Characterization of the Agricultural Supply of Desalinated Seawater in Southeastern Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Water Management in the Study Region
2.2. Sources of Information
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Desalinated Seawater Production and Supply to Agriculture
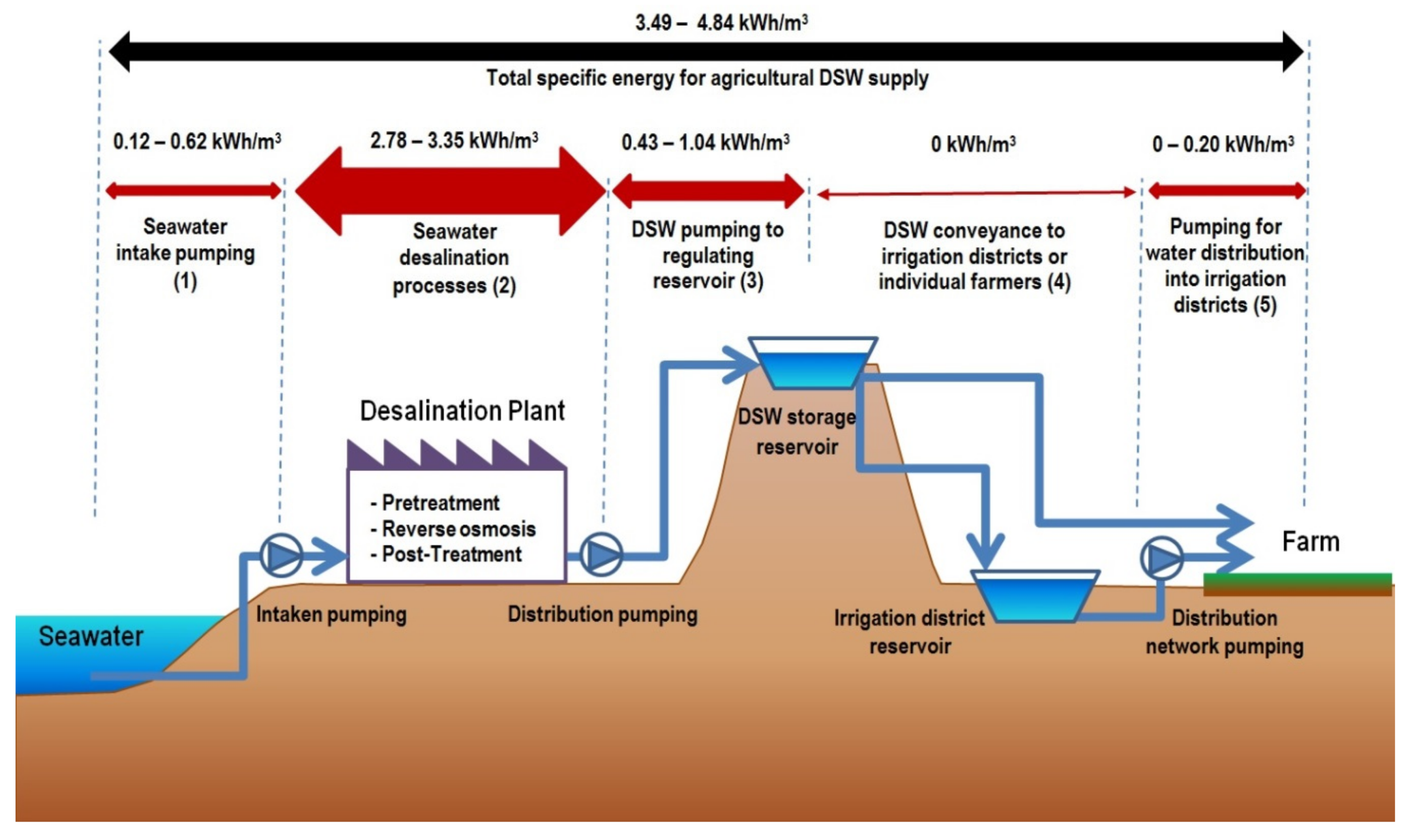
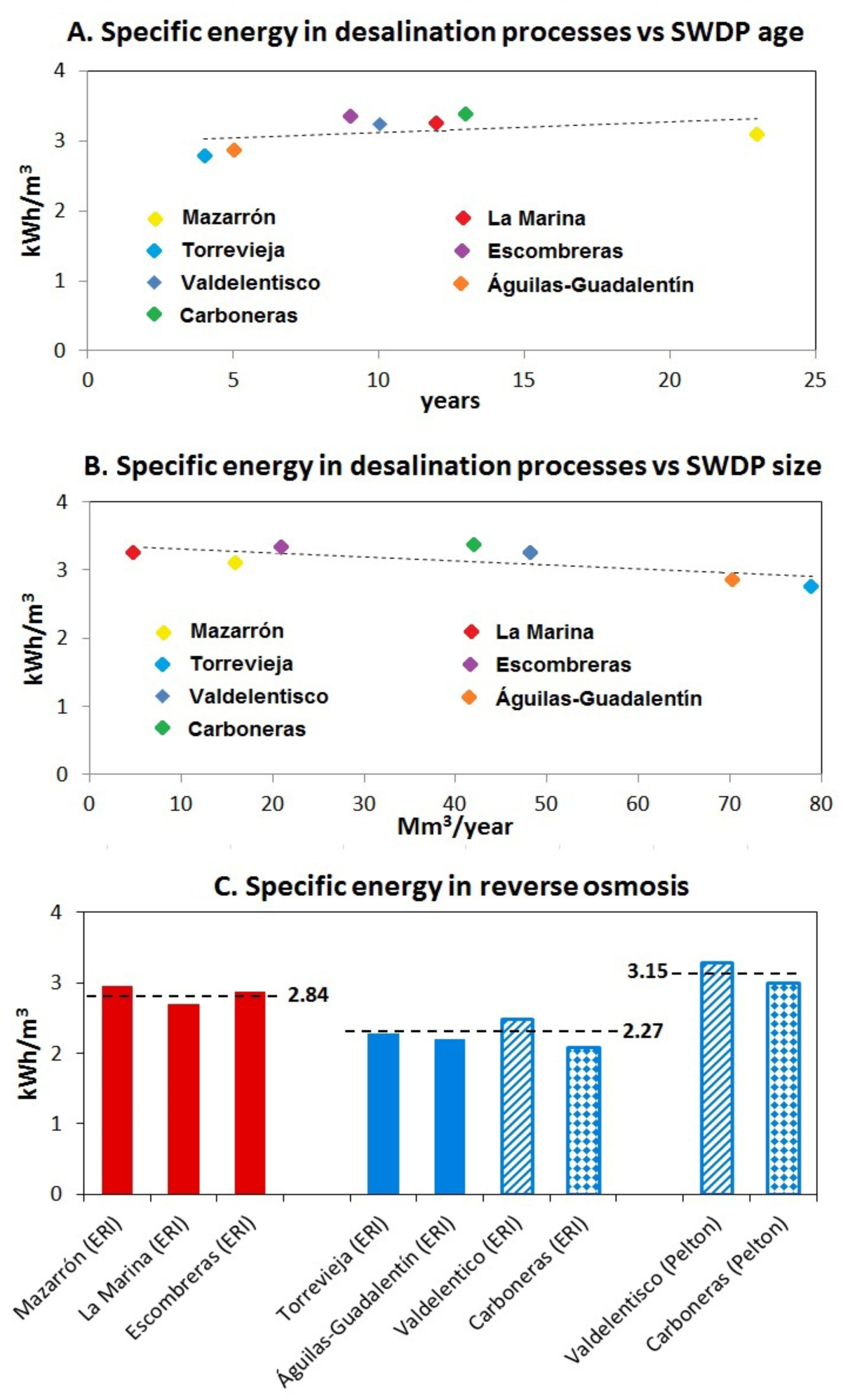
3.2. Energy Consumption of DSW for Agriculture
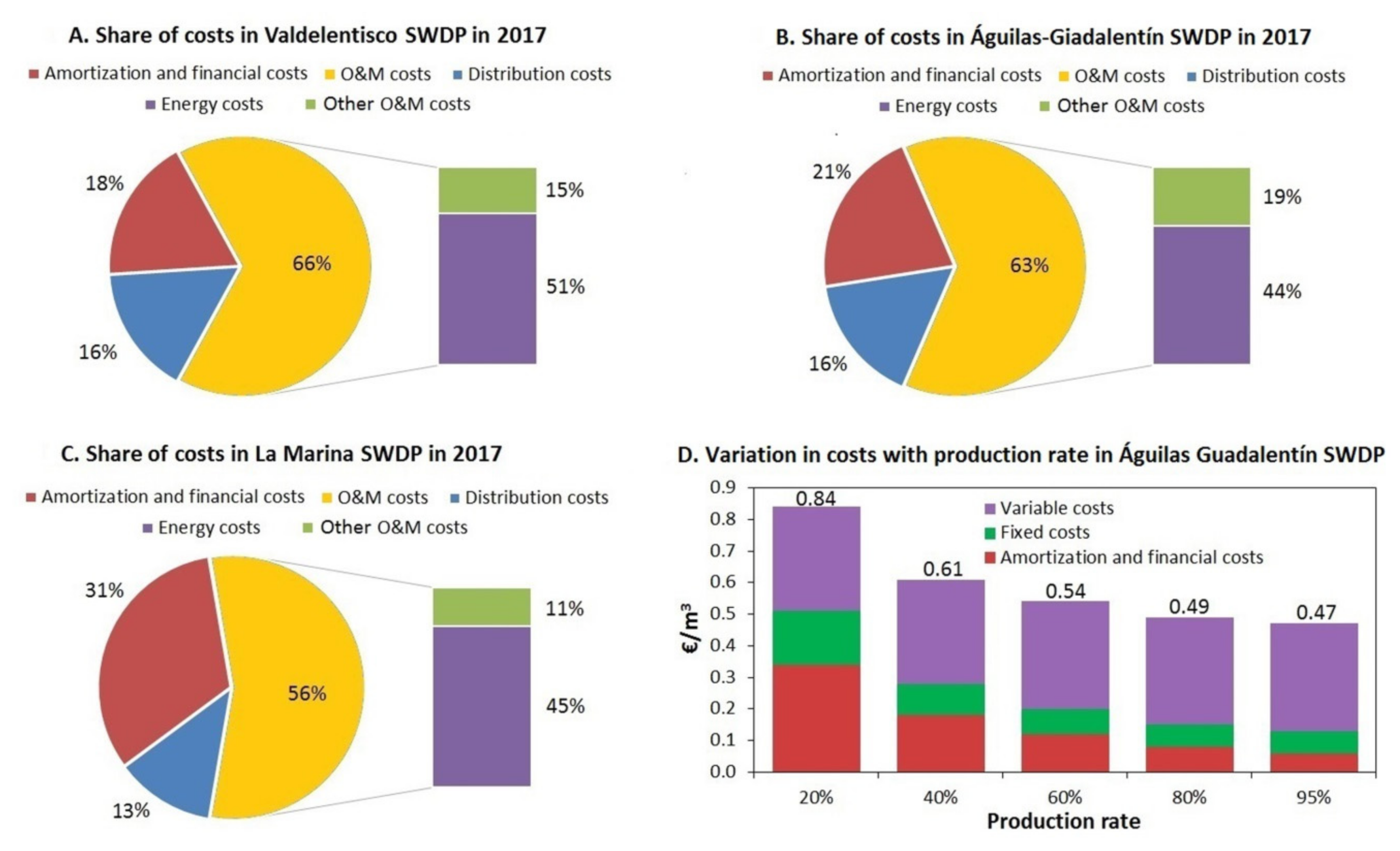
