Response of Water-Salt Migration to Brackish Water Irrigation with Different Irrigation Intervals and Sequences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Soil and Irrigation Water
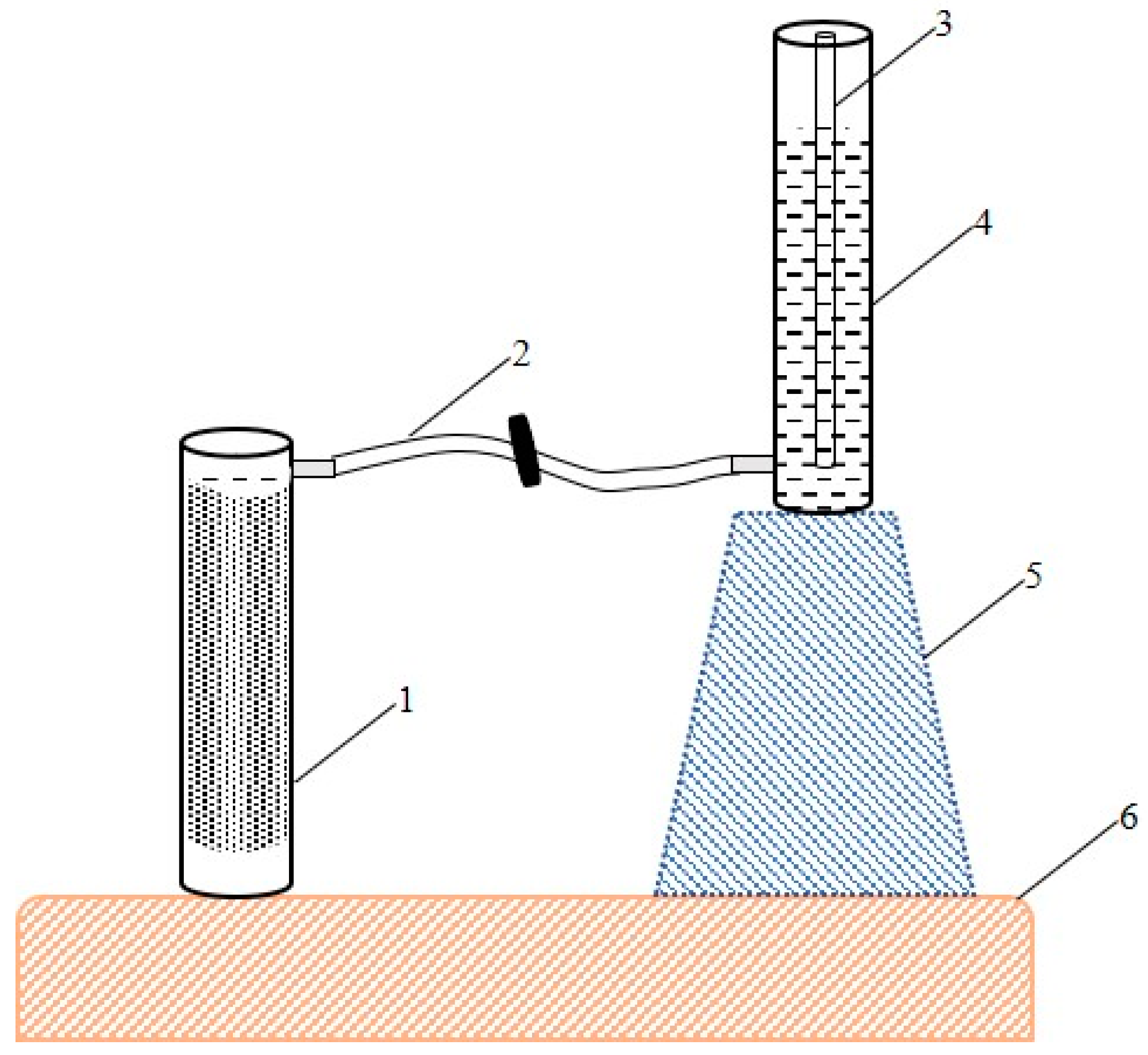
2.2. Infiltration Experiments
3. Data Analysis
4. Results
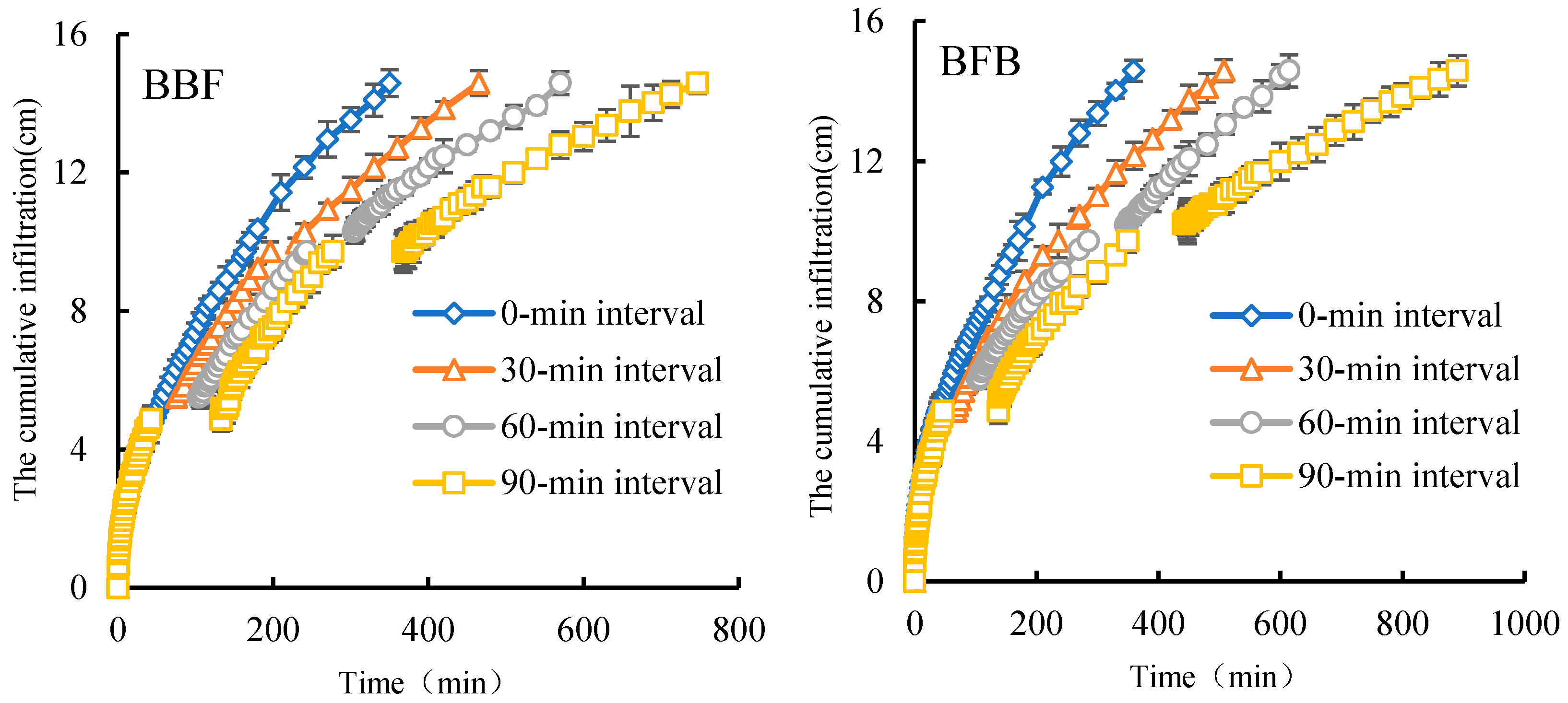
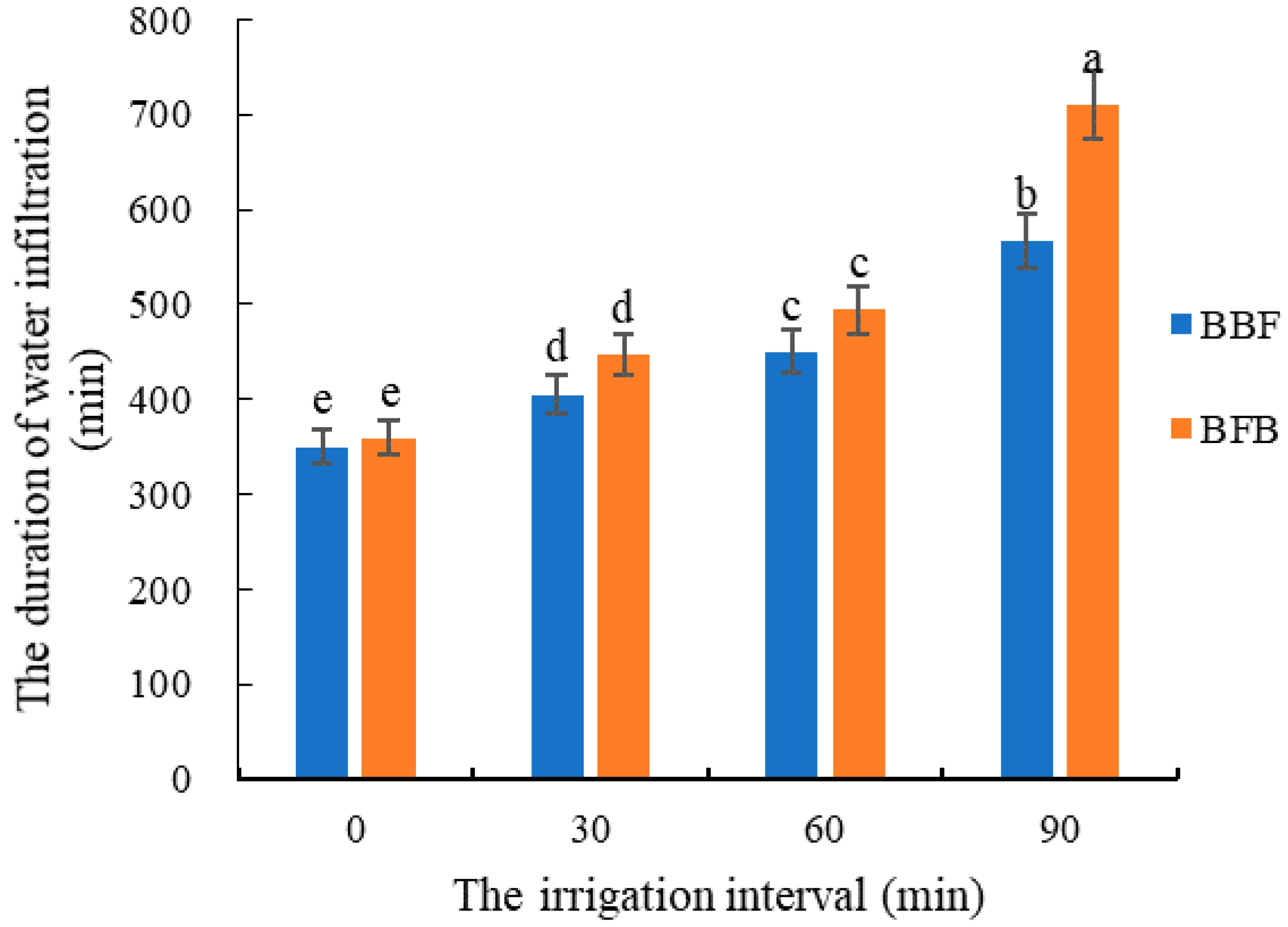
4.1. Effects of Irrigation with Brackish and Fresh Water on Water Infiltration
4.2. Effects of Irrigation with Brackish and Fresh Water on Salt Distribution
5. Discussion
5.1. Effects of Irrigation with Brackish and Fresh Water on Soil Water Content
5.2. Effects of Irrigation with Brackish and Fresh Water on Soil Salt Content
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, T.; Liu, X.H.; Sun, T. The effects of groundwater table and flood irrigation strategies on soil water and salt dynamics and reed water use in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Modell. 2011, 222, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.H.; Vervoort, R.W.; Suweis, S.; Guswa, A.J.; Rinaldo, A.; Seatm, V.D.Z. Stochastic modeling of salt accumulation in the root zone due to capillary flux from brackish groundwater. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1995–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunhikrishnan, A.; Bolan, N.S.; Müller, K.; Laurenson, S.; Naidu, R.; Kim, W.I. The influence of wastewater irrigation on the transformation and bioavailability of heavy metal(loid)s in soil. Adv. Agron. 2012, 115, 215–297. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakkoli, E.; Fatehi, F.; Coventry, S.; Rengasamy, P.; McDonald, G.K. Additive effects of Na+ and Cl− ions on barley growth under salinity stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.I.; Jin, M.G.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Liu, Y.F.; Xian, Y.; Shan, T.R.; Ping, X. Spatial distribution of soil moisture, soil salinity, and root density beneath a cotton field under mulched drip irrigation with brackish and fresh water. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, P.S. Saline water management for irrigation in India. Agric. Water Manage. 