Evolving Hybrid Generalized Space-Time Autoregressive Forecasting with Cascade Neural Network Particle Swarm Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
Multivariate Time Series VAR and GSTAR
- The symbol (+) is defined as greater than two times the standard error and indicates the relationship has a positive correlation.
- The symbol (−) represents a value of less than −2 times the standard error. It indicates that the relationship has a negative correlation.
- The symbol (.) denotes , which is between ±2 times the standard error and indicates no correlation.
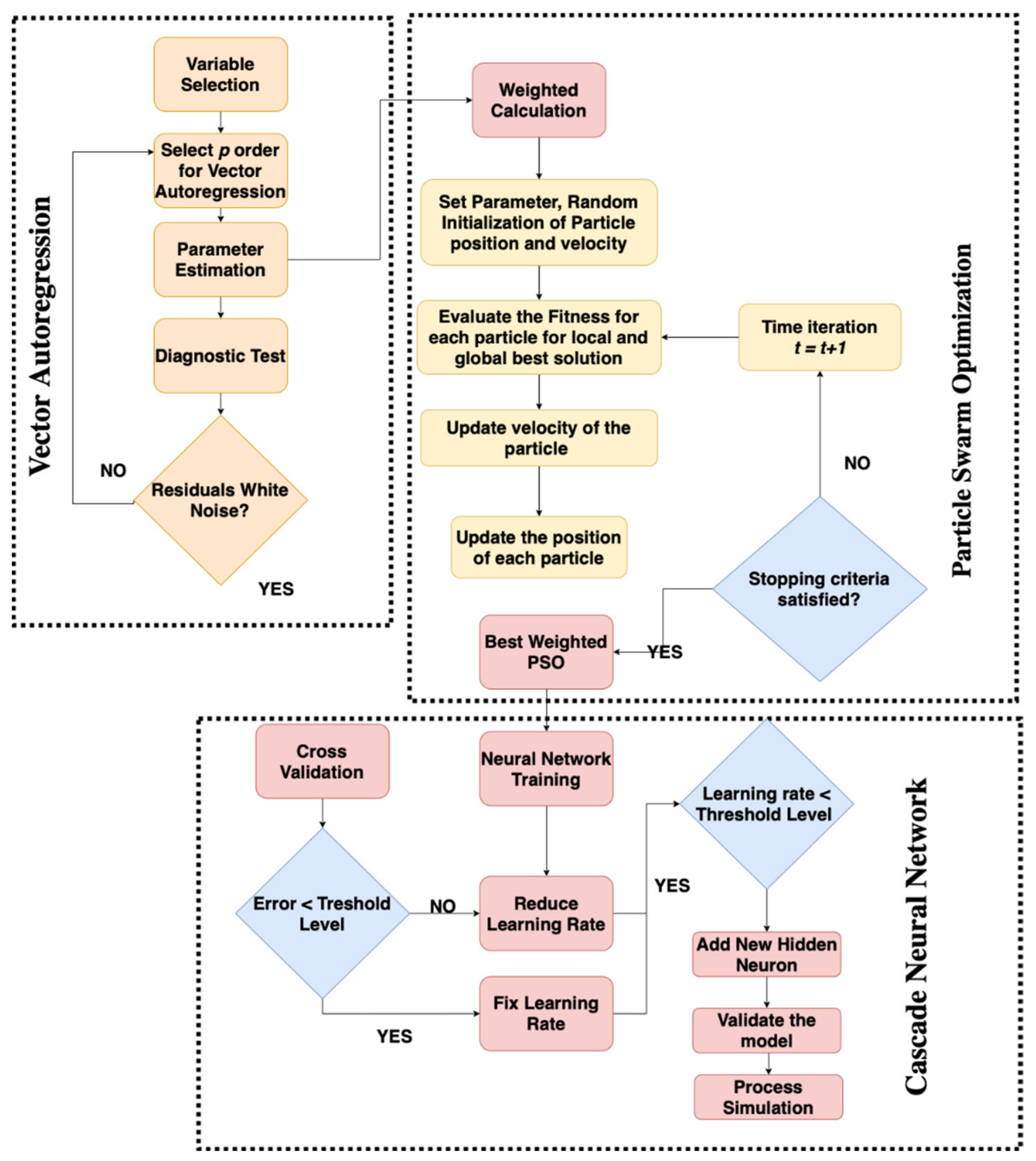
3. The Step Construction Cascade Neural Network with Particle Swarm Optimization
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, L.; Du, M.; Chen, Z. Air Pollution, Health Care Use and Medical Costs: Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2021, 95, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakolis, I.; Hammoud, R.; Stewart, R.; Beevers, S.; Dajnak, D.; MacCrimmon, S.; Broadbent, M.; Pritchard, M.; Shiode, N.; Fecht, D.; et al. Mental Health Consequences of Urban Air Pollution: Prospective Population-Based Longitudinal Survey. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2021, 56, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Review of Evidence on Health Aspects of Air Pollution—REVIHAAP; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Bilal, M.; Ho, H.C.; Omar, A. Urbanization and Regional Air Pollution across South Asian Developing Countries—A Nationwide Land Use Regression for Ambient PM2.5 Assessment in Pakistan. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gooijer, J.G.; Hyndman, R.J. 25 Years of Time Series Forecasting. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 443–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Hibon, M. The M3-Competition: Results, Conclusions and Implications. Int. J. Forecast. 2000, 16, 451–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Spiliotis, E.; Assimakopoulos, V. The M4 Competition: 100,000 Time Series and 61 Forecasting Methods. Int. J. Forecast. 2020, 36, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S. A Survey of Time Series. Int. Stat. Rev. 1976, 44, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraka, R.E.; Chen, R.C.; Yasin, H.; Lee, Y.; Pardamean, B. Hybrid Vector Autoregression Feedforward Neural Network with Genetic Algorithm Model for Forecasting Space-Time Pollution Data. Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartono, S. Time Series Forecasting by Using Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average: Subset, Multiplicative or Additive Model. J. Math. Stat. 2011, 7, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Spiliotis, E.; Assimakopoulos, V. M5 Accuracy Competition: Results, Findings, and Conclusions. Int. J. Forecast. 2022, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, E.; Wang, S.; Kang, Y.; Spiliotis, E.; Makridakis, S.; Assimakopoulos, V. Exploring the Representativeness of the M5 Competition Data. Int. J. Forecast. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewamalage, H.; Bergmeir, C.; Bandara, K. Global Models for Time Series Forecasting: A Simulation Study. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 124, 108441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, Q.; Liu, A.; Meng, F.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, W.; Wang, P.; Wang, C. Seeking Urbanization Security and Sustainability: Multi-Objective Optimization of Rainwater Harvesting Systems in China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhermi, N.; Suhartono; Prastyo, D.D.; Ali, B. Roll Motion Prediction Using a Hybrid Deep Learning and ARIMA Model. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 144, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartono; Maghfiroh, B.; Rahayu, S.P. Hybrid VARX-SVR and GSTARX-SVR for Forecasting Spatio-Temporal Data. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. IJITEE 2019, 8, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Aguilar, J.J.; Turias, I.J.; Jiménez-Come, M.J. Hybrid Approaches Based on SARIMA and Artificial Neural Networks for Inspection Time Series Forecasting. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2014, 67, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Ji, L.; Wu, C.W.D.; Tso, K.F.G. Using SARIMA–CNN–LSTM Approach to Forecast Daily Tourism Demand. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 49, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Investment Risk Model Based on Intelligent Fuzzy Neural Network and VaR. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 371, 112707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Modarres, R.; Eslamian, S.S. The Use of Time Series Modeling for the Determination of Rainfall Climates of Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting & Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; ISBN 8131716333. [Google Scholar]