3.3. Costs of DSW Supply to Agriculture
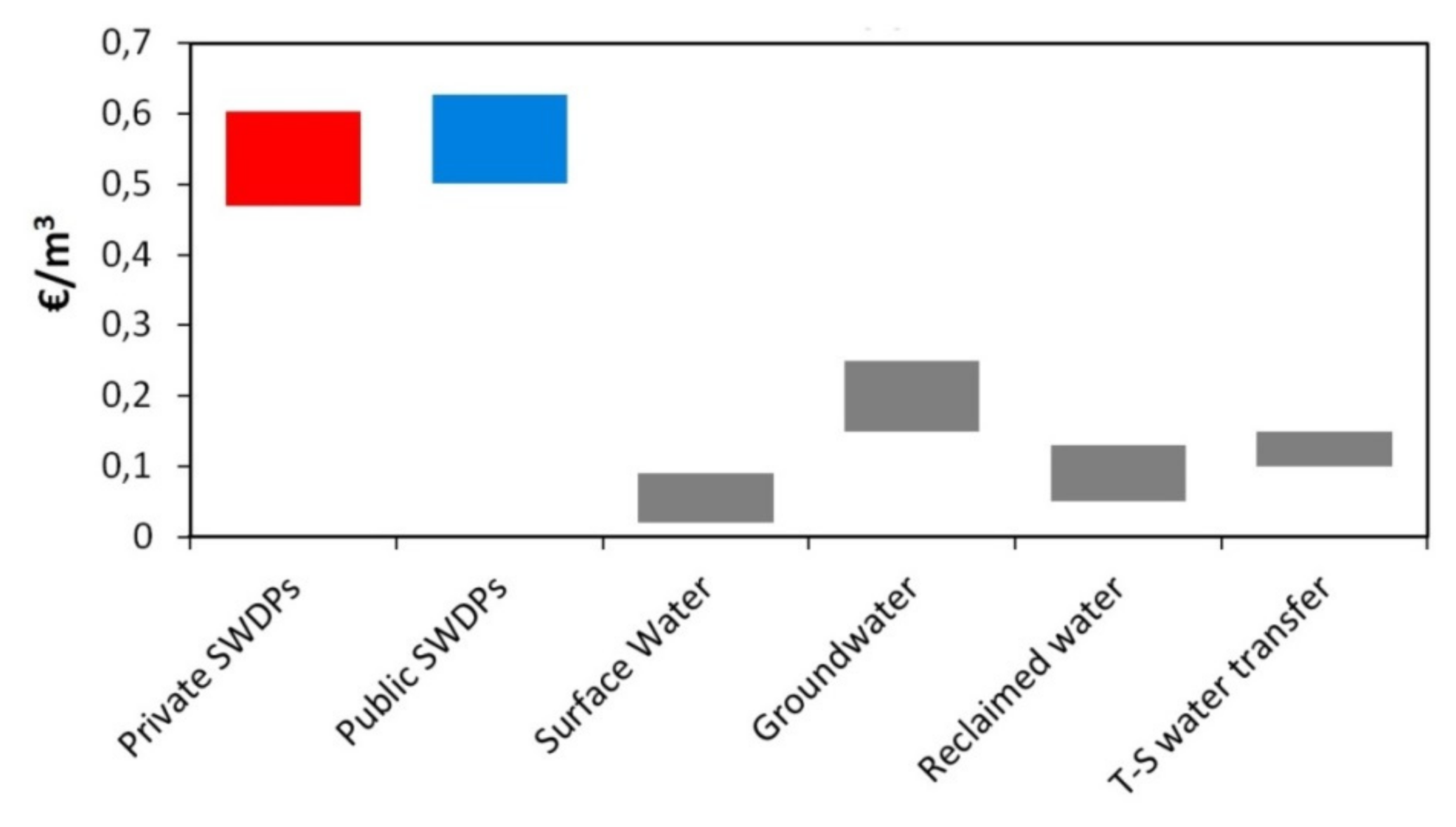
3.4. Price of DSW Supply to Farmers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). The 3rd United Nations World Water Development Report: Water in a Changing World; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2009; 318p. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; 151p. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, A.; Garrote, L.; Diz, A.; Schlickenrieder, J.; Martin-Carrasco, F. Re-thinking water policy priorities in the Mediterranean region in view of climate change. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediterranean Water Scarcity and Drought Working Group (MED WS&D WG). Mediterranean Water Scarcity and Drought Report; MED WS&D WG, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2008; Available online: www.emwis.net/topics/WaterScarcity (accessed on 30 March 2019).
