Role of Pond Sediments for Trapping Pesticides in an Agricultural Catchment (Auradé, SW France): Distribution and Controlling Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
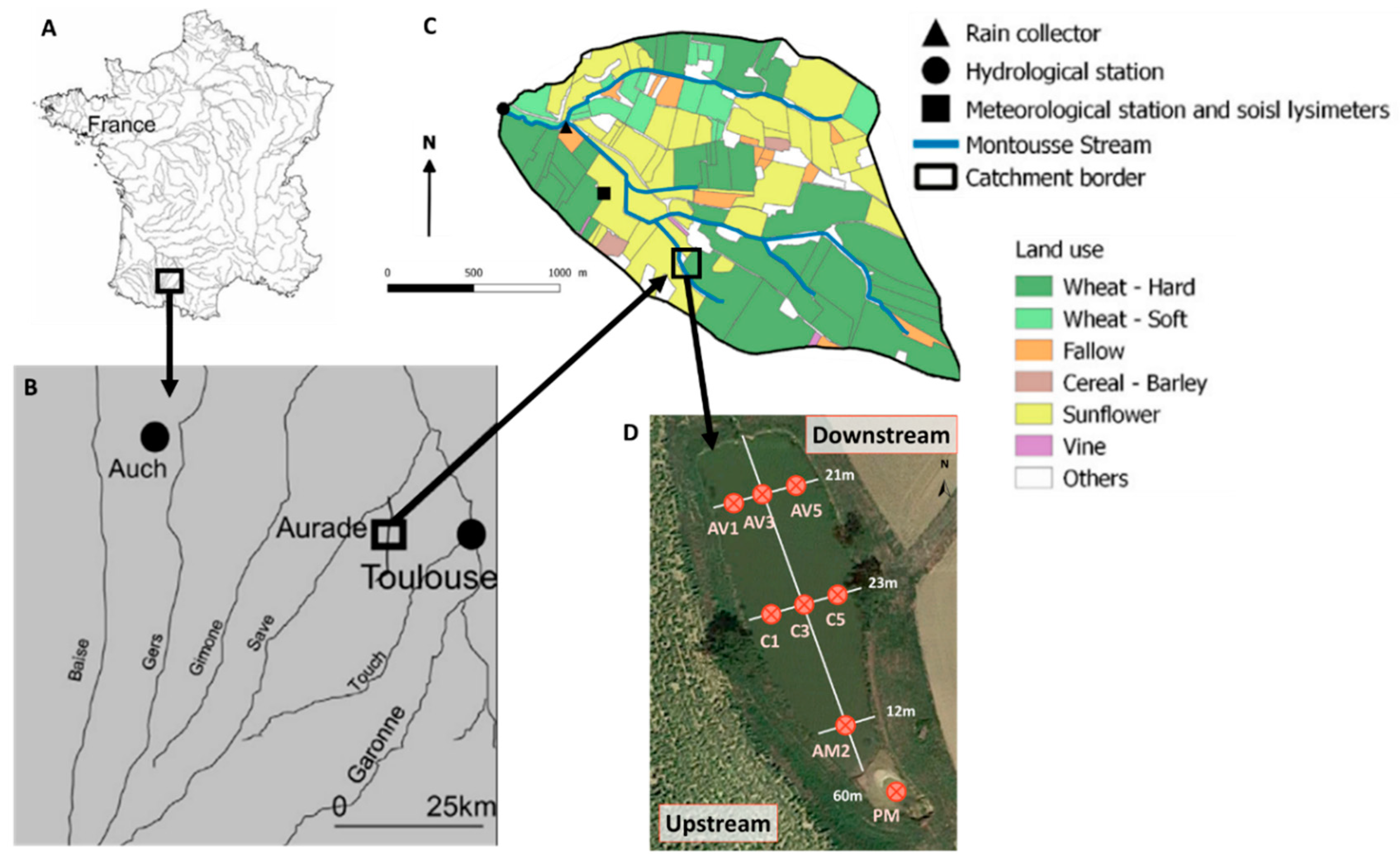
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. Pre-Treatment and Analysis of Water Samples
2.3.1. Physico-Chemical Parameters
2.3.2. Pesticide Quantification
2.4. Pre-Treatment and Analysis of Sediment Samples
2.4.1. Pre-Treatment of the Sediments
