Interactive Effect of Meteorological Drought and Vegetation Types on Root Zone Soil Moisture and Runoff in Rangeland Watersheds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Precipitation, Soil Moisture, and Streamflow Data
2.3. Meteorological Drought Index
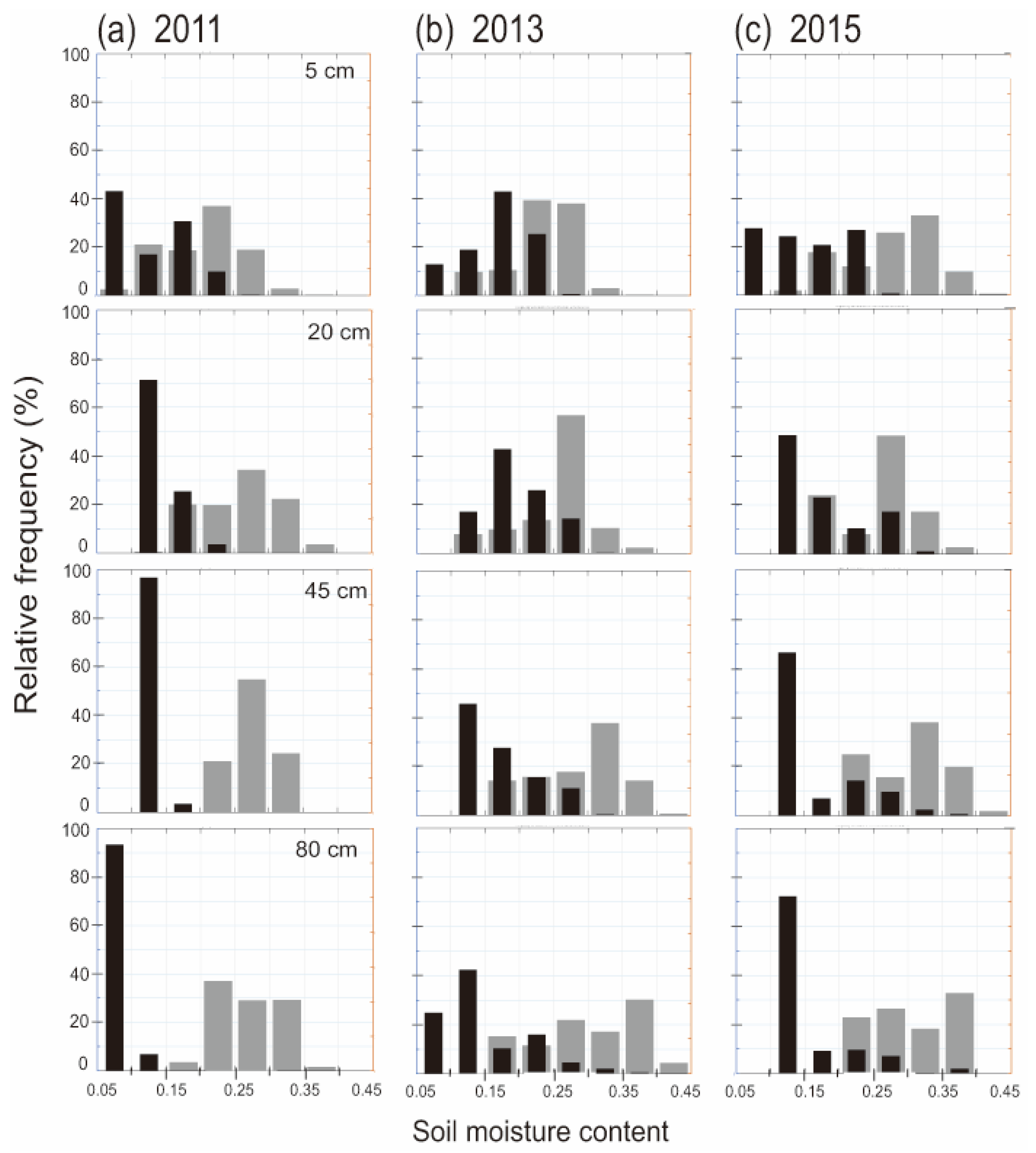
2.4. Frequency Distribution
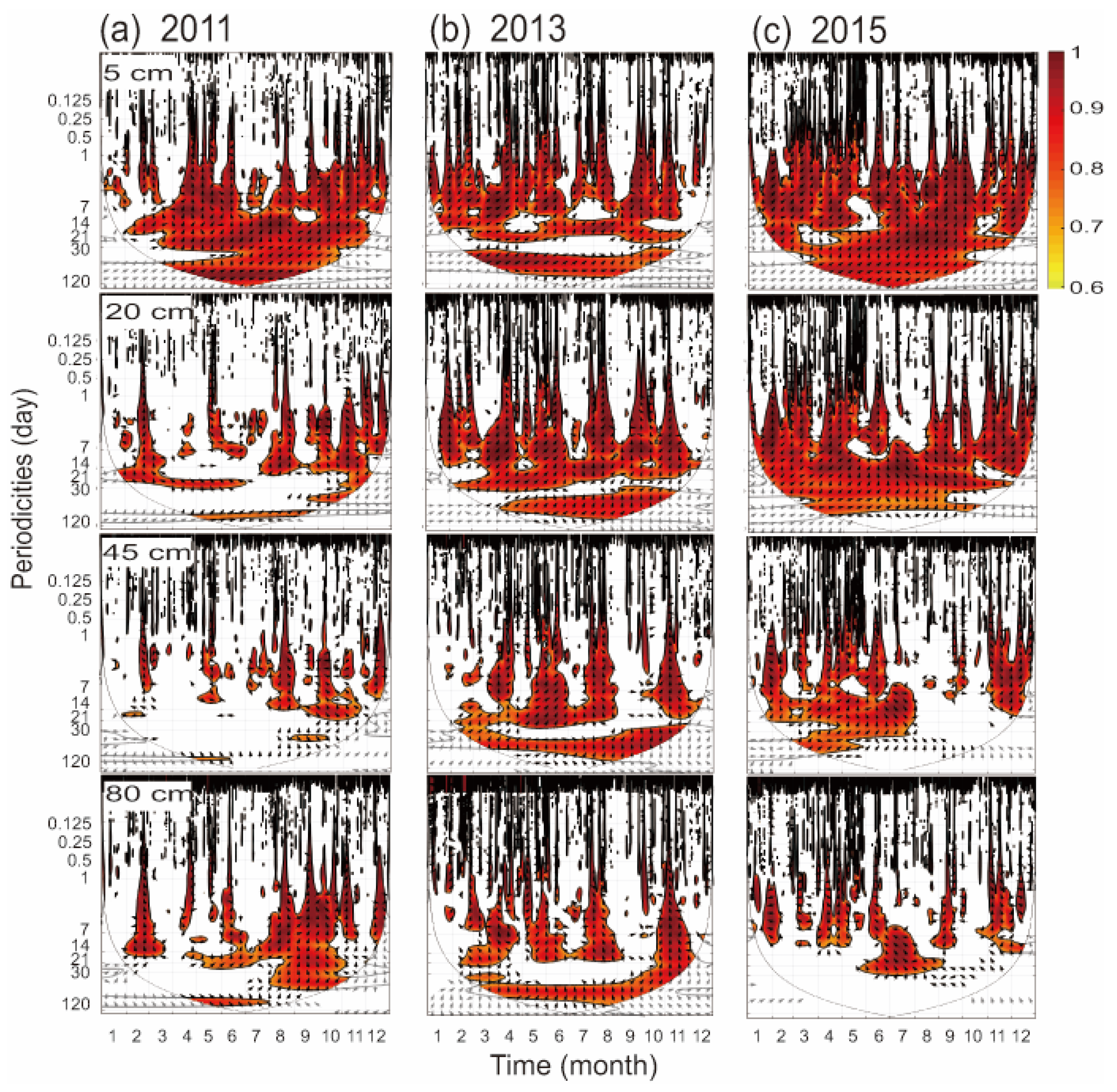
2.5. Wavelet Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Precipitation Characteristics
3.2. Impact of Woody Encroachment on Soil Moisture
3.3. Coherence between Precipitation and Soil Moisture
3.4. Runoff and Runoff Coefficients
4. Discussion
4.1. Storm Intensity, Infiltration Capacity, and Vegetation Impact
4.2. Drought Reduces the Coherence of Subsoil Soil Moisture to Precipitation Pulse
4.3. Increase in Soil Moisture Stress and Reduction in the Runoff from Redcedar Woodland
4.4. Water Resources Challenges in the South-Central Great Plains under Climate Change
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acharya, B.; Kharel, G.; Zou, C.B.; Wilcox, B.P.; Halihan, T. Woody plant encroachment impacts on groundwater recharge: A review. Water 2018, 10, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritsema, C.J.; Dekker, L.W. How water moves in a water repellent sandy soil: 2. Dynamics of fingered flow. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, S.H.; Shakesby, R.A.; Walsh, R.P.D. Soil water repellency: Its causes, characteristics and hydro-geomorphological significance. Earth Sci. Rev. 2000, 51, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. An approach toward a physical interpretation of infiltration-capacity 1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1941, 5, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Rawls, W.J.; Brakensiek, D.L.; Wight, J.R. Predicting runoff from rangeland catchments: A comparison of two models. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2401–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Stebler, E.; Will, R.E. Woody plant encroachment reduces annual runoff and shifts runoff mechanisms in the tallgrass prairie, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 4838–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loik, M.E.; Breshears, D.D.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Belnap, J. A multi-scale perspective of water pulses in dryland ecosystems: Climatology and ecohydrology of the western USA. Oecologia. 2004, 141, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basara, J.B.; Maybourn, J.N.; Peirano, C.M.; Tate, J.E.; Brown, P.J.; Hoey, J.D.; Smith, B.R. Drought and associated impacts in the Great Plains of the United States-A Review. Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, S.D.; Suarez, M.J.; Pegion, P.J.; Koster, R.D.; Bacmeister, J.T. Causes of long-term drought in the US Great Plains. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seager, R.; Hoerling, M. Atmosphere and ocean origins of North American droughts. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 4581–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkin, J.A.; Zhong, Y.; Hunt, E.D.; Basara, J.; Svoboda, M.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C. Assessing the evolution of soil moisture and vegetation conditions during a flash drought–flash recovery sequence over the South-Central United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2019, 20, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Gaitán, C.F.; Hong, Y.; McPherson, R.A. Analysis of precipitation projections over the climate gradient of the Arkansas Red River basin. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2017, 56, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkin, J.A.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.; Mladenova, I.E.; Basara, J.B.; Svoboda, M. Examining rapid onset drought development using the thermal infrared–based evaporative stress index. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1057–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otkin, J.A.; Zhong, Y.; Lorenz, D.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C. Exploring seasonal and regional relationships between the Evaporative Stress Index and surface weather and soil moisture anomalies across the United States. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5373–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.X.; Shao, M.A. Response of soil water dynamics to precipitation years under different vegetation types on the northern Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Land. 2016, 8, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hao, Y.H.; Stebler, E.; Tanaka, N.; Zou, C.B. Impact of plant functional types on coherence between precipitation and soil moisture: A wavelet analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 12197–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breshears, D.D.; Rich, P.M.; Barnes, F.J.; Campbell, K. Overstory-imposed heterogeneity in solar radiation and soil moisture in a semiarid woodland. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 1201–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wang, G.L. Impact of vegetation feedback on the response of precipitation to antecedent soil moisture anomalies over North America. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jackson, R.B. A global analysis of groundwater recharge for vegetation, climate, and soils. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, S.; Schimel, D.S.; Holland, E.A. Mechanisms of shrubland expansion, land use, climate or CO2? Clim. Chang. 1995, 29, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.M.; Knapp, A.K.; Brock, B.L. Expansion of woody plants in, tallgrass prairie: A fifteen-year study of fire and fire-grazing interactions. Am. Midl. Nat. 2002, 147, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Turton, D.J.; Will, R.E.; Engle, D.M.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Alteration of hydrological processes and streamflow with juniper (Juniperus virginiana) encroachment in a mesic grassland catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 6173–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wine, M.L.; Ochsner, T.E.; Sutradhar, A.; Pepin, R. Effects of eastern redcedar encroachment on soil hydraulic properties along Oklahoma’s grassland-forest ecotone. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; Allen, C.D. Ecohydrology of a resource-conserving semiarid woodland: Effects of scale and disturbance. Ecol. Monogr. 2003, 73, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilman, J.L.; Litvak, M.E.; McInnes, K.J.; Kjelgaard, J.F.; Kamps, R.H.; Schwinning, S. Water storage capacity controls energy partitioning and water use in karst ecosystems on the Edwards Plateau, Texas. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, G.L.; Will, R.E.; Turton, D.J.; Wilson, D.S.; Zou, C.B. Water use of Juniperus virginiana trees encroached into mesic prairies in Oklahoma, USA. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Laio, F.; Porporato, A.; Ridolfi, L.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Plants in water-controlled ecosystems: Active role in hydrologic processes and response to water stress - II. Probabilistic soil moisture dynamics. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porporato, A.; Daly, E.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Soil water balance and ecosystem response to climate change. Am. Nat. 2004, 164, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Isham, V.; Cox, D.R.; Manfreda, S.; Porporato, A. Space-time modeling of soil moisture: Stochastic rainfall forcing with heterogeneous vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Will, R.E.; Stebler, E. Calibration of swat model for woody plant encroachment using paired experimental watershed data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Proc. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D.; Kurths, J.; Holschneider, M. Nonstationary Gaussian processes in wavelet domain: Synthesis, estimation, and significance testing. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 016707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, J.W.; Thurow, T.L.; Taylor Jr, C.A. Hydrologic characteristics of vegetation types as affected by prescribed burning. J. Range Manag. 1997, 50, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.L.; Zou, C.B.; Stebler, E.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Allred, B. Pyric-herbivory and hydrological responses in tallgrass prairie. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 69, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Caterina, G.L.; Will, R.E.; Stebler, E.; Turton, D. Canopy interception for a tallgrass prairie under juniper encroachment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0141422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, B.S.; Halihan, T.; Zou, C.B.; Will, R.E. Vegetation controls on the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of deep moisture in the unsaturated zone. A hydrogeophysical evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Hao, Y.H.; Ochsner, T.E.; Zou, C.B. Woody plant encroachment alters soil hydrological properties and reduces downward flux of water in tallgrass prairie. Plant Soil 2017, 414, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaepfer, D.R.; Bradford, J.B.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Munson, S.M.; Tietjen, B.; Hall, S.A.; Wilson, S.D.; Duniway, M.C.; Jia, G.; Pyke, D.A.; et al. Climate change reduces extent of temperate drylands and intensifies drought in deep soils. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, R.S.; Scanlon, B.R.; Mpelasoka, F.S.; Reedy, R.C.; Gates, J.B.; Zhang, L. Potential climate change effects on groundwater recharge in the High Plains Aquifer, USA. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3936–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dale, J.; Zou, C.B.; Andrews, W.J.; Long, J.M.; Liang, Y.; Qiao, L. Climate, water use, and land surface transformation in an irrigation intensive watershed-Streamflow responses from 1950 through 2010. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Twidwell, D.; Bielski, C.H.; Fogarty, D.T.; Mittelstet, A.R.; Starks, P.J.; Will, R.E.; Zhong, Y.; Acharya, B.S. Impact of Eastern Redcedar Proliferation on Water Resources in the Great Plains USA—Current State of Knowledge. Water 2018, 10, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklahoma Water Resources Board. Oklahoma Comprehensive Water Plan: Executive Report; Oklahoma Water Resources Board: Oklahoma, OK, USA, 2012.
