Significance of Chlorinated Phenols Adsorption on Plastics and Bioplastics during Water Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sorption Experiments
2.3. Analytical Procedure, Quality Assurance and Quality Control
3. Results
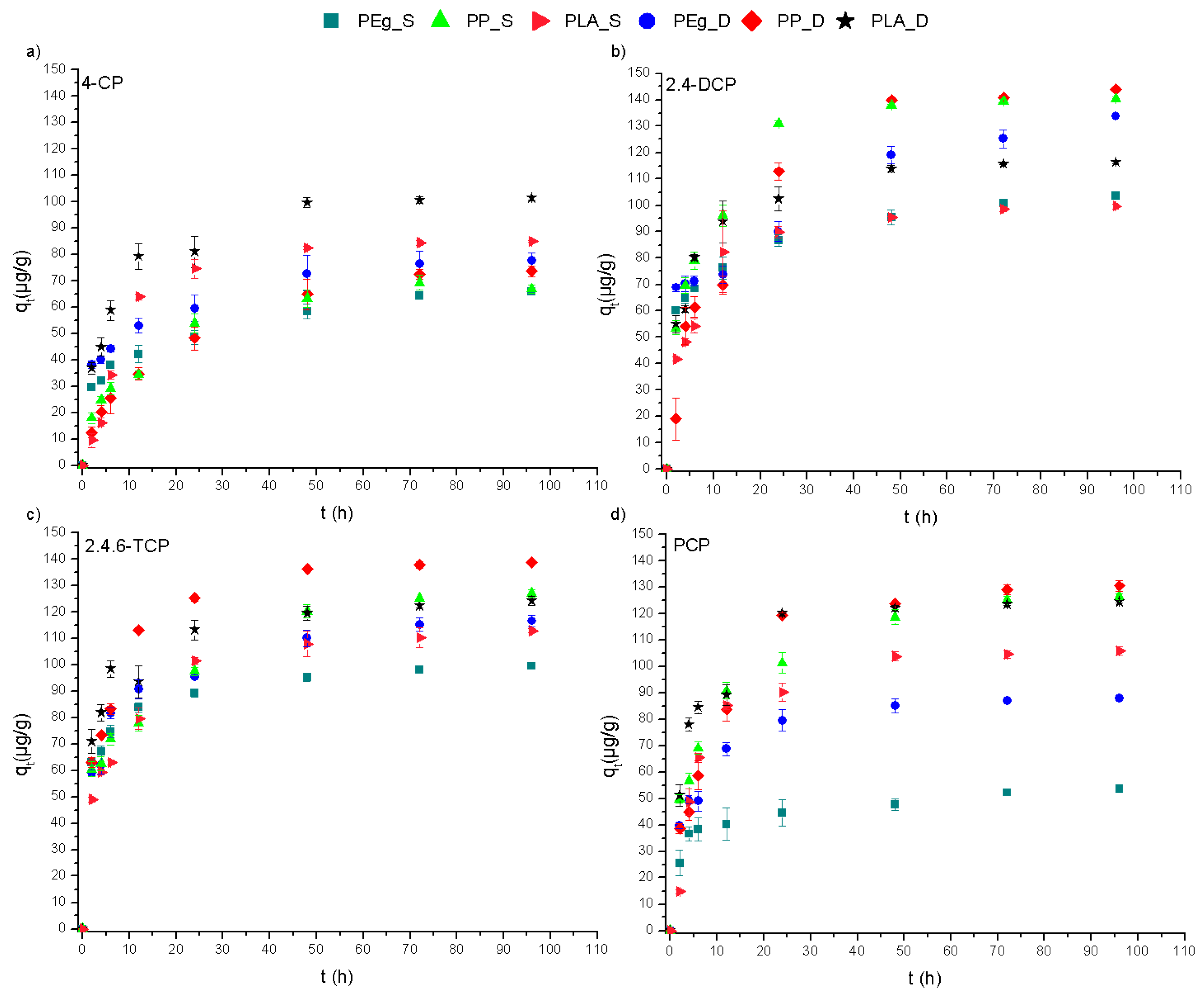
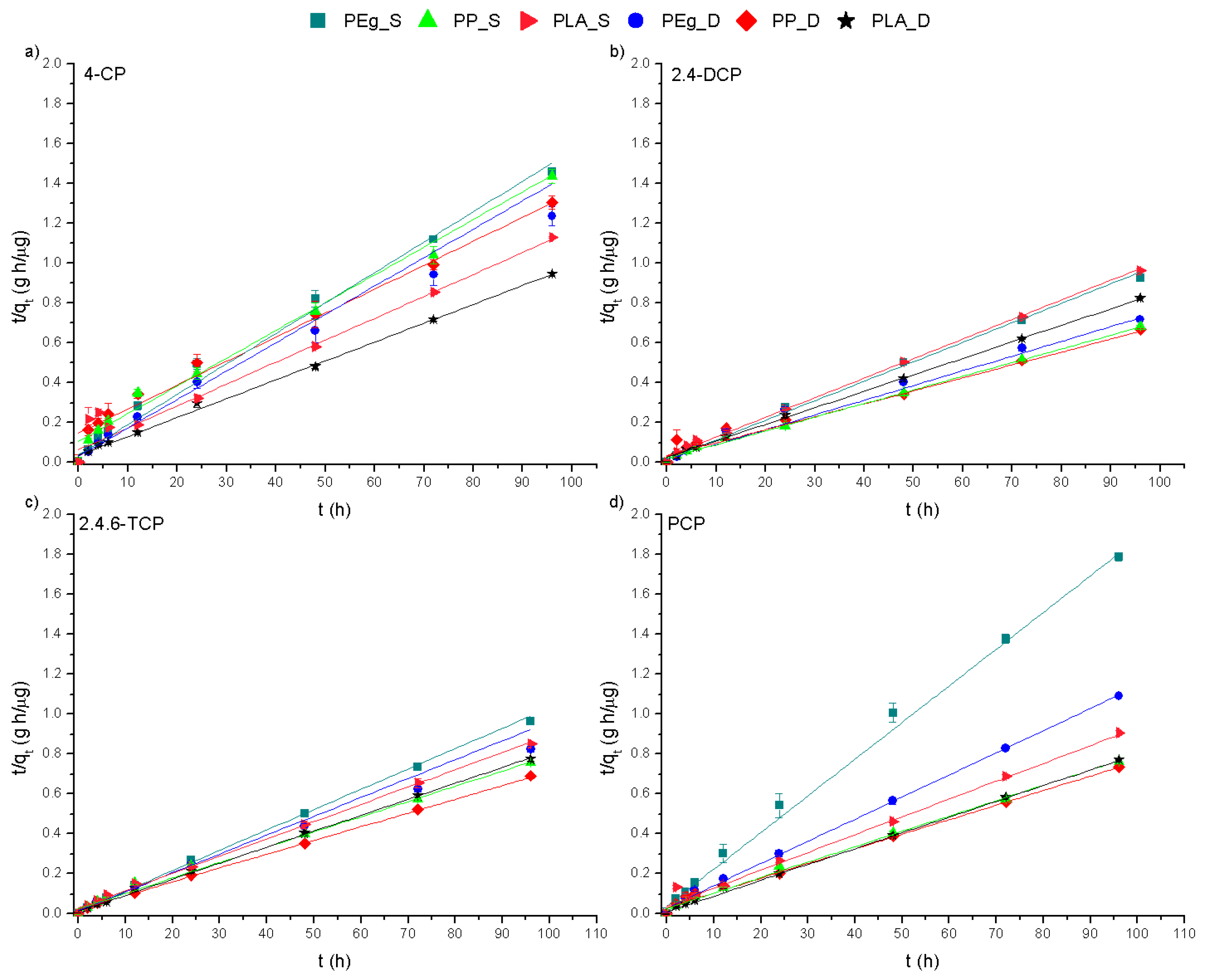
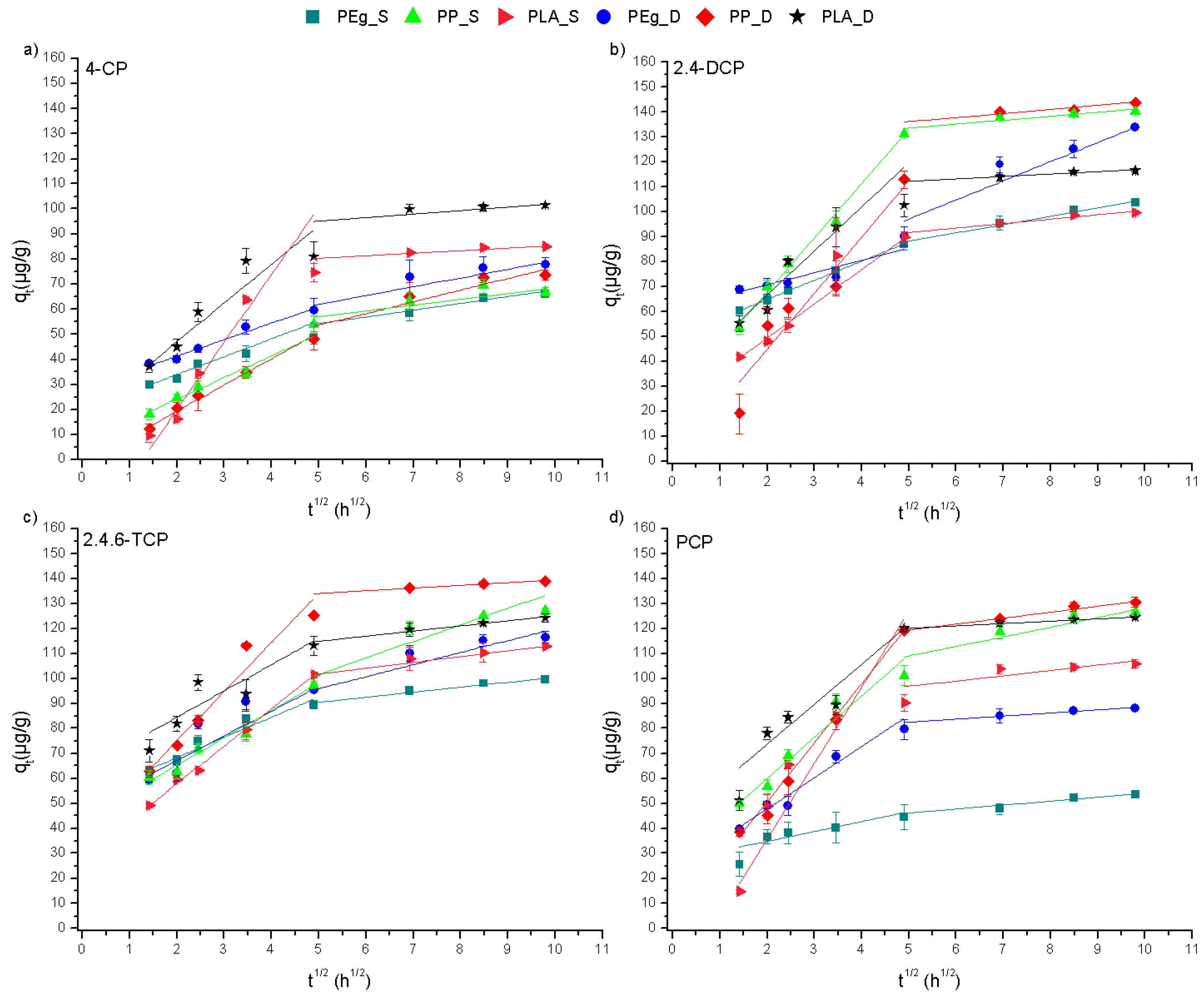
3.1. Sorption Kinetics
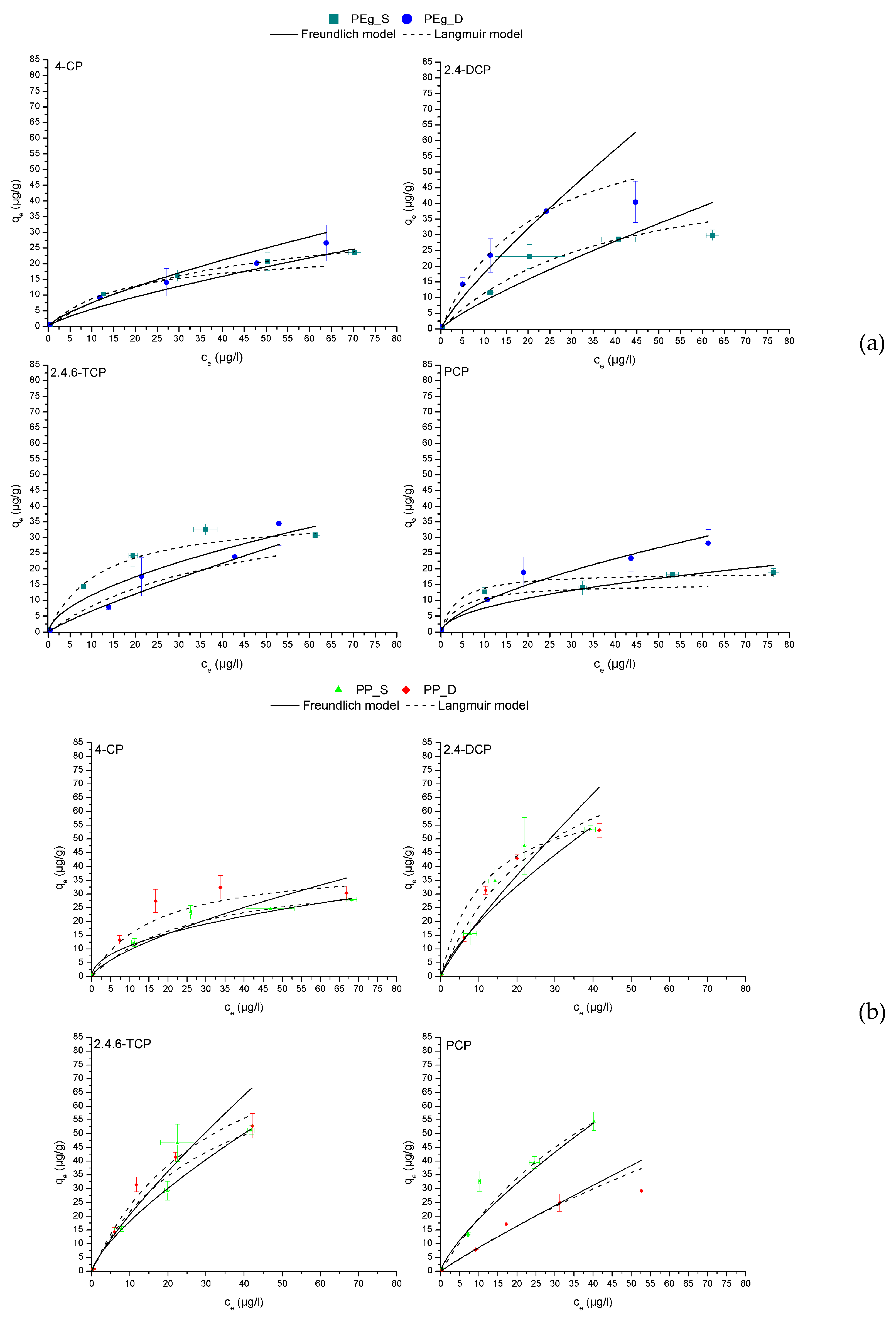
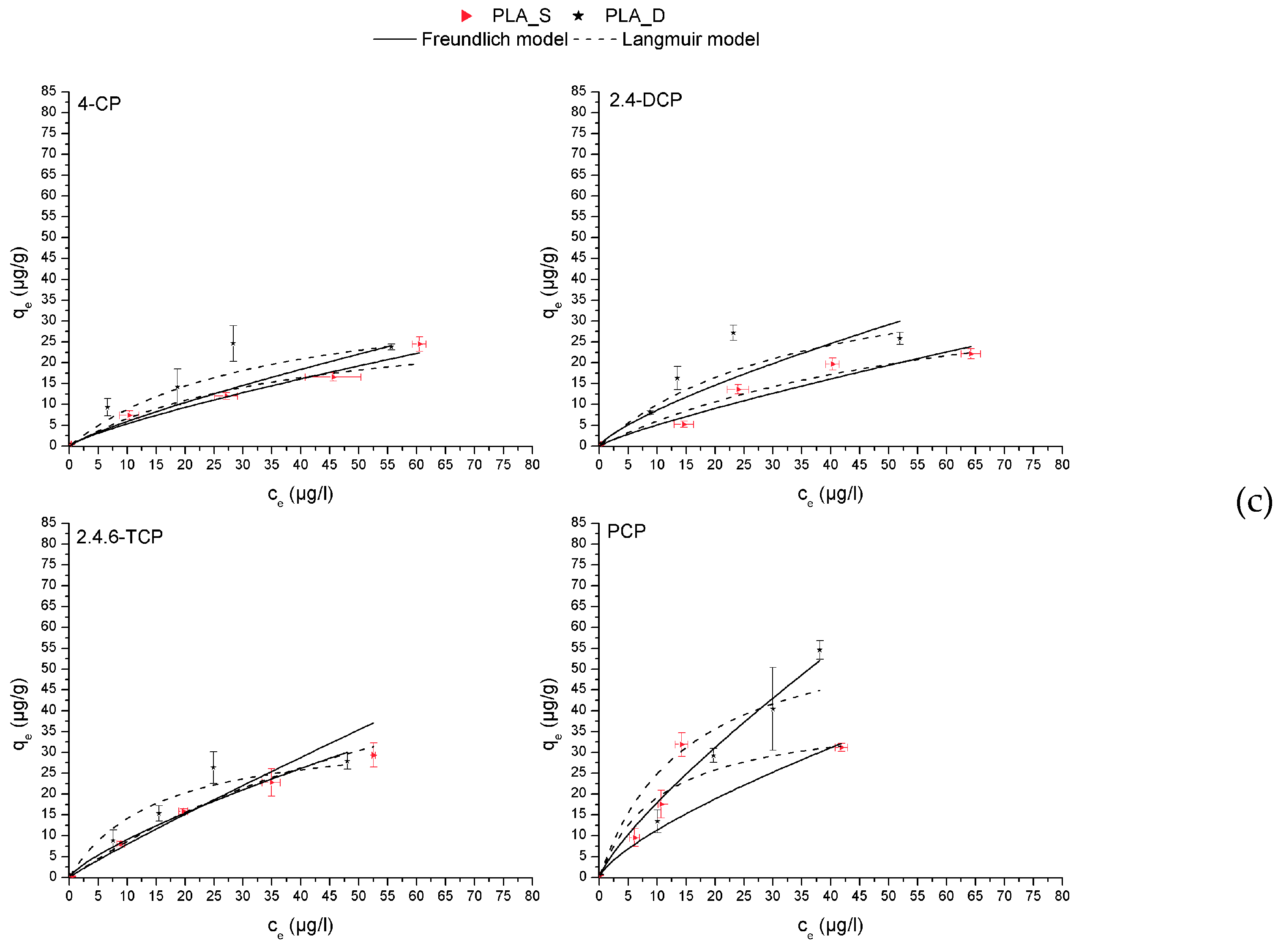
3.2. Adsorption Isotherms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czaplicka, M. Sources and transformations of chlorophenols in the natural environment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2004, 322, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikesland, P.J.; Fiss, E.M.; Wigginton, K.R.; McNeill, K.; Arnold, W.A. Halogenation of Bisphenol-A, Triclosan, and Phenols in Chlorinated Waters Containing Iodide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6764–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotna, K.; Cermakova, L.; Pivokonska, L.; Cajthaml, T.; Pivokonsky, M. Microplastics in drinking water treatment-Current knowledge and research needs-review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 667, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michałowicz, J.; Duda, W. Phenols-sources and toxicity. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 347–362. [Google Scholar]
