Emission Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Asphalt Concrete Manufacturing Facilities in South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ascon Manufacturing Facilities
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Estimation of Emission Factor
2.4. CALPUFF Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Emission Characteristics of PAHs
3.2. Estimation of Emission Factors for BaP
3.3. CALPUFF Modeling
4. Conclusions
- Measurements at 29 facilities located near residential areas revealed that BaP was consistently detectable, underscoring the pollutant’s environmental and public health relevance.
- Dryer fuel type was a dominant factor influencing BaP emission levels. Facilities using heavy oils with high aromatic content (BCO and VDO) emitted significantly higher concentrations of BaP than those using cleaner fuels (LNG and LPG).
- The calculated BaP emission factors were up to 6230 times greater than the standard values in the US EPA’s AP-42, indicating that existing international emission factors do not accurately reflect the specific processes and fuel-use characteristics of domestic manufacturing facilities.
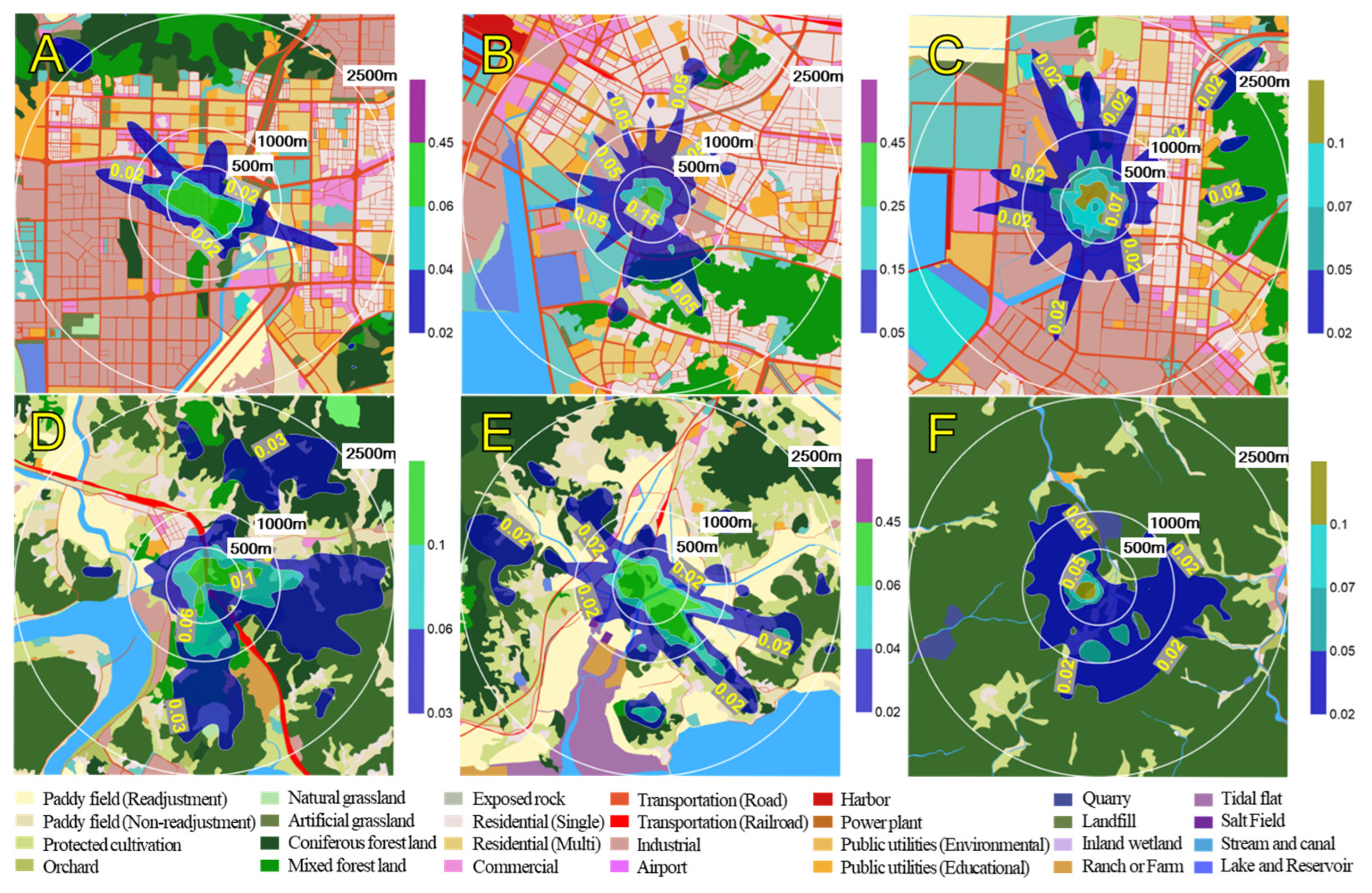
- Dispersion modeling showed elevated BaP concentrations within a 1 km radius of the facilities, with differing dispersion patterns in urban versus suburban areas.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ascon | Asphalt Concrete |
| VOCs | Volatile Organic Compounds |
| PAHs | Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| BaP | Benzo(a)pyrene |
| IARC | International Agency For Research On Cancer |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency |
| CALPUFF | California Puff |
| BCO | Fuel—Bunker C Oil |
| LNG | Liquefied Natural Gas |
