Spatiotemporal Variations of Drought and the Related Mitigation Effects of Artificial Precipitation Enhancement in Hengyang-Shaoyang Drought Corridor, Hunan Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Meteorological Data
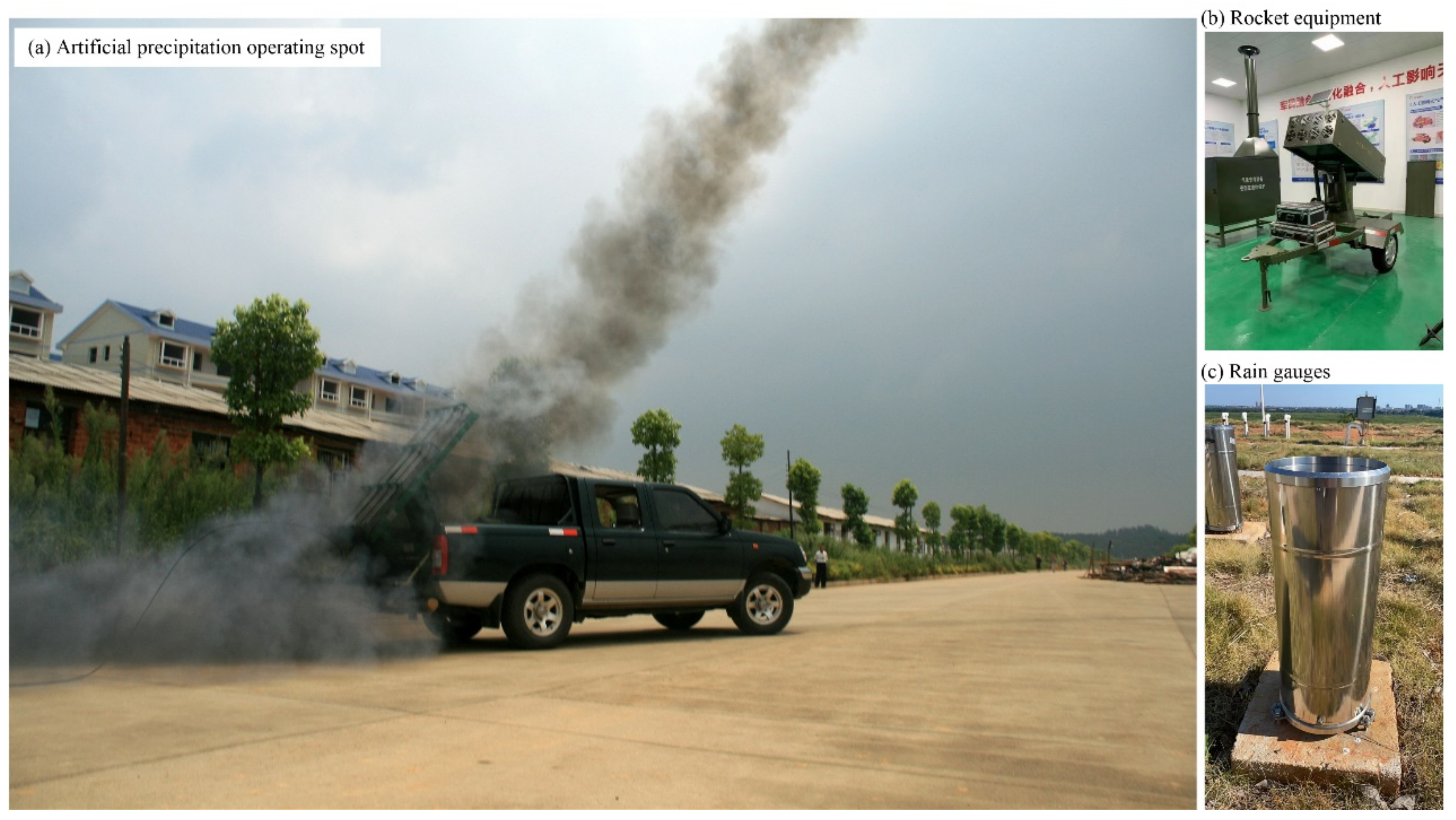
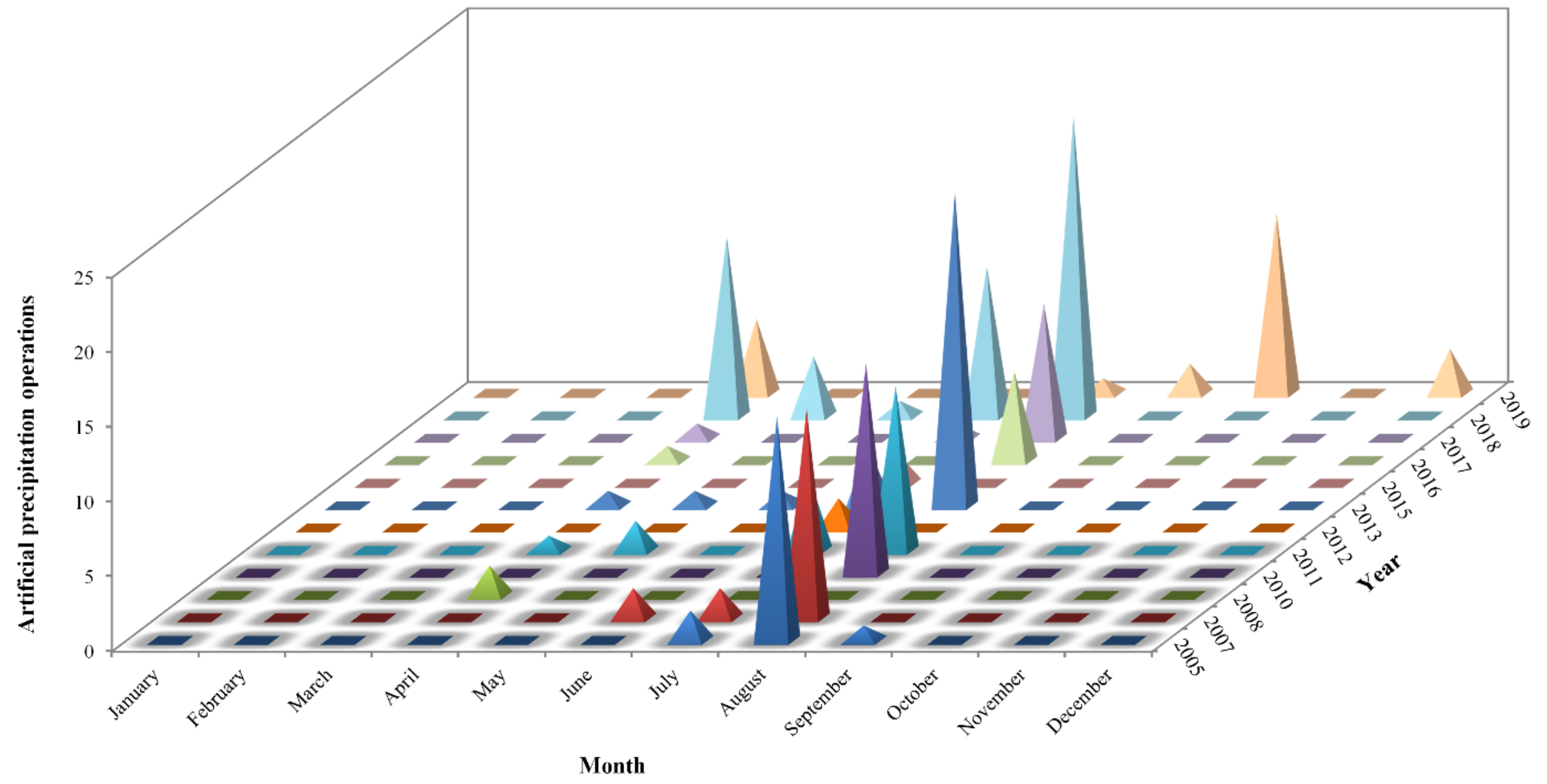
2.2.2. Artificial Precipitation Data
2.2.3. Other Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Standardized Precipitation Index
2.3.2. Drought Frequency
2.3.3. Drought Station Ratio
2.3.4. Drought Intensity
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Temporal Variability of Droughts
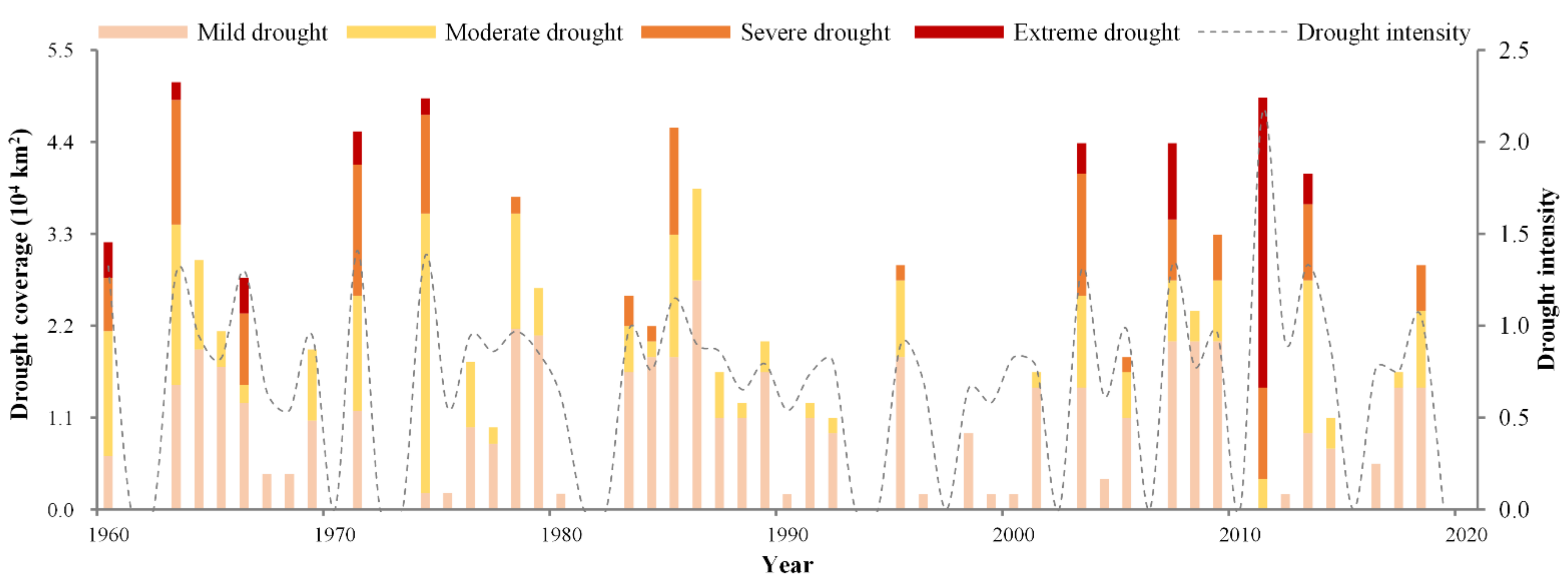
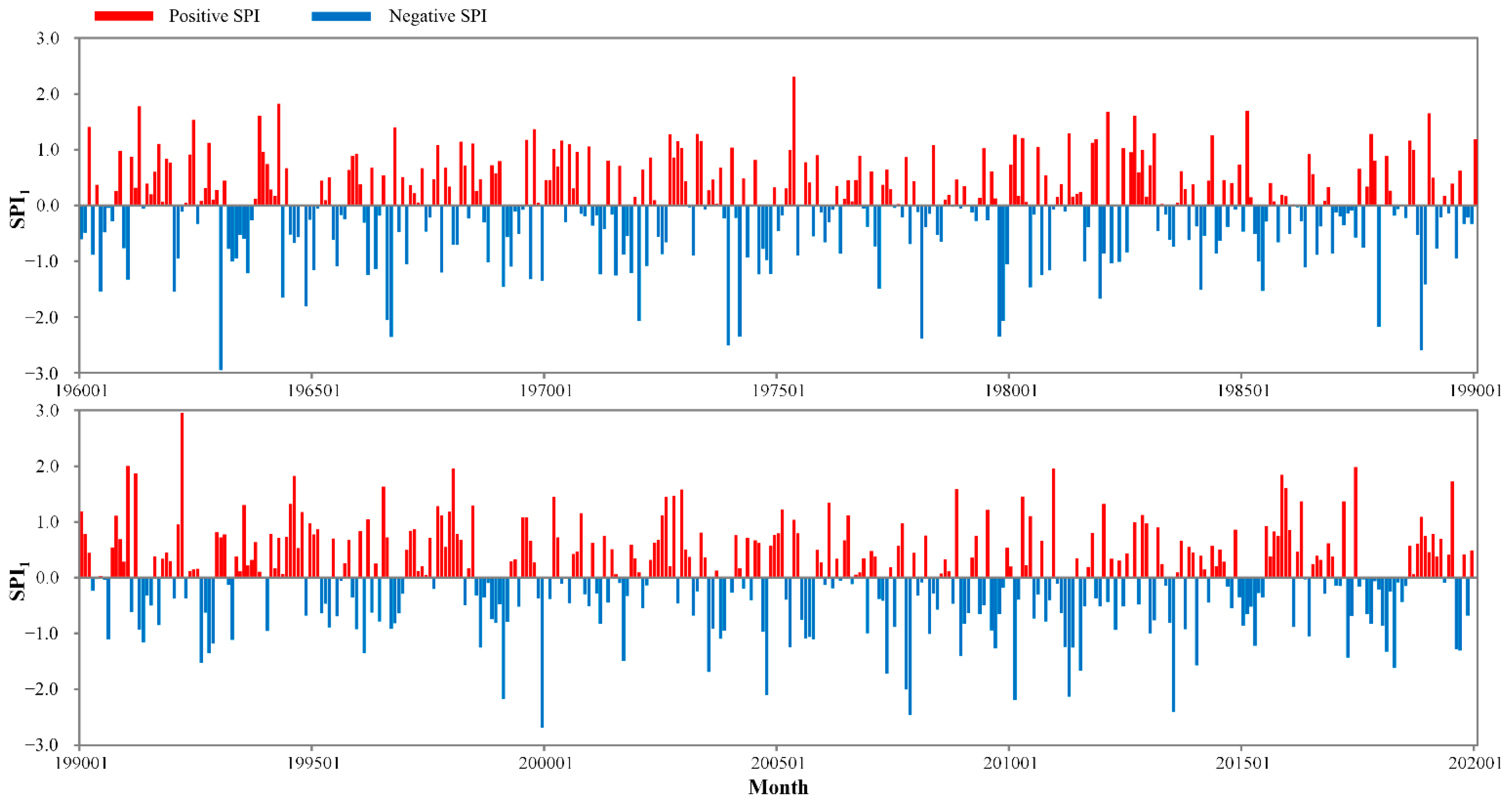
3.1.1. Interannual Variation
3.1.2. Seasonal Variation
3.1.3. Monthly Variation
3.2. Spatial Patterns of Droughts
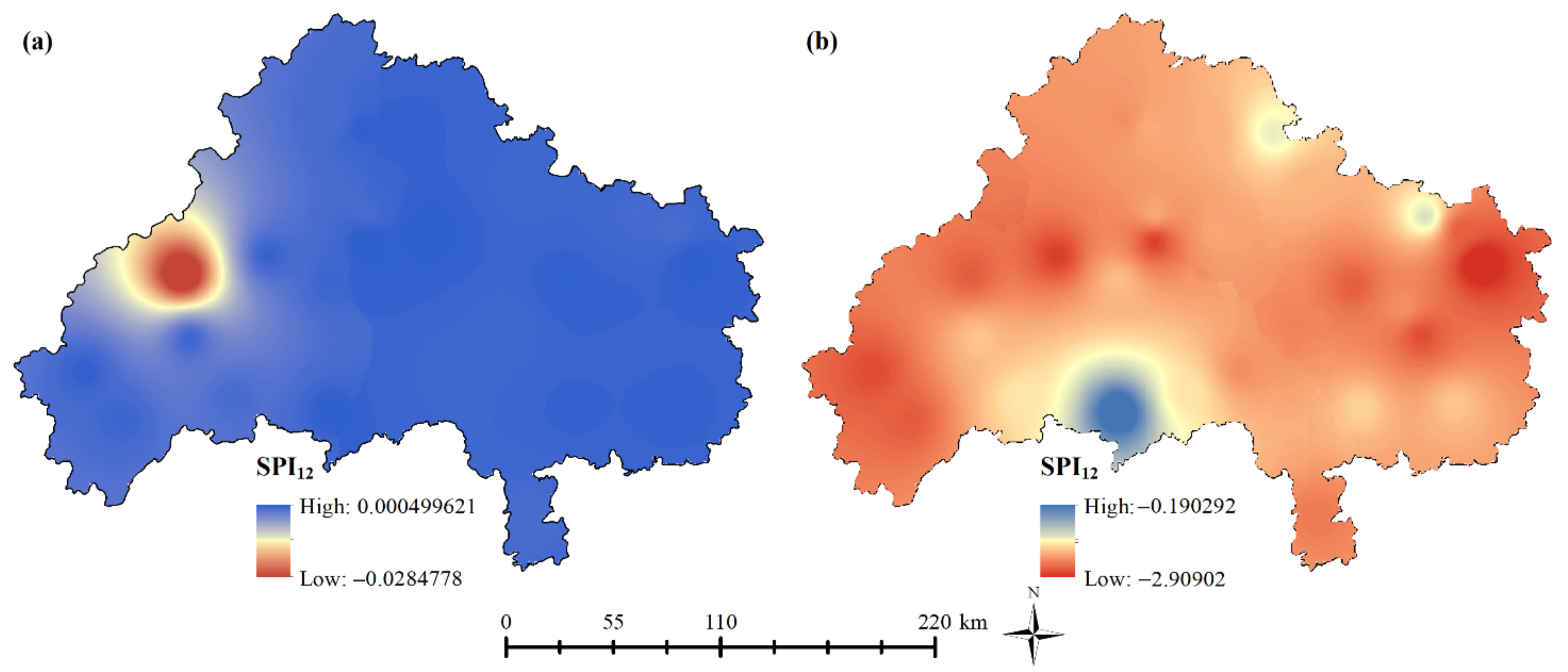
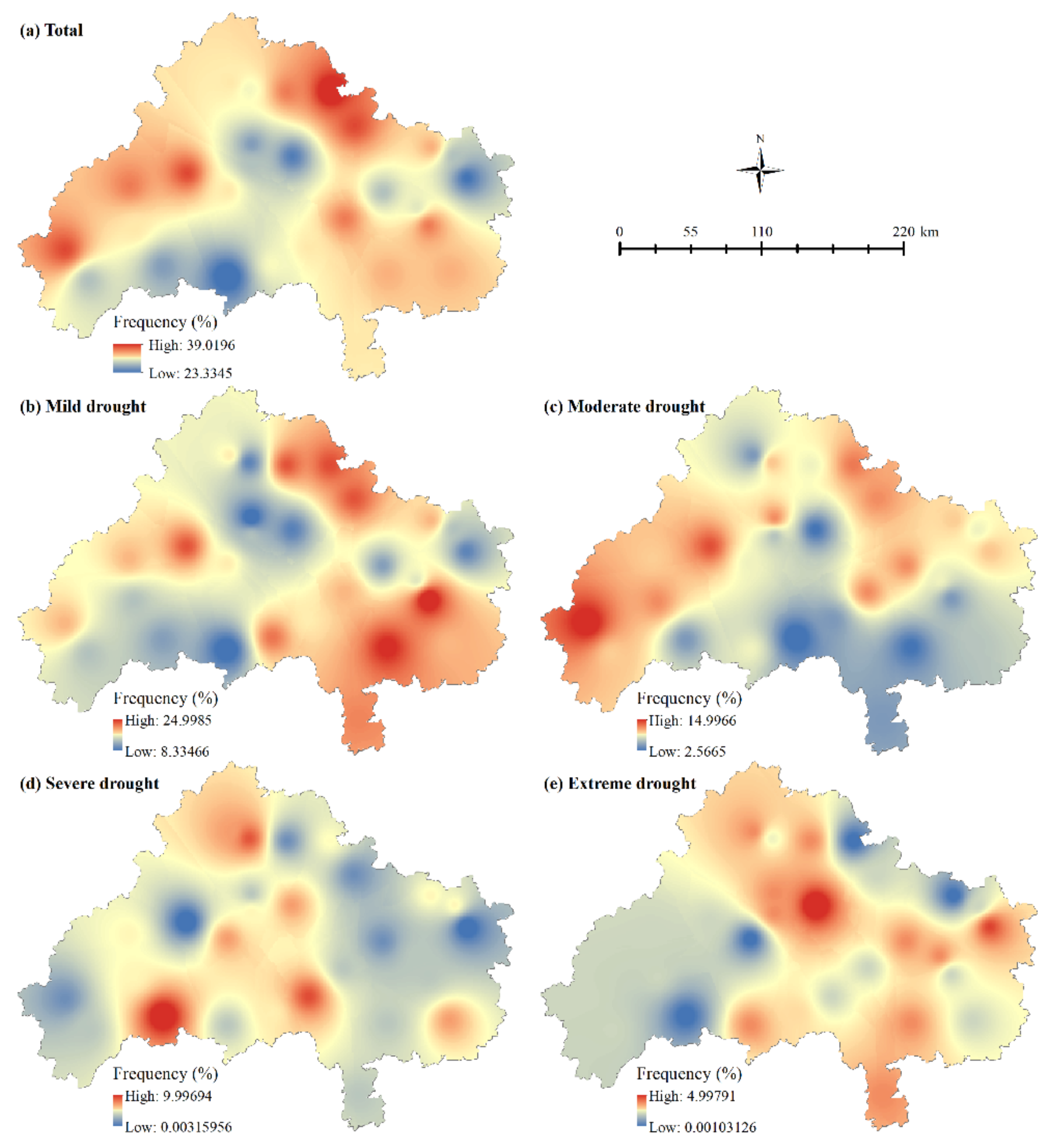
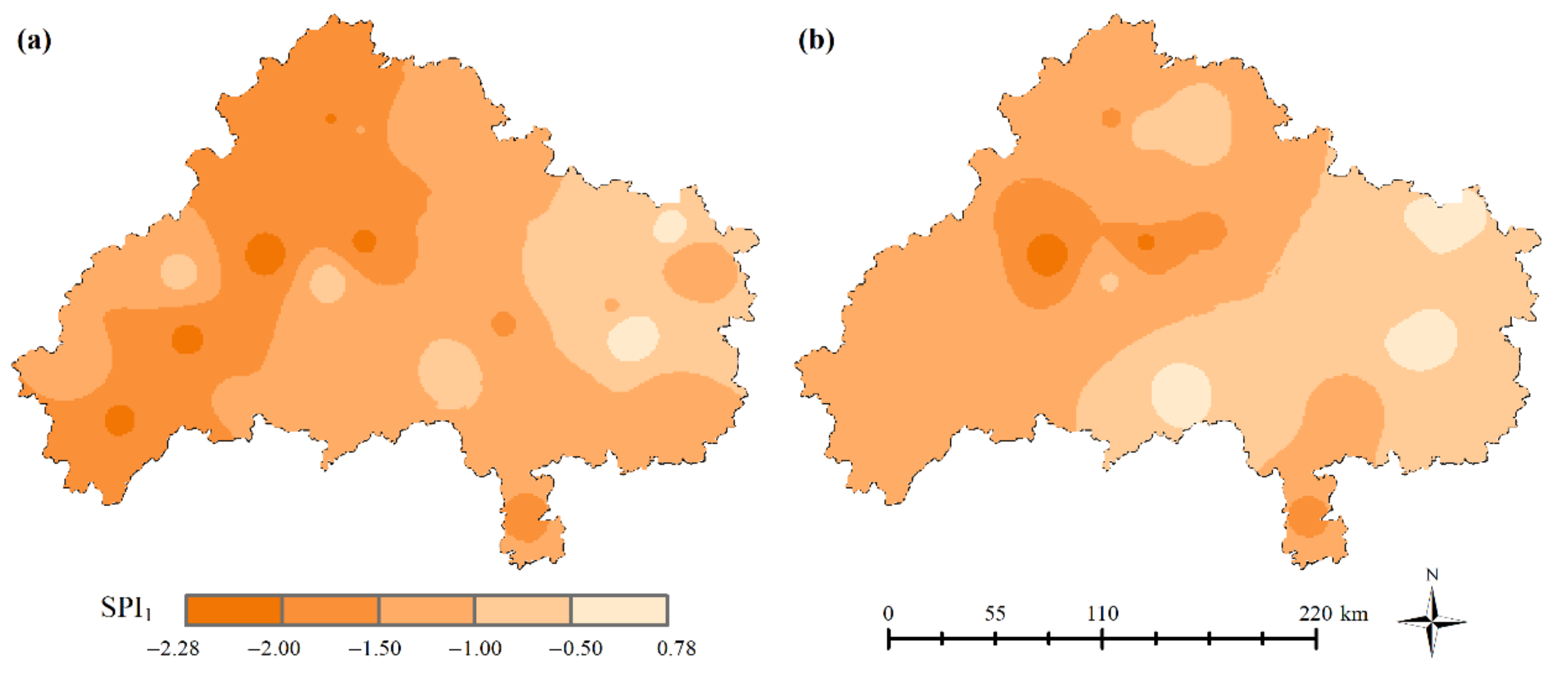
3.2.1. Spatial Analysis of Annual Drought
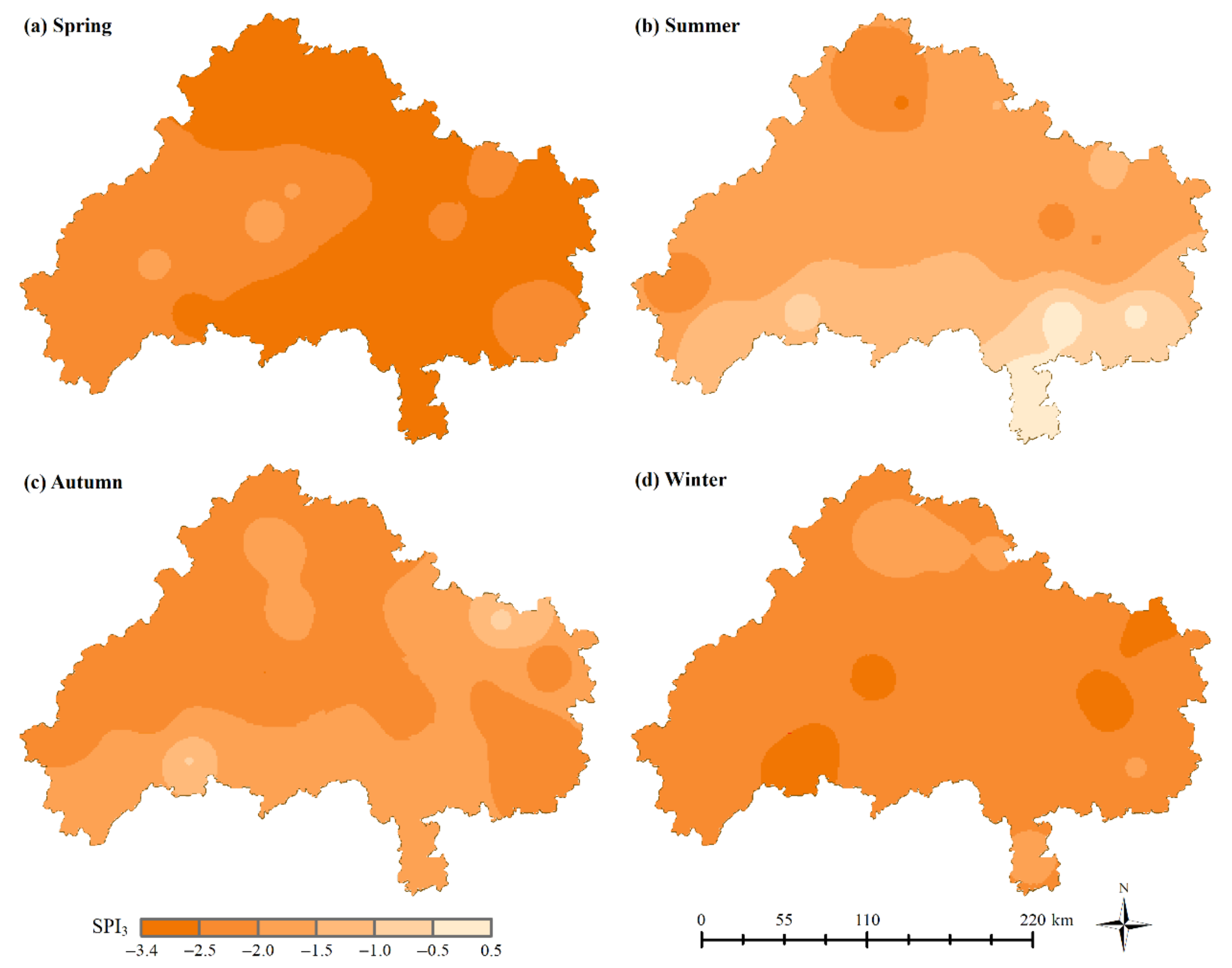
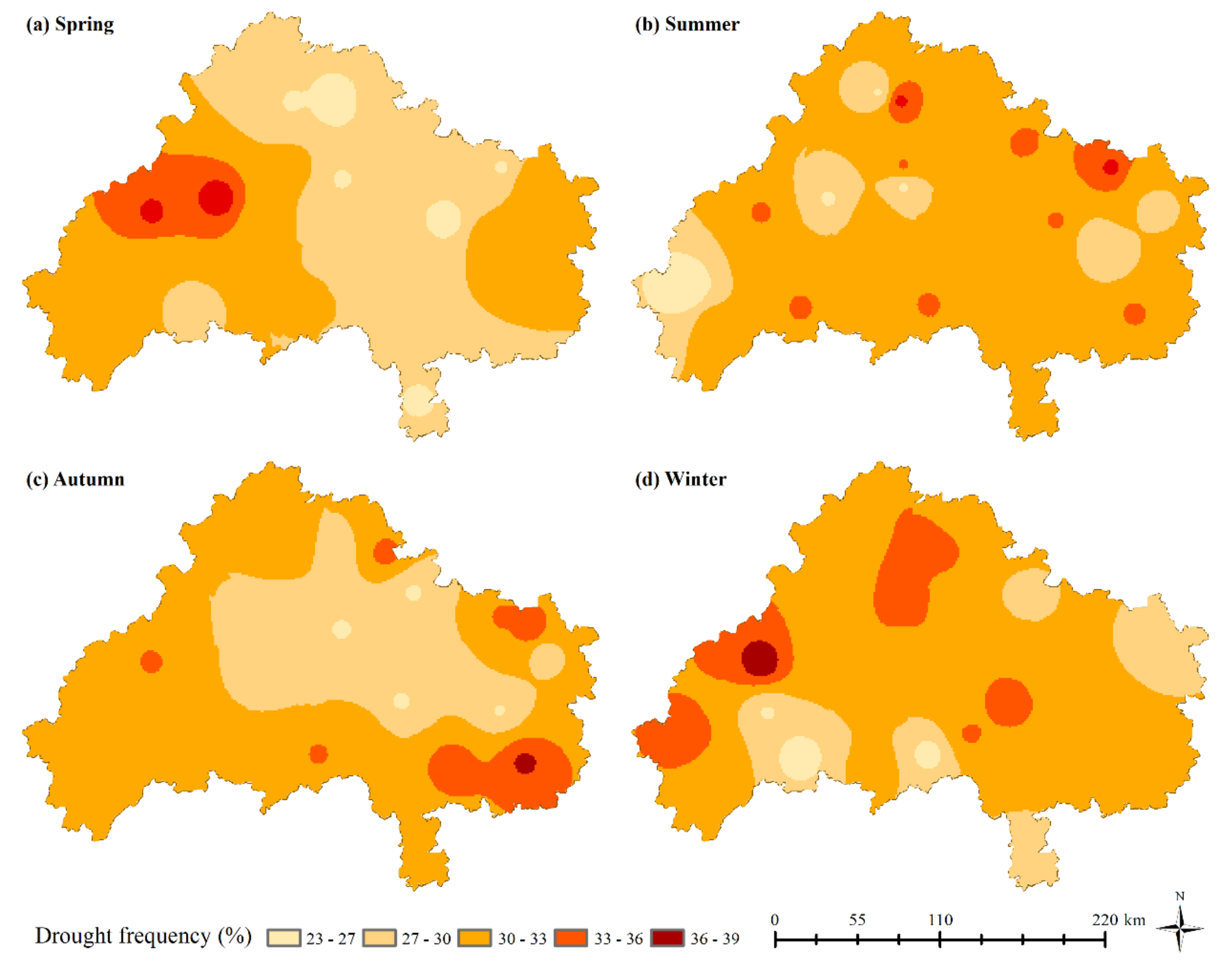
3.2.2. Spatial Analysis of Seasonal Drought
3.3. Mitigation Effects of Artificial Precipitation on Droughts
4. Discussion and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, X.; Zang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Yan, D. Study on spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of flood and drought disaster impacts on agriculture in China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 64, 102504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhou, J. Responses of precipitation and runoff to climate warming and Implications for future drought changes in China. Earths Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascolini-Campbell, M.; Reager, J.T.; Chandanpurkar, H.A.; Rodell, M. A 10 per cent increase in global land evapotranspiration from 2003 to 2019. Nature 2021, 593, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesk, C.; Rowhani, P.; Ramankutty, N. Influence of extreme weather disasters on global crop production. Nature 2016, 529, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, T.; Wei, J. Exploring drought conditions in the Three River Headwaters Region from 2002 to 2011 using multiple drought indices. Water 2019, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, G.; Alfieri, L.; Wyser, K.; Mentaschi, L.; Betts, R.A.; Carrao, H.; Spinoni, J.; Vogt, J.; Feyen, L. Global changes in drought conditions under different levels of warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Gilani, H. Global drought monitoring with drought severity index (DSI) using Google Earth Engine. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 146, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation: Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- UNCCD. Land and Drought. Available online: https://www.unccd.int/issues/land-and-drought (accessed on 18 October 2018).
- Parsons, L.A. Implications of CMIP6 projected drying trends for 21st century amazonian drought risk. Earths Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ha, K.J.; Yeo, J.H. New drought projections over East Asia using evapotranspiration deficits from the CMIP6 warming scenarios. Earths Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, S.; Yang, W.; Sun, Q. Effects and contributions of meteorological drought on agricultural drought under different climatic zones and vegetation types in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Hao, F.; Singh, V.P.; Zhang, X. Quantifying the relationship between compound dry and hot events and El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) at the global scale. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, M.N.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, J.Y.; Kim, T.W. Probabilistic characteristics of drought propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought in South Korea. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 2439–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Huang, J.; Fischer, T.; Wang, Y.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Zhai, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, A.; Zeng, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Drought losses in China might double between the 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10600–10605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, G.; Ni, S.; Wright, J.S.; Hall, J.; Ciais, P.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Assessing the impacts of extreme agricultural droughts in China under climate and socioeconomic changes. Earths Future 2018, 6, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, K.; Koffler, D.; Schöner, W.; Laaha, G. Exploring the link between meteorological drought and streamflow: Effects of climate-catchment interaction. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2468–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghelpour, P.; Guan, Y.; Bahrami-Pichaghchi, H.; Mohammadi, B.; Kisi, O.; Zhang, D. Using the MODIS sensor for snow cover modeling and the assessment of drought effects on snow cover in a mountainous area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobrossi, J.; Karam, F.; Mitri, G. Rain pattern analysis using the Standardized Precipitation Index for long-term drought characterization in Lebanon. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musonda, B.; Jing, Y.; Iyakaremye, V.; Ojara, M. Analysis of long-term variations of drought characteristics using standardized precipitation index over Zambia. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. Identifying spatial extent of meteorological droughts: An examination over a humid region. