Abstract
Three carbonaceous porous materials (biochar and activated carbon) were developed from the Tectona grandis tree sawdust. The applied process of two-stage preparation included pre-treatment through hydrothermal carbonization at 190 °C and subsequent pyrolysis at 800 °C. Two chemical activating agents (K2CO3 and ZnCl2) were used to prepared activated carbons (K2CO3-AC and ZnCl2-AC), respectively. They were characterized by textural property, morphology, and surface element components and applied to remove Cr(VI) from solution at various solution pH values and initial Cr(VI) concentrations. Results showed that the textural parameters (SBET and VTotal) of the prepared material were 1757 m2/g and 1.027 cm3/g for Zn-Cl2-AC, 1013 m2/g and 0.418 cm3/g for K2CO3-AC, and 792 m2/g and 0.345 cm3/g for biochar. The adsorption process reached the highest efficiency at pH 3.0. The Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity indicated the decreasing order: ZnCl2-AC (127 mg/g) > K2CO3-AC (103 mg/g) > biochar (83.5 mg/g). The removal mechanism of Cr(V) from solution was regarded as an adsorption-coupled reduction, namely (1) partial reduction of Cr(VI) into Cr(III) during the adsorption process and (2) adsorption of the Cr(VI) anions through electrostatic attraction and pore filling and the reduced Cr(III) cations through complexation, Cπ–cation interaction, cation exchange, and pore filing. Therefore, the prepared biochar and activated carbon can server as promising adsorbents to efficiently remove both Cr(VI) and Cr(III) from water.
1. Introduction
Industry often releases a large number of potentially toxic metals into surface water and groundwater. The existence of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI))—which is a strong oxidizing agent and highly toxic chemical substance—in the water environment has caused more potential health risk for human beings (especially cancer risks) [1,2]. This is because of its carcinogenic and mutagenic nature [3]. Meanwhile, Cr(III) that is classified as a hard acid can be easy to complex with some oxygen and donor ligands in solution [2]. Therefore, in 2004, WHO establishes a maximum allowable limit for total chromium (hexavalent chromium and trivalent chromium) concentration in drinking water at 50 μg/L. Similarly, the US Environmental Protection Agency sets a limitation of total chromium concentrations at 100 μg/L for potable water [1].
As reported in the literature, hexavalent chromium can be efficiently eliminated from water media through many advanced methods. These potential water treatment technologies include ion exchange [1], chemical precipitation [4], chemical coagulation and electrocoagulation [5], electrochemical method [6], biological treatment [7], physical filtration process using nanofiltration and microfiltration [8], and adsorption [9]. Among these existing removal methods, adsorption might be a selection priority, because of its great advantages, such as a low operation cost, high regeneration capacity, and excellent efficiency of hexavalent and trivalent chromium removal from water media even at low concentrations [2,9,10,11]. In water treatment, activated carbon (AC) and biochar have been acknowledged as promising adsorbents to remove both Cr(VI) anions and Cr(III) cations from the water media and widely applied in many potable water purification and sewage treatment plants. This is presumably because they exhibit an excellent level of porosity (i.e., larger surface area and high total volume), a high concentration of oxygen-containing functional groups (i.e., carboxylic and phenolic), and high mechanical strength [12,13,14,15,16,17]. According to an industrial research report [18], the global demand for AC is expected to increase by 4.2% per year and be up to 2.2 million metric tons by 2022, and the global AC market size is estimated at approximately USD 4.75 billion in 2022. However, the high cost of commercial AC restricts their large-scale use in industries [19,20].
In essence, AC can be prepared through a chemical or physical activation process. For the chemical activation, AC can be developed through some processes: one-stage, two-stage, and three-stage [21,22]. Although the one-stage chemical activation process is commonly used to prepare AC, the two-stage one through pre-hydrothermal carbonization can produce AC with a higher density of micro-porosity and larger specific surface area than the others [14,16,22,23,24]. Moreover, biochar—a carbonaceous porous material that has a similar characterization to AC—has served as an effective-cost adsorbent for water and wastewater treatment [19]. In general, biochar can be directly prepared through a pyrolysis process under a certain oxygen-limited condition (one-stage process) [17,19,20] or indirectly prepared though pre-hydrothermal carbonization and subsequent pyrolysis (two-stage process) [23,25]. Similar to AC, biochar was developed from the two-stage process exhibited a high concentration of micro-porosity [23].