- Gallard, H.; von Gunten, U. Chlorination of Phenols: Kinetics and Formation of Chloroform. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy Text with EEA Relevance: Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy; The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Environmental Quality Standards in the Field of Water Policy, Amending and Subsequently Repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and Amending Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council: Directive on EQS in the Field of Water Policy; The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union: Strasbourg, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 2004 Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Wang, W.; Wang, J. Comparative evaluation of sorption kinetics and isotherms of pyrene onto microplastics. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Pang, J.; Chen, S.; Jia, H. Sorption properties of tylosin on four different microplastics. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Kimura, Z.-I.; Nishimura, Y.; Shibayama, M.; Hiraishi, A. Removal of Hydrophobic Organic Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Biodegradable Polyesters. JWARP 2010, 2, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Paszkiewicz, S.; Szymczyk, A.; Pawlikowska, D.; Subocz, J.; Zenker, M.; Masztak, R. Electrically and Thermally Conductive Low Density Polyethylene-Based Nanocomposites Reinforced by MWCNT or HybridMWCNT/Graphene Nanoplatelets with Improved Thermo-Oxidative Stability. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddah, H.A. Polypropylene as a Promising Plastic: A Review. AJOP 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mandolfino, C. Polypropylene surface modification by low pressure plasma to increase adhesive bonding: Effect of process parameters. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2019, 366, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, J.C.; Tipton, A.J. Synthetic biodegradable polymers as orthopedic devices. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2335–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaavessina, M.; Ali, I.; Al-Zahrani, S.M. The Influences of Elastomer toward Crystallization of Poly (lactic acid). Procedia Chem. 2012, 4, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedermann, M.; Gmeiner, P.; Pessenlehner, S.; Haimann, M.; Hohenblum, P.; Habersack, H. A Methodology for Measuring Microplastic Transport in Large or Medium