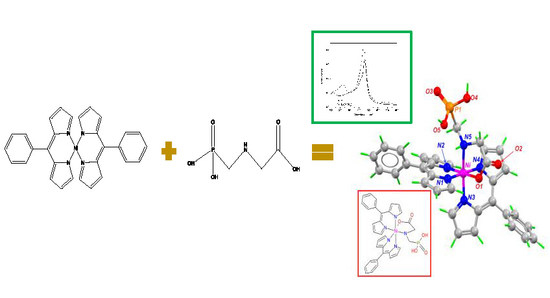
Spectrophotometric Detection of Glyphosate in Water by Complex Formation between Bis 5-Phenyldipyrrinate of Nickel (II) and Glyphosate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Apparatus
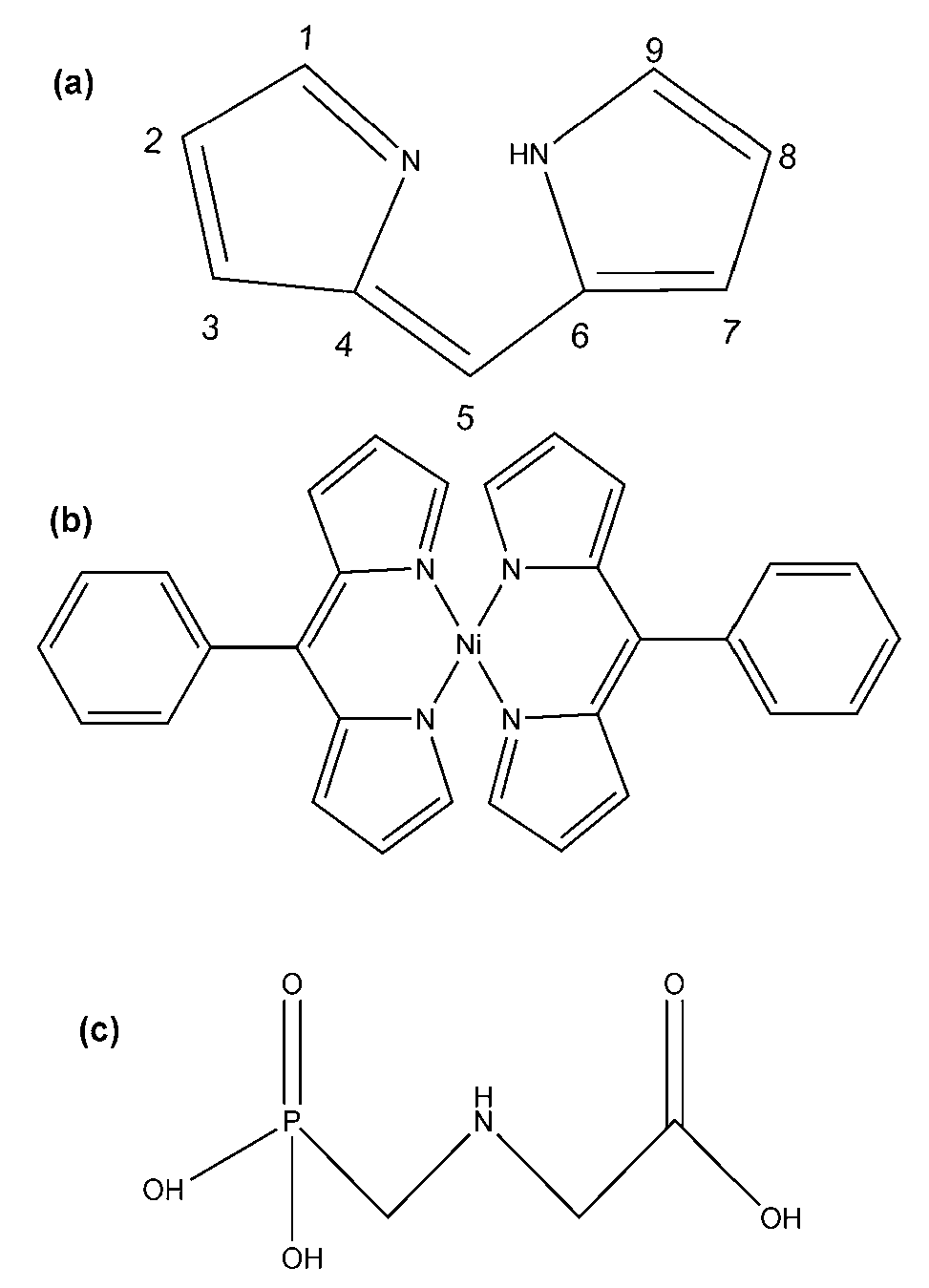
2.3. Synthesis of the (Ni(PhDP)2)
2.4. The Interaction between the (Ni(PhDP)2) Compound and Glyp
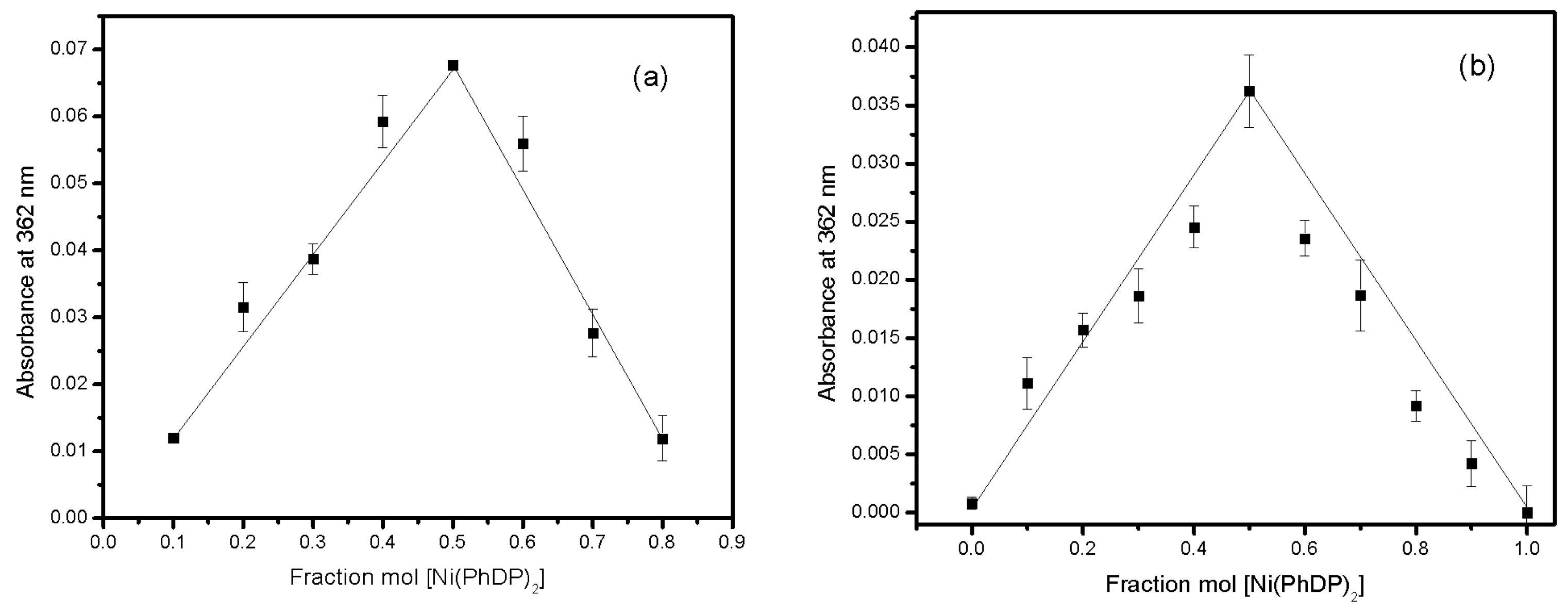
2.5. Complex Stoichiometry
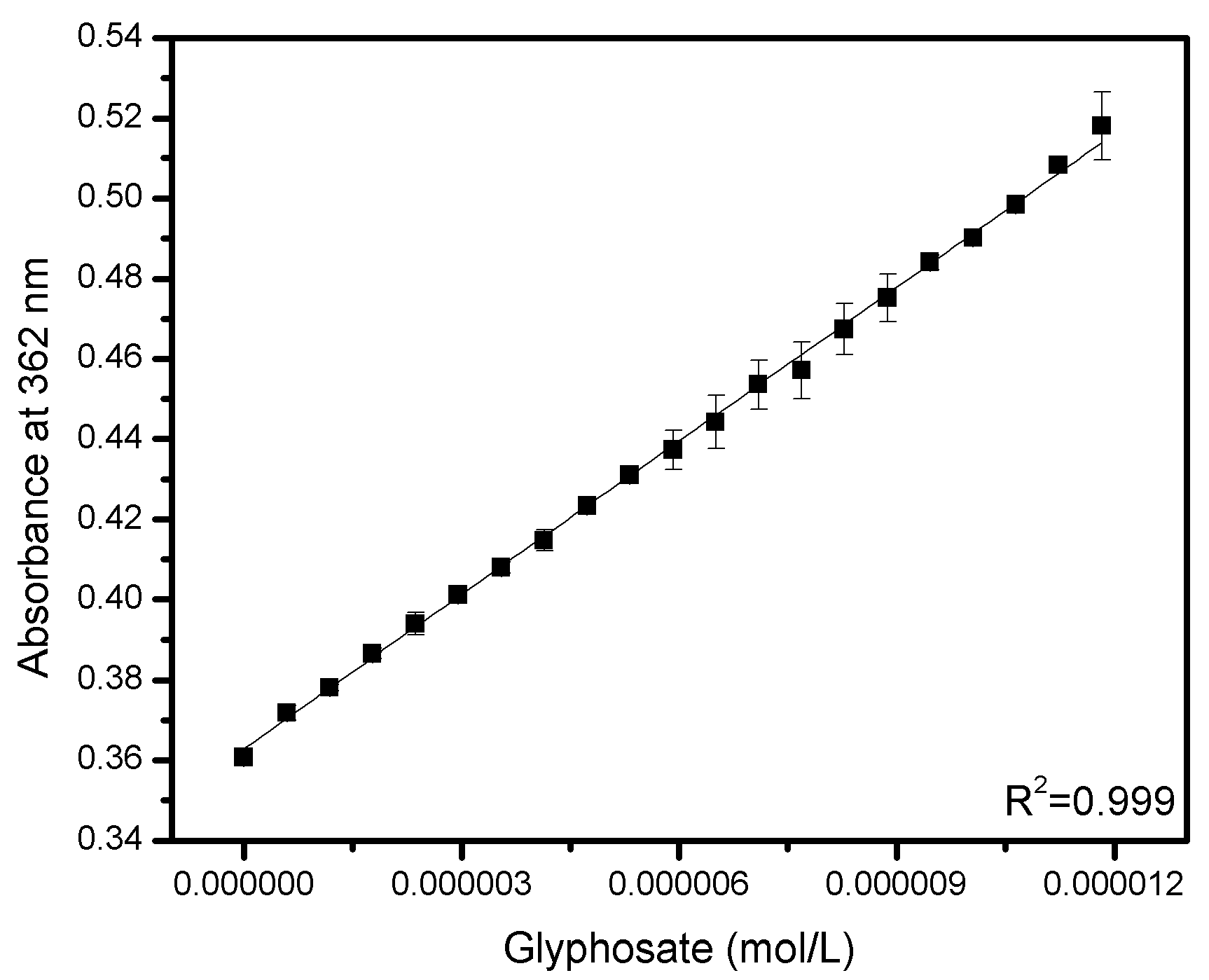
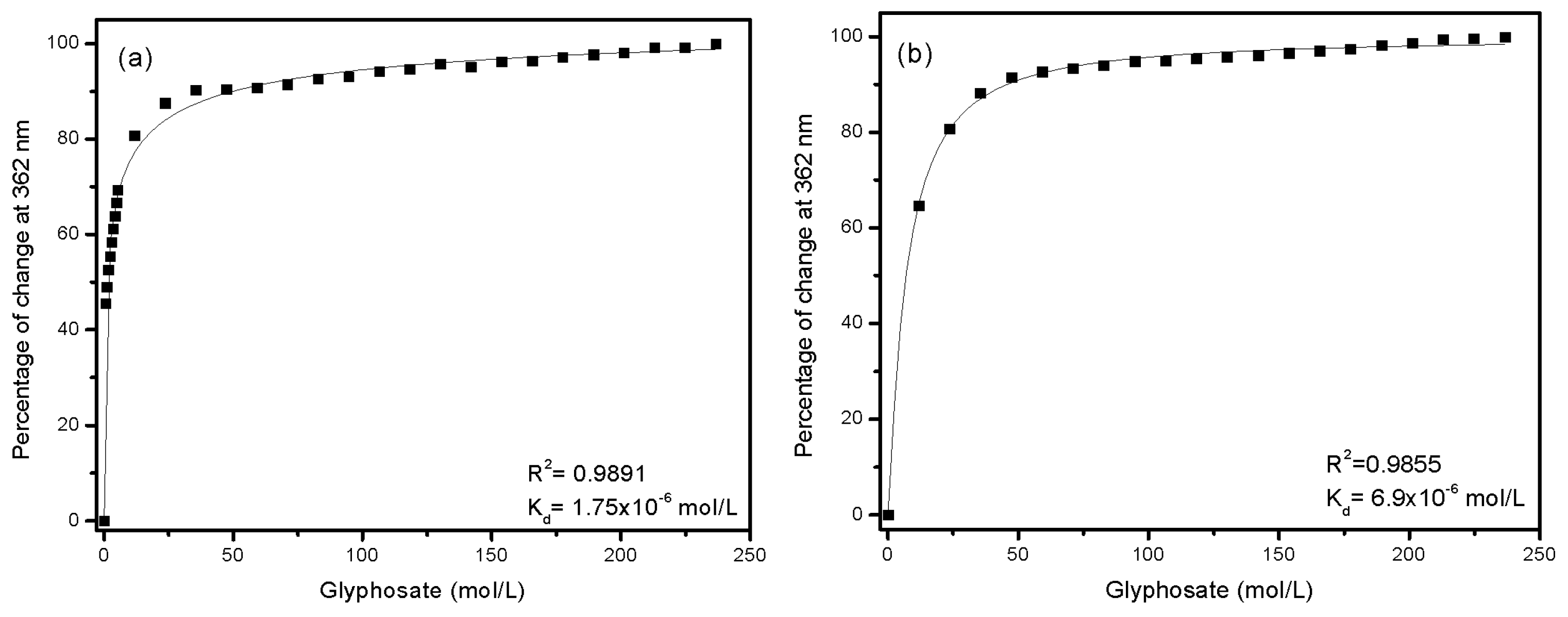
2.6. Determination of the Dissociation Constant (Kd)
2.7. The Analysis in Water Samples
2.8. Interfering Factors
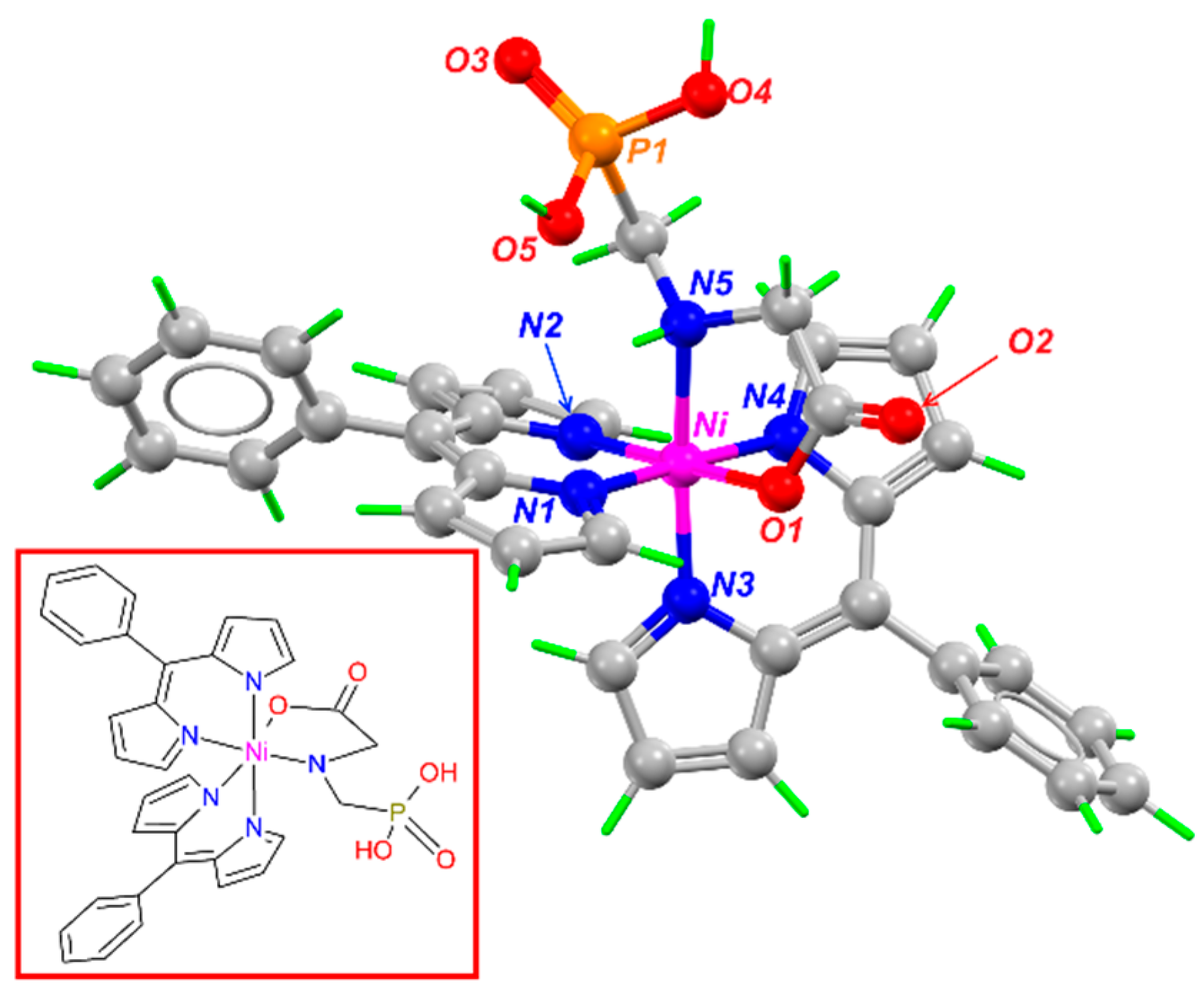
2.9. Theoretical Structure of the (NiGlyp(PhDP)2) Complex
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the (Ni(PhDP)2) Compound
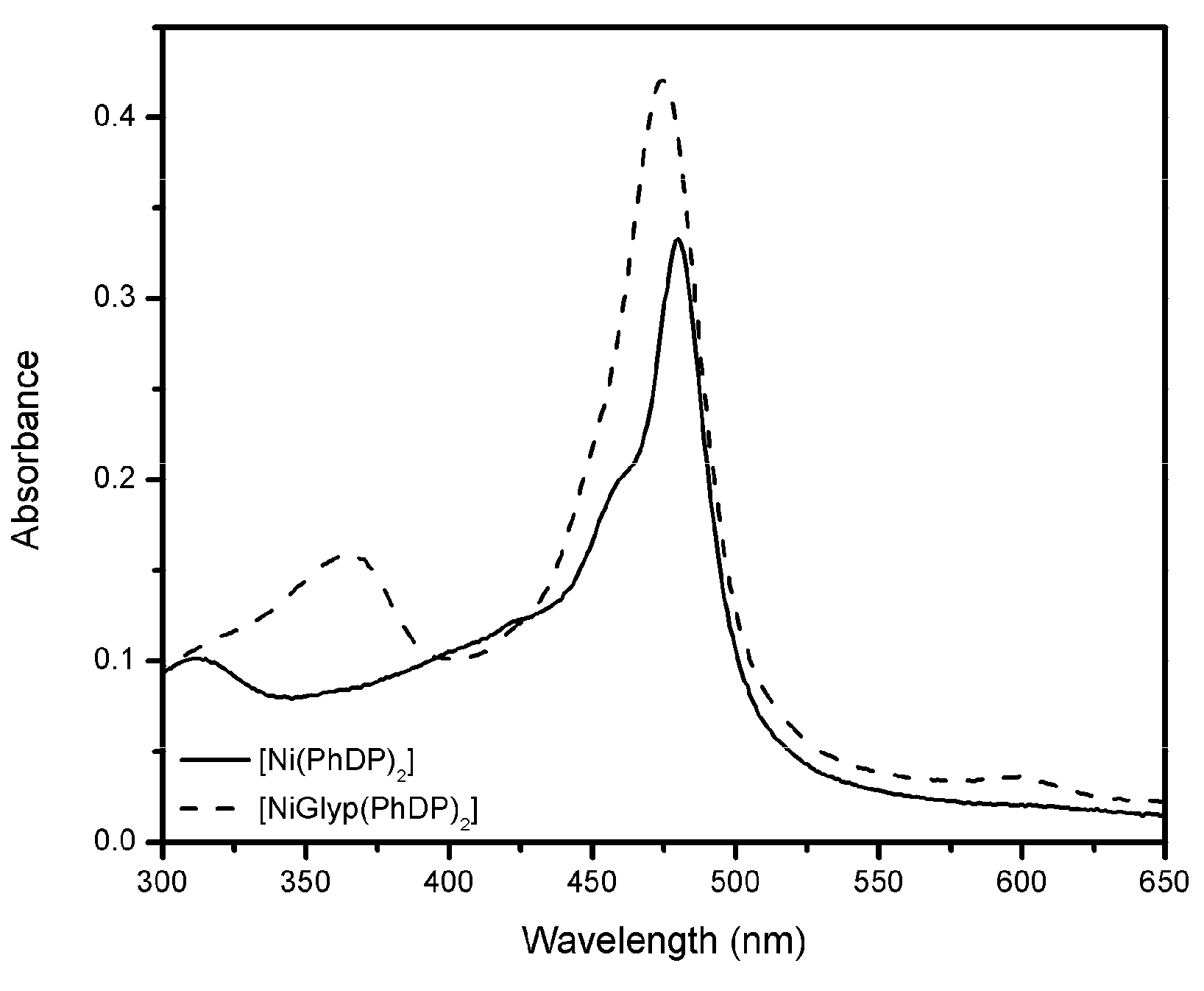
3.2. The Interaction between Glyp with (Ni(PhDP)2)
3.3. Stoichiometry
3.4. Dissociation Constant
3.5. Method Selectivity
3.6. Analysis of Spiked Water Samples
3.7. Theoretical Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dill, G.M.; Douglas, S.; Feng, P.C.C.; Kohn, F.; Kretzmer, K.; Mehrsheikh, A.; Bleeke, M.; Honegger, J.L.; Farmer, D.; Wright, D.; et