Effects of Packing Media and the Insertion of Vegetation on the Performance of Biological Trickling Filters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Unit
2.2. Operational Conditions
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
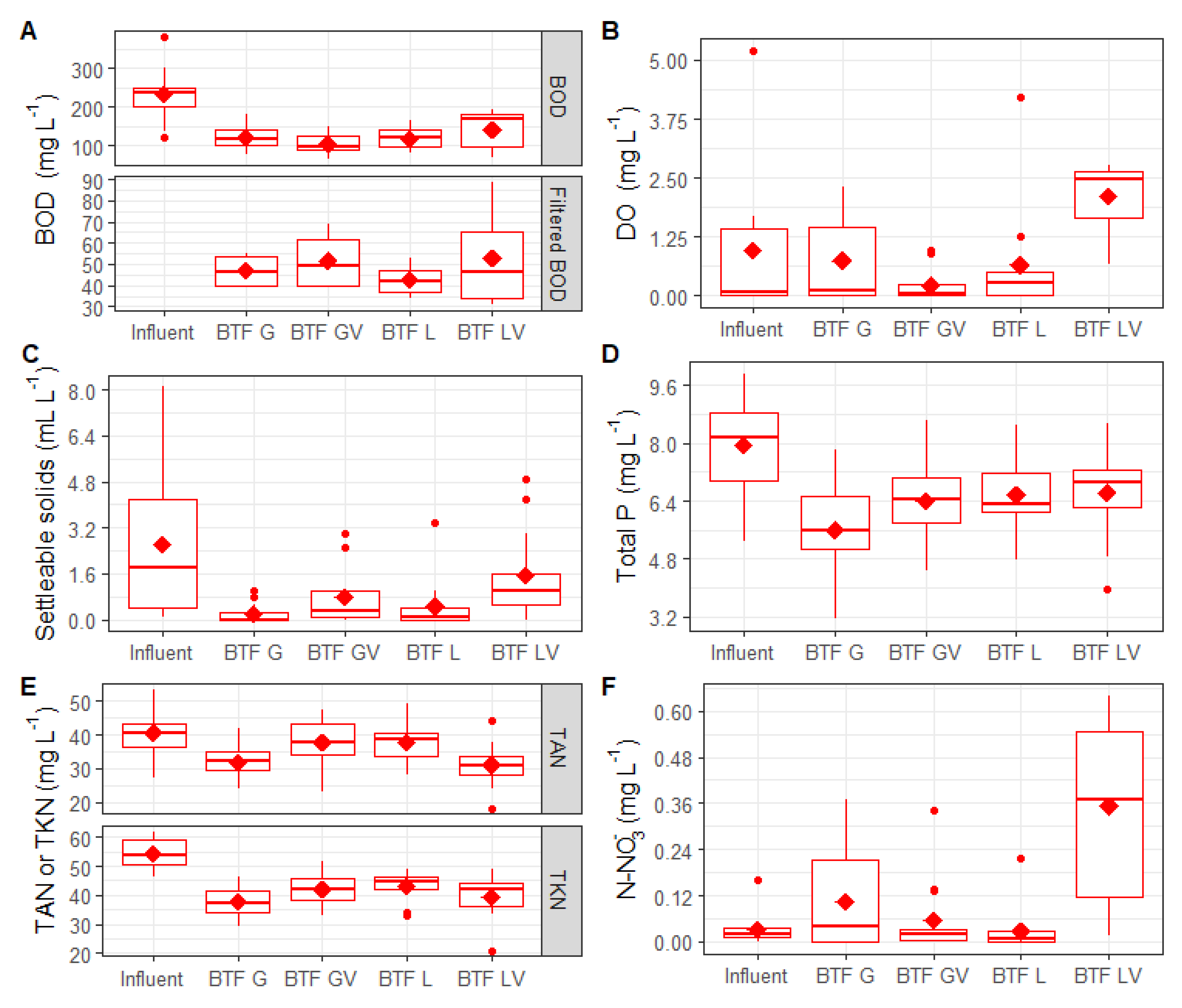
3.1. Performance of Organic Matter and Settleable Solids Removal
3.2. Performance for Phosphorus Removal
3.3. Performance for Nitrogen Series Removal
4. Conclusions
- Comparing the filters considering BOD, best performance on BTFL and BTFGV were noticed.
- In the four filters, there was a poor removal of total phosphorus, with no significant difference between them.
- Regarding TKN, the best performance was provided by BTFG. Concerning TAN, the BTFLV and BTFG filters were better and, for N-NO3−, BTFLV had a superior performance than the other BTFs.