- Wilcox, B.P. Shrub control and streamflow on rangelands: A process based viewpoint. J. Range Manag. 2002, 55, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaswamy, J.; Bonell, M.; Venkatesh, B.; Purandar, B.K.; Rakesh, K.N.; Lele, S.; Kiran, M.C.; Reddy, V.; Badiger, S. The groundwater recharge response and hydrologic services of tropical humid forest ecosystems to use and reforestation: Support for the "infiltration-evapotranspiration trade-off hypothesis". J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Wang, S.Y.S.; Lo, M.H.; Wu, W.Y. Concurrent increases in wet and dry extremes projected in Texas and combined effects on groundwater. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 054002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starks, P.J.; Moriasi, D.N. Impact of eastern redcedar encroachment on stream discharge in the North Canadian River basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 72, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Qiao, L.; Wilcox, B.P. Woodland expansion in central Oklahoma will significantly reduce streamflows–a modelling analysis. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.; McCluskey, M.; Arthur, K. Incorporating climate change into water supply, and yield studies: A demonstration and comparison of practical methods. In Proceedings of the World Environmental And Water Resources Congress 2012, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 20–24 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, E.S.; Ochsner, T.E.; Engle, D.M.; Carlson, J.D.; Twidwell, D.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Soil moisture affects growing-season wildfire size in the southern great plains. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.G.; Sheridan, G.J.; Lane, P.N.; Nyman, P.; Haydon, S. Wildfire effects on water quality in forest catchments: A review with implications for water supply. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| IGUE | Precipitation (P, mm) | Runoff (D, mm) | Runoff Coefficient (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grassland¶ | Woodland# | Grassland | Woodland | ||
| 2011 | 625.9 | 2.04 | 1.38 | 0.33 | 0.22 |
| 2012 | 630.3 | 50.81 | 21.29 | 8.06 | 3.38 |
| 2013 | 979.1 | 61.06 | 19.91 | 6.24 | 2.03 |
| 2014 | 707.8 | 13.98 | 9.31 | 1.98 | 1.32 |
| 2015 | 1020.7 | 142.47 | 55.85 | 13.96 | 5.47 |
| Mean (SE) | 792.75 (96.21) | 54.07 (27.6) | 21.54 (10.41) | 6.11 (2.69) | 2.48 (1.01) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Kharel, G.; An, L.; Stebler, E.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, C.B. Interactive Effect of Meteorological Drought and Vegetation Types on Root Zone Soil Moisture and Runoff in Rangeland Watersheds. Water 2019, 11, 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112357
Hao Y, Liu Q, Li C, Kharel G, An L, Stebler E, Zhong Y, Zou CB. Interactive Effect of Meteorological Drought and Vegetation Types on Root Zone Soil Moisture and Runoff in Rangeland Watersheds. Water. 2019; 11(11):2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112357
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Yonghong, Qi Liu, Chongwei Li, Gehendra Kharel, Lixing An, Elaine Stebler, Yu Zhong, and Chris B. Zou. 2019. "Interactive Effect of Meteorological Drought and Vegetation Types on Root Zone Soil Moisture and Runoff in Rangeland Watersheds" Water 11, no. 11: 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112357
APA StyleHao, Y., Liu, Q., Li, C., Kharel, G., An, L., Stebler, E., Zhong, Y., & Zou, C. B. (2019). Interactive Effect of Meteorological Drought and Vegetation Types on Root Zone Soil Moisture and Runoff in Rangeland Watersheds. Water, 11(11), 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11112357







