Abstract
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) are receiving global attention due to their persistence in the environment through wastewater effluent discharges and past improper industrial waste disposal. They are resistant to biological degradation and if present in wastewater are discharged into the environment. The US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) issued drinking water Health Advisories for PFOA and PFOS at 70 ng/L each and for the sum of the two. The need for an enforceable primary drinking water regulation under the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) is currently being assessed. The USEPA faces stringent legal constraints and technical barriers to develop a primary drinking water regulation for PFOA and PFOS. This review synthesizes current knowledge providing a publicly available, comprehensive point of reference for researchers, water utilities, industry, and regulatory agencies to better understand and address cross-cutting issues associated with regulation of PFOA and PFOS contamination of drinking water.
1. Introduction
Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are synthetic industrial chemicals used throughout the world. The Swedish Chemicals Agency (2015) [1] estimated that more than 4000 types of perfluoroalkyl substances have been synthesized, with more than 2000 on the global market. Global annual PFAS emissions steadily increased from 2002 to 2012, with a geographical shift of industrial sources away from North America, Europe and Japan towards emerging Asian economies and China [2,3]. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) has updated a comprehensive list of over 4700 PFAS-related chemicals on the global market based on the chemical abstract service (CAS) numbers [4].
PFASs are resistant to biological degradation, breaking down very slowly in the environment. When present in municipal and industrial wastewaters they typically pass through wastewater treatment plant processes and are discharged in the effluent. When used industrially, PFASs may be emitted into the air or accidently released to the environment [2,3]. They are poorly adsorbed by soils and aquifer materials and readily transported via surface water and ground water. Because of their longevity in the environment, PFASs and other synthetic organic chemicals with these properties are generally referred to as persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
To date most research attention globally has been given to two PFASs, perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS). Potential adverse human health effects from PFOA and PFOS in drinking water and POPs in the environment have been an ongoing concern for several decades. Improper disposal of industrial wastes containing PFASs in the decades prior to the enactment of environmental protection laws, PFAS presence in wastewater discharges, and releases to the air have distributed PFAS contaminants globally. Regulatory agencies in more than 12 countries have established guidelines or health advisory values for PFOA and PFOS in drinking water and/or groundwater.
In 2009 the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) identified PFOA and PFOS as contaminants of potential concern in drinking water. Major PFOA and PFOS contamination of the environment and drinking water supplies had been discovered in several states, in particular West Virginia [5], Ohio [6], and Minnesota [7]. PFOA and PFOS were included on the third drinking water contaminant candidate list (CCL) [8]. The CCL lists substances of potential health concern if present in drinking water, but for which the knowledge-base is too limited to determine whether a national regulation is needed. The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) requires updating of the CCL every five years. Where drinking water is contaminated with PFOA and PFOS, state agencies take action to address these situations.
Drinking water health advisories for PFOA and PFOS were issued by the USEPA in May 2016 [9,10]. Advisories provide technical information to state agencies and other public health officials on health effects, analytical methodologies, and treatment technologies to assist them in making risk management decisions. Advocacy groups and others were critical of the advisories, arguing that PFOA and PFOS should be regulated nationally [11,12]. In response, on February 14, 2019 the USEPA released a comprehensive action plan to address PFASs [13,14], stating for drinking water that:
“The next step in the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) process for issuing drinking water standards is to propose a regulatory determination. The Agency is also gathering and evaluating information to determine if regulation is appropriate for a broader class of PFAS”.
State agencies have the authority to act to address PFOA and PFOS contamination within their jurisdiction. States may adopt health advisories and regulations more stringent than the USEPA. Issuance of a national enforceable regulation for PFOA and PFOS involves considerations beyond the state level. PFOA and PFOS have drawn worldwide research attention, so much so that the knowledge-base for these contaminants has expanded dramatically since 2016. The USEPA is now deciding whether national drinking water regulations for PFOA and PFOS are warranted.
Originally enacted in 1974, the SDWA was amended in 1996 to establish specific procedures and conditions for issuing an enforceable national U.S. drinking water regulation [15]. Regulation of a contaminant in drinking water raises cross-cutting issues related to health, analysis, exposure, water treatment, risk assessment, and risk management. The purpose of this paper is to synthesize current knowledge to serve as a publicly available comprehensive starting point for researchers, water utilities, industry, and regulatory agencies to understand the issues most relevant to a drinking water regulation for PFOA and PFOS. This paper examines the rationale behind SDWA requirements for contaminant regulation as they apply to PFOA, PFOS, and other POPs that may be regulated in the future. Current knowledge regarding PFOA and PFOS is summarized and recommendations made for responding to PFOA and PFOS contamination regardless of whether a national regulation is established.
2. Authority to Regulate
The SDWA regulatory process is very thorough, taking several years to complete. The SDWA, the Administrative Procedure Act (APA) [16], and agency regulatory policies impose important constraints on contaminant regulation.
The majority of drinking water contaminants now regulated were established between 1986 and 1995 with many maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) based on prior regulations. In 1986 the SDWA was amended to require regulation of at least 25 contaminants every five years. Lack of information seriously hindered the regulation of new contaminants. Resource limitations made it impractical for the agency to meet this requirement, and regulatory activity came to a halt in the mid-1990s. To meet the SDWA requirement initially regulations for disinfectants, disinfection byproducts and additional surface water treatment rules were developed through formal regulatory negotiation. However, regulating 25 individual contaminants on a regular basis proved to be an impossible task.
In 1990 the USEPA Science Advisory Board issued the report Reducing Risk: Setting Priorities and Strategies for Environmental Protection [17]. This report was very influential during the decade of the 1990s for focusing the USEPA on setting priorities to address environmental risks that would achieve the greatest risk reduction. In 1996 the US Congress amended the SDWA to establish procedures aimed at enabling the USEPA to set priorities for regulating contaminants in drinking water.
The SDWA grants the USEPA the general authority to regulate a contaminant in drinking water if it finds the following three conditions are met [18]:
- The contaminant may have an adverse effect on the health of persons;
- The contaminant is known to occur or there is a substantial likelihood that the contaminant will occur in public water systems with a frequency and at levels of public health concern; and
- The regulation of the contaminant presents meaningful opportunity for health risk reduction for persons served by public water systems.
The SDWA conditions to regulate a new contaminant are intended to focus the agency’s efforts and limited resources on regulating contaminants which would achieve the greatest risk reduction nationally. Substances not present or are not likely to occur in drinking water nationally pose no actual health risk. A substance that does not and is not likely to have an adverse health effect poses no actual health risk. Drinking water regulations are to achieve a meaningful health risk reduction nationally. The SDWA also allows the agency to act to address contaminants that pose an urgent threat to public health [19].
3. Properties and Uses of PFOA and PFOS
PFOA and PFOS are both considered long-chain PFASs, which are perfluorocarboxilic acids with eight or more carbon atoms or perfluorosulfonic acids with six or more carbon atoms [20]. PFOA and PFOS are eight-carbon compounds (C8) having unique chemical properties including surface activity, thermal and acid resistance, and repelling both water and oil [20]. Commercial applications of PFASs include stain-resistant coatings for carpeting and upholstery, breathable water-resistant outdoor clothing, and greaseproof packaging. They are also used to manufacture fluoropolymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene [21]. PFASs are found in aqueous film-forming foams used to fight hydrocarbon fires [22].
PFOA was first used to manufacture commercial products in 1949 and was used to manufacture polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) for non-stick coatings. PFOS had been produced since the 1940s and was previously used in fabric protectors. Both PFOA and PFOS were used in a variety of other industrial and well-known consumer products. PFOA and PFOS are stable, non-volatile, and very soluble in water. They are highly mobile in the environment and have been detected in natural waters, wastewater effluents, treated drinking waters and a variety of food products in many countries [23,24]. When inhaled or ingested, PFOA and PFOS are readily absorbed into the human body. In 2009–2010 the National average blood serum levels in the United States were 3.1 ppb and 9.3 ppb for PFOS and PFOA, respectively [25]. These compounds are biologically stable and are not metabolized.
Major US manufacturers have voluntarily phased out production of PFOA and PFOS. In the year 2000 the US manufacturer 3M announced it would voluntarily phase out all production of PFOS due to concerns over potential lawsuits, regulatory pressure, and negative public perception. In 2006, eight US chemical manufacturers agreed to phase out all production and use of PFOA and related compounds by 2015. Both PFOA and PFOS are no longer produced in the United States. Since elimination of their use, blood serum levels for PFOA and PFOS in the United States have been declining [26]. Exposure to PFOA and PFOS remains possible due to legacy uses, existing and legacy uses on imported goods, degradation of precursors, and extremely high persistence in the human body and the environment. Although their use has been discontinued in the United States, they are still produced for commercial use in other countries [27,28].
4. Analytical Methods
Aqueous samples are typically analyzed for PFASs using liquid-liquid extraction, ion-pair extraction, or solid-phase extraction followed by HPLC-MS/MS or GC/MS [29]. In 2009, the USEPA released Method 537 for the analysis of 14 PFASs in drinking water using solid-phase extraction followed by Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) [30]. A highly-skilled analyst is required to generate reliable analytical results using this method. For US drinking water regulatory reporting, a laboratory must use an analytical method developed by the USEPA or a USEPA-approved equivalent method. Method 537 had limitations but garnered widespread application for analyzing water samples for PFOA and PFOS. The 2009 version of the method was expanded and improved to include additional analytes and lower detection limits.
4.1. USEPA Method 537.1
Method 537.1 [31] is the standard method for the analysis of 18 PFASs, and was issued in November 2018. Table 1 lists each PFAS covered by Method 537.1, with each acronym, Chemical Abstract Service Registration Number (CASRN), Detection Limit (DL), and single laboratory Lowest Concentration Minimum Reporting Level (LCMRL). The DL characterizes the accuracy of each method and is defined as the statistically calculated minimum concentration that can be measured with 99% confidence that the reported value is greater than zero. The DL is compound-dependent and is affected by extraction efficiency, sample matrix, fortification concentration, and instrument performance. The LCMRL is the lowest true concentration for which future recovery is predicted to fall, with high confidence (99%), and between 50 and 150% recovery.

Table 1.
Compounds detectable by USEPA Method 537.1 [31]. USEPA: US Environmental Protection Agency; CASRN: Chemical Abstract Service Registration Number; LCMRL: Lowest Concentration Minimum Reporting Level; DL: Detection Limit.
