Quantifying Landscape Pattern–Hydrological Process Linkage in Northwest Iran
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
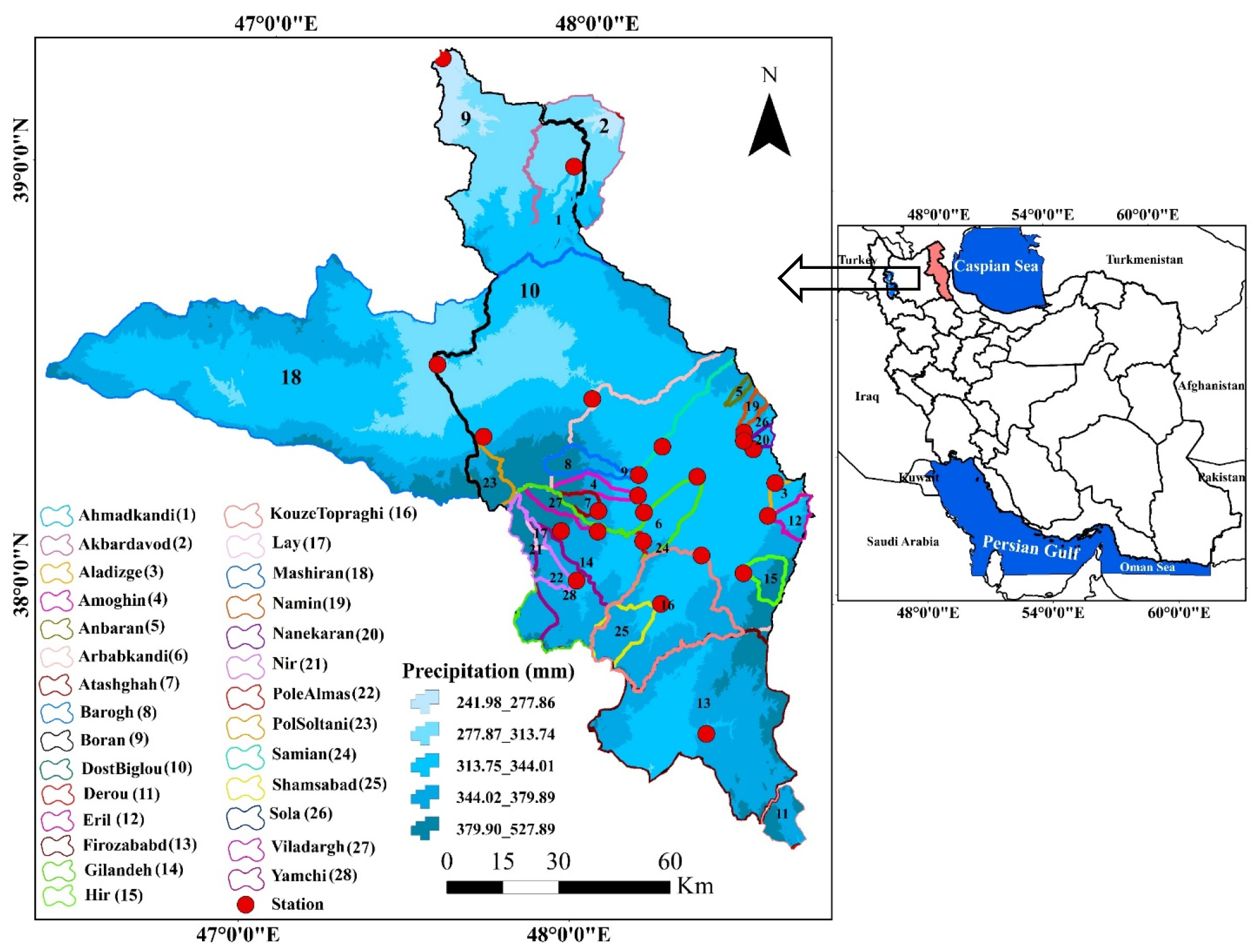
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Used
2.3. Landscape Metrics Calculation
2.4. RLI Characterization
2.5. Correlation and Regression Analysis
3. Results
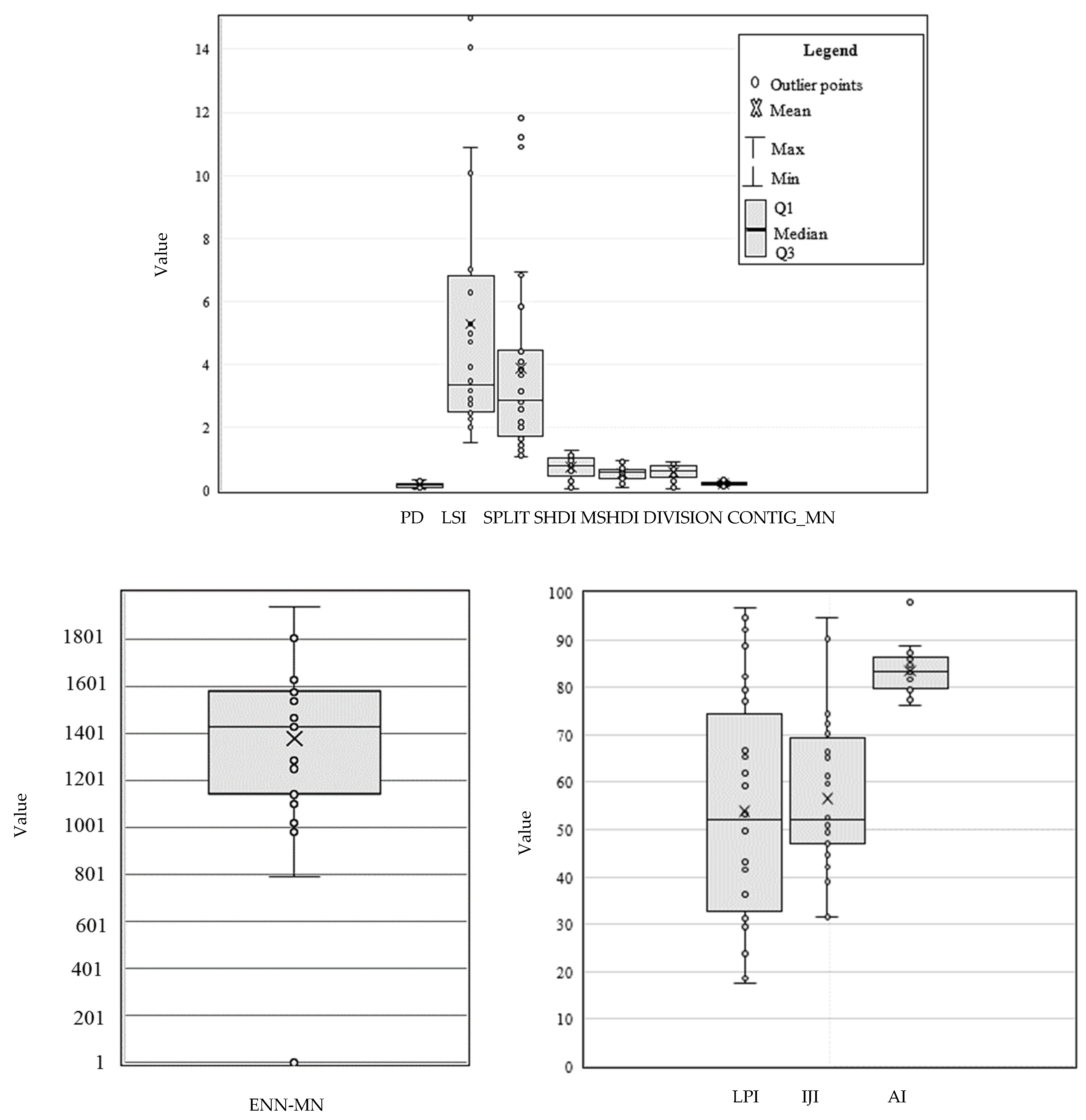
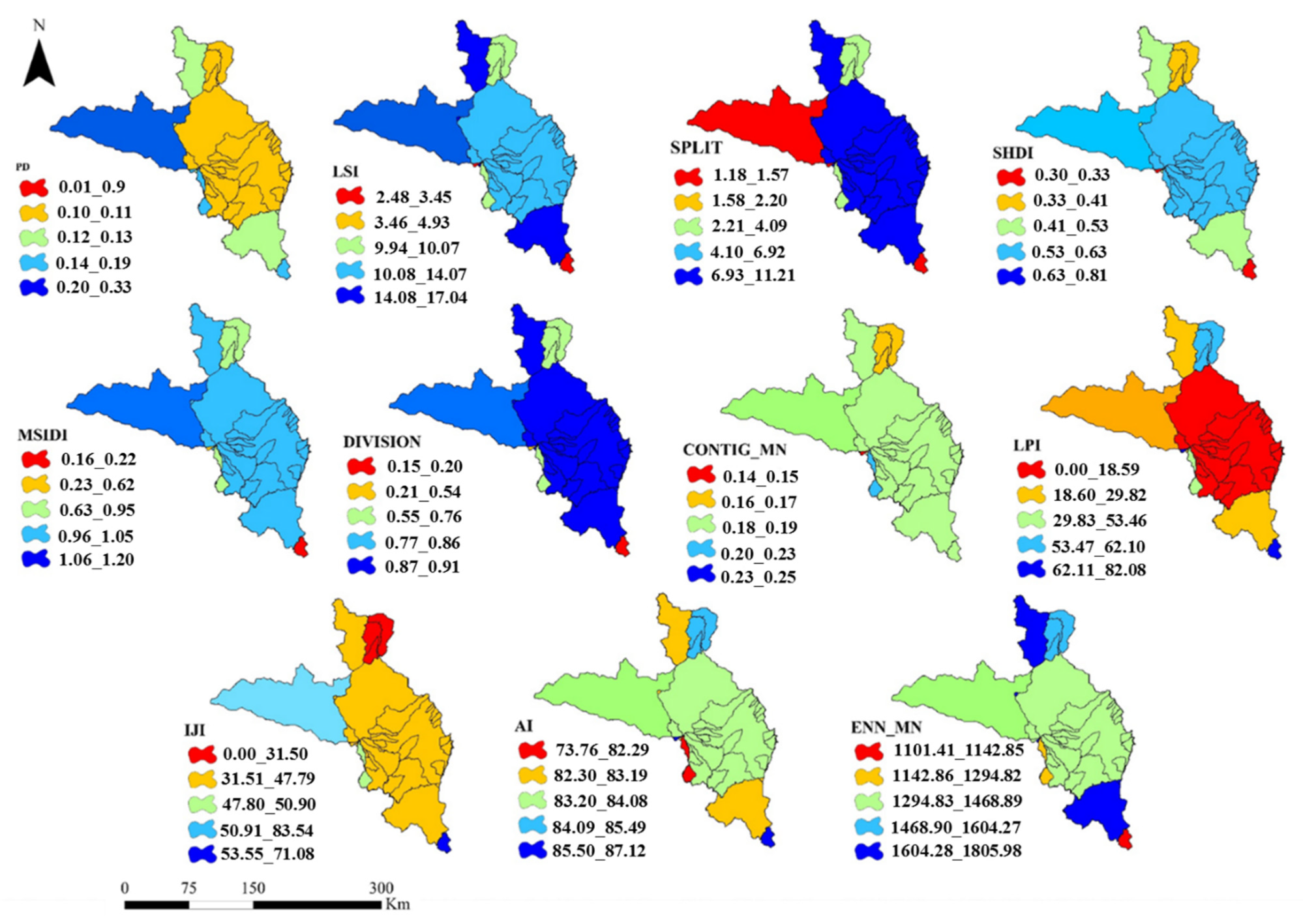
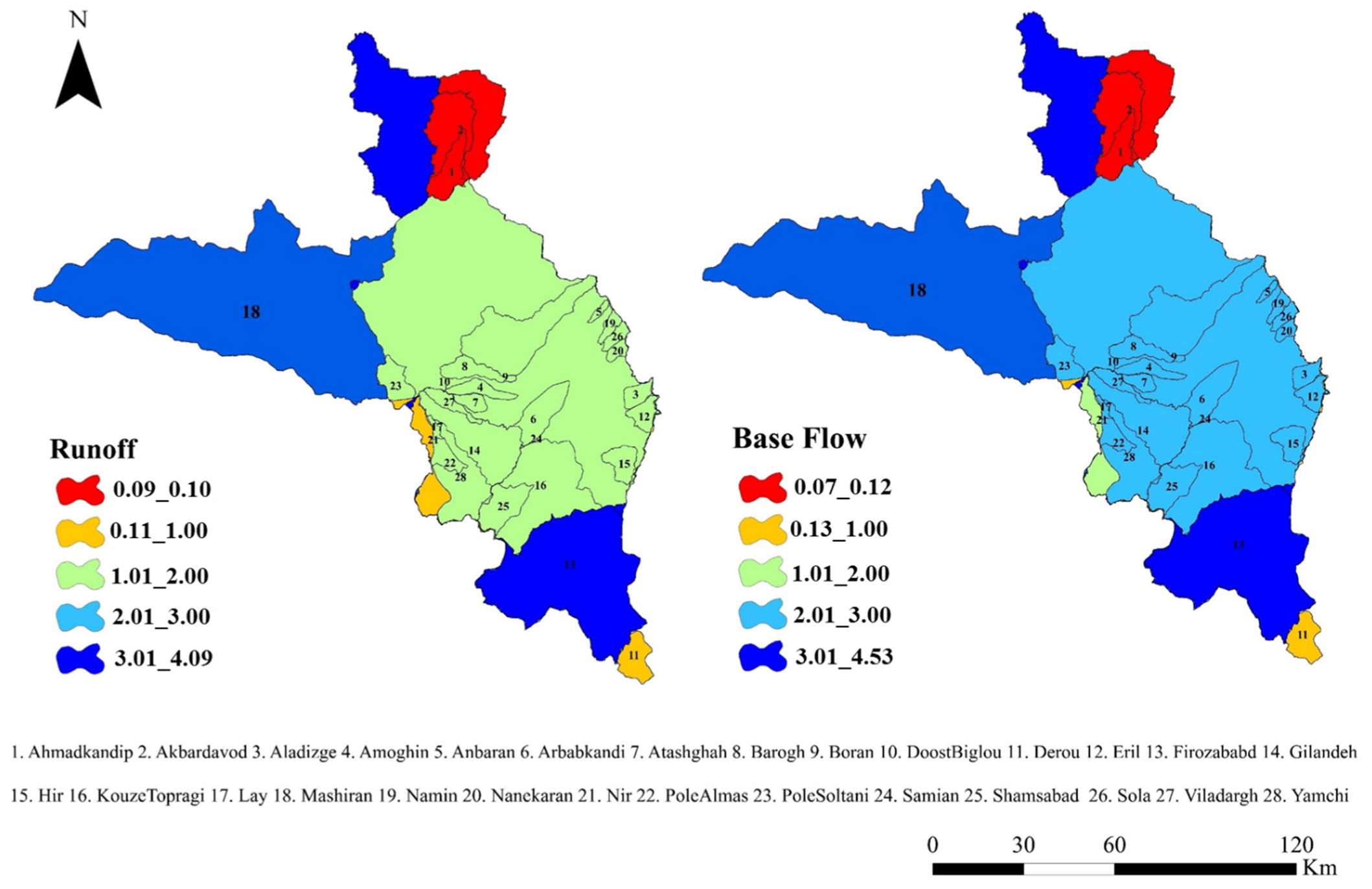
3.1. Spatial Changes of Landscape Metrics
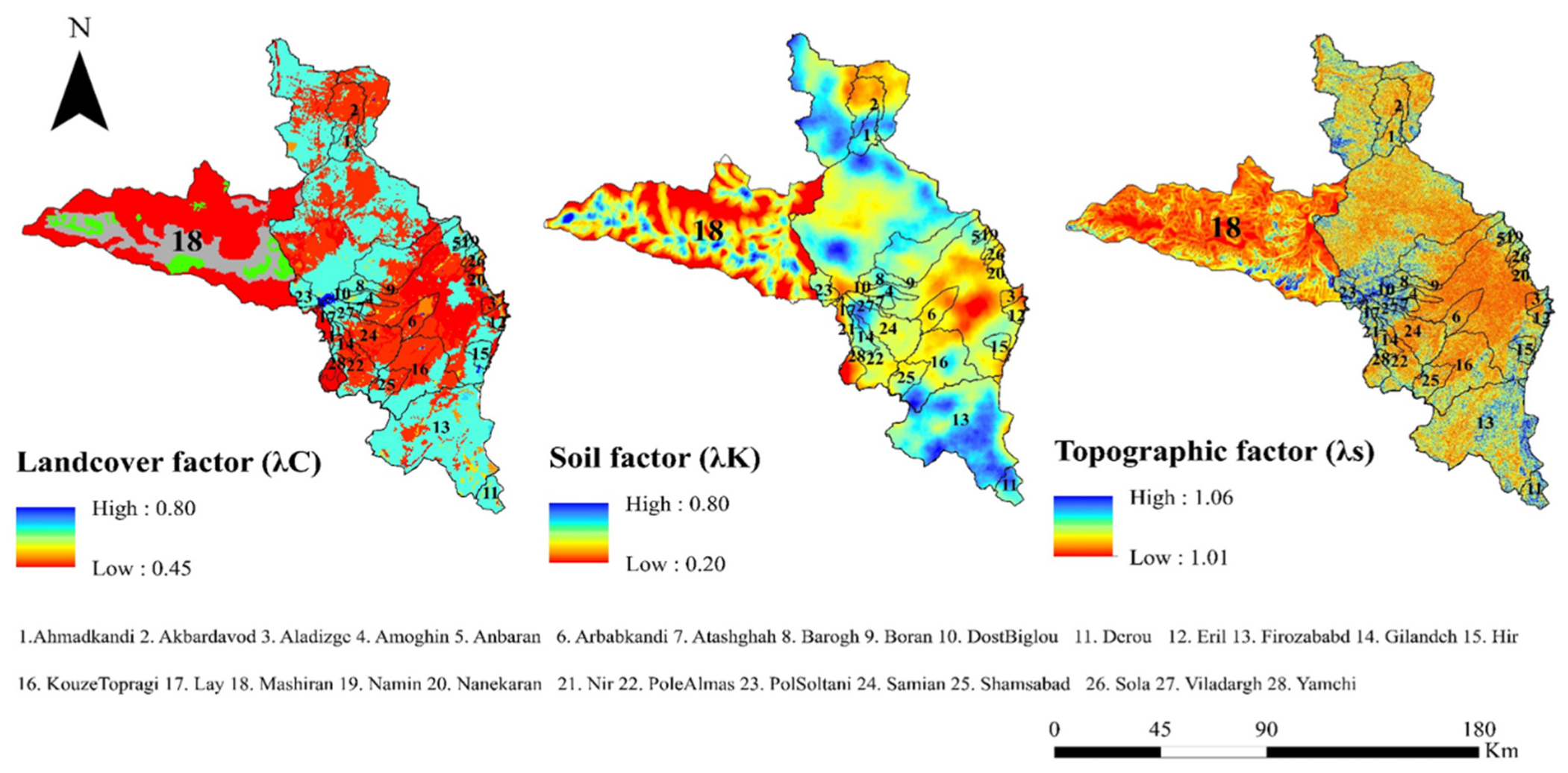
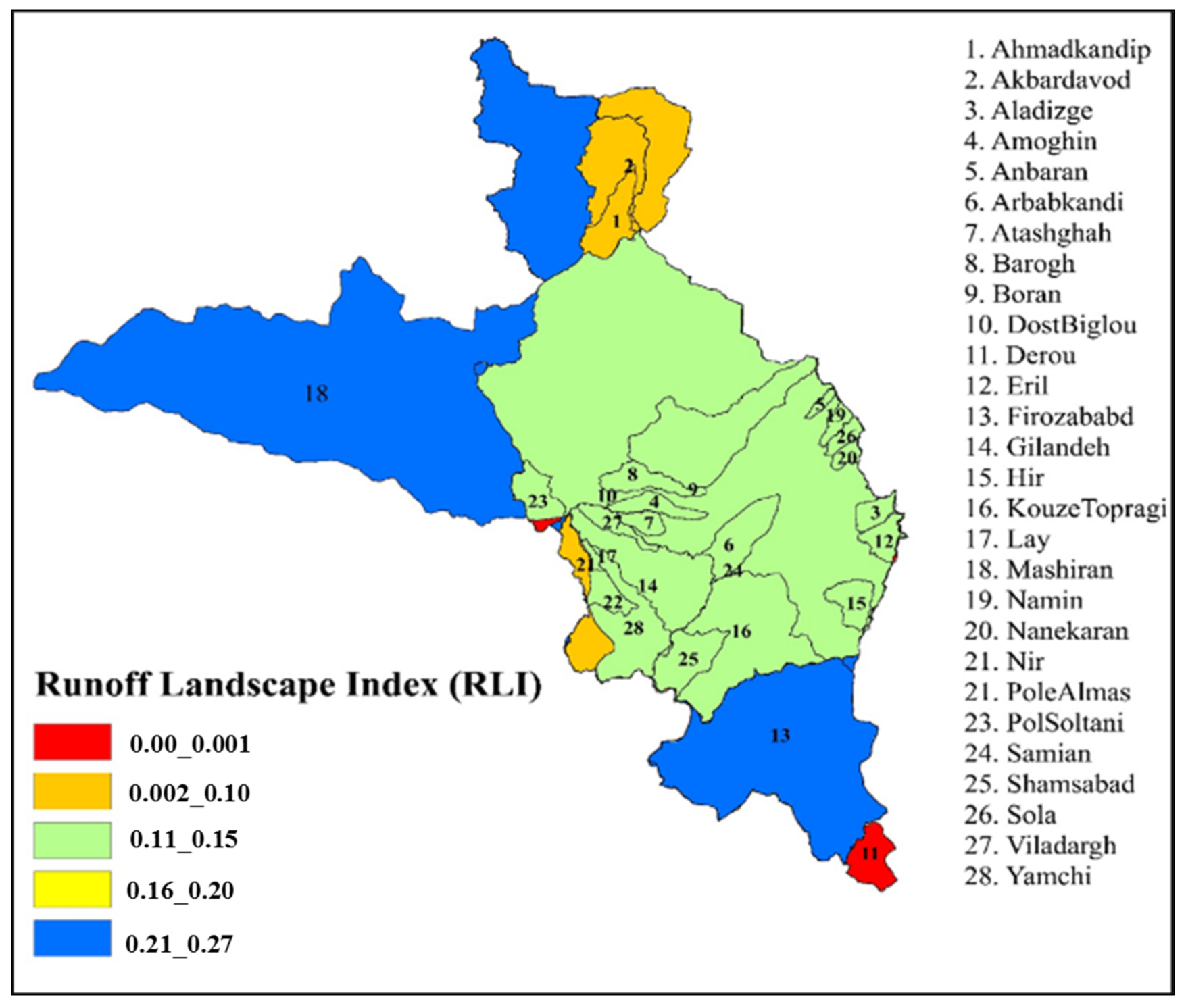
3.2. Spatial Changes in RLI and Its Factors
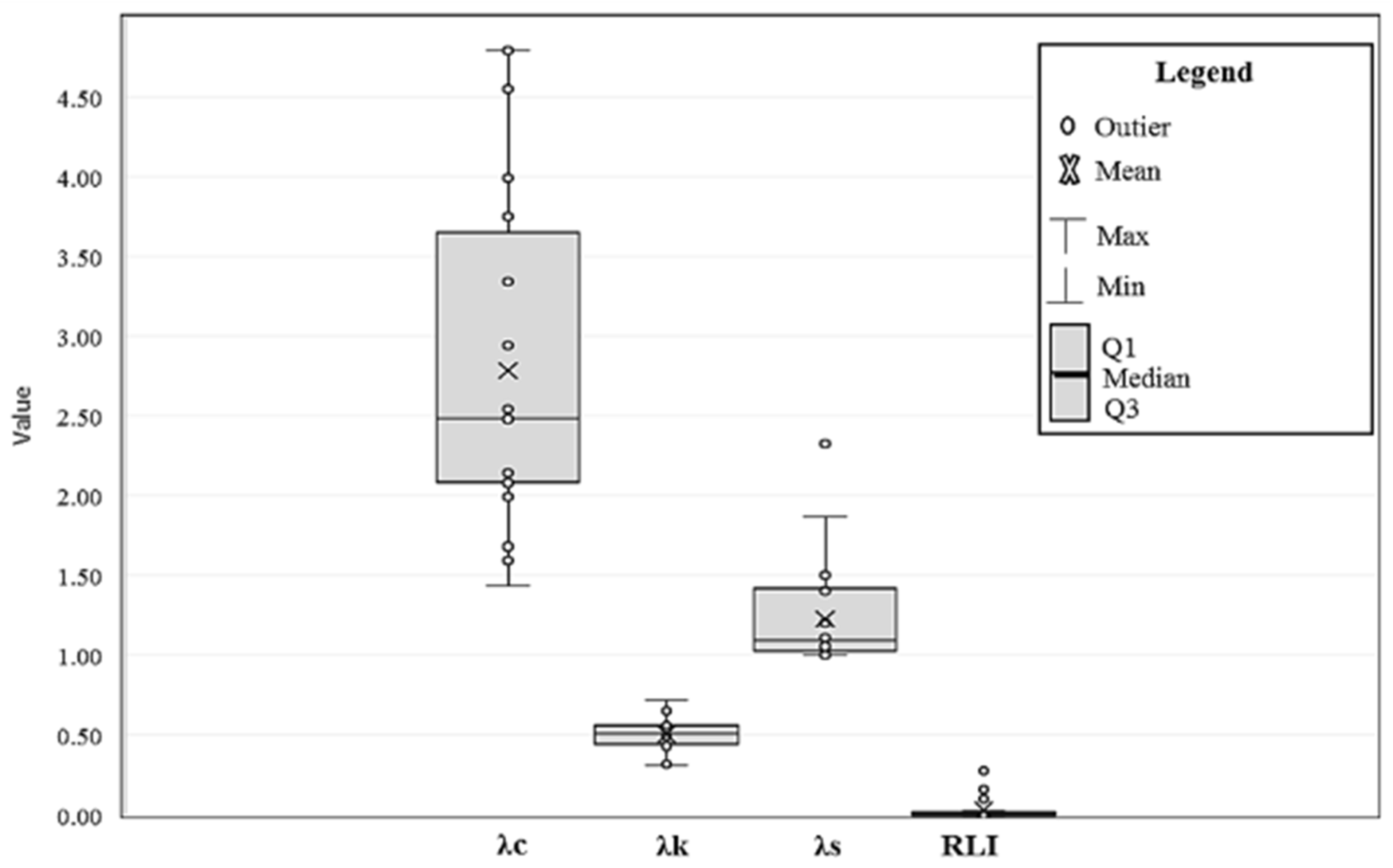
3.3. Results of Correlation and Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tola, S.Y.; Shetty, A. Land cover change and its implication to hydrological regimes and soil erosion in Awash River basin, Ethiopia: A systematic review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohutiar, J.; Kravcik, M. Water for an integrative climate paradigm. Int. J. Water 2010, 5, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, L.; Xu, K.; Xu, X.; Lian, J.; Ma, J. Development of a landscape indicator to evaluate the effect of landscape pattern on surface runoff in the Haihe River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2018, 566, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schickhoff, U.; Bobrowski, M.; Mal, S.; Schwab, N.; Singh, R. The world’s mountains in the anthropocene. In Mountain Landscapes in Transition. Sustainable Development Goals Series; Schickhoff, U., Singh, R., Mal, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xiao, N.; Qi, Y. Prediction and selection of appropriate landscape metrics and optimal scale ranges based on multi-scale interaction analysis. Land 2021, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.M.; Mitchell, B.R.; McGill, B.J. Constructing multimetric indices and testing ability of landscape metrics to assess condition of freshwater wetlands in the Northeastern US. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.; Zhang, H. Aggregating land use quantity and intensity to link water quality in upper catchment of Miyun Reservoir. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Mander, Ü.; Marja, R. Trends in the use of landscape spatial metrics as landscape indicators: A review. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 28, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, W.H.; Fontaine, M.; Rongé, K.; Hermy, M.; Muys, B. A quantitative indicator framework for stand level evaluation and monitoring of environmentally sustainable forest management. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, N.; Bhagwat, S.A.; Harris, J.; Maginnis, S.; Moreno, J.G.; Mueller, G.M.; Oldfield, S.; Walters, G. Measuring progress in status of land under forest landscape restoration using abiotic and biotic indicators. Restor. Ecol. 2018, 26, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Semprucci, F.; Vezzulli, L.; Balsamo, M.; Fabiano, M.; Albertelli, G. The use of nematodes in assessing ecological quality status in the Mediterranean coastal ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowińska-Świerkosz, B. Application of surrogate measures of ecological quality assessment: The introduction of the indicator of ecological landscape quality (IELQ). Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Hwang, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; Hwang, H.S.; Sung, H.C. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, W.; Huang, X. Spatial and seasonal patterns in stream water contamination across mountainous watersheds: Linkage with landscape characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Li, J. The correlation analysis on the landscape pattern index and hydrological processes in the Yanhe Watershed, China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boongaling, C.G.K.; Faustino-Eslava, D.V.; Lansigan, F.P. Modeling land use change impacts on hydrology and the use of landscape metrics as tools for watershed management: The case of an ungauged catchment in the Philippines. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieuwenhuyse, B.H.J.; Antoine, M.; Wyseure, G.; Govers, G. Pattern-process relationships in surface hydrology: Hydrological connectivity expressed in landscape metrics. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3760–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.D. The effects of current landscape configuration on streamflow within selected small watersheds of the Atlanta metropolitan region. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 5, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mirzaei, S.; Esmali Ouri, A.; Mostafazadeh, R.; Ghorbani, A.; Mirzaei, S. Flood hydrograph simulation and analysis of its components with landscape metrics in Amoughin Watershed, Ardabil Province. Iran. J. Ecohydrol. 2018, 5, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Park, Y. Urban green infrastructure and local flooding: The impact of landscape patterns on peak runoff in four Texas MSAs. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 77, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fang, G.; Yan, M.; Sui, C.; Ding, Z.; Lu, C. Flood-landscape ecological risk assessment under the background of urbanization. Water 2019, 11, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafazadeh, R.; Mehri, S. Trends in variability of flood coefficient in river gauge stations of Ardabil Province, Iran. J. Watershed Manag. Res. 2018, 9, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehri, S.; Mostafazadeh, R.; Esmali-Ouri, A.; Ghorbani, A. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Base flow Index (BFI) for the Ardabil Province rivers, Iran. J. Earth Space Phys. 2017, 43, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.T.; Cimino, J.; Ross, M. Calibration of base flow separation methods with streamflow conductivity. Groundwater 2007, 45, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, K.; Ding, J.; Gao, H. Surface runoff. In Observation and Measurement of Ecohydrological Processes; Li, X., Vereecken, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentsis, I.; Rosenthal, E.; Flexer, A.; Inbar, N. Assessing water withdrawals in scarce-data transboundary areas by use of dynamic precipitation–flow relationships: The case of the Hasbani River Basin. Water 2021, 13, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Neel, E.N. FRAGSTATS: Spatial pattern analysis program for categorical maps. Computer software program produced by the authors at the University of Massachusetts; Landscape Ecology Lab: Amherst, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 691–703. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1570009750070414208 (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Kang, N.; Sakamoto, T.; Imanishi, J.; Fukamachi, K.; Shibata, S.; Morimoto, Y. Characterizing the historical changes in land use and landscape spatial pattern on the Oguraike floodplain after the Meiji period. Intercult Underst 2013, 1, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Alaei, N.; Mostafazadeh, R.; Esmaliouri, A.; Sharari, M.; Hazbavi, Z. Assessment and comparison of landscape connectivity in KoozehTopraghi Watershed, Ardabil Province. Iran. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 8, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwongsitanon, N.; Taesombat, W. Effects of land cover on runoff coefficient. J. Hydrol. 