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology and the environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Alvarez, V.; Martín-Gorriz, B.; Soto-García, M. Seawater desalination for crop irrigation. A review of current experiences and revealed key issues. Desalination 2016, 381, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar Sánchez, J.A.; Belmonte Ureña, L.J.; Valera, D.L. Perceptions and acceptance of desalinated seawater for irrigation: A case study in the níjar district (Southeast Spain). Water 2017, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yoshikawa, S.; Iseri, Y.; Fujimori, S.; Kanae, S. An economic assessment of the global potential for seawater desalination to 2050. Water 2017, 9, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alvarez, V.; González-Ortega, M.J.; Martín-Gorriz, B.; Soto-García, M.; Maestre Valero, J.F. The use of desalinated seawater for crop irrigation in the Segura River Basin (south-eastern Spain). Desalination 2017, 364, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, A.; Israeli, Y.; Elingold, I.; Levi, M.; Levkovitch, I.; Russo, D.; Assouline, S. Irrigation with desalinated water: A step toward increasing water saving and crop yields. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermiyahu, U.; Tal, A.; Ben-Gal, A.; Bar-Tal, A.; Tarchitzky, J.; Lahav, O. Rethinking desalinated water quality and agriculture. Science 2007, 318, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, H.; Semiat, R. Sustainable RO desalination—Energy demand and environmental impact. Desalination 2017, 424, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.L.; Heck, N.; Reguero, B.G.; Potts, D.; Hovagimian, A.; Paytan, A. Biological and physical effects of brine discharge from the carlsbad desalination plant and implications for future desalination plant constructions. Water 2019, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gal, A.; Yermiyahu, U.; Cohen, S. Fertilization and blending alternatives for irrigation with desalinated water. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avni, N.; Eben-Chaime, M.; Oron, G. Optimizing desalinated sea water blending with other sources to meet magnesium requirements for potable and irrigation waters. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Kurtzman, D. Using desalinated water for irrigation: Its effect on field scale water flow and contaminant transport under cropped conditions. Water 2019, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, S.; Hoang, M.; Zarzo, D.; Olewniak, F.; Campos, E.; Bolto, B.; Barron, O. Desalination techniques—A review of the opportunities for desalination in agriculture. Desalination 2015, 364, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente de España (MAGRAMA). The water Governance System of Spain; MAGRAMA: Madrid, Spain, 2015; 31p.
- Zarzo, D.; Campos, E.; Terrero, P. Spanish experience in desalination for agriculture. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestre-Valero, J.F.; Martínez-Granados, D.; Martínez-Alvarez, V.; Calatrava, J. Socio-economic impact of evaporation losses from reservoirs under past, current and future water availability scenarios in the semi-arid Segura basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1411–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confederación Hidrográfica de la Cuenca del Segura (CHS). Plan Hidrológico de la Cuenca del Segura 2015–2021; CHS: Murcia, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer-Martinez, F.; Martínez-Paz, J.M. Climate change effects on the hydrology of the headwaters of the Tagus River: Implications for the management of the Tagus-Segura transfer. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6473–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Estrella, T. The problems of overexploitation of aquifers in semi-arid areas: The Murcia Region and the Segura Basin (South-east Spain) case. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 5729–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consejería Medio Ambiente y Ordenación del Territorio (CMAOT). Ciclo de Planificación Hidrológica 2015/2021. Demarcación Hidrográfica de las Cuencas Mediterráneas Andaluzas; CMAOT: Sevilla, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Caparros, P.; Contreras, J.I.; Baeza, R.; Segura, M.L.; Lao, M.T. Integral management of irrigation water in intensive horticultural systems of almería. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatrava, J.; Martínez-Grana, D. El valor de uso del agua en el regadío de la cuenca del Segura y en las zonas regables del trasvase Tajo-Segura. Econ. Agrar. Recurs. Nat. 2012, 12, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, H.; Sairí, D.; Rico-Amorós, A.M. The end of scarcity? Water desalination as the new cornucopia for Mediterranean Spain. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swyngedouw, E. Into the sea: Desalination as hydro-social fix in Spain. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2013, 103, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desalinated Seawater for Alternative and Sustainable Soilless Crop Production (DESEACROP). Available online: http://www.deseacrop.eu/ (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- ACUAMED. El uso del agua marina desalinizada en la agricultura de regadío. In Adaptive Measures to Mitigate the Shortage of Water for Irrigated Agriculture in Southeastern Spain, I Jornada Cátedra Trasvase y Sostenibilidad Jose Manuel Claver Valderas; Universidad Politécnica de Cartagena: Cartagena, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- ACUAMED. Informe Anual 2017; Ministerio para la transición ecológica: Madrid, Spain, 2017; 80p. [Google Scholar]
- Maestre-Valero, J.F.; González-Ortega, M.J.; Martínez-Álvarez, V.; Martin-Gorriz, B. The role of reclaimed water for crop irrigation in southeast Spain. Water Supply 2019, 19, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los Promotores de las Dos Nuevas Desaladoras Reciben Peticiones Para 100 hm3. Available online: www.laverdad.es/murcia/promotores-nuevas-desaladoras-20180218010505-ntvo.html (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Las Grandes Empresas del Campo de Cartagena se Unen Para Construir Dos Desaladoras. Available online: https://www.laverdad.es/murcia/grandes-empresas-campo-20171128014131-ntvo.html (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Ghalavand, Y.; Hatamipour, M.S.; Rahimi, A. A review on energy consumption of desalination processes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 1526–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gorriz, B.; Soto-García, M.; Martínez-Alvarez, V. Energy and greenhouse-gas emissions in irrigated agriculture of SE Spain. Effects of alternative water supply scenarios. Energy 2014, 77, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, D.L.; Yip, N.Y.; Gilron, J.; Elimelech, M. Seawater desalination for agriculture by integrated forward and reverse osmosis: Improved product water quality for potentially less energy. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stillwell, A.S.; Webber, M.E. Predicting the specific energy consumption of reverse osmosis desalination. Water 2016, 8, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACUAMED. Producción y uso de aguas desaladas para regadío. In Working Day on Irrigation Management under Water Scarcity Situation; Centro Nacional de Tecnología de Regadíos: San Fernando de Henares, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Karaghouli, A.; Kazmerski, L.L. Energy consumption and water production cost of conventional and renewable-energy-powered desalination processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, A.; Bragalli, C.; Lenzi, C.; Artina, S. Energy Efficiency optimization in water distribution systems. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzo, D.; Prats, D. Desalination and energy consumption. What can we expect in the near future? Desalination 2018, 427, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asociación Española de Desalación y Reutilización (AEDyR). (Bilbao, Spain). Conclusions of the VII Conference of the Spanish Desalination and Reuse Association. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Semiat, R. Energy issues in desalination processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8193–8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.M.; Chua, H.T. Thermodynamic perspective for the specific energy consumption of seawater desalination. Desalination 2016, 386, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Rosenberg, S.; Peery, M. Energy efficiency breakdown of reverse osmosis and its implications on future innovation roadmap for desalination. Desalination 2015, 368, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.M.; Peshev, D.; Livingston, A.G. Energy consumption for desalination—A comparison of forward osmosis with reverse osmosis, and the potential for perfect membranes. Desalination 2016, 377, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñate, B.; García-Rodríguez, L. Energy optimisation of existing SWRO (seawater reverse osmosis) plants with ERT (energy recovery turbines): Technical and thermoeconomic assessment. Energy 2011, 36, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swyngedouw, E.; Williams, J. From Spain’s hydro-deadlock to the desalination fix. Water Int. 2016, 41, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, A. Energy cost of desalination in the A.G.U.A. program. Investig. Geogr. 2014, 62, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ziolkowska, J.R. Is desalination affordable?—Regional cost and price analysis. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuente, E. Full cost in desalination. A case study of the Segura River Basin. Desalination 2012, 300, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiritos, E.; Lipchin, C. Desalination in Israel, Water Policy in Israel: Context, Issues and Options; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Tal, A.; Yermiyahu, U.; Ben-Gal, A.; Schwartz, A.; Faingold, I.; Seligmann, R. Optimization of calcium and magnesium concentrations for fertigation of tomato with desalinated water. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
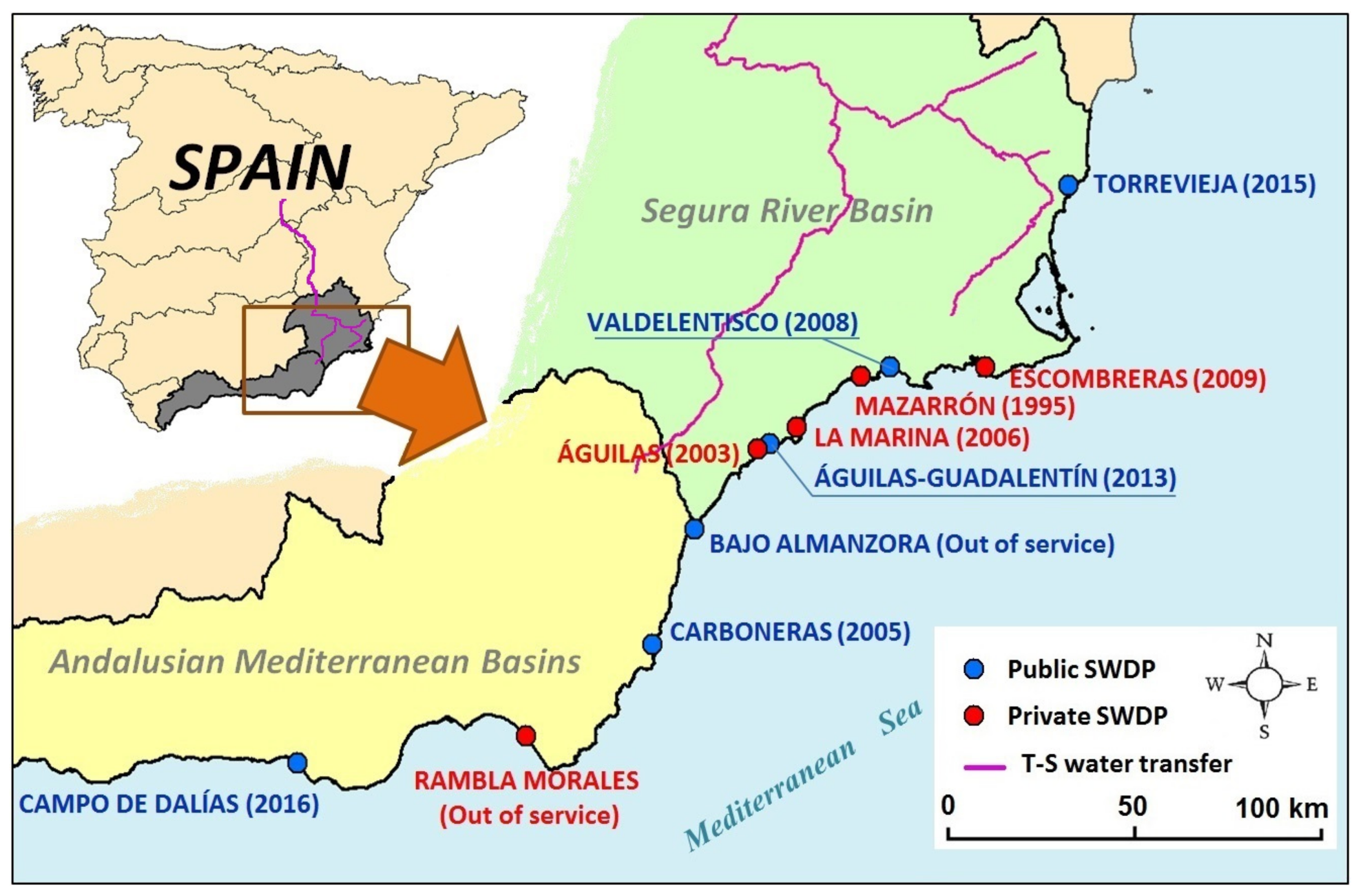
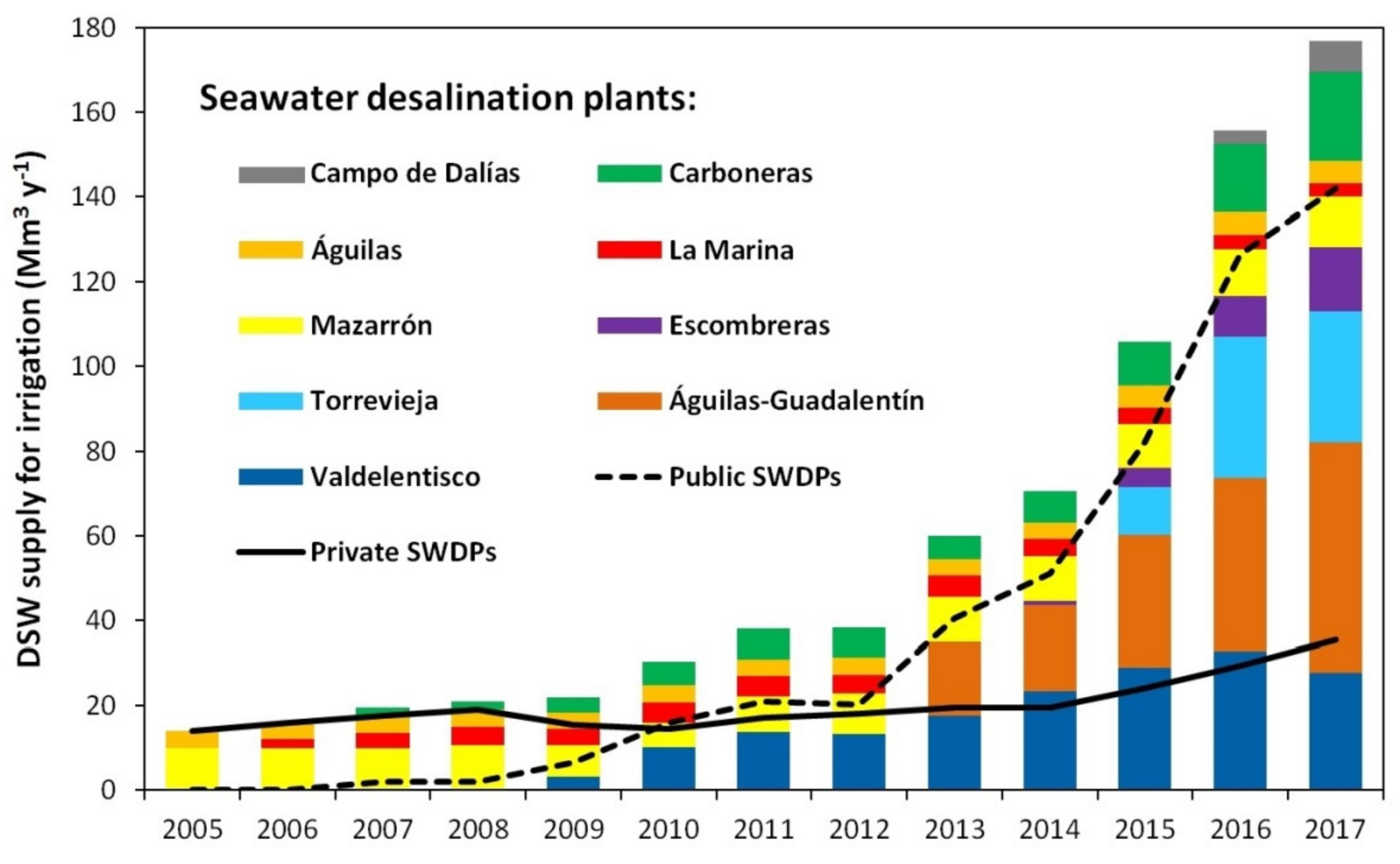
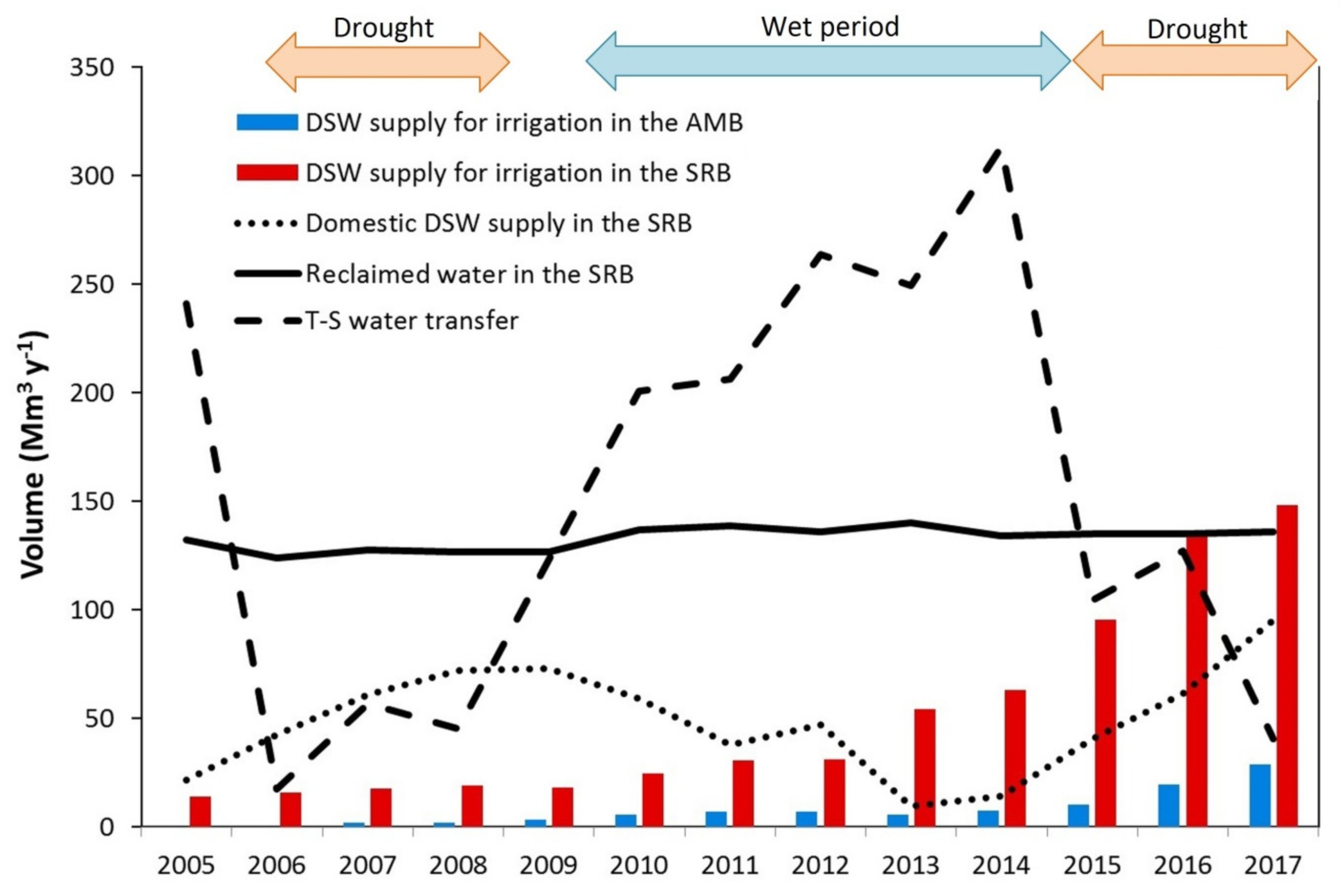
| Desalination Plant (SWDP) | Hydrographic Demarcation | Start-Up Year | Owner | Investment in SWDP (M€) | Total Production Capacity (Mm3/year) | Capacity for Irrigation (Mm3/year) | Supplied Irrigated Area (ha) | Main Crops | Distribution System for Irrigation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investment (M€) | Length (km) | Storage Capacity (Mm3) | |||||||||
