Comparative Characteristics of Percentage Edibility, Condition Index, Biochemical Constituents and Lipids Nutritional Quality Indices of Wild and Farmed Scallops (Flexopecten glaber)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection, Samples Preparation, Percentage Edibility and Condition Index of Bivalves
2.2. Proximate Composition
2.3. Fatty Acids
2.4. Lipid Nutritional Quality Indices (LNQI)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics. 2011/FAO Annuaire. Statistiques des PêChes et de L’aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018—Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; p. 210. [Google Scholar]
- Shumway, S.E.; Davis, C.; Downey, R.; Karney, R.; Kraeuter, J.; Parsons, J.; Rheault, R.; Wikfors, G. Shellfish aquaculture—In praise of sustainable economies and environments. World Aquac. 2012, 34, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Gianguzza, P.; Fanelli, G. The recruitment of scallops (and beyond) by two different artificial collectors (Gulf of Taranto. Mediterranean Sea). Aquac. Res. 2015, 47, 3319–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, T.C.; Smaal, A.C. The role of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis in the cycling of nutrients in the Oosterschelde estuary (The Netherlands). Hydrobiology 1994, 282, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, E.; Di Lena, G.; Nevigato, T.; Casini, I.; Marzetti, A.; Caproni, A. Seasonal changes in meat content, condition index and chemical composition of mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) cultured in two different Italian sites. Food Chem. 2002, 77, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orban, E.; Di Lena, G.; Nevigato, T.; Casini, I.; Caproni, R.; Santaroni, G.; Giulini, G. Nutritional and commercial quality of the striped venus clam, Chamelea gallina, from the Adriatic Sea. Food Chem. 2006, 101, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittenschober, D.; Nowak, V.; Charrondiere, U.R. Review of availability of food composition data for fish and shellfish. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4303–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anacleto, P.; Maulvault, A.L.; Bandarra, N.M.; Repolho, T.; Nunes, M.L.; Rosa, R.; Marques, A. Effect of warming on protein, glycogen and fatty acid content of native and invasive clams. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Papa, L.; Kelly, M.; Fanelli, G. Bioactive fatty acids of three commercial scallop species. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Giandomenico, S.; Denti, G.; Calò, M.; Spada, L.; Di Leo, A. Proximate, fatty acids and metals in edible marine bivalves from Italian market: Beneficial and risk for consumers health. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumway, S.E.; Parsons, G.J. Scallops: Biology, Ecology and Aquaculture, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; p. 1500. [Google Scholar]
- Strand, Ø.; Louro, A.; Duncan, P.F. European aquaculture. In Scallops, 3E; Shumway, S.E., Parsons, G.J., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 859–890. [Google Scholar]
