Carbon Emission Model and Emission Reduction Technology in the Asphalt Mixture Mixing Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analysis Boundary and Mixing Mechanism
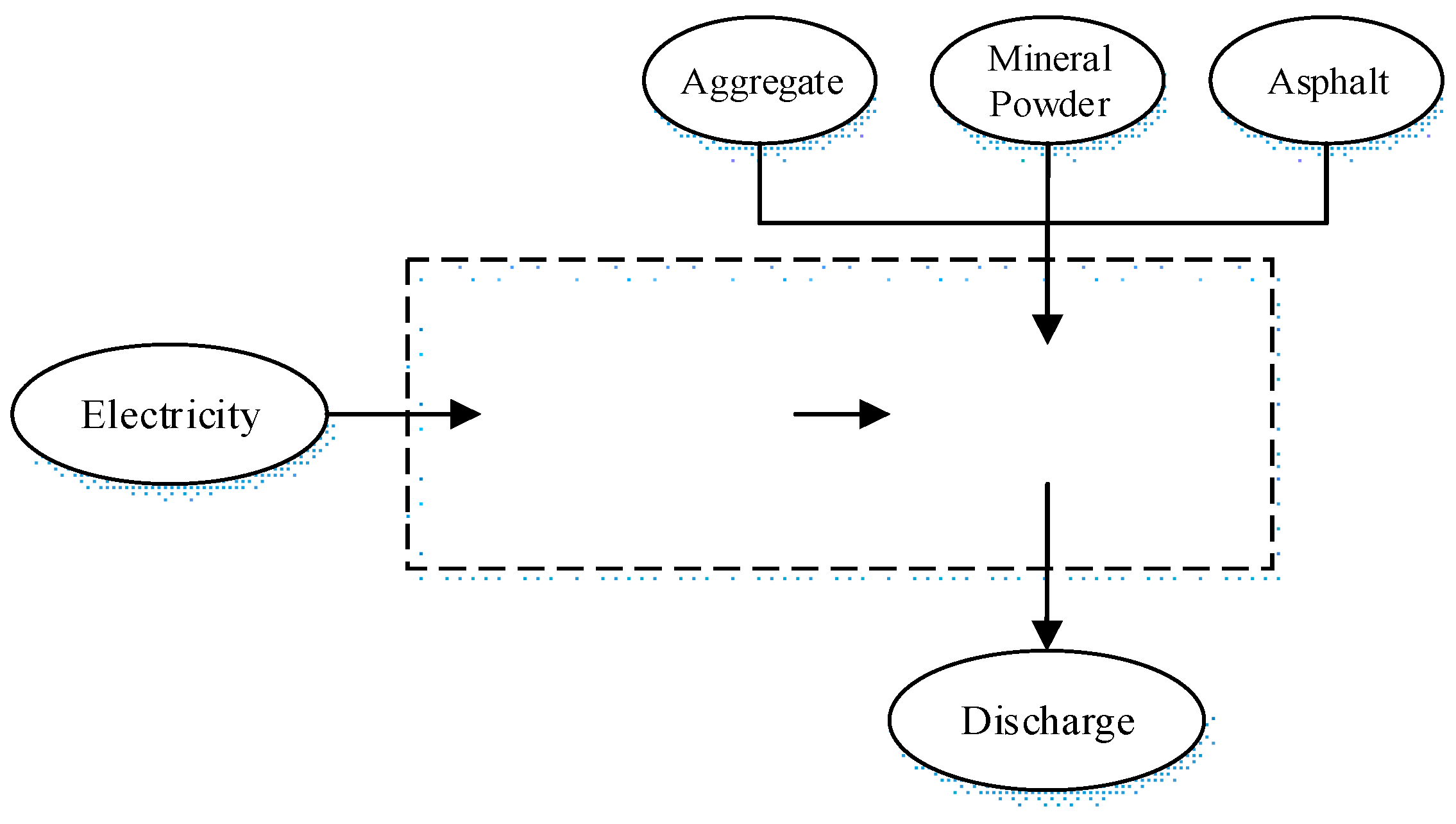
2.1. Analysis Boundary
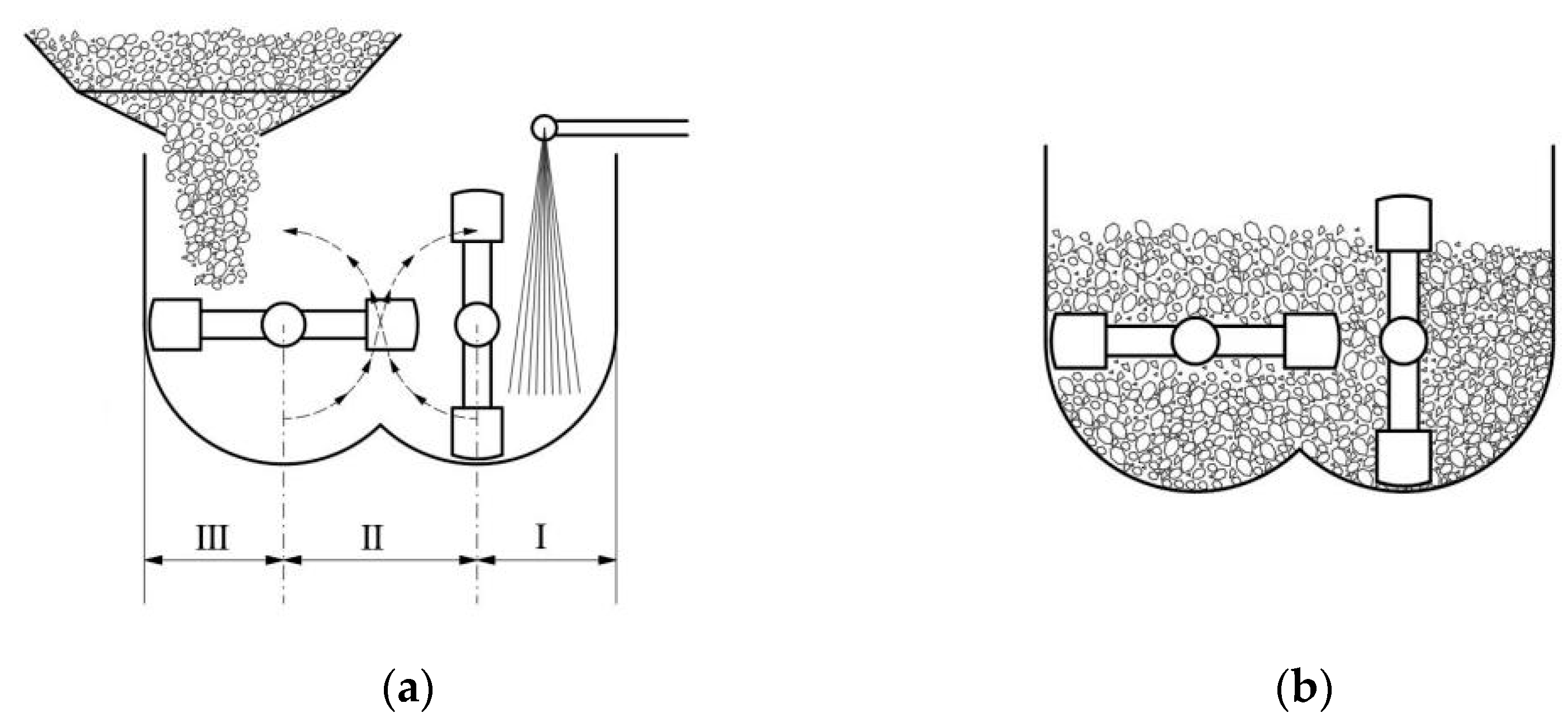
2.2. Structure of the Mixer
2.3. Mixing Mechanism
2.4. Mixing Quality Requirements
