Evaluation of Technology for the Analysis and Forecasting of Precipitation Using Cyclostationary EOF and Regression Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
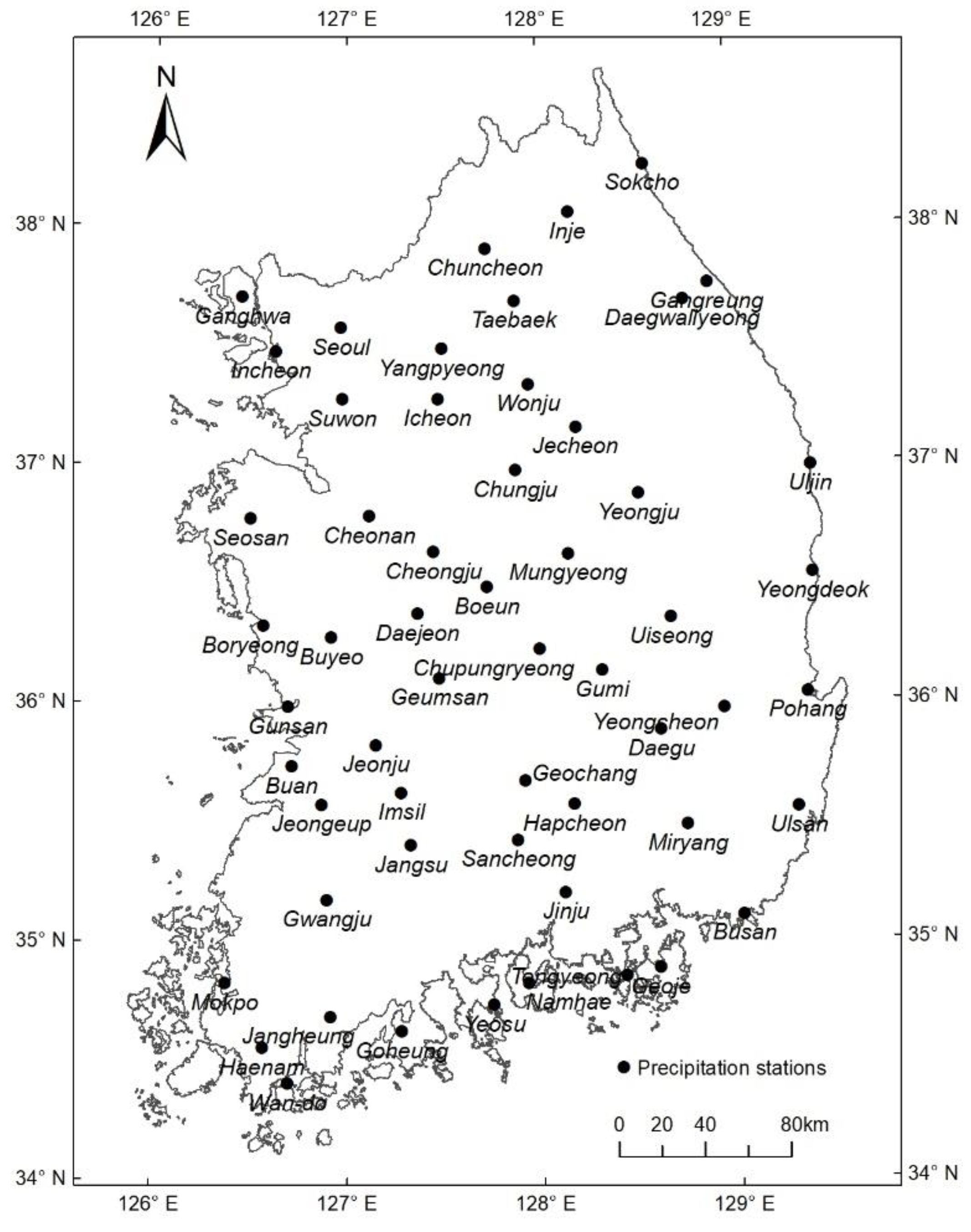
2.1. Data