- Berik, N.; Çankiriligil, C.; Gül, G. Mineral content of smooth scallop (Flexopecten glaber) caught Canakkale, Turkey and evaluation in terms of food safety. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 42, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telahigue, K.; Chetoui, I.; Rabeh, I.; Salah, M.; El, M. Comparative fatty acid profiles in edible parts of wild scallops from the Tunisian coast. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, E. La venericoltura in Italia. In Estado Actual del Cultivo y Manejo de Moluscos Bivalvos y su Proyecci on Futura. Factores que Afectan su Sustentabilidad en America Latina; Lovatelli, A., Farìas, A., Uriarte, I., Eds.; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2008; pp. 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Marčeta, T.; Da Ros, L.; Marin, M.G.; Codognotto, V.F.; Bressan, M. Overview of the biology of Flexopecten glaber in the North Western Adriatic Sea (Italy): A good candidate for future shellfish farming aims? Aquaculture 2016, 462, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berik, N.; Çankiriligil, C. Determination of proximate composition and sensory attributes of scallop (Flexopecten glaber) gonads. Mar. Sci. Tech. Bull. 2013, 2, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mohite, S.A.; Mohite, A.S.; Singh, H. On condition index and percentage edibility of the shortneck clam Paphia malabarica (Chemintz) from estuarine regions of Ratnagiri, west coast of India. Aquacult. Res. 2009, 40, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumus, I.; Stirling, H.P. Seasonal variations in the weight, condition index and biochemical composition of mussels (Mytilus edulis L.) in suspended culture in two Scottish sea lochs. Aquaculture 1998, 159, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association of Official Agricultural Chemists. Official Methods of Analyses of the Association of Analytical Chemists, 18th ed.; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the Principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric methods for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, H.; Southgate, D.A.T. Food Composition Data. Production, Management and Use; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003; p. 289. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht, T.L.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary Heart Disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, F. Effects of genotype, feeding system and slaughter weight on the quality of light lambs. II. Fatty acid composition of meat. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 77, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, H.; Berber, S.; Acarli, S.; Vural, P. Seasonal variation in the condition index, meat yield and biochemical composition of the flat oyster Ostrea edulis (Linnaeus, 1758) from the Dardanelles, Turkey. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 10, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Anibal, J.; Esteves, E.; Rocha, R. Seasonal variations in gross biochemical composition, percent edibility and condition index of the clam Ruditapes decussatus cultivated in the Ria Formosa (South Portugal). J. Shellfish Res. 2011, 30, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberoumad, A.; Pourshafi, K. Chemical and proximate composition properties of different fish species obtained from Iran. World J. Fish. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 237–239. [Google Scholar]