3. Methodology
3.1. Mathematical Model for Energy Consumption and CO2 Emission
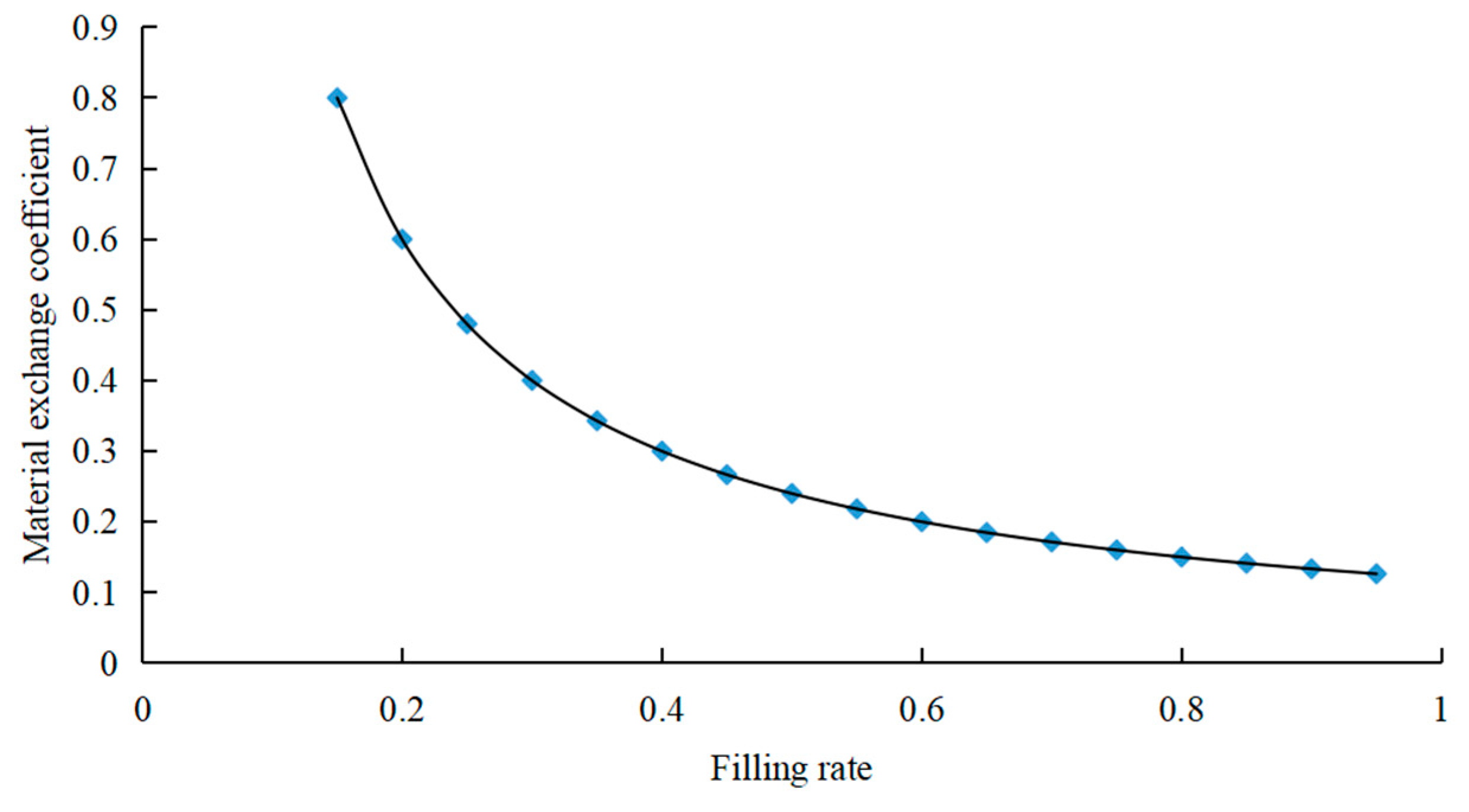
3.2. Model for the Mixing Time
3.3. Mathematical Model for CO2 Emissions during Mixing
4. Emission Reduction Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The CO2 emissions model for the mixing process reveals a direct proportional relationship between mixing time and mixing quality, with an initial rapid enhancement followed by gradual improvement and eventual stabilization. It is important to note that an excessive mixing time does not significantly improve the mixing quality but instead significantly escalates electricity consumption and CO2 emissions.