al. Glyphosate: Discovery, development, applications, and properties. In Glyphosate Resistance in Crops and Weeds: History, Development, and Management; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–34. ISBN 9780470410318. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, A.; Donaldson, D.; Kiely, T.; Wu, L. Pesticides Industry Sales, and Usage: 2006 and 2007 Market Estimates; USA Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 1–41.
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, H.H.; Dickeduisberg, M.; Theuvsen, L. Uses, and benefits of glyphosate in German arable farming. Crop Prot. 2012, 42, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglin, W.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Kuivila, K.M.; Dietze, J.E. Glyphosate and its degradation product AMPA occur frequently and widely in U.S. soils, surface water, groundwater, and precipitation. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón-Von Osten, J.; Dzul-Caamal, R. Glyphosate residues in groundwater, drinking water and urine of subsistence farmers from intensive agriculture localities: A survey in Hopelchén, Campeche, Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijekoon, N.; Yapa, N. Assessment of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on potential biodegradation of glyphosate in contaminated soil and aquifers. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, E.; Costa, J.L.; Bedmar, F.R.; Ramsier, C.; Kloepper, J.W. Changes in rhizosphere bacterial gene expression following glyphosate treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, M.; Schledorn, P.; Schrödl, W.; Hoppe, H.-W.; Lutz, W.; Shehata, A.A.D. Adsorption and mobility of glyphosate in different soils under no-till and conventional tillage. Geoderma 2016, 263, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Degenhardt, D.; Humphries, D.; Cessna, A.J.; Messing, P.; Badiou, P.H.; Raina, R.; Farenhorst, A.; Pennock, D.J. Dissipation of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water and sediment of two Canadian prairie wetlands. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2012, 47, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, P.; Flores, F.; Mueller, J.F.; Carter, S.; Negri, A.P. Glyphosate persistence in seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byer, J.D.; Struger, J.; Klawunn, P.; Todd, A.; Sverko, E.D. Low-cost monitoring of glyphosate