| LPG | Liquefied Petroleum Gas |
| VDO | Vacuum Distillation Oil |
References
- Lee, K.; Choi, S.; Kim, M.; Song, D.; Kim, K.-Y. Airborne levels of lung carcinogens at an ascon manufacturing site. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1411–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Lee, B.-K. Energy savings and reduction of CO2 emission using Ca(OH)2 incorporated zeolite as an additive for warm and hot mix asphalt production. Energy 2017, 136, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.; Golden, J.S.; Biligiri, K.P.; Kaloush, K. Modeling climate change impacts of pavement production and construction. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Tran, T.N. Effects of crumb rubber content and curing time on asphalt concrete and stone mastic asphalt using dry process. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2018, 11, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, F.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, S. Emission behavior, environmental impact and priority-controlled pollutants assessment of VOCs during asphalt pavement construction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.-W.; Lee, S.-B.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Hong, J.-H.; Kim, S.-K. A study on estimating PM emission from asphalt-concrete manufacturing facilities. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 30, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiying, L.; Wingtat, H.; Zhen, L. Air pollutant emissions and acoustic performance of hot mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 129, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.B.; Candido, J.; Baulé, S.D.S.; de Oliveira, Y.M.M.; Thives, L.P. Greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption in asphalt plants. Rev. Eletronica Em Gestao Educ. E Tecnol. Ambient. 