Modification and Validation of the Soil–Snow Module in the INM RAS Climate Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. INM-CM Modification
2.1. Initial Version of INM-CM Soil–Snow Module
2.2. Description of Modified Snow Module in INM-CM
3. Verification of INM-CM Soil–Snow Module
3.1. Local Simulations
3.2. Global Simulations
4. Results
4.1. Local Simulations
4.2. Global Simulations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| INM RAS | Marchuk Institute of Numerical Mathematics of the Russian Academy of Science |
| INM-CM | family of global climate models developed at INM RAS |
| SWE | snow water equivalent |
| NRMSE | root-mean-square error normalized by the standard deviation |
References
- Flanner, M.G.; Shell, K.M.; Barlage, M.; Perovich, D.K.; Tschudi, M.A. Radiative forcing and albedo feedback from the Northern Hemisphere cryosphere between 1979 and 2008. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Rind, D. The Effect of Snow Cover on the Climate. J. Clim. 1991, 4, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Entekhabi, D. Eurasian snow cover variability and northern hemisphere climate predictability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Barlow, M.; Kushner, P.J.; Saito, K. Stratosphere–Troposphere Coupling and Links with Eurasian Land Surface Variability. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5335–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hurk, B.; Kim, H.; Krinner, G.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Derksen, C.; Oki, T.; Douville, H.; Colin, J.; Ducharne, A.; Cheruy, F.; et al. LS3MIP (v1.0) contribution to CMIP6: The Land Surface, Snow and Soil moisture Model Intercomparison Project—Aims, setup and expected outcome. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 2809–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinner, G.; Derksen, C.; Essery, R.; Flanner, M.; Hagemann, S.; Clark, M.; Hall, A.; Rott, H.; Brutel-Vuilmet, C.; Kim, H.; et al. ESM-SnowMIP: Assessing snow models and quantifying snow-related climate feedbacks. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 5027–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudryk, L.; Santolaria-Otín, M.; Krinner, G.; Ménégoz, M.; Derksen, C.; Brutel-Vuilmet, C.; Brady, M.; Essery, R. Historical Northern Hemisphere snow cover trends and projected changes in the CMIP6 multi-model ensemble. Cryosphere 2020, 14, 2495–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volodin, E.M.; Mortikov, E.V.; Kostrykin, S.V.; Galin, V.Y.; Lykossov, V.N.; Gritsun, A.S.; Diansky, N.A.; Gusev, A.V.; Iakovlev, N.G.; Shestakova, A.A.; et al. Simulation of the modern climate using the INM-CM48 climate model. Russ. J. Numer. Anal. Math. Model. 2018, 33, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Min, S.K.; Zhang, X.; Sillmann, J.; Sandstad, M. Evaluation of the CMIP6 multi-model ensemble for climate extreme indices. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2020, 29, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volodin, E.; Lykossov, V. Parameterization of Heat and Moisture Transfer in the Soil-Vegetation System for Use in Atmospheric General Circulation Models: 1. Formulation and Simulations Based on Local Observational Data. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 1998, 34, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Volodina, E.E.; Bengtsson, L.; Lykossov, V. Parametrization of heat and water transfer through snowpack for simulation of seasonal variability of hydrological land parameters. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2000, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Volodin, E.M.; Gritsun, A.S. Simulation of Possible Future Climate Changes in the 21st Century in the INM-CM5 Climate Model. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2020, 56, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volodin, E.M. Possible Climate Change in Russia in the 21st Century Based on the INM-CM5-0 Climate Model. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2022, 47, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volodin, E.M. Simulation of Present-Day Climate with the INMCM60 Model. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2023, 59, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volodin, E.M.; Kostrykin, S.V. The aerosol module in the INM RAS climate model. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2016, 41, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, N.G. Reproduction of the large-scale state of water and sea ice in the Arctic Ocean in 1948–2002: Part 1. Numerical model. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2009, 45, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, Y.M.; Nasonova, O.N. The simulation of heat and water exchange at the land–atmosphere interface for the boreal grassland by the land-surface model SWAP. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 1893–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchment, L.S.; Demidov, V.N.; Motovilov, Y.G. Formirovanie rechnogo stoka: Fisiko-matematicheskie modeli (River Runoff Formation: Physically Based Models); Nauka: Moscow, Soviet Union, 1983. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Essery, R.; Morin, S.; Lejeune, Y.; B Ménard, C. A comparison of 1701 snow models using observations from an alpine site. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 55, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.A. A Point Energy and Mass Balance Model of a Snow Cover; NOAA Technical Report NWS 19; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, P.A.; MacKay, M.D.; Verseghy, D.L. Modified snow algorithms in the Canadian land surface scheme: Model runs and sensitivity analysis at three boreal forest stands. Atmosphere-Ocean 2006, 44, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, Y.; Dumont, M.; Panel, J.M.; Lafaysse, M.; Lapalus, P.; Le Gac, E.; Lesaffre, B.; Morin, S. 57 years (1960–2017) of snow and meteorological observations from a mid-altitude mountain site (Col de Porte, France, 1325 m of altitude). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reba, M.L.; Marks, D.; Seyfried, M.; Winstral, A.; Kumar, M.; Flerchinger, G. A long-term data set for hydrologic modeling in a snow-dominated mountain catchment. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W07702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwano, M.; Aoki, T.; Kuchiki, K.; Hosaka, M.; Kodama, Y. Snow Metamorphism and Albedo Process (SMAP) model for climate studies: Model validation using meteorological and snow impurity data measured at Sapporo, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117, F03008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, C.C.; Buck, K.A.; Raleigh, M.S.; Clark, M.P. Mountain system monitoring at Senator Beck Basin, San Juan Mountains, Colorado: A new integrative data source to develop and evaluate models of snow and hydrologic processes. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 1773–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essery, R.; Kontu, A.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Dumont, M.; Ménard, C.B. A 7-year dataset for driving and evaluating snow models at an Arctic site (Sodankylä, Finland). Geosci. Instrum. Methods Data Syst. 2016, 5, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, N. Weissfluhjoch Dataset for ESM-SnowMIP. 2017. Available online: https://envidat.ch/#/metadata/snowmip (accessed on 15 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Ménard, C.B.; Essery, R.; Barr, A.; Bartlett, P.; Derry, J.; Dumont, M.; Fierz, C.; Kim, H.; Kontu, A.; Lejeune, Y.; et al. Meteorological and evaluation datasets for snow modelling at 10 reference sites: Description of in situ and bias-corrected reanalysis data. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Barré, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.; Dominguez, J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. CAMS Global Reanalysis (EAC4) Monthly Averaged Fields. 2019. Available online: https://www.copernicus.eu/en/access-data/copernicus-services-catalogue/cams-global-reanalysis-eac4 (accessed on 30 September 2021).