- For a mixture with 5% asphalt content, when the deviation of the asphalt content is changed from 0.3% to 0.2%, the mixing time and the CO2 emissions will both increase by 14%. When the deviation is 0.1%, the mixing time and the CO2 emissions experience a nearly 40% increase.
- The capacity of the agitator also has an important influence on the CO2 emissions during mixing. Increasing the agitator’s capacity for a given engineering quantity leads to a reduction in overall CO2 emissions. Initially, this reduction is substantial, followed by a gradually decelerating rate, and it eventually stabilizes. When compared to an agitator of type 1500, employing agitators of types 2000, 3000, 4000, and 5000 yields CO2 emissions reductions of 13.2%, 26.3%, 32.9%, and 36.8%, respectively. Therefore, for large-scale projects, selecting a high-capacity agitator, preferably of type 4000 or higher, is recommended to minimize electricity consumption and CO2 emissions during the mixing process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, N.Y.Z.; Wang, Y.Q.; Bai, Q.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, P.R.; Xue, S.Q.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q.R. Road life-cycle carbon dioxide emissions and emission reduction technologies: A review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. Engl. Ed. 2022, 9, 532–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stripple, H. Life Cycle Assessment of Road. A Pilot Study for Inventory Analysis. Second Revised Edition; IVL Rapport; IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute: Gothenburg, Sweden; Linköping, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Bird, R.; Heidrich, O. Development of a life cycle assessment tool for construction and maintenance of asphalt pavements. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Duan, Z.; Wu, L.; Yang, D. Estimation of carbon dioxide emission in highway construction: A case study in southwest region of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Lu, Q. Estimation of albedo effect in pavement life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 64, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noland, R.B.; Hanson, C.S. Life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions associated with a highway reconstruction: A New Jersey case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoya, E.; El-Hamalawi, A.; Ison, S.G.; Frost, M.W.; Hazell, K. Development and Implementation of a Lifecycle Carbon Tool for Highway Maintenance. J. Transp. Eng. 2015, 141, 04014092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D. Estimation and uncertainty analysis on carbon dioxide emissions from construction phase of real highway projects in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrain, D.; Lechon, Y. Environmental footprint of a road pavement rehabilitation service in Spain. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankendaal, T.; Schuur, P.; Voordijk, H. Reducing the environmental impact of concrete and asphalt: A scenario approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatari, O.; Nazzal, M.; Kucukvar, M. Comparative sustainability assessment of warm-mix asphalts: A thermodynamic based hybrid life cycle analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 58, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celauro, C.; Corriere, F.; Guerrieri, M.; Lo Casto, B. Environmentally appraising different pavement and construction scenarios: A comparative analysis for a typical local road. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2015, 34, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulotta, T.M.; Mistretta, M.; Pratico, F.G. A life cycle scenario analysis of different pavement technologies for urban roads. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.; Bryce, J.; Flintsch, G.; Ferreira, A.; Diefenderfer, B. A life cycle assessment of in-place recycling and conventional pavement construction and maintenance practices. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2015, 11, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Carmen Rubio, M.; Moreno, F.; Jose Martinez-Echevarria, M.; Martinez, G.; Miguel Vazquez, J. Comparative analysis of emissions from the manufacture and use of hot and half-warm mix asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranhos, R.S.; Petter, C.O. Multivariate data analysis applied in Hot-Mix asphalt plants. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2013, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.B.; Candido, J.; Baule, S.D.; de Oliveira, Y.M.M.; Thives, L.P. Greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption in asphalt plants. Rev. Eletronica Gest. Educ. E Tecnol. Ambient. 2020, 24, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E. Asphalt mixtures emission and energy consumption: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, D.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, L.; Yu, B. Modeling and Validation of Energy Consumption in Asphalt Mixture Production. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2016, 142, 04016069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, P.; Hu, S.; Yang, L.; Gao, G. Rethinking the carbon dioxide emissions of road sector: Integrating advanced vehicle technologies and construction supply chains mitigation options under decarbonization plans. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurangzeb, Q.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ozer, H.; Yang, R. Hybrid life cycle assessment for asphalt mixtures with high RAP content. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, F.K.; Fakhri, M.; Azami, A. Evaluation of warm mix asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement and crumb rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Zanetti, M.C.; Santagata, E.; Blengini, G.A. Life cycle assessment applied to bituminous mixtures containing recycled materials: Crumb rubber and reclaimed asphalt pavement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 117, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alloza, A.M.; Malik, A.; Lenzen, M.; Gallego, J. Hybrid input-output life cycle assessment of warm mix asphalt mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Costa, A.; Benta, A. Economic and environmental impact study of warm mix asphalt compared to hot mix asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, J.; Pranjic, A.M.; Mladenovic, A.; Cotic, Z.; Jurjavcic, P. Environmental comparison of two alternative road pavement rehabilitation techniques: Cold-in-place-recycling versus traditional reconstruction. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 121, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.I.; Dotelli, G.; Brandini, N.; Zampori, L. Comparative life cycle assessment of asphalt pavements using reclaimed asphalt, warm mix technology and cold in-place recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 104, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. Research on the Mating and Layout of the Equipment and Facilities in the Typical Asphalt Mixture Mixing Plant. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. In Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; Cambridge, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, L.; Kandhal, S.; Brown, E.; Lee, D.; Kennedy, T. Hot Mix Asphalt Materials, Mixture Des5ign and Construction, 3rd ed.; NAPA Research and Education Foundation: Lanham, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Liu, N.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, K.; Shao, X. Influence of Mineral Particle Size on Mixing Time and Phase Mixing Technology. China J. Highw. Transp. 2017, 30, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Industrial Standards of the People’s Republic of China. MH/T 5011-2019 Specifications for Asphalt Pavement Construction of Civil Airports; China Civil Aviation Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Wu, Y.; Yao, H. Engineering Machinery Design; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, F.; Wu, S.; Tang, N. Modelling and experimental investigation on mixing technique of graphite modified conductive asphalt mixture. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNECE, The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. Life Cycle Assessment of Electricity Generation Options. 2021. Available online: https://unece.org/sed/documents/2021/10/reports/life-cycle-assessment-electricity-generation-options (accessed on 16 September 2023).



| Region | Electricity CO2 Emission Factor (kg/kW·h) |
|---|---|
| North China Region | 0.8843 |
| Northeast China Region | 0.7769 |
| East China Region | 0.7035 |
| Central China Region | 0.5257 |
| Southwest China Region | 0.6671 |
| South China Region | 0.5271 |
| Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agitator capacity/kg | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 | 3000 | 3500 | 4000 | 4500 | 5000 |
| CO2 emission reduction/% | 1 | 13.2 | 21.1 | 26.3 | 30.1 | 32.9 | 35.1 | 36.8 |
| Electricity Generation Sources | Life Cycle Carbon Emission Factors (kg CO2eq/kWh) |
|---|---|
| Coal power | 1.023 |
| Natural gas | 0.434 |
| Solar power | 0.037 |
| Wind power | 0.012 |
| Hydropower | 0.010 |
| Nuclear power | 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Carbon Emission Model and Emission Reduction Technology in the Asphalt Mixture Mixing Process. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101518
Liu N, Wang Y, Yang H. Carbon Emission Model and Emission Reduction Technology in the Asphalt Mixture Mixing Process. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(10):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101518
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Nieyangzi, Yuanqing Wang, and Haitao Yang. 2023. "Carbon Emission Model and Emission Reduction Technology in the Asphalt Mixture Mixing Process" Atmosphere 14, no. 10: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101518
APA StyleLiu, N., Wang, Y., & Yang, H. (2023). Carbon Emission Model and Emission Reduction Technology in the Asphalt Mixture Mixing Process. Atmosphere, 14(10), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101518