| Mazarrón (Virgen del Milagro) | Segura Basin | 1995 | Mazarrón irrigation district | 19 | 16 | 16 (100%) | 3595 | Tomato in greenhouse, citrus trees | 11 | 103 | 0.9 in 9 reservoirs |
| Águilas | Segura Basin | 2003 | Águilas irrigation district | - | 8 | 8 (100%) | 5524 | Tomato in greenhouse, lettuce | - | >100 | 0.40 in 5 reservoirs |
| La Marina | Segura Basin | 2006 | La Marina irrigation district | 13 | 5 | 4.8 (95%) | 1200 | Tomato in greenhouse, citrus trees | 1 | 5 | 0.75 in 3 reservoirs |
| Valdelentisco | Segura Basin | 2008 | ACUAMED (Spanish Government) | 128 | 48 | 37 (77%) | 21,340 | Winter vegetables, citrus trees | 96 | >100 | 2.60 in 4 reservoirs |
| Escombreras | Segura Basin | 2009 | Hydro Management company | 117 | 21 | 20.5 (98%) | 15,352 | Winter vegetables, citrus trees | * | 56 | 0.025 in 1 reservoir |
| Águilas-Guadalentín | Segura Basin | 2013 | ACUAMED (Spanish Government) | 203 | 70 | 58 (83%) | 30,751 | Citrus trees, lettuce, tomato | 44 | 36 | 0.12 in 1 reservoir |
| Torrevieja | Segura Basin | 2014 | ACUAMED (Spanish Government) | 264 | 80 | 40 (50%) | 42,319 | Winter vegetables, citrus trees | 29 | 21 | 246 in 1 dam |
| Carboneras | Andalusian Mediterranean Basins | 2005 | ACUAMED (Spanish Government) | 132 | 42 | 24.5 (58%) | 18,500 | Vegetables in greenhouse, mainly tomato | 226 | 120 | 0.6 in 6 reservoirs |
| Campo de Dalías | Andalusian Mediterranean Basins | 2016 | ACUAMED (Spanish Government) | 130 | 30 | 22.5 (75%) | 22,000 | Vegetables in greenhouse, mainly pepper | ** | 40.7 | 0.4 in 5 reservoirs |
| Rambla Morales | Andalusian Mediterranean Basins | - | Rambla Morales irrigation district | 39 | 22 | 22 (100%) | 3300 | Vegetables in greenhouse, mainly tomato | - | - | - |
| Bajo Almanzora | Andalusian Mediterranean Basins | - | ACUAMED (Spanish Government) | 88 | 20 | 15 (75%) | 24,000 | Tomato greenhouse and melon | ** | 15.3 | 0.08 in 1 reservoir |
| Desalination Plant (SWDP) | (1) | (2) | (3) + (4) | (5) | Total (kWh/m3) | Data from |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seawater Intake (kWh/m3) | Desalination Processes (kWh/m3) | DSW Pumping to Irrigation Districts (kWh/m3) | DSW Distribution in Irrigation Districts (kWh/m3) | |||
| Mazarrón | 0.42 | 3.06 | 1.00 | 0 (gravity-driven distribution) | 4.48 | Questionnaire |
| La Marina | 0.20 | 3.20 | 0.70 | 0 (gravity-driven distribution) | 4.10 | Questionnaire |
| Escombreras | 0.40 | 3.35 | 0.75 | 0 (gravity-driven distribution) | 4.50 | Questionnaire |
| Average value for Private SWDPs | - | - | - | - | 4.36 | - |
| Valdelentisco * | 0.36 | 3.24 | 0.92 | 0 (gravity-driven distribution) | 4.52 | Questionnaire, [31] and [39] |
| Águilas-Guadalentín | 0.37 | 2.85 | 1.04 | 0.20 | 4.46 | Questionnaire, [31] and [39] |
| Torrevieja | 0.12 | 2.78 | 0.43 | 0.16 | 3.49 | Questionnaire, [31] and [39] |
| Carboneras ** | 0.62 | 3.38 | 0.84 | 0 (gravity-driven distribution) | 4.84 | Questionnaire, [31] and [39] |
| Average value for Public SWDPs | - | - | - | - | 4.32 | - |
| Desalination Plant (SWDP) | Amortization and Financial Costs (€/m3) * | Operation and Maintenance Costs (€/m3) | Distribution to Irrigation Districts (€/m3) | Distribution within Irrigation Districts (€/m3) | Total (€/m3) | Data from | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Other O&M | ||||||
