Characteristic Variation of Particulate Matter-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) during Asian Dust Events, Based on Observations at a Japanese Background Site, Wajima, from 2010 to 2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
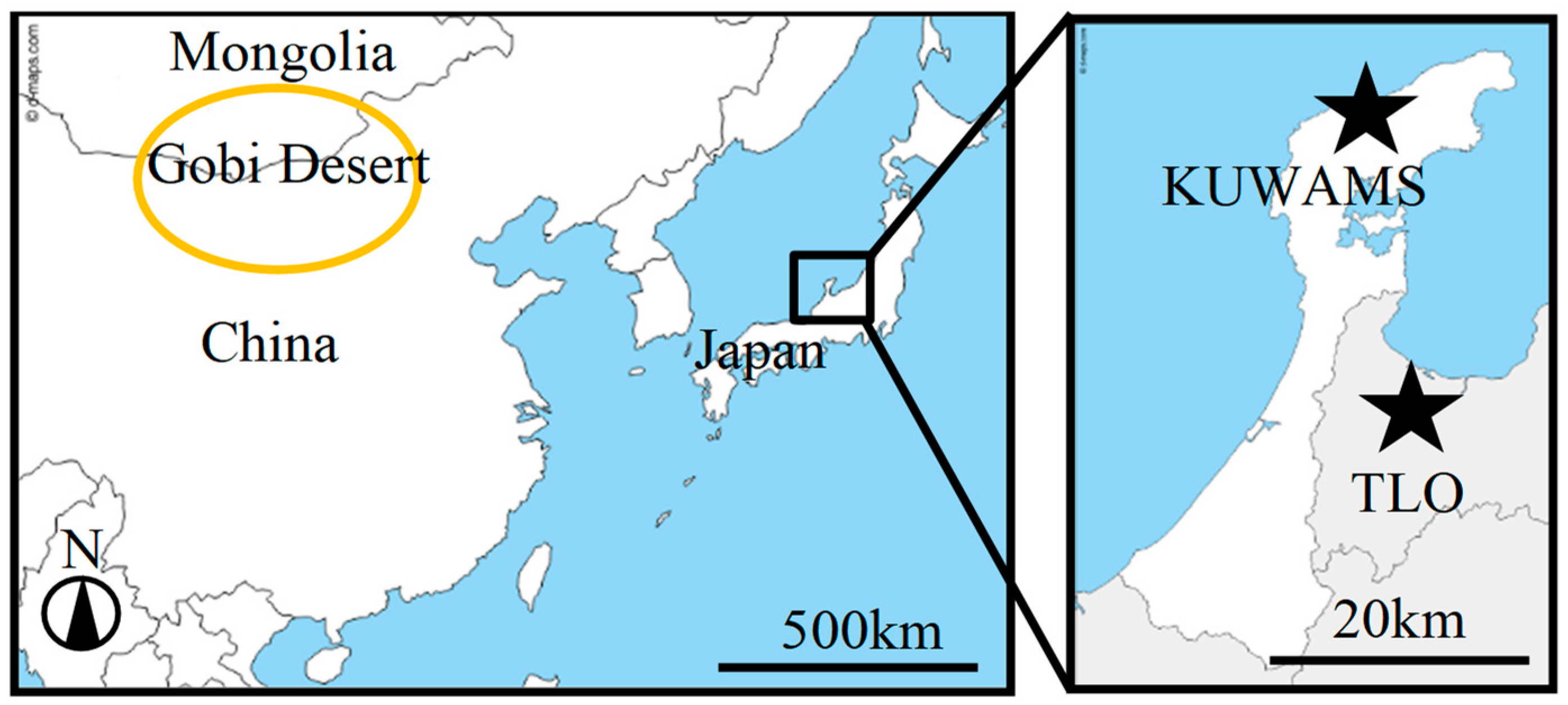
2.1. TSP Sampling
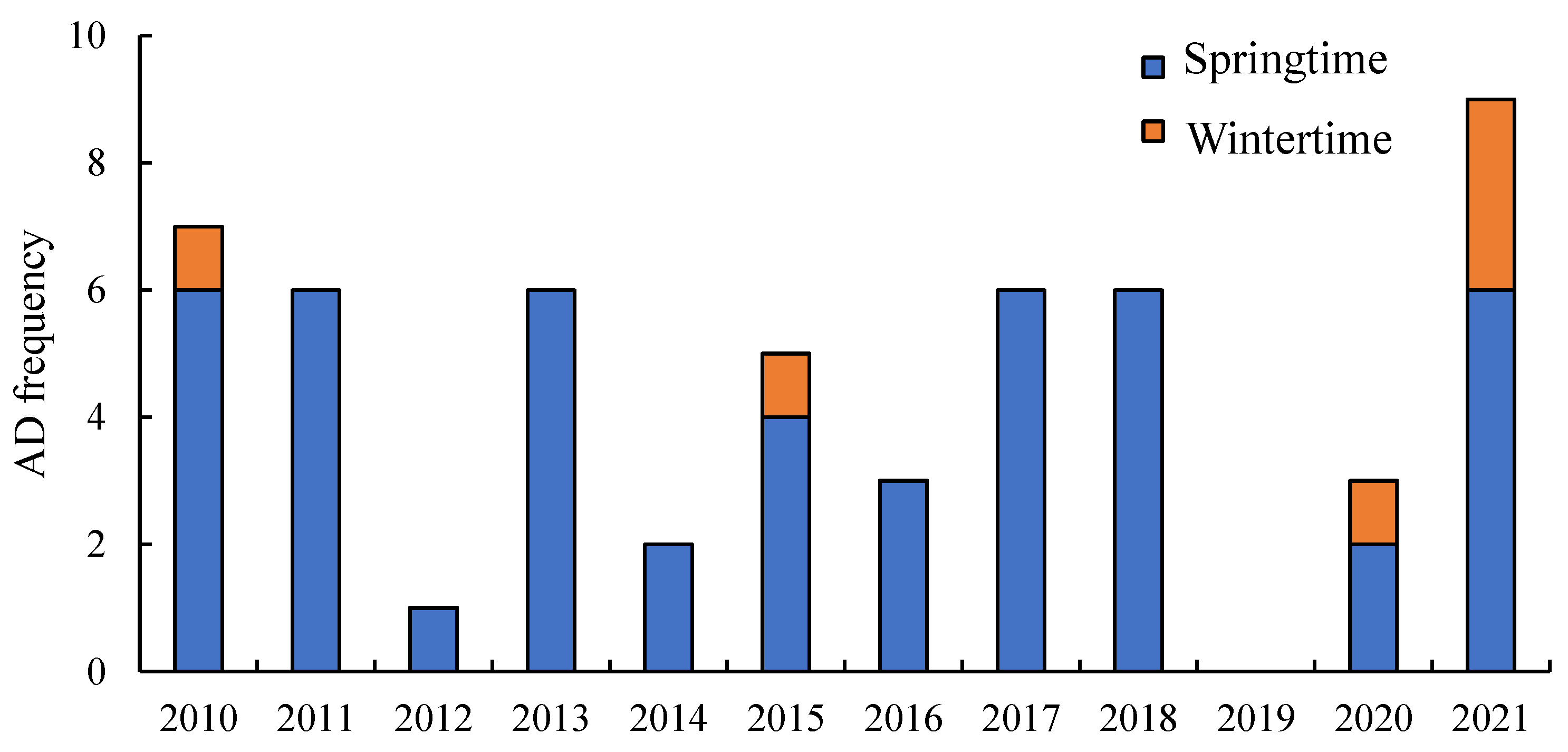
2.2. Asian Dust Periods
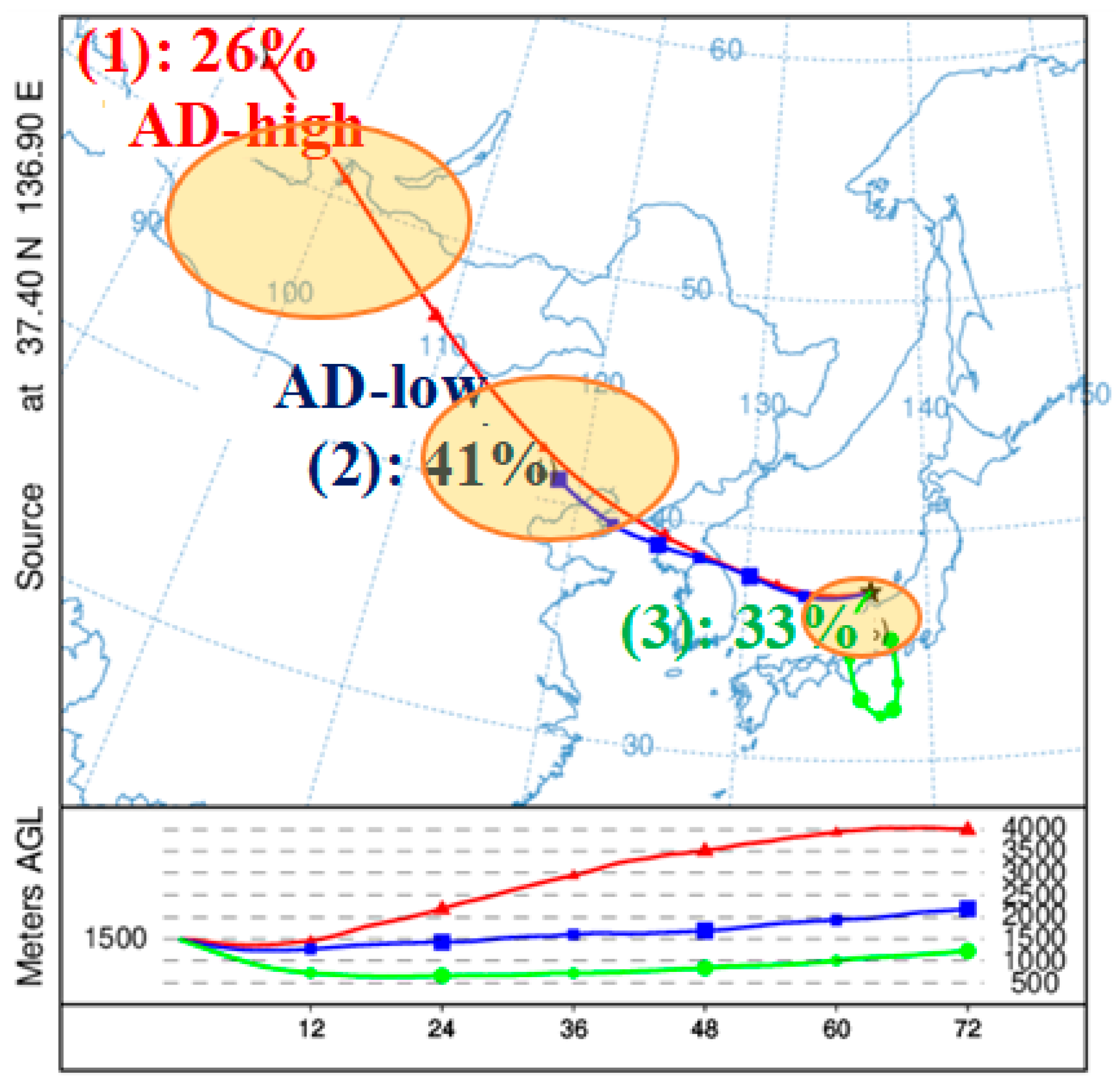
2.3. Backward Trajectory Cluster Analysis
2.4. PAH Analysis
2.5. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.6. Assessment of Health Risk
2.7. Source Identification of PAHs
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Source of Ads during Sample Periods
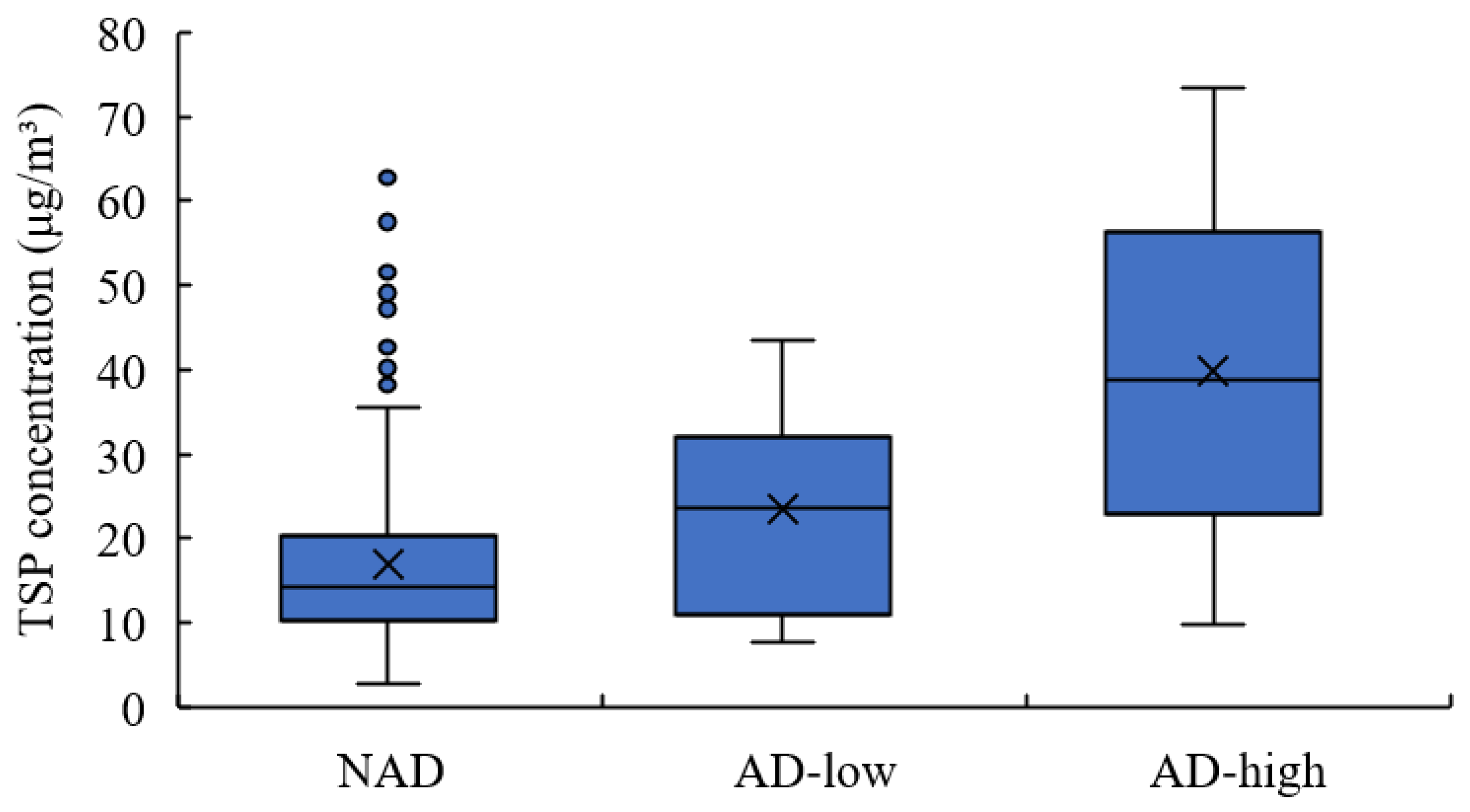
3.2. TSP Concentration
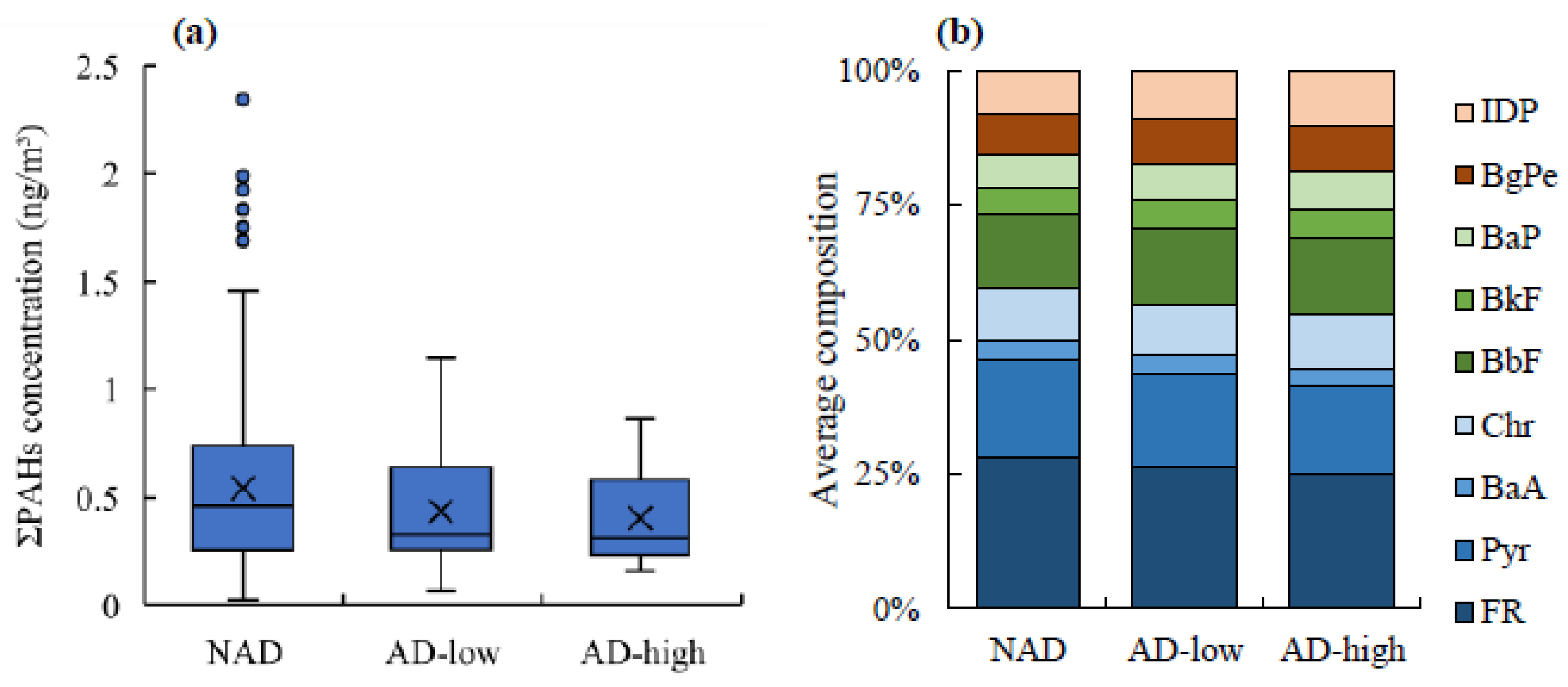
3.3. PAH Concentration, Composition, and Source
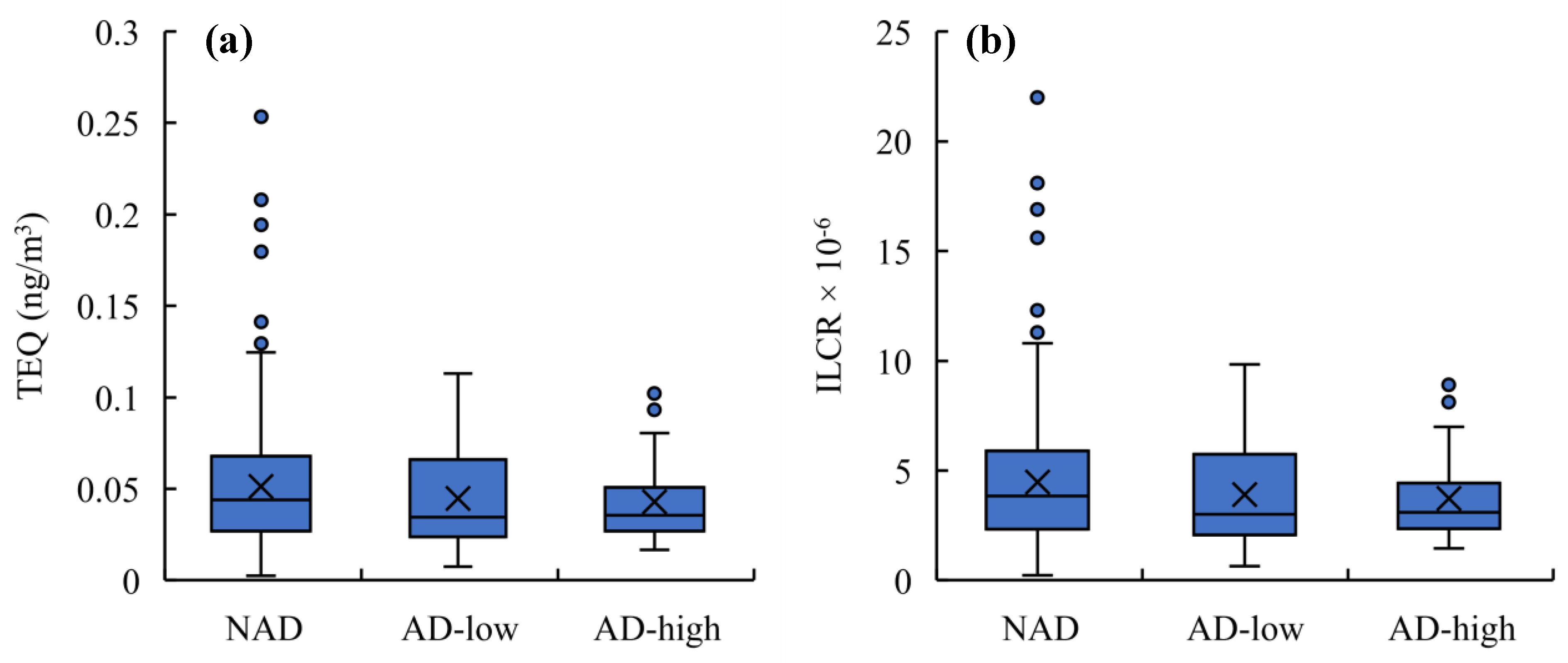
3.4. Health Risks of PAHs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sullivan, R.C.; Guazzotti, S.A.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Direct Observations of the Atmospheric Processing of Asian Mineral Dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1213–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, S.; Yorifuji, T.; Bae, S.; Honda, Y.; Lim, Y.-H.; Hong, Y.