Ionospheric Response to the Extreme Geomagnetic Storm of 10–11 May 2024 Based on Total Electron Content Observations in the Central Asian and East Asian Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
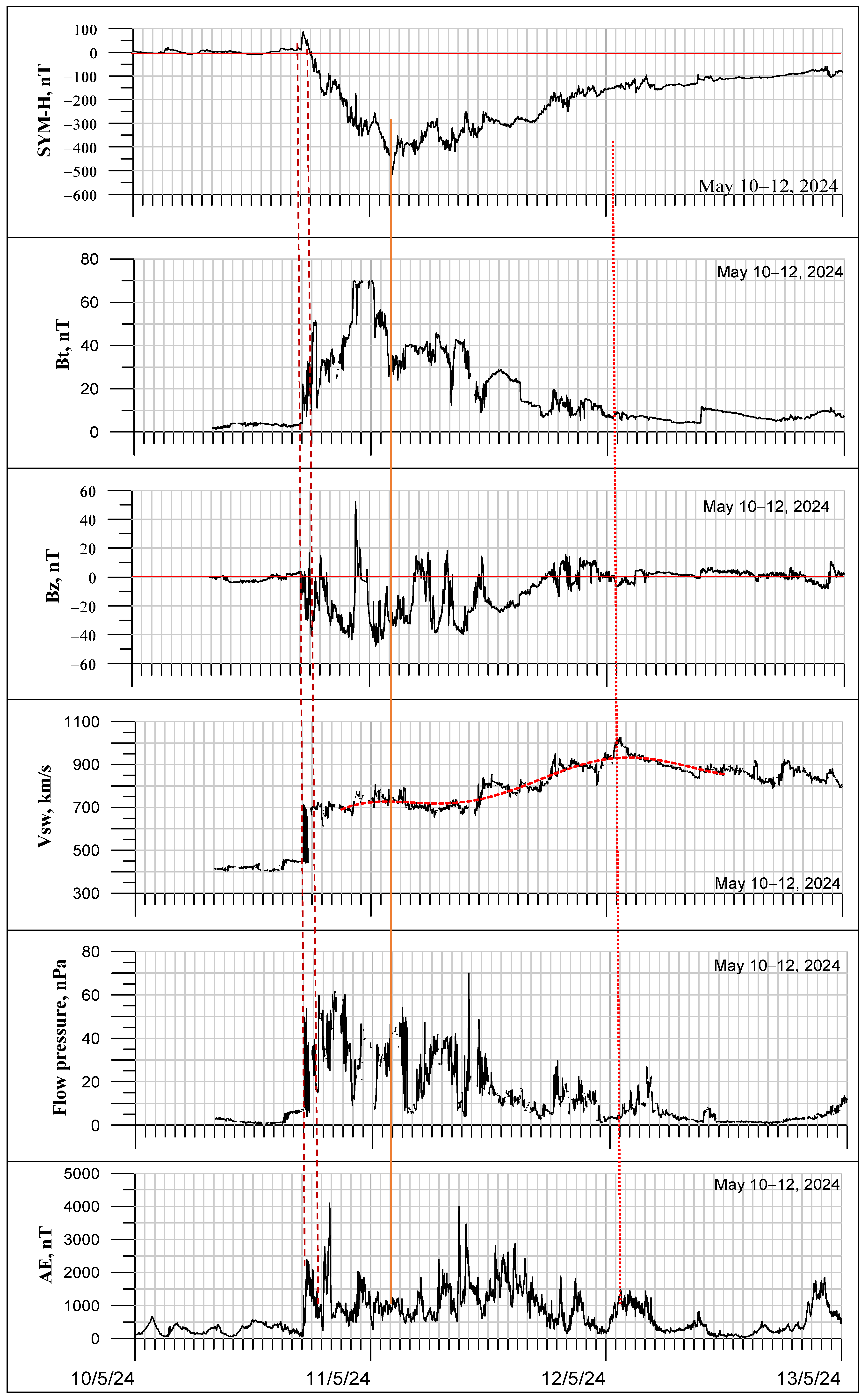
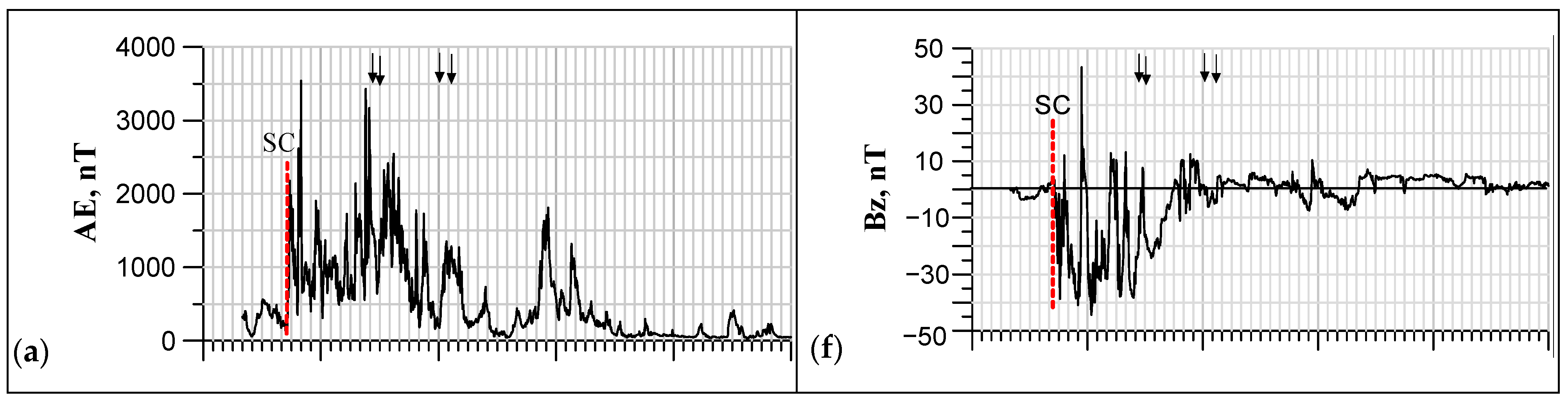
3.1. Solar Wind Parameters and Geomagnetic Indices
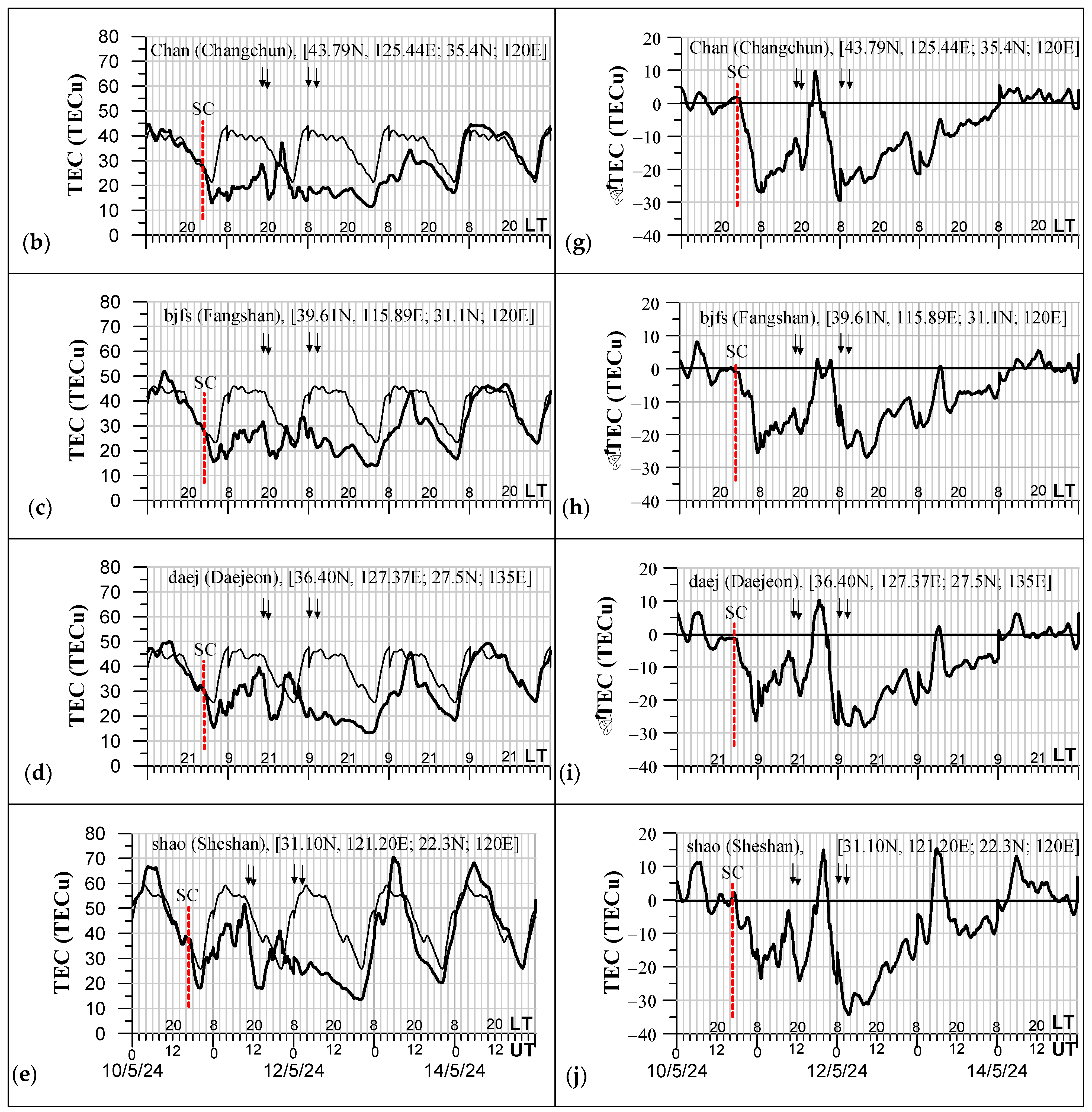
3.2. Observed Effects in the Ionosphere
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gopalswamy, N.; Yashiro, S.; Michalek, G.; Xie, H.; Lepping, R.P.; Howard, R.A. Solar source of the largest geomagnetic storm of cycle 23. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L12S09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglis, I.A.; Chang, L.C.; Dasso, S.; Gopalswamy, N.; Khabarova, O.V.; Kilpua, E.; Lopez, R.; Marsh, D.; Matthes, K.; Nandy, D.; et al. Predictability of variable solar–terrestrial coupling. Ann. Geophys. 2021, 39, 1013–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.-L.; Boteler, D.H.; Trichtchenko, L. Case studies of space weather events from their launching on the Sun to their impacts on power systems on the Earth. Ann. Geophys. 2002, 20, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzerotti, L.J. Space weather effects on technologies. In Space Weather; Song, P., Singer, H.J., Siscoe, G.L., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph Series 125; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Basu, S.; Makela, J.J.; MacKenzie, E.; Doherty, P.; Wright, J.W.; Rich, F.; Keskinen, M.J.; Sheehan, R.E.; Coster, A.J. Large magnetic storm-induced nighttime ionospheric flows at midlatitudes and their impacts on GPS-based navigation systems. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, A00A06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Demyanov, V.V.; Kondakova, T.N. Degradation of GPS performance in geomagnetically disturbed conditions. GPS Solut. 2003, 7, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, L. GIC observations and studies in the Hydro-Québec power system. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunt, C.T.; Coetzee, G. Transformer failures in regions incorrectly considered to have low GIC-risk. In Proceedings of the IEEE Lausanne Power Tech, Lausanne, Switzerland, 1–5 July 2007; pp. 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.; Li, X.; Luo, B.; Li, R.; Zhang, B.; Pham, K.; Ren, D.; Chen, X.; Lei, J.; Wang, Y. Unveiling the Space Weather during the Starlink Satellites Destruction Event on 4 February 2022. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Kil, H.; Choi, B.K.; Hong, J.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, D.H.; Roh, K.M.; Yoo, S.M.; et al. Ionospheric Responses to the May 2024 G5 Geomagnetic Storm Over Korea, Captured by the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI) Near Real-Time Ionospheric Monitoring System. J. Space Technol. Appl. 2024, 4, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.S.; Correira, J.; Lumpe, J.D.; Eastes, R.W.; Gan, Q.; Laskar, F.I.; Aryal, S.; Wang, W.; Burns, A.G.; Beland, S.; et al. GOLD observations of the thermospheric response to the 10–12 May 2024 Gannon superstorm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL110506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulasi Ram, S.; Veenadhari, B.; Dimri, A.P.; Bulusu, J.; Bagiya, M.; Gurubaran, S.; Parihar, N.; Remya, B.; Seemala, G.; Singh, R.; et al. Super-intense geomagnetic storm on 10–11 May 2024: Possible mechanisms and impacts. Space Weather 2024, 22, e2024SW004121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Scipion, D.E.; Kuyeng, K.; Condor, P.; De La Jara, C.; Velasquez, J.P.; Flores, R.; Ivan, E.; Souza, J.R.; Migliozzi, M. Ionospheric disturbances observed over the Peruvian sector during the Mother’s Day Storm (G5-level) on 10–12 May 2024. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2024JA033003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojilova, R.; Mukhtarov, P.; Pancheva, D. Global Ionospheric Response During Extreme Geomagnetic Storm in May 2024. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.-S.; Lee, C.; Lee, D.-Y.; Ham, Y.-B.