4.2. Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring
In the United States, PFOA and PFOS are two of 97 chemicals listed on the fourth drinking water contaminant candidate list (CCL 4) [32] published in 2016. As noted above, for a listed substance to be regulated, sufficient knowledge must be available in order for a regulation to meet the SDWA regulatory requirements.
To assess the extent of contamination in the United States, the SDWA authorizes collection of nationwide occurrence data through the unregulated contaminant monitoring rule (UCMR) [33]. Under the UCMR, occurrence data is collected for a maximum of 30 analytes in a five-year cycle. Samples are collected at all public water systems serving >10,000 people and at a statistical sample of public water systems serving <10,000 people. Monitoring of PFOA, PFOS, perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS), perfluoroheptanoic acid (PFHpA), perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS), and perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA) was required in the third UCMR (UCMR 3) between 2013 and 2015 [34].
4.3. Minimum Reporting Level (MRL)
For each contaminant monitored under the UCMR, a minimum reporting level (MRL) is specified. The MRL is the minimum concentration at which a contaminant is reliably quantitated by individual laboratories [34]. At or above the MRL, a competent drinking water laboratory should be expected to obtain 50–150% recovery or better. The MRL differs from the minimum detection level by considering both the standard deviation of low concentration analyses (precision) and the accuracy of the measurements as they impact achievement of data quality objectives for spike recovery. MRLs reflect the performance of competent commercial laboratories and are not based on the performance of a particular instrument or single laboratory. Table 1 presents the MRLs for the PFASs monitored under UCMR3.
4.4. Practical Quantitation Level (PQL)
For a drinking water regulation to be enforceable the MCL must be set at a concentration providing a clear delineation between test results above and below the standard not affected by variability in laboratory performance. The practical quantitation level (PQL) is typically used for this purpose. The PQL is the lowest concentration of an analyte that can be reliably measured within specified limits of precision and accuracy during routine laboratory operating conditions. The PQL, MRL, DL, and LCMRL for a contaminant may all differ. An interim reporting limit and PQL for PFOA of 6 ng/L has been adopted by New Jersey to support development of groundwater quality standards [35]. A PQL for PFOA and PFOS has not been established by the USEPA.
5. Occurrence in Public Water Systems
Drinking water supplies are vulnerable to PFOA and PFOS contamination from a variety of sources. PFOA was first discovered because of harmful effects due to leakage from landfills that had received PFAS-related industrial wastes [5,6,36,37,38]. Airports and fire training areas have been contaminated by PFASs contained in aqueous film-forming foams used during firefighting training activities [39]. Wastewater treatment plant discharges, biodegradation of precursors during wastewater treatment, and land application of biosolids are potential sources of PFOA and PFOS in drinking water supplies. Once in the environment PFOA and PFOS are stable and bioaccumulate into the food chain [40,41].
PFOA, PFOS, and many PFASs have been detected in the environment and in drinking water worldwide. Selected studies and the range of PFOA and PFOS concentrations reported are listed in Table 2. Most studies listed analyzed samples for several PFASs in addition to PFOA and PFOS. A few studies reported the ΣPFAS with the number of compounds tested differing between studies. The concentrations presented in Table 2 are not directly comparable between studies because of differences in the number of compounds tested, the analytical methods used, and the prevailing laboratory quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC).

Table 2.
Concentrations of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) reported in selected studies.
The number of water systems impacted is a key factor when determining whether to regulate a contaminant under the SDWA. As mentioned above, a contaminant must be known or likely to be present in drinking water at levels of public health concern to warrant a national regulation. Table 3 presents the results of PFAS monitoring under UCMR 3 [33]. MRLs for PFOA and PFOS were set at 20 ng/L and 40 ng/L, respectively. At least one of the PFASs was detected in samples taken from 36 states and territories. MRLs do not represent levels considered “significant” or “harmful.” Detection of a contaminant above the MRL does not necessarily represent cause for concern [34]. All six PFASs were tested at 4920 public water systems. The MRL for PFOA was exceeded by 117 water systems representing 2.4% of the water systems tested. The MRL for PFOS was exceeded in 95 water systems, representing 2.2% of the water systems tested.

Table 3.
PFAS monitoring results under the unregulated contaminant monitoring rule (UCMR) 3 [34].1.
The UCMR 3 monitoring results represent the only available statistically valid survey of national occurrence for the PFASs tested. When analyzing UCMR data the numbers of water systems exceeding the MRL are a function of the concentration at which the MRL is established. Water systems impacted by PFASs are unevenly distributed across the United States, and the number of systems affected may be greater than suggested by UCMR3 data [62]. One laboratory performing UCMR 3 testing reanalyzed its own UCMR 3 data (~1800 water systems) using an in-house MRL at 5 ng/L for all six PFAS. The percentage of water systems detecting at least one of the six PFASs was 5.3%, as compared to the USEPA estimate of 3.9% at the higher MRLs [62].
To assess the health significance of UCMR monitoring results a Health Reference Level (HRL) was established at 70 ng/L each for PFOA and PFOS [34]. HRLs are risk-derived concentrations against which occurrence data are compared to determine if contaminants may occur at levels of public health concern. HRLs do not represent final determinations but are derived as screening levels prior to development of a formal exposure assessment. The 0.07 μg/L HRL for PFOA was exceeded by 13 water systems or 0.3% of the water systems tested. The 0.07 μg/L HRL for PFOS was exceeded by 46 water systems or 0.9% of the water systems tested. At the time of UCMR 3 sampling, the USEPA provisional drinking water health advisory levels for PFOA and PFOS were 0.400 μg/L and 0.200 μg/L, respectively [63].
In a joint effort between the USEPA and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), paired samples from 25 drinking water treatment plants were analyzed for 247 chemical and microbial contaminants of emerging concern. Data from this study on the occurrence of PFSA in the source water are now available [60]. Although the number of water plants sampled do not represent a statistically valid national estimate, the results do provide insight into the occurrence of PFOA and PFOS. PFOA was detected in 100% of source water samples, was quantified in 76% of samples, and occurred at a median concentration of 6.32 μg/L with a maximum of 112 μg/L. PFOS was detected in 96% of source water samples, was quantified in 88% of samples, and occurred at a median concentration of 0.00228 μg/L with a maximum of 0.0483 μg/L.
Of the 17 PFASs monitored in the USEPA/USGS study, 14 were qualitatively detected and 12 were quantitatively detected at least once in source water samples [60]. PFOA and PFBS were the only analytes qualitatively detected in the source water samples at all 25 water plants. PFOS, PFBA, PFDA, PFHpA, PFHxS, PFHxA, PFNA, and PFPeA were qualitatively detected in a least 90% of source water samples.
When selecting contaminants in drinking water to regulate, the USEPA is to select contaminants presenting the greatest public health concern. Effects of contaminants upon subgroups of the general population at greater risks are also considered discussed below.
6. Human Health Effects
Considerable research attention has been given identifying the effect of PFOA and PFOS exposure on human health. The PFOA and PFOS health advisory level of 0.07 μg/L for each and the sum of the two are based on assessment of the health effects information available at that time. Health effects assessments are performed in accordance with USEPA guidelines for human health risk assessment [64]. Adverse effects observed following exposure to PFOA and PFOS are the same or similar [10] and include effects in humans on serum lipids, birth weight, and serum antibodies [65,66]. A few animal studies observed effects on the liver, neonate development, and responses to immunological challenges. Both compounds were associated with tumors in long-term animal studies [67]. Detailed reviews of the toxicological and epidemiological issues associated with PFOA and PFOS have been published [68,69]. Key risk assessment decisions affecting the regulation of PFOA and PFOS are discussed below.
6.1. Exposure Assessment
Assessing potential human health risks from exposure to a contaminant in drinking water requires professional judgment to evaluate the applicability of both animal and human studies to drinking water exposures. PFOA and PFOS are excreted from the body very slowly [70]. The half-life of PFOA in the human body has been estimated in the range of 2.3 to 3.94 years and 4.3 years for PFOS, respectively [71]. Biomonitoring of blood serum levels is used to assess PFOA and PFOS exposure and body burden. Measured serum levels are then analyzed using a single-compartment pharmacokinetic model to estimate a corresponding drinking water concentration [72].
Blood serum levels are highly dependent the amount of PFOA and PFOS taken into the body. Drinking water is a major source of exposure contributing to increased serum levels [73]. Figure 1 illustrates the effect of PFOA and PFOS exposure on blood serum levels from several studies in different settings [26]. Occupational exposures (e.g., 3M workers and Dupont workers) result in the highest serum levels. Serum levels at contaminated sites depend upon drinking water concentration, age (e.g., Pease NH community), length of time since exposure was discontinued (e.g., Northern Alabama Community), and whether water treatment was installed. Blood serum levels in the general population (e.g., NHANES) now are much lower than those at prior contaminated sites shown in Figure 1.
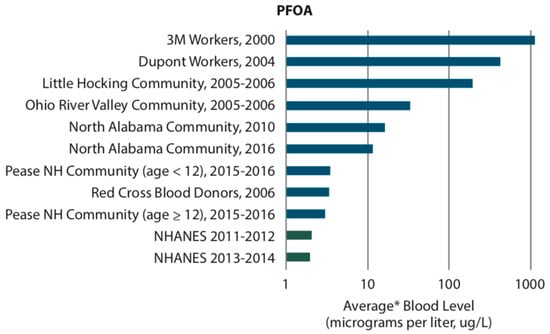
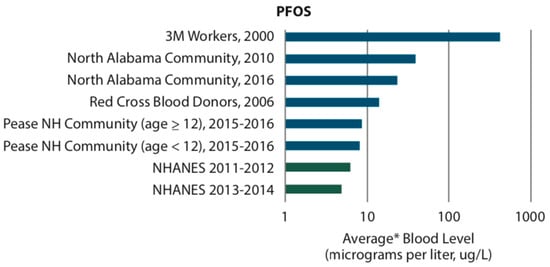
Figure 1.
Blood levels in people who were exposed to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA, upper panel) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS, lower panel) [26]. Figure 1 references: 3M Workers, 2000 [74]; Dupont Workers, 2004 [75]; Little Hocking Community, 2005-2006 [76]; Ohio River Valley Community, 2005-2006 [77]; North Alabama Community [78]; Pease NH Community [79]; Red Cross Blood Donors, 2006 [80]; NHANES [25].