-C. Asian Dust Effect on Cause-Specific Mortality in Five Cities across South Korea and Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, S.; Yorifuji, T.; Suzuki, E. Asian Dust and Daily Emergency Ambulance Calls among Elderly People in Japan. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fu, J.S.; Zhang, W.; Tang, A.; et al. Asian Dust over Northern China and Its Impact on the Downstream Aerosol Chemistry in 2004. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D00K09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-I.; Son, S.-W.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, R.J.; Chen, D. Contrasting Synoptic Weather Patterns between Non-Dust High Particulate Matter Events and Asian Dust Events in Seoul, South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Naoe, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Inomata, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Aerosol Concentrations Observed at Mt. Haruna, Japan, in Relation to Long-Range Transport of Asian Mineral Dust Aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4638–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, S.; Onishi, K.; Mu, H.; Kurozawa, Y. The Effect of Asian Dust Events on the Daily Symptoms in Yonago, Japan: A Pilot Study on Healthy Subjects. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2011, 66, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Hakamata, M.; Sato, K.; Okada, Y.; Yang, X.; Tatematsu, M.; Toriba, A.; Kameda, T.; Hayakawa, K. Atmospheric Behaviors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons at a Japanese Remote Background Site, Noto Peninsula, from 2004 to 2014. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Zhang, H.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N. Impact of the COVID-19 Outbreak on the Long-Range Transport of Particulate Pahs in East Asia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Xing, W.L.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; Wei, Y.; Tang, N. Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Common Air Pollutants at Wajima, a Remote Background Site in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, M.; Yoshikawa, A.; Muraki, H.; Arao, K.; Uno, I. Transport of Mineral and Anthropogenic Aerosols during a Kosa Event over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC 3-1–AAC 3-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, L.; Han, C.; Akutagawa, T.; Endo, O.; Yamauchi, M.; Neroda, A.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Five East Asian Cities: Seasonal Characteristics, Health Risks, and Yearly Variations. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Hayakawa, K.; Toriba, A.; Tang, N. Impact of COVID-19 Outbreak on the Long-Range Transport of Common Air Pollutants in KUWAMS. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Tang, N. Personal PM2.5-Bound PAH Exposure and Lung Function in Healthy Office Workers: A Pilot Study in Beijing and Baoding, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 133, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A. Atmospheric Behaviors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in East Asia. Genes Environ. 2014, 36, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ambade, B.; Sankar, T.K.; Sethi, S.S.; Kurwadkar, S. Source Identification and Health Risk Assessment of Atmospheric PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Jamshedpur, India. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 52, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Takami, A.; Sato, K.; Shimizu, A.; Yoshino, A.; et al. Comparative Analysis of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHS), Nitro-Pahs (NPAHS), and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions (WSIIS) at Two Background Sites in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; He, H. Synergistic Reaction between SO2 and NO2 on Mineral Oxides: A Potential Formation Pathway of Sulfate Aerosol. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-Y.; Okada, Y.; Tang, N.; Matsunaga, S.; Tamura, K.; Lin, J.-M.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Long-Range Transport of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from China to Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Yang, L.; Nakatsubo, R.; Wei, Y.; Bi, J.; Shima, M.; Toriba, A.; et al. Natural Aeolian Dust Particles Have No Substantial Effect on Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Laboratory Study Based on Naphthalene. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Hattori, T.; Taga, R.; Igarashi, K.; Yang, X.; Tamura, K.; Kakimoto, H.; Mishukov, V.F.; Toriba, A.; Kizu, R.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitropolycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Air Particulates and Their Relationship to Emission Sources in the Pan-Japan Sea Countries. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5817–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Sato, K.; Tokuda, T.; Tatematsu, M.; Hama, H.; Suematsu, C.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Factors Affecting Atmospheric 1-, 2-Nitropyrenes and 2-Nitrofluoranthene in Winter at Noto Peninsula, a Remote Background Site, Japan. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Hu, M.; Chen, B.; Han, C.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; et al. Long-Term Variabi lity of Inorganic Ions in TSP at a Remote Background Site in Japan (Wajima) from 2005 to 2015. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Nagao, S.; Chen, B.; Tang, N. Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Different Types of Asian Dust in Wajima, a Background Site in Japan. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Environment Studies. Available online: https://www-lidar.nies.go.jp/Toyama/archives/ (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Murayama, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Uno, I.; Kinoshita, K.; Aoki, K.; Hagiwara, N.; Liu, Z.; Matsui, I.; Sakai, T.; Shibata, T.; et al. Ground-Based Network Observation of Asian Dust Events of April 1998 in East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18345–18359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Arao, K.; Chen, Y. Continuous Lidar Observations of Asian Dust in Beijing, Nagasaki and Tsukuba. In Proceedings of the Third International Asia-Pacific Environmental Remote Sensing Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere, Ocean, Environment, and Space, Hangzhou, China, 23–27 October 2002; SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 4893, pp. 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Arao, K.; Uno, I.; Murayama, T.; Kagawa, N.; Aoki, K.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A.A. Continuous Observations of Asian Dust and Other Aerosols by Polarization Lidars in China and Japan during ACE-Asia. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2004, 109, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HYSPLIT Air Resources Laboratory. Available online: https://www.arl.noaa.gov/documents/reports/hysplit_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2023).
