Temperature Forecasting Correction Based on Operational GRAPES-3km Model Using Machine Learning Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
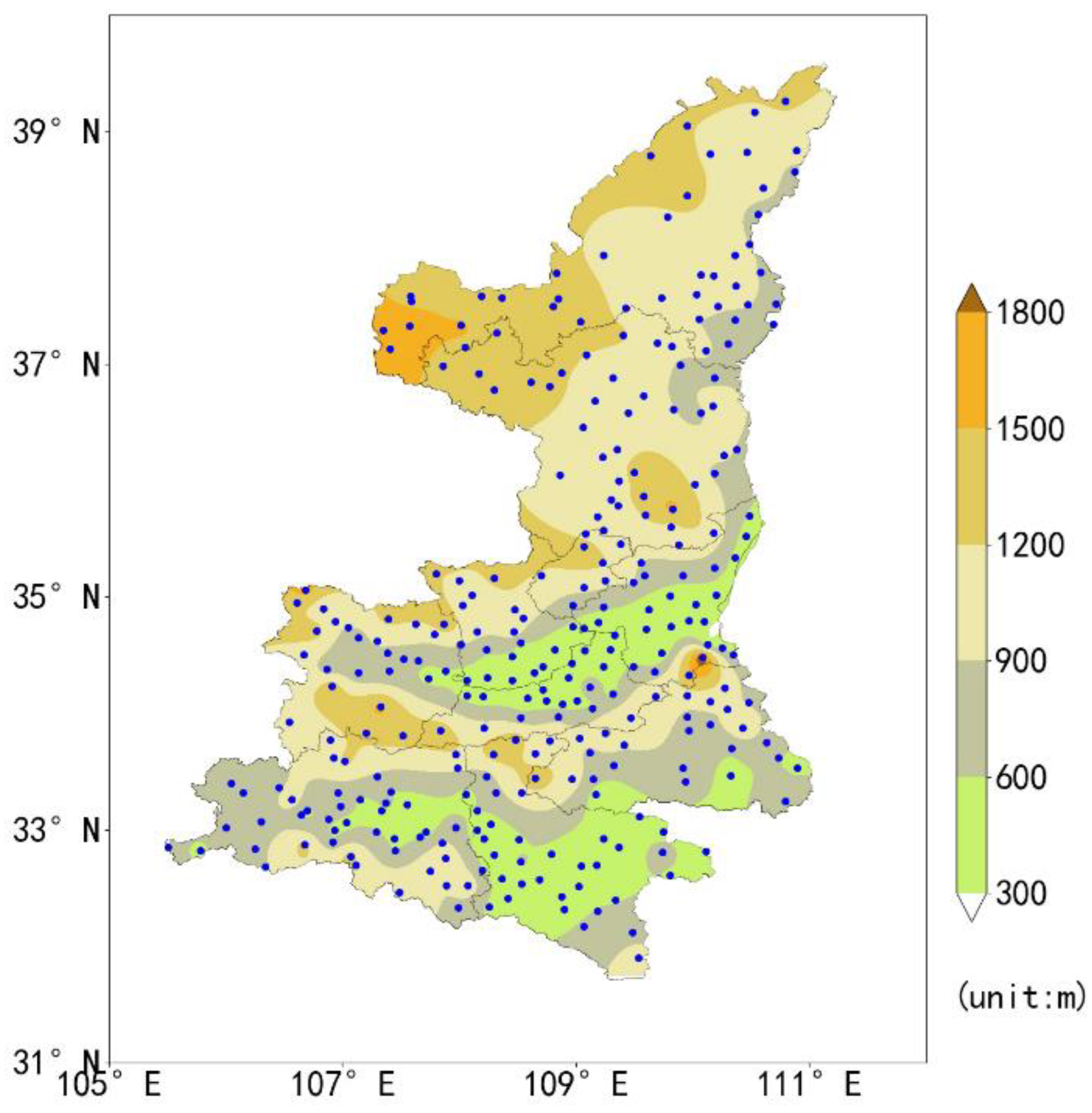
2. Model Forecast and Observation Data
3. Data Preprocessing
4. Methods and Modeling
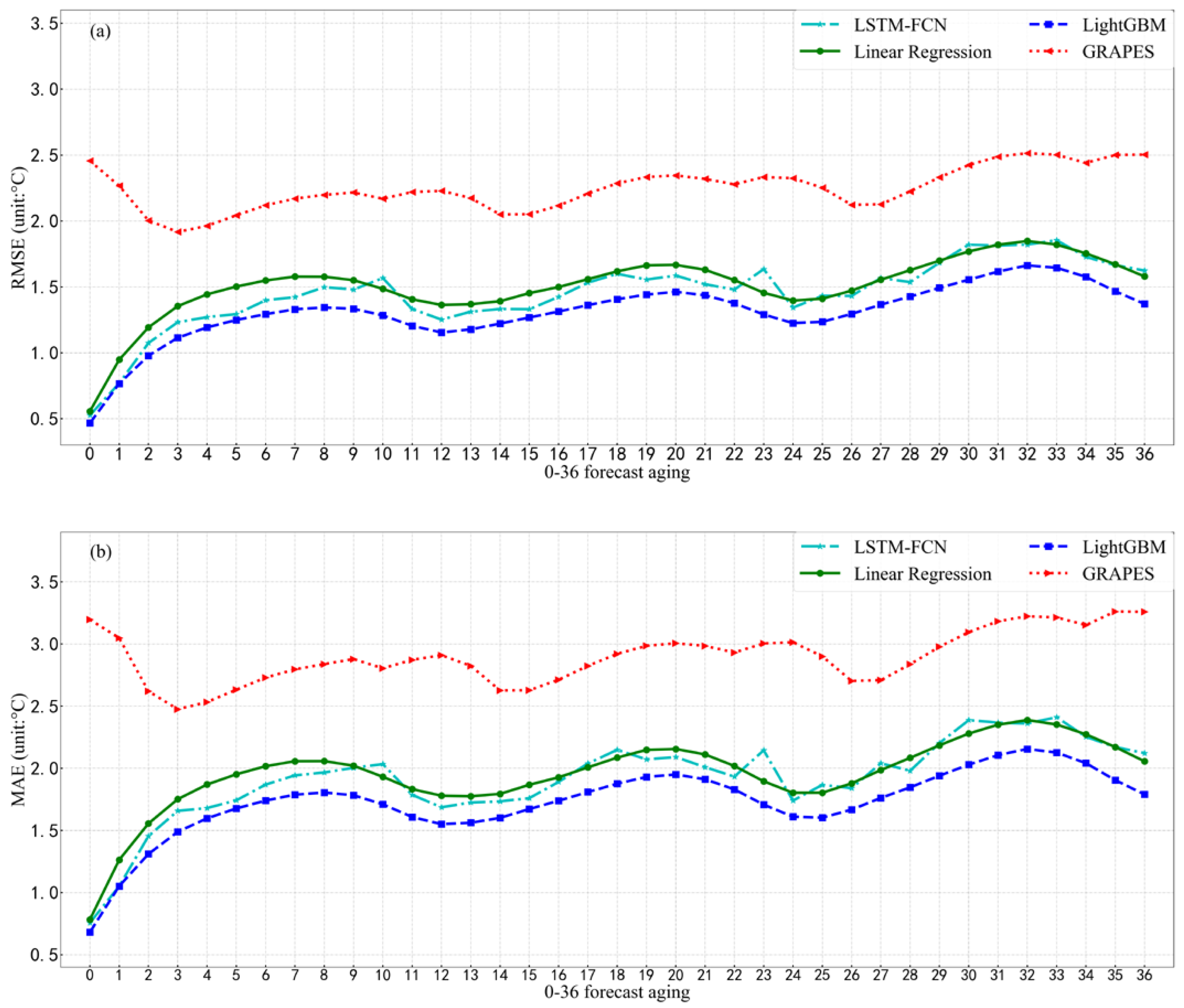
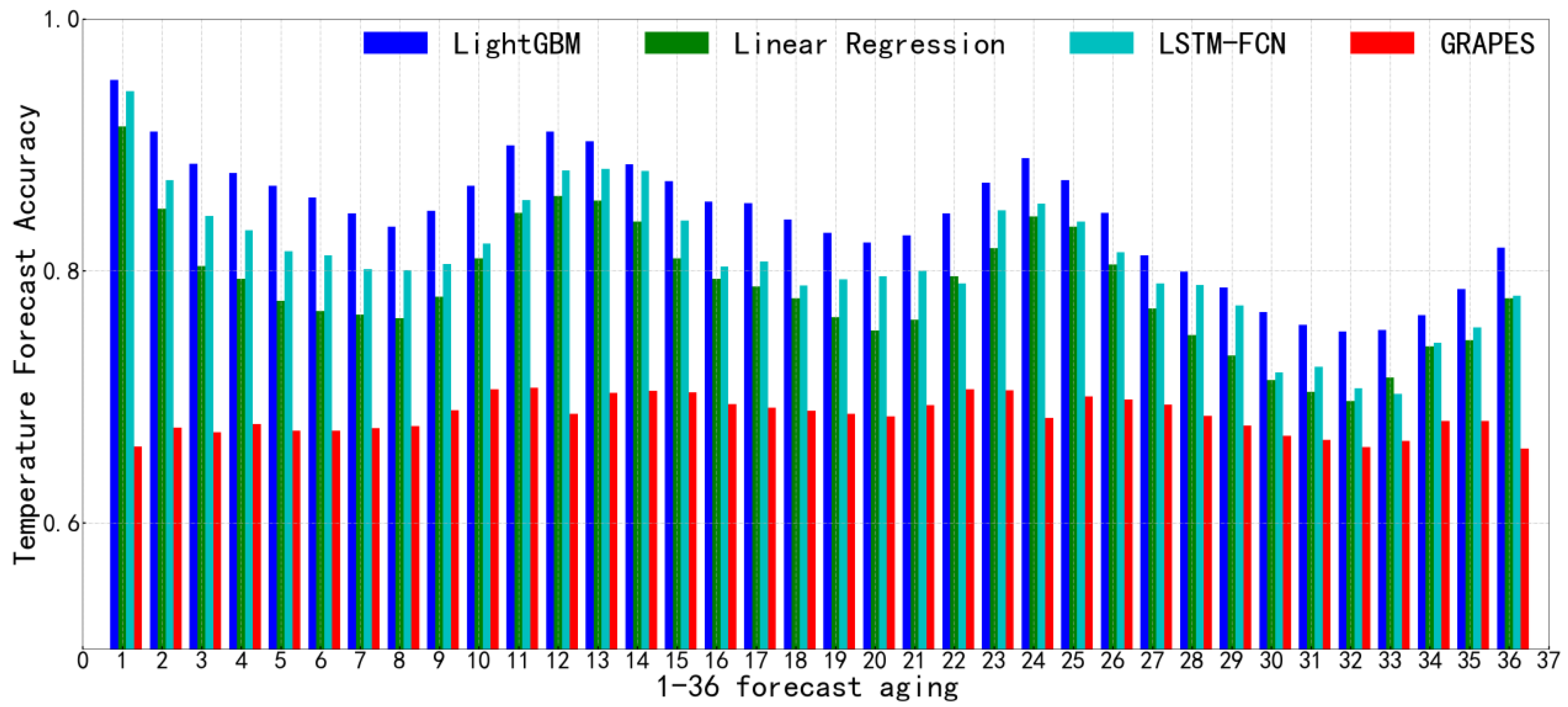
5. Verification Scores
6. Results
7. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slingo, J.; Palmer, T. Uncertainty in weather and climate prediction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 4751–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Toth, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, D. Bias correction for global ensemble forecast. Weather Forecast. 2012, 27, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prog, P.; Marzban, C.; Sandgathe, S.; Kalnay, E. MOS, Perfect Prog, and Reanalysis. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 134, 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, W.H.; Lewis, F. Computer Forecasts of Maximum and Minimum Temperatures. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1970, 9, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glahn, H.R.; Lowry, D.A. The Use of Model Output Statistics (MOS) in Objective Weather Forecasting. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1972, 11, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.A.; Leslie, L.M. A Single-Station Approach to Model Output Statistics Temperature Forecast Error Assessment. Weather Forecast. 2005, 20, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Cui, B.; Zhu, Y. Improvement of statistical postprocessing using GEFS reforecast information. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.Y.Y.; Steenburgh, W.J. Strengths and weaknesses of MOS, running-mean bias removal, and Kalman filter techniques for improving model forecasts over the western United States. Weather Forecast. 2007, 22, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.R.; Hamid, M. Multi-Model Ensemble Analysis of Runoff Extremes for Climate Change Impact Assessments. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bothwell, P.D.; Richardson, L.M. Forecasting lightning using a perfect prog technique applied to multiple operational models. Int. Conf. Atmos. Electr. ICAE 2014, 2014, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lerch, S.; Baran, S. Similarity-based semilocal estimation of post-processing models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 2017, 66, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.A.; Hurrell, J.W.; Ebert-Uphoff, I.; Anderson, C.; Anderson, D. Viewing Forced Climate Patterns Through an AI Lens. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 13389–13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toms, B.A.; Kashinath, K.; Prabhat; Yang, D. Testing the reliability of interpretable neural networks in geoscience using the Madden-Julian oscillation. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 4495–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, E.A.; Toms, B.; Hurrell, J.W.; Ebert-Uphoff, I.; Anderson, C.; Anderson, D. Indicator Patterns of Forced Change Learned by an Artificial Neural Network. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt-Meyer, O.; Brenowitz, N.D.; Clark, S.K.; Henn, B.; Kwa, A.; McGibbon, J.; Perkins, W.A.; Bretherton, C.S. Correcting Weather and Climate Models by Machine Learning Nudged Historical Simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL092555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasp, S.; Pritchard, M.S.; Gentine, P. Deep learning to represent subgrid processes in climate models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9684–9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuval, J.; O’Gorman, P.A.; Hill, C.N. Use of Neural Networks for Stable, Accurate and Physically Consistent Parameterization of Subgrid Atmospheric Processes With Good Performance at Reduced Precision. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenowitz, N.D.; Bretherton, C.S. Spatially Extended Tests of a Neural Network Parametrization Trained by Coarse-Graining. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 2728–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, Y.G.; Kim, J.H.; Luo, J.J. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature 2019, 573, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.M.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, B.S. The development of a quantitative precipitation forecast correction technique based on machine learning for hydrological applications. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, G.J.; Lucas, D.D. Machine Learning Predictions of a Multiresolution Climate Model Ensemble. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4273–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnopolsky, V.M.; Lin, Y. A neural network nonlinear multimodel ensemble to improve precipitation forecasts over continental US. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 649450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mitra, A.K.; Bohra, A.K.; Iyengar, G.R.; Durai, V.R. Multi-model ensemble (MME) prediction of rainfall using neural networks during monsoon season in India. Meteorol. Appl. 2012, 19, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyn, J.A.; Durran, D.R.; Caruana, R. Can Machines Learn to Predict Weather? Using Deep Learning to Predict Gridded 500-hPa Geopotential Height from Historical Weather Data. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 2680–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, B.; Wang, D. A multi-model integration method for monthly streamflow prediction: Modified stacking ensemble strategy. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 22, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farchi, A.; Laloyaux, P.; Bonavita, M.; Bocquet, M. Using machine learning to correct model error in data assimilation and forecast applications. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 3067–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Ahn, H.; Seok, J. Coordinate-RNN for error correction on numerical weather prediction. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–27 January 2018; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Ham, Y.G.; Joo, Y.S.; Son, S.W. Deep learning for bias correction of MJO prediction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frnda, J.; Durica, M.; Nedoma, J.; Zabka, S.; Martinek, R.; Kostelansky, M. A weather forecast model accuracy analysis and ecmwf enhancement proposal by neural network. Sensors 2019, 19, 5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonavita, M.; Laloyaux, P. Machine Learning for Model Error Inference and Correction. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasp, S.; Lerch, S. Neural networks for postprocessing ensemble weather forecasts. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 146, 3885–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, W.E.; Subramanian, A.C.; Delle Monache, L.; Xie, S.P.; Ralph, F.M. Improving Atmospheric River Forecasts with Machine Learning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10627–10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; Song, L.; Qin, R. A Deep Learning Method for Bias Correction of ECMWF 24–240 h Forecasts. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1444–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, C.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.C.; Yu, C.; Xia, J.J.; Wang, Y.C.; et al. A Model Output Machine Learning Method for Grid Temperature Forecasts in the Beijing Area. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanyan, K.; Haochen, L.; Jiangjiang, X.; Yingxin, Z. Post-processing for NWP Outputs Based on Machine Learning for 2022 Winter Olympics Games over Complex Terrain. EGU Gen. Assem. 2020, 2020, 10463. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.W.; Huang, X.M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tsui, C.; Huang, X. Ensemble Learning for Bias Correction of Station Temperature Forecast Based on ECMWF Products. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2020, 31, 494–503. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D.; Yoo, C.; Im, J.; Cha, D.H. Comparative Assessment of Various Machine Learning-Based Bias Correction Methods for Numerical Weather Prediction Model Forecasts of Extreme Air Temperatures in Urban Areas. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2019EA000740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. A data-driven multi-model ensemble for deterministic and probabilistic precipitation forecasting at seasonal scale. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 3355–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.S.; Chen, Q.Y.; Sun, J.; Han, W.; Gong, J.D.; Li, Z.C.; Wang, J.J. Development of Operational Global Medium-Range Forecast System in National Meteorological Centre. Meteor Mon. 2021, 47, 645–654. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.S.; Su, Y.; Hu, J.L.; Wang, J.C.S. Development and Operation Transformation of GRAPES Global Middle-range Forecast System. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2017, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, F.; Majumdar, S.; Darabi, H.; Chen, S. LSTM Fully Convolutional Networks for Time Series Classification. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sujath, R.; Chatterjee, J.M.; Hassanien, A.E. A machine learning forecasting model for COVID-19 pandemic in India. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2020, 34, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.P.; Bai, Q.M.; Gao, H.Y. Comparative correction of air temperature forecast from ECMWF Model by the decaying averaging and the simple linear regression methods. Meteor Mon. 2019, 45, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Ortego, P.; Diez-Olivan, A.; Del Ser, J.; Veiga, F.; Penalva, M.; Sierra, B. Evolutionary LSTM-FCN networks for pattern classification in industrial processes. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2020, 54, 100650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S. Long Short-term Memory. Neural Comput. 2016, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Application of improved LightGBM model in blood glucose prediction. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mucs, D.; Norinder, U.; Svensson, F. LightGBM: An Effective and Scalable Algorithm for Prediction of Chemical Toxicity-Application to the Tox21 and Mutagenicity Data Sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 4150–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Pan, S.