6.2. Reference Dose
The Reference Dose (RfD) represents an estimate (with uncertainty spanning perhaps an order of magnitude) of a daily human exposure to the human population (including sensitive subgroups) that is likely to be without an appreciable risk of deleterious effects during a lifetime [81]. The RfD considers adverse health effects other than cancer calculated in accordance with USEPA guidelines [81].
The health advisory RfD for PFOA is based on a pharmacokinetic Human Equivalent Dose (HED) derived from serum levels at the lowest observed adverse effects level (LOAEL) for a developmental study in mice [82]. An uncertainty factor of 300 was applied to account for “extrapolation from a LOAEL to a no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL), variability in the human population, and differences in the ways humans and rodents respond to the PFOA that reaches their tissues” [9]. Human studies demonstrate an association of PFOA exposure and effects on serum lipids, antibody responses, fetal growth and development, and the liver. Human epidemiology studies were deemed sufficient to conclude that PFOA exposure is a human health hazard but were considered inadequate for quantitative risk assessment [9]. An RfD for PFOA of 0.00002 mg/kg/day was derived based on developmental effects in neonates to provide protection to both the sensitive life stages and the general population [9].
The RfD for PFOS is based on a pharmacokinetic HED derived from serum levels at the NOAEL from a developmental study in rats [83]. An uncertainty factor of 30 was applied to account for variability in the human population and differences in human response to the PFOS reaching their tissues compared to rats [10]. An RfD of 0.00002 mg/kg/day was derived for PFOS based on the most sensitive end point to provide protection to the general population and sensitive life stages [10].
The RfD is calculated to be protective of sensitive populations. Following the 2016 issuance of USEPA health advisories the Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) reassessed its health-based guideline value for PFOA and PFOS. An Excel-based toxicokinetic model was constructed and applied to derive a guidance value for PFOA. The model incorporates body burden at birth (placental transfer), ingestion of breastmilk, and age-specific water intake rates [7]. At a relative source contribution of 50%, the calculated serum concentration allocated or ‘allowed’ to result from ingestion of water was 0.065 mg/L. The water concentration calculated to maintain a PFOA serum concentration at or below 0.065 mg/L throughout life for the formula-fed reasonable maximally exposed (RME) scenario and the breast-fed RME scenario was 0.15 μg/L and 0.035 μg/L, respectively [7]. Based on this assessment MDH set its final health-based PFOA guidance value at 0.035 μg/L.
6.3. Carcinogenicity
Epidemiology studies demonstrate an association of serum PFOA with kidney and testicular tumors among highly exposed members of the general population [66,67,84]. PFOA has been found to cause tumors in one or more organs of rats, including the liver, testes, and pancreas. Cancer risk was assessed following USEPA guidelines for carcinogen risk assessment [85]. Based on the weight of evidence PFOA was classified as having Suggestive Evidence of Carcinogenic Potential [9]. A quantitative dose–response assessment is not usually developed when there is only suggestive evidence unless a well-conducted study is available. A cancer dose–response based on Butenhoff et al. 2012 [86] was developed for PFOA and testicular tumors. The cancer slope factor was estimated at 0.07 mg/kg-day. A PFOA concentration of 0.5 μg/L results in a theoretical 1:1,000,000 cancer risk for an 80 kg adult drinking 2.5 L of water per day [9].
Epidemiology studies have not found a direct correlation between PFOS exposure and the incidence of carcinogenicity in humans [10]. In the only chronic oral toxicity and carcinogenicity study of PFOS in rats, liver and thyroid tumors were identified in both the controls and exposed animals at levels that did not show a direct relationship to dose [67]. The evidence for cancer in animals was judged too limited to support a quantitative cancer assessment. Based on the weight of evidence PFOS was classified as having Suggestive Evidence of Carcinogenic Potential [10]. An independent review of the carcinogenic risk of PFOS following the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) evaluation process concluded “that cancer risk for PFOS, according to the IARC method, is not classifiable as carcinogenic to humans [87].
6.4. Relative Source Contribution (RSC)
The dominant source of human exposure to PFOA and PFOS is diet (water and food). Zhang et al. 2019 [73] detected both PFOA and PFOS in more than 70% of both blood samples and water samples from 13 cities in China. A correlation between the geometric mean blood levels in the general population and the corresponding mean drinking water concentration was found for PFOA (r = 0.87, n = 13, p < 0.001) but not observed for PFOS [73].
Paper with treated coatings have a high potential for migration of PFASs to food [88]. Food can also become contaminated with PFOA from preparation in nonstick cookware coated with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) [88]. PFOA was previously used in the manufacture of several types of food packaging. In January 2016, the US Food and Drug Administration amended its food additive regulations to no longer allow for the use of PFA-containing food-contact substances [89]. Because of its widespread use in carpets, upholstered furniture, and other textiles, PFOA has been detected in indoor dust from homes, offices, vehicles, and other indoor spaces [90,91,92]. Workers in shops selling clothing treated with a fabric protector may also be exposed to PFASs [93]. PFOA may penetrate human skin under certain conditions [94].
Several studies have examined the relative contribution of different routes of exposure to PFOA and PFOS [92,94,95]. A Relative Source Contribution (RSC) is applied in the health advisory calculation to ensure an individual’s total exposure from a contaminant does not exceed the RfD. The RSC is the portion of the RfD attributed to drinking water. The remainder to the RfD is allotted to other potential sources. The USEPA followed an Exposure Decision Tree methodology to derive an RSC of 20% for PFOA and PFOS each. The RSC for the health advisory is based on exposure to the general population. In cases where data are lacking an RSC value of 20% is used as a minimum default value. If exposure to sources other than drinking water are not expected then the RSC may be raised to 80% maximum default value.
6.5. Immunosuppression
Both human and animal studies have demonstrated the potential effect of PFOA and PFOS on the immune systems. In 2016 the National Toxicology Program (NTP) released a monograph on immunotoxicity associated with exposure to PFOA or PFOS [96]. The goal of the study was to assess evidence of PFOA or PFOS being associated with immunotoxicity in humans. Their literature search and screening process identified 33 human studies, 93 animal studies, and 27 in vitro/mechanistic studies relevant to this assessment. The NTP concluded that both PFOA and PFOS are presumed to be an immune hazard to humans based on a high level of evidence that they suppress the antibody response from animal studies and a moderate level of evidence from studies in humans [96]. The report acknowledges that the mechanisms of toxicity for both compounds are not clearly understood.
Several studies have identified immunotoxicity as an important effect of PFOS [69,97,98]. The plaque-forming cell (PFC) response, which reflects suppression of the immune response to a foreign antigen, is “among the most sensitive effects” [10]. The USEPA considered but did not use immunotoxicity as the endpoint for deriving the RfD for PFOS citing a “lack of human dosing information and lack of low-dose confirmation of effects in animals for the short-duration study.” [10] After reviewing the available epidemiologic studies, the agency stated [10]:
“A limitation of epidemiology studies that evaluate the immune response following PFOS exposure is that these studies have not demonstrated whether immune parameters measured in clinically normal individuals accurately reflect the risk of future immunological diseases. Given the immune system’s capacity for repair and regeneration, apparent abnormalities that are detected at one point in time might resolve before producing any adverse clinical health effect”.
Some investigators have suggested the RfD for PFOS (0.00002 mg/kg/day) is too high because it is based on a developmental endpoint rather than immunotoxicity [98,99]. Pachkowski et al. 2019 [100] derived a PFOS reference dose (RfDIm) using decreased plaque-forming cell (PFC) response in mice as the immune endpoint. This endpoint reflects suppression of the immune response to a foreign antigen. An RfDIm of 1.8 ng/kg/day was derived based on a PFOS target human serum level of 22.5 ng/mL. This target concentration was derived from the mouse NOAEL in Dong et al. (2009) [100]. An uncertainty factor of 3 was applied to “account for potential toxicodynamic differences between mice and humans”. An uncertainty factor of 10 was applied as the “standard default assumption” to account for the range of sensitivity within the human population. These uncertainty factors values applied by Pachkowski et al. 2019 [100] are identical to those applied by the USEPA to derive the PFOS health advisory. The resulting estimated RfDIm is approximately one-order of magnitude lower than the RfD derived by the USEPA but it is within the general range of uncertainty attributed to an RfD estimate [81].
Chang et al. [101] systematically reviewed 24 PFOA and PFOS epidemiology studies of the general population, occupationally exposed workers, children and adults. Studies reviewed included ten studies of immune biomarker levels or gene expression patterns, ten studies of atopic of allergic disorders, five studies of infectious diseases, four studies of vaccine responses, and five studies of chronic inflammatory or autoimmune conditions. The mode of action, the level, duration, and/or timing of exposure are uncertain. The investigators concluded [101]:
“With few, often methodologically limited studies of any particular health condition, generally inconsistent results, and an inability to exclude confounding bias, or chance as an explanation for observed associations, the available epidemiologic evidence is insufficient to reach a conclusion about a causal relationship between exposure to PFOA and PFOS and any immune-related health condition in humans. When interpreting such studies, an immunodeficiency should not be presumed to exist when there is no evidence of a clinical abnormality”.
6.6. Maximum Contaminant Level Goal (MCLG)
A drinking water regulation for PFOA and PFOS will include a maximum contaminant level goal (MCLG) for each contaminant. The MCLG is a non-enforceable health goal which directly influences the level at which an enforceable MCL would be established, as discussed below. The USEPA’s policy is to set the MCLG at zero for contaminants known to be or are probable human carcinogens. Because the evidence of carcinogenic potential for PFOA and PFOS is only suggestive, the MCLG would be calculated based on noncancer effects using the RfD and RSC.
7. Best Available Technology (BAT)
The SDWA requires the MCL to be set as close to the MCLG as is feasible when a contaminant is regulated. “Feasible” means feasible with the use of the best technology, treatment techniques, and other means which the USEPA finds after examination for efficacy under field conditions and not solely under laboratory conditions (taking cost into consideration) [102]. Technologies meeting this feasibility criterion are called best available technologies (BAT) and must be listed in each proposed and final regulation.
PFASs are not biodegradable under typical water treatment conditions and must be removed from water using physical/chemical processes. Removal of PFASs from drinking water and wastewater in bench-scale studies and with various conventional processes has been reviewed previously [103,104,105]. A critical review of published data on removal of PFOA and PFOS at full-scale water treatment plants is also available [106]. Technology for drinking water treatment involves a subset of a wider variety of technologies available for remediating contaminated groundwater [107,108].