1996, 30, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Simulations on direct and cyclic use of saline waters for sustaining cotton–wheat in a semi-arid area of north-west India. Agric. Water Manage. 2004, 66, 1–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Isaac, R.K. Use of saline water for irrigation in monsoon climate and deep water table regions: Simulation modeling with SWAP. Agric. Water Manage. 2012, 115, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlon, U.Z.; Murtaza, G.; Ghafoor, A. Amelioration of saline-sodic soil with amendments using brackish water, canal water and their combination. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2012, 14, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yazar, A.; Incekaya, Ç; Sezen, S.M.; Jacobsen, S.E. Saline water irrigation of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) under Mediterranean conditions. Crop Pasture Sci. 2015, 66, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Qang, Q.J.; Wang, Y.J. Soil infiltration properties with slight saline water intermittent application. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 14–19, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Ye, H.Y.; Shi, X.N. Research of soil water and salt transport feature for alternative irrigation of fresh and saline water. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 24, 50–53, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Guan, B.; Yu, J.B.; Hou, A.X.; Han, G.X.; Wang, G.M.; Qu, F.Z.; Xia, J.B.; Wang, X.H. The ecological adaptability of Phragmites australis to interactive effects of water level and salt stress in the Yellow River Delta. Aquat. Ecol. 2017, 51, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.X.; Liu, G.C.; Xia, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.Y. Use of biochar-compost to improve properties and productivity of the degraded coastal soil in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.H.; Gao, M.S.; Hou, G.H. Evolutionary process of saline-water intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Wu, J.C.; Ye, S.J.; Zhang, Y.X. Hydrogeological and hydrogeochemical studies for salt water intrusion on the south coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Ground Water 2010, 38, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, P.; Yitayew, M. Irrigation and Drainage Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Wang, Y.K.; Ma, L.H.; Lin, P.H.; Duan, X.S. Investigation on undisturbed soil water redistribution under drip irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2010, 29, 44–49, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.N.; He, F.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Shao, H.B.; Pan, Y.H.; Yang, R.Y.; Li, W.X.; Li, P.; Zheng, M.Z. Analysis of saline groundwater infiltration into two loam soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3795–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.J.; Feng, Q.; Li, F.R.; Li, C.S. Simulation of soil water and salt transfer under mulched furrow irrigation with saline water. Geoderma 2015, 241–242, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Xu, H.L.; Zhao, S.J.; Shan, J.J.; Chen, X.B. Saline soil desalination by honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica Thunb.) depends on salt resistance mechanism. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 88, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G.; White, R.E.; Darrah, P.R.; Jury, W.A. A transfer function model of solute transport through soil: 3. The convection-dispersion equation. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishan, A.K.; Banasik, K.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Gholami, L.; Hejduk, L. Effects of rain intensity and initial soil moisture on hydrological responses in laboratory conditions. Int. Agrophys. 2015, 29, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, N.; Gupta, A.D.; Loof, R. Salinity and sodicity influences on infiltration during surge flow irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2001, 20, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.D.; Wang, Q.J. Effect of saline water surge flow border irrigation on soli water salt distribution. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2010, 41, 53–58, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.L.; Bi, Y.J.; Guo, X.H.; Xiang, X.H.; Ma, J.J.; Liu, J.Y. Analysis of soil water and salt distribution of saline water intermittent water supply mode. Water Saving Irrig. 