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q.G.; Li, L.; Peng, L.; Feng, H. Influence of the accuracy of reference crop evapotranspiration on drought monitoring using standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index in mainland China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 31, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Lu, C.; Chen, Y. Assessing agricultural drought in the Anthropocene: A modified palmer drought severity index. Water 2017, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, S.; Ullah, K.; Shuanglin, L.; Gao, S.; Khan, A.H.; Mahmood, R. Comparison of various drought indices to monitor drought status in Pakistan. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, G.G.; Tang, Q.; Hosseini-Moghari, S.M.; Liu, X.; Gebremicael, T.G.; Leng, G.; Kebede, A.; Xu, X.; Yun, X. Projected impacts of climate change on drought patterns over East Africa. Earths Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Naumann, G.; Carrao, H.; Barbosa, P.; Vogt, J. World drought frequency, duration, and severity for 1951–2010. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2792–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Zhang, K. PDSI-based analysis of characteristics and spatiotemporal changes of meteorological drought in China from 1982 to 2015. Water Resour. Prot. 2020, 36, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Huang, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, C. Ensemble drought exposure projection for multifactorial interactive effects of climate change and population dynamics: Application to the Pearl River Basin. Earths Future 2021, 9, e2021EF002215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, R. Spatial analysis of annual precipitation lines of 800 mm in the Eastern Monsoon of China. Plateau Meteorol. 