant species on runoff and soil erosion in a Mediterranean shrubland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.X.; Yang, Y.; An, S.S.; Zhu, Z.L. Effects of different vegetation restoration measures on soil aggregate stability and erodibility on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2020, 185, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, G.C.; Ma, T.T.; Chen, L.; Cheng, Y.T.; Li, P.; Li, Z.B.; Zhang, Y.X. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil aggregates, organic carbon, and nitrogen in the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2023, 231, 107340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geißler, C.; Bohnke, M.; Bruelheide, H.; Shi, X.; Scholten, T. Splash erosion potential under tree canopies in subtropical SE China. Catena 2012, 91, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.Y. Responses of Runoff and Soil Loss on Slopes to Land Use Management and Rainfall Characteristics in Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anh, P.T.Q.; Gomi, T.; MacDonald, L.H.; Mizugaki, S.; Khoa, P.V.; Furuichi, T. Linkages among land use, macronutrient levels, and soil erosion in northern Vietnam: A plot-scale study. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.J.; Zhang, G.H.; Yang, H.Y.; Wang, H. Soil resistance to flowing water erosion of seven typical plant communities on steep gully slopes on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2019, 173, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, W.X.; Zhou, M.; Zhuo, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, F.S.; Huang, Y.H.; Lin, J.S. Runoff and sediment characteristics of a typical watershed after continuous soil erosion control in the red soil region of Southern China. Catena 2023, 233, 107484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.G.; Adam, M.A. The impact of vegetative cover type on runoff and soil erosion under different land uses. Catena 2010, 81, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.F.; Wang, L.; Shi, Z.H. Runoff and soil erosion of field plots in a subtropical mountainous region of China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Moya, J.; Alvarado, A.; Forsythe, W.; Ramírez, L.; Algeet-Abarquero, N.; Marchamalo-Sacristán, M. Soil erosion under teak (Tectona grandis L.f.) plantations: General patterns, assumptions and controversies. Catena 2014, 123, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Tan, Q.Y.; Liu, G.B.; Xu, M.X. Impacts of mixed forests on controlling soil erosion in China. Catena 2022, 213, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Dunkerley, D.; López-Vicente, M.; Shi, Z.H.; Wu, G.L. Trade-off between surface runoff and soil erosion during the implementation of ecological restoration programs in semiarid regions: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.G.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Li, F.R.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.K. Response of runoff and soil loss to reforestation and rainfall type in red soil region of southern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Jia, F.Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.D.; Zhang, H.D.; Yang, Y. Effects of surficial condition and rainfall intensity on runoff in a loess hilly area, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.G.; Ma, J.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, Z.B.; Ma, B. The influence of wheat straw mulching and straw length on infiltration, runoff and soil loss. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, 14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.G.; Xie, S.H.; Li, Y.; Mo, M.H.; Nie, X.F. Analysis of erosive rainfall distribution and sediment yield on long-term field monitoring sloping bare land of red soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 129–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Jiao, J.Y.; Tang, B.Z.; Cao, B.T.; Li, H. Response of runoff and soil erosion to erosive rainstorm events and vegetation restoration on abandoned slope farmland in the Loess Plateau region, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.L.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Ma, Y.S.; Wu, G.L. Regulation of alpine meadow patch coverage on runoff and sediment under natural rainfall on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.J.; Shao, Q.Q. Spatial pattern of soil erosion drivers and the contribution rate of human activities on the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2015: A boundary line from northeast to southwest. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Y.; Qin, Q.S.; Geng, H.J.; Zheng, F.L.; Zhang, X.C.J.; Li, G.F.; Xu, X.Z.; Zhang, J.Q. Effects of upslope inflow rate, tillage depth, and slope gradients on hillslope erosion processes and hydrodynamic mechanisms. Catena 2023, 228, 107189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Deng, D.P.; Liao, Q.D.; Ying, B. Analysis on the influence of rainfall characteristics on soil and water loss in rocky desertification region. Carbonates Evaporites 2021, 36, 36–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, S.; Fowler, H.J.; Evans, J.P.; Alexander, L.V.; Berg, P.; Johnson, F.; Kendon, E.J.; Lenderink, G.; Roberts, N.M. Future changes to the intensity and frequency of short-duration extreme rainfall. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 522–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Brazier, R.E. Dealing with Uncertainty in Erosion Model Predictions; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, W.W.; Ding, J.Y.; Ferreira, C.S.S. Soil erodibility for water and wind erosion and its relationship to vegetation and soil properties in China’s drylands. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunovic, I.; Viduka, A.; Magdic, I.; Telak, L.J.; Francos, M.; Pereira, P. Agricultural and Forest Land-Use Impact on Soil Properties in Zagreb Periurban Area (Croatia). Agronomy 2020, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.S.; Zhu, D.Y.; Wu, Z.G.; Cao, Z. Extreme rainfall erosivity: Research advances and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 917, 170425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Plot | Soil Bulk Density (g/cm3) | pH | Soil Organic Matter (%) | Soil Particle Composition (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–0.001 | 0.001–0.01 | 0.01–0.05 | 0.05–1 | ||||
| CK | 1.54 | 4.44 | 0.15 | 4.52 | 25.66 | 34.09 | 35.73 |
| GL | 1.27 | 4.78 | 0.30 | 3.48 | 26.95 | 37.12 | 32.45 |
| AL | 1.68 | 4.35 | 0.18 | 3.28 | 34.43 | 31.24 | 31.05 |
| OL | 1.43 | 4.30 | 0.34 | 2.45 | 28.86 | 35.58 | 33.11 |
| FL1 | 1.35 | 4.09 | 0.29 | 2.52 | 29.62 | 32.33 | 35.53 |
| FL2 | 1.46 | 4.17 | 0.27 | 2.96 | 28.05 | 36.28 | 32.71 |
| FL3 | 1.31 | 4.54 | 0.40 | 2.87 | 26.11 | 37.22 | 33.80 |
| FL4 | 1.36 | 4.04 | 0.28 | 2.73 | 23.38 | 38.11 | 35.78 |
| Plot | Tree | Undergrowth Vegetation | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Height (cm) | Basal Diameter (cm) | Crown Diameter (cm) | Canopy Density (%) | Types | Species | Coverage (%) | Height (cm) | Coverage × Height | |
| CK | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| GL | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Herbaceous | Paspalun notatum | 86 ± 11.34 | 6.5 ± 0.67 | -- |
| AL | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Crops | Sweet potato | 64 ± 2.64 | 14 ± 0.98 | -- |
| OL | Myrica rubra | 365 ± 3.50 | 8.9 ± 0.20 | 293 ± 1.67 | 47 ± 5.16 | Herbaceous | Dicranopteris dichotoma, Cynodon dactylon | 70 ± 19.77 | 24 ± 2.32 | 1715 ± 233.64 b |
