Periods of Extreme Shallow Depth Hinder but Do Not Stop Long-Term Improvements of Water Quality in Lake Apopka, Florida (USA)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
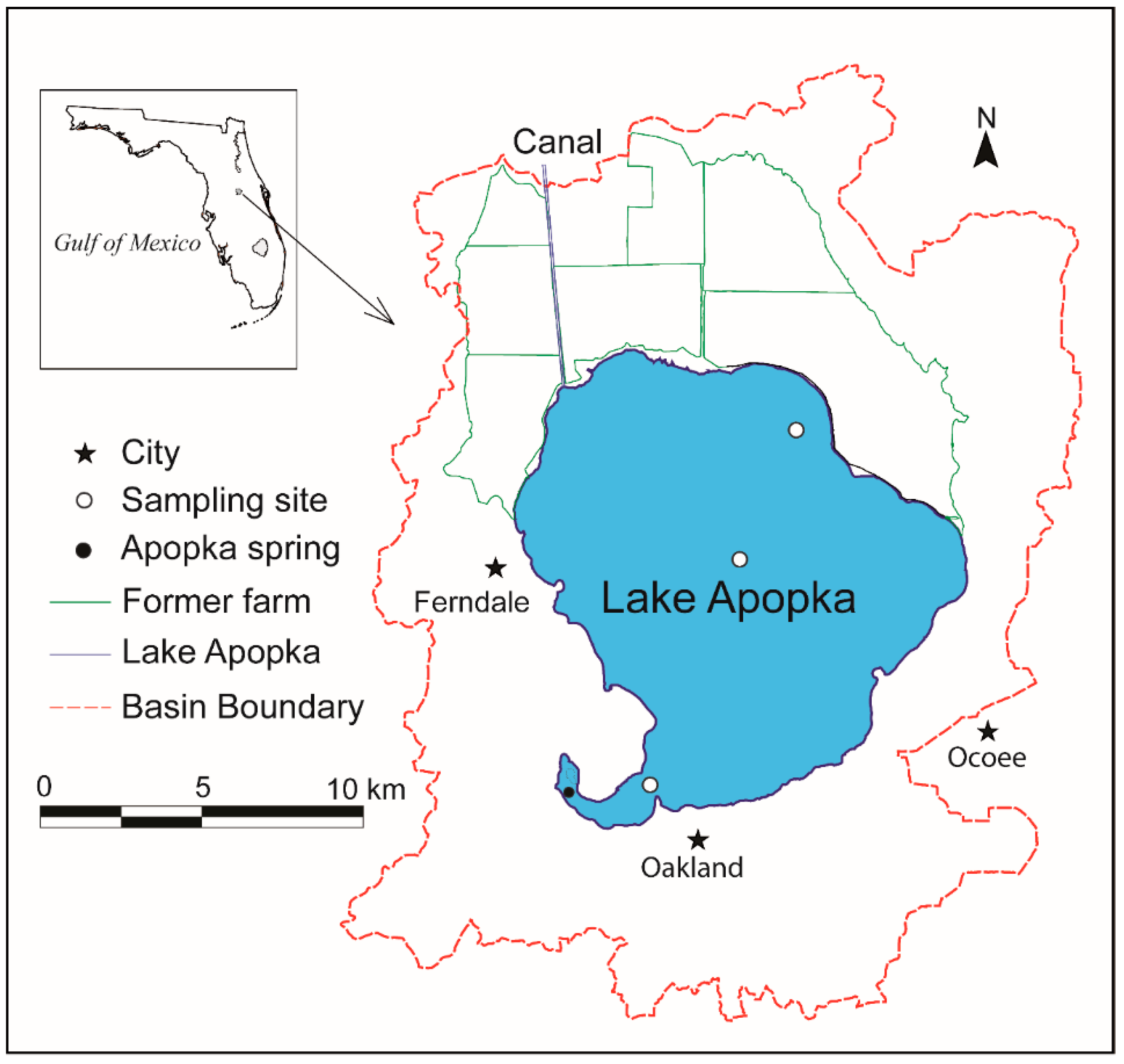
2.1. Description of the Lake
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Statistical Analyses
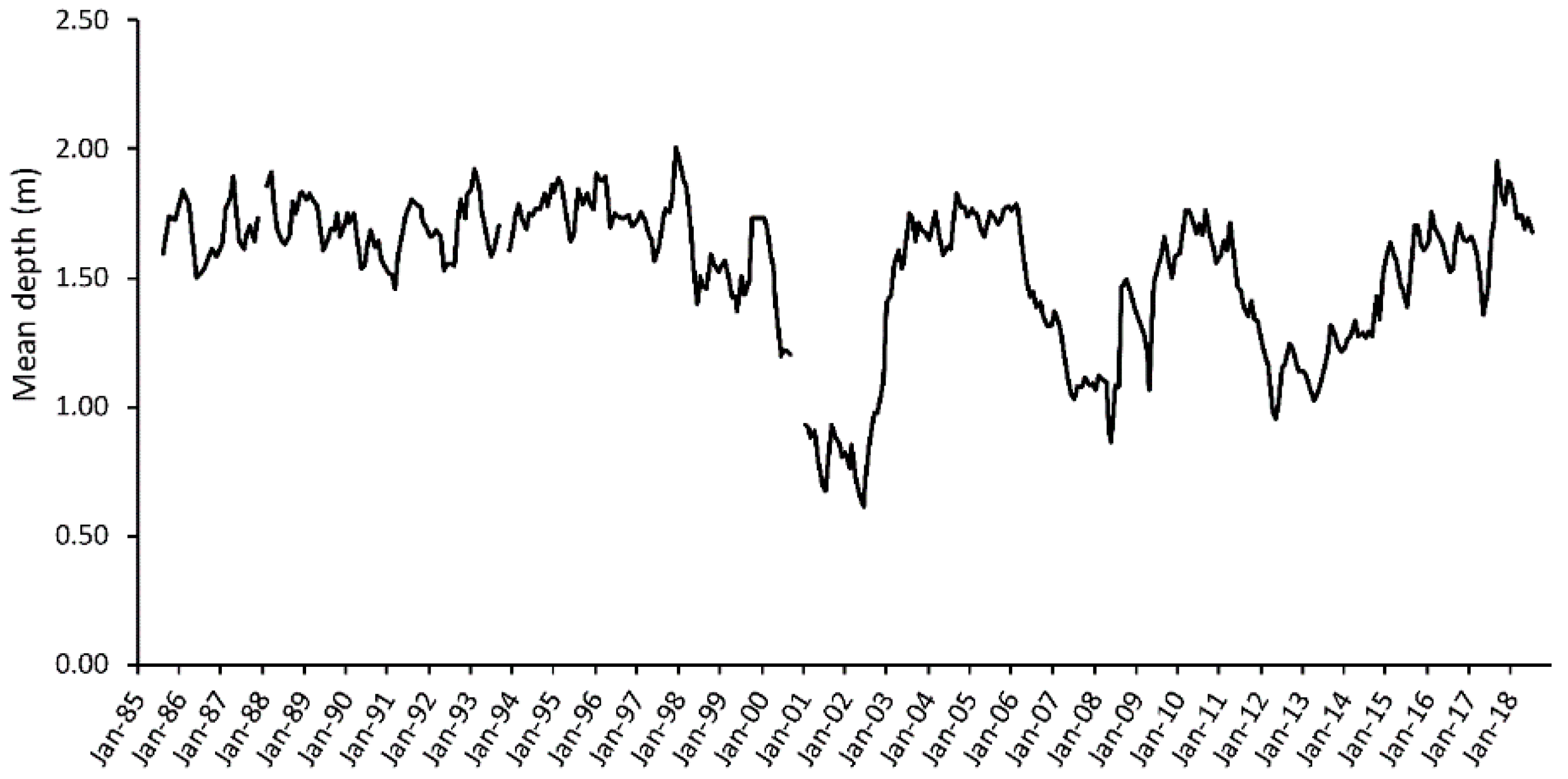
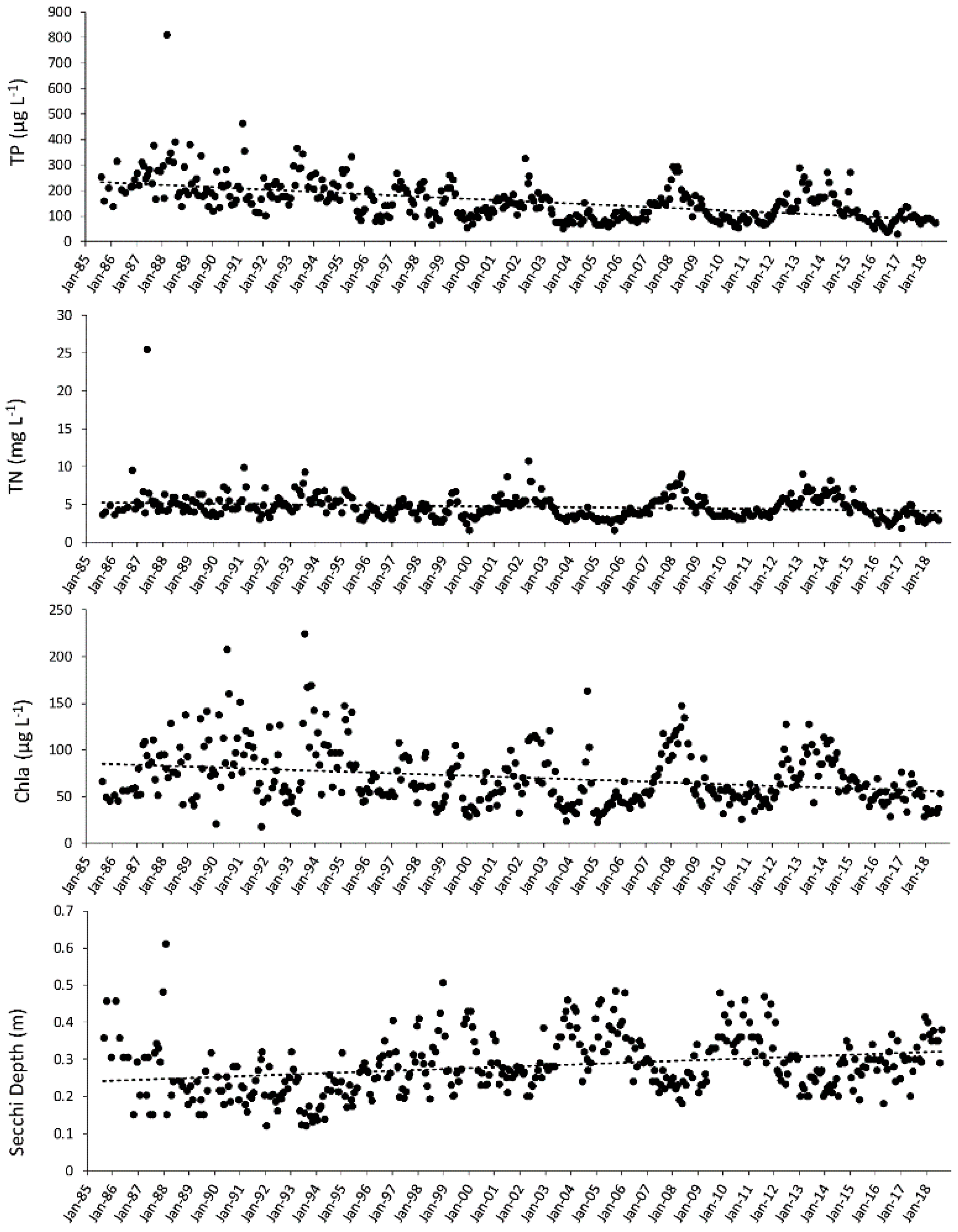
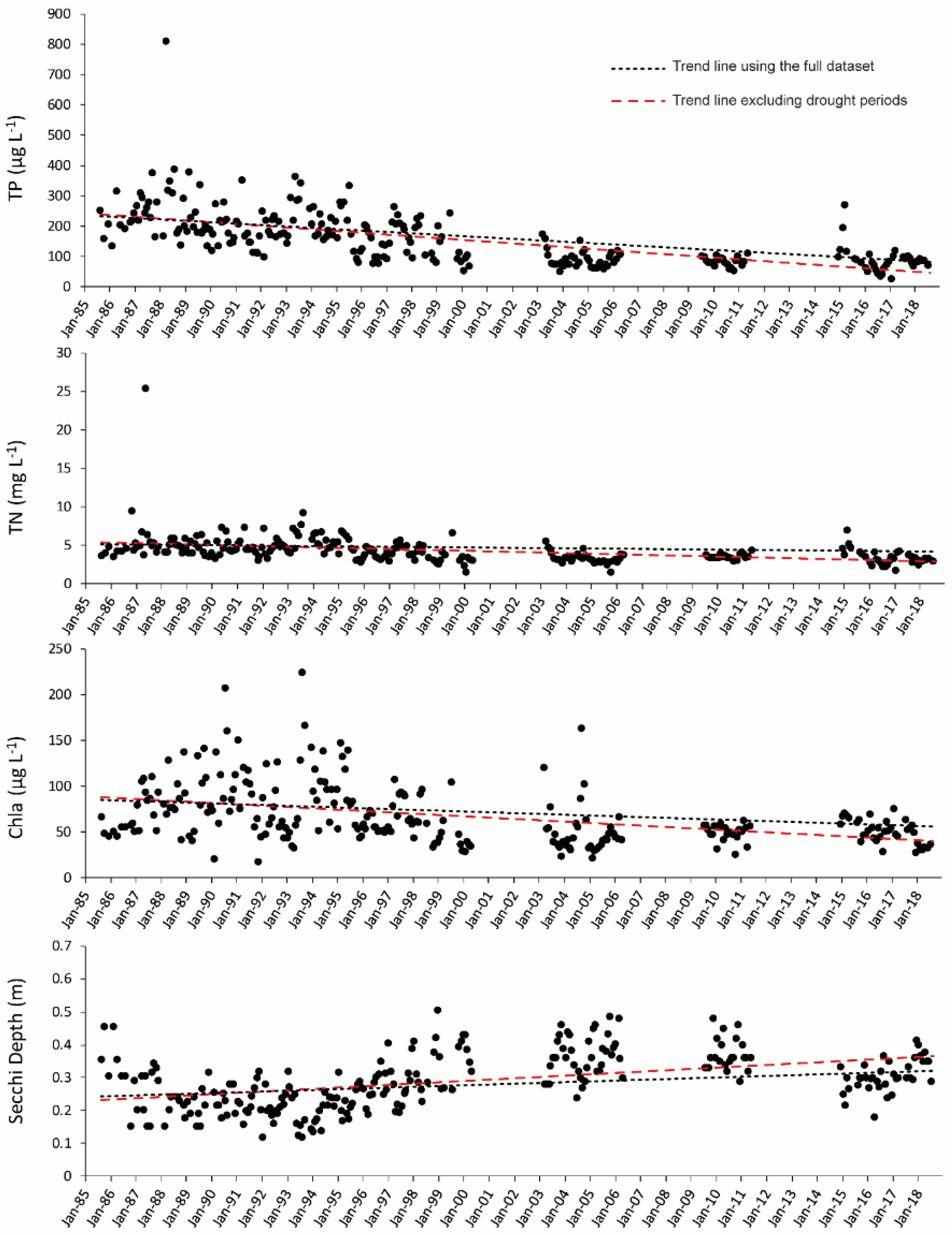
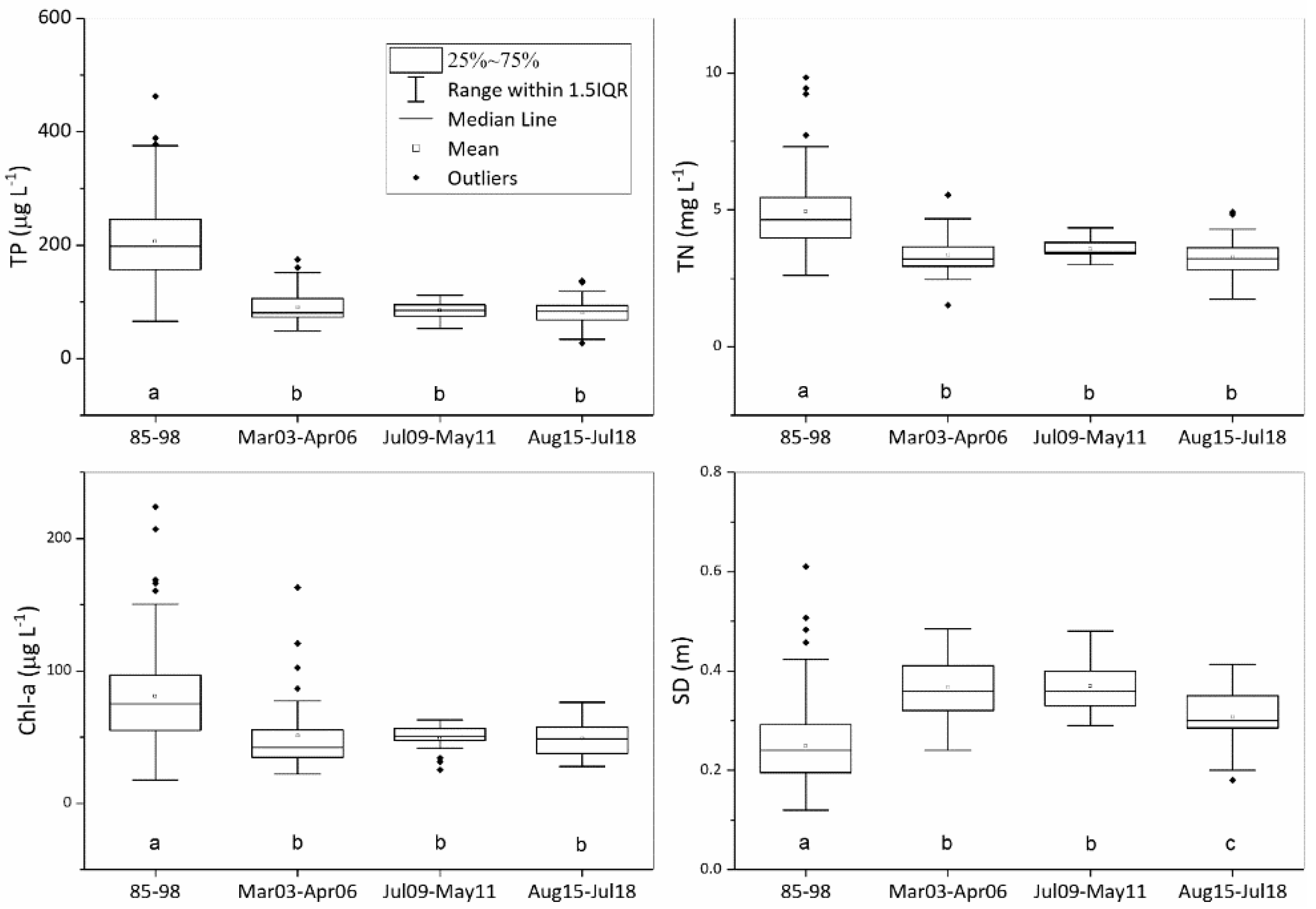
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouvy, M.; Molica, R.; Oliveira, S.D.; Marinho, M.; Beker, B. Dynamics of a toxic cyanobacterial bloom (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) in a shallow reservoir in the semi-arid region of northeast Brazil. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 20, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvy, M.; Falcão, D.; Marinho, M.; Pagano, M.; Moura, A. Occurrence of Cylindrospermopsis (Cyanobacteria) in 39 Brazilian tropical reservoirs during the 1998 drought. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 23, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, J.; Attayde, J.L.; Vasconcelos, F.R.; Dantas, D.D.F.; Huszar, V.L.M. Drought-induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2016, 770, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.; Cho, E.-A.; Kim, H.-W.; Joo, G.-J. Microcystis bloom formation in the lower Nakdong River, South Korea: Importance of hydrodynamics and nutrient loading. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nõges, T.; Nõges, P.; Laugaste, R. Water level as the mediator between climate change and phytoplankton composition in a large shallow temperate lake. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichwaldt, E.S.; Ghadouani, A. Effects of rainfall patterns on toxic cyanobacterial blooms in a changing climate: Between simplistic scenarios and complex dynamics. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1372–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havens, K.E.; Ji, G.; Beaver, J.R.; Fulton, R.S.; Teacher, C.E. Dynamics of cyanobacteria blooms are linked to the hydrology of shallow Florida lakes and provide insight into possible impacts of climate change. Hydrobiologia 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E.; Ji, G. Multiyear oscillations in depth affect water quality in Lake Apopka. Inland Waters 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Core Writing Team; Pachauri, R.K.; Meyer, L. 2014: Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 151. [Google Scholar]
- Conrow, R.; Lowe, E.F.; Coveney, M.F.; Rauschenberger, R.H.; Masson, G. Restoration of Lake Apopka’s North Shore Marsh: High Hopes, Tough Times, and Persistent Progress. In Wildlife Ecotoxicology: Forensic Approaches; Elliott, J.E., Bishop, C.A., Morrissey, C.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoge, V.R.; Conrow, R.; Stites, D.L.; Coveney, M.F.; Marzolf, E.R.; Lowe, E.F.; Battoe, L.E. SWIM (Surface Water Improvement and Management) Plan for Lake Apopka, Florida; St Johns River Water Management District: Palatka, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, F. Cost of Bringing Lake Apopka Back to Life. Available online: https://www.wftv.com/news/9-investigates/9-investigates-cost-of-bringing-lake-apopka-back-to-life/495058639 (accessed on 17 February 2017).