2020, 39, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, F. Advances of the 400 mm isohyet and wetness and dryness changes in the mainland of China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Gu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Spatio-temporal pattern and evolution trend of drought disaster in China in recent seventy years. J. Nat. Disasters 2019, 28, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Mei, P. Temporal and spatial characteristics of drought in China under climate change. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 42, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Yu, J.; Ye, M.; Xie, J. Analysis of the characteristics of regional flash drought in China. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2021, 41, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, F.; Villegas, J.C.; Breshears, D.D. Spatial extent of the North American Monsoon: Increased cross-regional linkages via atmospheric pathways. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L07401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apurv, T.; Cai, X. Impact of droughts on water supply in U.S. watersheds: The role of renewable surface and groundwater resources. Earths Future 2020, 8, e2020EF001648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Fan, Z.; Xu, J.; Lan, M.; Jiang, Y. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation of extreme drought in Hunan Province. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2018, 36, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liao, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhou, J.; Tan, X. Spatial and temporal variation of meteorological drought days in Hunan Province. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2013, 34, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, B. Spatio-temporal characteristics of persistent regional meteorological drought in Summer and Autumn in Hunan. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2021, 39, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Qin, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. Spatial-temporal distribution pattern and trend analysis of rainfalls in the ‘Heng Shao drought corridor’. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 3097–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhyavitri, A.; Perdana, M.A.; Sutikno, S.; Widodo, F.H. The roles of weather modification technology in mitigation of the peat fires during a period of dry season in Bengkalis, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 309, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, H. Effect evaluation of artificial rainfall enhancement in the Shiyang River Basin of Hexi Corridor in the latest 10 years. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidey, E.; Dikinya, O.; Sebego, R.; Segosebe, E.; Zenebe, A. Modeling the spatio-temporal meteorological drought characteristics using the standardized precipitation index (SPI) in Raya and its Environs, Northern Ethiopia. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 2, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh Kumar, M.; Murthy, C.S.; Sesha Sai, M.V.R.; Roy, P.S. On the use of Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) for drought intensity assessment. Meteorol. Appl. 2009, 16, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi Zarch, M.A.; Sivakumar, B.; Sharma, A. Droughts in a warming climate: A global assessment of Standardized precipitation index (SPI) and Reconnaissance drought index (RDI). J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambua, R.M.; Mutua, B.M.; Raude, J.M. Detection of spatial, temporal and trend of meteorological drought using standardized precipitation index (SPI) and effective drought index (EDI) in the upper Tana river basin, Kenya. Open J. Mod. Hydrol. 