2.4.2. Texture and Micro-Granulometry
2.4.3. Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Analysis
2.5. Pesticide Analysis
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Composition of Water and Sediment
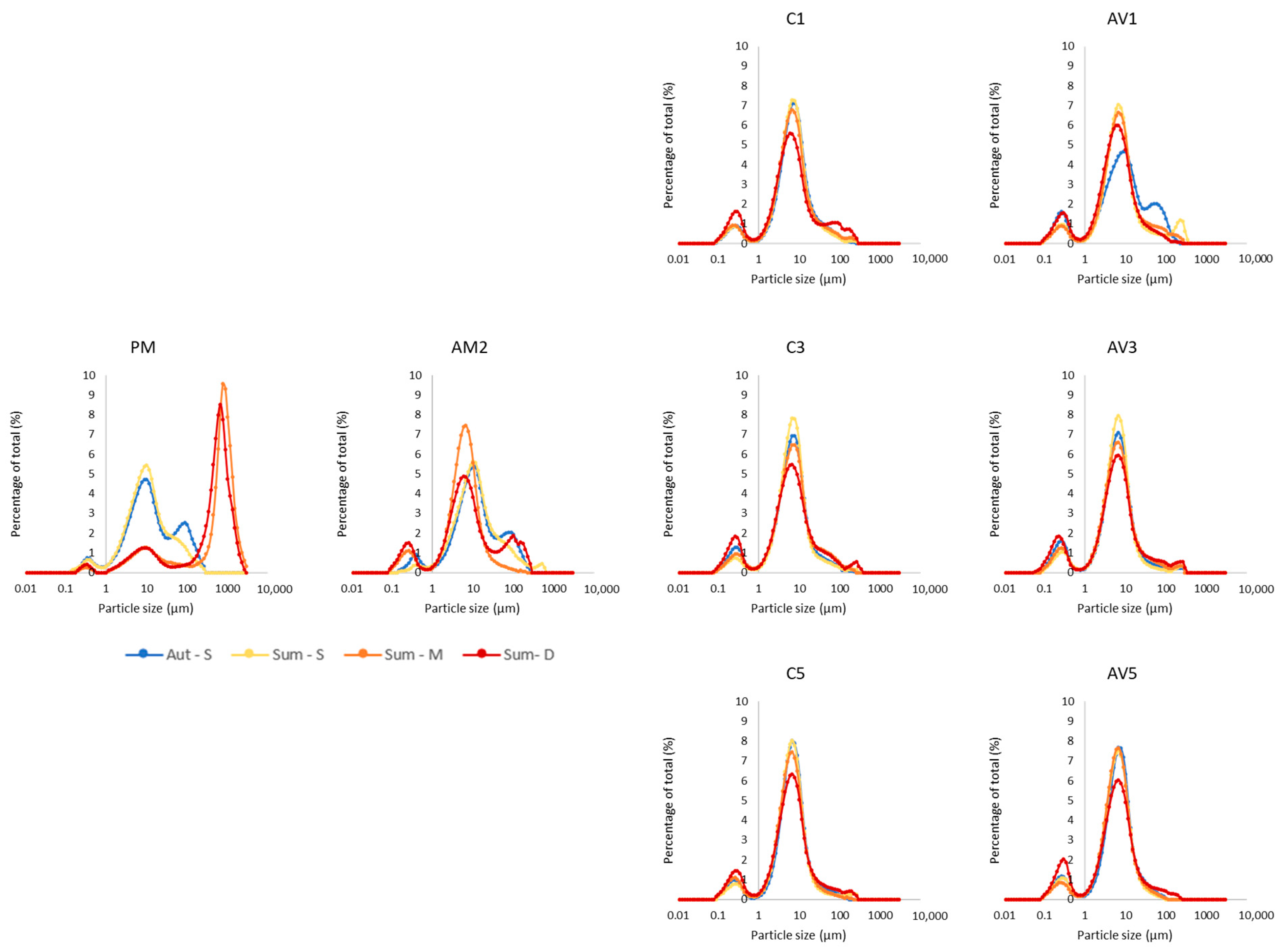
3.2. Sediment Texture
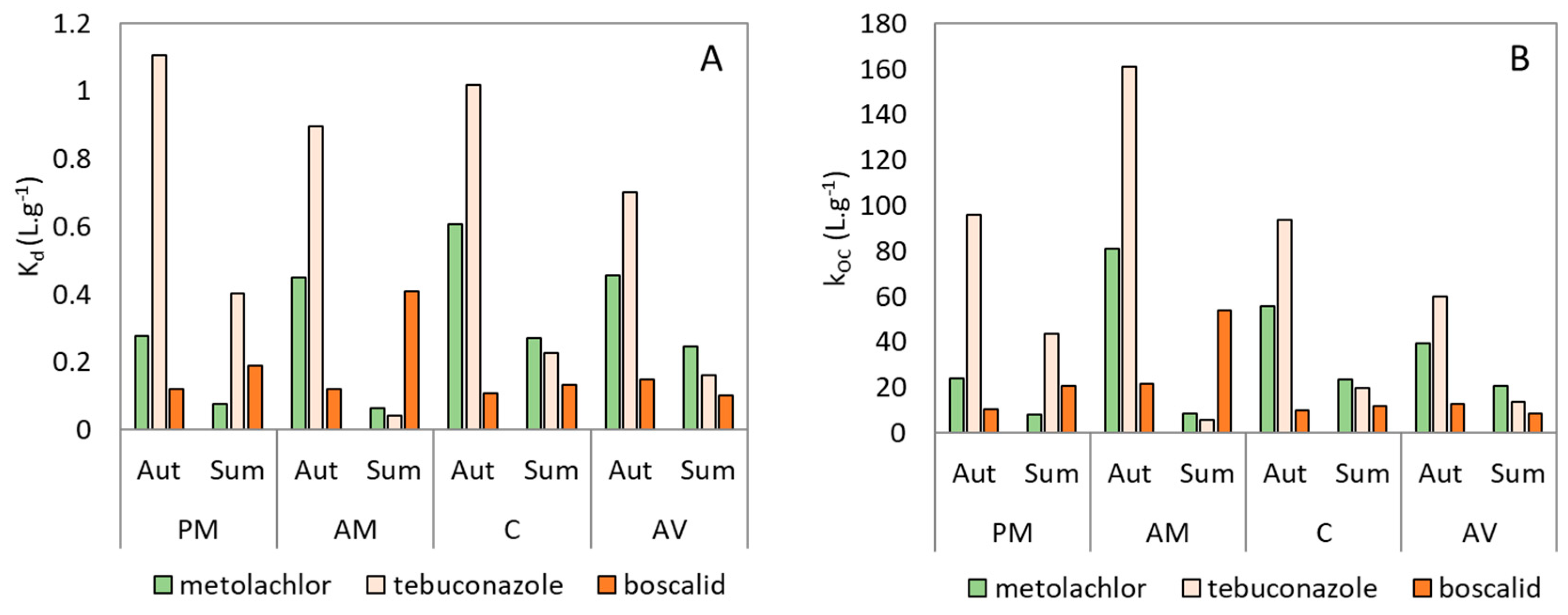
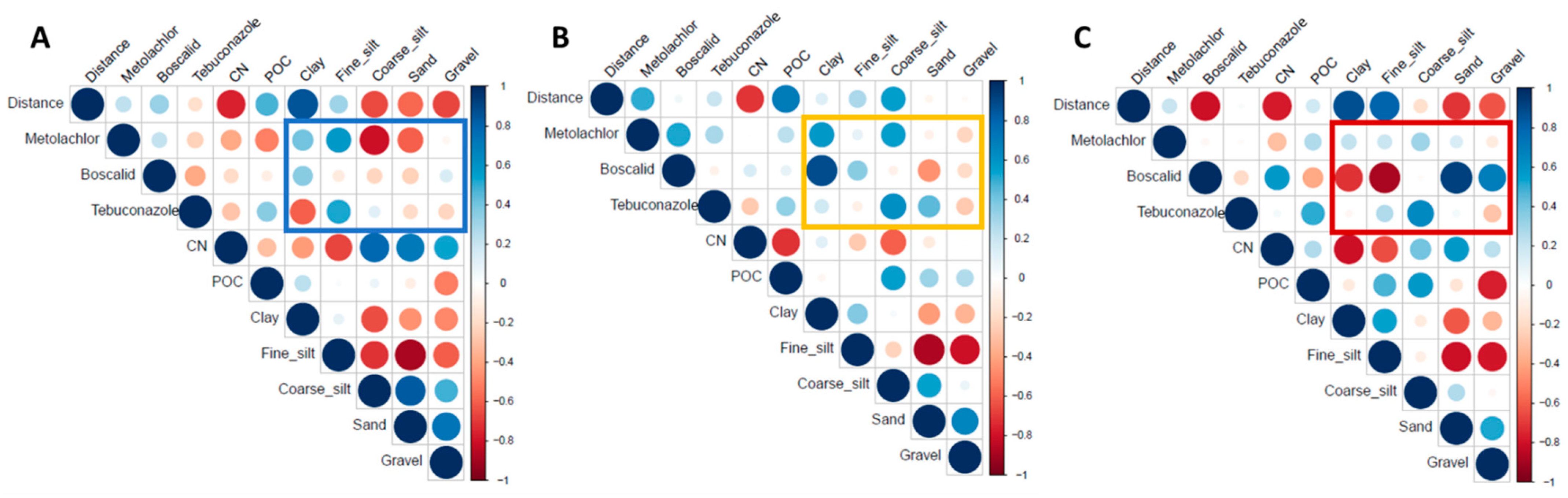
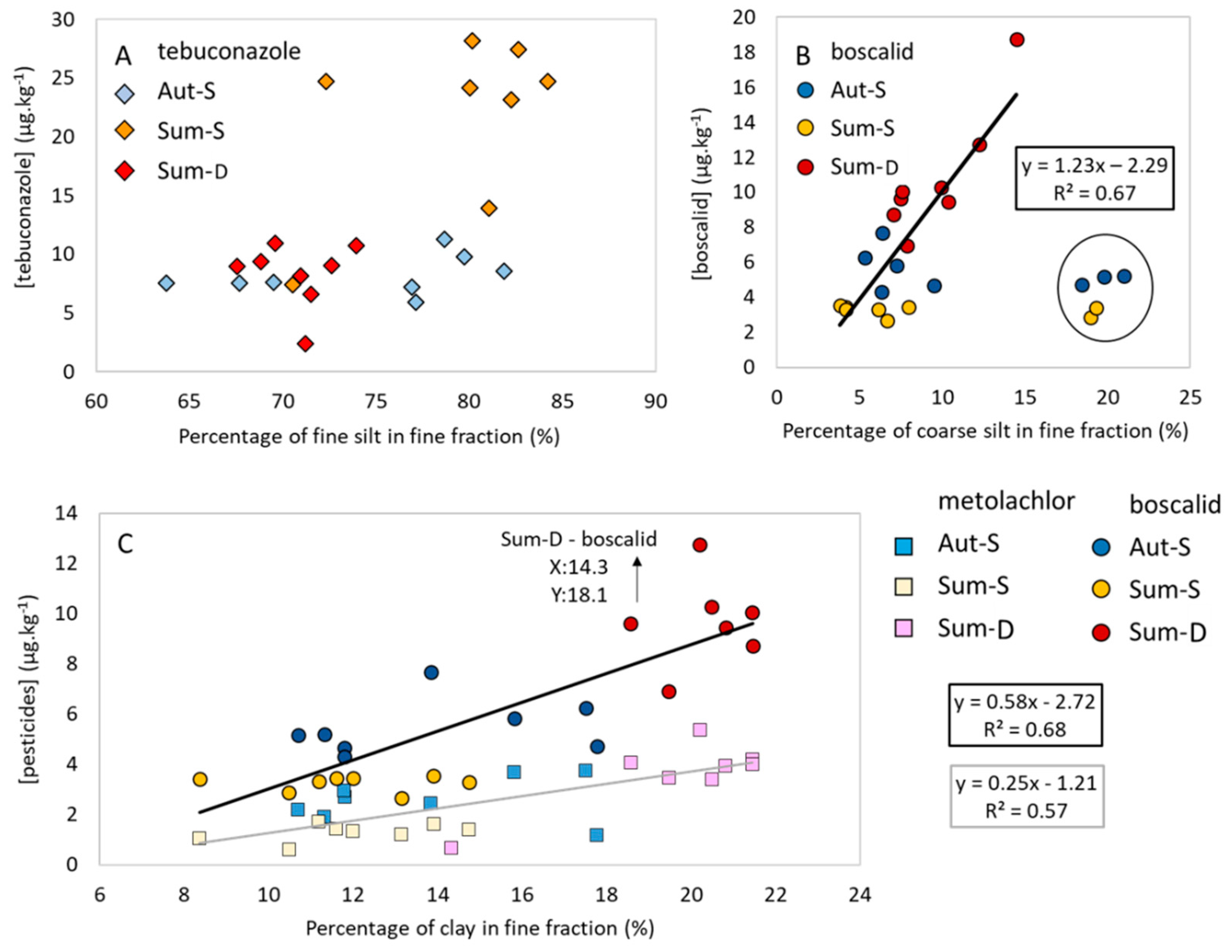
3.3. Relationship between Pesticide Concentrations and Physico-Chemical Parameters