Rivers. Water 2018, 10, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. The sorption kinetics and isotherms of sulfamethoxazole with polyethylene microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.W.; Chakravorti, R.K. Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed bed adsorbers. AICHE J. 1974, 20, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into Modeling of Adsorption Isotherm Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffer, T.; Hofmann, T. Sorption of non-polar organic compounds by micro-sized plastic particles in aqueous solution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Microplastics play a minor role in tetracycline sorption in the presence of dissolved organic matter. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubić, A.; Leovac, A.; Molnar, J.; Krčmar, D.; Paunović, O.; Ivančev-Tumbas, I. Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter from the Danube River Before and After Ozone Oxidation. In Proceedings of the 6th Symposium Chemistry and Environmental Protection EnviroChem, Vršac, Serbia, 21–24 May 2013; pp. 282–283. [Google Scholar]
| Compound | Particle size (mm) | Density (g/cm3) | Crystal- linity (%) | Melting Temp. (°C) | Glass Transition Temp. (ºC) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEg | 3.0 * | 0.918 * | 44.0 | 114 | −120 | [14] |
| PP | 3.0 * | 0.9 * | 38.0 | 165 | −18 | [15,16] |
| PLA | 3.0 * | 1.24 * | 20.9 | 173–178 | 60–65 | [17,18] |
| Compound | MW | logKow a | Vi a | Sw a | pKa a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-CP | 129 | 2.40 | 1.02 | 27,100 | 9.41 |
| 2,4-DCP | 163 | 3.06 | 1.14 | 4500 | 7.90 |
| 2,4,6-TCP | 197 | 3.69 | 1.26 | 800 | 6.40 |
| PCP | 266 | 5.12 | 1.39 | 14 | 4.80 |
| Parameter | Synthetic Water | Danube River Water |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.23 ± 0.06 | 7.45 ± 0.07 |
| Electro conductivity 25 °C (μS/cm) | 226 ± 23 | 333 ± 7.0 |
| Dissolved organic carbon (mg/L) | <0.5 | 2.84 ± 0.12 |
| Chloride concentration (mg/L) | 52.1 ± 3.59 | 44.0 ± 1.52 |
| Sulphate concentration (mg/L) | 21.2 ± 4.89 | 25.5 ± 3.18 |
| Hydrogen carbonate concentration (mg/L) | 134 ± 6 | 218 ± 43 |
| Compounds | Solid Phase | k2 (h−1) | R2 | qe (Theoretical) | qe (Experimental) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-CP | PEg_S | 0.0063 | 0.9890 | 65.85 | 65.49 |
| PEg_D | 0.0065 | 0.9460 | 77.69 | 70.22 | |
| PP_S | 0.0018 | 0.9749 | 66.85 | 71.84 | |
| PP_D | 0.0010 | 0.9815 | 73.62 | 83.13 | |
| PLA_S | 0.0019 | 0.9939 | 85.02 | 90.83 | |
| PLA_D | 0.0025 | 0.9981 | 101.4 | 105.6 | |