2020, 24, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Anbuudayasankar, S.P.; Variyer, S. Scheduling and optimization of refinery operation under fluctuating bitumen demand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 14, 170–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, B.; Sen, S.; Dhananjayan, V.; Narayana, J. Personal exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and inhalation risk assessment among asphalt hot mixed plant and road paving workers. In Aerosol Science and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germin-Aizac, J.; Maitre, A.; Balducci, F.; Montlevier, S.; Marques, M.; Tribouiller, J.; Demeilliers, C.; Persoons, R. Bitumen fumes and PAHs in asphalt road paving: Emission characteristics, determinants of exposure and environmental impact. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Lu, Y. VOCs generated in asphalt pavement construction and their health effects on workers. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2014, 140, 04013051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, C.; Ağış, E.R.; Büyükşekerci, M.; Gündüzöz, M.; Tutkun, L.; Yılmaz, Ö.H. Occupational exposure to asphalt fume can cause oxidative DNA damage among road paving workers. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2018, 61, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Slezakova, K.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pereira, M.C.; Morais, S. Children environmental exposure to PM and PAHs: A review on indoor and outdoor levels, sources and health impacts. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Phee, Y.G.; Cho, S.W.; Ok, G.; Shon, B.H.; Lee, K.; Lim, H.S. Concentration level and distribution characteristics of PAHs at ambient air in industrial complex area. Clean Technol. 