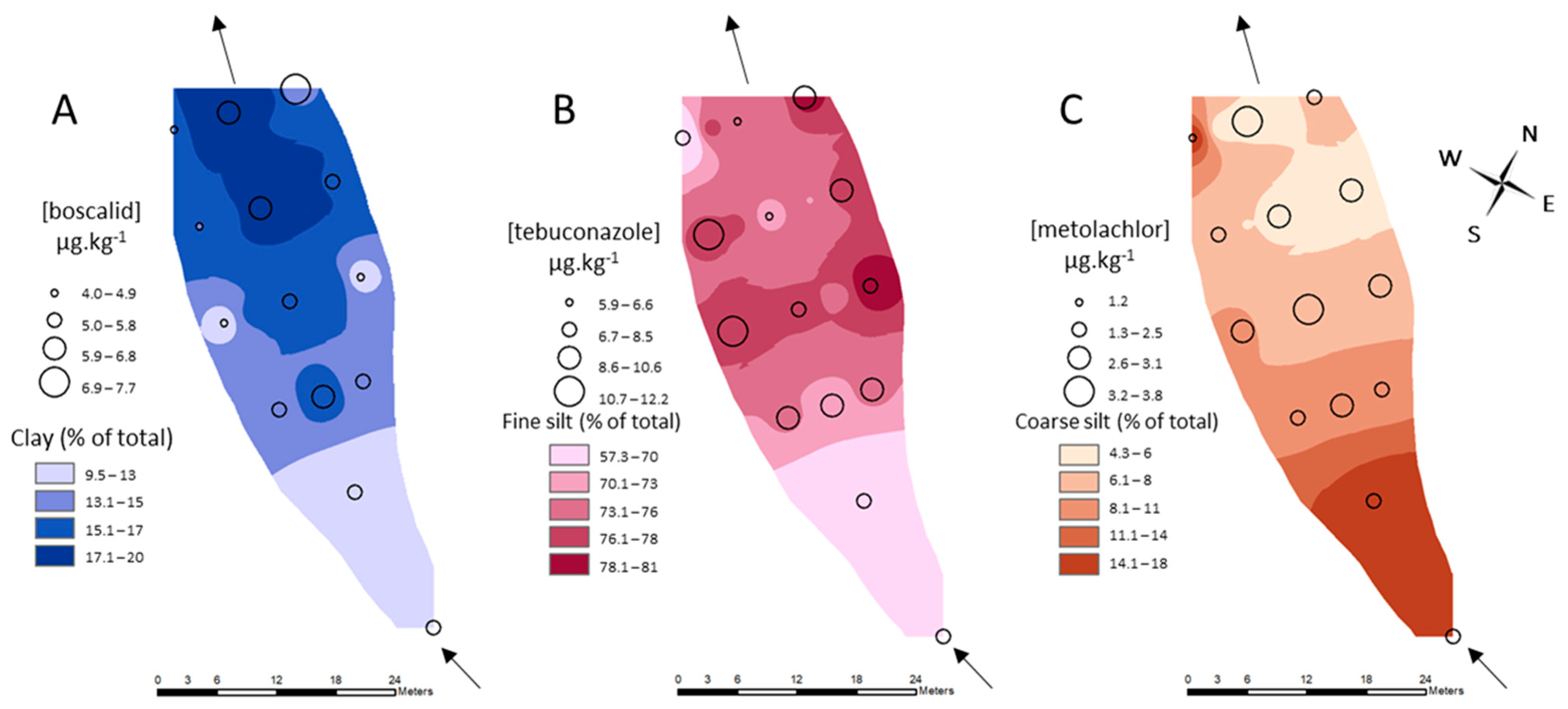
3.4. Spatial Distribution of Sediment Texture and Pesticide Concentration
4. Discussion
4.1. Pesticide Origin and Seasonal Effect
4.2. Factors Controlling Pesticide Concentration and Distribution
4.2.1. Sediment Texture
4.2.2. Sediment Depth
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeLorenzo, M.E.; Scott, G.I.; Ross, P.E. Toxicity of pesticides to aquatic microorganisms: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multigner, L. Effets retardés des pesticides sur la santé humaine. Environ. Risques St. 2005, 4, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Knisel, W.G. CREAMS: A Field-Scale Model for Chemicals, Runoff, and Erosion from Agricultural Management Systems; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Conservation Research Report No. 26; U.S. Government Printing Office: 1980 0-310-945/SEA-15; Department Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1980; p. 640.