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.; Miyashita, Y.; Yang, T.; et al. Observational overview of the May 2024 g5-level geo-magnetic storm: From solar eruptions to terrestrial consequences. J. Astron. Space Sci. 2024, 41, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Trivedi, R.; Jain, S.; Choudhary, R.K. Effects of the Super Intense Geomagnetic Storm on 10-11 May, 2024 on Total Electron Content at Bhopal. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierrard, V.; Verhulst, T.G.W.; Chevalier, J.-M.; Bergeot, N.; Winant, A. Effects of the Geomagnetic Superstorms of 10–11 May 2024 and 7–11 October 2024 on the Ionosphere and Plasmasphere. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, D.K.; Martinis, C.R.; Daniell, R.E.; Eastes, R.W.; Wang, W.; McClintock, W.E.; Michell, R.G.; England, S. GOLD observations of the merging of the Southern Crest of the equatorial ionization anomaly and aurora during the 10 and 11 May 2024 Mother’s Day super geomagnetic storm. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, B.; Yu, T.; Hao, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, G.; He, M.; Mao, T.; Li, G.; Ren, Z. East–west difference in the ionospheric response during the recovery phase of May 2024 super geomagnetic storm over the East Asian. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2024JA033170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, F.; Erol, C.B.; Arikan, O. Regularized estimation of vertical total electron content from Global Positioning System data. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2003, 108, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, F.; Erol, C.B.; Arikan, O. Regularized estimation of vertical total electron content from GPS data for a desired time period. Radio Sci. 2004, 39, RS6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayir, H.; Arikan, F.; Arikan, O.; Erol, C.B. Total electron content estimation with Reg-Est. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, A11312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, F.; Nayir, H.; Sezen, U.; Arikan, O. Estimation of single station interfrequency receiver bias using GPS-TEC. Radio Sci. 2008, 43, RS4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezen, U.; Arikan, F.; Arikan, O.; Ugurlu, O.; Sadeghimorad, A. Online, automatic, near-real time estimation of GPS-TEC: IONOLAB-TEC. Space Weather 2013, 11, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, C.A.; Prölss, G.W. Classification and mean behavior of magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 14209–14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, H.; Ebihara, Y.; Mishev, A.; Koldobskiy, S.; Kusano, K.; Isobe, H.; Bechet, S.; Yashiro, S.; Iwai, K.; Shinbori, A.; et al. The Solar and Geomagnetic Storms in 2024 May: A Flash Data Report. Astrophys. J. 2025, 979, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prölss, G. Ionospheric F-region storms. In Handbook of Atmospheric Electrodynamics; Volland, H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 195–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonsanto, M.J. Ionospheric Storms—A Review. Space Sci. Rev. 1999, 88, 563–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.D.; Lastovicka, J. Effects of Geomagnetic Storms on the Ionosphere and Atmosphere. Int. J. Geomagn. Aeron. 2001, 2, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Mendillo, M. Storms in the ionosphere: Patterns and processes for total electron content. Rev. Geophys. 2006, 44, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prölss, G.W. Ionospheric Storms at Mid-Latitude: A Short Review. In Midlatitude Ionospheric Dynamics and Disturbances; Kintner, P.M., Jr., Coster, A.J., Fuller-Rowell, T., Mannucci, A.J., Mendillo, M., Heelis, R., Eds.; Geophysical Monograph Series 181; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.D. Ionospheric F-region response to geomagnetic disturbances. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 52, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, A.V.; Foster, J.C. Daytime thermosphere above Millstone Hill during severe geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17275–17282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, A.V.; Förster, M. Day-to-day thermosphere parameter variation as deduced from Millstone Hill incoherent scatter radar observations during March 16–22, 1990 magnetic storm period. Ann. Geophys. 1997, 15, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Station Code (Station Name, Location) | Geog. Lat. (°N) | Geog. Long. (°E) | Geom. Lat. (°N) | Time Zone (°E) | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chum (Chumish, Kazakhstan) | 42.99 | 74.75 | 35.3 | UTC+5 | CAR |
| Chan (Changchun, China) | 43.79 | 125.44 | 35.4 | UTC+8 | EAR |
| Bjfs (Fangshan, China) | 39.61 | 115.89 | 31.1 | UTC+8 | EAR |
| Daej (Daejeon, Korea) | 36.40 | 127.37 | 27.5 | UTC+9 | EAR |
| Shao (Sheshan, China) | 31.10 | 121.20 | 22.3 | UTC+8 | EAR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordiyenko, G.; Arikan, F.; Litvinov, Y.; Zhiganbaev, M. Ionospheric Response to the Extreme Geomagnetic Storm of 10–11 May 2024 Based on Total Electron Content Observations in the Central Asian and East Asian Regions. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070854
Gordiyenko G, Arikan F, Litvinov Y, Zhiganbaev M. Ionospheric Response to the Extreme Geomagnetic Storm of 10–11 May 2024 Based on Total Electron Content Observations in the Central Asian and East Asian Regions. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070854
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordiyenko, Galina, Feza Arikan, Yuriy Litvinov, and Murat Zhiganbaev. 2025. "Ionospheric Response to the Extreme Geomagnetic Storm of 10–11 May 2024 Based on Total Electron Content Observations in the Central Asian and East Asian Regions" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070854
APA StyleGordiyenko, G., Arikan, F., Litvinov, Y., & Zhiganbaev, M. (2025). Ionospheric Response to the Extreme Geomagnetic Storm of 10–11 May 2024 Based on Total Electron Content Observations in the Central Asian and East Asian Regions. Atmosphere, 16(7), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070854