| FL1 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | Shrub Herbaceous | Paspalum wettsteinii, Lespedeza bicolor | 85 ± 12.99 | 37 ± 19.97 | 3315 ± 867.14 a |
| FL2 | Liquidambar formosana, Schima superba | 668 ± 6.83 | 6.1 ± 0.48 | 326 ± 3.25 | 65 ± 8.37 | Shrub Herbaceous | Miscanthus floridulus, Lespedeza bicolor | 82 ± 25.69 | 15 ± 1.04 | 1224 ± 170.50 b |
| FL3 | Pinus massoniana | 743 ± 5.67 | 5.8 ± 0.25 | 392 ± 1.55 | 65 ± 8.37 | Herbaceous | Paspalum wettsteinii | 13 ± 1.56 | 5.2 ± 0.64 | -- |
| FL4 | Pinus massoniana | 777 ± 6.06 | 11.6 ± 0.58 | 499 ± 5.50 | 52 ± 13.29 | Shrub Herbaceous | Paspalum wettsteinii, Lespedeza bicolor | 75 ± 23.00 | 24 ± 1.97 | 1859 ± 267.80 b |
| Variables | Time Scales | CK | GL | AL | OL | FL1 | FL2 | FL3 | FL4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC % | Annual | 0.566 ± 0.149 A | 0.088 ± 0.022 Ba | 0.094 ± 0.050 Ba | 0.021 ± 0.012 Bb | 0.014 ± 0.009 Bb | 0.028 ± 0.014 Bb | 0.118 ± 0.056 Ba | 0.035 ± 0.016 Bb |
| Type I | 0.505 ± 0.148 A | 0.075 ± 0.030 Bab | 0.077 ± 0.026 Bab | 0.019 ± 0.017 Bc | 0.014 ± 0.014 Bc | 0.032 ± 0.024 Bbc | 0.110 ± 0.062 Ba | 0.026 ± 0.017 Bbc | |
| Type II | 0.544 ± 0.093 A | 0.102 ± 0.030 Ba | 0.114 ± 0.083 Ba | 0.023 ± 0.015 Bb | 0.015 ± 0.008 Bb | 0.036 ± 0.018 Bb | 0.126 ± 0.060 Ba | 0.045 ± 0.024 Bb | |
| Type III | 0.476 ± 0.100 A | 0.077 ± 0.036 Bab | 0.068 ± 0.031 Bab | 0.014 ± 0.007 Bc | 0.011 ± 0.008 Bc | 0.019 ± 0.010 Bc | 0.109 ± 0.060 Ba | 0.033 ± 0.017 Bbc | |
| SLC t·km−2·mm−1 | Annual | 4.050 ± 1.983 A | 0.203 ± 0.260 Bb | 0.527 ± 0.415 Ba | 0.034 ± 0.032 Bb | 0.039 ± 0.027 Bb | 0.042 ± 0.029 Bb | 0.281 ± 0.131 Bab | 0.063 ± 0.029 Bb |
| Type I | 2.946 ± 1.213 A | 0.052 ± 0.081 Bb | 0.197 ± 0.081 Ba | 0.016 ± 0.007 Bb | 0.017 ± 0.008 Bb | 0.018 ± 0.004 Bb | 0.235 ± 0.097 Ba | 0.033 ± 0.034 Bb | |
| Type II | 5.760 ± 2.207 A | 0.289 ± 0.431 Bab | 0.691 ± 0.658 Ba | 0.047 ± 0.034 Bb | 0.056 ± 0.034 Bb | 0.073 ± 0.049 Bb | 0.391 ± 0.207 Bab | 0.081 ± 0.035 Bb | |
| Type III | 3.342 ± 1.524 A | 0.136 ± 0.229 Bab | 0.300 ± 0.128 Ba | 0.022 ± 0.014 Bb | 0.033 ± 0.021 Bb | 0.026 ± 0.014 Bb | 0.267 ± 0.105 Ba | 0.047 ± 0.024 Bb |
| Land Use | Project | P (mm) | Im (mm·h−1) | I30 (mm·h−1) | EI30 (MJ·mm·hm−2·h−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold | MI | Threshold | MI | Threshold | MI | Threshold | MI | ||
| GL | R | 11.00 | 0.23 | 1.20 | 0.21 | 8.06 | 0.23 | 21.86 | 0.26 |
| S | 12.20 | 0.26 | 1.20 | 0.23 | 8.18 | 0.27 | 28.10 | 0.28 | |
| AL | R | 11.80 | 0.21 | 1.10 | 0.17 | 7.10 | 0.19 | 18.07 | 0.20 |
| S | 12.00 | 0.21 | 1.00 | 0.17 | 6.00 | 0.16 | 17.28 | 0.24 | |
| OL | R | 11.00 | 0.31 | 1.10 | 0.36 | 8.06 | 0.34 | 25.40 | 0.28 |
| S | 8.50 | 0.39 | 0.90 | 0.38 | 5.30 | 0.38 | 13.50 | 0.33 | |
| FL1 | R | 12.20 | 0.39 | 1.10 | 0.47 | 6.04 | 0.46 | 19.65 | 0.37 |
| S | 9.20 | 0.46 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 4.06 | 0.53 | 12.27 | 0.44 | |
| FL2 | R | 12.50 | 0.46 | 1.40 | 0.49 | 8.06 | 0.49 | 25.40 | 0.42 |
| S | 8.50 | 0.57 | 0.90 | 0.58 | 5.03 | 0.58 | 13.06 | 0.51 | |
| FL3 | R | 11.00 | 0.20 | 1.10 | 0.18 | 6.04 | 0.20 | 17.07 | 0.23 |
| S | 9.60 | 0.19 | 0.90 | 0.17 | 5.03 | 0.18 | 12.96 | 0.19 | |
| FL4 | R | 11.00 | 0.24 | 1.20 | 0.23 | 6.04 | 0.24 | 13.06 | 0.23 |
| S | 8.50 | 0.27 | 0.90 | 0.23 | 5.00 | 0.23 | 10.50 | 0.24 | |
| Rainfall Type | No. | Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (min) | P (mm) | Im (mm/h) | I30 (mm/h) | EI30 (MJ·mm·hm−2·h−1) | ||
| Type I | 24 | 2220.00 ± 785.90 A | 83.60 ± 23.80 A | 2.65 ± 1.36 B | 28.28 ± 17.26 | 584.71 ± 518.68 A |
| Type II | 218 | 376.35 ± 270.06 C | 16.71 ± 9.33 C | 5.76 ± 8.03 A | 21.65 ± 43.11 | 102.09 ± 168.33 B |