Therefore, in this study, we developed advantageous activated carbons derived from the lignocellulosic wood chips of Tectona grandis sawdust tree through the two-stage activation process using K2CO3 or ZnCl2 as potential chemical activating reagents. In addition, Tectona grandis sawdust-derived biochar was prepared simultaneously without any presence of chemical activating reagent. They were applied to remove Cr(VI) from solution under different solution pH values and initial Cr(VI) concentrations. The relevant adsorption mechanism was also explored and proposed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Biochar and Activated Carbon
The tropical hardwood sawdusts of Tectona grandis tree—used as the feedstock (raw) material to prepare the carbonaceous materials—were collected, washed repeatedly with distilled deionized water, dried over-night at 80 °C, and then sieved into relatively uniform particles (0.106–0.215 mm). The carbonaceous porous materials were prepared through the two-stage process. First, approximately 10 g of the feedstock was mixed with distilled deionized water in a 150 mL beaker for 30 min. Subsequently, the mixture was transferred into a Teflon autoclave and heated at 190 °C for 24 h to produce hydrochar. After the hydrothermal carbonization process, the brown hydrochar was filtrated, washed intensively with distilled deionized water, and dried over-night at 105 °C. Second, approximately 10 g of dried hydrochar (denoted as the precursor) was mixed with a certain activating agent (K2CO3 or ZnCl2) at different impregnation ratios (w/w) of the activating reagent/precursor (i.e., 0.75:1, 1:1, 1.25:1, 1.75:1, and 2:1). The mixtures of activating reagent/precursor were then dried at 80 °C for 24 h to remove water. Subsequently, they were pyrolyzed at 800 °C for 4 h under an oxygen-limited condition (using a porcelain crucible covered with a lid) to obtain ACs. Notably, the biochar sample was directly prepared from hydrochar (without any activating agents) through the pyrolysis process at 800 °C for 4 h.
The carbonaceous porous materials (i.e., biochar and AC) were washed with 0.1 M HCl and then distilled deionized water until the pH value of filtrate reached around 7.0. They were dried at 105 °C until their moisture content was less than 5% and stored in some brown bottles until further use. Notably, a primary adsorption test demonstrated that the optimal impregnation ratio of the activating reagent/precursor was obtained at 1.75:1 for ZnCl2 and 0.75:1 for K2CO3. In other words, the AC samples prepared at the impregnation ratios of ZnCl2:hydrochar (1.75:1; denoted as ZnCl2-AC) and K2CO3:hydrochar (0.75:1; denoted as K2CO3-AC) exhibited an excellent adsorption capacity compared to those prepared at the other impregnation ratios (data not shown). As a result, the AC (ZnCl2-AC and K2CO3-AC) and biochar (as the blank adsorbent) samples were characterized and used as selective adsorbents in this study. Furthermore, a commercial activated-charcoal (CAC, Norit RB4C) purchased from Sigma–Aldrich used for the comparison of the adsorption efficiency. The textural property of CAC has been published in our recent work [26].
2.2. Characterization of Biochar and Activated Carbon
The prepared carbonaceous materials were characterized by various advanced techniques. Their textural properties were calculated from the adsorption/desorption isotherm of nitrogen gas (Micromeritics ASAP 2020; ATS Scientific Inc., Burlington, ON, Canada). Scanning electron microscope (SEM; Hitachi S-3000N, Hitachi Scientific Instruments, Tokyo, Japan) was applied to analyze their surface morphology. The main elements on the surface of materials were determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS; Thermo Fisher K-Alpha; the Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). In addition, the XPS technique was applied to confirm the presence of chromium species on the surface of laden carbonaceous materials. This technique plays an important role in confirming the relevant adsorption mechanism. The surface charge of carbonaceous materials (pHPZC) was determined by the common drift method [19,22,26].
2.3. Batch Adsorption Study
A stock solution (1000 mg/L) of Cr(VI) was prepared from pure potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7; purchased from SIGMA). The working Cr(VI) solutions were directly diluted from the stock solution. The adsorption process of Cr(VI) onto the carbonaceous porous materials was conducted under batch experiment. Approximately 0.02 g of adsorbent was added into a series of 150-mL Erlenmeyer Flask containing 50 mL of Cr(VI) at different initial Cr(VI) concentrations (5–200 mg/L). The pH value of the solution was adjusted and maintained during the adsorption process using 1 M NaOH and 1M HCl. The parafilm-covered flasks were shaken at 150 rpm for 24 h at 30 °C. After the complete adsorption process, the mixture of laden adsorbent and adsorbate was separated by a glass fiber filter (0.2-μm). The concentration of chromium in solution was determined by the atomic absorption spectrometry technique (Avanta/AAS, GBC). The AAS technique can determine the concentration of total chromium (hexavalent and trivalent chromium) in solution. The amount of chromium adsorbed onto the carbonaceous porous materials (qe; mg/g) at equilibrium was calculated based on the mass balance equation (Equation (1)).
where Co and Ce (mg/L) are the chromium concentrations in solution at beginning and equilibrium, respectively; m (g) is the mass of used carbonaceous porous materials; and V (L) is the volume of the working chromium solution. All adsorption studies were conducted in triplicate, and the data were reported as average ± standard deviation (SD).
2.4. Adsorption Isotherm Model
In general, the parameter of each adsorption isotherm model has different meanings. Depending on the main purposes of study, the isotherm model can be selected and applied for appreciation. In this study, we applied some common and helpful models to model the experimental data of adsorption equilibrium. They include the Langmuir [27], Freundlich [28], and Redlich–Peterson [29] models. In addition, to minimize the respective error functions, the non-linear optimization technique was used to calculate the relevant adsorption parameters of the selective models [30].