- Mudryk, L.R.; Derksen, C. CanSISE Observation-Based Ensemble of Northern Hemisphere Terrestrial Snow Water Equivalent, Version 2. 2017. Available online: https://nsidc.org/data/nsidc-0668/versions/2 (accessed on 29 September 2021). [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.L. An observation-based formulation of snow cover fraction and its evaluation over large North American river basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.C.; Lawrence, D.M. A new fractional snow-covered area parameterization for the Community Land Model and its effect on the surface energy balance. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Hall, D.K.; Mote, T.L. PMEaSUREs Northern Hemisphere Terrestrial Snow Cover Extent Daily 25 km EASE-Grid 2.0, Version 1; NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014; Available online: https://nsidc.org/data/nsidc-0530/versions/1 (accessed on 10 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Menard, C.B.; Essery, R.; Krinner, G.; Arduini, G.; Bartlett, P.; Boone, A.; Brutel-Vuilmet, C.; Burke, E.; Cuntz, M.; Dai, Y.; et al. Scientific and Human Errors in a Snow Model Intercomparison. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, E61–E79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travova, S.V.; Stepanenko, V.M.; Medvedev, A.I.; Tolstykh, M.A.; Bogomolov, V.Y. Quality of Soil Simulation by the INM RAS–MSU Soil Scheme as a Part of the SL-AV Weather Prediction Model. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2022, 47, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Estilow, T.W.; NOAA Climate Data Record Program. NOAA Climate Data Record (CDR) of Northern Hemisphere (NH) Snow Cover Extent (SCE), Version 1; NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Asheville, NC, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/metadata/landing-page/bin/iso?id=gov.noaa.ncdc:C00756 (accessed on 30 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Arzhanov, M.M.; Demchenko, P.F.; Eliseev, A.V.; Mokhov, I.I. Simulation of characteristics of thermal and hydrologic soil regimes in equilibrium numerical experiments with a climate model of intermediate complexity. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2008, 44, 548–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, A.V.; Mokhov, I.I.; Arzhanov, M.M.; Demchenko, P.F.; Denisov, S.N. Interaction of the methane cycle and processes in wetland ecosystems in a climate model of intermediate complexity. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2008, 44, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanner, M.G.; Zender, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Rasch, P.J. Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, E. Investigation on Wet-Snow Metamorphism in Respect of Liquid-Water Content. Ann. Glaciol. 1989, 13, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenkov, A.Y.; Kostrykin, S.V. Estimation of Radiative Forcing from Snow Darkening with Black Carbon Using Climate Model Data. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2021, 57, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, C.; Essery, R. ESM-SnowMIP meteorological and evaluation datasets at ten reference sites (in situ and bias corrected reanalysis data). Pangaea 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenkov, A.; Volodin, E.; Kostrykin, S.; Tarasevich, M.; Vorobyeva, V. Modification and Verification of Soil-Snow Module of INM RAS Climate Model. 2023. Available online: https://b2share.eudat.eu (accessed on 15 December 2023). [CrossRef]

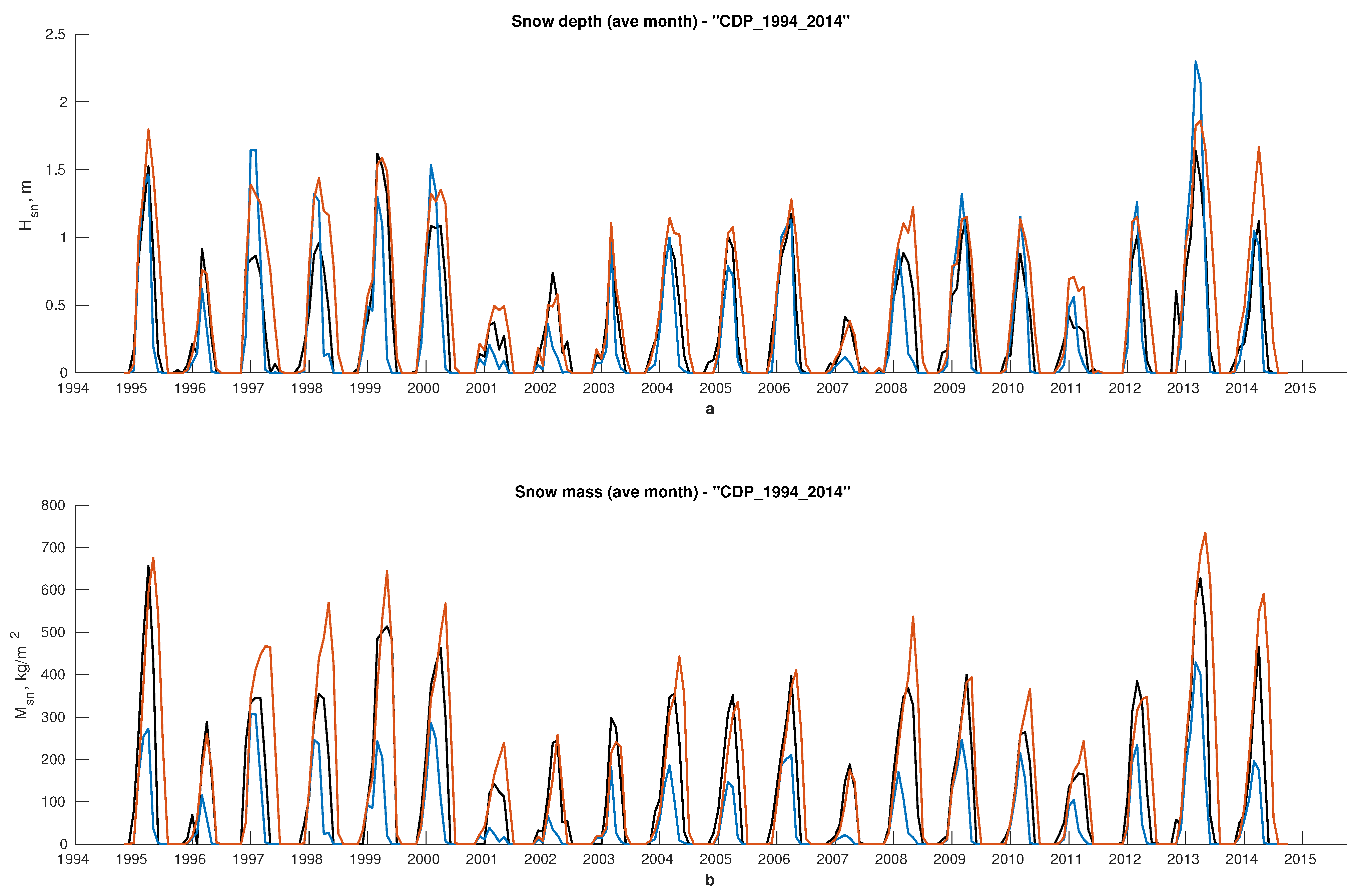