2011, 410, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Onda, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Yang, D.Y. Plot-scale study of surface runoff on well-covered forest floors under different canopy species. Quat. Int. 2014, 344, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaadi, A.M. Comparison of canopy interception loss in evergreen and deciduous trees used in afforestation projects. J. Wood Forest Sci. Technol. 2009, 16, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Nezamdost, H.; Sefidi, K.; Rasoulzadeh, A.; Sadeghi, M. Quantifying throughfall, stemflow, and rainfall interception in a Fagus orientalis forest and a Picea abies plantation in Siahkal, Gilan. Iran. J. Forest. 2017, 9, 385–397. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, M.T.; Attarod, P.; Marvi Mohadjer, M.R.; Rahmani, R.; Fathi, J. Canopy interception loss in a pure oriental beech (Fagus orientalis Lipsky) stand during the summer season. Iran. J. Forest. 2009, 1, 175–185. [Google Scholar]
- Fathizadeh, O.; Attarod, P.; Pypker, T.G.; Darvishsefat, A.A.; Zahedi Amiri, G. Seasonal variability of rainfall interception and canopy storage capacity measured under individual Oak (Quercus brantii) Trees in Western Iran. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 15, 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, S.M.M.; Attarod, P. Afforestations impact of Pinus eldarica and Cupressus arizonica on rainfall interception in a semiarid climate zone. J. For. Wood Prod. 2015, 68, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, S.; Rahmani, R. Seasonal and periodic variability of stemflow, throughfall, and interception loss of Oriental beech stands in Shast-Kalate forest. Iran. J. Forest. 2018, 9, 527–540. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati, V.; Payam, H.; Mattaji, A.; Akef, M.; Babaei, K.S.; Fallahchai, M. Interception, throughfall and stemflow of the oriental beech (Fagus orientalis lipsky) trees in the Caspian region (siyahkal shenrood forests). J. Sci. Tec. Nat. Resourc. 2012, 6, 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini Ghaleh Bahmani, S.M.; Attarod, P.; Ahmadi, M.T.; Marvi Mohadjer, M.R.; Etemad, V. Stemflow generations in natural and pure stands of Chestnut leaved oak (Quercus castaneifolia C.A.M) and Oriental beech (Fagus orientalis Lipsky) within the summer season. Iran. J. Forest. Poplar Res. 2010, 18, 666. Available online: https://ijfpr.areeo.ac.ir/article_107658.html?lang=en (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Esmailpour Zarimehr, A.; Dastorani, M.; Farzam, M. Evaluation of the rainfall interception condition in some shrub species (Case study: Campus of the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad). Iran. J. Ecohydrol. 