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Zhang, L.; Toriba, A.; Nagao, S.; Suzuki, N.; Honda, M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Estimation of Gaseous Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Characteristics of Atmospheric PAHs at a Traffic Site in Kanazawa, Japan. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnesota Department of Health. Guidance for Evaluating the Cancer Potency of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Mixtures in Environmental Samples; Environmental Health Division, Environmental Surveillance and Assessment Section, Minnesota Department of Health: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Morisaki, H.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.; Hu, M.; Shima, M.; et al. Characteristics of Air Pollutants inside and Outside a Primary School Classroom in Beijing and Respiratory Health Impact on Children. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, H.; Deutsch-Wenzel, R.P.; Habs, M.; Ivankovic, S.; Schmähl, D. Investigation of the tumorigenic response to benzo(a)pyrene in aqueous caffeine solution applied orally to Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1981, 102, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N.; Nagato, E.; Toriba, A.; Lin, J.-M.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Qing, W.; Yang, X.; Mishukov, V.; et al. Long-Term Trends in Urban Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitropolycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: China, Russia, and Korea from 1999 to 2014. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Development of a Relative Potency Factor (RPF) Approach for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Mixtures. External Review Draft; Environmental Protection Agency; Integrated Risk Information System: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Manoli, E.; Kouras, A.; Samara, C. Profile Analysis of Ambient and Source Emitted Particle-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Three Sites in Northern Greece. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. PAH Diagnostic Ratios for the Identification of Pollution Emission Sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Torre-Roche, R.J.; Lee, W.-Y.; Campos-Díaz, S.I. Soil-Borne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in El Paso, Texas: Analysis of a Potential Problem in the United States/Mexico Border Region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River Basin: A Critical Appraisal of PAH Ratios as Indicators of PAH Source and Composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Suzuki, G.; Morisaki, H.; Tokuda, T.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Lin, J.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Atmospheric Behaviors of Particulate-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitropolycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Beijing, China from 2004 to 2010. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Ho, C.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J. Quiescence of Asian Dust Events in South Korea and Japan during 2012 Spring: Dust Outbreaks and Transports. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 114, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, T.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Jian, B.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J. New Insights into the Asian Dust Cycle Derived from CALIPSO Lidar Measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 272, 112906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ueda, H.; Matsuda, K.; Zhang, R.; Arao, K.; Kanai, Y.; Hasome, H. Model Study on Particle Size Segregation and Deposition during Asian Dust Events in March 2002. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2004, 109, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Q.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Tian, P.; et al. The Mixing State of Mineral Dusts with Typical Anthropogenic Pollutants: A Mechanism Study. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 209, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, R.E.; Kubátová, A.; Kozliak, E.I. An Approach to the Estimation of Adsorption Enthalpies of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Particle Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 6029–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, N.; Romanias, M.N.; Riffault, V.; Thevenet, F. Investigating Water Adsorption onto Natural Mineral Dust Particles: Linking DRIFTS Experiments and BET Theory. Aeolian Res. 2017, 27, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeineddine, M.N.; Romanias, M.N.; Riffault, V.; Thévenet, F. Heterogeneous Interaction of Various Natural Dust Samples with Isopropyl Alcohol as a Probe VOC. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 4911–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamamura, S.; Sato, T.; Ota, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, N.; Hayakawa, K. Long-Range Transport of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) from the Eastern Asian Continent to Kanazawa, Japan with Asian Dust. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2580–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air Quality Standards. European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/air/quality/standards.htm (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2000: Health Systems: Improving Performance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; ISBN 92-4-156198-X. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA (United States of Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. In Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part B, Development of Risk-Based Preliminary Remediation Goals); EPA/540/R-92/003; USA Office of Emerage and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
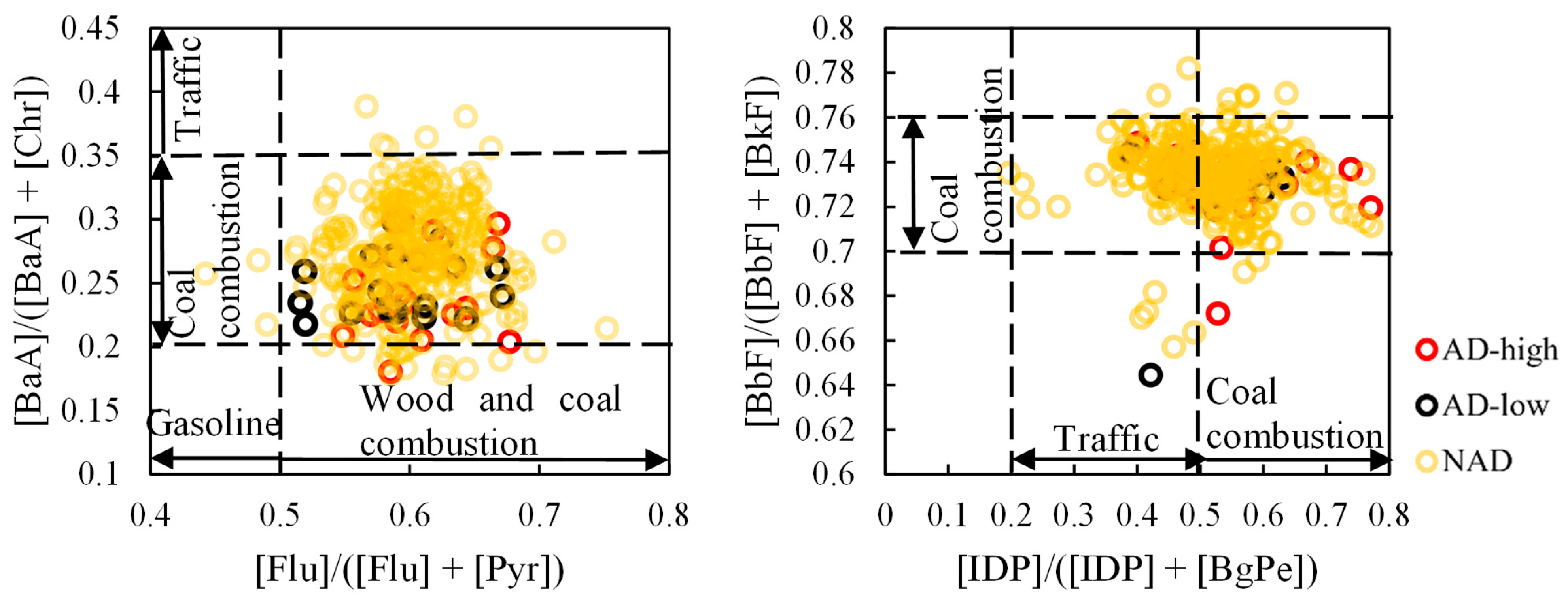
| Diagnostic Ratio | Value Range | Source |
|---|---|---|
| [Flu]/([Flu] + [Pyr]) | 0.4–0.5 | Gasoline combustion [39] |
| >0.5 | Wood and coal combustion [40] | |
| [BaA]/([BaA] + [Chr]) | 0.2–0.35 | Coal combustion [38,40] |
| >0.35 | Traffic emission [38,40] | |
| [IDP]/([IDP] + [BgPe]) | 0.2–0.5 | Traffic emission [38,40] |
| >0.5 | Coal combustion [38,40] | |
| [BbF]/([BbF] + [BkF]) | 0.7–0.76 | Coal combustion [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Matsuki, A.; Nagao, S.; Chen, B.; Tang, N. Characteristic Variation of Particulate Matter-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) during Asian Dust Events, Based on Observations at a Japanese Background Site, Wajima, from 2010 to 2021. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101519
Bai P, Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhang L, Matsuki A, Nagao S, Chen B, Tang N. Characteristic Variation of Particulate Matter-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) during Asian Dust Events, Based on Observations at a Japanese Background Site, Wajima, from 2010 to 2021. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(10):1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101519
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Pengchu, Yan Wang, Hao Zhang, Xuan Zhang, Lulu Zhang, Atsushi Matsuki, Seiya Nagao, Bin Chen, and Ning Tang. 2023. "Characteristic Variation of Particulate Matter-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) during Asian Dust Events, Based on Observations at a Japanese Background Site, Wajima, from 2010 to 2021" Atmosphere 14, no. 10: 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101519
APA StyleBai, P., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, L., Matsuki, A., Nagao, S., Chen, B., & Tang, N. (2023). Characteristic Variation of Particulate Matter-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) during Asian Dust Events, Based on Observations at a Japanese Background Site, Wajima, from 2010 to 2021. Atmosphere, 14(10), 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101519