2011, 17, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. AP-42: Compilation of Air Emissions Factors from Stationary Sources, Chapter 11: Mineral Products Industry. U.S. EPA. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-factors-and-quantification/ap-42-compilation-air-emissions-factors (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Kim, O.; Song, Y.; Lee, J. Estimation of benzo(a)pyrene emission from fuel combustion in the Seosan area. J. Environ. Health Sci. 2017, 43, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilakos, C.; Levi, L.; Maggos, T.; Hatzianestis, J.; Michopoulos, J.; Helmis, C. Gas–particle concentration and sources of PAHs in suburban Athens. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.Y.; Kang, Y.-H.; Song, S.-K.; Kim, Y.-K. Comparison of CALPUFF and HYSPLIT models for dispersion of radioactive materials. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 31, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirithian, D.; Thepanondh, S.; Laowagul, W.; Morknoy, D. Atmospheric dispersion of PAHs from agricultural residue burning in Chiang Rai. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Ali, S.; Sardar, S.; Irfan, N.; Al-Damkhi, A. Evaluating the performance of an integrated CALPUFF-MM5 modeling system for predicting SO2 emission from a refinery. Clean Techn. Environ. Policy 2011, 13, 841–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Lee, T.; Lee, I.H.; Jeon, E.C. Analysis about CO diffusion change caused by climate change using CALPUFF. J. Clim. Change Res. 2017, 8, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Cheng, I.; Xiao, R.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, L. Emissions database development and dispersion model predictions in Canadian oil sands region. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğruparmak, Ş.Ç.; Pekey, H.; Arslanbaş, D. Odor dispersion modeling with CALPUFF: Case study in Kocaeli, Turkey. Environ. Forensics 2017, 19, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Fadlallah, S.O. Effects of vehicle emissions on the atmosphere of Sultan Qaboos University in Oman. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamin, A.; Samara, F.; Al-Tamimi, A.K. Environmental risk assessment of sustainable concrete through PAHs. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi, A.; Makoundou, C.; Coupe, S.J.; Sangiorgi, C. Leaching of PAHs from rubber modified asphalt pavements. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 153983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Gao, P.; Laux, S.J.; Ma, L.Q.; Townsend, T.G. Contribution of asphalt products to total and bioaccessible PAHs. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova, E.M.; Kasimov, N.S.; Kosheleva, N.E. PAHs in urban soils sealed under asphalt concrete. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2020, 491, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowska, B.; Mokra, K.; Michałowicz, J. Benzo(a)pyrene: Occurrence, human exposure and toxicity mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Australia. Emission Estimation Technique Manual for Hot Mix Asphalt Manufacturing. National Pollutant Inventory, Version 1.0. 2001. Available online: https://cwm.unitar.org/publications/publications/cbl/prtr/pdf/cat5/fasphalt.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Ventura, A.; Jullien, A.; Monéron, P. PAHs emitted from hot-mix drum asphalt plant: Effect of recycled bitumen. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 6, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-J.; Chao, W.-H.; Shih, M.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chen, T.J.H.; Tsai, P.-J. Emissions of PAHs from batch hot mix asphalt plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5274–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. AP-42, Fifth Edition, Vol I: Ch. 11.1 Hot Mix Asphalt Plants. U.S. EPA. 2004. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Gibson, N.; Stewart, R.; Rankin, E. Air quality assessment of benzo(a)pyrene from asphalt plant operation. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
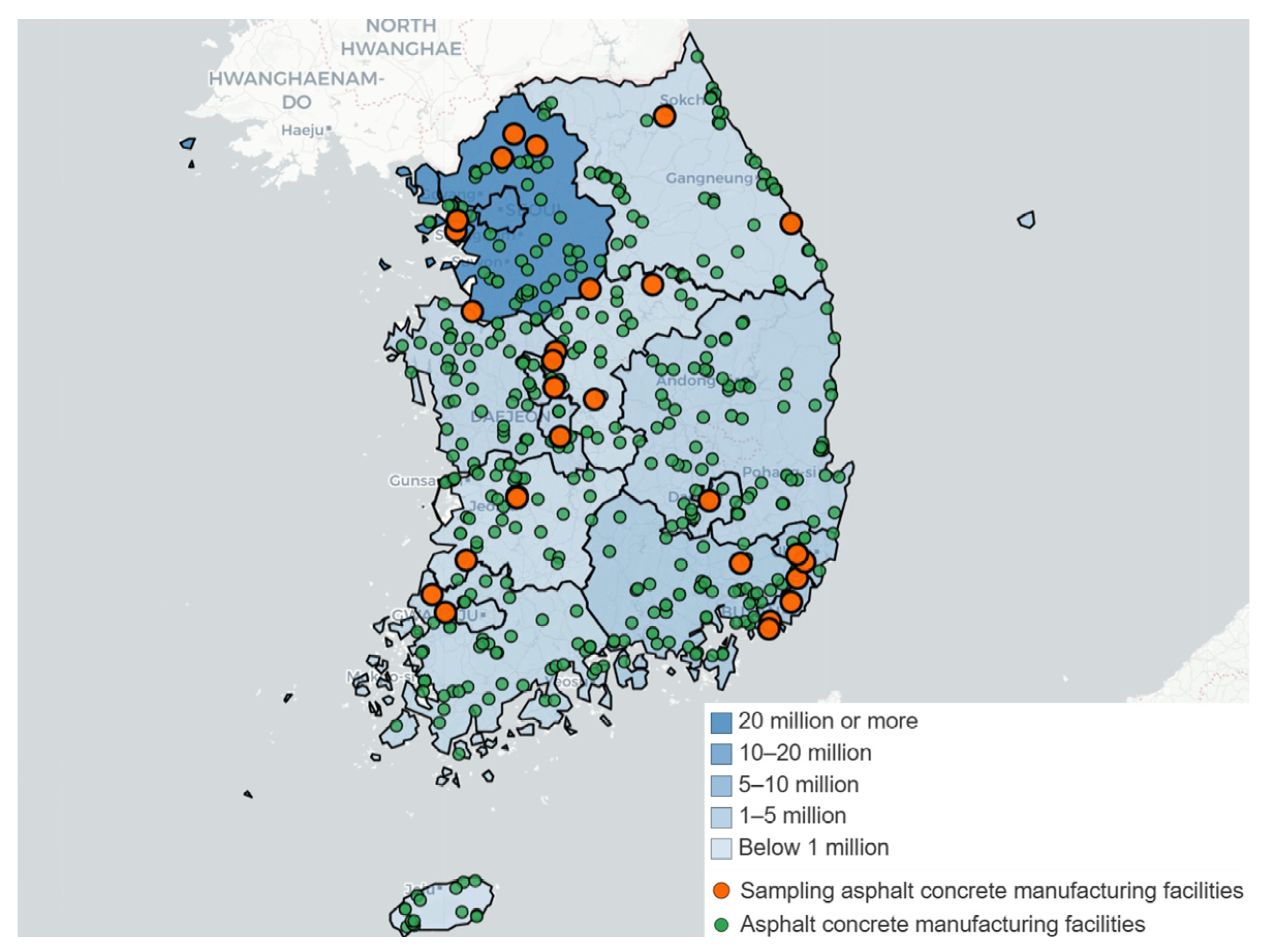

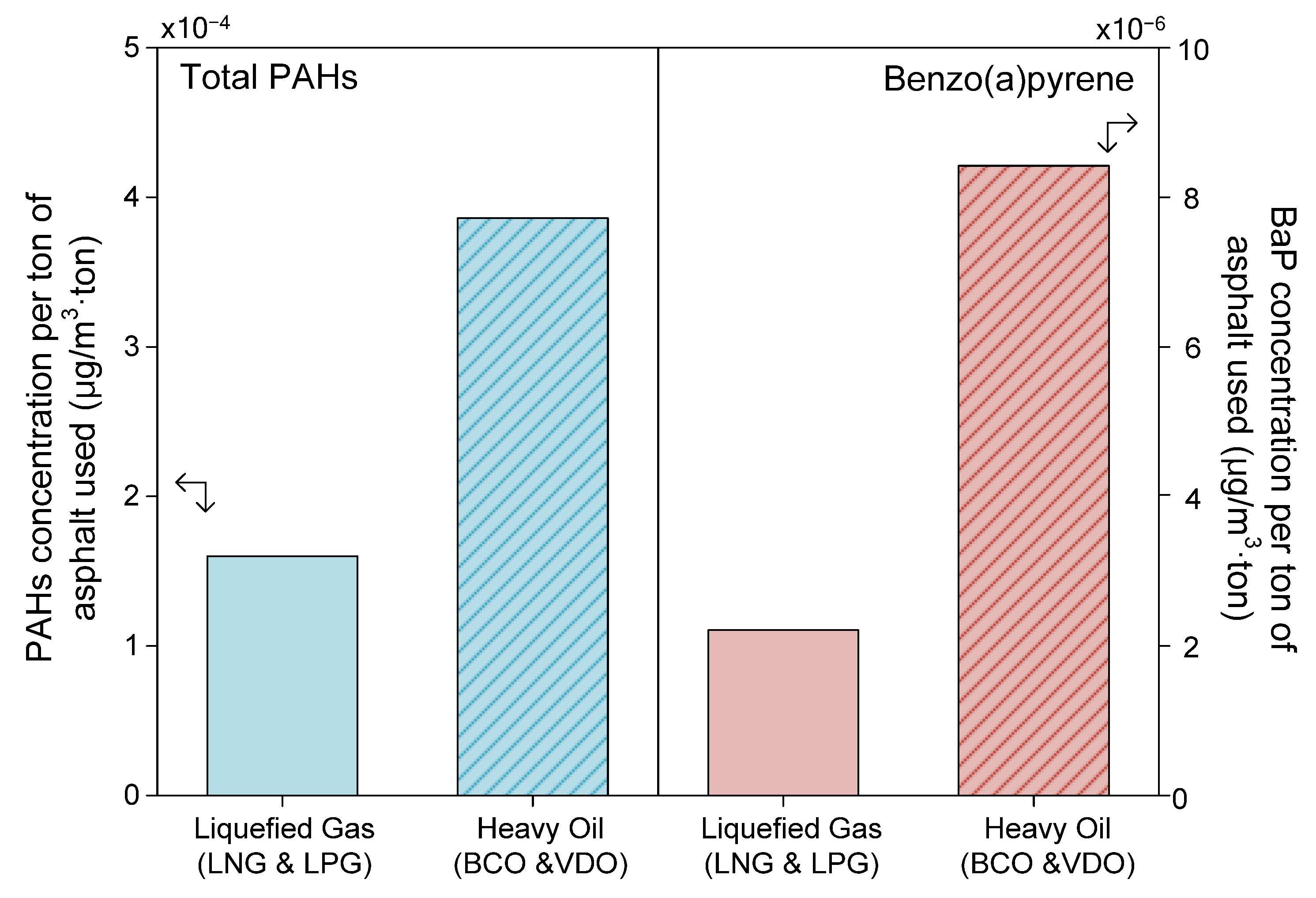
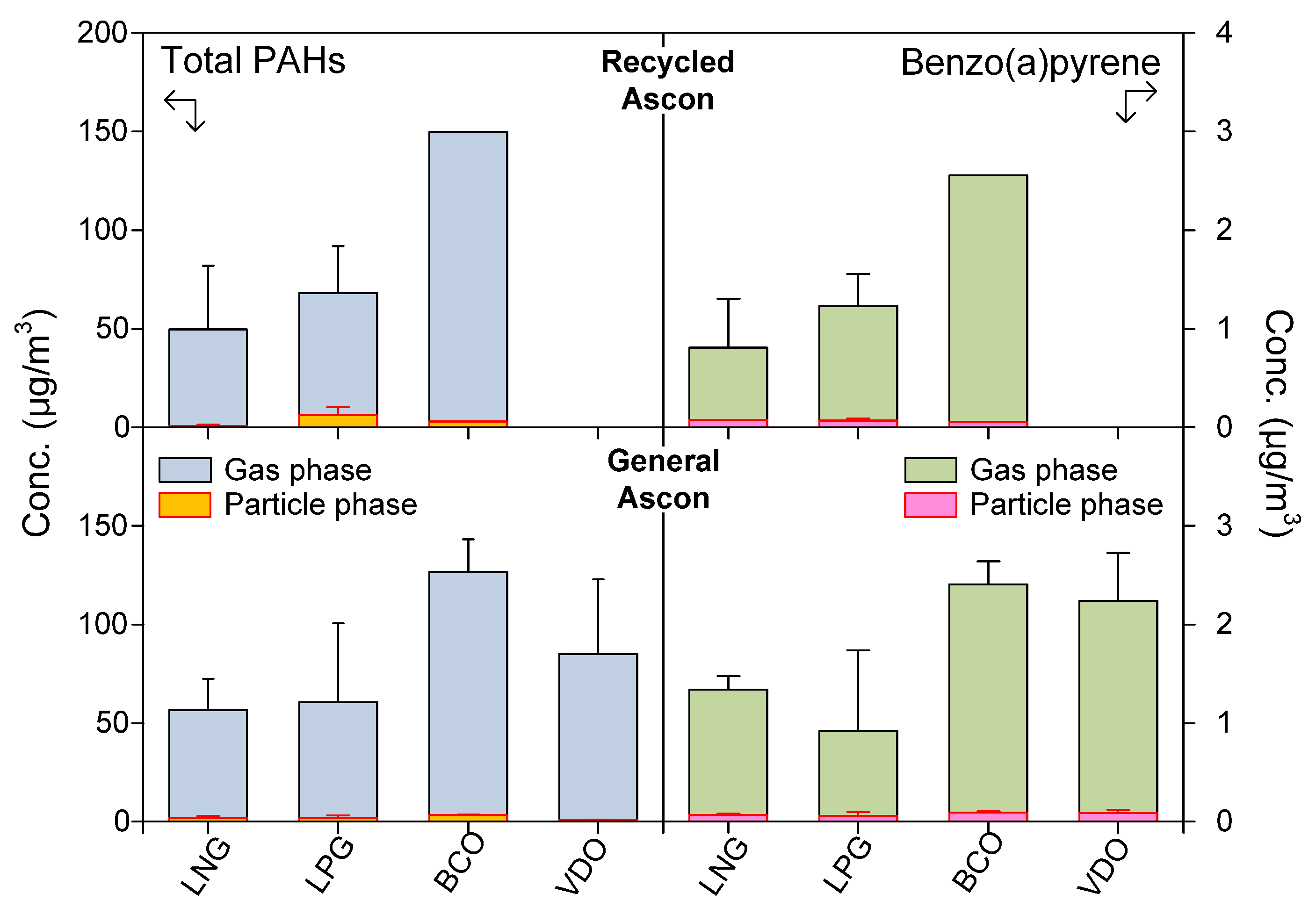
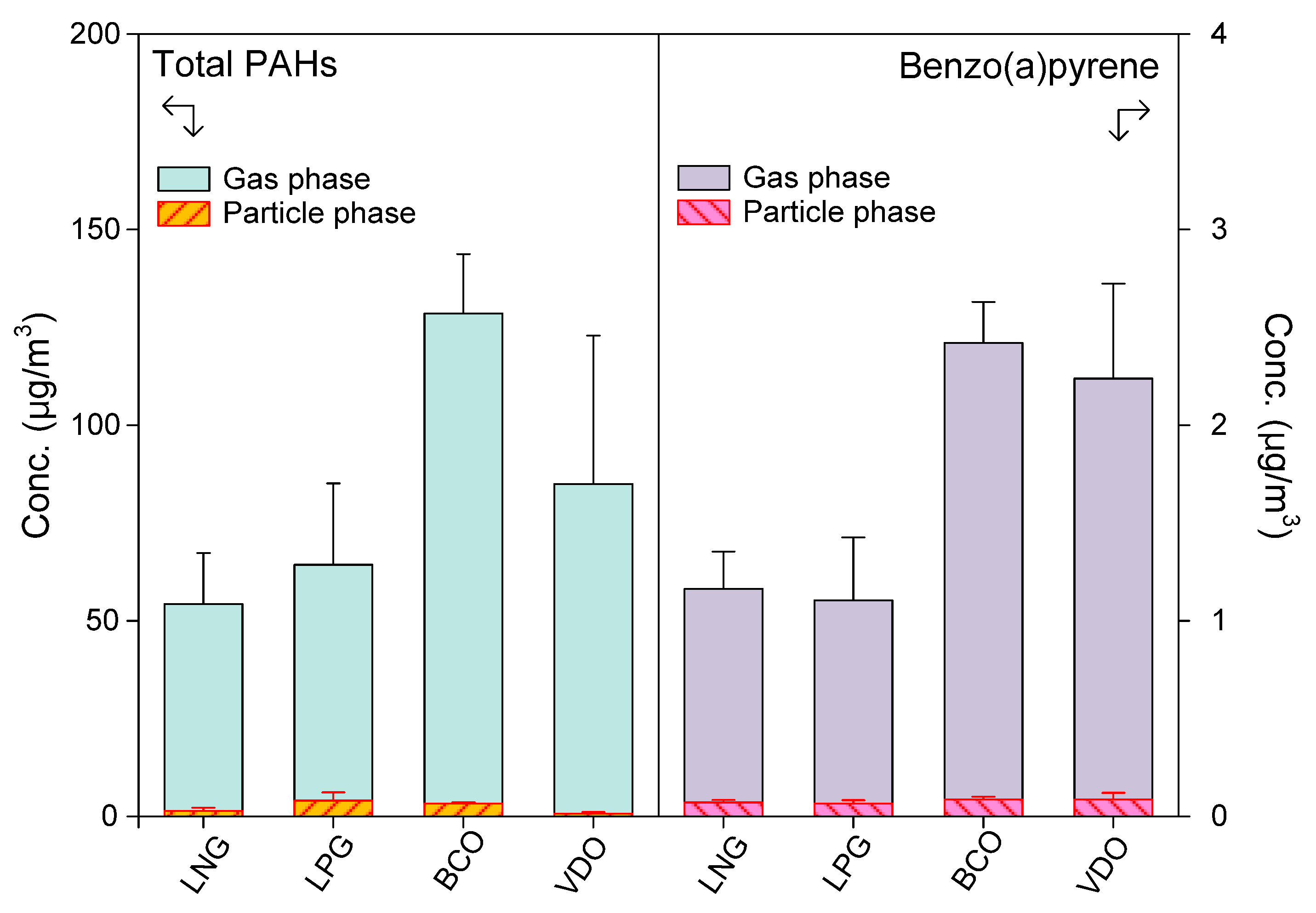
| Ascon Production Type | Number | |
|---|---|---|
| Recycled ascon | LNG | 3 |
| LPG | 3 | |
| BCO | 1 | |
| General ascon | LNG | 7 |
| LPG | 3 | |
| BCO | 10 | |
| VDO | 2 | |
| No. | Compounds | No. | Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Naphthalene | 17 | Benzo(j,k)fluoranthene |
| 2 | Biphenyl | 18 | Benzo(a)fluoranthene |
| 3 | Acenaphthylene | 19 | Benzo(e)pyrene |
| 4 | Acenaphthene | 20 | Benzo(a)pyrene |
| 5 | Fluorene | 21 | Perylene |
| 6 | Dibenzothiophene | 22 | Dibenz(a,h)anthracene |
| 7 | Phenanthrene | 23 | Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene |
| 8 | Anthracene | 24 | Dibenz(a,c)anthracene |
| 9 | 4H-Cyclopenta(def)phenanthrene | 25 | Benzo(b)chrysene |
| 10 | Fluoranthene | 26 | Dibenz(a,j)anthracene |
| 11 | Pyrene | 27 | Benzo(ghi)perylene |
| 12 | Benzo(c)phenanthrene | 28 | Anthanthrene |
| 13 | Benz(a)anthracene | 29 | Picene |
| 14 | Chrysene | 30 | Coronene |
| 15 | Triphenylene | 31 | Dibenzo(a,e)pyrene |