| 2,4-DCP | PEg_S | 0.0059 | 0.9912 | 103.7 | 102.2 |
| PEg_D | 0.0032 | 0.9925 | 133.8 | 135.3 | |
| PP_S | 0.0022 | 0.9978 | 140.4 | 145.8 | |
| PP_D | 0.0012 | 0.9915 | 143.8 | 153.8 | |
| PLA_S | 0.0031 | 0.9977 | 99.62 | 101.8 | |
| PLA_D | 0.0026 | 0.9993 | 116.4 | 120.6 | |
| 2,4,6-TCP | PEg_S | 0.0085 | 0.9973 | 99.56 | 98.14 |
| PEg_D | 0.0056 | 0.9930 | 116.5 | 105.8 | |
| PP_S | 0.0022 | 0.9974 | 126.9 | 130.7 | |
| PP_D | 0.0020 | 0.9991 | 138.9 | 145.6 | |
| PLA_S | 0.0026 | 0.9937 | 112.9 | 115.6 | |
| PLA_D | 0.0046 | 0.9992 | 124.1 | 125.2 | |
| PCP | PEg_S | 0.0087 | 0.9990 | 53.68 | 54.38 |
| PEg_D | 0.0041 | 0.9985 | 88.05 | 90.09 | |
| PP_S | 0.0021 | 0.9952 | 126.3 | 129.9 | |
| PP_D | 0.0017 | 0.9935 | 130.5 | 136.8 | |
| PLA_S | 0.0020 | 0.9789 | 105.9 | 112.1 | |
| PLA_D | 0.0060 | 0.9988 | 124.5 | 126.7 |
| Compounds | Adsorbents | Freundlich model | Langmuir model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | n | KF(µg/g)/(µg/L)n | R2 | qmax(µg/g) | KL(l/µg) | ||
| 4-CP | PEg_S | 0.9478 | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.9892 | 37.03 | 0.0255 |
| PEg_D | 0.9816 | 0.74 | 1.36 | 0.9825 | 24.55 | 0.0551 | |
| PP_S | 0.9974 | 0.48 | 3.69 | 0.9984 | 39.17 | 0.0365 | |
| PP_D | 0.8292 | 0.69 | 1.98 | 0.9687 | 41.15 | 0.0599 | |