7.1. Conventional Treatment
Conventional coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration are relatively ineffective for removing PFOA and PFOS [105,106,109,110]. At coagulant doses typically applied to treat surface water coagulation removed less than 35% of PFOA and PFOS [111,112]. Bench studies of coagulation with ferric chloride and powdered activated carbon (PAC) increased removal of PFOA and PFOS up to >90% but the initial contaminant concentration was 1 mg/L [112]. Polyaluminum chloride at an initial dose of 5 mg/L was found more effective than alum and ferric for removing PFOA and PFOS [113]. Polyaluminum chloride enhanced with PAC addition was found effective for removing PFOA [114].
A natural coagulant (Moringe oleifera) proved to be very effective in removing PFOA and PFOS compared to conventional coagulants, with reduction efficiencies of 72% and 65%, respectively [113]. Addition of M. oleifera and PAC (10 min contact time) with coagulation (at 5 mg/L) improved removal efficiency up to 94% and 98% for PFOA and PFOS, respectively [113]. Sedimentation plus rapid sand filters achieved high-removals of PFOA (85%) and PFOS (86%) associated with particulates but low removals from the aqueous phase [115].
7.2. Oxidation Processes
Chlorine and ozone-based oxidation processes at a typical water treatment plant doses and contact times have not been effective of removing PFOA, PFOS, and other PFASs [61,116]. PFASs are resistant to chlorination or chloramination even when combined with other unit processes such as PAC and UV irradiation [61]. Advanced oxidation processes in general are ineffective for destroying PFOA and PFOS [116]. Studies of persulfate oxidation at temperatures normally encountered in the natural environment achieved an 80.5% decomposition efficiency of PFOA at 20 °C, but long reaction times are required, rendering this process unfeasible at full-scale [117].
7.3. Adsorption
Granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption is one of the few treatment processes demonstrating significant PFAS removal from water [61,107,118]. GAC is effective in removing PFOA and PFOS in the absence of competing organics [106,119,120]. Designed appropriately, GAC will remove a contaminant to below detection limits. As the number of bed volumes of water treated increases the column effluent concentrations also increase until the contaminant level breaks through the bed. Contaminant breakthrough can be sudden or slow over time, but ultimately the influent concentration is reached at which time the column is exhausted. Once the GAC in a column has been exhausted it must be replaced and disposed of or be reactivated and reused.
When treating natural waters competitive adsorption and preloading of dissolved organic matter (DOM) must be considered. PFAS removal efficiency with GAC is highly variable with PFAS chain length based on the type of DOM and PFAS [120]. In addition, breakthrough of PFBA before PFOA and PFOS has been observed [106]. Contaminant removal is generally improved with an increase in empty bed contact time [113].
GAC is used as a biological filter to control taste and odor or to remove biologically degradable constituents such as DOM which serve as disinfection byproduct precursors. Water plants using GAC for taste and odor control or DOM removal typically replace or reactivate GAC every few years. Fresh GAC is effective at removing PFOA and PFOS. Use of GAC over one year was not effective in removing PFOA and PFOS [61,109]. PFOA and PFOS were found to increase after GAC treatment during summer months [107].
GAC filters can be costly to operate and maintain [121]. Costs are primarily determined by the flow rate of water to be treated, the influent PFOA and PFOS concentration, the presence of other PFASs to be removed, the presence of natural organic matter, GAC replacement frequency, design empty-bed contact time, and the number of bed volumes treated. Pretreatment processes may be necessary prior to GAC. To lower the cost, alternative adsorbents have been evaluated in exploratory studies. PFOS removal from water was evaluated using biochar, ash, and carbon nanotubes [122]. Carbon nanotubes exhibited higher sorption capacities for PFOS than biochar and ash.
PAC has been found effective for removing PFOA and PFOS in laboratory studies [123,124,125]. Compared to GAC, PAC exhibits a higher adsorption capacity and faster adsorption kinetics due to its fine particle size [123,124]. Separation and recovery of PAC from the water treated is more difficult than GAC due to its fine particle size. Coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation are usually required to separate spent PAC from the water treated. PAC is typically used at a water plant only once, separated with other solids for further residuals treatment and disposal. In bench-studies ultrafine magnetic activated carbon consisting of Fe3O4 and PAC allowed separation of spend PAC from residuals using a magnet [126]. Methanol was used to regenerate the PAC for reuse up to five times.
7.4. Anion Exchange
Studies have found anion exchange to be effective for removing PFOA, PFOS, and other PFASs [107,109,110]. Anion exchange can be very effective for removing both PFASs and DOM, even with high levels of background DOM (9 mg carbon L−1) [119]. When compared with GAC, anion exchange was preferred because PFAS chain length was less relevant compared to GAC, more effective at removing total DOM, and more effective at removing the most hydrophobic DOM compounds [119].
7.5. Membrane Processes
Microfiltration and ultrafiltration are low-pressure membrane processes commonly used in drinking water treatment to remove particulate matter and microorganisms. PFOA and PFOS are not removed by these processes alone due to their large membrane pore size [121].
Reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) are high-pressure membrane processes not widely used for drinking water treatment but commonly used for desalination, treating brackish water, and treating wastewater for reuse [107]. RO is a proven technology for removing PFOA and PFOS, achieving up to >99% removal [116]. NF also rejects PFOA and PFOS, with about 95% rejection achieved for PFASs with molecular weights >300 g/mol [105]. NF rejection of PFOA and PFOS is highly affected by the pH of the water treated.
7.6. Treatment Process Selection
In general, a water utility may use any treatment technology acceptable to their state primacy agency to comply with a drinking water regulation. The technology selected may or may not be designated as BAT by the USEPA. However, the USEPA is required to specify BAT to meet a drinking water regulation in each proposed and final rule. A water utility seeking a variance from a regulation must agree to install a BAT.
The SDWA allows the USEPA to set an MCL or a treatment technique requirement [127]. An MCL must be set as close to the MCLG as feasible [128]. Alternatively, a treatment technique requirement obligates water systems to install the specified or equivalent treatment to the satisfaction of the state regulatory agency. The treatment technique rule is used when it is not practical or feasible to determine the level of a contaminant through laboratory testing. For example, filtration and disinfection of surface water are required to protect against waterborne disease because testing for every pathogen potentially present in surface water sources is not feasible. In the case of PFOA and PFOS, analytical methods are available as discussed above but concentration variability must also be considered. An MCL would be specified if it is feasible to reliably detect PFOA and PFOS in source and treated water during compliance monitoring. Otherwise, a treatment technique rule may be appropriate.
8. Best Available Science
Drinking water regulations established by the USEPA are to be based on the highest-quality science. Specifically, the SDWA requires [129] that:
“To the degree that an Agency action is based on science, the Administrator shall use (1) the best available, peer-reviewed science and supporting studies conducted in accordance with sound and objective scientific practices; and (2) data collected by accepted methods or best available methods (if the reliability of the method and the nature of the decision justifies use of the data”.
This requirement has important implications for developing drinking water regulations for PFASs. A USEPA regulatory action may be legally challenged in the US District Court of Appeals for the District of Columba (DC) if the science upon which the regulatory action was based is arbitrary and capricious. In practice, the science behind each science-based decision will be thoroughly scrutinized by all stakeholders affected. In a prior case, the DC Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that the USEPA had failed to use the best available science in setting an MCLG of zero for chloroform. Specifically, the court ruled [130] that:
“EPA cannot reject the best available evidence simply because of the possibility of contradiction in the future by evidence unavailable at the time of the action—a possibility that will always be present.”
This court decision has two important implications: (1) the agency may be acting illegally when it relies on default assumptions when the best available science supports a less (or more) conservative approached for assessing risk, and (2) the best available science is the scientific evidence available at the time of a rule-making decision. The possibility of contradiction based on further scientific data or peer review is not a legitimate basis for rejecting the science that currently exists.
The SDWA gives US federal courts jurisdiction to review USEPA actions. Though contentious, judicial review is an integral and important component of the US regulatory process. A stakeholder with standing may file a petition for judicial review of a final rule. The judicial review is limited to the administrative record and the court gives substantial deference to the USEPA when reviewing its rules. Specifically, the Court of Appeals has stated [131] that:
“We will reverse (a) USEPA action only if it is arbitrary, capricious, and abuse of discretion, or otherwise not in accordance with law (…) This highly deferential standard of review presumes Agency action to be valid (…) The rationale for deference is particularly strong when USEPA is evaluating scientific data within its technical expertise; In an area characterized by scientific and technological uncertainty, (…) this court must proceed with particular caution, avoiding all temptation to direct the Agency in its choice between rational alternatives. Despite this deferential standard, we must ensure that USEPA has examined the relevant data and has articulated an adequate explanation for its action (…) The USEPA is required to give reasonable responses to all significant comments in a rulemaking proceeding (…) We will therefore overturn a rule-making as arbitrary and capricious where USPEA has failed to respond to specific challenges that are sufficiently central to its decision”.
To establish an enforceable regulation for PFOA and PFOS the detection, occurrence, exposure, health effects, human health risks, treatment technology, national costs of removal from drinking water, as well as national benefits expected from regulation must be thoroughly assessed. Decisions made in the regulatory process must be based on the best available science to avoid issuing an arbitrary and capricious regulation.
9. Costs and Benefits
At the time a new drinking water regulation is proposed the USEPA is required to publish a determination as to whether the benefits of the MCL selected justify, or do not justify, the costs of meeting the MCL based on a health risk reduction and cost analysis (HRRCA) [132]. The cost of a regulation includes capital costs for treatment installation, operation and maintenance costs, and compliance monitoring costs. The number of water systems in the United States to be affected by alternative regulatory levels is estimated. A decision tree of treatment options and unit costs is developed, and assumptions made to estimate how many water systems would install a particular process to comply with the regulation. National capital cost and operation and maintenance costs are estimated by multiplying the number of water systems using a particular treatment technology by the unit cost for that technology. The USEPA estimates costs and benefits of regulating PFOA and PFOS on a national basis using statistical projections of the number of water systems affected and unit treatment cost models. However, the cost faced by any particular water to remove PFOA and PFOS is likely to be higher than USEPA estimates.