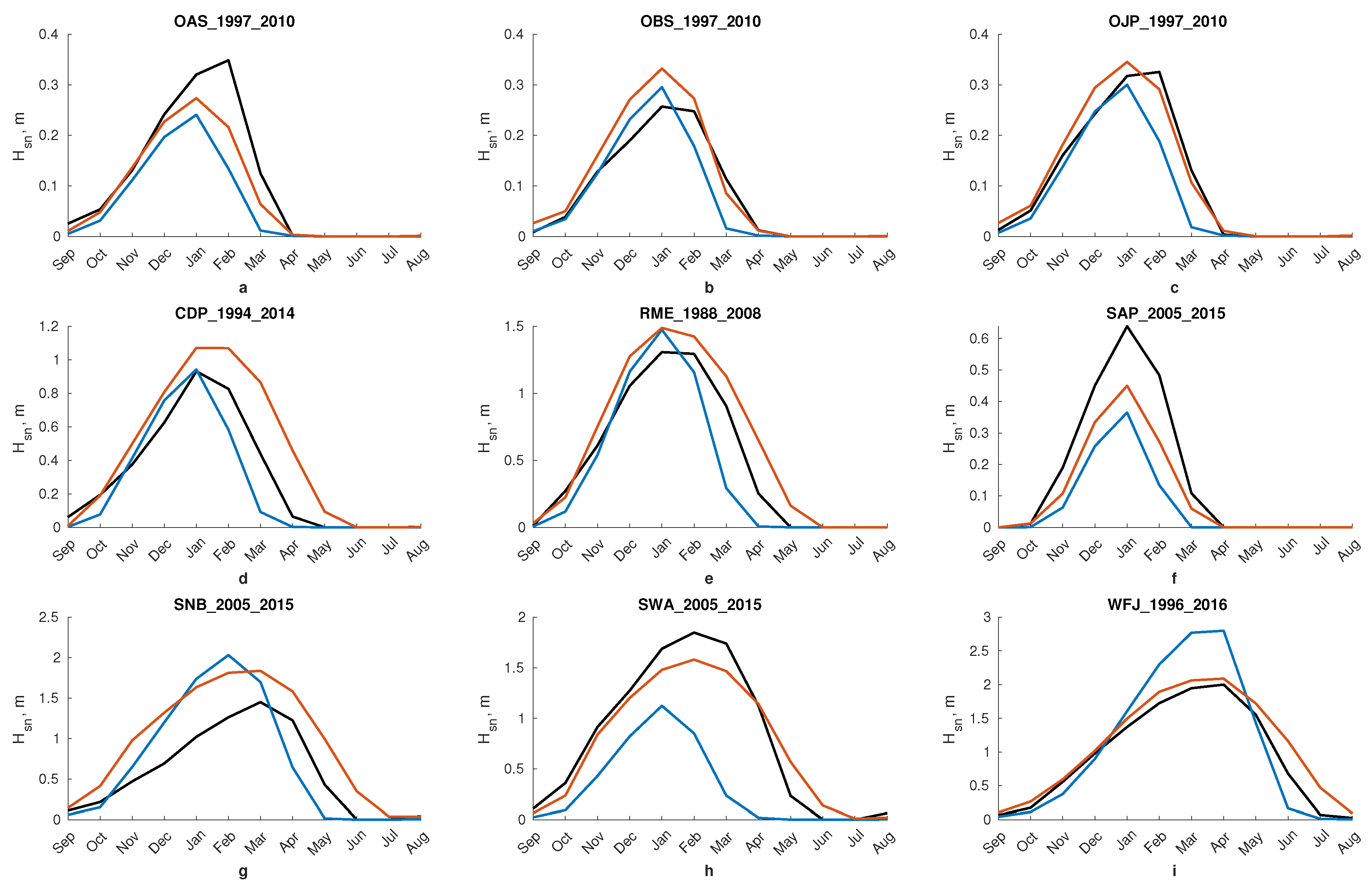
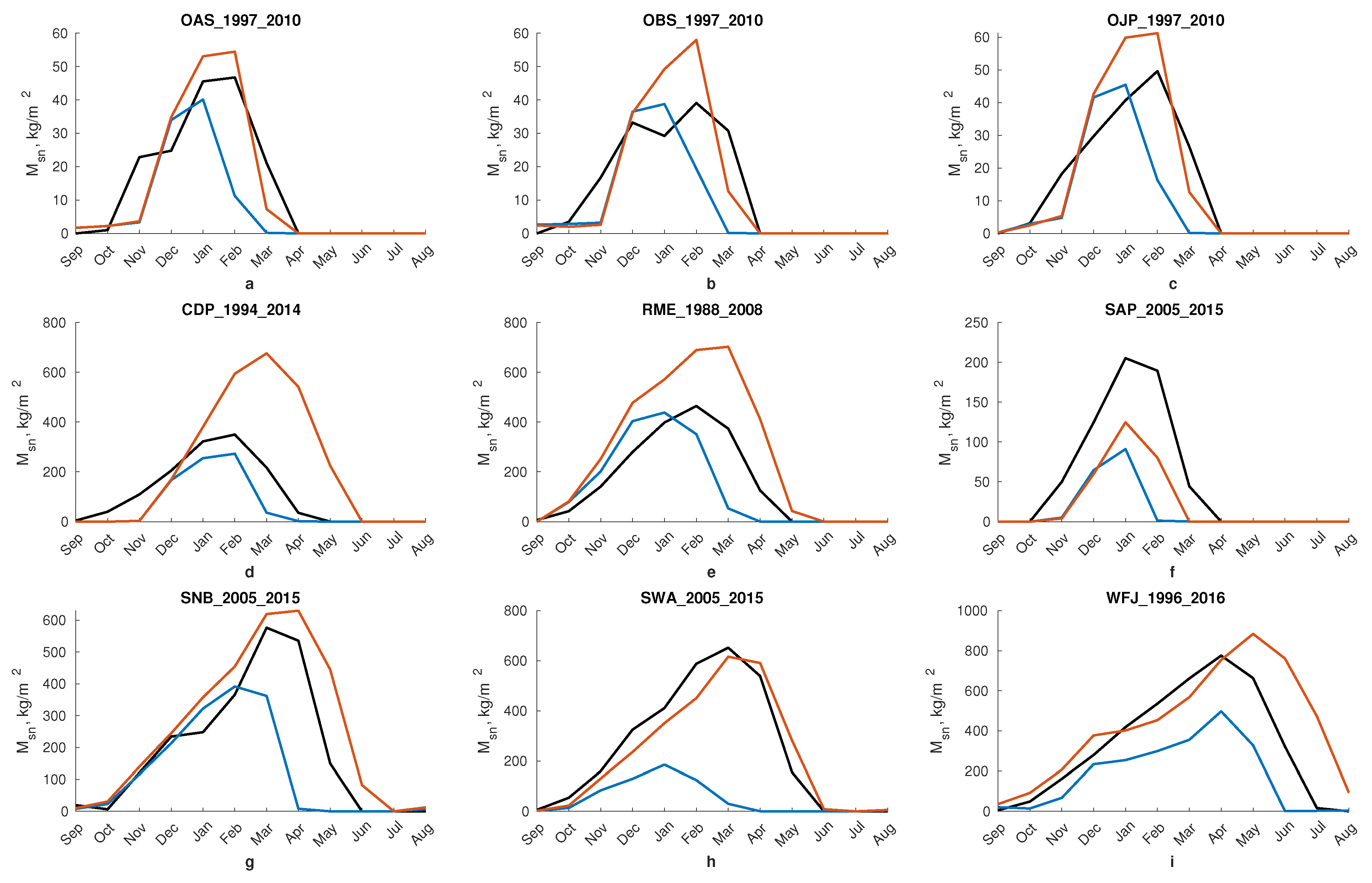

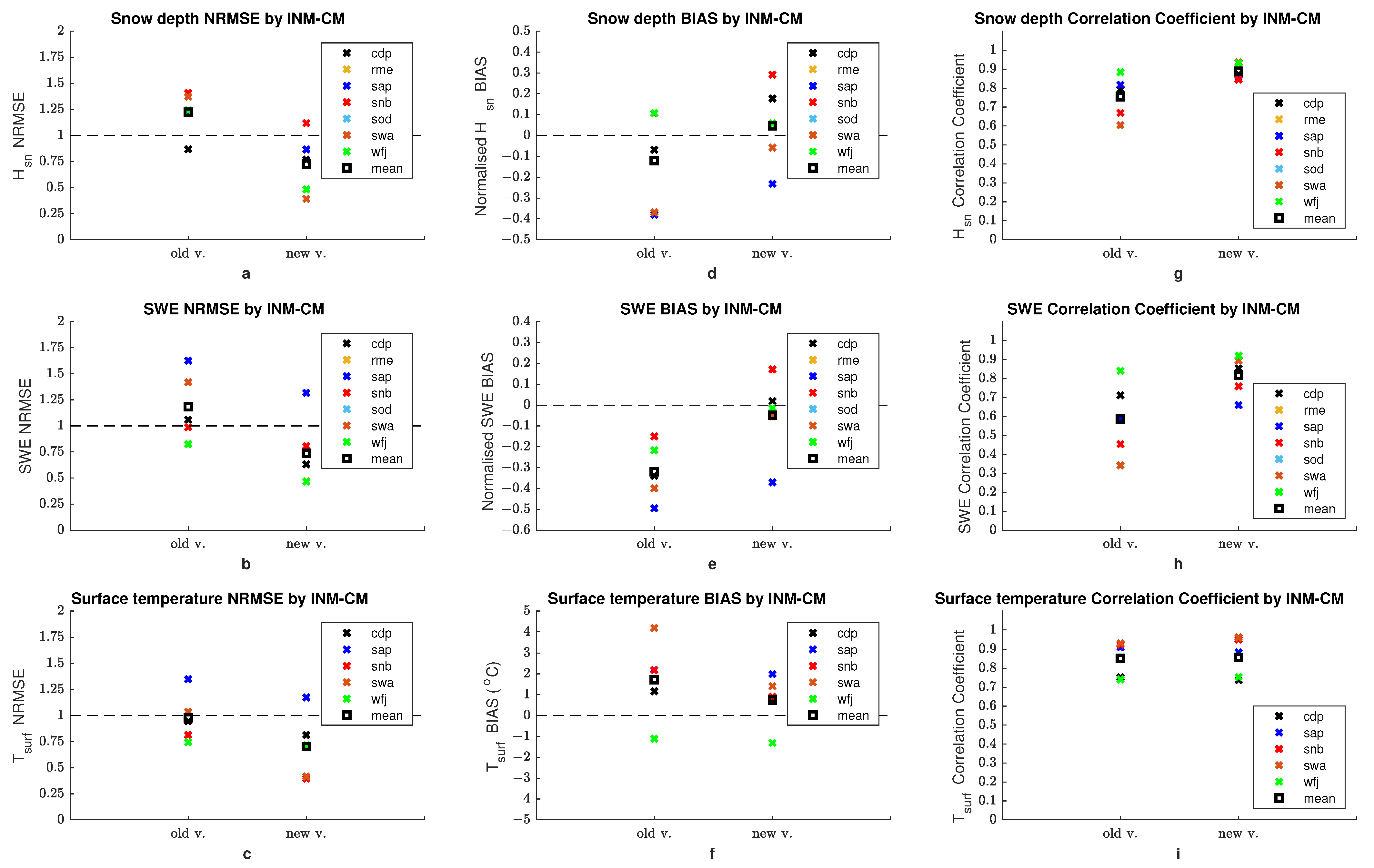
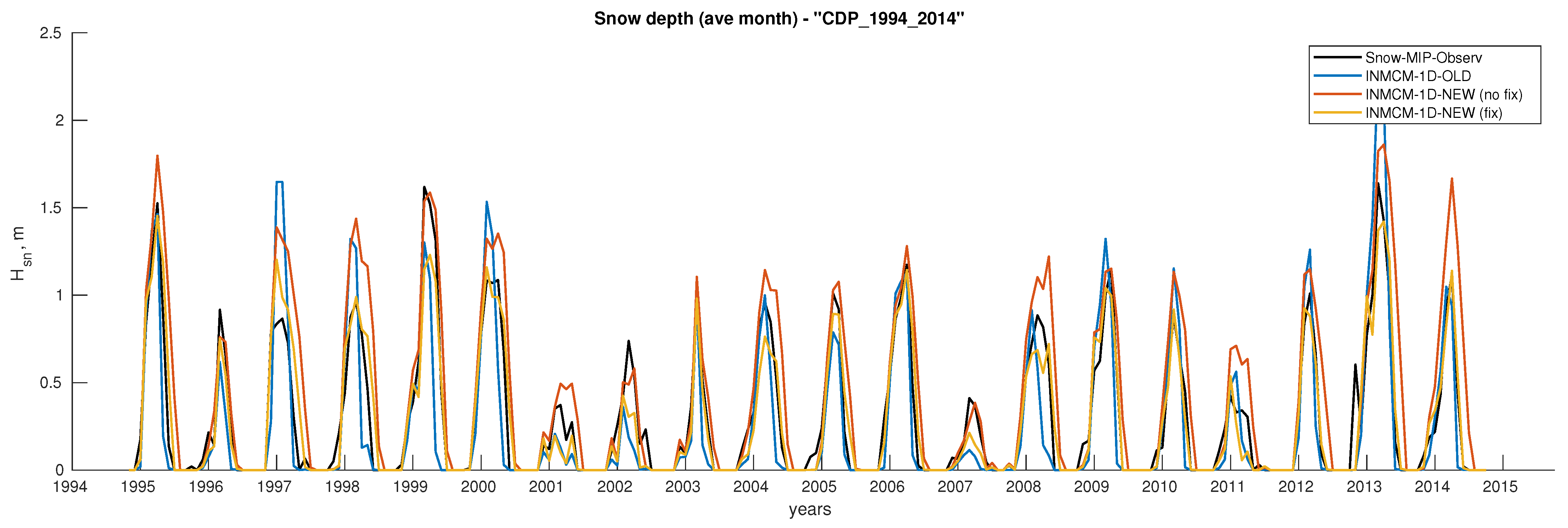
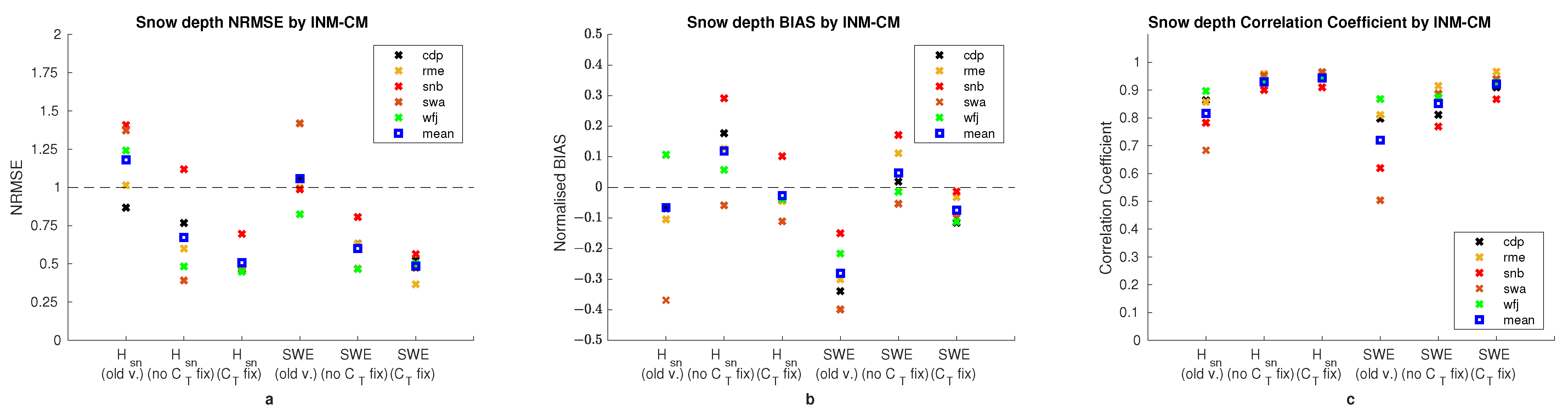
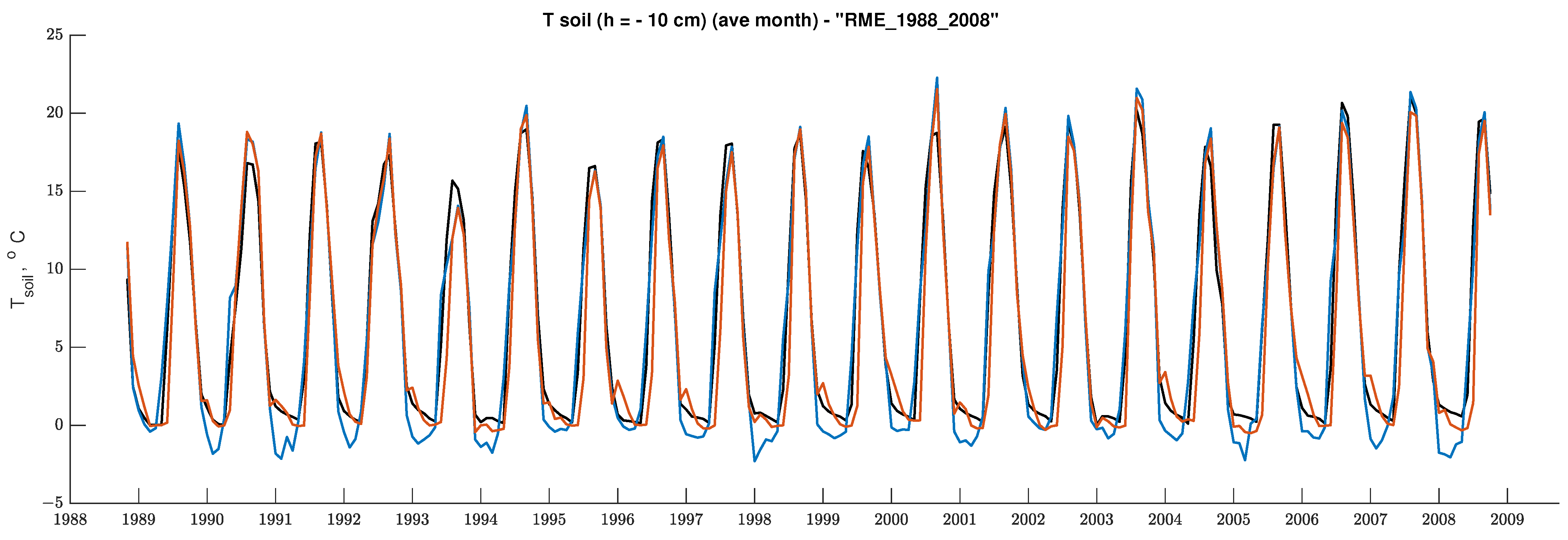
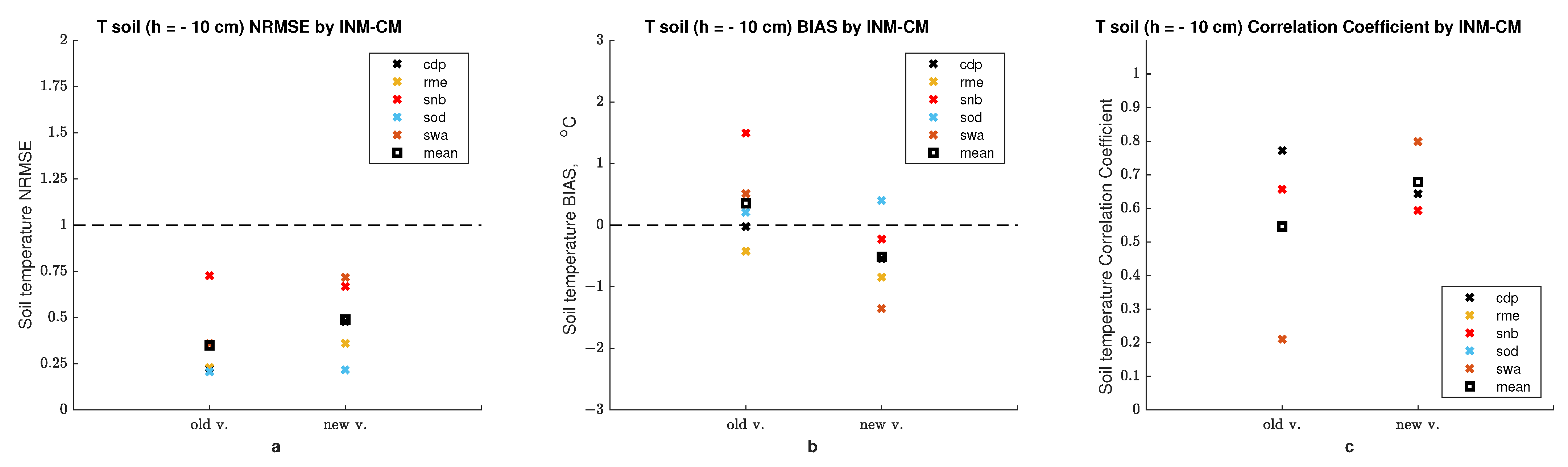
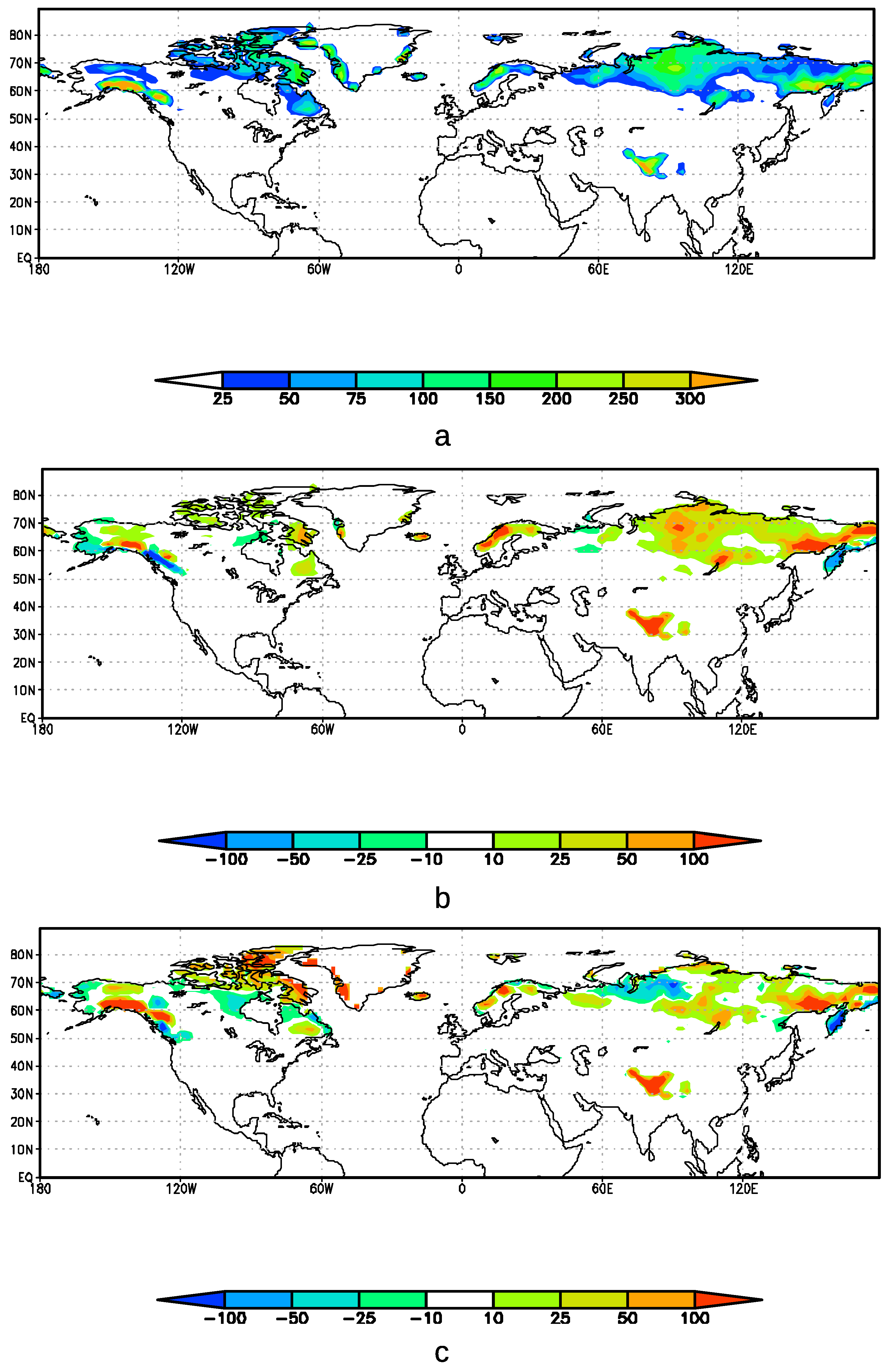
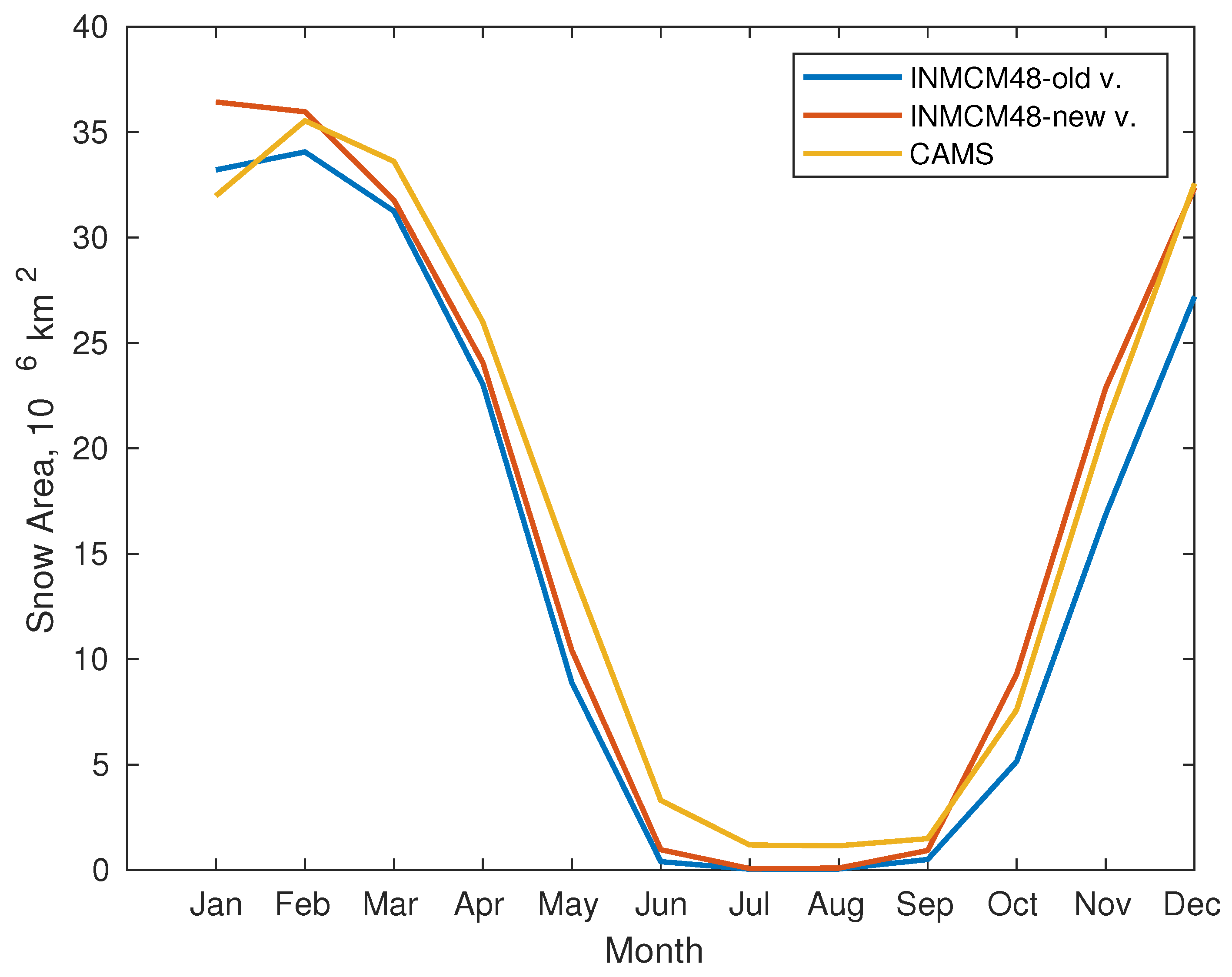

| Site | Lat | Lon | Elevation | Start | Finish | Tag | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BERM Old Aspen | 600 m | 1 October 1997 | 30 September 2010 | OAS | [22] | ||
| BERMS Old Black Spruce | 629 m | 1 October 1997 | 30 September 2010 | OBS | [22] | ||
| BERMS Old Jack Pine | 579 m | 1 October 1997 | 30 September 2010 | OJP | [22] | ||
| Col de Porte | 1325 m | 1 October 1994 | 30 September 2014 | CDP | [23] | ||
| Reynolds Mountain East | 2060 m | 1 October 1988 | 30 September 2008 | RME | [24] | ||
