Measuring and Modelling Soil Evaporation in an Irrigated Olive Orchard to Improve Water Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
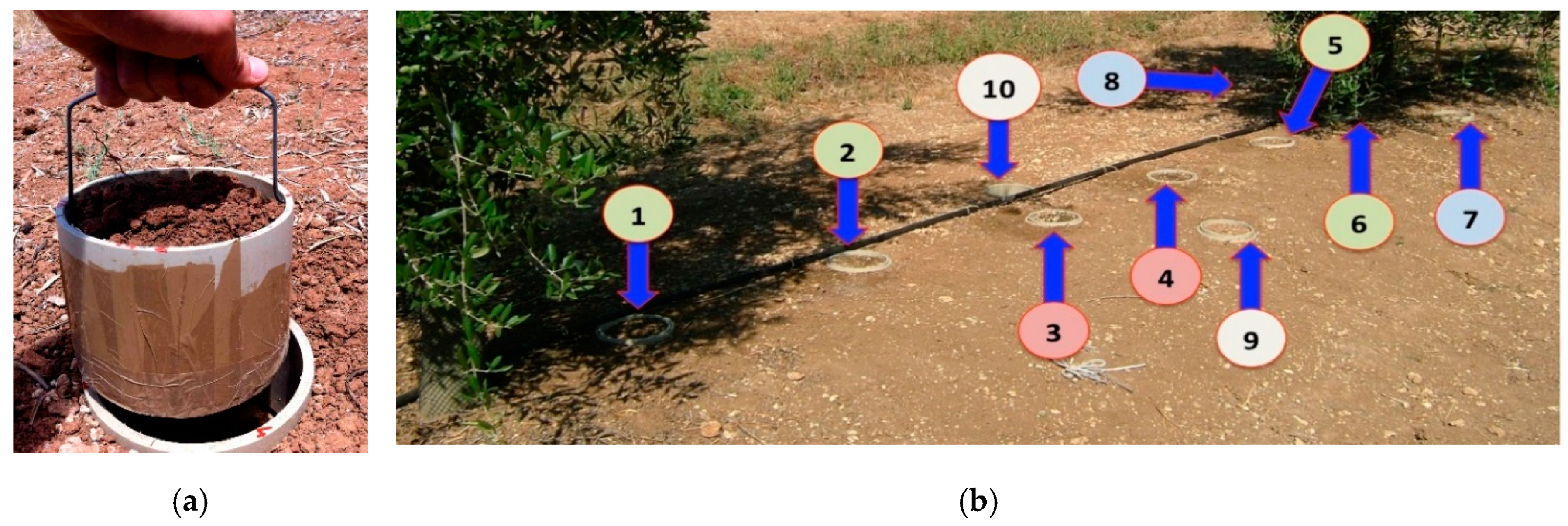
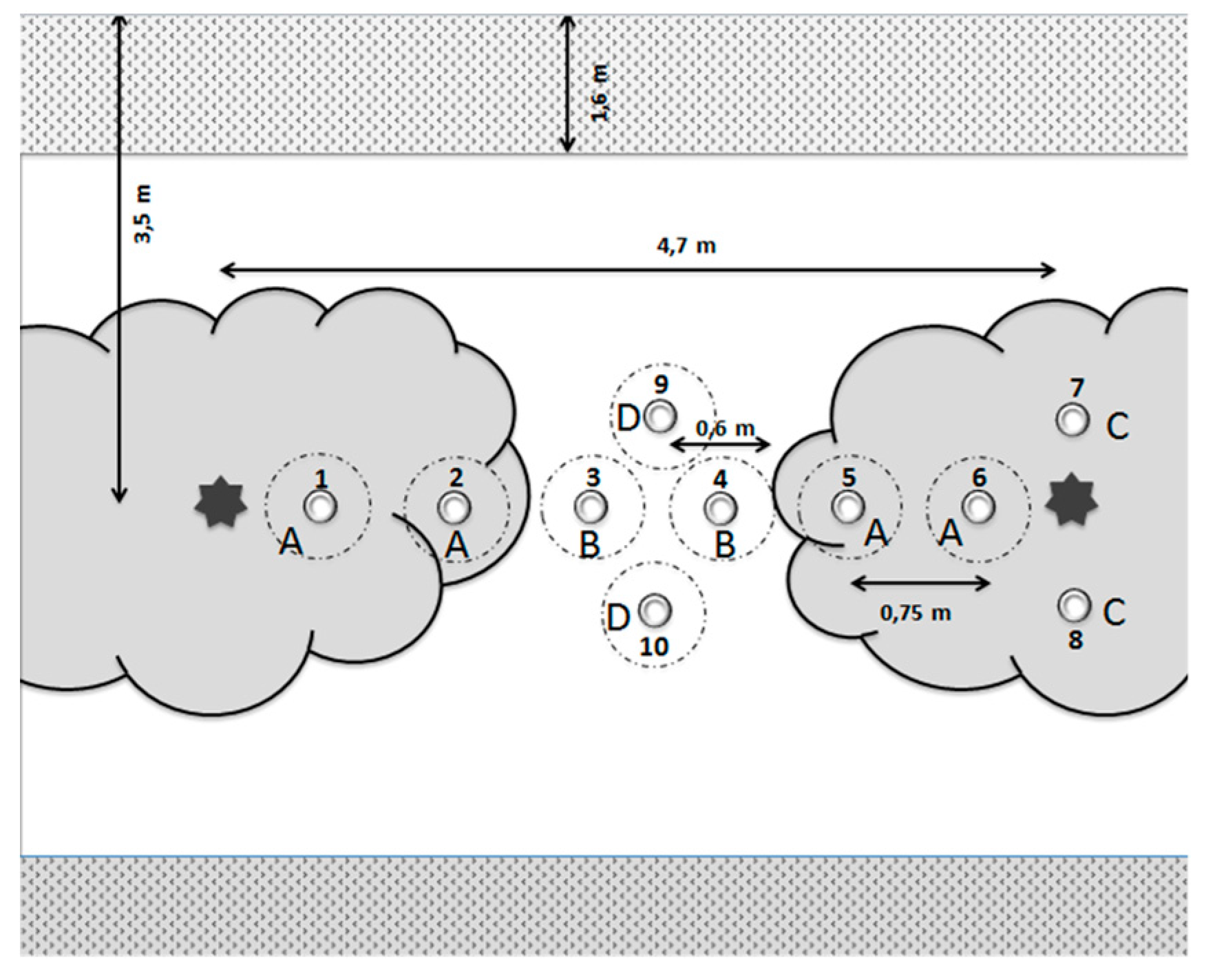
2.2. Measurement of Soil Evaporation
2.3. Measurement of Radiation Transmissivity and Ground Cover
2.4. Model Description and Validation
3. Results and Discussion
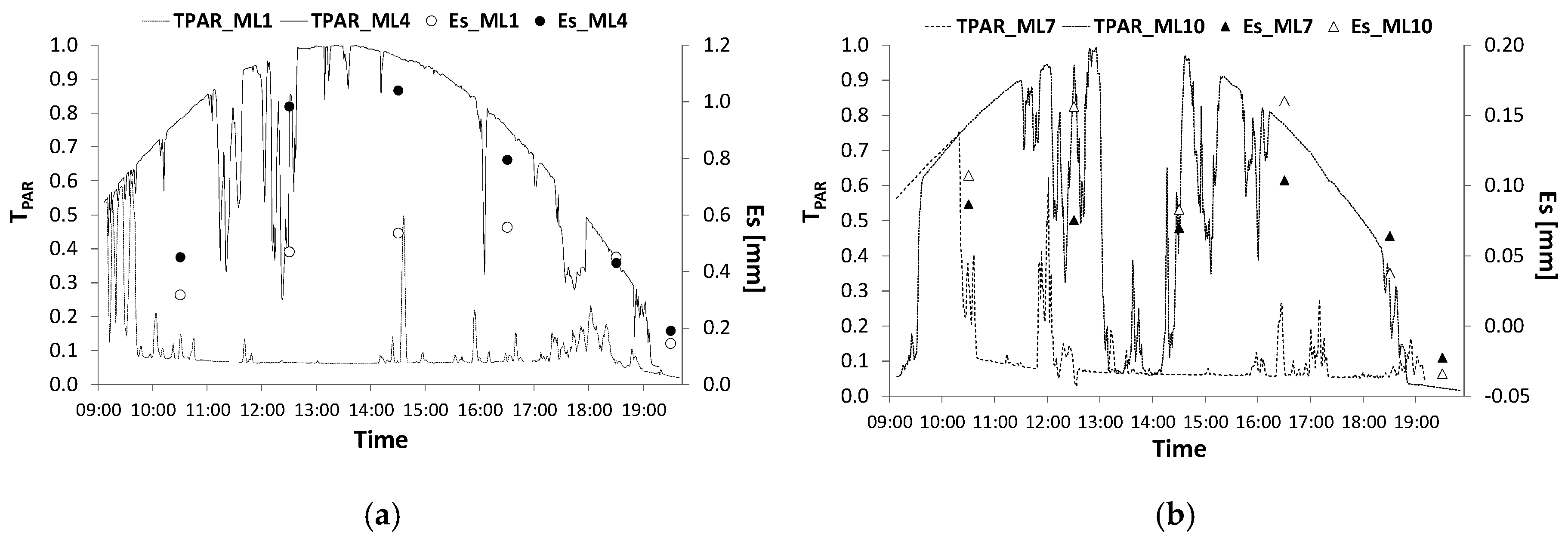
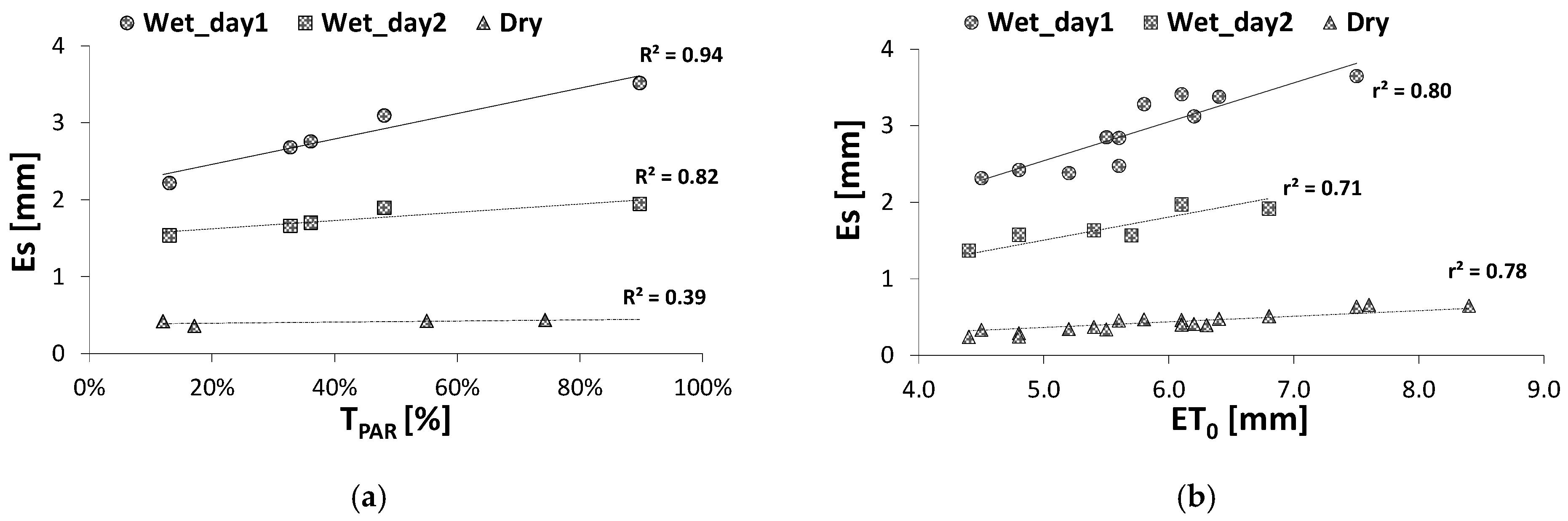
3.1. Soil Evaporation and Its Relationship with PAR Transmissivity
3.2. Ground Cover Measurements
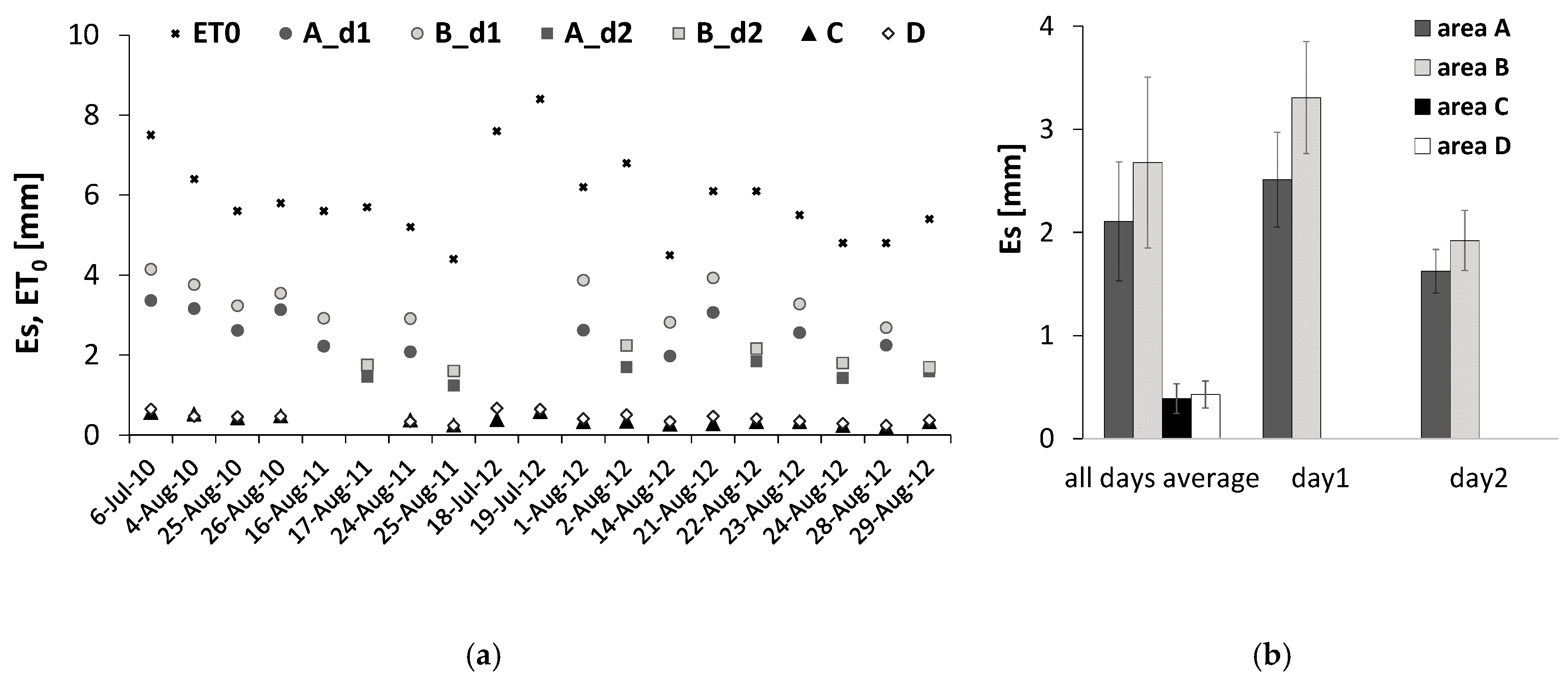
3.3. Average Soil Evaporation from Measurements
3.4. Model Calibration and Validation
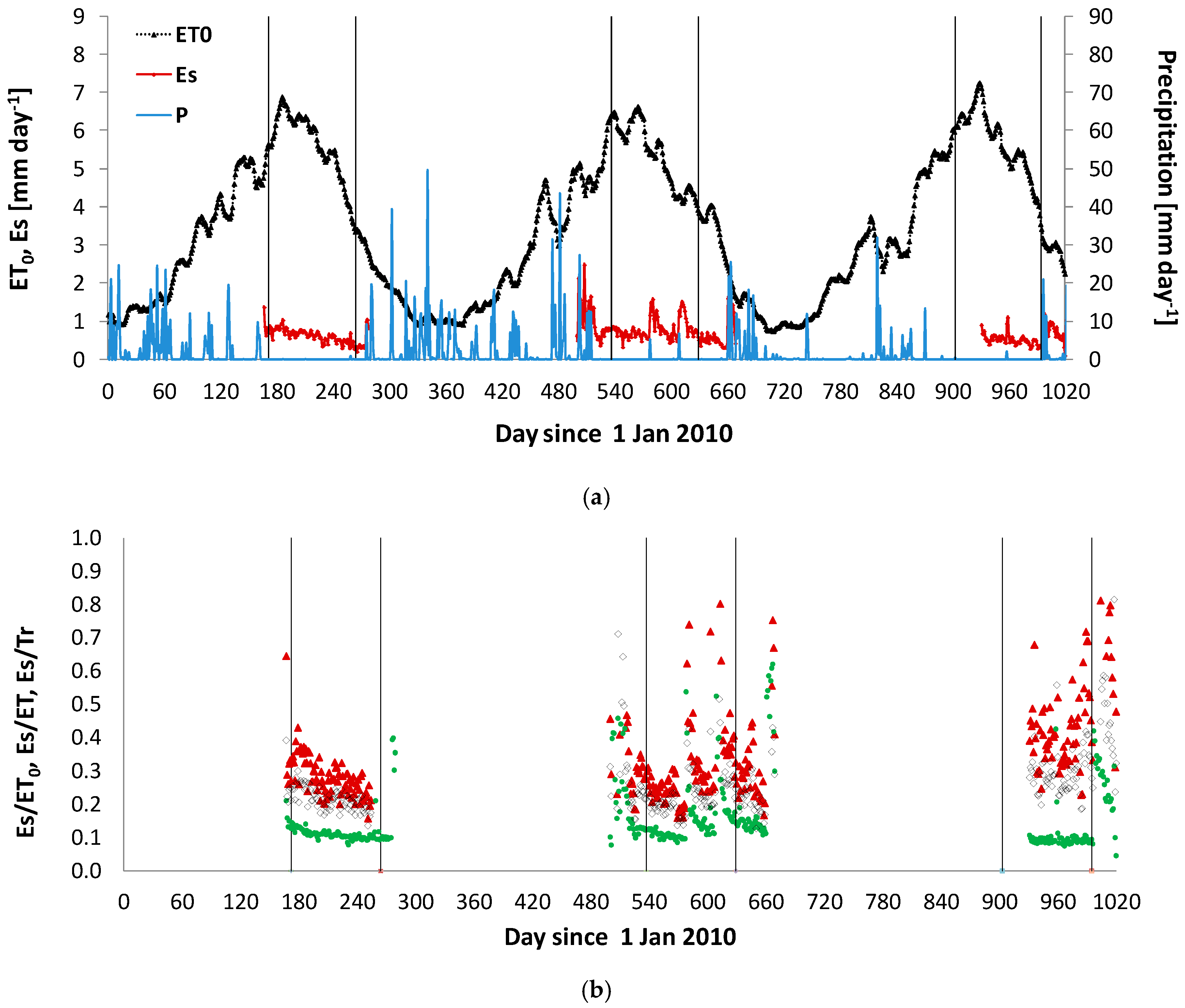
3.5. Model Application at Seasonal Scale
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, L.S. Inter-relationships between irrigation scheduling methods and on-farm irrigation systems. In Proceedings of the ICID/FAO Workshop on Irrigation Scheduling, Rome, Italy, 12–13 September 1995; FAO-Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zeggaf, T.A.; Filali, M.Y. Problématique et perspectives de l’efficience d’utilisation de l’eau agricole au Maghreb. In l’Etat des Ressources en Eau au Maghreb en 2009; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2010; pp. 203–217. ISBN 978-9954-8068-3-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lacirignola, C.; Hamdy, A.; Todorovic, M. Regional action program on “water resources management”: An overview of actions towards better water use in mediterranean agriculture. In