- Both BTFLV and BTFG had more variables that excelled (three for each), indicating the best settings from the studied filters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, I.; Khan, Z.M.; Peng, C.; Naz, I.; Sultan, M.; Ali, M.; Mahmood, M.H.; Niaz, Y. Identification and elucidation of the designing and operational issues of trickling filter systems for wastewater treatment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 2431–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowski, W.; Karolinczak, B. Application of trickling filter and vertical flow constructed wetland bed to treat sewage from craft brewery. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Sperling, M. Introdução à Qualidade das Águas e ao Tratamento de Esgotos, 4th ed.; UFMG: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zahin, M.W. Cost analysis of trickling-filtration and activated-sludge Plants for the treatment of municipal wastewater. In Proceedings of the Seventh Saudi Engineering Conference, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2–5 December 2014; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, H.A.; Muhammad, M.H.; Ismail, N.I. A review of biological drinking water treatment technologies for contaminants removal from polluted water resources. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria, J.A.R. Filtro Biológico Aeróbio-Anoxico para Remoção de Nitrogenio de Efluentes de Reatores UASB. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, P.G.S.D.; Oliveira, S.C.; Chernicharo, C.A.D.L. Operation of trickling filters post-UASB reactors without the secondary sedimentation stage. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2011, 16, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalhori, E.M.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Ghahramani, E.; Kazemian, H.; Zarrabi, M. Enhancement of the adsorption capacity of the light-weight expanded clay aggregate surface for the metronidazole antibiotic by coating with MgO nanoparticles: Studies on the kinetic, isotherm, and effects of environmental parameters. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łożyńska, J.; Bańkowska-Sobczak, A.; Popek, Z.; Dunalska, J.A. Selection of P-reactive materials for treatment of hypolimnetic water withdrawn from eutrophic lakes. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2020, 16, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapater-Pereyra, M.; Lavrnić, S.; van Dien, F.; van Bruggen, J.J.A.; Lens, P.N.L. Constructed wetroofs: A novel approach for the treatment and reuse of domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopata, M.; Czerniejewski, P.; Wiśniewski, G.; Czerniawski, R.; Drozdowski, J. The use of expanded clay aggregate for the pretreatment of surface waters on the example of a tributary of Lake Klasztorne Górne in Strzelce Krajeńskie. Limnol. Rev. 2017, 17, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, X.C.; Nguyen, D.D.; Tran, Q.B.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Tran, T.K.A.; Tran, T.C.P.; Nguyen, T.H.G.; Tran, T.N.T.; La, D.D.; Chang, S.W.; et al. Two-step system consisting of novel vertical flow and free water surface constructed wetland for effective sewage treatment and reuse. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlih, R.; Bydalek, F.; Klumpp, E.; Yaghi, N.; Bol, R.; Wenk, J. Light-expanded clay aggregate (LECA) as a substrate in constructed wetlands—A review. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 148, 105783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Goswami, P.; Lavania, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Lavania, U.C. Vetiver grass is a potential candidate for phytoremediation of iron ore mine spoil dumps. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 132, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleei, M.M.; Ghomi, N.K.; Jozi, S.A. Arsenic Removal of Contaminated Soils by Phytoremediation of Vetiver Grass, Chara Algae and Water Hyacinth. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyar, R.; Ardejani, F.D.; Farahbakhsh, M.; Norouzi, P.; Yavarzadeh, M.; Maghsoudy, S. Potential of Vetiver grass for the phytoremediation of a real multi-contaminated soil, assisted by electrokinetic. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panja, S.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R. Vetiver grass (Chrysopogon zizanioides) is capable of removing insensitive high explosives from munition industry wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 209, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholipour, M.; Mehrabanjoubani, P.; Abdolzadeh, A.; Raghimi, M.; Seyedkhademi, S.; Karimi, E.; Sadeghipour, H.R. Facilitated decrease of anions and cations in influent and effluent of sewage treatment plant by vetiver grass (Chrysopogon zizanioides): The uptake of nitrate, nitrite, ammonium, and phosphate. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21506–21516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, C.; Rafiq, M.T.; Ding, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Aziz, R.; Yang, X. Screening wetland plants for nutrient uptake and bioenergy feedstock production. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2014, 16, 213–216. [Google Scholar]
- Angassa, K.; Leta, S.; Mulat, W.; Kloos, H.; Meers, E. Organic Matter and Nutrient Removal Performance of Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands Planted with Phragmite karka and Vetiveria zizanioide for Treating Municipal Wastewater. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, J.K.; Alves, C.M.; Gnansounou, E. A review on moringa tree and vetiver grass—Potential biorefinery feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, W.; Eddy, P. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse; McGraw-Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jordão, E.P.; Pessoa, C.A. Tratamento de Esgotos Domésticos (Domestic Sewage Treatment); ABES: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.E.; Skogley, E.O.; Schaff, B.E.; Kim, J.J. A simple spectrophotometric determination of endosulfan in river water and soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1998, 62, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA/AWWA/WEF. Standard Method for Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA/AWWA/WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 10th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781119492443. [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto, N.; Ohara, T.; Hinobayashi, J.; Hashimoto, T. Roughness and temperature effects on the filter media of a trickling filter for nitrification. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.C.; Álvarez-Hornos, F.J.; San-Valero, P.; Marzal, P.; Gabaldón, C. Microbial community analysis in biotrickling filters treating isopropanol air emissions. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2789–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queluz, J.G.T. Eficiência de Alagados Construídos para o Tratamento de Águas Residuárias com Baixas Cargas Orgânicas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Botucatu, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, H.V.D.; Ribeiro, C.B.D.M.; Borges, A.C.; Bastos, R.R. Sistemas Alagados Construídos em Batelada: Remoção de Demanda Bioquímica de Oxigênio e regulação de pH no tratamento de efluentes de laticínios. Rev. Ambient. Agua 2015, 10, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, M.X.; Carvalho, K.Q.; Passig, F.H.; Borges, A.C.; Filippe, T.C.; Azevedo, J.C.R.; Nagalli, A. Performance of different substrates in constructed wetlands planted with E. crassipes treating low-strength sewage under subtropical conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Tandukar, M.; Sugiyana, D.; Uemura, S.