- Suhartono; Prastyo, D.D.; Kuswanto, H.; Lee, M.H. Comparison between VAR, GSTAR, FFNN-VAR and FFNN-GSTAR Models for Forecasting Oil Production Methods. Mat. Malays. J. Ind. Appl. Math. 2018, 34, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bebis, G.; Georgiopoulos, M. Feed-Forward Neural Networks. IEEE Potentials 1994, 13, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.N.; Tan, K.K.; Lee, T.H.; Giam, T.S. Decentralized Adaptive Control of Nonlinear Systems Using Neural Networks. Proc. IEEE Conf. Decis. Control 2002, 2, 1757–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodyanskiy, Y.V.; Tyshchenko, A.K.; Deineko, A.A. An Evolving Radial Basis Neural Network with Adaptive Learning of Its Parameters and Architecture. Autom. Control Comput. Sci. 2015, 49, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorot, X.; Bengio, Y. Understanding the Difficulty of Training Deep Feedforward Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Setti Ballas, Italy, 13–15 May 2010; Volume 9, pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Recknagel, F. Applications of Machine Learning to Ecological Modelling. Ecol. Model. 2001, 146, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toharudin, T.; Pontoh, R.S.; Caraka, R.E.; Zahroh, S.; Lee, Y.; Chen, R.C. Employing Long Short-Term Memory and Facebook Prophet Model in Air Temperature Forecasting. Commun. Stat. Simul. Comput. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmini, S.; Jihan, N.; Jayasinghe, M.; Perera, S. Sales Forecasting Using Multivariate Long Short Term Memory Networks. PeerJ Prepr. 2019, 7, e27712v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamak, P.T.; Yujian, L.; Gadosey, P.K. A Comparison between ARIMA, LSTM, and GRU for Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Algorithms, Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Sanya, China, 20–22 December 2019; pp. 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D. Human Skeleton Detection and Extraction in Dance Video Based on PSO-Enabled LSTM Neural Network. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 2545151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AgaAzizi, S.; Rasekh, M.; Abbaspour-Gilandeh, Y.; Kianmehr, M.H. Identification of Impurity in Wheat Mass Based on Video Processing Using Artificial Neural Network and PSO Algorithm. J. Food Processing Preserv. 2021, 45, e15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei Chafi, Z.; Afrakhte, H. Short-Term Load Forecasting Using Neural Network and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) Algorithm. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5598267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarto, M.; D’urso, G.; Giardini, C.; Maccarini, G.; Carminati, M. A Comparison between Finite Element Model (Fem) Simulation and an Integrated Artificial Neural Network (Ann)-Particle Swarm Optimization (Pso) Approach to Forecast Performances of Micro Electro Discharge Machining (Micro-Edm) Drilling. Micromachines 2021, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartono; Wahyuningrum, S.R.; Setiawan; Akbar, M.S. GSTARX-GLS Model for Spatio-Temporal Data Forecasting. Malays. J. Math. Sci. 2016, 10, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Astutik, S.; Iriawan, N.; Nair, G.; Suhartono. Sutikno Bayesian State Space Modeling for Spatio-Temporal Rainfall Disaggregation. Int. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2013, 37, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Suhartono, A. Comparative Study of Forecasting Models for Trend and Seasonal Time Series: Does Complex Model Always Yield Better Forecast Than Simple Model. J. Tek. Ind. 2005, 7, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforge, D.; Watlet, A.; Kaufmann, O.; Van Camp, M.; Vanclooster, M. Time-Series Clustering Approaches for Subsurface Zonation and Hydrofacies Detection Using a Real Time-Lapse Electrical Resistivity Dataset. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 184, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartono, S.; Subanar, S. Some Comments on the Theorem Providing Stationarity Condition for Gstar Models in the Paper by Borovkova Et Al. J. Indones. Math. Soc. 2007, 13, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchjana, B.N.; Borovkova, S.A.; Lopuhaa, H.P. Least Squares Estimation of Generalized Space Time AutoRegressive (GSTAR) Model and Its Properties. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2012; Volume 1450, pp. 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.W.S.; Hamilton, J.D. Time Series Analysis; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 837–900. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle Swarm Optimization. In 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks Proceedings; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraka, R.E.; Chen, R.C.; Yasin, H.; Pardamean, B.; Toharudin, T.; Wu, S.H. Prediction of Status Particulate Matter 2.5 Using State Markov Chain Stochastic Process and HYBRID VAR-NN-PSO. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 161654–161665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, C.M.; Rashid, T.A. Dragonfly Algorithm and Its Applications in Applied Science Survey. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 9293617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursheed, M.U.N.; Nadeem, M.F.; Khalil, A.; Sajjad, I.A.; Raza, A.; Iqbal, M.Q.; Bo, R.; Rehman, W.U. Review of Flower Pollination Algorithm: Applications and Variants. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies, ICEET 2020, Lahore, Pakistan, 22–23 February 2020; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. A Powerful and Efficient Algorithm for Numerical Function Optimization: Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) Algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 39, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, S.; Prastuti, M. S-GSTAR-SUR Model for Seasonal Spatio Temporal Data Forecasting. Malays. J. Math. Sci. 2016, 10, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, P.; Swindlehurst, A. Space-Time Autoregressive Filtering for Matched Subspace STAP. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storvik, G.; Frigessi, A.; Hirst, D. Stationary Space-Time Gaussian Fields and Their Time Autoregressive Representation. Stat. Modeling 2002, 2, 139–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Wang, J.; Haworth, J.; Heydecker, B.; Chow, A. A Dynamic Spatial Weight Matrix and Localized Space-Time Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average for Network Modeling. Geogr. Anal. 2014, 46, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prastyo, D.D.; Nabila, F.S.; Suhartono; Lee, M.H.; Suhermi, N.; Fam, S.F. VAR and GSTAR-Based Feature Selection in Support Vector Regression for Multivariate Spatio-Temporal Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Communications in Computer and Information Science, Dresden, Germany, 10–11 October 2019; pp. 46–57. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Matoha, S.; Lubis, D.A.; Falah, A.N.; Jaya, I.G.N.M.; Hermawan, E.; Ruchjana, B.N. Implementation of Generalized Space Time Autoregressive (GSTAR)-Kriging Model for Predicting Rainfall Data at Unobserved Locations in West Java. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2018, 12, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraka, R.E.; Yasin, H.; Chen, R.C.; Goldameir, N.E.; Supatmanto, B.D.; Toharudin, T.; Basyuni, M.; Gio, P.U. Evolving Hybrid Cascade Neural Network Genetic Algorithm Space-Time Forecasting. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, H.; Ruchjana, B.N.; Darmawan, G. Development of Generalized Space Time Autoregressive Integrated with ARCH Error (GSTARI—ARCH) Model Based on Consumer Price Index Phenomenon at Several Cities in North Sumatera Province. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Borovkova, S.; Lopuhaä, H.P.; Ruchjana, B.N. Consistency and Asymptotic Normality of Least Squares Estimators in Generalized STAR Models. Stat. Neerl. 2008, 62, 482–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yundari, Y.; Huda, N.M.; Pasaribu, U.S.; Mukhaiyar, U.; Sari, K.N. Stationary process in GSTAR (1;1) through kernel function approach. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2268, p. 020010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Z. Ozone Pollution: A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riojas-Rodríguez, H.; Romieu, I.; Hernández-Ávila, M. Air Pollution. In Occupational and Environmental Health; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780190662677. [Google Scholar]
- Deryugina, T.; Heutel, G.; Miller, N.H.; Molitor, D.; Reif, J. The Mortality and Medical Costs of Air Pollution: Evidence from Changes in Wind Direction. Am. Econ. Rev. 2019, 109, 4178–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, H. Global Air Quality and Pollution. Science 2003, 302, 1716–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Cai, G. An Application of Phytoremediation to River Pollution Remediation. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 1904–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Masseran, N.; Safari, M.A.M. Modeling the Transition Behaviors of PM 10 Pollution Index. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masseran, N.; Mohd Safari, M.A. Intensity–Duration–Frequency Approach for Risk Assessment of Air Pollution Events. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Dhurafi, N.A.; Masseran, N.; Zamzuri, Z.H. Hierarchical-Generalized Pareto Model for Estimation of Unhealthy Air Pollution Index. Environ. Modeling Assess. 2020, 25, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, E.; de Marco, A.; Pompei, E. Five-Year Volume Growth of European Beech Does Not Respond to Ozone Pollution in Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 8233–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraka, R.E.; Yusra, Y.; Toharudin, T.; Chen, R.; Basyuni, M. Did Noise Pollution Really Improve during COVID-19? Evidence from Taiwan. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.; Tu, J.Y.; Hsu, S.C.; Chen, W.N. Case Study of the Asian Dust and Pollutant Event in Spring 2006: Source, Transport, and Contribution to Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 478, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, J. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives the Effect of COVID-19 and Subsequent Social Distancing on Travel Behavior. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2020, 5, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B.; He, B.J. Delineating the Spatial-Temporal Variation of Air Pollution with Urbanization in the Belt and Road Initiative Area. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 91, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayialis, S.P.; Kechagias, E.P.; Konstantakopoulos, G.D. A City Logistics System for Freight Transportation: Integrating Information Technology and Operational Research. Oper. Res. 2022, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Parnell, J.; Kessissoglou, N. Spatially Differentiated Profiles for Road Traffic Noise Pollution across a State Road Network. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 172, 107641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.C. Traffic Flow Forecasting by Seasonal SVR with Chaotic Simulated Annealing Algorithm. Neurocomputing 2011, 74, 2096–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.W.; Hong, W.C.; Kang, H.G. Urban Traffic Flow Forecasting Using Gauss-SVR with Cat Mapping, Cloud Model and PSO Hybrid Algorithm. Neurocomputing 2013, 99, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagias, E.P.; Gayialis, S.P.; Konstantakopoulos, G.D.; Papadopoulos, G.A. Traffic Flow Forecasting for City Logistics: A Literature Review and Evaluation. Int. J. Decis. Support Syst. 2019, 4, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

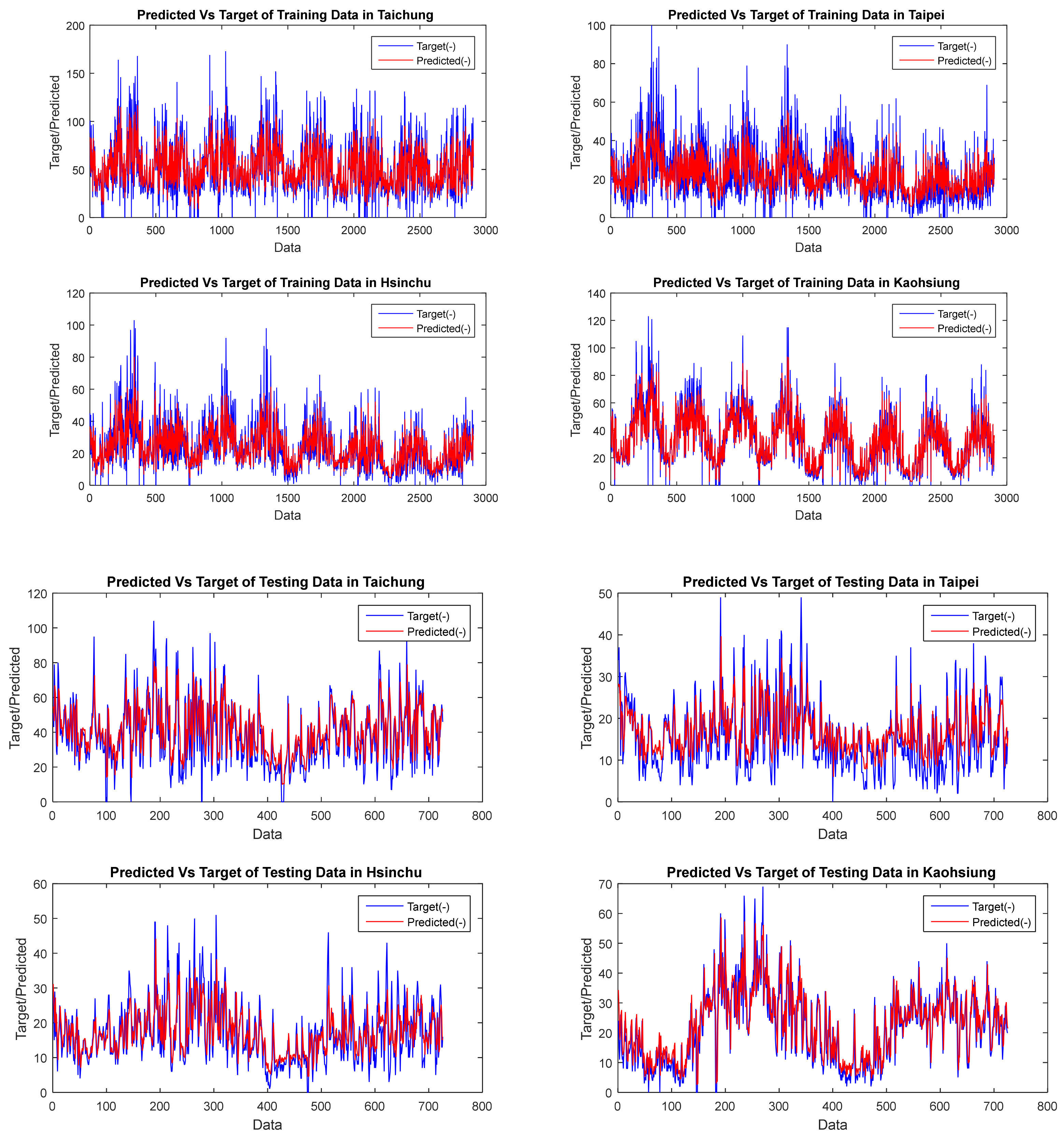
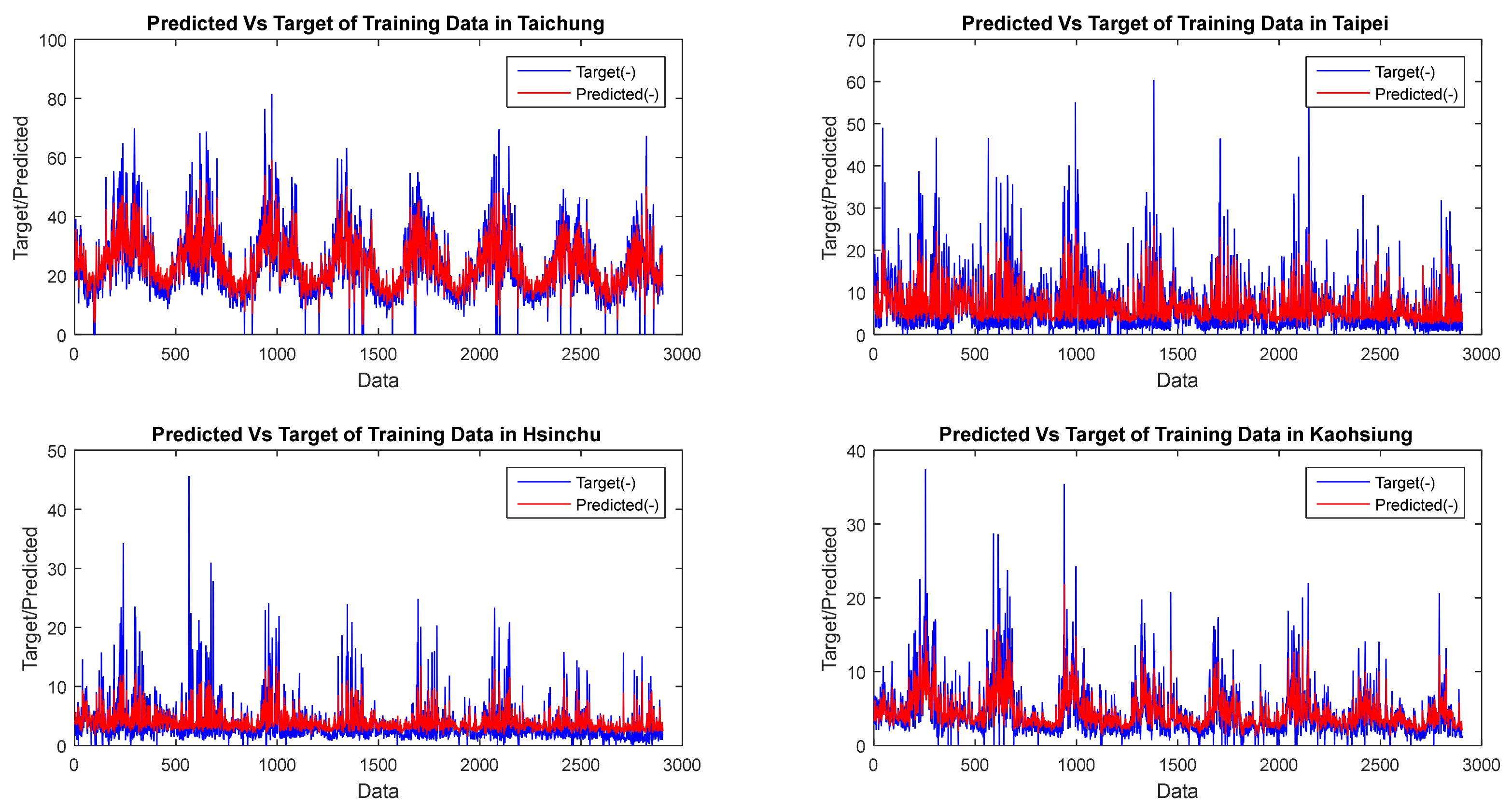
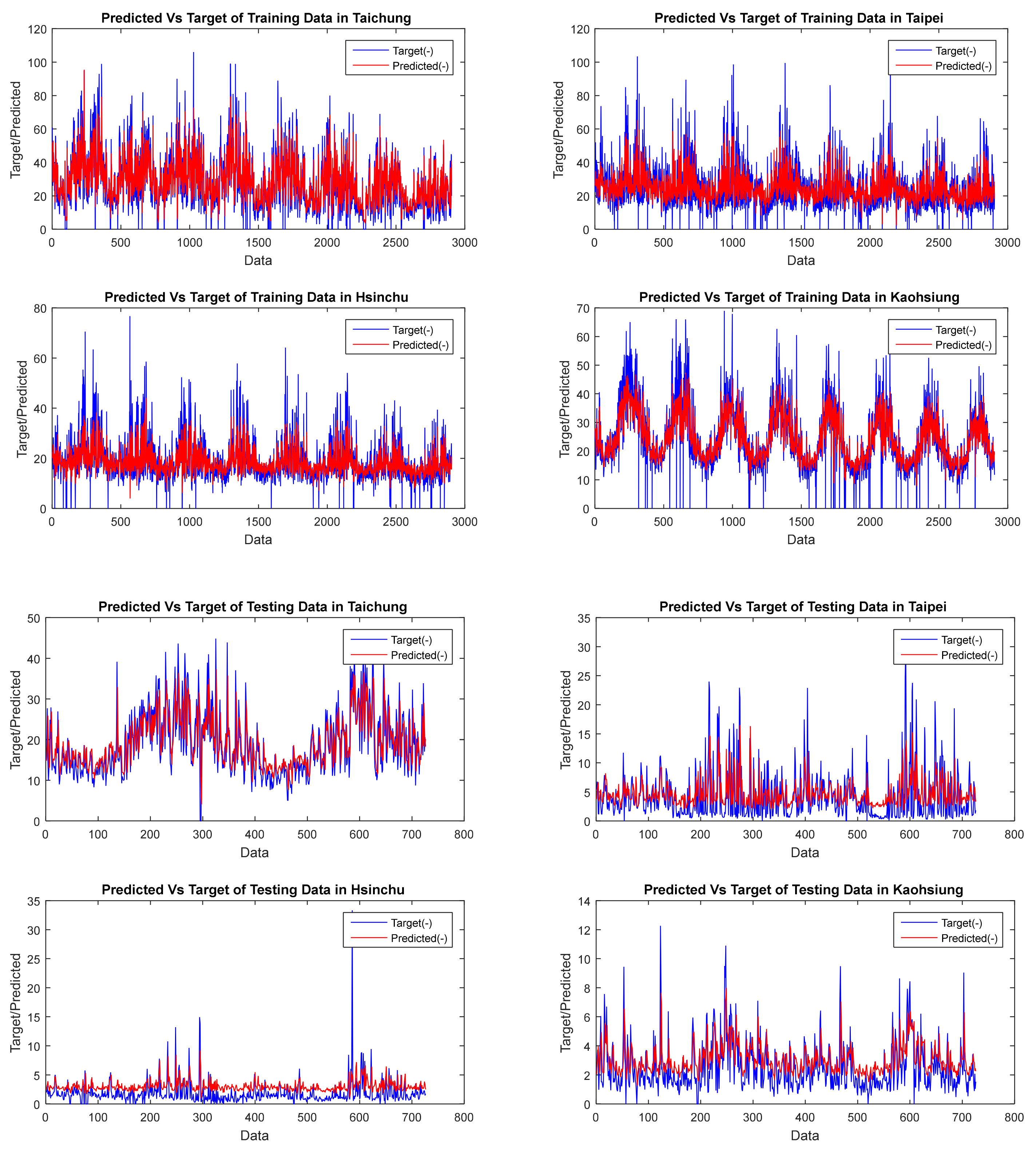

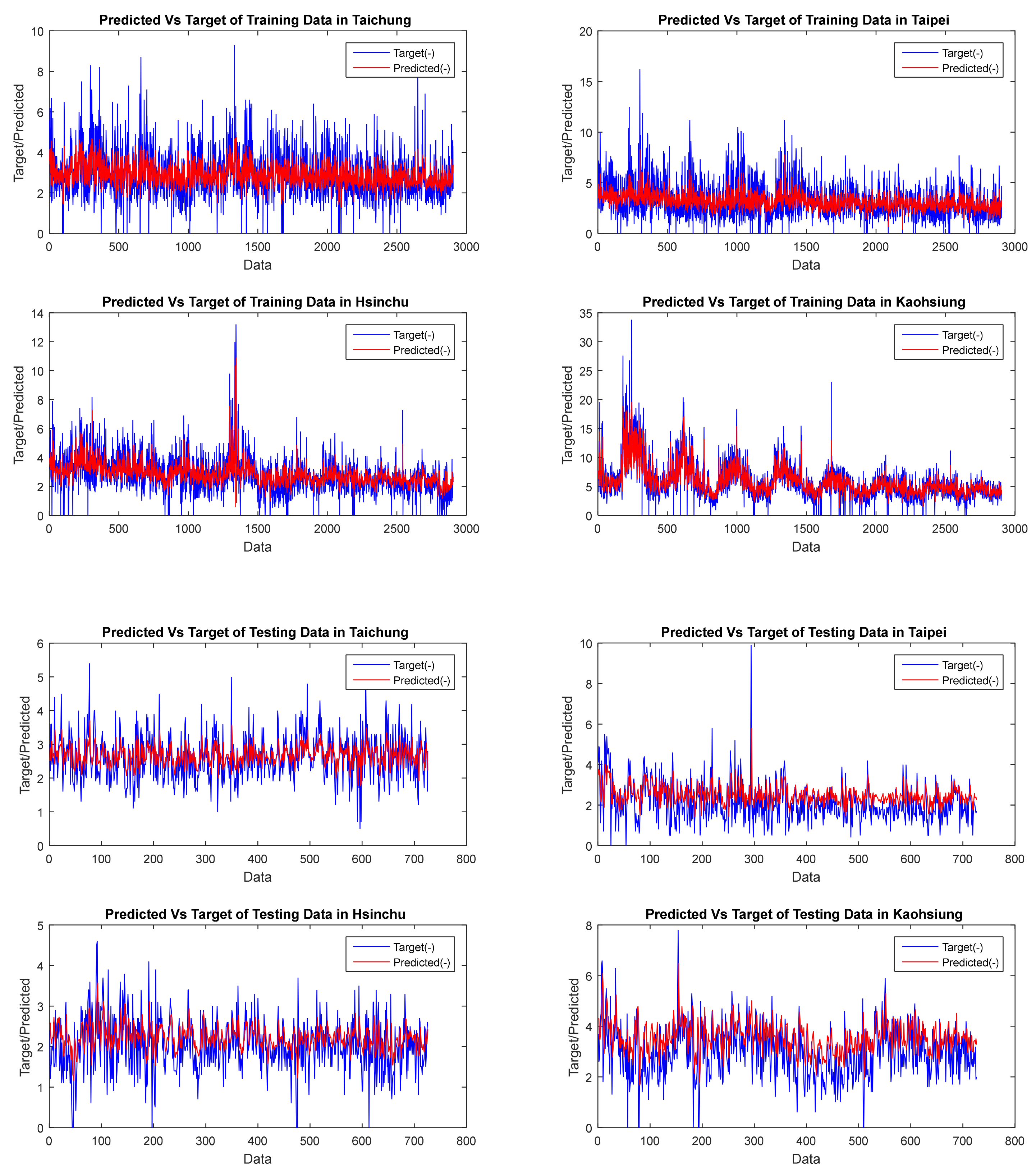
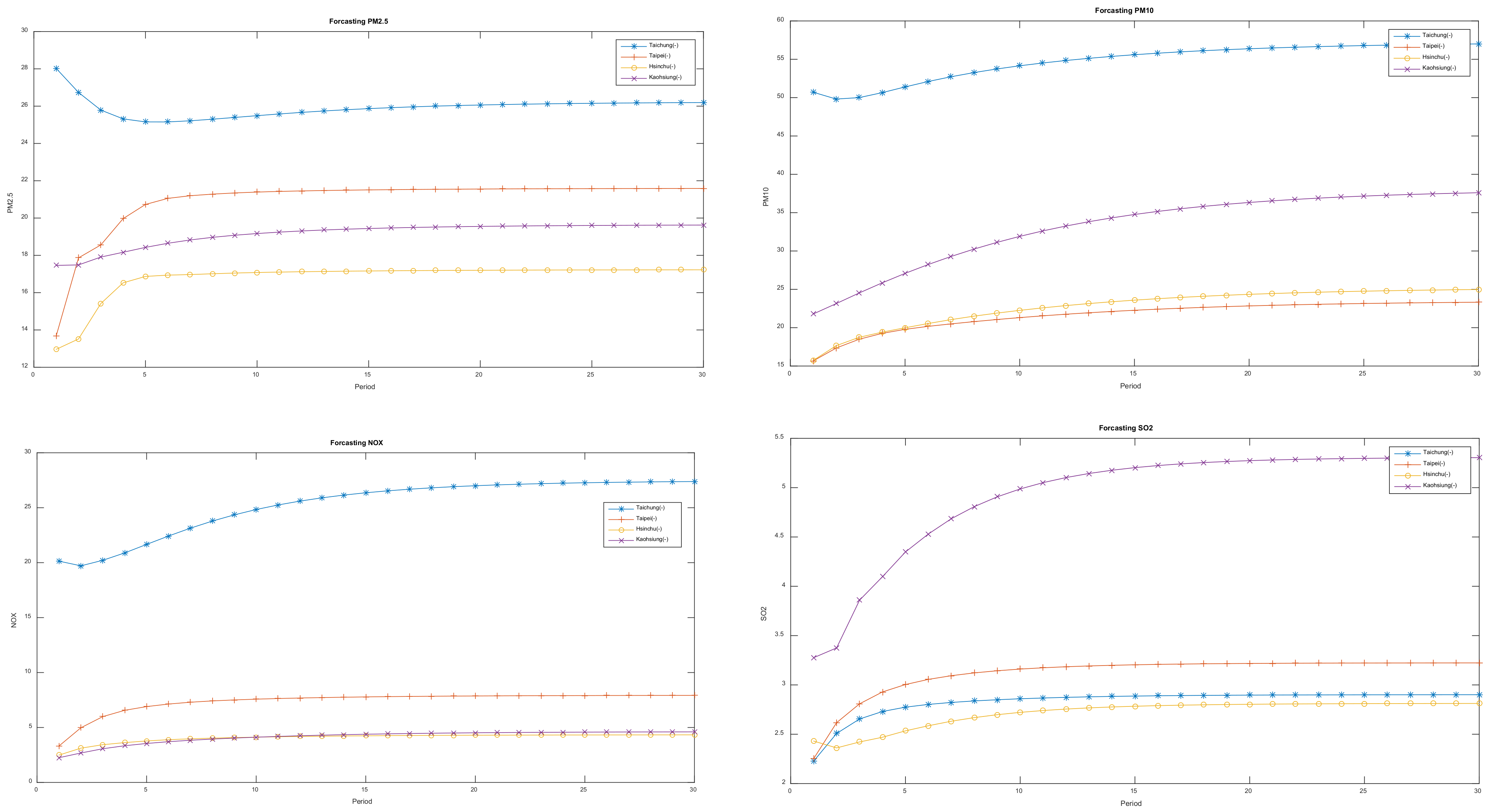
| GSTAR CFNN | Dataset | FVAL | OBJ | Training | Testing | Average | Elapsed Time (Seconds) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | SMAPE | RMSE | MAE | SMAPE | RMSE | MAE | SMAPE | |||||
| GSTAR (1) | NOX | 0.7470 | 0.7470 | 5.2660 | 3.2622 | 0.0049 | 4.7143 | 2.4282 | 0.0268 | 4.9902 | 2.8452 | 0.0159 | 229.0739 |
| PM2.5 | 1.1580 | 1.1580 | 9.2831 | 6.5054 | 0.0041 | 6.7955 | 4.9921 | 0.0205 | 8.0393 | 5.7488 | 0.0123 | 91.236504 | |
| PM10 | 0.735571 | 0.7356 | 13.0906 | 9.1146 | 0.0038 | 9.2994 | 6.5805 | 0.016 | 11.1950 | 7.8476 | 0.0099 * | 90.51314 | |
| SO2 | 2.643 | 2.643 | 1.5409 | 1.0592 | 0.0057 | 0.9035 | 0.6893 | 0.0265 | 1.2222 | 0.8743 | 0.0161 | 95.544592 | |
| GSTAR (2) | NOX | 0.715855 | 0.7159 | 5.203 | 3.2747 | 0.005 | 3.7358 | 2.4901 | 0.0239 | 4.4694 | 2.8824 | 0.0145 * | 106.778741 |