Regional Action Programme (RAP): Water Resources Management and Water Saving in Irrigated Agriculture (WASIA PROJECT); Hamdy, A., Ed.; CIHEAM: Bari, Italy, 2003; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J.R. Evaporation, and moisture and heat fields in the soil. J. Meteorol. 1957, 14, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.T. Model for predicting evaporation from a row crop with incomplete cover. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Applications of Soil Physics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; ISBN 0123485800. [Google Scholar]
- Kool, D.; Ben-Gal, A.; Agam, N.; Šimůnek, J.; Heitman, J.L.; Sauer, T.J.; Lazarovitch, N. Spatial and diurnal below canopy evaporation in a desert vineyard: Measurements and modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7035–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroosnijder, L. Soil evaporation: Test of a practical approach under semi-arid conditions. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 1987, 35, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, M.; Snyder, R.L.; Schulbach, K.; Jackson, L.E. Crop growth and water use model for lettuce. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1996, 122, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritz, Z.; Lindroth, A.; Gärdenäs, A. Open ventilated chamber system for measurements of H2O and CO2 fluxes from the soil surface. Soil Technol. 1997, 10, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiri, A.Z. Evapotranspiration partitioning techniques for improved water use efficiency. In Evapotranspiration-From Measurements to Agricultural and Environmental Applications; Gerosa, G., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; p. 410. ISBN 978-953-307-512-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.S.; Holwill, C.J. Soil evaporation from tiger-bush in south-west Niger. J. Hydrol. 1997, 188, 426–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusa, I.; Sedgley, R.; Tennant, D. Evaporation from bare soil in south-western Australia—A test of two models using lysimetry. Aust. J. 1994, 32, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusinkveld, B.G.; Berkowicz, S.M.; Jacobs, A.F.G.; Holtslag, A.A.M.; Hillen, W.C.A.M. An automated microlysimeter to study dew formation and evaporation in arid and semiarid regions. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J.L. Evaporation and environment. In The State and Movement of Water in Living Organisms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1965; Volume 19, pp. 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, E.A.; Calera, A. Bare soil evaporation under high evaporation demand: A proposed modification to the FAO-56 model. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.I.; Valancogne, C.; Daudet, F.-A.; Ameglio, T.; Pacheco, C.A.; Michaelsen, J. Evapotranspiration and crop-water relations in a peach orchard. In Proceedings of the International Conference Evapotranspiration and Irrigation Scheduling, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–6 November 1996; pp. 