| Type III | 74 | 1367.57 ± 544.03 B | 33.43 ± 15.38 B | 1.86 ± 1.50 B | 15.87 ± 15.91 | 160.65 ± 245.87 B |
| Type IV | 4 | 1317.50 ± 406.95 | 34.75 ± 18.80 | 7.81 ± 4.14 | 1317.50 ± 406.95 | 57.82 ± 56.00 |
| Plot | Type I | Type II | Type III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Function | R2 | p | Regression Function | R2 | p | Regression Function | R2 | p | |
| CK | S = 0.053R1.010 | 0.563 | <0.01 | S = 0.111R1.019 | 0.472 | <0.01 | S = 0.005R1.757 | 0.578 | <0.01 |
| GL | S = 0.006R0.567 | 0.352 | <0.01 | S = 0.019R0.998 | 0.146 | <0.01 | S = 0.010R0.902 | 0.149 | <0.01 |
| AL | S = 0.037R0.840 | 0.738 | <0.01 | S = 0.040R1.241 | 0.503 | <0.01 | S = 0.053R0.756 | 0.641 | <0.01 |
| OL | S = 0.012R0.225 | 0.284 | <0.01 | S = 0.016R0.498 | 0.425 | <0.01 | S = 0.010R0.109 | 0.523 | <0.01 |
| FL1 | S = 0.015R0.674 | 0.902 | <0.01 | S = 0.027R0.692 | 0.518 | <0.01 | S = 0.020R0.467 | 0.412 | <0.01 |
| FL2 | S = 0.012R0.341 | 0.930 | <0.01 | S = 0.019R0.456 | 0.542 | <0.01 | S = 0.011R0.006 | 0.606 | <0.01 |
| FL3 | S = 0.040R0.733 | 0.554 | <0.01 | S = 0.039R0.775 | 0.645 | <0.01 | S = 0.033R0.782 | 0.697 | <0.01 |
| FL4 | S = 0.014R0.328 | 0.460 | <0.01 | S = 0.020R0.540 | 0.438 | <0.01 | S = 0.013R0.957 | 0.582 | <0.01 |
| Factors | R | S | RC | SLC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | F | p | |
| Land use | 38.259 | <0.01 | 26.378 | <0.01 | 164.753 | <0.01 | 80.672 | <0.01 |
| Rainfall type | 6.043 | <0.01 | 7.510 | <0.01 | 2.636 | 0.076 | 7.367 | <0.01 |
| Land use × Rainfall type | 1.867 | <0.05 | 4.845 | <0.01 | 0.272 | 0.996 | 3.814 | <0.01 |
| Region | Rainfall (mm) | Runoff (mm) | Soil Erosion (t·km−2·a−1) | Reference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | AL | SL | GL | OL | FL | BL | AL | SL | GL | OL | FL | ||||
| China | -- | 129.1 | 66.6 | -- | 72.4 | 90.0 | 45.2 | 5435 | 2678 | -- | 644 | 820 | 151 | Zhao et al., 2022 [36] | |
| Loess Plateau, China | Cold and arid regions | 175.4 | 67.1 | 57.4 | 12.2 | 8.3 | -- | 17.4 | 8740 | 5440 | 680 | 1930 | -- | 1120 | Zhang et al., 2021 [37] |
| Semi-arid region | 348.2 | 93.7 | 97.2 | 18.6 | 10.4 | -- | 29.3 | 10,520 | 5580 | 2070 | 1960 | -- | 2670 | ||
| Semi-humid region | 537.5 | 127.6 | 124.5 | 26.7 | 12.8 | -- | 34.9 | 13,410 | 7690 | 2340 | 2410 | -- | 3560 | ||
| Red soil region, China | 1300–2000 | 434.1 | 110.9 | 214.2 | 152.0 | 110.9 | 164.0 | 6165 | 1428 | 607 | 605 | 1649 | 1175 | Chen et al., 2021 [23] | |
| 1695.5 | 714.3 | 122.6 | 11.3 | 114.1 | 22.4 | 18.1–165.7 | 6153 | 596 | 30 | 178 | 31 | 27–316 | Present study | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J. Water Erosion Response to Rainfall Type on Typical Land Use Slopes in the Red Soil Region of Southern China. Water 2024, 16, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081076
Wang H, Wang X, Yang S, Zhang Z, Jiang F, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Lin J. Water Erosion Response to Rainfall Type on Typical Land Use Slopes in the Red Soil Region of Southern China. Water. 2024; 16(8):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081076
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, He, Xiaopeng Wang, Shuncheng Yang, Zhi Zhang, Fangshi Jiang, Yue Zhang, Yanhe Huang, and Jinshi Lin. 2024. "Water Erosion Response to Rainfall Type on Typical Land Use Slopes in the Red Soil Region of Southern China" Water 16, no. 8: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081076
APA StyleWang, H., Wang, X., Yang, S., Zhang, Z., Jiang, F., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., & Lin, J. (2024). Water Erosion Response to Rainfall Type on Typical Land Use Slopes in the Red Soil Region of Southern China. Water, 16(8), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081076