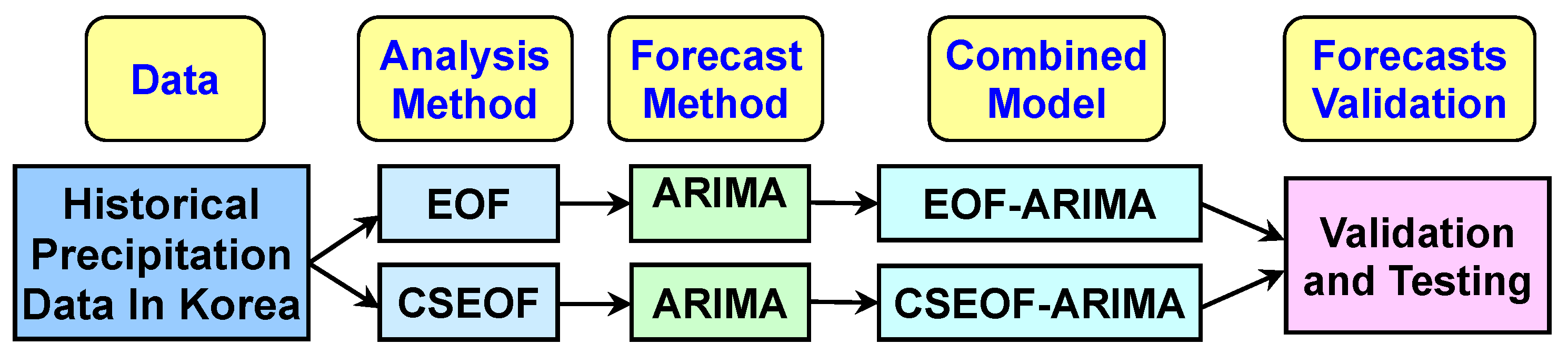
2.2. Methodology
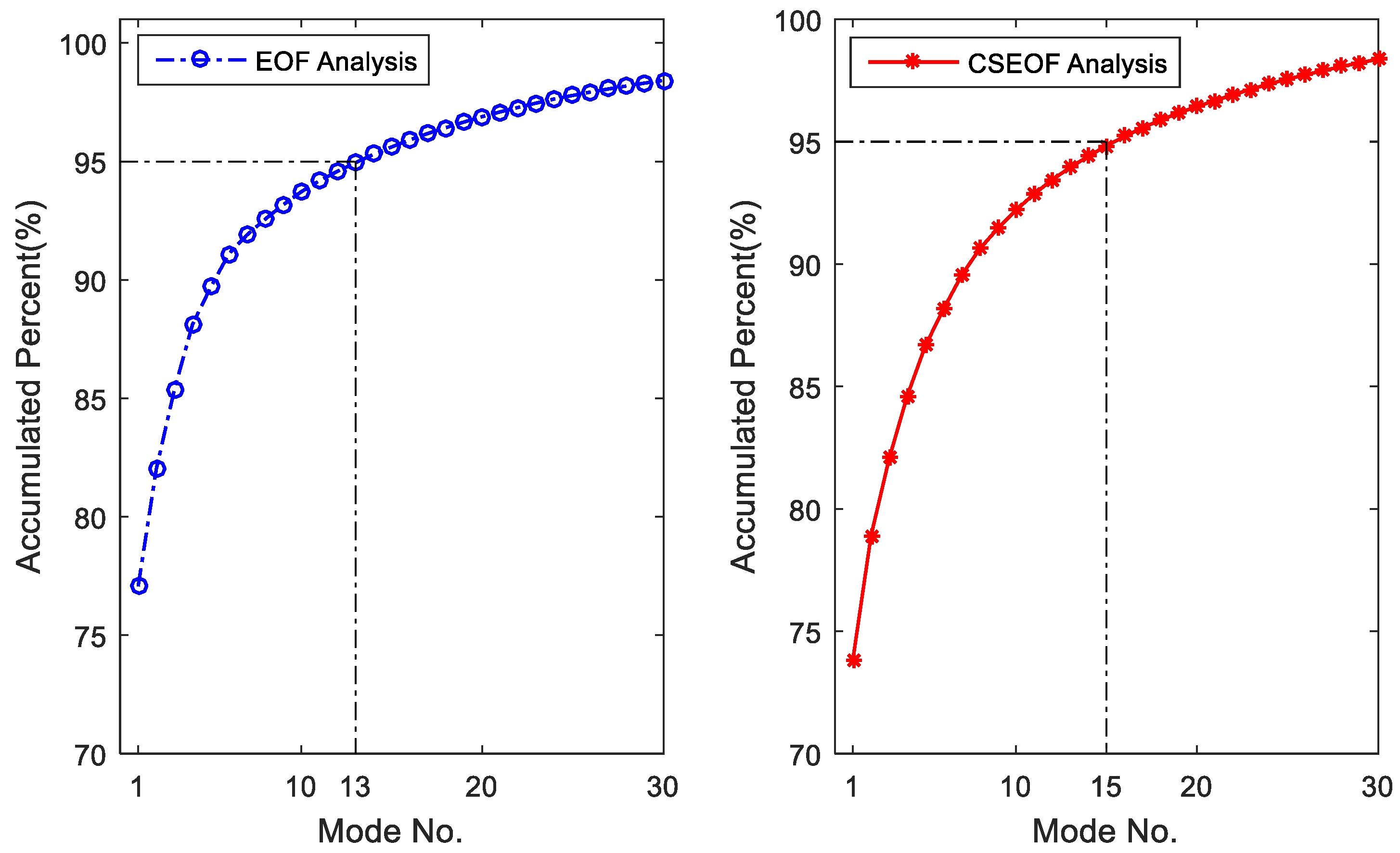