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Singh, V.P. Evaluation and generalization of radiation-based methods for calculating evaporation. Hydrol. Proc. 2000, 14, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, N.; Tezza, L.; Häusler, M.; Lourenço, S.; Pacheco, C.A.; Ferreira, M.I. Three years of monitoring evapotranspiration components and crop and stress coefficients in a deficit irrigated intensive olive orchard. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 191, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.R.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- FAO-UNESCO; IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources, A Framework for International Classification, Correlation and Communication; World Soil Resources Reports n. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daamen, C.; Simmonds, L.; Wallace, J.; Laryea, K.; Sivakumar, M. Use of microlysimeters to measure evaporation from sandy soils. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1993, 65, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.I.; Valancogne, C.; Michaelsen, J.; Pacheco, C.A.; Ameglio, T.; Daudet, F.A. Evapotranspiration, water stress indicators and soil water balance in a Prunus persica orchard, in central Portugal. Acta Hortic. 1997, 449, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paço, T.A.; Ferreira, M.I.; Conceição, N. Peach orchard evapotranspiration in a sandy soil: Comparison between eddy covariance measurements and estimates by the FAO 56 approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.I.; Paço, T.A.; Silvestre, J.; Silva, R.M. Evapotranspiration estimates and water stress indicators for irrigation scheduling in woody plants. In Agricultural Water Management Research Trends; Sorensen, M.L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 129–170. ISBN 9781604565799. [Google Scholar]
- Boast, C.W.; Robertson, T.M. A “micro-lysimeter” method for determining evaporation from bare soil: Description and laboratory evaluation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunusa, I.A.M.; Sedgley, R.H.; Belford, R.K.; Tennant, D. Dynamics of water use in a dry mediterranean environment I. Soil evaporation little affected by presence of plant canopy. Agric. Water Manag. 1993, 24, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.E.; Arkin, G.F. A light interception method for measuring row crop ground cover. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.E.; Ayars, J.E. Grapevine water use and the crop coefficient are linear functions of the shaded area measured beneath the canopy. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 132, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, S.P.; Ritchie, G.; Frantz, J.M.; Pinnock, D.; Bugbee, B. Real-time imaging of ground cover: Relationships with radiation capture, canopy photosynthesis, and daily growth rate. In Digital Imaging and Spectral Techniques: Applications to Precision Agriculture and Crop Physiology; American Society of Agronomy: Logan, UT, USA, 2003; Volume 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonachela, S.; Orgaz, F.; Villalobos, F.J.; Fereres, E. Measurement and