Compliance monitoring costs are estimated based on the monitoring strategy applied to document water system compliance. Analytical methods for PFOA and PFOS require highly trained laboratory analysts and advanced laboratory equipment, and are of relatively high cost. If the standardized monitoring framework [133] is applied, initial monitoring for PFOA and PFOS would be required. Subsequent monitoring frequency would be based on initial monitoring results with waivers typically granted if concentrations are reliably and consistently below the MCL and if the water source is not vulnerable to contamination.
Adverse effects on health are quantified at the concentrations typically found in drinking water. Unquantifiable health benefits are important and considered, but quantifiable benefits form the primary bases of HRRCA. To determine the health benefits of a regulation, the difference between the prevailing ambient drinking water concentrations prior to regulation and the concentrations expected after installation of water treatment is determined on a national basis to assess exposure reduction. In the case of PFOA and PFOS, exposure reduction is expected to result in benefits regarding human serum lipids, birth weight, and serum antibodies. Reliably quantifying specific health benefits associated with exposure reduction may not be possible.
10. Regulatory Determination
The SDWA requires the USEPA to make determinations on whether or not to regulate at least five listed contaminants [134]. A notice of preliminary determination and opportunity for public comment must precede publication of final determinations. A determination to regulate a contaminant is based on findings that the criteria for health effects, occurrence, and risk reduction discussed above are met. Findings must be based on the best available public health information, including occurrence data collected during UCMR monitoring.
11. Other US Standards and Advisories
Regulatory agencies in states experiencing environmental and/or drinking water contamination of PFOA and PFOS have been very active in conducting research and setting health standards and advisories. Each state has laws governing the regulation of drinking water implemented by an agency of the state government. In general, states are not bound by SDWA legal requirements when establishing drinking water regulations but their rules must be at least as stringent as the USEPA. States typically have fewer procedural and technical constraints than the USEPA, allowing them to adopt a regulatory approach that best fits the needs of their jurisdiction.
State regulatory agencies in the United States are taking different approaches to address PFOA and PFOS in drinking water and at contaminated sites. Ten states have adopted the USEPA health advisory levels for PFOA and PFOS (Alaska, Arizona, Alabama, Colorado, Maine, Massachusetts, Michigan, New York, Rhode Island, and West Virginia) [135]. Nevada adopted a basic comparison level for PFOA and PFOS at 667 ng/L for each [136]. Exceeding a basic comparison level does not automatically designate a site as needing a response action but suggests further evaluation of health risks is warranted.
California [137] adopted non-regulatory, health-based notification levels for PFOA and PFOS of 14 ng/L and 13 ng/L, respectively. Notification levels are as set as a precautionary measure although water systems are not required to conduct monitoring. If test results exceed the notification level, then the water system must comply with state public notification requirements. When notification levels for PFOA and PFOS are exceeded and concentrations cannot be reduced below the USEPA health advisory levels removing the source from service is recommended [137].
Minnesota [6] and New Jersey [99] conducted independent risk assessments (discussed above) basing their advisory levels on different toxicological endpoints. The Minnesota health advisory levels for PFOA and PFOS are 35 ng/L and 27 ng/L, respectively [138]. The New Jersey health advisory levels for PFOA and PFOS are 14 and 13 ng/L, respectively [139].
A few states have addressed other PFASs in addition to PFOA and PFOS. New Jersey set a health advisory limit for PFNA at 13 ng/L [139]. Vermont established a health advisory limit of 20 ng/L for the sum of PFOA, PFOS, PFHxS, PFHpA, and PFNA [140].
The USEPA issued a draft interim recommendation for addressing ground water contaminated with PFOA and PFOS at sites being evaluated and addressed under federal cleanup programs [141]. For ground water contaminated with PFOA or PFOS, a screening level of 40 ng/L is proposed. A risk-based screening level is used to calculate a Hazard Quotient (HQ). Further evaluation of a contaminated site would be warranted if the PFOA or PFOS HQ is above 0.1. At sites where contaminant concentrations are below screening levels, no further action or study is generally warranted. In cases where the HQ exceeds 0.1, a decision to take remedial clean up action would be typically based on the results of a baseline risk assessment [141]. The health advisory for the combined concentration of PFOA and PFOS (70 ng/L) would be used to develop a preliminary remediation goal which may be modified as appropriate to protect human health and the environment.
The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA or Superfund) authorizes the Agency of Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) to prepare a toxicological profile for the hazardous substances most commonly found in facilities from the CERCLA National Priorities List and that pose the most significant potential threat to human health [67]. A draft profile for 14 PFASs was published for public comment in June 2018. Toxicological profiles are synthesis, non-regulatory documents reflecting the ATSDR’s assessment of all relevant toxicologic testing and information about these substances. The ATSDR preparation of a toxicological profile is not subject to SDWA requirements.
ATSDR toxicological profile risk assessment calculations differ from the regulatory health effects and risk assessment required of the USEPA under the SDWA. If adequate data is available, ATSDR calculates a minimum risk level using a methodology similar to the USEPA calculation of the RfD. Oral minimal risk levels were proposed for PFOA (3 × 10−6 mg/kg/day), PFOS (2 × 10−6 mg/kg/day), PFHxS (2 × 10−5 mg/kg/day), and PFNA (3 × 10−6 mg/kg/day) [67]. Minimal risk levels are intended to serve as screening levels to identify hazardous waste sites where further investigation is needed. They may also be used to identify sites not expected to cause adverse health effects. Minimal risk levels are not enforceable nor intended to define clean up or action levels for ATSDR or other agencies [142].
12. International Standards
Many countries have established guidelines or action levels for PFOA and PFOS which typically are non-enforceable screening levels. Summary lists of international standards for PFASs are available [136]. A few countries have set regulatory standards. For example, Health Canada established a maximum acceptable concentration for PFOA [143] and PFOS [144] at 200 ng/L and 600 ng/L, respectively. When both are present the sum of the ratios of PFOA and PFOS detected concentrations to the corresponding maximum allowable concentration should not exceed 1. Denmark established a health-based standard for PFOA and PFOS at 100 ng/L for each [145]. Germany set a health-based drinking water standard for PFOA and PFOS at 300 ng/L for each [146]. An administrative drinking water standard for PFOA and PFOS was set at 100 ng/L for each.
13. Summary and Conclusions
PFOA and PFOS are persistent organic pollutants receiving global attention. They are two of over 4700 PFASs synthesized, many of which are in active industrial use. PFOA and PFOS have unique chemical characteristics and were manufactured and in a wide variety of industrial and consumer products used in the United States from the 1940s to 2015. Consequently, the US population has already been exposed to these substances and have low levels of them in their blood serum. Although PFOA and PFOS are no longer manufactured in the United States, the US population may still be exposed to them from legacy uses, past improper industrial waste disposal, and their transport in the environment from other countries where they are manufactured and/or used.
For drinking water regulation to be enforceable, the MCL must reflect a clear delineation between test results above and below the MCL, unaffected by variability in laboratory performance. If PFOA and PFOS are to be regulated the USEPA will establish a PQL for each. If the best treatment technology available can lower PFOA and PFOS concentrations to below the PQL, then the MCL for noncarcinogenic substances is typically set at MCLG or the PQL whichever is highest. For substances known or likely to be carcinogenic to humans the MCLG is zero, in which case the enforceable limit is set at the PQL.
PFOA and PFOS have been detected in the environment and in drinking water worldwide (Table 2). A contaminant must be known or likely to be present in drinking water at levels of public health concern to warrant a national regulation. The UCMR 3 monitoring results represent the only available statistically valid survey of national occurrence for the PFASs tested. When analyzing UCMR data, the numbers of water systems exceeding the MRL are a function of the concentration at which the MRL is established. The public health significance is evidenced by the number of water systems exceeding the HRL. The 70 ng/L HRL for PFOA was exceeded by only 13 water systems or 0.3% of the water systems tested. The 70 ng/L HRL for PFOS was exceeded by only 46 water systems or 0.9% of the water systems tested. To be regulated, a determination must be made that PFOA and PFOS are known or likely to be present in drinking water at concentrations of public health concern.
Assessing adverse health effects of PFOA and PFOS exposure involves several important scientific issues. Biomonitoring of blood serum levels indicates the body burden posed by PFOA and PFOS exposure. The RfD established for a regulation may differ from the RfD used to derive the health advisories depending on the decisions made in determining the toxicological endpoint (e.g., developmental or immunological), pharmacokinetic modeling, and interpretation of toxicological studies (e.g., LOAEL, NOAEL, uncertainty factors). Toxicological and risk assessment considerations will be a significant factor in setting MCLGs for PFOA and PFOS.
The RSC is applied to ensure an individual’s total exposure from a contaminant does not exceed the RfD. The RSC is the portion of the RfD attributed to drinking water. The remainder to the RfD is allotted to other potential sources. A default value of 20% was used to derive the health advisories based on exposure to the general population. Unless additional data become available, this same RSC default value will be used to develop a national regulation for PFOA and PFOS.
The SDWA requires the MCL to be set as close to the MCLG as is feasible. “Feasible” means feasible with the use of the best technology, treatment techniques, and other means which the USEPA finds after examination for efficacy under field conditions and not solely under laboratory conditions (taking cost into consideration) [102]. Few technologies meet this feasibility criterion. GAC adsorption, anion exchange, and reverse osmosis remove PFOA and PFOS. The effectiveness of treatment technology and the PQL usually have the most influence on the MCL determination. If PFOA and PFOS are regulated, the effectiveness and cost of treatment technology or other means being considered must be determined. The USEPA is required to make a determination whether the national benefits justify the national cost for each final national primary drinking water regulation.
The best available peer-reviewed science and supporting studies “conducted in accordance with sound and objective scientific practices” are to be used when a regulatory decision is based on science. Only data collected by accepted methods or best available methods are to be used if the reliability of the method and the nature of the decision justifies use of the data [129].
At the time a new drinking water regulation is proposed, the USEPA is required to publish a determination as to whether the benefits of the MCL selected justify, or do not justify, the costs of meeting the MCL based on a health risk reduction and cost analysis (HRRCA) [132]. The cost of a regulation includes capital costs for treatment installation, operation and maintenance costs, and compliance monitoring costs.
The quantifiable and unquantifiable benefits of the regulation must be estimated if a regulation is developed. Adverse effects on health are quantified at the concentrations before and after treatment. Quantified benefits form the primary basis of HRRCA, which presents the costs and benefits of each alternative MCL under consideration.