- Oliver, D.P.; Kookana, R.; Anderson, J.S.; Cox, J.W.; Waller, N.; Smith, L.H. Off-site transport of pesticides in dissolved and particulate forms from two land uses in the Mt. Lofty Ranges, South Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 106, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payraudeau, S.; Gregoire, C. Modelling pesticides transfer to surface water at the catchment scale: A multi-criteria analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 32, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulou-Vrynioti, K.; Alexakis, D.; Bathrellos, G.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Vryniotis, D.; Vassiliades, E.; Gamvroula, D. Distribution of trace elements in stream sediments of Arta plain (western Hellas): The influence of geomorphological parameters. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 134, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macary, F.; Morin, S.; Probst, J.-L.; Saudubray, F. A multi-scale method to assess pesticide contamination risks in agricultural watersheds. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macary, F.; Almeida-Dias, J.; Uny, D.; Probst, A. Assessment of the effects of best environmental practices on reducing pesticide contamination in surface water, using multi-criteria modelling combined with a GIS. Int. J. Multicriteria Decis. Mak. 2013, 3, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colin, F.; Puech, C.; De Marsily, G. Relations between triazine flux, catchment topography and distance between maize fields and the drainage network. J. Hydrol. 2000, 236, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E.; Bathrellos, G.D.; Skilodimou, H.D.; Gamvroula, D.E. Applied sciences Land Suitability Mapping Using Geochemical and Spatial Analysis Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazartigues, A.; Banas, D.; Feidt, C.; Brun-Bellut, J.; Thomas, M. Pesticide pressure and fish farming in barrage pond in Northeastern France Part I: Site characterization and water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2802–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R. Field Studies on Exposure, Effects, and Risk Mitigation of Aquatic Nonpoint-Source Insecticide Pollution: A Review. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 419–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margoum, C.; Malessard, C.; Gouy, V. Investigation of various physicochemical and environmental parameter influence on pesticide sorption to ditch bed substratum by means of experimental design. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalogridi, E.-C.; Christophoridis, C.; Bizani, E.; Drimaropoulou, G.; Fytianos, K. Part II: Temporal and spatial distribution of multiclass pesticide residues in lake sediments of northern Greece: Application of an optimized MAE-LC-MS/MS pretreatment and analytical method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7252–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgheib, S.; Moilleron, R.; Saad, M.; Chebbo, G. Partition of pollution between dissolved and particulate phases: What about emerging substances in urban stormwater catchments? Water Res. 2011, 45, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, L.; Merlina, G.; Probst, J.-L. The role of storm flows in concentration of pesticides associated with particulate and dissolved fractions as a threat to aquatic ecosystems—Case study: The agricultural watershed of Save river (Southwest of France). Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2011, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Azzi, D.; Probst, J.-L.; Teisserenc, R.; Merlina, G.; Baqué, D.; Julien, F.; Payre-Suc, V.; Guiresse, A.M. Trace Element and Pesticide Dynamics During a Flood Event in the Save Agricultural Watershed: Soil-River Transfer Pathways and Controlling Factors. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boithias, L.; Sauvage, S.; Merlina, G.; Jean, S.; Probst, J.-L.; Pérez, J.M.S. New insight into pesticide partition coefficient Kd for modelling pesticide fluvial transport: Application to an agricultural catchment in south-western France. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignati, D.; Valsecchi, S.; Polesello, S.; Patrolecco, L.; Dominik, J. Pollutant partitioning for monitoring surface waters. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suba, J.D.; Essington, M.E. Adsorption of fluometuron and norflurazon: Effect of tillage and dissolved organic carbon. Soil Sci. 1999, 164, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, L.; Probst, J.-L.; Merlina, G.; Marchand, A.-L.; Durbe, G.; Probst, A. Flood event impact on pesticide transfer in a small agricultural catchment (Montoussé at Auradé, south west France). Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Maguhn, J.; Spitzauer, P.; Kettrup, A. Sorption of pesticides in the sediment of the Teufelsweiher pond (Southern Germany). I: Equilibrium assessments, effect of organic carbon content and pH. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissant, L.; Beauvais, C.; Lafrance, P.; Deblois, C. Pesticides in fluvial wetlands catchments under intensive agricultural activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 404, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; Williams, P.; Whitfield, M.; Nicolet, P.; Weatherby, A. 15 years of pond assessment in Britain: Results and lessons learned from the work of Pond Conservation. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2005, 15, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, C.; Payraudeau, S.; Domange, N. Use and fate of 17 pesticides applied on a vineyard catchment. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2010, 90, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Probst, A. Influence of ponds on hazardous metal distribution in sediments at a catchment scale (agricultural critical zone, S-W France). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, E.; Payraudeau, S.; Faivre, E.; Grégoire, C.; Gangloff, S.; Imfeld, G. Removal of pesticide mixtures in a stormwater wetland collecting runoff from a vineyard catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.T.; Rodgers, J.H., Jr.; Cooper, C.M.; Smith, S., Jr. Constructed wetlands for mitigation of atrazine-associated agricultural runoff. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 110, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imfeld, G.; Braeckevelt, M.; Kuschk, P.; Richnow, H. Monitoring and assessing processes of organic chemicals removal in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, V.; Puigagut, J.; García, J.; Bayona, J.M. Behavior of selected priority organic pollutants in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands: A preliminary screening. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, S.; Elsaesser, D.; Grégoire, C.; Imfeld, G.; Niehaus, E.; Passeport, E.; Payraudeau, S.; Schäfer, R.B.; Tournebize, J.; Schulz, R. Pesticide Risk Mitigation by Vegetated Treatment Systems: A Meta-Analysis. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrentó, C.; Bakkour, R.; Ryabenko, E.; Ponsin, V.; Prasuhn, V.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Elsner, M.; Hunkeler, D. Fate of Four Herbicides in an Irrigated Field Cropped with Corn: Lysimeter Experiments. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 13, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koranteng, S.S.; Darko, D.A.; Nukpezah, D.; Ameka, G.K. Pesticides bioconcentration potential of aquatic plants in the volta lake. W. Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 26, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Headley, J.V.; Gandrass, J.; Kuballa, J.; Peru, A.K.M.; Gong, Y. Rates of Sorption and Partitioning of Contaminants in River Biofilm. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3968–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, R.; O’Geen, A.; Goh, K.S.; Bondarenko, S.; Gan, J. Efficacy of Constructed Wetlands in Pesticide Removal from Tailwaters in the Central Valley, California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2925–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, R.; Dousset, S.; Billet, D.; Benoît, M. Sorption of selected pesticides on soils, sediment and straw from a constructed agricultural drainage ditch or pond. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Azzi, D.; Laurent, F.; Roussiez, V.; Chou, L.; Guiresse, M.; Probst, J.-L. Adsorption of Aclonifen, Alachlor, Cd and Cu onto Natural River Suspended Matter in the Context of Multi-Pollutions: Influence of Contaminant Co-Presence and Order of Input into the Aqueous Solution. Water 2018, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spark, K.M.; Swift, R.S. Effect of soil composition and dissolved organic matter on pesticide sorption. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 298, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.B.; Wilkerson, G.G.; Reinhardt, C.F. Calculating pesticide sorption coefficients (Kd) using selected soil properties. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Riise, G.; Lundekvam, H.; Mulder, J.; Haugen, L. Influences of suspended particles on the runoff of pesticides from an agricultural field at Askim, SE-Norway. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.S.; Hjelmsø, M.H. Agricultural soils, pesticides and microbial diversity. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagi, T. Behavior of Pesticides in Water-Sediment Systems. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 187, 133–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imfeld, G.; Payraudeau, S.; Tournebize, J.; Sauvage, S.; Macary, F.; Chaumont, C.; Probst, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.-M.; Bahi, A.; Chaumet, B.; et al. The Role of Ponds in Pesticide Dissipation at the Agricultural Catchment Scale: A Critical Review. Water 2021, 13, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, A.-S.; Probst, A.; Probst, J.-L. Impact of nitrogenous fertilizers on carbonate dissolution in small agricultural catchments: Implications for weathering CO2 uptake at regional and global scales. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 3105–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponnou-Delaffon, V.; Probst, A.; Payre-Suc, V.; Granouillac, F.; Ferrant, S.; Perrin, A.-S.; Probst, J.-L. Long and short-term trends of stream hydrochemistry and high frequency surveys as indicators of the influence of climate change, agricultural practices and internal processes (Aurade agricultural catchment, SW France). Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, A.; Moussa, I.; Payre, V.; Probst, A.; Probst, J.-L. Flood survey of nitrate behaviour using nitrogen isotope tracing in the critical zone of a French agricultural catchment. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2015, 347, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boithias, L.; Sauvage, S.; Taghavi, L.; Merlina, G.; Probst, J.-L.; Pérez, J.M.S. Occurrence of metolachlor and trifluralin losses in the Save river agricultural catchment during floods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 196, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guiresse, M.; Revel, J. Erosion due to cultivation of calcareous clay soils on hillsides in south-west France. II. Effect of ploughing down the steepest slope. Soil Tillage Res. 1995, 35, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Probst, A.; Barret, M.; Payre-Suc, V.; Camboulive, T.; Granouillac, F. Spatial variation of denitrification and key controlling factors in streams and ponds sediments from a critical zone (southwestern France). Appl. Geochem. 2021, 131, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.E. Pesticide-Clay-Water Interactions; Guenzi, W.D., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, W.J. Quantitative structure–activity relationships for predicting soil–sediment sorption coefficients for organic chemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1771–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVault, D.A.; Gérino, M.; Laplanche, C.; Julien, F.; Winterton, P.; Merlina, G.; Delmas, F.; Lim, P.