simulation of evaporation from soil in olive orchards. Irrig. Sci. 1999, 18, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorenbos, J.; Pruitt, W.O. Guidelines for Predicting Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 24; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1977; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- McJannet, D.L.; Webster, I.T.; Cook, F.J. An area-dependent wind function for estimating open water evaporation using land-based meteorological data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 31, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lin, J.; Dai, Y. Numerical modeling of soil evaporation process and its stages dividing during a drying cycle. Geofluids 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gran, M.; Carrera, J.; Olivella, S.; Saaltink, M.W. Modeling evaporation processes in a saline soil from saturation to oven dry conditions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agam, N.N.; Berliner, P.R. Diurnal water content changes in the bare soil of a coastal desert. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojima, E.; Tamagawa, I.; Turner, J.V. Experimental investigation of evaporation and condensation in a sandy soil under simulated arid conditions. J. Jpn. Soc. Hydrol. Water Res. 2011, 24, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häusler, M.; Ferreira, M.I.; Conceição, N. Assessment of vegetation parameters in olive trees in the region of Alentejo: A comparison of direct and indirect methods. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1038, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, W.D.; Kanemasu, E.T.; Raney, R.J.; Stone, L.R. Evaluation of an evapotranspiration model for corn. Agronomy 1977, 69, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Espejo, A.; Fernández, J.E.; Verhoef, A.; Knight, J.R.; Villagarcía, L. The use of high-resolution weighing lysimeters to improve estimates of soil evaporation in drip-irrigated olive orchards. Acta Hortic. 2008, 791, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonachela, S.; Orgaz, F.; Villalobos, F.J.; Fereres, E. Soil evaporation from drip-irrigated olive orchards. Irrig. Sci. 2001, 20, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, N.; Paço, T.A.; Ferreira, M.I. Medição e estimativa da evaporação do solo em condições de rega localizada. Revista de Ciências Agrárias (SCAP) 2005, 3, 77–92. [Google Scholar]
- Paço, T.A.; Pôças, I.; Cunha, M.; Silvestre, J.C.; Santos, F.L.; Paredes, P.; Pereira, L.S. Evapotranspiration and crop coefficients for a super intensive olive orchard. An application of SIMDualKc and METRIC models using ground and satellite observations. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, F.; Orgaz, F.; Testi, L.; Fereres, E. Measurement and modeling of evapotranspiration of olive (Olea europaea L.) orchards. Eur. J. Agron. 2000, 13, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
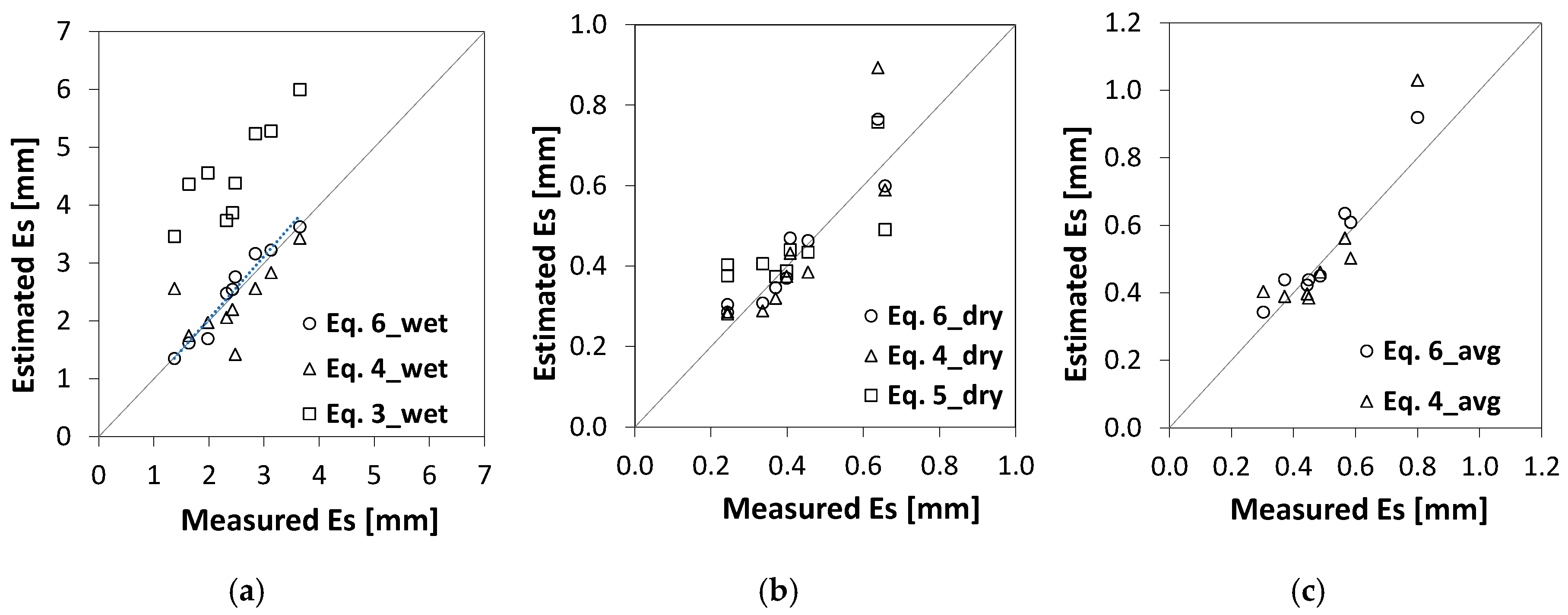