- Coveney, M.F. Water Quality Changes in Lake Apopka, Florida, and the St. Johns River Water Management District’s Restoration Program; St. Johns River Water Management District: Palatka, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, R.; Hoyer, M.; Canfield, D., Jr. The restoration of Lake Apopka in relation to alternative stable states. Hydrobiologia 1999, 394, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveney, M.F.; Stites, D.L.; Lowe, E.F.; Battoe, L.E.; Conrow, R. Nutrient removal from eutrophic lake water by wetland filtration. Ecol. Eng. 2002, 19, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveney, M.F.; Lowe, E.F.; Battoe, L.E.; Marzolf, E.R.; Conrow, R. Response of a eutrophic, shallow subtropical lake to reduced nutrient loading. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1718–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaus, M.H.; Godwin, W.; Battoe, L.; Coveney, M.; Lowe, E.; Roth, R.; Hawkins, C.; Vindigni, M.; Weinberg, C.; Zimmerman, A. Impact of the removal of gizzard shad (Dorosoma cepedianum) on nutrient cycles in Lake Apopka, Florida. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 2401–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelske, C.L. Comment on the origin of the “fluid mud layer” in Lake Apopka, Florida. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2472–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, J.F.; McKee, G.D. Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastewater; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
- Andrade, J.M.; Estévez-Pérez, M.G. Statistical comparison of the slopes of two regression lines: A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 838, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.; Goerner, S.; Powers, R.; Grow, S.; Johnson, R.; Nicholson, D.; Schlein, E.; Truenow, K.; Woosley, L. Harris Chain of Lakes Restoration Council Report to the Florida Legislature; Harris Chain of Lakes Restoration Council: Fruitland Park, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Havens, K.E.; Phlips, E.J.; Cichra, M.F.; Li, B.L. Light availability as a possible regulator of cyanobacteria species composition in a shallow subtropical lake. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 39, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrick, H.J.; Aldridge, F.J.; Schelske, C.L. Wind Influences phytoplankton biomass and composition in a shallow, productive lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Bush, R.T.; Mao, R.; Xiong, L.H.; Ye, C. Extreme drought causes distinct water acidification and eutrophication in the Lower Lakes (Lakes Alexandrina and Albert), Australia. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wang, W.B.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.B.; Liu, Y.D. Regime shift in Lake Dianchi (China) during the last 50 years. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Qian, X.; Wu, H.F.; Li, H.M.; Pan, H.; Han, C.M. Combined effects of submerged macrophytes and aquatic animals on the restoration of a eutrophic water body-A case study of Gonghu Bay, Lake Taihu. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Ma, J.R.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Jeppesen, E.; Shi, K.; Brookes, J.D.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. Improving water quality in China: Environmental investment pays dividends. Water Res. 2017, 118, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, G.; Havens, K. Periods of Extreme Shallow Depth Hinder but Do Not Stop Long-Term Improvements of Water Quality in Lake Apopka, Florida (USA). Water 2019, 11, 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030538
Ji G, Havens K. Periods of Extreme Shallow Depth Hinder but Do Not Stop Long-Term Improvements of Water Quality in Lake Apopka, Florida (USA). Water. 2019; 11(3):538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030538
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Gaohua, and Karl Havens. 2019. "Periods of Extreme Shallow Depth Hinder but Do Not Stop Long-Term Improvements of Water Quality in Lake Apopka, Florida (USA)" Water 11, no. 3: 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030538
APA StyleJi, G., & Havens, K. (2019). Periods of Extreme Shallow Depth Hinder but Do Not Stop Long-Term Improvements of Water Quality in Lake Apopka, Florida (USA). Water, 11(3), 538. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030538