2015, 6, 42–46, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.J.; Wang, Q.J.; Xue, J. Infiltration characteristic contrast analysis of fresh water and saline water. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2010, 41, 70–75, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Beesley, L.; Eduardo, M.J.; Clemente, R.; Lepp, N.; Dickinson, N. Mobility of arsenic, cadmium and zinc in a multi-element contaminated soil profile assessed by in-situ soil pore water sampling, column leaching and sequential extraction. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akramkhanov, A.; Martius, C.; Park, S.J.; Hendrickx, J.M.H. Environmental factors of spatial distribution of soil salinity on flat irrigated terrain. Geoderma 2011, 16, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawad, G.A.; Arslan, A.; Gaihbe, A.; Kadouri, F. The effects of saline irrigation water management and salt tolerant tomato varieties on sustainable production of tomato in Syria (1999–2002). Agric. Water Manage. 2005, 78, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.Y.; Yang, P.L.; Lv, Y. Laboratory experiment on the redistribution of soil salinity under saline and fresh water alternate irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2007, 23, 88–91, (In Chinese with an English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
| Soil Texture | Particle size Composition (%) | Field Capacity (%) | Initial Water (%) | pH | Electrical Conductivity (mS/cm) | Total Salt (g/kg) | Cl− | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravel | Silt | Clay | (g/kg) | |||||||||
| Silty loam | 11.6 | 48.7 | 39.7 | 28.04 | 1.04 | 7.4 | 1.88 | 4.50 | 0.27 | 0.57 | 0.30 | 2.90 |
| Treatment | Irrigation Interval (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 | |
| BBF | 28.01 ± 0.33a | 29.24 ± 0.60a | 28.47 ± 0.39a | 29.71 ± 0.33a |
| BFB | 28.85 ± 0.75a | 29.66 ± 0.29a | 29.36 ± 0.92a | 29.98 ± 0.48a |
| Treatment | Irrigation Interval (min) | Soil Depth (cm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–12 | 12–32 | 0–32 | ||