| Sapporo | 15 m | 1 October 2005 | 30 September 2015 | SAP | [25] | ||
| Senator Beck | 3714 m | 1 October 2005 | 30 September 2015 | SNB | [26] | ||
| Sodankyla | 179 m | 1 October 2007 | 30 September 2014 | SOD | [27] | ||
| Swamp Angel | 3371 m | 1 October 2005 | 30 September 2015 | SWA | [26] | ||
| Weissfluhjoch | 2540 m | 1 September 1996 | 31 August 2016 | WFJ | [28] |
| Quality Metrics | INM-CM (Old v.) | INM-CM (New v.) |
|---|---|---|
| NRMSE | ||
| Normalized bias | ||
| correlation coefficient | ||
| SWE NRMSE | ||
| Normalized SWE bias | ||
| SWE correlation coefficient | ||
| NRMSE | ||
| bias (°C) | ||
| correlation coefficient | ||
| (at m) NRMSE | ||
| (at m) bias (°C) | ||
| (at m) correlation coefficient |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chernenkov, A.; Volodin, E.; Kostrykin, S.; Tarasevich, M.; Vorobyeva, V. Modification and Validation of the Soil–Snow Module in the INM RAS Climate Model. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040422
Chernenkov A, Volodin E, Kostrykin S, Tarasevich M, Vorobyeva V. Modification and Validation of the Soil–Snow Module in the INM RAS Climate Model. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):422. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040422
Chicago/Turabian StyleChernenkov, Alexey, Evgeny Volodin, Sergey Kostrykin, Maria Tarasevich, and Vasilisa Vorobyeva. 2024. "Modification and Validation of the Soil–Snow Module in the INM RAS Climate Model" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040422
APA StyleChernenkov, A., Volodin, E., Kostrykin, S., Tarasevich, M., & Vorobyeva, V. (2024). Modification and Validation of the Soil–Snow Module in the INM RAS Climate Model. Atmosphere, 15(4), 422. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040422