A decision whether to regulate PFOA and PFOS is anticipated as part of the Regulatory Determination 4. The USEPA decided to not regulate 24 contaminants in prior Regulatory Determinations 1, 2, and 3. [147,148,149] A specific rationale for the decision to not regulate was provided for each contaminant. Prior decisions provide a backdrop and precedent for the decision whether to regulate PFOA and PFOS. For example, aldrin and dieldrin are not regulated because their use had been banned and they had “a low frequency and low level of occurrence in drinking water.“ The percentage of water systems exceeding the HRL for aldrin and dieldrin were 0.494% and 0.2%, respectively. Hexachloropentadiene occurs in public water systems but is not regulated because it did not occur at a frequency or level of public health concern. Manganese is not regulated because it was “generally not considered to be very toxic when ingested with the diet and drinking water accounts for a relatively small proportion of manganese intake”.
The frequency of occurrence and potential health risks are a significant factor for the PFOA and PFOS determination. In Regulatory Determination 1 metribuzin and naphthalene were not regulated because they were “not known to occur (…) at a level of public health concern” and were infrequently detected. Other contaminants for which a determination was made to not regulate include the dacthal mono- and di-acid degradates; 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethylene (DDE); 1,3-dichloropropene; 2,4-dinitrotoluene; 2,6-dinitrotoluene; s-ethyl dipropylthiocarbamate (EPTC); fonofos; terbacil; 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane; dimethoate, 1,3-dinitrobenzene, terbufos; and terbufos sulfone. [147,148,149].
A majority of states have accepted and are applying the USEPA health advisory limits for PFOA and PFOS. Several states performed independent risk assessments and set state-specific advisory limits, especially states where significant environmental contamination had occurred due to improper industrial waste disposal. International agencies, ATSDR, and state agencies independently develop advisory limits within the constraints of their prevailing legal requirements. The USEPA PFOA and PFOS health advisory limits and any future drinking water regulations are developed under the SDWA [15], APA [16], and the agency’s regulatory policies, which are more stringent than the requirements faced by other agencies.
PFOA and PFOS contamination will continue to be addressed by state agencies and USEPA regional offices regardless of whether these contaminants are regulated nationally. Contamination first discovered occurred prior to enactment of present environmental laws and were addressed through litigation [36,37]. Several thousand lawsuits were filed against the manufacturers of PFOA and PFOS resulting in large monetary settlements [150,151,152]. Affected water systems and consumers can access a wealth of information on PFOA and PFOS from the USEPA and many state agencies.
Several agencies have been actively addressing PFOA and PFOS contamination for well over a decade. Much has been learned but extensive research is still needed to answer key questions. Two congressionally mandated research grants have been initiated. Investigators at Oregon State University and North Caroline State University have been granted US$2.6 million to define and predict the toxicity of PFASs, in work that is due for completion in April 2022 [153]. A research team from the Colorado School of Mines, Duke University, Michigan State University, North Carolina State University, and the University of Colorado at Denver has been granted US$2.45 million to develop actionable data on the fate, transport, bioaccumulation, and exposure of a large suite of PFASs in nationally representative PFAS-impacted communities, in a study due for completion in April 2022 [154]. As knowledge gaps are filled by these and other studies, better decisions can be made on how best to reduce total PFAS exposure.
Author Contributions
This article was written and produced entirely by the author from May to August 2019 while the author was a visiting scholar at the Chung Yuan Christian University, Taoyuan City, Taiwan, The author examined over 320 articles, reports and government documents citing the most relevant in this review. Tables were prepared from data extracted from the original literature cited. Figure 1 is in the public domain.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- KEMI The Swedish Chemicals Agency. Occurrence and Use of Highly Fluorinated Substances and Alternatives. Report 7/15. 2015. Available online: https://www.kemi.se/global/rapporter/2015/report-7-15-occurrence-and-use-of-highly-fluorinated-substances-and-alternatives.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Buck, R.C.; Hungerbuhler, K. Global emission inventories for C4–C14 perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid (PFCA) homologues from 1951 to 2030, Part I: Production and emissions from quantifiable sources. Environ. Int. 2014, 70, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Buck, R.C.; Hungerbuhler, K. Global emission inventories for C4–C14 perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acid (PFCA) homologues from 1951 to 2030, part II: The remaining pieces of the puzzle. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD). Toward a New Comprehensive Global Database of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): Summary Report on Updating the OECD 2007 List of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs). Series on Risk Management No. 39, ENV/JM/MONO(2018)7. 4 May 2018. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/portal-perfluorinated-chemicals/ (accessed on 19 July 2019).
- Herrick, R.L.; Buckholz, J.; Biro, F.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Xie, C.; Pinney, S.M. Polyfluoroalkyl substance exposure in the Mid-Ohio River Valley, 1991–2012. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzke, J. Investigating Drinking Water Contamination in Ohio by Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Ohio EPA, Division of Drinking and Ground Waters: Columbus, OH, USA, 22 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goeden, H.M.; Greene, C.W.; Jacobus, J.A. A transgenerational toxicokinetic model and its use in derivation of Minnesota PFOA water guidance. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemol. 2019, 29, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List 3 (CCL3)—Final. Fed. Regist. 2009, 74, 51850–51862. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Drinking Water Health Advisory for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). EPA 822-R-16-005; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, May 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-05/documents/pfoa_health_advisory_final_508.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- USEPA. Drinking Water Health Advisory for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS). EPA 822-R-16-004; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, May 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-05/documents/pfos_health_advisory_final_508.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Cordner, A.; De La Rosa, V.Y.; Schaider, L.A.; Rudel, R.A.; Richter, L.; Brown, P. Guideline levels for PFOA and PFOS in drinking water: The role of scientific uncertainty, risk assessment decisions, and social factors. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemol. 2019, 29, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, J.; Stabenow, D.; Warren, E.; Durban, R.; Manchin, J.; Harris, K.; Gillibrand, K.; Murray, P.; Carper, T.; Coons, C.; et al. Letter from United States Senators to EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt. 13 April 2018. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1LgpWUVI-wfvSW90LtTzjymSNm_BAZTj1/view (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- USEPA. EPA’s Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Action Plan. EPA 823R18004; 2009. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-02/documents/pfas_action_plan_021319_508compliant_1.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- USEPA. Fact Sheet: EPA’s PFAS Action Plan: A Summary of Key Actions. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-02/documents/pfas_action_factsheet_021319_final_508compliant.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Public Law 104–182, The Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 1996. Available online: https://www.congress.gov/bill/104th-congress/senate-bill/1316 (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Administrative Conference. A Guide to Federal Agency Rulemaking, 2nd ed.; Office of the Chairman, Administrative Conference of the United States: Washington, DC, USA, 1991.
- USEPA Science Advisory Board. Reducing Risk: Setting Priorities and Strategies for Environmental Protection; SAB-E-90-021; USEPA Science Advisory Board: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Public Law 99–339. 1986 Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments. Sec. 1412(b)(3)(A). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/104/plaws/publ182/PLAW-104publ182.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Public Law 104–182. The Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 1996. Sec.1412(b)(1)(D). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/104/plaws/publ182/PLAW-104publ182.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, A.S.; Van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Libelo, E. Polyfluorintated compounds: Past, present, and future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7954–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzen-Hanson, K.A.; Roberts, S.C.; Choyke, S.; Oetjen, K.; McAlees, A.; Riddell, N.; McCrindle, R.; Ferguson, P.L.; Higgins, C.P.; Field, J.A. Discovery of 40 Classes of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Historical Aqueous Film-Forming Foams (AFFFs) and AFFF-Impacted Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2047–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.-M.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liang-Ying, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F.; Zeng, E.Y. Global distribution of perfluorochemicals (PFCs) in potential human exposure source—A review. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunacheva, C.; Shivakoti, B.R.; Lien, N.P.H.; Harada, H. Worldwide surveys of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in water environment in recent years. Water Sci. Technol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fourth National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals, Updated Tables, January 2019; Dept. of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/ (accessed on 15 April 2019).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the U.S. Population; Dept. of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017.
- Interstate Technology Regulatory Council (ITRC). History and Use of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS); ITRC: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.W.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A never-ending story of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, S.F.; Yoshikane, M.; Onoda, Y.; Nishihama, Y.; Iwai-Shimada, M.; Takagi, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Isobe, T. Worldwide trends in tracing poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the environment. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, J.A.; Grimmett, P.E.; Boutin, B.K. Method 537, Determination of Selected Perfluoro Alkyl Acids in Drinking Water by Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS); Version 1.1, EPA/600/R-08/092; USEPA Office of Research and Development: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2009.
- Shoemaker, J.A.; Tettenhorst, D.R. Method 537.1, Determination of Selected Per- and Polyfluorinated Alkyl Subtances in Drinking Water by Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS); Version 1.0, EPA/600/R-18/352; USEPA Office of Research and Development: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2018.