| 16 | Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 32 | Dibenzo(b,k)fluoranthene |
| Parameter | Condition |
|---|---|
| Detector | MS (Agilent 5973N, Agilent technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) |
| Column | J&W HP-5 (30 m × 0.32 mm× 0.25 µm) |
| Column flow | 1.5 mL/min |
| Auto Injector | G4513A |
| Purge flow | He (99.999%), 15.0 mL/min |
| Inlet temperature | 280 °C |
| GC temperature program | 60 °C (5 min) → 10 °C/min → 200 °C (5 min) → 10 °C/min → 200 °C (5 min) → 310 °C (10 min) → 320 °C (5 min) |
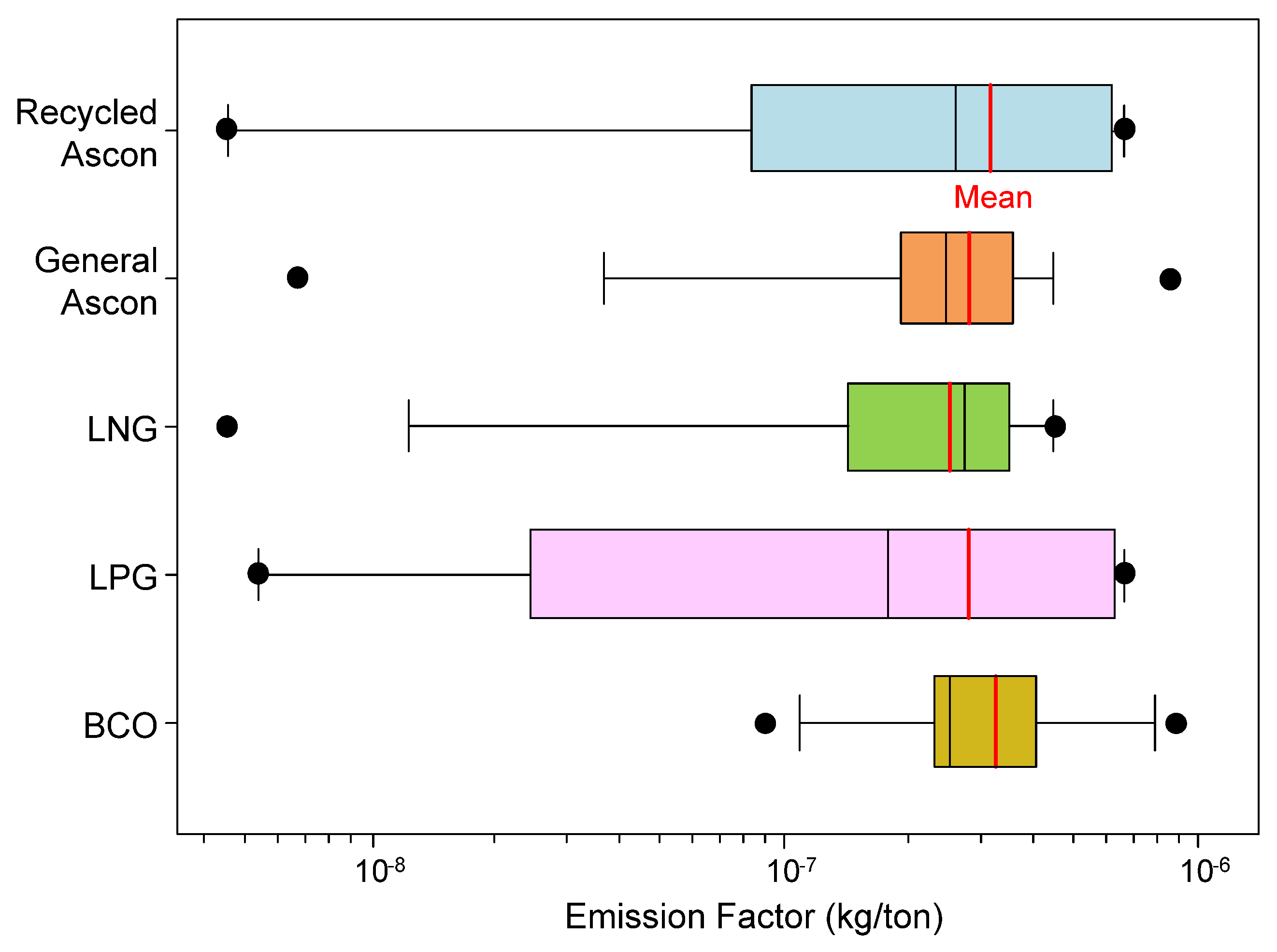
| Ascon Production Type | Minimum | Median | Mean | Maximum | Standard Deviation | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Ascon | 4.45 × 10−9 | 2.59 × 10−7 | 3.14 × 10−7 | 6.63 × 10−7 | 2.42 × 10−7 | 7 |
| General Ascon | 5.34 × 10−9 | 2.63 × 10−7 | 3.03 × 10−7 | 8.78 × 10−7 | 1.97 × 10−7 | 22 |
| LNG | 4.45 × 10−9 | 2.73 × 10−7 | 2.51 × 10−7 | 4.53 × 10−7 | 1.36 × 10−7 | 10 |
| LPG | 5.34 × 10−9 | 1.78 × 10−7 | 2.79 × 10−7 | 6.63 × 10−7 | 2.91 × 10−7 | 6 |
| BCO | 8.97 × 10−8 | 2.51 × 10−7 | 3.26 × 10−7 | 8.78 × 10−7 | 2.08 × 10−7 | 11 |
| Area | Number of Emission Sources (ea) | BaP | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul/Gyeonggi/Incheon | 72 | 0.00203 | 25.4 |
| Busan/Ulsan/Gyeongnam | 77 | 0.00100 | 12.5 |
| Daegu/Gyeongbuk | 82 | 0.00096 | 12.0 |
| Gwangju/Jeonnam | 58 | 0.00104 | 13.0 |
| Daejeon/Sejong/Chungnam | 68 | 0.00109 | 13.6 |
| Gangwon | 55 | 0.00061 | 7.6 |
| Chungbuk | 39 | 0.00056 | 7.0 |
| Jeonbuk | 48 | 0.00048 | 6.0 |
| Jeju | 16 | 0.00022 | 2.8 |
| Sum | 515 | 0.00800 | 100.0 |
| Ascon Facility | Stack Specifications | BaP Concentration (ng/m3) | BaP Emission * (g/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exhaust Gas Quantity (m3/min) | Temperature (°C) | Stack Diameter (m) | Stack Height (m) | |||