2018, 8, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramudya, Y.; Onishi, T. Assessment of the standardized precipitation index (SPI) in Tegal City, Central Java, Indonesia. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Surakarta, Indonesia, 2018; Volume 129, p. 012019. [Google Scholar]
- Azimi, S.; Azhdary Moghaddam, M. Modeling short term rainfall forecast using neural networks, and Gaussian process classification based on the SPI drought index. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 1369–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.D.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration of time scales. In Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology; American Meteorological Society: Anaheim, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Du, L. Characteristic of spring and summer drought variations and its relation with maize yield in Shanxi Province in 1972–2012 based on SPI. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2018, 36, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Kuang, W.; Deng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, S. Trend of precipitation variations and their spatial patterns in Hunan Province over 56 years (1960–2015). J. Southwest Univ. 2021, 43, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liu, Z. Time regularity analysis and trend prediction of agricultural drought disaster in Hunan Province. J. Hunan Univ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 19, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zou, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, J.; Liu, J.; Quan, B. Spatial-temporal variations of terrestrial evapotranspiration across China from 2000 to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Drought Categories | Drought Frequency (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December | |
| Mild drought | 15.7 | 14.6 | 15.5 | 13.7 | 14.2 | 15.3 | 14.1 | 13.1 | 12.7 | 15.2 | 13.0 | 10.2 |
| Moderate drought | 8.5 | 6.8 | 9.0 | 8.8 | 8.9 | 10.2 | 8.7 | 6.7 | 7.7 | 9.6 | 7.6 | 7.5 |
| Severe drought | 3.6 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 4.7 | 4.4 | 4.7 | 4.1 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 3.3 | 2.2 | 3.3 |
| Extreme drought | 2.8 | 4.2 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 4.8 | 4.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Tang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X. Spatiotemporal Variations of Drought and the Related Mitigation Effects of Artificial Precipitation Enhancement in Hengyang-Shaoyang Drought Corridor, Hunan Province, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081307
Zhang Z, Fu J, Tang W, Liu Y, Zhang H, Fang X. Spatiotemporal Variations of Drought and the Related Mitigation Effects of Artificial Precipitation Enhancement in Hengyang-Shaoyang Drought Corridor, Hunan Province, China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081307
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhongbo, Jing Fu, Wenwen Tang, Yuan Liu, Haibo Zhang, and Xiaohong Fang. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Variations of Drought and the Related Mitigation Effects of Artificial Precipitation Enhancement in Hengyang-Shaoyang Drought Corridor, Hunan Province, China" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081307
APA StyleZhang, Z., Fu, J., Tang, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, H., & Fang, X. (2022). Spatiotemporal Variations of Drought and the Related Mitigation Effects of Artificial Precipitation Enhancement in Hengyang-Shaoyang Drought Corridor, Hunan Province, China. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081307