- USEPA. Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List 4—Final. Fed. Regist. 2016, 81, 81099–81114. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Revisions to the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR 3) for Public Water Systems. Fed. Regist. 2012, 77, 26072–26101. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. The Third Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR 3): Data Summary; EPA 815-S-17-001; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection. Interim Practical Quantitation Level (PQL) Determination to Support Interim Specific Ground Water Quality Standard Development for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). Division of Science and Research; 6 March 2019. Available online: https://www.nj.gov/dep/dsr/supportdocs/PFOA_PQL.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Rich, N. The Lawyer Who Became DuPont’s Worst Nightmare. The New York Times Magazine, 6 January 2016. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/01/10/magazine/the-lawyer-who-became-duponts-worst-nightmare.html (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Mordock, J. Taking on duPont: Illnesses, Deaths Blamed on Pollution from W. VA Plant. Delaware Online. 1 April 2016. Available online: https://www.delawareonline.com/story/news/2016/04/01/dupont-illnesses-deaths-c8/81151346/ (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. Perfluorochemicals (PFCs). Undated Webpage. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/waste/perfluorochemicals-pfcs (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Hu, X.C.; Andrews, D.Q.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bruton, T.A.; Schaider, L.A.; Granjean, P.; Lohmann, R.; Carignan, C.C.; Blum, A.; Balan, S.A.; et al. Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gin, K.Y.H.; Chang, V.W.C.; Goh, B.P.L. Novel perspectives on the bioaccumulation of PFCs–The concentration dependency. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9758–9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Kannan, K. Distribution and partitioning of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids in surface soil, plants, and earthworms at a contaminated site. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Eaglesham, G.; Mueller, J. Concentrations of PFOS, PFOA and other perfluorinated alkyl acids in Australian drinking water. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, D.; Coggan, T.L.; Robson, T.C.; Currell, M.; Clarke, B.O. Investigating recycled water use as a diffuse source of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) to groundwater in Melbourne, Australia. Sci. Total Envrion. 2018, 644, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Roach, A.; Eaglesham, G.; Bartkow, M.E.; Edge, K.; Mueller, J.F. Perfluorinated alkyl acids in water, sediment and wildlife from Sydney Harbor and surroundings. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2869–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furdui, V.I.; Crozier, P.W.; Reiner, E.J.; Mabury, S.A. Trace level determination of perfluorinated compounds in water by direct injection. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, Y.L.; Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Lu, G.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Kannan, K.; Yamashita, N. Perfluorinated Compounds in Tap Water from China and Several Other Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4824–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaboré, H.A.; Duy, S.V.; Munoz, G.; Méité, L.; Desrosiers, M.; Liu, J.; Sory, T.K.; Sauvé, S. Worldwide drinking water occurrence and levels of newly-identified perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Geng, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, J. A review of spatial and temporal assessment of PFOS and PFOA contamination in China. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 25, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, M.K.; Miyake, Y.; Yeung, W.Y.; Ho, Y.M.; Taniyasu, S.; Rostowski, P.; Yamashita, N.; Zhou, B.S.; Shi, X.J.; Wang, J.X.; et al. Perfluorinated compounds in the Pearl River and Yangtze River of China. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, J.; Wang, T. Seasonal and annual variations in removal efficiency of perfluoro alkyl substances by different wastewater treatment processes. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yamashita, N.; Dai, J. Detection and fate of perfluoroalkyl substances in municipal wastewater treatment plants in economically developed areas of China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, N.; He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z. Perfluoroalkyl acids in drinking water of China 2017: Distribution characteristics, influencing factors and potential risks. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.H.; Liu, W.; Sato, I.; Nakayama, S.F.; Sasaki, K.; Saito, N.; Tsuda, S. PFOS and PFOA in environmental and tap water in China. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Felizeter, S.; Strum, R.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Polyfluorinated compounds in waste water treatment plant effluents and surface waters along the River Elbe, Germany. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunantha, G.; Vasudenvan, N. Assessment of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate in surface water. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, F.; Adachi, F.; Miyano, K.; Tanaka, H.; Mimura, M.; Watanabe, I.; Tanabe, S.; Kannan, K. Perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in raw and treated tap water from Osaka, Japan. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafeiraki, E.; Costopoulou, D.; Vassiliadou, I.; Leondiadis, L.; Dassenakis, E.; Traag, W.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P.; van Leeuwn, S.P.J. Determination of perfluoroalkylated substances (PFASs) in drinking water from the Netherlands and Greece. Food Addit. Contam. A 2015, 32, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsma, S.H.; Koekkoek, J.C.; van Velzen, M.J.M.; de Boer, J. The PFOA substitute GenX detected in the environment near a fluoropolymer manufacturing plant in the Netherlands. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.Y.-C.; Panchangam, S.C.; Lo, C.-C. The impact of semiconductor, electronics and optoelectronic industries on downstream perfluorinated chemical contamination in Taiwan rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, J.S.; Vigo, C.; Boone, T.; Byrne, C.; Ferrario, J.; Benson, R.; Donohue, J.; Simmons, J.E.; Kolpin, D.W.; Furlong, E.T.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in source and treated drinking water of the United State. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, O.; Snyder, S.A. Occurrence of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylates and Sulfonates in Drinking Water and Related Waters from the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9089–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, M. PFAS Monitoring in a Post Health Advisory World—What Should We Be Doing? Presented at AWWA New York Section Conference. 2017. Available online: https://nysawwa.org/docs/presentations/2017/FINAL-PFAS%20Monitoring%20in%20Post%20health%20Advisory%20World-What%20Should%20We%20Be%20Doing-2017.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- USEPA. Provisional Health Advisory for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS); Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 8 January 2009. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/pfoa-pfos-provisional.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- USEPA. Framework for Human Health Risk Assessment to Inform Decision Making; EPA/100/R-14/001; Risk Assessment Forum: Washington, DC, USA, April 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2014-12/documents/hhra-framework-final-2014.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- USEPA. Health Effects Support Document for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA); EPA 822-R-16-003; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- USEPA. Health Effects Support Document for Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS); EPA 822-R-16-002; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Perfluoroalkyls–Draft for Public Comment; US Dept of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id=1117&tid=237 (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Dong, Z.; Bahar, M.M.; Jit, J.; Kennedy, B.; Priestly, B.; Ng, J.; Lamb, D.; Liu, Y.; Duan, L.; Naidu, R. Issues raised by the reference doses for perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooactanoic acid. Environ. Int. 2017, 105, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, G.B.; Gleason, J.A.; Cooper, K.R. Key scientific issues in developing drinking water guidelines for perfluoroalkyl acids: Contaminants of emerging concern. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2002855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesn, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresham, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of Serum Elimination of Perfluorooctanesulfonate, Perfluorohexanesulfonate, and Perfluorooctanoate in Retired Fluorochemical Production Workers. Envrion. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fletcher, T.; Mucs, D.; Scott, K.; Lindh, C.H.; Tallving, P.; Jakobsson, K. Half-lives of PFOS, PFHxS and PFOA after end of exposure to contaminated drinking water. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loccisano, A.E.; Campbell, J.L.; Andersen, M.E.; Clewell, H.J. Evaluation and prediction of pharmacokinetics of PFOA and PFOS in the monkey and human using a PBPK model. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2011, 59, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Kang, Q.; Peng, H.; Ding, M.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, M.; Tao, S.; et al. Relationship between perfluoroactanoate and perfluorooctane sulfonate blood concentrations in the general population and routine drinking water exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Berlew, M.M.; Mandel, J.H. Epidemiologic assessment of worker serum perfluoroactanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) concentrations and medical surveillance examinations. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 45, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, C.J.; Lenonard, R.C.; Kreckmann, K.H.; Slade, M.D.; Cullen, M.R. Longitudinal study of serum lipids and liver enzymes in workers with occupational exposure to ammonium perfluorooctanoate. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2007, 49, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, E.A.; Zhang, H.; Shofer, F.S.; Freeman, D.; Rodway, N.V.; Desai, C.; Shaw, L.M. Community exposure to perfluorooctanoate: Relationships between serum levels and certain health parameters. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 48, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Jin, C.; MacNeil, J.; Lally, C.; Ducatman, A.; Vieira, V.; Fletcher, T. Predictors of PFOA levels in a community surrounding a chemical plant. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, R.R.; Moore, S.M.; Tierney, B.C.; Ye, X.; Calafate, A.M.; Campbell, S.; Woudneh, M.B.; Fisher, J. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human serum and urine samples from a residentially exposed community. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.R.; Chan, B.P.; Talbot, E.A.; Nassif, J.; Bean, C.; Cavallo, S.J.; Metcalf, E.; Simone, K.; Woolf, A.D. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure assessment in a community exposed to contaminated drinking water, New Hampshire, 2015. Int. J. Hyg. Envir. Heal. 2018, 221, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Mair, D.C.; Lange, C.C.; Harrington, L.M.; Church, T.R.; Goldberg, C.L.; Herron, R.M.; Hanna, H.; Nobiletti, J.B.; Rios, J.A.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in American Red Cross adult blood donors, 2000–2015. Environ. Res. 2017, 157, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. A Review of the Reference Dose and Reference Concentration Processes; EPA/630/P-02/0002F; Risk Assessment Forum: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2014-12/documents/rfd-final.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Lau, C.; Thibodeaux, J.R.; Hanson, R.G.; Narotsky, M.G.; Rogers, J.M.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J. Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid exposure during pregnancy in the mouse. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 90, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebker, D.J.; Case, R.G.; York, R.G.; Moore, J.A.; Hansen, K.J.; Butenoff, J.L. Two-generation reproduction and cross-foster studies of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) in rats. Toxicology 2005, 215, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicole, W. PFOA and Cancer in a Highly Exposed Community. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, A340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment; EPA/630/P-03/001F; Risk Assessment Forum: Washington, DC, USA, March 2005. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2013-09/documents/cancer_guidelines_final_3-25-05.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Butenhoff, J.L.; Kennedy, G.L.; Chang, S.C.; Olsen, G.W. Chronic dietary toxicity and carcinogenicity study with ammonium perfluorooctanotae in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicology 2012, 298, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta-Cortes, R.; Farias, P.; Hoyo-Vadillo, C.; Kleiche-Dray, M. Carcinogenic risk of emerging persistent organic pollutant perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS): A proposal of classification. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2017, 83, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, T.H.; White, K.; Honigfort, P.; Twaroski, M.L.; Neches, R.; Walker, R.A. Perfluorochemicals: Potential sources of and migration from food packaging. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USFDA. Indirect Food Additives: Paper and Paperboard Components. Fed. Regist. 2016, 81, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, A.J.; Webster, T.F.; Watkins, D.J.; Strynar, M.J.; Kato, K.; Calafat, A.M.; Vieira, V.M.; McClean, M.D. Polyfluorinated compounds in dust from homes, offices, and vehicles as predictors of concentrations in office workers’ serum. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, D.; Horowitz, L.; Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; Hungerbühler, K. Estimating Consumer Exposure to PFOS and PFOA. Risk Anal. 2008, 28, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Oh, J.-E. Assessment of individual-based perfluoroalkyl substances exposure by multiple human exposure sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Cai, D.; Guo, M.; Li, M.; Li, X. Per- and polyfluorinated compounds in sales women’s urine linked to indoor dust in clothing shops. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franko, J.; Meade, B.J.; Frasch, H.F.; Barbero, A.M.; Anderson, S.E. Dermal Penetration Potential of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Human and Mouse Skin. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2012, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbink, V.G.; Berger, U.; Cousins, I.T. Estimating human exposure to PFOS isomers and PFCA homologues: The relative importance of direct and indirect (precursor) exposure. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology Program. NTP Monograph on Immunotoxicity Associated with Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) or Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS); Office of Health Assessment and Translation: Research Triangle Park/Durham, NC, USA, 2016.