| BBF | 0 | 63.82 ± 0.22c | 29.72 ± 0.62e | 42.51 ± 0.45d |
| 30 | 65.19 ± 0.37b | 33.01 ± 0.56d | 45.08 ± 0.21c | |
| 60 | 63.95 ± 0.46c | 36.33 ± 0.23c | 46.69 ± 0.32b | |
| 90 | 66.98 ± 0.25a | 38.32 ± 0.34b | 49.07 ± 0.29a | |
| BFB | 0 | 51.60 ± 0.90f | 32.21 ± 0.66d | 39.48 ± 0.71e |
| 30 | 51.88 ± 0.64f | 35.71 ± 0.21c | 41.77 ± 0.27d | |
| 60 | 55.68 ± 0.41e | 38.92 ± 0.28b | 45.21 ± 0.31c | |
| 90 | 57.30 ± 0.37d | 40.13 ± 0.27a | 46.57 ± 0.26b | |
| Treatment | Irrigation Interval (min) | Soil Depth (cm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–12 | 12–32 | 0–32 | ||
| BBF | 0 | 20.04 ± 0.27c | 25.43 ± 0.30a | 23.41 ± 0.28b |
| 30 | 17.21 ± 0.46e | 24.82 ± 0.13ab | 21.97 ± 0.24c | |
| 60 | 15.55 ± 0.14f | 24.39 ± 0.22bc | 21.08 ± 0.09d | |
| 90 | 13.10 ± 0.58g | 23.08 ± 0.43d | 19.34 ± 0.48e | |
| BFB | 0 | 23.19 ± 0.38a | 24.95 ± 0.53ab | 24.29 ± 0.19a |
| 30 | 23.70 ± 0.59a | 23.83 ± 0.12c | 23.78 ± 0.15ab | |
| 60 | 21.72 ± 0.34b | 23.13 ± 0.14de | 22.60 ± 0.19c | |
| 90 | 18.26 ± 0.26d | 22.72 ± 0.36e | 21.05 ± 0.13d | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Yang, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z. Response of Water-Salt Migration to Brackish Water Irrigation with Different Irrigation Intervals and Sequences. Water 2019, 11, 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102089
Zhu J, Yang M, Sun J, Zhang Z. Response of Water-Salt Migration to Brackish Water Irrigation with Different Irrigation Intervals and Sequences. Water. 2019; 11(10):2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102089
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jinjin, Mao Yang, Junna Sun, and Zhenhua Zhang. 2019. "Response of Water-Salt Migration to Brackish Water Irrigation with Different Irrigation Intervals and Sequences" Water 11, no. 10: 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102089
APA StyleZhu, J., Yang, M., Sun, J., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Response of Water-Salt Migration to Brackish Water Irrigation with Different Irrigation Intervals and Sequences. Water, 11(10), 2089. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11102089