The Langmuir equation:
The Freundlich equation:
The Redlich–Peterson model:
where Qomax (mg/g) is the maximum saturated monolayer adsorption capacity of adsorbent; KL (L/mg) is the Langmuir constant related to the affinity between an adsorbent and adsorbate; KF ((mg/g)(L/mg)n) is the Freundlich constant, which characterizes the strength of adsorption; n (dimensionless) is a Freundlich intensity parameter; KRP (L/g) and aRP (mg/L)−g are the Redlich–Peterson constants; and g (dimensionless) is an exponent whose value must lie between 0 and 1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Property of Prepared Biochar and Activated Carbon
Specific surface area plays a key role in estimating the adsorption capacity and mechanism of various contaminants onto a certain adsorbent. The determining method of specific surface area is often based on the nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm at 77 K. The specific surface area (SBET; m2/g) of a material is commonly determined by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) equation. Meanwhile, the total pore volume often is calculated by the relevant amount of nitrogen adsorption at a relative pressure (p/p°) of around 0.99 [23]. Figure 1 provides the isotherms of nitrogen physisorption of three carbon samples. According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) technical report [31], the gas physisorption isotherms can be classified as Type Ia for biochar and Type Ib for activated carbons (K2CO3-AC and ZnCl2-AC), suggesting that these materials exhibited a high quantity of micropore volume. Notably, a hysteresis appears in the multilayer range of the nitrogen physical adsorption isotherm by ZnCl2-AC, implying that ZnCl2-AC exhibited a micropore or mesopore structure.
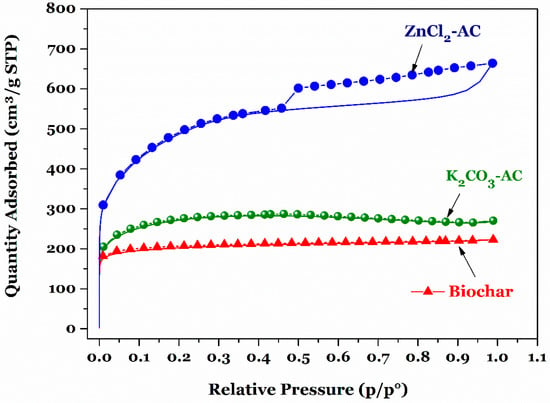
Figure 1.
Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm of the biochar and activated carbon (AC) samples.
Table 1 summaries some corresponding textural properties of three prepared samples. As expected, the chemical activation process (using K2CO3 and ZnCl2 as chemical activating agents) can effectively simulate the porosity development of the feedstock material compared to the pyrolysis process alone (without any chemical activating agents). The SBET values of three adsorbent solids decreased in the following order: 1757 ± 8.81 m2/g (ZnCl2-AC) > 1013 ± 1.62 m2/g (K2CO3-AC) > 792 ± 0.52 m2/g (biochar). Therefore, it can be concluded that the ZnCl2 (an effective dehydration reagent) can act as a more effective chemical activating reagent than K2CO3 (a dehydrogenation reagent). An identical conclusion was obtained by Chen and coworkers [12] for the preparation of tobacco stem through chemical activation process using K2CO3 and ZnCl2. Three prepared carbonaceous porous materials with large specific surface area and high total pore volume (Table 1) were expected to have an outstanding adsorption capacity towards chromium ions in a water environment.

Table 1.
Textural property of the prepared biochar and two activated carbon (AC) samples and CAC.
The morphological property of the prepared samples was analyzed by the SEM technique. Figure 2 shows the different morphologies among there porous materials samples. The biochar sample exhibited a rough surface morphology with little porosity (Figure 2a). In contrast, the typical irregular and heterogeneous surface morphology with sponge-like structures were observed in the AC samples (Figure 2b–c). The formation of well-developed pores in AC during pyrolysis was caused by the strong evaporation of K2CO3 or ZnCl2 under the high carbonization temperature of 800 °C. Moreover, Figure 2d indicates that the primary element composites were carbon and oxygen. Clearly, biochar and activated carbon are carbon-enriched materials that are approximately 86% to 91% carbon. In addition, three prepared samples had a high content of oxygen, suggesting that they might exhibit a high content of oxygen-containing functional groups on their surface [12,13,15,32]. The oxygen-bearing functionality has been known as the most active groups in adsorbing various potentially toxic metals through inner-sphere complexation and out-sphere complexation [33,34].
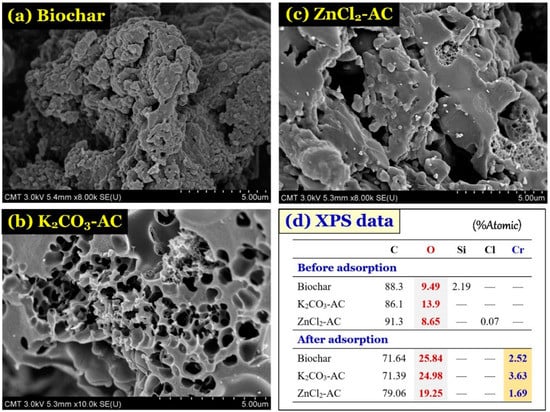

Figure 2.