2019, 6, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, P.; Attarod, P.; Hojjati, S.M. Rainfall interception in a natural stand of a Fagus orientalis and a Picea abies plantation within the growing season in Kelardasht Region, North of Iran. J. For. Wood Prod. 2015, 67, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jia, L.; Hu, G.; Zhou, J. Mapping of interception loss of vegetation in the Heihe River basin of China using remote sensing observations. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, C.B.; Caterina, G.L.; Will, R.E.; Stebler, E.; Turton, D. Canopy interception for a tallgrass prairie under juniper encroachment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciężkowski, W.; Berezowski, T.; Kleniewska, M.; Szporak-Wasilewska, S.; Chormański, J. Modelling wetland growing season rainfall interception losses based on maximum canopy storage measurements. Water 2018, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.; Sadeghi, S.M.M.; Van Stan II, J.T.; Chaichi, M.R. Rainfall interception and redistribution by maize farmland in central Iran. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 27, 100656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, C.; Qin, D.; Guo, Y.; Ge, H. Regional runoff study based on MODCYCLE distributed hydrology model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Becciu, G.; Paoletti, A. Random characteristics of runoff coefficient in urban catchments. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Escobar, A.; González-Sosa, E.; Véliz-Chávez, C.; Ventura-Ramos, E.; Ramos-Salinas, M. Rainfall interception and distribution patterns of gross precipitation around an isolated Ficus benjamina tree in an urban area. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Tang, C.; Zheng, H. Characteristics of the surface-subsurface flow generation and sediment yield to the rainfall regime and land-cover by long-term in-situ observation in the red soil region, Southern China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarotto, P.; Stamm, C.; Prasuhn, V.; Fluhler, H. A parsimonious soil-type based rainfall-runoff model simultaneously tested in four small agricultural catchments. J. Hydrol. 2006, 321, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshleger, N.; Shoshany, M.; Karnibad, L.; Arbel, S.; Getkerm, M. Generalising relationships between runoff-rainfall coefficients and impervious areas: An integration of data from case studies in Israel with data sets from Australia and the USA. Urban Water J. 2009, 6, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwue, E.I.; Harrilal, A. Effect of soil type, peat, slope, compaction effort and their interactions on infiltration, runoff and raindrop erosion of some Trinidadian soils. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 105, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X. Effects of rainfall intensity, underlying surface and slope gradient on soil infiltration under simulated rainfall experiments. Catena 2013, 104, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.D. Runoff behaviour of water harvesting microcatchments. Agric. Water Manag. 1986, 11, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. VII. Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution.-III. Regression, heredity, and panmixia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1896, 187, 253–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihamta, M.R.; Zare Chahouki, M.A. Principles of Statistics for the Natural Resources Science; University of Tehran Press: Tehran, Iran, 2010; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Kakehmami, A.; Moameri, M.; Ghorbani, A.; Ghafari, S. Analysis of land use/cover changes in Ardabil province using landscape metrics. J. RS GIS Nat. Resourc. 2020, 11, 68–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafazadeh, R.; Jafari, A.; Keivan-behjou, F. Comparing the rangelands structure and degradation of landscape connectivity in Iril Sub-Watersheds, Ardabil Province. Iran. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiyari Darabad, F.; Hamzeei, M.; Alaei, N.; Mostafazadeh, R. Spatial variations of landscape metrics in riparian area vegetation of Gharesou River Reaches under the effect of different land uses, Ardabil Province. Geogr. Plann. Space Quart. J. 2021, 10, 219–234. [Google Scholar]
- Puigdefábregas, J. The role of vegetation patterns in structuring runoff and sediment fluxes in drylands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2005, 30, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, M.; Roberts, J.M.; Rosier, P.T.W.; Gowing, D.J. Measuring and modelling the rainfall interception loss by hedgerows in southern England. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 141, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Landscape Metric | Symbol | Unit | Formula | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patch density | PD | No. per 100 ha | PD > 0 | |
| Landscape shape index | LSI | Dimensionless | LSI ≥ 1 | |
| Splitting index | SPLIT | Dimensionless | 1 ≦ SPLIT ≦ number of cells in the landscape squared | |
| Shannon’s diversity index | SHDI | Dimensionless | 0 ≦ SHDI ≦ 1 | |