- Karnjanapratum, S.; Benjaku, S.; Soottawat, K.; Hideki, T.; Tassi, Y.H. Chemical compositions and nutritional value of Asian hard clam (Meretrix lusoria) from the coast of Andaman Sea. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4138–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Venkatesan, V.; Rajagopal, S. Biochemical composition of different body parts of Gafrarium tumidum (Roding, 1798) from Mandapam, Southeast coast of India. Afr. J. Biotech. 2012, 11, 1700–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, N.; Murugan, S.; Bharadhirajan, P. Biochemical composition of marine bivalve Donax incarnatus (Gmelin, 1791) from Cuddalore southeast coast of India. Int. J. Adv. Phar. Biol. Chem 2014, 3, 575–582. [Google Scholar]
- Ademolu, K.O.; Idowu, A.B.; Mafiana, C.F.; Osinowo, O.A. Performance, proximate and mineral analyses of African giant land snail (Archachatina marginata) fed different nitrogen sources. Afr. J. Biotech. 2004, 3, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbuaro, O.; Oso, J.A.; Edward, J.B.; Ogunleye, R.F. Nutritional status of four species of giant land snails in Nigeria. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2006, 7, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margret, S.M. A Survey on Biodiversity of Molluscs in Trash Fish Landing of Colachal and Kadipatinam and Searching of Gastropods and Bivalves for Human Consumption. Ph.D. Thesis, Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tamil Nadu, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jayanthi, G.; Muthusamy, A.; Chelladurai, G.; Karthigarani, M.; Kumaraguru, A. Comparative studies on biochemical analysis of some economically important marine gastropods along Gulf of Mannar region, southeast coast of India. J. Coast. Life Med. 2016, 4, 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Sargent, J.R. Origins and function of egg lipids nutritional implications. In Broodstock Management and Egg and Larval Activity; Bromage, N.R., Roberts, R.J., Eds.; Black Well Sciences: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 353–372. [Google Scholar]
- Telahigue, K.; Hajji, T.; Rabeh, I.; El Cafsi, M. The Effect of starvation on the biochemical composition of the digestive gland, the gonads and the adductor muscle of the scallop Flexopecten glaber. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 4, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Reiriz, M.J.; Pérez-Camacho, A.; Peteiro, L.G.; Labarta, U. Growth and kinetics of lipids and fatty acids of the clam Venerupis pullastra during larval development and postlarvae. Aquac. Nutr. 2011, 17, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, N.V. Fatty Acids of marine mollusks: Impact of diet, bacterial symbiosis and biosynthetic Potential. Biomulecules 2019, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsella, J.R.; Lokesh, B.R.; Stone, R.A. Dietary n3 polyunsatured fatty acids and amelioration of cardiovascular disease: Possible mechanisms. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S.; Appel, L.J. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C. Functional roles of fatty acids and their effects on human health. J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2015, 39, 185–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashek, D.G.; Wu, C. MUFAs American Society for Nutrition. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Chakkalakal, S.J.; Joseph, D.; Joy, M. Nutritional Composition of Edible Oysters (Crassostrea madrasensis L.) from the Southwest Coast of India. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 25, 1172–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancheva, M.; Merdzhanova, A.; Dobreva, D.A. Fat soluble vitamins, cholesterol, and Fatty Acid composition of Wild and Farmed Black Mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) consumed in Bulgaria. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 26, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Omega-3 fatty acids in health and disease and in growth and development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 54, 438–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.S.; Von Schacky, C. The Omega-3 Index: A New Risk Factor for Sudden Cardiac Death? Prev. Med. 2004, 39, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, S.; Miura, K.; Sasaki, S.; Yoshita, K.; Morikawa, Y.; Ishizaki, M.; Kido, T.; Naruse, Y.; Nakagawa, H. Dietary intake of fatty acids and serum C-reactive protein in Japanese. J. Epidem. 2007, 17, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel-Tandukar, K.; Nanri, A.; Matsushita, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Ohta, M.; Sato, M.; Mizoue, T. Dietary intakes of α-linolenic and linoleic acids are inversely associated with serum C-reactive protein levels among Japanese men. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsche, K.L. Too much linoleic acid promotes inflammation—Doesn’t it? Prostag. Leukotr. Ess. Fatty Acids 2008, 79, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F.; Cicek, E.; Polat, A.; Kuley, E. Fat content and fatty acid compositions of 34 marine water fish species from the Mediterranean Sea. International. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 464–475. [Google Scholar]
- Careaga, V.P.; Muniain, C.; Maier, M.S. Fatty acid composition of the edible sea cucumber Athyonidium Chilensis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Biandolino, F. Total lipid content and fatty acid composition of commercially important fish species from the Mediterranean, Mar Grande Sea. Food. Chem. 2012, 131, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azpeitia, K.; Rìos, Y.; Garcia, I.; Pagaldai, J.; Mendiola, D.A. Sensory and nutritional validation of open ocean mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk.) cultured in SE Bay of Biscay (Basque Country) compared to their commercial counterparts from Galician Rìas (Spain). Int. Aquat. Res. 2017, 9, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prato, E.; Fanelli, G.; Parlapiano, I.; Biandolino, F. Bioactive fatty acids in seafood from Ionian Sea and relation to dietary recommendations. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Miller, L.A.; Perren, M.; Addis, P.B. Omega-3 fatty acids in Lake Superior fish. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids: Evolutionary aspects. In Omega-6/Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acid Ratio: The Scientific Evidence; Simopoulos, A.P., Cleland, L.G., Eds.; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2003; Volume 92, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Asha, K.K.; Anandan, R.; Mathew, S.; Lakshmanan, P.T. Biochemical profile of oyster Crassostrea madrasensis and its nutritional attributes. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, G.M.; Pascoal, J.C.M.; Torres, E.A.F.S.; Soares, R.A.M.; Mendonça, S.; Sampaio, G.R.; Correia, M.S.; Cabral, C.C.V.Q.; Junior, C.R.C.; Lopez, A.M.Q. Influence of seasonality on the chemical composition of oysters (Crassostrea rhizophorae). J. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiovascular Review Group. Nutritional aspects of Cardiovascular Disease: Report of the Cardiovascular Review Group, Committee on Medical Aspects of Food Policy; HMSO: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.H.; Mencia-Huerta, J.M.; Shih, C.; Corey, E.J.; Lewis, R.A.; Austen, K.F. Effects of exogenous arachidonic, eicosapentaenoic, and docosahexaenoic acids on the generation of 5-lipoxygenase pathway products by ionophore-activated human neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 74, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskiet, F.A.J. Pathophysiology and evolutionary aspects of dietary fats and long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids across the life cycle. In Fat Detection: Taste, Texture, and Post Ingestive Effects; Montmayeur, J.P., le Coutre, J., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- HMSO UK. Nutritional aspects of cardiovascular disease. In Report on Health and Social Subjects; HMSO: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; WHO. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Report No. 978. In Proceedings of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on the Risks and Benefits of Fish Consumption, Rome, Italy, 25–29 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
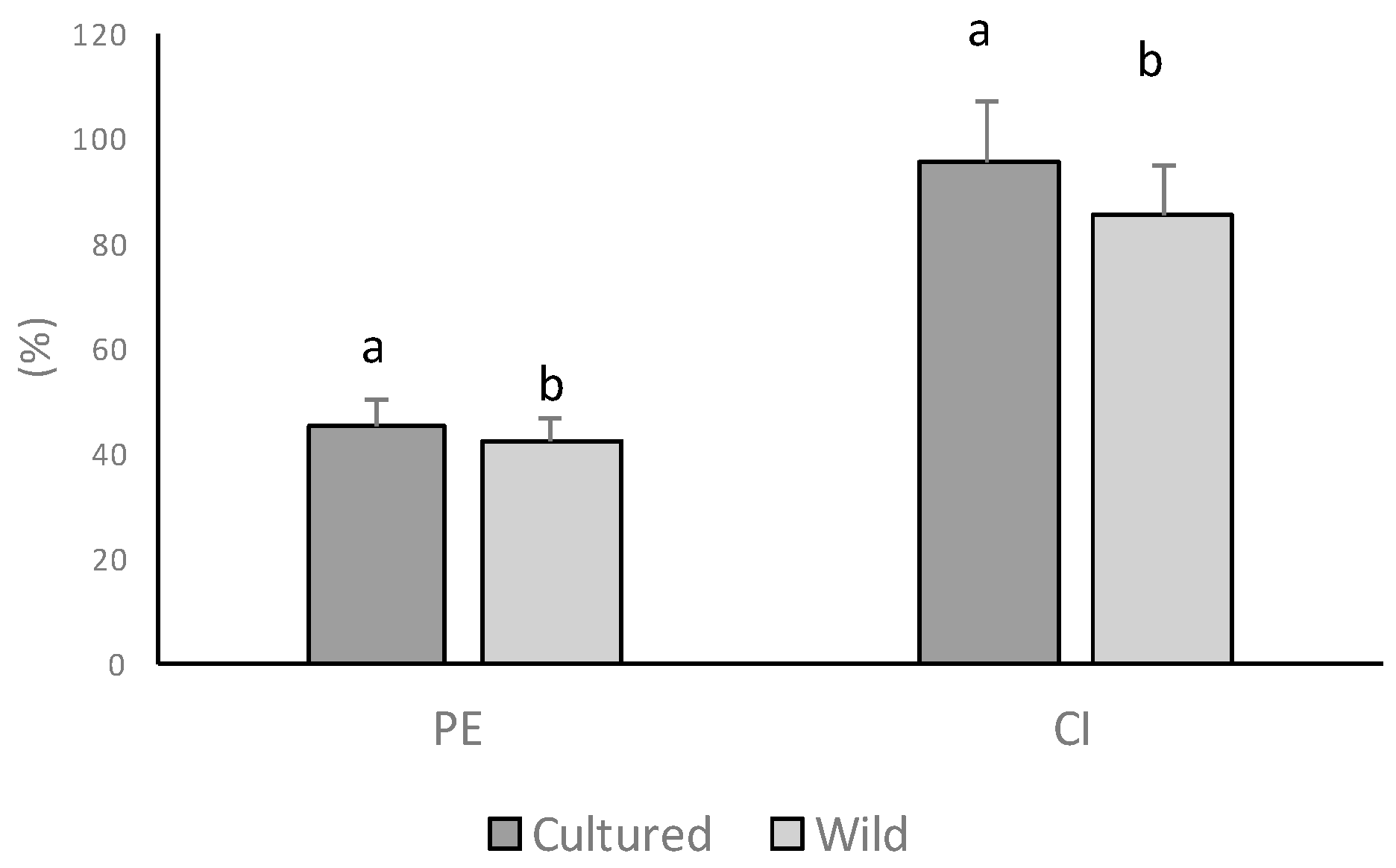
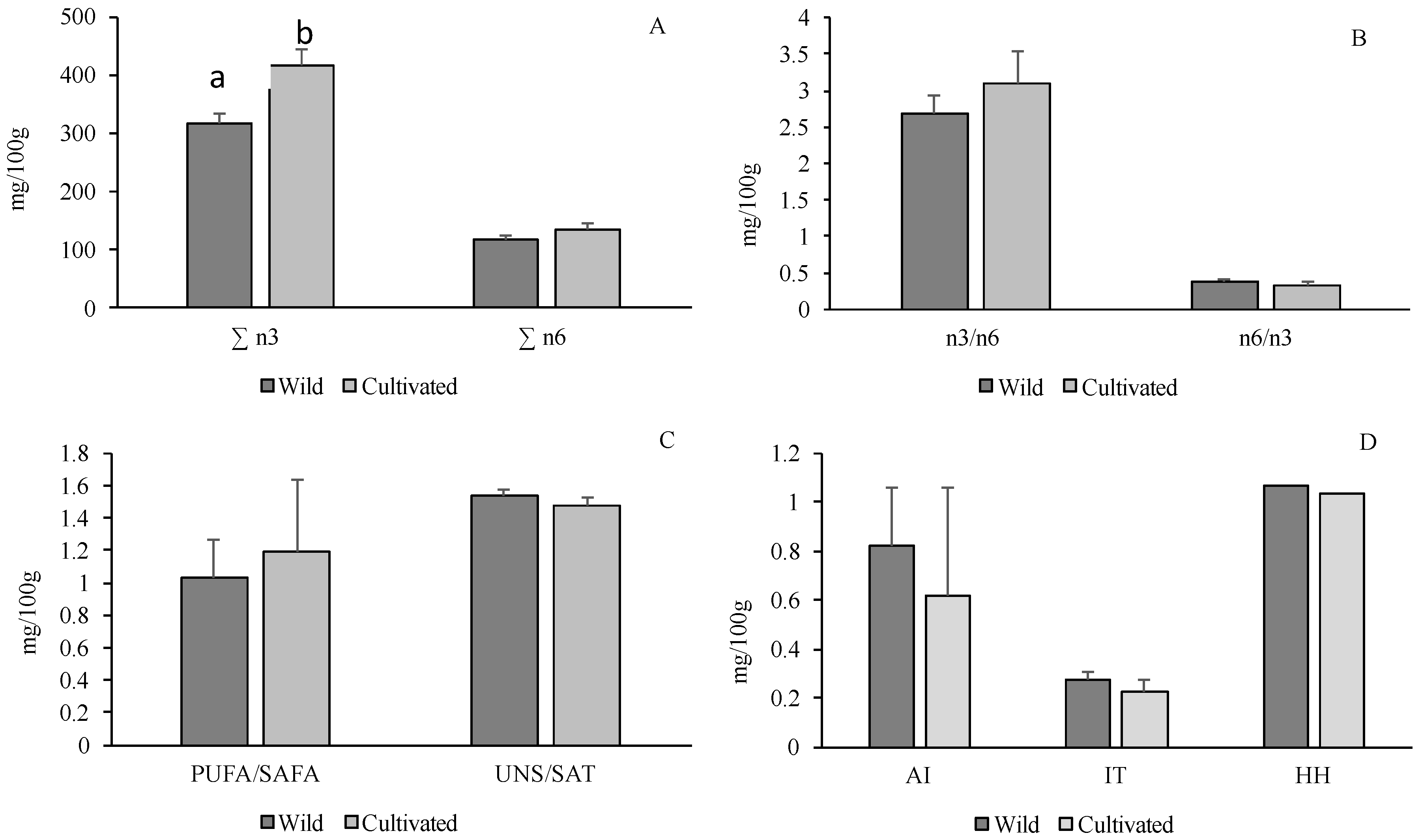
| Wild | Cultivated | |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 84.53 ± 1.5 | 83.17 ± 0.8 |
| Ash (g/100 g) | 3.51 ± 1.7 | 3.78 ± 0.8 |
| Protein (g/100 g) | 8.50 ± 1.2 a | 11.62 ± 1.1 b |
| Lipid (g/100 g) | 1.45 ± 0.3 a | 1.70 ± 0.2 b |
| Carbohydrate (g/100 g) | 0.03 ± 0.1 | 0.03 ± 0.1 |
| Wild | Cultured | |
|---|---|---|
| C14:0 | 56.25 ± 43.13 (5.54) | 44.42 ± 8.93 (3.73) |
| C15:0 | 18.26 ± 30.85 (1.80) | 1.35 ± 0.56 (0.11) |