(a–c) Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of biochar and activated carbons; and (d) their surface element component.
3.2. Effect of pH on Adsorption Capacity of Prepared Biochar and Activated Carbon
The solution pH is the most important parameter in the adsorption study because it greatly affects the dominant species of adsorbate and the surface charge of adsorbent under a working solution. According to the relative distribution of aqueous hexavalent chromium as a function of pH and Cr(VI) concentration, hydrogen chromate (HCrO4−) anion is regarded as the dominant anionic chromium species than the others (H2CrO4, CrO42−, Cr2O72−, and HCr2O7−) in a solution within the solution pH range from 1.0 to 6.5 [2,9,35,36]. In addition, when the chromium concentration in solution is higher than 1000 mg/L, dichromate (Cr2O72−) anion is naturally formed in solution [2,35]. In this study, the maximum concentration of Cr(VI) is around 200 mg/L; therefore, the dominant species of Cr(VI) in solution is HCrO4− anions. Moreover, the pHPZC values of prepared carbonaceous materials were higher than 8.0, suggesting that the surface charge of such materials was dominantly positive when the solution pH values were lower than 8.0. Therefore, Cr(VI) anions in solution can be electrostatically attracted by the positively charged surface of the carbon materials.
In general, to obtain the accurate comparison of adsorption efficiency of an adsorbate (i.e., potentially toxic metals) onto a certain adsorbent (i.e., carbon-based materials), the Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity (Qomax; calculated from Equation (2)) is often recommended instead of using the qe value (obtained from Equation (1)) [2,30,37,38]. In addition, the experimental data of Cr(VI) adsorption onto the carbon materials well fitted the Langmuir model. Therefore, in this study, we discussed the pH-dependence on the maximum adsorption capacity (Qomax) of the biochar and activated carbons (Figure 3). The results demonstrated that the adsorption capacity of three carbonaceous materials remarkably decreased when the solution pH values increased from 3.0 to 7.0. The decreasing adsorption capacity of the biochar and activated carbon at a higher solution pH value resulted from decreasing electrostatic attraction between the positively charged surface of materials (i.e., —COOH2+, —OH2+, and —NH3+) and the HCrO4− anions in solution. A similar trend adsorption was reported by the other scholars for the adsorption of Cr(VI) onto biochar [10,11,15], prepared activated carbon [13,32,39,40,41], commercial activated carbon [41], and multiwalled carbon nanotubes [42].
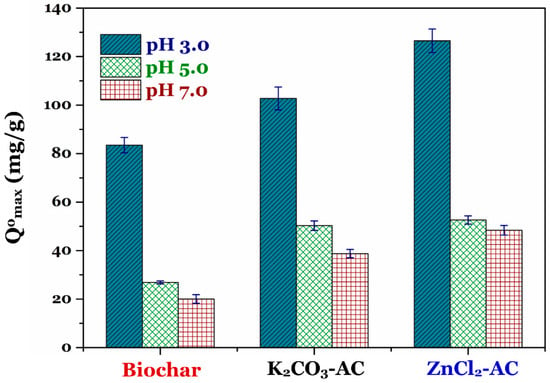
Figure 3.
Effect of pH values on the Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity (Qomax; mg/g) of the prepared biochar and two activated carbons toward Cr(VI) in solution (Note: the data are represented as average ± standard error).
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
The adsorption isotherm plays an important role in identifying the region whether the experimental data of Cr(VI) adsorption onto the carbonaceous materials are located. According to [43], the adsorption isotherms of Cr(VI) by the prepared biochar and activated carbon (Figure 4) were classified as the F(Freundlich)-type or possible L(Langmuir)-type; a concave downward curve is typical identification of such types. The result suggested that the prepared carbonaceous materials exhibited a high affinity of chromium ions in the solution.
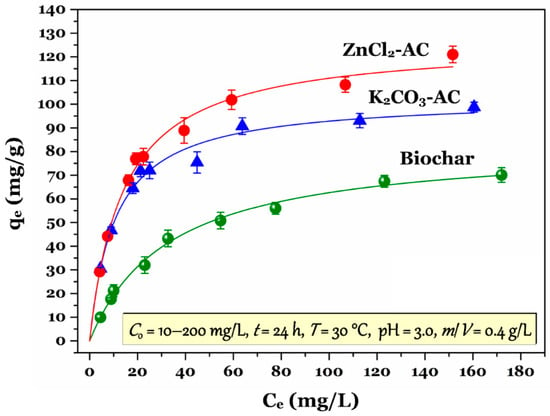
Figure 4.
Adsorption isotherm of Cr(VI) by the prepared biochar and activated carbon samples (Note: the data are represented as average ± standard deviation).