in surface waters using the ELISA method: An evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6052–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin, E.; Şahan, S.; Ülgen, A.; Şahin, U. DLLME-spectrophotometric determination of glyphosate residue in legumes. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.M.; Lorenz, N.; Hoilett, N.; Lee, N.R.; Dick, R.P.; Liles, M. Detection of Glyphosate Residues in Animals and Humans. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zouaoui, K.; Dulaurent, S.; Gaulier, J.M.; Moesch, C.; Lachatre, G. Determination of glyphosate and AMPA in blood and urine from humans: About 13 cases of acute intoxication. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 226, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, V.C.; De Gerónimo, E.; Marino, D.; Primost, J.; Carriquiriborde, P.; Costa, J.L. Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörtl, M.; Németh, G.; Juracsek, J.; Darvas, B.; Kamp, L.; Rubio, F.; Székács, A. Determination of glyphosate residues in Hungarian water samples by immunoassay. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Sorohan, B. Removal of glyphosate from aqueous environment by adsorption using water industrial residual. Desalination 2011, 271, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Toledo, J.; Castro, R.; Rivero-Pérez, N.; Bello-Mendoza, R.; Sánchez, D. Occurrence of glyphosate in water bodies derived from intensive agriculture in a tropical region of southern Mexico. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, M.A.; Ares, I.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Martínez, M.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A. Neurotransmitter changes in rat brain regions following glyphosate exposure. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, A.L.; Mello, F.C.C.; Alves-Balvedi, R.P.; Rodrigues, L.P.; Goulart, L.R. Glyphosate detection: Methods, needs and challenges. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 291–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; He, M.M.; Shin, K.; Mai, V.; Jeong, K.C.; Finckh, M.R.; Morris, J.G. Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USA Environmental Protection Agency. Method 547 Determination of Glyphosate in Drinking Water By Direct-Aqueous-Injection HPLC, Post-Column Derivatization, and Fluorescence Detection; USA Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 1.