| Mazarrón | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.11 | - | 0.08 | 0.68 | Questionnaire |
| La Marina | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.08 | - | 0.09 | 0.72 | Questionnaire |
| Average value for Private SWDPs | - | - | - | - | - | 0.70 | - |
| Valdelentisco | 0.10 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.09 | - | 0.57 | Questionnaire and adapted from [30] |
| Águilas-Guadalentín | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.53 | Questionnaire and adapted from [30] |
| Average value for Public SWDPs | - | - | - | - | - | 0.55 | - |
| Desalination Plant (SWDP) | Production Price (€/m3) | 10% Taxes (€/m3) | Conveyance to Irrigation Districts (€/m3) | Distribution within Irrigation Districts (€/m3) | Final Price to Farmers (€/m3) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mazarrón (Virgen del Milagro) | 0.40 | - | - | 0.08 | 0.48 | The SWDP is located in the irrigation district. Amortization and financial costs were subsidized. |
| La Marina | 0.62 | - | - | 0.09 | 0.47 | The SWDP is located in the irrigation district. Final price is lower than DSW price since it is blended with brackish groundwater before supplying farmers. |
| Escombreras | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.60 | The SWDP is located far from the irrigation district. This SWDP also supplies directly to some farmers with its own conveyance/distribution network. |
| Average value for Private SWDPs | - | - | - | - | 0.52 | - |
| Valdelentisco | 0.57 | 0.06 | * | * | 0.63 | The SWDP is located far from the irrigation district, but it has a conveyance/distribution network with on-farm hydrants. |
| Águilas-Guadalentín | 0.42 | 0.04 | * | 0.04 | 0.50 | The SWDP is located far from the irrigation district. The price in supply contracts ranges from 0.38 to 0.50, with 0.42 being the average value. |
| Torrevieja | 0.49 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.59 | The SWDP is located far from the irrigation district and only supplies to irrigation districts. |
| Carboneras | 0.49 | 0.05 | * | 0.02 | 0.55 | The SWDP is located far from the irrigation district. DSW is gravity-driven distributed into the irrigation district. |
| Campo de Dalías | 0.5 | 0.05 | * | 0.03 | 0.58 | The SWDP is located in the irrigation district. |
| Average value for Public SWDPs | - | - | - | - | 0.55 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Alvarez, V.; Maestre-Valero, J.F.; González-Ortega, M.J.; Gallego-Elvira, B.; Martin-Gorriz, B. Characterization of the Agricultural Supply of Desalinated Seawater in Southeastern Spain. Water 2019, 11, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061233
Martínez-Alvarez V, Maestre-Valero JF, González-Ortega MJ, Gallego-Elvira B, Martin-Gorriz B. Characterization of the Agricultural Supply of Desalinated Seawater in Southeastern Spain. Water. 2019; 11(6):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061233
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Alvarez, Victoriano, Jose F. Maestre-Valero, Manuel J. González-Ortega, Belén Gallego-Elvira, and Bernardo Martin-Gorriz. 2019. "Characterization of the Agricultural Supply of Desalinated Seawater in Southeastern Spain" Water 11, no. 6: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061233
APA StyleMartínez-Alvarez, V., Maestre-Valero, J. F., González-Ortega, M. J., Gallego-Elvira, B., & Martin-Gorriz, B. (2019). Characterization of the Agricultural Supply of Desalinated Seawater in Southeastern Spain. Water, 11(6), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11061233