| PM2.5 | 2.02728 | 2.0273 | 9.2237 | 6.4361 | 0.0042 | 6.7847 | 4.9562 | 0.0199 | 8.0042 | 5.6962 | 0.0121 * | 120.178632 | |
| PM10 | 2.4187 | 2.4187 | 12.9489 | 8.9896 | 0.0036 | 9.1351 | 6.4255 | 0.0167 | 11.0420 | 7.7076 | 0.0102 | 196.033143 | |
| SO2 | 7.79396 | 7.794 | 1.5172 | 1.0465 | 0.0056 | 0.8858 | 0.6726 | 0.0257 | 1.2015 | 0.8596 | 0.0157 * | 206.967525 | |
| VAR (1) | NOX | 3.20116 | 3.2012 | 5.1847 | 3.2426 | 13.5834 | 3.7378 | 2.4028 | 12.4158 | 4.4613 | 2.8227 | 12.9996 | 83.651723 |
| PM2.5 | 5.99995 | 6 | 9.2164 | 6.4473 | 7.5802 | 6.8311 | 5.0247 | 6.8707 | 8.0238 | 5.7360 | 7.2255 | 83.842196 | |
| PM10 | 3.31837 | 3.3184 | 12.9178 | 8.9778 | 7.23 | 9.2731 | 6.5761 | 8.4924 | 11.0955 | 7.7770 | 7.8612 | 84.947817 | |
| SO2 | 2.65504 | 2.655 | 1.5349 | 1.0506 | 6.8211 | 0.9185 | 0.7007 | 6.4913 | 1.2267 | 0.8757 | 6.6562 | 75.589595 | |
| VAR (2) | NOX | 7.50572 | 7.5057 | 5.0466 | 3.1183 | 12.0234 | 3.6744 | 2.3254 | 11.8713 | 4.3605 | 2.7219 | 11.9474 | 82.196178 |
| PM2.5 | 5.31512 | 5.3151 | 9.1431 | 6.3854 | 7.8689 | 6.777 | 5.0306 | 7.2665 | 7.9601 | 5.7080 | 7.5677 | 269.645339 | |
| PM10 | 3.72273 | 3.7227 | 12.7213 | 8.7579 | 6.9237 | 9.0049 | 6.3091 | 7.9569 | 10.8631 | 7.5335 | 7.4403 | 105.356041 | |
| SO2 | 5.47567 | 5.4757 | 1.493 | 1.027 | 6.7956 | 0.9068 | 0.6823 | 7.1553 | 1.1999 | 0.8547 | 6.9755 | 161.550041 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toharudin, T.; Caraka, R.E.; Yasin, H.; Pardamean, B. Evolving Hybrid Generalized Space-Time Autoregressive Forecasting with Cascade Neural Network Particle Swarm Optimization. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060875
Toharudin T, Caraka RE, Yasin H, Pardamean B. Evolving Hybrid Generalized Space-Time Autoregressive Forecasting with Cascade Neural Network Particle Swarm Optimization. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(6):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060875
Chicago/Turabian StyleToharudin, Toni, Rezzy Eko Caraka, Hasbi Yasin, and Bens Pardamean. 2022. "Evolving Hybrid Generalized Space-Time Autoregressive Forecasting with Cascade Neural Network Particle Swarm Optimization" Atmosphere 13, no. 6: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060875
APA StyleToharudin, T., Caraka, R. E., Yasin, H., & Pardamean, B. (2022). Evolving Hybrid Generalized Space-Time Autoregressive Forecasting with Cascade Neural Network Particle Swarm Optimization. Atmosphere, 13(6), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060875