- Peden-Adams, M.M.; Keller, J.M.; Eudaly, J.G.; Berger, J.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Keil, D.E. Suppression of humnoral immunity is mice following exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 104, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienthal, H.; Dieter, H.H.; Holzer, J.; Wilhelm, M. Recent experimental results of effects of perfluoroalkyl substances in laboratory animals–Relation to current regulations and guidance values. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachkowski, B.; Post, G.B.; Stern, A.H. The derivation of a Reference Dose (RfD) for Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) based on immune suppression. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zheng, L.; Liu, W.; Jin, Y.H.; He, Q.C. Chronic effects of perfluorooctanesulfonate exposure on immunotoxicity in adult male C57B1/6 mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.-O.; Boffetta, P.; Wedner, H.J.; Mandel, J.S. A critical review of perfluorooactanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate exposure and immunological health conditions in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 279–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1986 SDWA Amendments Sec. 1412(b)(4)(D). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/bill/99th-congress/senate-bill/124 (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Rayne, S.; Forest, K. Perfluoroalkyl sulfonic and carboxylic acids: A critical review of physicochemical properties, levels and patterns in waters and wastewaters, and treatment methods. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2009, 44, 1145–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Cheng, J.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffman, M.R. Treatment technologies for aqueous perfluoroocatanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA). Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2009, 3, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschauzier, C.; Beerendonk, E.; Scholte-Veenendall, P.; Voogt, P.D. Impact of Treatment Processes on the Removal of Perfluoroalkyl Acids from Drinking Water Production Chain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleman, T.D.; Higgins, C.P.; Quinones, O.; Vanderford, B.J.; Kolstad, C.; Zeigler-Holady, J.C.; Dickenson, E.R.V. Treatment of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in U.S. full-scale water treatment systems. Water Res. 2014, 51, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.F.; Peldszus, S.; Anderson, W.B. Behaviours and fate of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2014, 50, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Darlington, R.; Benotti, M.; Deeb, R.; Hawley, E. Novel treatment technologies for PFAS compounds: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Adachi, F.; Miyano, K.; Koizumi, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Watanabe, I.; Tanabe, S.; Kannan, K. Fate of perfluoroocatanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in drinking water treatment processes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3925–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Eaglesham, G.; Reungoat, J.; Poussade, Y.; Bartkow, M.; Lawrence, M.; Mueller, J.F. Removal of PFOS, PFOA and other perfluoroalkyl acids at water reclamation plants in South East Queensland Australia. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Simcik, J.F.; Gulliver, J.S. Mechanisms for removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) from drinking water by conventional and enhanced coagulation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Niu, J.; Xu, Z.; Gao, D.; Shi, J.; Sun, X.; Huang, Q. Removal of perfluorooctanoate sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) form water by coagulation: Mechanisms and influencing factors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 434, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, B.K.; Pramanki, S.K.; Suja, F. A comparative study of coagulation, granular- and powdered activated carbon for the removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in drinking water treatment. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, G.; Huan, J.; Fan, Q. Removal of perfluorooctanoate from surface water by polyaluminum chloride coagulation. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunacheva, C.; Fuji, S.; Tanaka, S.; Boontanon, S.K.; Poothong, S.; Wongwatthana, T.; Shivakoti, B.R. Perfluorinated compounds contamination in tap water and bottled water in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2010, 59, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espana, V.A.A.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. Treatment Technologies for aqueous perfluoroocatanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA): A critical review with an emphasis on field testing. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Lo, S.-L.; Lin, Y.-L. Persulfate oxidation of perfluorooctanoic acid under the temperatures of 20–40 °C. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.D.; Franco, R.; Mimna, R.; Zappa, L. Comparison of Activated Carbons for Removal of Perfluorinated Compounds from Drinking Water. J. AWWA 2018, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleaf, P.; Englund, S.; Ostlund, A.; Lindegren, K.; Wiberg, K. Removal efficiency of multiple poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water using granular activated carbon (GAC) and anion exchange )AE) column tests. Water Res. 2017, 120, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothawala, K.H.; Kohler, S.J.; Ostund, A.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Influence of dissolved organic matter concentration and composition of the removal efficiency of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) during drinking water treatment. Water Res. 2017, 121, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoslett, J.; Massara, T.M.; Malamis, S.; Ahmad, D.; van den Boogaert, I.; Katsou, E.; Ahmad, B.; Ghazal, H.; Simons, S.; Wrobel, L.; et al. Surface water filtration using granular media and membranes: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 639, 1268–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Qiao, J.; Chen, H. A comparative study on sorption of perfluoroactane sulfonate. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Bo, X.; Liu, G.; Zhou, Q. Equilibrium and kinetics study on the adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid from aqueous solution onto powdered activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Deng, S.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Sorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate on activated carbons and resins: Kinetic and isotherm study. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.C.; Børresen, M.H.; Schlabach, M.; Cornelissen, G. Sorption of perfluorinated compounds from contaminated water to activated carbon. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Fang, X.; Maimaiti, A.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Efficient removal of perfluroinated compounds from water using a regenerable magnetic activated carbon. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Public Law 104–182, The Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 1996, Section 1412(b)(7). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/104/plaws/publ182/PLAW-104publ182.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Public Law 104–182, The Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 1996, Section 1412(b)(4)(B). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/104/plaws/publ182/PLAW-104publ182.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Public Law 104–182, The Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 1996, Section 1412(b)(4)(D). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/104/plaws/publ182/PLAW-104publ182.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- U.S. Court of Appeals. Chlorine Chemistry Council and Chemical Manufacturers Association v. EPA.; U.S. Court of Appeals, Case 99–1627; District of Columbia Circui: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- U.S. Court of Appeals. International Fabricare Institute for Itself and on Behalf of its Members v. USEPA.; U.S. Court of Appeals, Case 91–1838; District of Columbia Circuit: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- Public Law 104–182, The Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 1996, Section 1412(b)(3)(C). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/104/plaws/publ182/PLAW-104publ182.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- USEPA. Standardized Monitoring Framework, Office of Water; EPA 570/F-91-045; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1991.
- Public Law 104–182, The Safe Drinking Water Act Amendments of 1996, Section 1412(b)(1)(B)(ii). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/104/plaws/publ182/PLAW-104publ182.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Orange County Water District. PFOA and PFOS Occurrence in the Santa Anna River Watershed; OCWD Presentation to SAWPA EC Task Force; Orange County Water District: Fountain Valley, CA, USA, 2019.
- ITRC. PFAS Fact Sheet Table 4–1. Standards and Guidance Values for PFAS in Groundwater, Drinking Water, and Surface Water/Effluent (Wastewater). June 2019. Available online: https://pfas-1.itrcweb.org/fact-sheets/ (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- California State Water Resources Control Board. Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid (PFOS) Webpage, Division of Drinking Water. 2019. Available online: https://www.waterboards.ca.gov/drinking_water/certlic/drinkingwater/PFOA_PFOS.html (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- Minnesota Department of Health. Human Health-Based Water Guidance Table. 2019. Available online: https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/risk/guidance/gw/table.html (accessed on 13 August 2109).
- New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection. Site Remediation Program Website, Contaminants of Emerging Concern. 13 March 2019. Available online: https://www.nj.gov/dep/srp/emerging-contaminants/ (accessed on 13 August 2109).
- Vermont Department of Health. Memo from Schwer, C. to Chapmann, M. and Englander, D. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS); Vermont Drinking Water Health Advisory: Burlington, VT, USA, 2016.
- USEPA. Draft Interim Recommendations to Address Groundwater Contaminated with Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluoroctane Sulfonate. April 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-04/documents/draft_interim_recommendations_for_addressing_groundwater_contaminated_with_pfoa_and_pfos_public_comment_draft_4-24-19.508post.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- ATSDR. Toxic Substances Portal, Minimal Risk Levels (MRLs)—For Professionals. 21 June 2018. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/mrls/index.asp (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document. Perfluoroactane Acid (PFOA). December 2018. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/healthy-living/guidelines-canadian-drinking-water-quality-technical-document-perfluorooctanoic-acid/document.html (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Health Canada. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality: Guideline Technical Document. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS). December 2018. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/healthy-living/guidelines-canadian-drinking-water-quality-guideline-technical-document-perfluorooctane-sulfonate/document.html#1.0 (accessed on 31 July 2019).
- Larsen, P.B.; Giovalle, E. Danish Ministry of the Environment. Perfluoroalkylated Substances: PFOA, PFOS and PFOSA: Evaluation of Health Hazards and Proposal of a Health Based Quality Criterion for Drinking Water, Soil and Ground Water; Environmental project No. 1665; The Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015; Available online: http://www2.mst.dk/Udgiv/publications/2015/04/978-87-93283-01-5.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- German Ministry of Health. Assessment of PFOA in the Drinking Water of the German Hochsauerlandkreis. Provisional Evaluation of PFT in Drinking Water with the Guide Substances Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) as Examples. 2006. Available online: http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/sites/default/files/medien/pdfs/pft-in-drinking-water.pdf (accessed on 23 May 2019).
- USEPA. Contaminant Candidate List Regulatory Determination Support Document for Aldrin and Dieldrin; EPA-815-R-03-010; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2003.
- USEPA. Regulatory Determinations Support Document for Selected Contaminants from the Second Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List (CCL2); EPA 815-R-08-012; Office of Water: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- USEPA. Announcement of Final Regulatory Determinations for Contaminants on the Third Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List. Fed. Regist. 2016, 81, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mordock, J. DuPont, Chemours to Pay $670 Million over PFOA Suits. Delaware News Journal, Delaware Online. 17 February 2017. Available online: http://delonline.us/2kCechH (accessed on 13 August 2019).
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. 3M and PFCs: 2018 Settlement Website, Undated. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/waste/3m-and-pfcs-2018-settlement (accessed on 13 August 2019).
- Reisch, M.S. 3M settles PFAS suit in Alabama. Chem. Eng. News 2019, 97, 12. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. System Toxicological Approaches to Define and Predict the Toxicity of Per- and Poly-Fluoroalkyl Substances. EPA Grant No. R839481. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.abstractDetail/abstract/10950/report/0 (accessed on 22 September 2019).
- USEPA. PFAS United: Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances- US National Investigation of Transport and Exposure from Drinking Water and Diet. EPA Grant No. R839482; 1 May 2019. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncer_abstracts/index.cfm/fuseaction/display.abstractDetail/abstract/10951/report/0 (accessed on 22 September 2019).
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).