Examination of the Climate Factors That Reduced Wheat Yield in Northwest India during the 2000s
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methods
2.2.1. Wheat Yield
2.2.2. Climate Data Sources
2.2.3. Hydrological Factors
2.2.4. Other Factors:
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Wheat Yield Variation
3.2. Climate Impacts on Wheat Yield
3.2.1. Drought Indices
3.2.2. Temperature
3.2.3. Water Balance
3.2.4. Correlation between Climate Factors and Wheat Yield
3.3. Contribution from Other Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.N.; Aggarwal, P.K. Vulnerability of wheat production to climate change in India. Clim. Res. 2014, 59, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mustard, A. India Grain and Feed Annual Grain Report Number IN2026; USDA Foreign Agricultural Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Commission of Agricultural Costs and Prices. Available online: https://cacp.dacnet.nic.in/ (accessed on 17 May 2018).
- Mudasser, M.; Hussain, I.; Aslam, M. Constraints to Land-and Water Productivity of Wheat in India and Pakistan: A Comparative Analysis; International Water Management: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kalra, N.; Chakraborty, D.; Sharma, A.; Rai, H.K.; Jolly, M.; Chander, S.; Kumar, P.R.; Bhadraray, S.; Barman, D.; Mittal, R.B.; et al. Effect of increasing temperature on yield of some winter crops in northwest India. Curr. Sci. 2008, 94, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Monasterio, R.J.I.; Dhillon, S.S.; Fischer, R.A. Date of sowing effects on grain yield and yield components of irrigated spring wheat cultivars and relationships with radiation and temperature in Ludhiana, India. Field Crops Res. 1994, 37, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.N.; Joshi, B.P.; Singh, G. Water use and yield response of wheat to irrigation and nitrogen on an alluvial soil in North India. Agric. Water Manag. 1987, 12, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.R.; Craufurd, P.Q.; Ellis, R.H.; Porter, J.R.; Prasad, V.P.V. Temperature variability and the yield of annual crops. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.; Ellis, R.H.; Wheeler, T.R.; Hadley, P. Effect of high temperature stress at anthesis on grain yield and biomass of field-grown crops of wheat. Ann. Bot. 1998, 82, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.D.; Gesch, R.W.; Sinclair, T.R.; Hartwell, A.L. The effect of vapor pressure deficit on maize transpiration response to a drying soil. Plant Soil 2002, 239, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Gourdji, S.M. The influence of climate change on global crop productivity. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, B.; Smale, M.; Braun, H.J.; Duveiller, E.; Reynolds, M.; Muricho, G. Crops that feed the world 10. Past successes and future challenges to the role played by wheat in global food security. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.R.; Gawith, M. Temperatures and the growth and development of wheat: A review. Eur. J Agron. 1998, 10, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q. Temperature thresholds and crop production: A review. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Lobell, D.B.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y.; Simona, B.; Ciais, P.; et al. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9326–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://www.fao.org/home/en/ (accessed on 22 October 2015).
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P.A. Global monthly precipitation estimates from satellite-observed outgoing longwave radiation. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evaporation index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.; Poli, P.; Brugge, R.; Fielding, K.; Fuentes, M.; Kallberg, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A. The ERA-Interim Archive, ECMWF; Version 2.0; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.; Fanning, C.; Enz, J.W.; Eberlein, C.V. Use of Growing-Degree Days to Determine Spring Wheat Growth Stages; North Dakota Coop. Ext. Ser. EB-37: Fargo, ND, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy, B.; Munot, A.A.; Kothawale, D.R. All India monthly and seasonal rainfall series: 1871–1993. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1995, 49, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirement-FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998; Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/X0490E/x0490e00.htm#Contents (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Aslam, M.A.; Ahmed, M.; Stockle, C.O.; Higgins, S.S.; Hassan, F.U.; Hayat, R. Can growing degree days and photoperiod predict spring wheat phenology? Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asseng, S.; Foster, I.; Turner, N.C. The impact of temperature variability on wheat yield. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 997–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Sibley, A.; Ortiz-Monasterio, J.I. Extreme heat effects on wheat senescence in India. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutall, J.G.; Barlow, K.M.; Delahunty, A.J.; Christy, B.P.; O’Leary, G.J. Acute high temperature response on wheat. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, T.; Wardlaw, I.F. The response to high temperature shock and humidity changes prior to and during the early stages of grain development in wheat. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 1990, 17, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.K. Global climate change and Indian agriculture, impacts adaptation and mitigation. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 78, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Gillies, R.R.; Cho, C. What caused the Winter Drought in Western Nepal during Recent Years? J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8241–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Velicogna, I.; Famiglietti, J.S. Satellite-based estimation of groundwater depletion in India. Nature 2009, 460, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, C.V.; Raju, A.D.; Satyanarayana, G.C.; Kumar, P.V.; Chiranjeevi, G.; Suchitra, P. An observational evidence of decrease in Indian summer monsoon rainfall in the recent three decades of global warming era. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 127, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




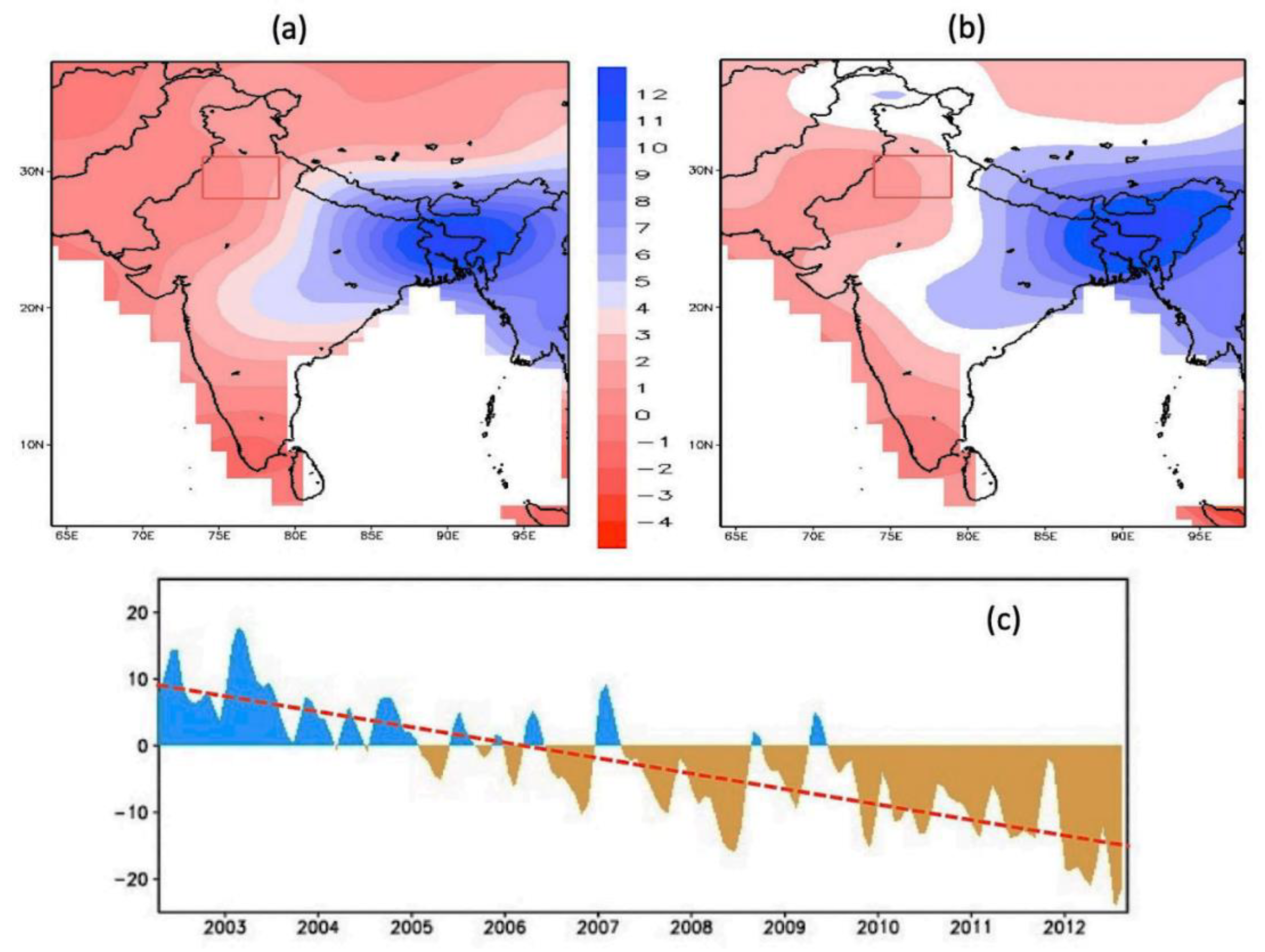
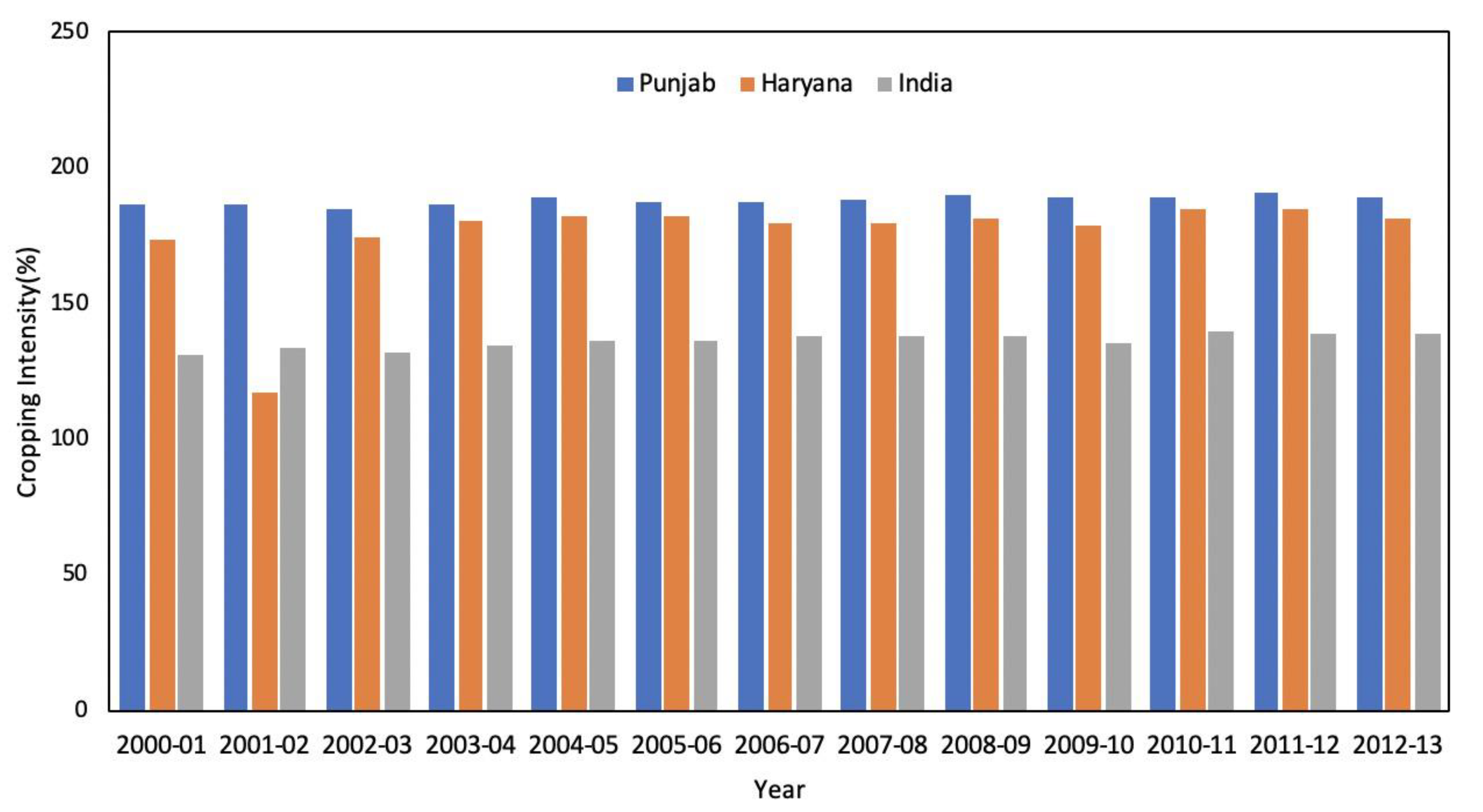


| Climate Parameters | Wheat Yield | Correlation Co-Efficient |
| Winter Precipitation (November–March) | 0.19 | |
| Air Temperature (November–March) | 0.12 | |
| Monsoon Precipitation (November–September) | −0.33 | |
| Potential Evaporation (PET) (November–March) | 0.29 | |
| Soil Moisture Storage (November–March) | 0.31 | |
| Standard Precipitation and Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) (November–March) | 0.42 | |
| Outgoing Longwave Radiation Precipitation Index (OLR) (November–March) | 0.47 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukherjee, A.; Wang, S.-Y.S.; Promchote, P. Examination of the Climate Factors That Reduced Wheat Yield in Northwest India during the 2000s. Water 2019, 11, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020343
Mukherjee A, Wang S-YS, Promchote P. Examination of the Climate Factors That Reduced Wheat Yield in Northwest India during the 2000s. Water. 2019; 11(2):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020343
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukherjee, Avik, S.-Y. Simon Wang, and Parichart Promchote. 2019. "Examination of the Climate Factors That Reduced Wheat Yield in Northwest India during the 2000s" Water 11, no. 2: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020343
APA StyleMukherjee, A., Wang, S.-Y. S., & Promchote, P. (2019). Examination of the Climate Factors That Reduced Wheat Yield in Northwest India during the 2000s. Water, 11(2), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020343