| PLA_S | 0.9869 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 0.9762 | 32.74 | 0.0252 | |
| PLA_D | 0.9835 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.9938 | 38.40 | 0.0298 | |
| 2,4-DCP | PEg_S | 0.9949 | 0.83 | 1.33 | 0.9989 | 55.60 | 0.0258 |
| PEg_D | 0.9998 | 0.84 | 2.58 | 0.9998 | 71.36 | 0.0457 | |
| PP_S | 0.9970 | 0.74 | 3.63 | 0.9945 | 68.98 | 0.0869 | |
| PP_D | 0.9347 | 0.85 | 2.86 | 0.9884 | 100.2 | 0.0338 | |
| PLA_S | 0.9585 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.9423 | 45.48 | 0.0152 | |
| PLA_D | 0.9268 | 0.76 | 1.52 | 0.9392 | 46.35 | 0.0275 | |
| 2,4,6-TCP | PEg_S | 0.9397 | 0.59 | 3.02 | 0.9390 | 37.47 | 0.0839 |
| PEg_D | 0.9897 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.9919 | 44.95 | 0.0222 | |
| PP_S | 0.9960 | 0.73 | 3.37 | 0.9631 | 87.13 | 0.0330 | |
| PP_D | 0.9599 | 0.82 | 3.14 | 0.9911 | 100.1 | 0.0313 | |
| PLA_S | 0.9703 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.9881 | 82.23 | 0.0118 | |
| PLA_D | 0.9668 | 0.76 | 1.59 | 0.9796 | 35.59 | 0.0662 | |
| PCP | PEg_S | 0.9521 | 0.51 | 2.32 | 0.9913 | 18.93 | 0.2681 |
| PEg_D | 0.9958 | 0.63 | 2.24 | 0.9349 | 15.32 | 0.2261 | |
| PP_S | 0.9708 | 0.75 | 3.39 | 0.9438 | 135.2 | 0.0167 | |
| PP_D | 0.9884 | 0.93 | 1.02 | 0.9898 | 168.2 | 0.0054 | |
