Analysis of the Influencing Factors and Sources of Brown Carbon Light Absorption in a Typical Megacity of the Yangtze River Delta, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site and Instrumentation
2.2. Calculation of Optical Parameters
2.3. Primary and Secondary OC
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. PSCF Model
2.4.2. PMF Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seasonal Variation in BrC Absorption Parameters
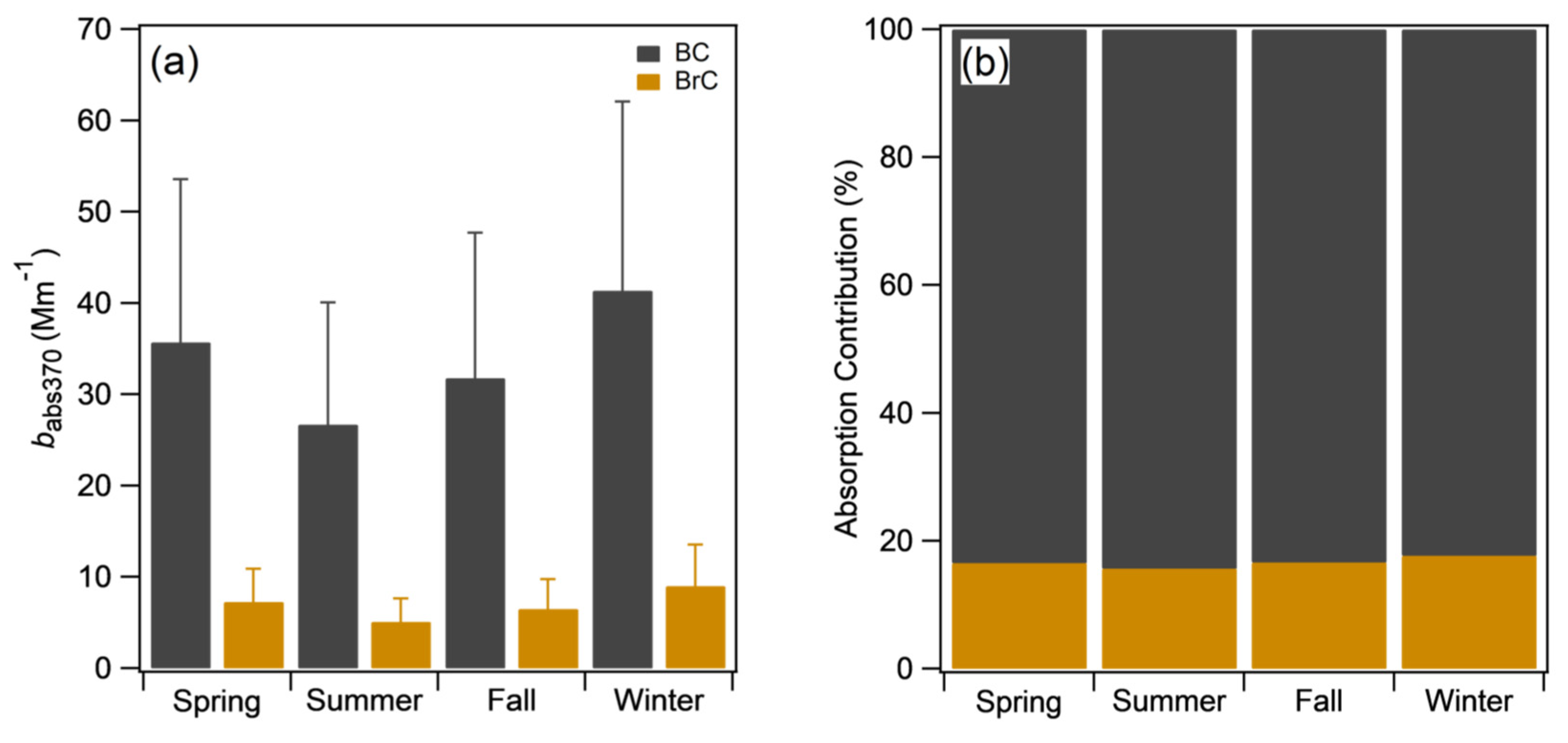
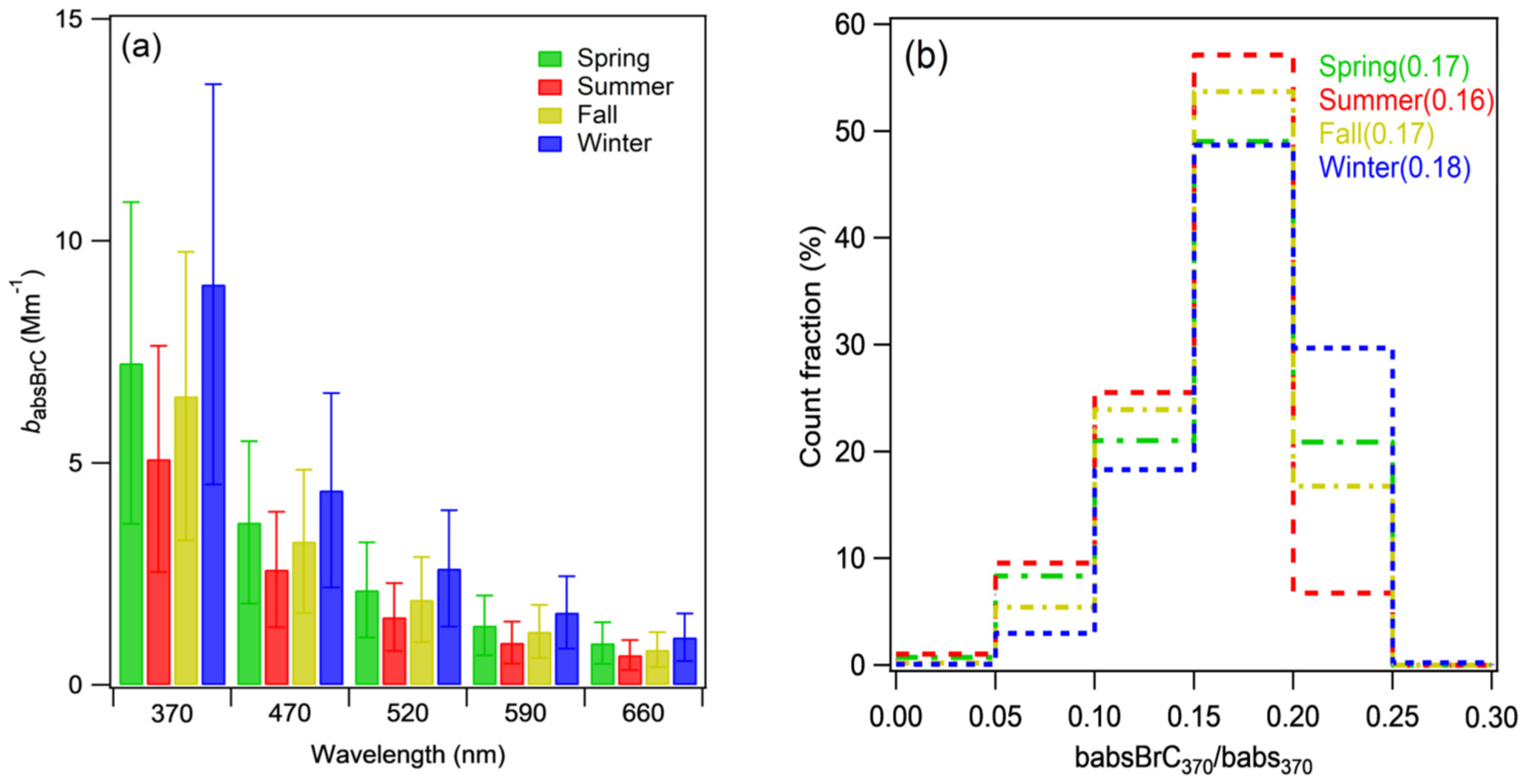
3.1.1. BrC Absorption Coefficient
3.1.2. Absorption Ångström Exponent (AAE)
3.1.3. Mass Absorption Cross-Section (MAC)
3.2. The Factors Affecting the Light Absorption of BrC
3.2.1. The Effect of PM2.5 Concentration on the Light Absorption of BrC
3.2.2. The Effect of Photochemistry on the Light Absorption of BrC
3.3. Source Apportionment of BrC
3.3.1. PMF Analysis
3.3.2. PSCF Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2004, 109, D21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencsér, A. Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.T.L.; Crozier, P.A.; Anderson, J.R. Brown carbon spheres in East Asian outflow and their optical properties. Science 2008, 321, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, R. From measurements to models: Toward accurate representation of brown carbon in climate calculations. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Arola, A.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H.; Andrade, M.; Labow, G.; Eck, T.F.; Li, Z.; Dickerson, R.R.; et al. Impacts of brown carbon from biomass burning on surface UV and ozone photochemistry in the Amazon Basin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bergin, M.; Guo, H.; King, L.; Kotra, N.; Edgerton, E.; Weber, R. Size-resolved measurements of brown carbon in water and methanol extracts and estimates of their contribution to ambient fine-particle light absorption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12389–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Fan, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Tao, J.; Chen, L.; Song, S. Light absorption properties and source contributions of black and brown carbon in Guangxi, southern China. Atmos. Res. 2024, 302, 107317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, F.; Zhou, X.; Yu, R.; Lü, C.; He, J. Water-soluble brown carbon in atmospheric aerosols from the resource-dependent cities: Optical properties, chemical compositions and sources. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, K.b.; Du, Z.y.; Engling, G.; Liu, J.m.; Ma, Y.l.; Zheng, M.; Weber, R.J. The characteristics of brown carbon aerosol during winter in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, R.; Shamjad, P.; Thamban, N.; Tripathi, S.; Rastogi, N. Temporal characteristics of brown carbon over the central Indo-Gangetic Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6765–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zheng, M.; Bosch, C.; Andersson, A.; Desyaterik, Y.; Sullivan, A.P.; Collett, J.L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; He, K. Important fossil source contribution to brown carbon in Beijing during winter. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Wei, S.; Zhu, M.; Song, J.; Peng, P. Comprehensive characterization of humic-like substances in smoke PM2.5 emitted from the combustion of biomass materials and fossil fuels. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13321–13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitzler, E.G.; Gerrebos, N.G.; Carter, T.S.; Huang, Y.; Heald, C.L.; Bertram, A.K.; Abbatt, J.P. Rate of atmospheric brown carbon whitening governed by environmental conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2205610119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilardoni, S.; Massoli, P.; Paglione, M.; Giulianelli, L.; Carbone, C.; Rinaldi, M.; Decesari, S.; Sandrini, S.; Costabile, F.; Gobbi, G.P. Direct observation of aqueous secondary organic aerosol from biomass-burning emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10013–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C. Aqueous production of secondary organic aerosol from fossil-fuel emissions in winter Beijing haze. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022179118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W. Characterizing water-soluble brown carbon in fine particles in four typical cities in northwestern China during wintertime: Integrating optical properties with chemical processes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 12609–12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhong, G.; Zhu, S.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G. Dual carbon isotope-based source apportionment and light absorption properties of water-soluble organic carbon in PM2.5 over China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.H.; Surratt, J.D.; Weber, R.J. Sources, composition and absorption Ångstrom exponent of light-absorbing organic components in aerosol extracts from the Los Angeles Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3685–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y. Light absorption properties of brown carbon (BrC) in autumn and winter in Beijing: Composition, formation and contribution of nitrated aromatic compounds. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, R.J.; Yang, L.; Guo, J.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J.; Wang, T.; Ni, H.; Han, Y.; Li, Y. Characterization of the light-absorbing properties, chromophore composition and sources of brown carbon aerosol in Xi’an, northwestern China. Atmos. Chem. 2020, 20, 5129–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhu, C.; Cao, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, S. Methanol extracted brown carbon in PM2.5 Over Xi’an, China: Seasonal variation of optical properties and sources identification. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.F.; Huang, X.F.; Cao, L.M.; Cui, J.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, C.N.; Lan, Z.J.; He, L.Y. Light absorption of brown carbon aerosol in the PRD region of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, X.; Hays, M.D.; Lewandowski, M.; Offenberg, J.; Kleindienst, T.E.; Holder, A.L. Light absorption of secondary organic aerosol: Composition and contribution of nitroaromatic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11607–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, B.; Lei, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, C.; Zhou, M.; Miao, Q.; Wei, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. Characteristics, formation, and sources of PM2.5 in 2020 in Suzhou, Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Au, W.C.; Law, H.; Lam, C.H.; Nah, T. Formation and evolution of brown carbon during aqueous-phase nitrate-mediated photooxidation of guaiacol and 5-nitroguaiacol. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 254, 118401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ge, X.; Chen, H.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Bao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M. Seasonal light absorption properties of water-soluble brown carbon in atmospheric fine particles in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Son, J.H.