- Kaczyński, P.; Łozowicka, B. Liquid chromatographic determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid residues in rapeseed with MS/MS detection or derivatization/fluorescence detection. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Stripeikis, J.; Iñón, F.; Tudino, M. A simplified approach to the determination of N-nitroso glyphosate in technical glyphosate using HPLC with post-derivatization and colorimetric detection. Talanta 2007, 72, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.X.; Cai, Q.; Yang, Z. Determination of glyphosate and phosphate in water by ion chromatography-Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. A. 2005, 1100, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, M.; Pozo, Ó.J.; Sancho, J.V.; López, F.J.; Hernández, F. Re-evaluation of glyphosate determination in water by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1134, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.A.; Strahan, A.P.; Thurman, E.M. Methods of Analysis by the USA Geological Survey Organic Geochemistry Research Group—Determination of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Glufosinate in Water Using Online Solid-Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Sp; Department of the Interior Washington: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Ibáñez, M.; Pozo, Ó.J.; Sancho, J.V.; López, F.J.; Hernández, F. Residue determination of glyphosate, glufosinate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water and soil samples by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1081, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla-Alonso, D.J.; Garza-Tapia, M.; Chávez-Montes, A.; González-Horta, A.; Waksman de Torres, N.H.; Castro-Ríos, R. New temperature-assisted ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method for the determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in water samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2017, 40, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.P.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Pereira, E.A. Determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid by capillary electrophoresis with indirect detection using pyridine-2, 6-dicarboxylic acid or 3, 5-dinitrobenzoic acid. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Coy, A.M.; Ibáñez, M.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernández, F. Improvements in the analytical methodology for the residue determination of the herbicide glyphosate in soils by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, N.; Asano, M.; Kuse, A.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Nagasaki, Y.; Ueno, Y. Rapid determination of glyphosate, glufosinate, bialaphos, and their major metabolites in serum by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2011, 1218, 3675–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, J.; Yang, W.; Tang, J. A simple label-free colorimetric method for glyphosate detection based on the inhibition of the peroxidase-like activity of Cu(II). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, L.K.S.; Chigome, S.; Torto, N.; Frost, C.L.; Pletschke, B.I. A novel colorimetric sensor strip for the detection of glyphosate in water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.A.; Majithiya, R.P.; Rohit, J.V.; Basu, H.; Singhal, R.K.; Kailasa, S.K. Mg2+ion as a tuner for colorimetric sensing of glyphosate with improved sensitivity: Via the aggregation of 2-mercapto-5-nitrobenzimidazole capped silver nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47741–47752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiman, C.V.; Avena, M.J.; Garrido, M.; Fernández Band, B.; Zanini, G.P. A simple and rapid spectrophotometric method to quantify the herbicide glyphosate in aqueous media. Application to adsorption isotherms on soils and goethite. Geoderma 2012, 170, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettazzi, F.; Romero Natale, A.; Torres, E.; Palchetti, I. Glyphosate determination by coupling an immuno-magnetic assay with electrochemical sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Hyne, R.V.; Desseille, K.L. An amperometric method for the detection of amitrole, glyphosate and its aminomethyl-phosphonic acid metabolite in environmental waters using passive samplers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 675, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songa, E.A.; Arotiba, O.A.; Owino, J.H.O.; Jahed, N.; Baker, P.G.L.; Iwuoha, E.I. Electrochemical detection of glyphosate herbicide using horseradish peroxidase immobilized on the sulfonated polymer matrix. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 75, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchís, J.; Kantiani, L.; Llorca, M.; Rubio, F.; Ginebreda, A.; Fraile, J.; Garrido, T.; Farré, M. Determination of glyphosate in groundwater samples using an ultrasensitive immunoassay and confirmation by on-line solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2335–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, E.; Szekacs, A.; Kovacs, B.; Olah, M.; Horvath, R.; Szekacs, I. Label-free optical biosensor for real-time monitoring the cytotoxicity of xenobiotics: A proof of principle study on glyphosate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 351, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, J.S.; Dimaki, M.; Mortensen, J.; Svendsen, W.E. Detection of glyphosate in drinking water: A fast and direct detection method without sample pretreatment. Sensors 2018, 18, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, C.; Kulkarni, M.; Haram, S.; Aiyer, R.; Karve, M. A novel inhibition based biosensor using urease nanoconjugate entrapped biocomposite membrane for potentiometric glyphosate detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, M.; Albrecht, M.; Albrecht, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Arai, T.; Nabeshima, T. Red/near-infrared luminescence tuning of group-14 element complexes of dipyrrins based on a central atom. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Pan, T.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Xie, Y.; Qin, Y. Boronic acid functionalized boron dipyrromethene fluorescent probes: Preparation, characterization, and saccharides sensing applications. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10214–10220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jargilo, A.; Grabowska, I.; Radecka, H.; Sulima, M.; Marszalek, I.; Wyslouch-Cieszyńska, A.; Dehaen, W.; Radecki, J. Redox-Active Dipyrromethene-Cu(II) Monolayer for Oriented Immobilization of His-Tagged RAGE Domains—the Base of Electrochemical Biosensor for Determination of Aβ16-23′. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarocka, U.; Sawicka, R.; Stachyra, A.; Góra-Sochacka, A.; Sirko, A.; Zagórski-Ostoja, W.; Sączyńska, V.; Porębska, A.; Dehaen, W.; Radecki, J.; et al. A biosensor based on electroactive dipyrromethene-Cu(II) layer deposited onto gold electrodes for the detection of antibodies against avian influenza virus type H5N1 in hen sera. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7807–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brückner, C.; Karunaratne, V.; Rettig, S.J.; Dolphin, D. Synthesis of meso-phenyl-4, 6-dipyrrins, preparation of their Cu(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) chelates, and structural characterization of bis[meso-phenyl-4, 6-dipyrrinato]Ni(II). Can. J. Chem. 1996, 74, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renny, J.S.; Tomasevich, L.L.; Tallmadge, E.H.; Collum, D.B. Method of continuous variations: Applications of job plots to the study of molecular associations in organometallic chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11998–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenprakhon, P.; Sucharitakul, J.; Panijpan, B.; Chaiyen, P. Measuring binding affinity of protein-ligand interaction using spectrophotometry: Binding of neutral red to riboflavin-binding protein. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. The Inhomogeneous Electron Gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects *. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133–A1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16; Revision B.01; Gaussian. Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, W. Synthesis and electrochemistry of meso-substitutes dipyrromethene nickel (II) complexes. Polyhedron 2015, 102, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2018 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories Tables; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Chevreuil, M.; Blanchoud, H.; Guery, B.; Moreau-Guigon, E.; Couturier, G.; Botta, F.; Alliot, F.; Fauchon, N.; Lavison, G. Transfer of glyphosate and its degradate AMPA to surface waters through urban sewerage systems. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Jennings, A. Worldwide regulations of standard values of pesticides for human health risk control: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.S.; Tóth, I.V.; Pezza, L.; Pezza, H.R.; Lima, J.L.F.C. Determination of glyphosate in water samples by multi-pumping flow system coupled to a liquid waveguide capillary cell. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Hu, X. Fluorescent carbon dots for glyphosate determination based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer and logic gate operation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, Z.D.; MacCarthy, P. Novel approach to Job’s method: An undergraduate experiment. J. Chem. Educ. 1986, 63, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Sackmann, E.K.; Wypisniak, K.; Hornsby, M.; Datwani, S.S.; Herr, A.E. Determination of equilibrium dissociation constants for recombinant antibodies by high-throughput affinity electrophoresis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, M.S.; Ramalho, T.C.; Botrel, D.F.; da Cunha, E.F.F.; de Mello, W.C. Understanding the inactivation process of organophosphorus herbicides: A DFT study of glyphosate metallic complexes with Zn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Co3+, Fe3+, Cr3+, and Al3+. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2012, 112, 2752–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ololade, I.A.; Oladoja, N.A.; Oloye, F.F.; Alomaja, F.; Akerele, D.D.; Iwaye, J.; Aikpokpodion, P. Sorption of Glyphosate on Soil Components: The Roles of Metal Oxides and Organic Materials. Soil Sediment Contam. 2014, 23, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yola, M.L. Electrochemical activity enhancement of monodisperse boron nitride quantum dots on graphene oxide: Its application for simultaneous detection of organophosphate pesticides in real samples. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Biswas, S.; Kole, R.K. GC-MS/MS determination and ecological risk assessment of pesticides in the aquatic system: A case study in Hooghly River basin in West Bengal, India. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ccanccapa, A.; Masiá, A.; Navarro-Ortega, A.; Picó, Y.; Barceló, D. Pesticides in the Ebro River basin: Occurrence and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demonte, L.D.; Michlig, N.; Gaggiotti, M.; Adam, C.G.; Beldoménico, H.R.; Repetti, M.R. Determination of glyphosate, AMPA and glufosinate in dairy farm water from Argentina using a simplified UHPLC-MS/MS method. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, G.; Aparicio, V.C.; Bastos, M.C.; De Gerónimo, E.; Labanowski, J.; Prestes, O.D.; Zanella, R.; dos Santos, D.R. Indiscriminate use of glyphosate impregnates river epilithic biofilms in southern Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menelaou, M.; Dakanali, M.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Drouza, C.; Lalioti, N.; Salifoglou, A. pH-Specific synthetic chemistry, and spectroscopic, structural, electrochemical and magnetic susceptibility studies in binary Ni(II)-(carboxy)phosphonate systems. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 3331–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleka, E.N.; Mavros, P.P.; Zamboulis, D.; Matis, K.A. Removal of phosphates from water by a hybrid flotation-membrane filtration cell. Desalination 2006, 198, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, V.; Hoggard, P.E. Metal Complexes of Glyphosate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Method | LOD (mol/L) | LOQ (mol/L) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| This method | 2.01 × 10−7 | 9.87 × 10−7 | Rapid, effective, selective, facile, and sensitive |
| Spectrophotometry with multi-pumping flow system [59] | 1 × 10−6 | 3 × 10−6 | Rapid, effective and selective, but needs pre-treatments |
| Fluorescence resonance energy transfer [60] | 6 × 10−7 | 1 | Rapid, effective and selective, but needs expensive equipment |
| Electrochemical sensing [43] | 2 × 10−6 | 1 | Rapid, effective and selective, but needs expensive equipment and reagents |
| Colorimetric sensor [35] | 6 × 10−7 | 1 | Effective and sensitive, but it requires complex synthetizing steps |
| Compounds | Absorbance at 362 nm | Standard Deviation | Interference (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| None (NiGlyp(PhDP)2) | 0.42 | 0.012 | 0.0 |
| Salts | |||
| FeCl3·6H2O | 0.43 | 0.008 | 2.57 |
| CaCl2·2H2O | 0.41 | 0.008 | 0.19 |
| NaNO3 | 0.42 | 0.007 | 0.78 |
| MgCl2·6H2O | 0.44 | 0.008 | 3.66 |
| Mixture of salts | 0.45 | 0.010 | 5.49 |
| Organophosphorus pesticides | |||
| Parathion | 0.42 | 0.012 | 1.47 |
| Dimethoate | 0.45 | 0.011 | 4.28 |
| Diclofenthion | 0.43 | 0.002 | 0.22 |
| Mixture of pesticides | 0.46 | 0.002 | 7.51 |
| Phosphates | |||
| Na2PO4·H2O | 0.41 | 0.003 | 2.57 |
| Na2HPO4·7H2O | 0.41 | 0.003 | 2.75 |
| (NH4)2HPO4 | 0.42 | 0.008 | 0.81 |
| Mixture of phosphates | 0.43 | 0.005 | 0.67 |
| Metabolite of glyp | |||
| AMPA | 0.42 | 0.12 | 0.0 |
| Parameters | Water Matrix | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potable | Urban | Groundwater | Treated Wastewater | |
| pH | 7.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 |
| Specific conductance (µs/cm) | 0.05 | 424.00 | 523.00 | 1448.00 |
| Temperature (°C) | 25.00 | 25.30 | 25.30 | 24.70 |
| COD (mg/L) | 2.00 | 152.70 | 97.20 | 651.38 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 0.73 | 76.48 | 42.00 | 320.62 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 20.00 | 75.00 | 115.00 | 145.00 |
| Fe2+ (µg/L) | 51.00 | 68.00 | 67.50 | 178.50 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 0.00 | 27.50 | 40.00 | 90.00 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 0.00 | 10.00 | 30.0 | 10.00 |
| NO3-N (mg/L) | 1.10 | 1.65 | 18.35 | 24.00 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 5.00 | 82.75 | 99.45 | 104.00 |
| PO43− (mg/L) | 0.10 | 4.80 | 0.94 | 40.20 |
| P2O5 (mg/L) | 0.08 | 4.53 | 0.67 | 31.00 |
| Free chlorine (mg/L) | 0.07 | 0.35 | 0.007 | 0.10 |
| Water Matrix | Glyp Added (× 10−6 mol/L) | Glyp Determined (× 10−6 mol/L) | Coefficient of Variation (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potable | 4.10 | 3.72 | 2.89 | 89.58 |
| 5.90 | 5.14 | 0.34 | 87.20 | |
| Urban | 4.10 | 3.66 | 2.09 | 88.64 |
| 5.90 | 5.32 | 0.61 | 89.97 | |
| Groundwater | 4.10 | 4.02 | 2.38 | 96.49 |
| 5.90 | 6.32 | 0.82 | 106.99 | |
| Treated wastewater | 4.10 | 4.90 | 1.31 | 118.67 |
| 5.90 | 7.03 | 0.99 | 119.04 |
| (NiGlyp(PhDP)2) | (Ni(PhDP)2) (a) and Ni(Glyp)2 (b) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bond | Distance (Å) | Bond | Distance (Å) |
| Ni-N(1) | 1.93 | Ni-N (a) | 1.88 |
| Ni-N(2) | 1.93 | Ni-N (b) | 2.01 |
| Ni-N(3) | 1.94 | Ni-O (b) | 2.05 |
| Ni-N(4) | 1.90 | ||
| Ni-N(5) | 2.08 | ||
| Ni-O | 1.89 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero-Natale, A.; Palchetti, I.; Avelar, M.; González-Vergara, E.; Garate-Morales, J.L.; Torres, E. Spectrophotometric Detection of Glyphosate in Water by Complex Formation between Bis 5-Phenyldipyrrinate of Nickel (II) and Glyphosate. Water 2019, 11, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040719
Romero-Natale A, Palchetti I, Avelar M, González-Vergara E, Garate-Morales JL, Torres E. Spectrophotometric Detection of Glyphosate in Water by Complex Formation between Bis 5-Phenyldipyrrinate of Nickel (II) and Glyphosate. Water. 2019; 11(4):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040719
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero-Natale, Aline, Ilaria Palchetti, Mayra Avelar, Enrique González-Vergara, José Luis Garate-Morales, and Eduardo Torres. 2019. "Spectrophotometric Detection of Glyphosate in Water by Complex Formation between Bis 5-Phenyldipyrrinate of Nickel (II) and Glyphosate" Water 11, no. 4: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040719
APA StyleRomero-Natale, A., Palchetti, I., Avelar, M., González-Vergara, E., Garate-Morales, J. L., & Torres, E. (2019). Spectrophotometric Detection of Glyphosate in Water by Complex Formation between Bis 5-Phenyldipyrrinate of Nickel (II) and Glyphosate. Water, 11(4), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040719