As shown in Table 2, the experimental data of adsorption equilibrium can be satisfactorily described by the selective models of adsorption isotherm, with the coefficient of determination (R2) being higher than 0.98. Figure 4 shows the modeling of the Langmuir model for the experimental data under the given experiment conditions. According to the corresponding parameters of the Langmuir model in Table 2, the maximum adsorption capacity (Qomax; mg/g) of the prepared carbonaceous porous adsorbents followed the decreasing order: ZnCl2-AC (127 mg/g) > K2CO3-AC (103 mg/g) > biochar (83.5 mg/g). Clearly, the tendency of Cr(VI) adsorption onto the biochar and activated carbon samples (Table 2) was well consistent with that of their SBET values (Table 1). Their specific surface area (SBET; m2/g) values were ranked as follows: ZnCl2-AC (1757 m2/g) > K2CO3-AC (1013 m2/g) > biochar (792 m2/g). This means that the activated carbon prepared through ZnCl2 activation exhibited an excellent adsorption capacity to Cr(VI) ions and large specific surface area compared to that through K2CO3 activation. In addition, the maximum adsorption capacity of the biochar and ACs was overwhelmingly higher than that of their precursor (hydrochar; Qomax = 4.5 mg/g) and raw material (Tectona grandis sawdust biosorbent; Qomax = 3.8 mg/g), confirming that the prepared carbonaceous porous materials exhibited a higher affinity toward chromium ions in the solution than their precursor and raw material. Interestingly, in the same experimental conditions, the prepared biochar and AC samples (83.5–127 mg/g) exhibited a higher Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity than commercial activated-charcoal did (52.6 mg/g), suggesting that they have a potential application in large-scale industry.

Table 2.
Corresponding parameter of chromium adsorption isotherms onto the biochar and ACs.
Notably, Figure 5a provides the XPS survey spectra of the biochar and ACs. The presence of Cr element on the spectra assuredly confirmed that chromium was successfully adsorbed by the carbon materials. In addition, the oxygen content of three adsorbent samples (%atomic determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; Figure 2d) significantly increased after the adsorption of Cr(VI) in solution, namely increasing from 9.49% to 25.8% (for biochar), 13.9% to 25.0% (for K2CO3-AC), and 8.6% to 19.3% (for ZnCl2-AC). An analogous result was reported by Chen and colleagues [32] for the Cr(VI) adsorption by commercial activated carbon, they reported that the oxygen contents of commercial activated carbon (CAC) before and after adsorption of Cr(VI) was 18.4% and 20.5% (%atomic determined by XPS), respectively. An increase in oxygen content of the biochar and activated carbon samples after adsorption resulted from the additional presence of oxygen element derived from the HCrO4− oxyanions.
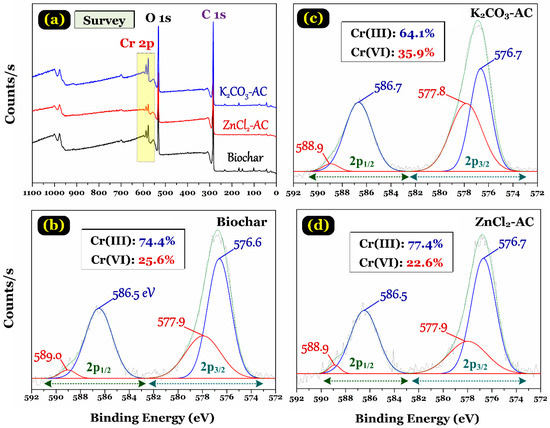
Figure 5.
(a) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) survey spectrum of the prepared biochar and two activated carbon samples, and (b–d) high-resolution spectrum of Cr 2p in these samples. (Note: the initial Cr(VI) concentration is approximately 200 mg/L).
Furthermore, a comparison of the maximum adsorption capacity (Qomax; mg/g) of Cr(VI) onto the biochar and activated carbon samples in this study and other kinds of relevant adsorbent materials in the literature is provided in Table 3. The comparative performance corroborated that two activated carbons (103–127 mg/g) and biochar (83.5 mg/g) reported this study exhibited a higher Qomax value that most prepared activated carbons (23.6–55.2 mg/g), commercial activated carbons (48.5–52.6 mg/g), functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes (85.8 mg/g), and biochars (2.15–24.6 mg/g) in the previous studies. Accordingly, they are expected as a promising adsorbent for real application in removing chromium ions from water and wastewater.

Table 3.
Comparison of the maximum adsorption capacity (Qomax; mg/g) of the biochar and activated carbon in this study and the other corresponding adsorbents in the literature.
3.4. Adsorption Mechanism
As aforementioned, the solution pH has a strong effect on the adsorption mechanism of chromium. In this study, the adsorption mechanism of chromium (the dominant HCrO4− species) was explored at solution pH 3.0 because three prepared adsorbents exhibited excellent adsorption capacity under this condition (Figure 3). The biochar and ACs samples possessed large specific surface area and high total pore volume (Table 1). In general, an adsorbent with excellent textural property has been acknowledged to exhibit an outstanding adsorption capacity to various contaminants (including hexavalent chromium and trivalent chromium) through the integral adsorption mechanism of pore-filling.