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M.; Pinelli, E. Herbicide accumulation and evolution in reservoir sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karaouzas, I.; Lambropoulou, D.; Skoulikidis, N.T.; Albanis, T.A. Levels, sources and spatiotemporal variation of nutrients and micropollutants in small streams of a Mediterranean River basin. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 3064–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smalling, K.L.; Reilly, T.J.; Sandstrom, M.W.; Kuivila, K.M. Occurrence and persistence of fungicides in bed sediments and suspended solids from three targeted use areas in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budd, R.; O’Geen, A.; Goh, K.S.; Bondarenko, S.; Gan, J. Removal mechanisms and fate of insecticides in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, H. Assessing the impact of pesticides on the environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 60, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoire, C.; Elsaesser, D.; Huguenot, D.; Lange, J.; Lebeau, T.; Merli, A.; Mose, R.; Passeport, E.; Payraudeau, S.; Schuetz, T.; et al. Mitigation of agricultural nonpoint-source pesticide pollution in artificial wetland ecosystems. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2008, 7, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeiro, M.; Facorro, R.; Dagnac, T.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Llompart, M. Photodegradation of multiclass fungicides in the aquatic environment and determination by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19181–19193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Arias, C.A.; Brix, H.; Carvalho, P.N. Removal of the pesticide tebuconazole in constructed wetlands: Design comparison, influencing factors and modelling. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohlin, H.S.; Mörth, C.-M.; Holm, N.G. Point source influences on the carbon and nitrogen geochemistry of sediments in the Stockholm inner archipelago, Sweden. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, R.; Dousset, S.; Billet, D. Influence of substrate water saturation on pesticide dissipation in constructed wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, E.; Imfeld, G. Pesticide Mass Budget in a Stormwater Wetland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8603–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leleyter, L.; Probst, J.-L. A New Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Particulate Trace Elements in River Sediments. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1999, 73, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Yamazaki, S.; Terashima, Y. Sorption of Anionic Pentachlorophenol (PCP) in Aquatic Environments: The Effect of pH. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.E.; Karickhoff, S.W. Sorption Estimates for Modeling. In Pesticides in the Soil Environment; No. 2; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1990; pp. 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Bur, T.; Probst, J.; N’Guessan, M.; Probst, A. Distribution and origin of lead in stream sediments from small agricultural catchments draining Miocene molassic deposits (SW France). Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, B.; Pignatello, J.J. Dual-Mode Sorption of Low-Polarity Compounds in Glassy Poly(Vinyl Chloride) and Soil Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, L.; Lindhardt, B.; Rosenberg, P.; Clausen, L.; Fabricius, I. Pesticide Sorption by Low Organic Carbon Sediments: A Screening for Seven Herbicides. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqueda, C.; Undabeytia, T.; Villaverde, J.; Morillo, E. Behaviour of glyphosate in a reservoir and the surrounding agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593–594, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Seasonal and spatial distributions and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yangtze Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Chen, L. Sorption specificity and desorption hysteresis of gibberellic acid on ferrihydrite compared to goethite, hematite, montmorillonite, and kaolinite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 19068–19075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachara, J.; Smith, S.; Kuzel, L. Adsorption and dissociation of Co-EDTA complexes in iron oxide-containing subsurface sands. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 4825–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, J.; Uusitalo, R.; Leppänen, J.; Yli-Halla, M. Sediment from Agricultural Constructed Wetland Immobilizes Soil Phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaullier, C.; Dousset, S.; Billet, D.; Baran, N. Is pesticide sorption by constructed wetland sediments governed by water level and water dynamics? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14324–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farenhorst, A.; McQueen, D.; Saiyed, I.; Hilderbrand, C.; Li, S.; Lobb, D.; Messing, P.; Schumacher, T.; Papiernik, S.; Lindstrom, M. Variations in soil properties and herbicide sorption coefficients with depth in relation to PRZM (pesticide root zone model) calculations. Geoderma 2009, 150, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, W.R.; Krapac, I.G. Adsorption and Desorption of Atrazine and Deethylatrazine by Low Organic Carbon Geologic Materials. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braskerud, B.; Haarstad, K. Screening the retention of thirteen pesticides in a small constructed wetland. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalling, K.L.; Aelion, C.M. Distribution of atrazine into three chemical fractions: Impact of sediment depth and organic carbon content. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labadie, P.; Cundy, A.B.; Stone, K.; Andrews, M.; Valbonesi, S.; Hill, E.M. Evidence for the Migration of Steroidal Estrogens through River Bed Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4299–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bur, T.; Probst, A.; Bianco, A.; Gandois, L.; Crouau, Y. Determining cadmium critical concentrations in natural soils by assessing Collembola mortality, reproduction and growth. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steelman, C.M.; Meyer, J.R.; Wanner, P.; Swanson, B.J.; Conway-White, O.; Parker, B.L. The importance of transects for characterizing aged organic contaminant plumes in groundwater. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2020, 235, 103728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygar, T.M.; Bábek, O.; Sedlacek, J.; Lenďáková, Z.; Faměra, M.; Štojdl, J.; Pacina, J.; Tolaszová, J.; Kříženecká, S. Segregation and retention of As, potentially toxic metals, and organic pollutants in a reservoir from the Ohře River (the Czech Republic). J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2931–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Gaudet, J.-P.; Gerino, M.; Desrosiers, G.; Châtelliers, M.C.D. Influence of macroinvertebrates on physico-chemical and microbial processes in hyporheic sediments. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 17, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (A) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Water | Water Height cm | pH | Conductivity µS·cm−1 | T °C | O2 mg·L−1 | DOC mg·L−1 | [metolachlor] ng·L−1 | [tebuconazole] ng·L−1 | [boscalid] ng·L−1 | ||||||||||||
| Season | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | |||
| Mean | 46.4 | 36.3 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 794.0 | 703.3 | 9.3 | 20.5 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 5.6 * | 9.9 * | 8.8 * | 49.3 * | 43.6 | 42.8 | |||
| sd | 1.2 | 2.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 23.8 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 10.4 | 0.8 | 9.6 | |||
| min | 30.0 | 30.0 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 751.0 | 703.0 | 8.8 | 20.1 | 5.2 | 4.5 | 4.1 | 3.4 | 4.9 | 8.0 | 6.8 | 18.4 | 42.1 | 15.1 | |||
| max | 50.0 | 50.0 | 7.9 | 8.0 | 833.0 | 704.0 | 10.2 | 21.1 | 10.9 | 10.0 | 5.4 | 5.1 | 6.8 | 10.7 | 11.0 | 62.7 | 45.7 | 58.1 | |||
| (B) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sediments | POC mg·g−1 | C/N | Clays % | Fine silts % | Coarse silts % | Sands % | Gravels % | ||||||||||||||
| Season– Core depth | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D |
| Mean | 11.4 | 10.9 | 9.0 | 5.4 | 6.5 | 5.9 | 13.2 | 11.5 | 17.2 | 70.8 | 76.0 | 60.4 | 10.8 | 8.4 | 7.7 | 5.0 | 3.1 | 4.8 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 9.8 |
| sd | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 2.0 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 9.0 |
| min | 9.8 | 7.6 | 6.8 | 4.8 | 6.0 | 5.5 | 9.4 | 7.6 | 3.2 | 57.3 | 65.1 | 15.9 | 5.2 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| max | 13.1 | 12.3 | 10.2 | 6.4 | 7.8 | 6.3 | 17.1 | 14.7 | 20.9 | 80.9 | 82.4 | 71.3 | 17.7 | 17.5 | 10.6 | 14.6 | 7.2 | 12.5 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 72.8 |
| (C) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sediments | [metolachlor] (µg·kg−1) | [tebuconazole] (µg·kg−1) | [boscalid] (µg·kg−1) | Kd met (L·g−1) | Kd tebu (L·g−1) | Kd bosc (L·g−1) | Koc met (L·g−1) | Koc tebu (L·g−1) | Koc bosc (L·g−1) | ||||||||||||
| Season– Core depth | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut-S | Sum-S | Sum-D | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum | Aut | Sum |
| Mean | 2.6 * | 1.3 * | 3.6 | 8.1 * | 21.7 * | 8.3 | 5.5 * | 3.3 * | 10.8 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 0.94 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 48.8 | 18.8 | 96.1 | 18.8 | 12.8 | 16.9 |
| sd | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 7.8 | 4.1 | 14.0 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 5.7 |
| min | 1.9 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 5.9 | 7.4 | 2.3 | 4.3 | 2.7 | 6.9 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.70 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 24.0 | 8.3 | 60.0 | 5.6 | 9.9 | 5.9 |
| max | 3.8 | 1.7 | 5.4 | 11.3 | 28.1 | 11.3 | 7.7 | 3.5 | 8.7 | 0.61 | 0.51 | 1.11 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.41 | 81.1 | 43.9 | 160.9 | 43.6 | 21.6 | 54.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaumet, B.; Probst, J.-L.; Eon, P.; Camboulive, T.; Riboul, D.; Payré-Suc, V.; Granouillac, F.; Probst, A. Role of Pond Sediments for Trapping Pesticides in an Agricultural Catchment (Auradé, SW France): Distribution and Controlling Factors. Water 2021, 13, 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131734
Chaumet B, Probst J-L, Eon P, Camboulive T, Riboul D, Payré-Suc V, Granouillac F, Probst A. Role of Pond Sediments for Trapping Pesticides in an Agricultural Catchment (Auradé, SW France): Distribution and Controlling Factors. Water. 2021; 13(13):1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131734
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaumet, Betty, Jean-Luc Probst, Pierre Eon, Thierry Camboulive, David Riboul, Virginie Payré-Suc, Franck Granouillac, and Anne Probst. 2021. "Role of Pond Sediments for Trapping Pesticides in an Agricultural Catchment (Auradé, SW France): Distribution and Controlling Factors" Water 13, no. 13: 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131734
APA StyleChaumet, B., Probst, J.-L., Eon, P., Camboulive, T., Riboul, D., Payré-Suc, V., Granouillac, F., & Probst, A. (2021). Role of Pond Sediments for Trapping Pesticides in an Agricultural Catchment (Auradé, SW France): Distribution and Controlling Factors. Water, 13(13), 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131734