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H. Development of a sixth-generation down-flow hanging sponge (DHS) reactor using rigid sponge media for post-treatment of UASB treating municipal sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepehri, A.; Sarrafzadeh, M. Activity enhancement of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge process: Metabolite reduction and CO2 mitigation intensification process. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, F.X.; Li, Y. Enhancement of nitrogen removal in towery hybrid constructed wetland to treat domestic wastewater for small rural communities. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danh, L.T.; Truong, P.; Mammucari, R.; Tran, T.; Foster, N. Vetiver grass, Vetiveria zizanioides: A choice plant for phytoremediation of heavy metals and organic wastes. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2009, 11, 664–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnansounou, E.; Alves, C.M.; Raman, J.K. Multiple applications of vetiver grass—A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Darajeh, N.; Idris, A.; Masoumi, H.R.F.; Nourani, A.; Truong, P.; Sairi, N.A. Modeling BOD and COD removal from Palm Oil Mill Secondary Effluent in floating wetland by Chrysopogon zizanioides (L.) using response surface methodology. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
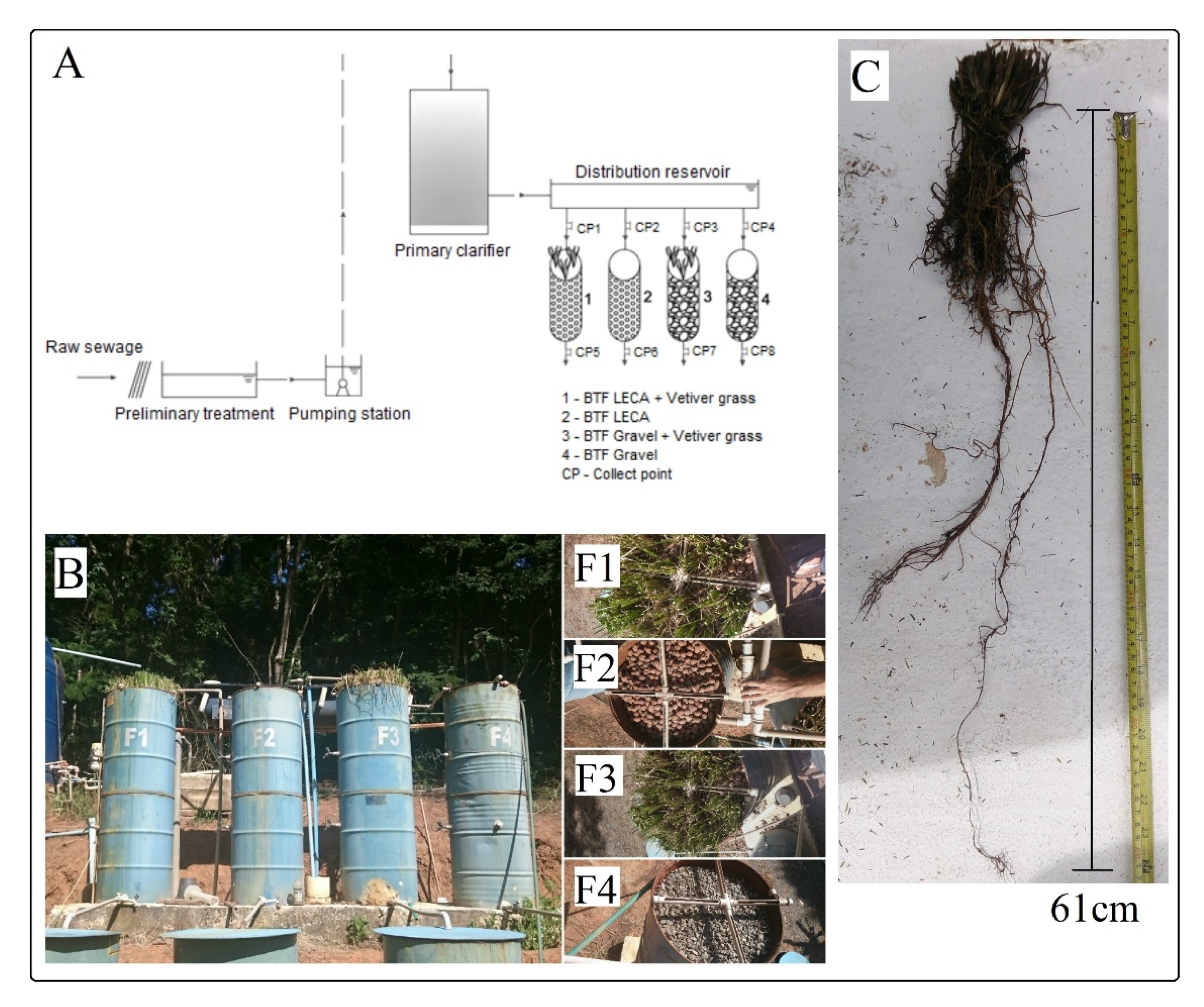
| Operating Characteristics | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Influent flow rate (for each BTF) | 0.75 | m3 d−1 |
| Adopted OLR as BOD | 0.3 | kg m−3 d−1 |
| HLR | 2.7 | m3 m−2 d−1 |
| Volume for each filter | 0.5 | m3 |
| Adopted influent BOD | 200 | mg L−1 |
| Physicochemical Variables | Method/Apparatus |
|---|---|
| BOD | Hach HQ440D Digital Measurer |
| TKN | Semimicro Kjeldahl |
| TAN | Semimicro Kjeldahl |
| N-NO3− | Colorimetry |
| Total Phosphorus | Spectrophotometry |
| Temperature | Hach MP-6 Sensor |
| pH | Hach MP-6 Sensor |
| OD | Hach HQ440D Digital Measurer |
| Settleable solids | Imhoff Cone |
| BTF Media | Vegetation | |
|---|---|---|
| With Vetiver Grass | Without Vetiver Grass | |
| Gravel | 104 mg L−¹ b A | 120 mg L−¹ a A |
| LECA | 142 mg L−¹ a A | 119 mg L−¹ a B |
| Factor | Factor Level | Phosphorus Concentration (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Media | Gravel | 6.02 b |
| LECA | 6.61 a | |
| Vegetation | With Vetiver Grass | 6.53 a |
| Without Vetiver Grass | 6.10 a |
| Nitrogen Specie | BTF Media | Vegetation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vetiver Grass | Without Vetiver Grass | ||
| TKN (mg L−¹) | Gravel | 42.1 a A | 37.6 b B |
| LECA | 39.5 a A | 43.1 a A | |
| TAN (mg L−¹) | Gravel | 39.2 a A | 32.7 b B |
| LECA | 31.0 b B | 37.7 a A | |
| N-NO3− (mg L−¹) | Gravel | 0.06 a | 0.10 a |
| LECA | 0.35 b | 0.03 a | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, V.F.; Silva, G.J.d.; Borges, A.C. Effects of Packing Media and the Insertion of Vegetation on the Performance of Biological Trickling Filters. Water 2021, 13, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131735
Martins VF, Silva GJd, Borges AC. Effects of Packing Media and the Insertion of Vegetation on the Performance of Biological Trickling Filters. Water. 2021; 13(13):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131735
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Vinícius Ferreira, Greicelene Jesus da Silva, and Alisson Carraro Borges. 2021. "Effects of Packing Media and the Insertion of Vegetation on the Performance of Biological Trickling Filters" Water 13, no. 13: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131735
APA StyleMartins, V. F., Silva, G. J. d., & Borges, A. C. (2021). Effects of Packing Media and the Insertion of Vegetation on the Performance of Biological Trickling Filters. Water, 13(13), 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131735