In essence, when Cr(VI) oxyanions in solution are in contact with some certain functionality (acting as electron-donor groups such as —COOH, —OH, and —NH2) on the surface of the adsorbent, they are naturally reduced to less toxic Cr(III) cations through the common redox reaction. This is because Cr(VI) has a high redox (oxidation/reduction) potential value (usually higher than +1.35 V) under standard conditions [9,30,44,45]. In this study, the electrons in Equation (5) were provided by the oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of biochar and activated carbon.
HCrO4− + 7H+ + 3e− ⇌ Cr3+ + 4H2O (E° = +1.35).
However, if reduced Cr(III) does not present on the surface of the prepared carbon materials, the adsorption mechanism will only involve the adsorption of Cr(VI) oxyanions. In contrast, if both reduced Cr(III) and Cr(VI) ions co-exist on the materials’ surface, the adsorption mechanism will be an “adsorption-coupled reduction” [9,32,42,45]. To confirm the oxidation state and coordination environment of chromium bound to the biochar and activated carbon samples, the XPS analysis of such materials after adsorbing Cr(VI) was conducted. The narrow spectra of Cr 2p XPS indicated the coexistence of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) on the surface of the adsorbents (Figure 5b–d). Taking ZnCl2-AC as a typical example, Cr(VI) was identified at the binding energy of 577.9 eV (Cr 2p3/2) and 588.9 eV (Cr 2p1/2); meanwhile, Cr(III) was 576.7 eV (Cr 2p3/2) and 586.5 eV (Cr 2p1/2). Clearly, the binding energy of Cr(III) was lower than that of Cr(VI), which is well consistent with the previous literature [15,36,46,47] and some critical comment works [48,49]. Similarly, some authors investigated the binding energy of relevant standard chemicals (i.e., K2Cr2O7 and CrCl3 as the blank samples) by the XPS techniques. They also conduced that Cr(VI) exhibited a higher binding energy than Cr(III) because hexavalent chromium is more electrophilic than Cr(III) [46,47]. Notably, the mechanism of Cr(VI) removal from water media by various adsorbents through adsorption-coupled reduction has been confirmed by many scholars, such as activated carbon [13,32], multiwalled carbon nanotubes [42], biochar [15,47], layered double hydroxides [32,36], graphene oxide [50], and even biosorbent [46,51].
Notably, Figure 5 shows that the Cr(III) metal is the dominant species present on the surface of three carbon samples, with the percentage of Cr(III) accounting for 77.4% (ZnCl2-AC), 74.4% (biochar), 64.1% (K2CO3-AC). The result suggested that the majority of Cr(VI) anions was reduced to less toxic Cr(III) cations, and the reduced Cr(III) was adequately adsorbed by the biochar and the activated carbon samples rather than Cr(VI). Similarly, some scholars found that after the Cr(VI) adsorption, the percentage of Cr(III) on the surface of laden adsorbent (using XPS technique) was approximately 97.1% for the biochar adsorbent [15] and 78.9% for the AC adsorbent [32]. According to the literature, the Cr3+ metal ions can be adsorbed by carbonaceous porous material through (1) cation–π interaction (also known as Cπ–cation interaction) between the aromatic π-system in the carbon samples and metallic Cr(III) cation [42,52], (2) complexation with the oxygen-containing functional groups (i.e., carboxyl and phenolic groups) [15,50,53], cation exchange with alkaline (K+ and Na+) and alkaline earth (Ca2+ and Mg2+) metal ions [15,51], and (3) pore filling [32]. In addition, although the adsorption mechanism of Cr(III) involved in the precipitation of Cr(OH)3 on the surface of carbon material (i.e., biochar and multiwalled carbon nanotubes) has been reported in the literature works [15,42], this mechanism was ruled out in this study. This is because the adsorption study was conducted under the acidic condition.
To sum up, the removal mechanism of Cr(VI) by the biochar and activated carbon samples was the principle adsorption-coupled reduction (Figure 6). Namely, Cr(VI) ions solution were partially reduced into Cr(III) ions during the process of Cr(VI) adsorption. The adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) primarily involved the electrostatic attraction and pore filling; meanwhile, that of Cr(III) was the complexation, Cπ—cation, cation exchange, and pore filling.
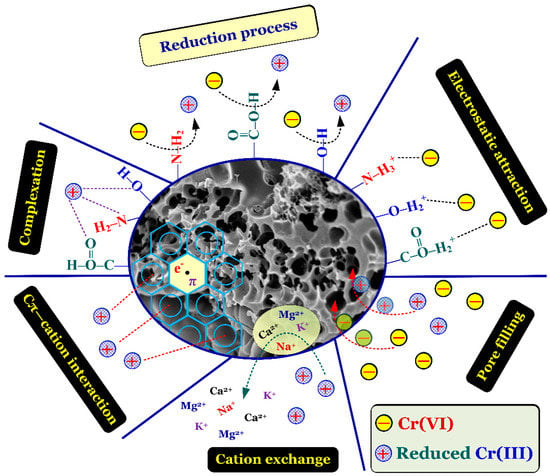
Figure 6.