| C16:0 | 253.32 ± 21.96 * (24.96) | 319.32 ± 29.78 * (26.83) |
| C17:0 | 18.54 ± 2.89 (1.83) | 18.64 ± 1.81 (1.57) |
| C18:0 | 39.57 ± 19.91 * (3.90) | 77.35 ± 11.72 * (6.50) |
| C20:0 | 2.92 ± 2.27 (0.29) | 1.98 ± 0.72 (0.17) |
| C21:0 | 3.09 ± 0.33 (0.30) | 4.01 ± 1.22 (0.34) |
| ∑SAFA | 398.19 ± 55.08 (39.22) | 467.07 ± 25.66 (39.25) |
| C14:1 | 1.3 ± 0.49 (0.13) | 1.54 ± 0.47 (0.13) |
| C16:1 | 82.67 ± 9.10 * (8.14) | 45.62 ± 7.74 * (3.83) |
| C17:1 | 8.67 ± 0.89 (0.89) | 9.72 ± 2.93 (0.82) |
| C18:1n9t | 10.21 ± 2.21 (1.00) | 11.98 ± 2.75 (1.01) |
| C18:1n9c | 6.43 ± 0.64 (0.63) | 3.23 ± 1.89 (0.27) |
| C18:1n7 | 55.61 ± 45.94 (7.84) | 54.62 ± 11.40 (4.59) |
| C20:1n9 | 3.07 ± 0.62 (0.27) | 2.97 ± 1.19 (0.25) |
| C22:1n9 | 3.71 ± 0.13 (0.36) | 4.88 ± 0.74 (0.41) |
| ∑MUFA | 195.65 ± 16.03 (19.27) | 134.57 ± 7.11 (11.31) |
| C18:2n6t | 12.65 ± 1.49 (1.24) | 14.75 ± 9.86 (2.56) |
| C18:2n6c | 30.09 ± 1.05 (2.96) | 36.25 ± 9.80 (3.05) |
| C18:3n6 | 3.75 ± 0.18 * (0.37) | 1.58 ± 0.29 * (0.13) |
| C18:3n3 | 38.66 ± 4.94 (3.81) | 40.62 ± 2.85 (3.41) |
| C18:4n3 | 62.91 ± 1.92 (6.20) | 52.95 ± 17.65 (4.45) |
| C20:2 | 1.71 ± 0.38 * (0.17) | 7.14 ± 3.14 * (0.6) |
| C22:0 + 20:3n6 | 32.02 ± 6.51 * (3.15) | 65.65 ± 17.65 * (5.52) |
| C20:3n3 + 22:1 | 9.89 ± 0.32 * (0.97) | 44.23 ± 20.02 * (1.40) |
| C20:4n6 | 39.44 ± 2.95 * (3.88) | 16.66 ± 4.76 * (3.43) |
| C22:2 | 0.89 ± 0.16 * (0.09) | 40.86 ± 11.74 * (0.06) |
| C20:5n3 | 101.11 ± 2.25 (9.96) | 105.91 ± 4.12 (8.90) |
| C22:5n3 | 23.81 ± 5.19 (2.34) | 7.21± 1.07 (0.61) |
| C22:6n3 | 81.06 ± 10.25 * (7.98) | 163.43 ± 4.95 * (13.73) |
| ∑ PUFA | 403.02 ± 49.24 * (39.70) | 553.79 ± 13.78 * (46.54) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biandolino, F.; Parlapiano, I.; Grattagliano, A.; Fanelli, G.; Prato, E. Comparative Characteristics of Percentage Edibility, Condition Index, Biochemical Constituents and Lipids Nutritional Quality Indices of Wild and Farmed Scallops (Flexopecten glaber). Water 2020, 12, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061777
Biandolino F, Parlapiano I, Grattagliano A, Fanelli G, Prato E. Comparative Characteristics of Percentage Edibility, Condition Index, Biochemical Constituents and Lipids Nutritional Quality Indices of Wild and Farmed Scallops (Flexopecten glaber). Water. 2020; 12(6):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061777
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiandolino, Francesca, Isabella Parlapiano, Asia Grattagliano, Giovanni Fanelli, and Ermelinda Prato. 2020. "Comparative Characteristics of Percentage Edibility, Condition Index, Biochemical Constituents and Lipids Nutritional Quality Indices of Wild and Farmed Scallops (Flexopecten glaber)" Water 12, no. 6: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061777
APA StyleBiandolino, F., Parlapiano, I., Grattagliano, A., Fanelli, G., & Prato, E. (2020). Comparative Characteristics of Percentage Edibility, Condition Index, Biochemical Constituents and Lipids Nutritional Quality Indices of Wild and Farmed Scallops (Flexopecten glaber). Water, 12(6), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061777