| PLA_S | 0.9531 | 0.73 | 2.15 | 0.9817 | 62.74 | 0.0940 | |
| PLA_D | 0.9925 | 0.80 | 2.88 | 0.9246 | 39.54 | 0.0658 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tubić, A.; Lončarski, M.; Maletić, S.; Molnar Jazić, J.; Watson, M.; Tričković, J.; Agbaba, J. Significance of Chlorinated Phenols Adsorption on Plastics and Bioplastics during Water Treatment. Water 2019, 11, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112358
Tubić A, Lončarski M, Maletić S, Molnar Jazić J, Watson M, Tričković J, Agbaba J. Significance of Chlorinated Phenols Adsorption on Plastics and Bioplastics during Water Treatment. Water. 2019; 11(11):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112358
Chicago/Turabian StyleTubić, Aleksandra, Maja Lončarski, Snežana Maletić, Jelena Molnar Jazić, Malcolm Watson, Jelena Tričković, and Jasmina Agbaba. 2019. "Significance of Chlorinated Phenols Adsorption on Plastics and Bioplastics during Water Treatment" Water 11, no. 11: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112358
APA StyleTubić, A., Lončarski, M., Maletić, S., Molnar Jazić, J., Watson, M., Tričković, J., & Agbaba, J. (2019). Significance of Chlorinated Phenols Adsorption on Plastics and Bioplastics during Water Treatment. Water, 11(11), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112358