| Modified Simpson’s diversity index | MSIDI | Dimensionless | MSIDI ≥ 0, without limit | |
| Landscape division index | DIVISION | Dimensionless | 0 ≦ DIVISION ≦ 1 | |
| Contiguity index distribution | CONTIG_MN | Dimensionless | 0 ≦ CONTIG_MN ≦ 1 | |
| Largest patch index | LPI | % | 0 < LPI ≦ 100 | |
| Interspersion and juxtaposition index | IJI | % | 0 < IJI ≦ 100 | |
| Aggregation index | AI | % | 0 ≦ AI ≦ 100 | |
| Mean Euclidean nearest neighbor distance | ENN_MN | m | ENN_MN > 0, without limit. |
| Land Cover Classification | Reference | Study Area | Rainfall Interception Loss (%) | Land Cover Factor (λC) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | Pinus nigra | [32] | Reforest Campus of University Agriculture Shirvan | 34.77 | 0.46 |
| Cupressus sempervirens | 44.97 | 0.45 | |||
| Robinia pseudoacacia | 9.78 | 0.8 | |||
| Platanus orientalis | 5.5 | 0.83 | |||
| Natural stand (Fagus orientalis) and exotic plantation (Picea abies) | [33] | Siahkal Forests, Gilan | 11.7 | 0.77 | |
| Fagus orientalis Lipsky | [34] | Kheyrud forest research station of University of Tehran | 33.7 | 0.47 | |
| Quercus brantii | [35] | Zagros forests, Ilam | 58.26 | 0.41 | |
| Pinus eldarica | [36] | Tehran Chitgar Forest Park | 59.25 | 0.41 | |
| Cupressus | 62.28 | ||||
| Fagus orientalis Lipsky | [37] | Educational-research Forest of Shast-Kalateh of Gorgan | 60.7 | 0.40 | |
| Fagus Orientalis Lipsky | [38] | Siyahkal Shenrood Forests (Caspian Region) | 51.3 | 0.40 | |
| Quercus castaneifolia | [39] | Kheyrud Forest Research Station of Tehran | 0.26 | 0.79 | |
| Shrub lands | Rosa persica | [40] | Campus of the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Khorasan Razavi | 22 | 0.78 |
| Peganum harmala | 39 | 0.45 | |||
| Fagus orientalis and a Picea abies | [41] | Kelardasht Region, North of Iran | 48.6 26.5 | 0.43 0.75 | |
| Bush | [42] | Haihe River Basin, China | 11.26 | 0.79 | |
| Grassland | Belongs to grasslands with long grass | [43] | South Central Great Plains, USA | 44 | 0.55 |
| Grass | [42] | Haihe River Basin, China | 3.78 | 0.85 | |
| Wetlands | Appartient à un lagon natural | [44] | Upstream of the Biebrza watershed, Poland | 13 | 0.80 |
| Agricultural land | Fermes corn | [45] | Agricultural land in Varmin, located southwest of Tehran (Iran) | 11.2–19.9 | 0.40 |
| Urban land | Urban areas | [46] | Tianjin, Haihe Watershed, China | 48.2–64 | 0.50 |
| Urban catchments | [47] | 20 urban watersheds from around the world | 32.82 | ||
| Evergreen benjamin tree F. | [48] | Querétaro City in central Mexico | 2.4 | 0.78 | |