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, J. Characterizing atmospheric brown carbon and its emission sources during wintertime in Shanghai, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.B.; Lü, S.J.; Wang, F.L.; Du, W.; Liu, S.J.; Ding, Z.J.; Wang, G.H. Pollution characteristics and sources of wintertime atmospheric brown carbon at a background site of the Yangtze River Delta Region in China. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, T.; Kong, S.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.; Wei, P.; Wei, C. Spatial distribution and sources of winter black carbon and brown carbon in six Chinese megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, R.; Ma, Y.; He, K. Characteristics of aerosol pollution during heavy haze events in Suzhou, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7357–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, T.A.; Ramachandran, S. Black carbon aerosol mass concentration, absorption and single scattering albedo from single and dual spot aethalometers: Radiative implications. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 119, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingartner, E.; Saathoff, H.; Schnaiter, M.; Streit, N.; Bitnar, B.; Baltensperger, U. Absorption of light by soot particles: Determination of the absorption coefficient by means of aethalometers. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yue, X.; Song, M.; Zhang, G.; Ming, J. Black carbon: The concentration and sources study at the Nam Co Lake, the Tibetan Plateau from 2015 to 2016. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandradewi, J.; Prévôt, A.S.; Szidat, S.; Perron, N.; Alfarra, M.R.; Lanz, V.A.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. Using aerosol light absorption measurements for the quantitative determination of wood burning and traffic emission contributions to particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3316–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Ran, W.; Han, Y.; Prévôt, A.S.; Cao, J. Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on the optical properties and radiative effects of urban brown carbon aerosol. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pani, S.K.; Lin, N.H.; Griffith, S.M.; Chantara, S.; Lee, C.T.; Thepnuan, D.; Tsai, Y.I. Brown carbon light absorption over an urban environment in northern peninsular Southeast Asia. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Tang, G.; Chen, P.; Du, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Vertical characterization of aerosol optical properties and brown carbon in winter in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.M.; Tan, H.B.; Li, Y.J.; Li, Z.J.; Schurman, M.I.; Liu, L.; Wu, C.; Chan, C.K. Chemical characteristics of brown carbon in atmospheric particles at a suburban site near Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16409–16418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.Z. Estimation and uncertainty analysis of secondary organic carbon using 1 year of hourly organic and elemental carbon data. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2019, 124, 2774–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Shen, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Ma, Y.; Wu, X.; Qin, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, R. Aerosols chemical composition, light extinction, and source apportionment near a desert margin city, Yulin, China. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.S.; Qu, Y.; Dai, W.T.; Zhang, N.N.; Zhang, Z.S.; Cao, J.J. Nonnegligible biogenic organic aerosol and the correlations with light absorption at three high altitude locations in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 291, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Fu, S.; Qu, L.; Ji, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. PMF and PSCF based source apportionment of PM2.5 at a regional background site in North China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tan, H.; Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Qin, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Cai, M.; Ma, Y. Light absorption properties and potential sources of particulate brown carbon in the Pearl River Delta region of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11669–11685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Su, D.; Mi, K.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H. Spatiotemporal distribution, light absorption characteristics, and source apportionments of black and brown carbon in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 919, 170796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lack, D.; Langridge, J. On the attribution of black and brown carbon light absorption using the Ångström exponent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10535–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaiter, M.; Wurm, G. Experiments on light scattering and extinction by small, micrometer-sized aggregates of spheres. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yan, F.; Kang, S.; Chen, P.; Hu, Z.; Gao, S.; Qu, B.; Sillanpää, M. Light absorption characteristics of carbonaceous aerosols in two remote stations of the southern fringe of the Tibetan Plateau, China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Noble, C.A.; Prather, K.A. Size and chemical characterization of individual particles resulting from biomass burning of local Southern California species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3068–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Maung, M.W.; Win, M.S.; Feng, J.; Yao, X. Carbonaceous aerosol and inorganic ions of PM2.5 in Yangon and Mandalay of Myanmar: Seasonal and spatial variations in composition and sources. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wang, F.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Lu, P.; Guo, Z. Carbonaceous aerosols in urban Chongqing, China: Seasonal variation, source apportionment, and long-range transport. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, S.; Li, J.; Lang, J.; Wen, W.; Yang, X.; Tian, L. Source apportionment and seasonal variation of PM2.5 carbonaceous aerosol in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thepnuan, D.; Chantara, S.; Lee, C.T.; Lin, N.H.; Tsai, Y.I. Molecular markers for biomass burning associated with the characterization of PM2.5 and component sources during dry season haze episodes in Upper South East Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 658, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ge, X.; Aruffo, E. Analysis of the Influencing Factors and Sources of Brown Carbon Light Absorption in a Typical Megacity of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040421
Xu S, Wang J, Li Y, Zhang N, Ge X, Aruffo E. Analysis of the Influencing Factors and Sources of Brown Carbon Light Absorption in a Typical Megacity of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040421
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shanshu, Junfeng Wang, Yue’e Li, Ning Zhang, Xinlei Ge, and Eleonora Aruffo. 2024. "Analysis of the Influencing Factors and Sources of Brown Carbon Light Absorption in a Typical Megacity of the Yangtze River Delta, China" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040421
APA StyleXu, S., Wang, J., Li, Y., Zhang, N., Ge, X., & Aruffo, E. (2024). Analysis of the Influencing Factors and Sources of Brown Carbon Light Absorption in a Typical Megacity of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmosphere, 15(4), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040421