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, C.; Pan, H.; Zhu, X. Application of the machine learning lightgbm model to the prediction of the water levels of the lower columbia river. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Learning rate | 0.03 |
| Boost type | GBDT |
| Max depth | 5 |
| Num leaves | 120 |
| Objective | Regression_12 |
| Feature fraction | 0.8 |
| Bagging fraction | 0.9 |
| Bagging freq | 5 |
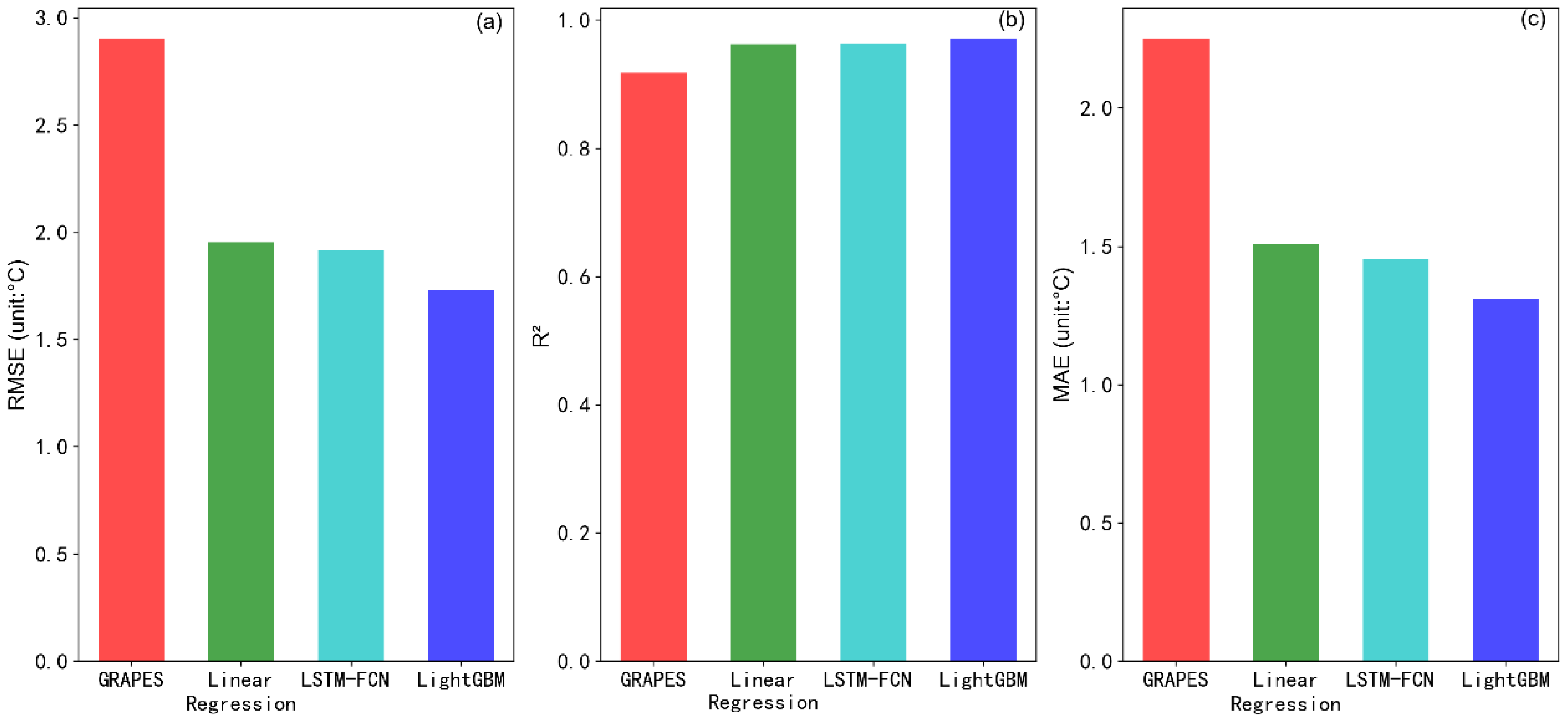
| Model | RMSE | RMSE Correction Improvement Rate | R2 | R2 Correction Improvement Rate | MAE | MAE Correction Improvement Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRAPES-3km | 2.472 | - | 0.721 | - | 1.946 | - |
| Linear Regression | 1.665 | 0.326 | 0.877 | 0.216 | 1.299 | 0.333 |
| LSTM-FCN | 1.679 | 0.321 | 0.876 | 0.214 | 1.288 | 0.338 |
| LightGBM | 1.485 | 0.399 | 0.903 | 0.252 | 1.140 | 0.414 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Feng, D.; You, X.; Wu, W. Temperature Forecasting Correction Based on Operational GRAPES-3km Model Using Machine Learning Methods. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020362
Zhang H, Wang Y, Chen D, Feng D, You X, Wu W. Temperature Forecasting Correction Based on Operational GRAPES-3km Model Using Machine Learning Methods. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(2):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020362
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hui, Yaqiang Wang, Dandan Chen, Dian Feng, Xiaoxiong You, and Weichen Wu. 2022. "Temperature Forecasting Correction Based on Operational GRAPES-3km Model Using Machine Learning Methods" Atmosphere 13, no. 2: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020362
APA StyleZhang, H., Wang, Y., Chen, D., Feng, D., You, X., & Wu, W. (2022). Temperature Forecasting Correction Based on Operational GRAPES-3km Model Using Machine Learning Methods. Atmosphere, 13(2), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020362