| Rural land | Rural areas | [46] | Tianjin, Haihe Watershed, China | 85–66 | 0.40 |
| Bare land | Bare land | [49] | Yangou Watershed, southern China | 21.28 | 0.80 |
| Drainage Class | Very Poor | Poor | Imperfectly | Moderately Good | good | Somewhat Excessive | Excessive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runoff coefficient | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| PD | LPI | LSI | CONTIGMN | ENNMN | IJI | DIVISION | SPLIT | SHDI | MSIDI | AI | Base flow | Runoff | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| LPI | 0.99 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| LSI | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| CONTIGMN | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| ENNMN | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| IJI | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||||||
| DIVISION | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | ||||||
| SPLIT | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |||||
| MSIDI | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | ||||
| SHEI | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |||
| AI | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Base flow | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 1.00 | |
| Runoff | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| RLI | −0.36 | −0.58 | 0.94 | −0.26 | 0.16 | −0.21 | 0.53 | 0.88 | 0.42 | −0.01 | 0.06 | 0.89 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasoulzadeh, A.; Mostafazadeh, R.; Mobaser, J.A.; Alaei, N.; Hazbavi, Z.; Kisi, O. Quantifying Landscape Pattern–Hydrological Process Linkage in Northwest Iran. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121814
Rasoulzadeh A, Mostafazadeh R, Mobaser JA, Alaei N, Hazbavi Z, Kisi O. Quantifying Landscape Pattern–Hydrological Process Linkage in Northwest Iran. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(12):1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121814
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasoulzadeh, Ali, Raoof Mostafazadeh, Javanshir Azizi Mobaser, Nazila Alaei, Zeinab Hazbavi, and Ozgur Kisi. 2023. "Quantifying Landscape Pattern–Hydrological Process Linkage in Northwest Iran" Atmosphere 14, no. 12: 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121814
APA StyleRasoulzadeh, A., Mostafazadeh, R., Mobaser, J. A., Alaei, N., Hazbavi, Z., & Kisi, O. (2023). Quantifying Landscape Pattern–Hydrological Process Linkage in Northwest Iran. Atmosphere, 14(12), 1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14121814