| A | 222.4 | 109.0 | 1.40 | 10 | 2071 | 7.67 × 10−6 |
| B | 395.3 | 61.3 | 1.10 | 12 | 1754 | 1.16 × 10−5 |
| C | 398.0 | 95.8 | 1.50 | 20 | 1401 | 8.64 × 10−6 |
| D | 513.2 | 99.1 | 1.40 | 13 | 1422 | 1.22 × 10−5 |
| E | 255.2 | 62.0 | 1.44 | 18 | 1829 | 7.78 × 10−6 |
| F | 100.5 | 82.0 | 1.45 | 15 | 1776 | 2.97 × 10−6 |
| Ascon Company | BaP Concentration Within 500 m Radius (ng/m3) | BaP Concentration Between 500 and 1000 m Radius (ng/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 0.370 | 0.073 |
| B | 0.488 | 0.192 |
| C | 0.209 | 0.074 |
| D | 0.218 | 0.142 |
| E | 0.407 | 0.156 |
| F | 0.361 | 0.072 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil, H.N.; Gong, B.; Kang, D.I.; Jo, H.; Kim, K.; Jeong, J.E. Emission Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Asphalt Concrete Manufacturing Facilities in South Korea. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091006
Gil HN, Gong B, Kang DI, Jo H, Kim K, Jeong JE. Emission Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Asphalt Concrete Manufacturing Facilities in South Korea. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(9):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil, Han Nui, Buju Gong, Dae Il Kang, Heeji Jo, Keehong Kim, and Ji Eun Jeong. 2025. "Emission Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Asphalt Concrete Manufacturing Facilities in South Korea" Atmosphere 16, no. 9: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091006
APA StyleGil, H. N., Gong, B., Kang, D. I., Jo, H., Kim, K., & Jeong, J. E. (2025). Emission Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Asphalt Concrete Manufacturing Facilities in South Korea. Atmosphere, 16(9), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091006