Proposed removal mechanism (adsorption-coupled reduction) of chromium by the carbonaceous porous materials.
4. Conclusions
The Cr(VI) contaminant in solution was efficiently removed by three carbonaceous porous materials. Under the same adsorptive experiment conditions, the maximum adsorption capacity (Qomax) of chromium was ordered as follows: ZnCl2-AC (127 mg/g) > K2CO3-AC (103 mg/g) > biochar (84 mg/g), which is consistent with the order of specific surface area (SBET): 1757 m2/g > 1013 m2/g > 792 m2/g, respectively. The adsorption mechanism of chromium ions onto the carbonaceous porous material was relatively similar and primarily regarded as adsorption-coupled reduction. During the process of Cr(VI) adsorption, Cr(VI) was partially reduced into Cr(III) through the redox reaction. A part of un-reduced Cr(VI) anions was adsorbed by the carbonaceous porous materials through electrostatic attraction (mainly between HCrO4− anions and the —COOH2+ and —OH2+ groups on the materials’ surface) and pore filing. Meanwhile, the reduced Cr(III) cations were adsorbed by the carbonaceous porous through complexation with the main oxygen-containing functional groups on the materials’ surface, Cπ—cation interaction, cation exchange, and pore filing. It can be concluded that the process of two-stage preparation can produce biochar and activated carbon with a high micro-porosity, large specific surface area, and excellent adsorption capacity to chromium ions in solution.
Author Contributions
The paper was written with the contributions of all co-authors. All authors share equal contributions in this work. A.T.V. contributed substantially to the design of the study, the analyses, validation, and interpretation of experimental data, and the original draft preparation. V.P.N. did the experiments and interpreted experimental data. A.O. took responsibility for methodology and software. A.N. and B.T.D.J. played an integral role in the formal analysis and English corrections. H.N.T. analysed and verified the experimental data, made the figures, wrote the manuscript, replied to comments, and corrected the proof. H.-P.C. contributed to the supervision, conceptualization, validation, interpretation, project administration, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and approved the submission.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Chung Yuan Christian University for technical and financial supports.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Korak, J.A.; Huggins, R.; Arias-Paic, M. Regeneration of pilot-scale ion exchange columns for hexavalent chromium removal. Water Res. 2017, 118, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri- and hexavalent chromium from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 762–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharchaou, I.; Py, J.-S.; Cambier, S.; Loizeau, J.-L.; Cornelis, G.; Rousselle, P.; Battaglia, E.; Vignati, D.A.L. Chromium hazard and risk assessment: New insights from a detailed speciation study in a standard test medium. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yue, R.; Guo, F.; Xu, Z. Selective separation of chromium from sulphuric acid leaching solutions of mixed electroplating sludge using phosphate precipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Domínguez, A.; Rivera-Huerta, M.L.; Pérez-Castrejón, S.; Garrido-Hoyos, S.E.; Villegas-Mendoza, I.E.; Gelover-Santiago, S.L.; Drogui, P.; Buelna, G. Chromium removal from drinking water by redox-assisted coagulation: Chemical versus electrocoagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Gan, Y.; Liang, T.; Wan, H.; Wang, P. A miniaturized electrochemical system for high sensitive determination of chromium(VI) by screen-printed carbon electrode with gold nanoparticles modification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Kavallari, I.; Nyktari, E.; Kaldis, A.; Panousi, E.; Nikitopoulos, G.; Antoniou, K.; Nasioka, M. Biological groundwater treatment for chromium removal at low hexavalent chromium concentrations. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, G.; Kargar, M. Nanofiltration and microfiltration for the removal of chromium, total dissolved solids, and sulfate from water. MethodsX 2019, 6, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Nguyen, D.T.; Le, G.T.; Tomul, F.; Lima, E.C.; Woo, S.H.; Sarmah, A.K.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. Adsorption mechanism of hexavalent chromium onto layered double hydroxides-based adsorbents: A systematic in-depth review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Lv, Q. Removal efficiency and mechanism of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by maize straw biochars derived at different pyrolysis temperatures. Water 2019, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytłak, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Dobrowolski, R. Sorption and desorption of Cr(VI) ions from water by biochars in different environmental conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5985–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, S. Preparation and characterization of activated carbons from tobacco stem by chemical activation. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z. Removal of chromium (VI) from water by porous carbon derived from corn straw: Influencing factors, regeneration and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran Hai, N.; Huang, F.-C.; Lee, C.-K.; Chao, H.-P. Activated carbon derived from spherical hydrochar functionalized with triethylenetetramine: Synthesis, characterizations, and adsorption application. Green Process. Synth. 2017, 6, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, W.; Liu, S.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium using banana pseudostem biochar and its mechanism. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-C.; Lee, C.-K.; Han, Y.-L.; Chao, W.-C.; Chao, H.-P. Preparation of activated carbon using micro-nano carbon spheres through chemical activation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2805–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boakye, P.; Tran, H.N.; Lee, D.S.; Woo, S.H. Effect of water washing pretreatment on property and adsorption capacity of macroalgae-derived biochar. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedonia. Global Activated Carbon-Demand and Sales Forecasts, Market Share, Market Size, Market Leaders; The Freedonia Group: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Effect of pyrolysis temperatures and times on the adsorption of cadmium onto orange peel derived biochar. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Wang, Y.; You, S.; Chao, H. Sustainable biochar derived from agricultural wastes for removal of methylene green 5 from aqueous solution: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, and mechanism analysis. In Air, Gas, and Water Pollution Control Using Industrial and Agricultural Solid Wastes Adsorbents, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 255–291. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Fast and efficient adsorption of methylene green 5 on activated carbon prepared from new chemical activation method. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Wen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-F.; You, S.-J. Highly efficient removal of hazardous aromatic pollutants by micro-nano spherical carbons synthesized from different chemical activation methods: A comparison study. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1376–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Lee, C.-K.; Nguyen, T.V.; Chao, H.-P. Saccharide-derived microporous spherical biochar prepared from hydrothermal carbonization and different pyrolysis temperatures: Synthesis, characterization, and application in water treatment. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2747–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A.B.; Mokaya, R. High density hydrogen storage in superactivated carbons from hydrothermally carbonized renewable organic materials. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Lee, C.-K.; Vu, M.T.; Chao, H.-P. Removal of copper, lead, methylene green 5, and acid red 1 by saccharide-derived spherical biochar prepared at low calcination temperatures: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Wang, Y.-F.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Insights into the mechanism of cationic dye adsorption on activated charcoal: The importance of π–π interactions. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D.L. A useful adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark Alexander, V.; Olivier James, P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing Kenneth, S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; An, D.; Sun, S.; Gao, J.; Qian, L. Reduction and Removal of Chromium VI in Water by Powdered Activated Carbon. Materials 2018, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: A comparison study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2671–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Chao, H.-P. Adsorption and desorption of potentially toxic metals on modified biosorbents through new green grafting process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12808–12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.K.; Clifford, D. Chromate ion exchange mechanism for cooling water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1986, 25, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-P.; Wang, Y.-C.; Tran, H.N. Removal of hexavalent chromium from groundwater by Mg/Al-layered double hydroxides using characteristics of in-situ synthesis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption and me. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.N.; Lin, C.-C.; Chao, H.-P. Amino acids-intercalated Mg/Al layered double hydroxides as dual-electronic adsorbent for effective removal of cationic and oxyanionic metal ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jena, H.M. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous phase by high surface area activated carbon prepared by chemical activation with ZnCl2. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enniya, I.; Rghioui, L.; Jourani, A. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solution on activated carbon prepared from apple peels. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 7, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadi, N.K.; Chen, X.D.; Farid, M.M.; Lu, M.G.Q. Adsorption kinetics for the removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorbents derived from used tyres and sawdust. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 84, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Kumar, A.S.; Jiang, S.-J.; Tseng, W.-L. Effective adsorption of chromium(VI)/Cr(III) from aqueous solution using ionic liquid functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a super sorbent. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7044–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C. Adsorption of organic molecules from aqueous solutions on carbon materials. Carbon 2004, 42, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.-S.; Park, J.M. Studies on hexavalent chromium biosorption by chemically-treated biomass of Ecklonia sp. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.-S.; Park, J.M. Mechanisms of the removal of hexavalent chromium by biomaterials or biomaterial-based activated carbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.-S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.M. How to study Cr(VI) biosorption: Use of fermentation waste for detoxifying Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 136, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, B.; Paul, D.; Singh, A.; Gupta, T. Removal of hexavalent chromium upon interaction with biochar under acidic conditions: Mechanistic insights and application. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16786–16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.N. Comment on “simultaneous and efficient removal of Cr(VI) and methyl orange on LDHs decorated porous carbons”. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Pham, V.V.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Nguyen, P.T. Comment on “Removal of hexavalent chromium by biochar supported nZVI composite: Batch and fixed-bed column evaluations, mechanisms, and secondary contamination prevention”. Chemosphere 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, X.; Chen, B. A New Insight of Graphene oxide-Fe(III) Complex Photochemical Behaviors under Visible Light Irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Yun, Y.-S.; Park, J.M. XAS and XPS studies on chromium-binding groups of biomaterial during Cr(VI) biosorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M. Adsorption of Cr(III) on ozonised activated carbon. Importance of Cπ—cation interactions. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3335–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arim, A.L.; Quina, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M. Uptake of trivalent chromium from aqueous solutions by xanthate pine bark: Characterization, batch and column studies. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 121, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).