| Evaluation Parameters | Equation (6)_Wet (a = 0.43; b = 0.35) | Equation (4)_Wet | Equation (3)_Wet (a = 0.43) | Equation (6)_Dry (a = 0.2; b = 0.6) | Equation (4)_Dry | Equation (5)_Dry (C = 7.5 mm day−0.5) | Equation (6)_Avg (a = 0.2; b = 0.6) | Equation (4)_Avg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | 0.95 *** | 0.15 * | 0.11 ** | 0.86 *** | 0.75 ** | 0.23 * | 0.94 *** | 0.78 *** |
| Slope | 1.03 | 0.92 | 1.8 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.03 | 1.07 | 1.04 |
| CRM (%) | 2.2 | 0.6 | 96.1 | 5.5 | 2.2 | 15.2 | 5.9 | 02 |
| MAE (mm) | 0.15 (6%) | 0.4 (17%) | 2.12 (86%) | 0.05 (12%) | 0.07 (16%) | 0.08 (19%) | 0.05 (10%) | 0.06 (13%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tezza, L.; Häusler, M.; Conceição, N.; Ferreira, M.I. Measuring and Modelling Soil Evaporation in an Irrigated Olive Orchard to Improve Water Management. Water 2019, 11, 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122529
Tezza L, Häusler M, Conceição N, Ferreira MI. Measuring and Modelling Soil Evaporation in an Irrigated Olive Orchard to Improve Water Management. Water. 2019; 11(12):2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122529
Chicago/Turabian StyleTezza, Luca, Melanie Häusler, Nuno Conceição, and Maria Isabel Ferreira. 2019. "Measuring and Modelling Soil Evaporation in an Irrigated Olive Orchard to Improve Water Management" Water 11, no. 12: 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122529
APA StyleTezza, L., Häusler, M., Conceição, N., & Ferreira, M. I. (2019). Measuring and Modelling Soil Evaporation in an Irrigated Olive Orchard to Improve Water Management. Water, 11(12), 2529. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122529