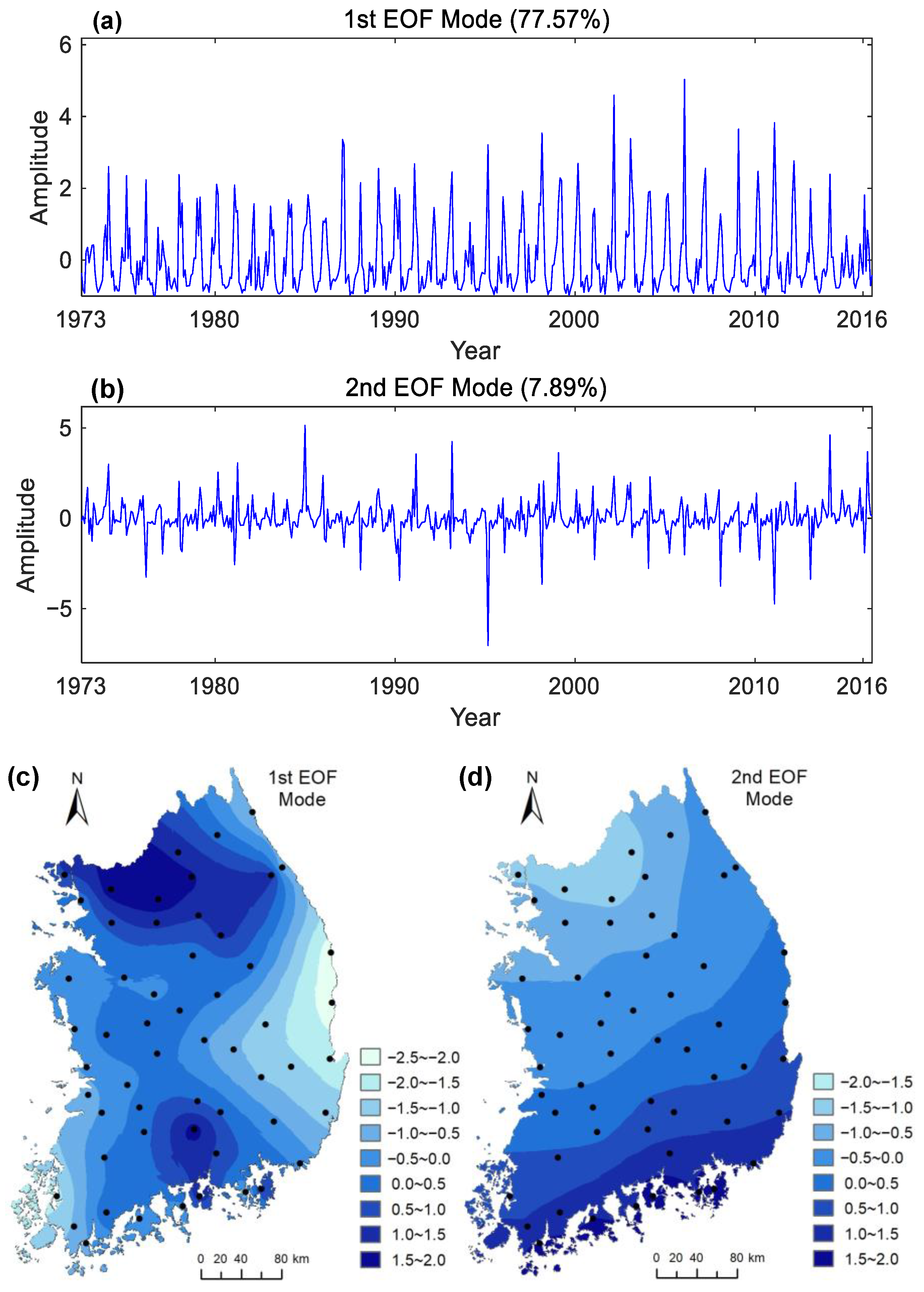
2.2.1. Empirical Orthogonal Function
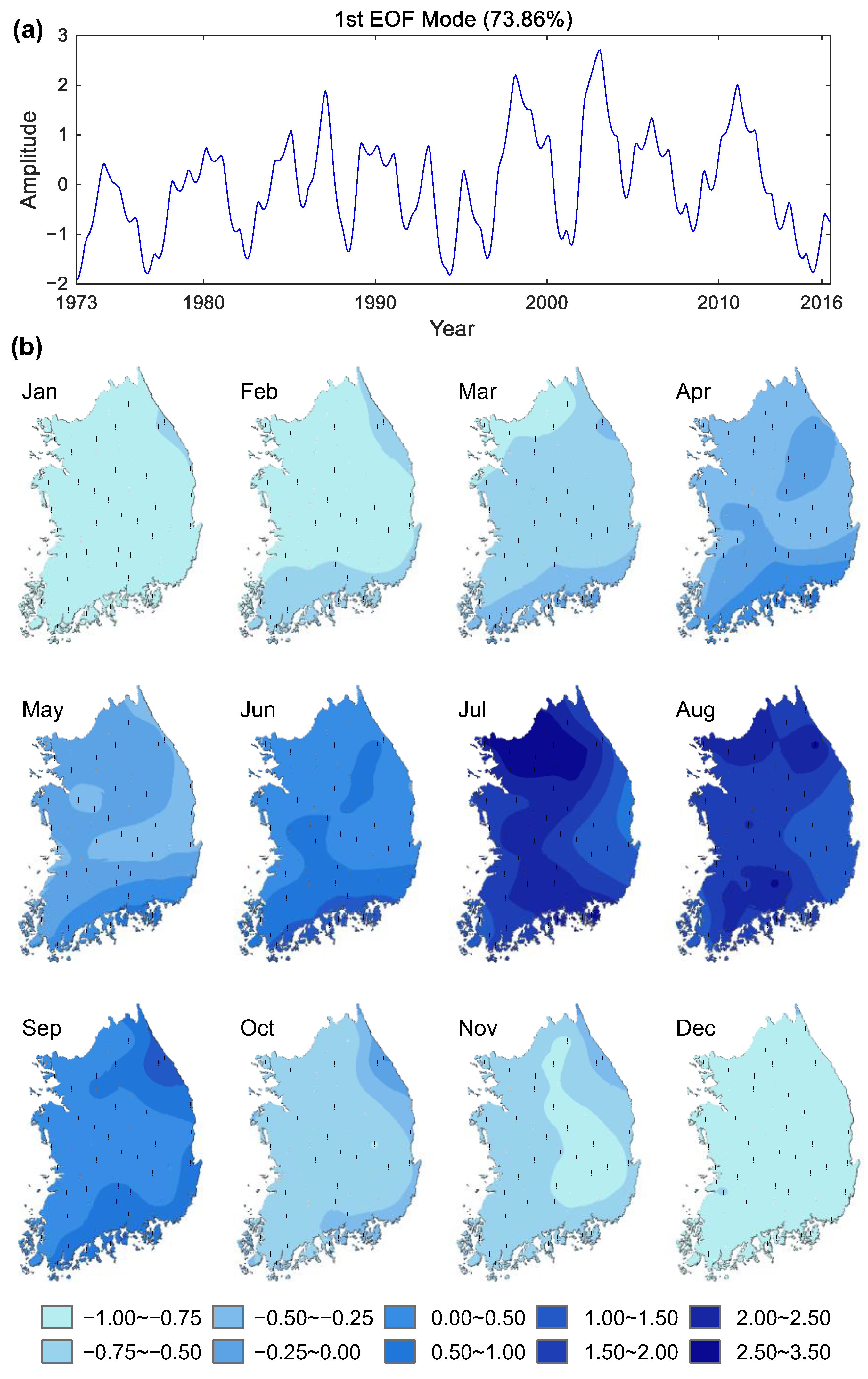
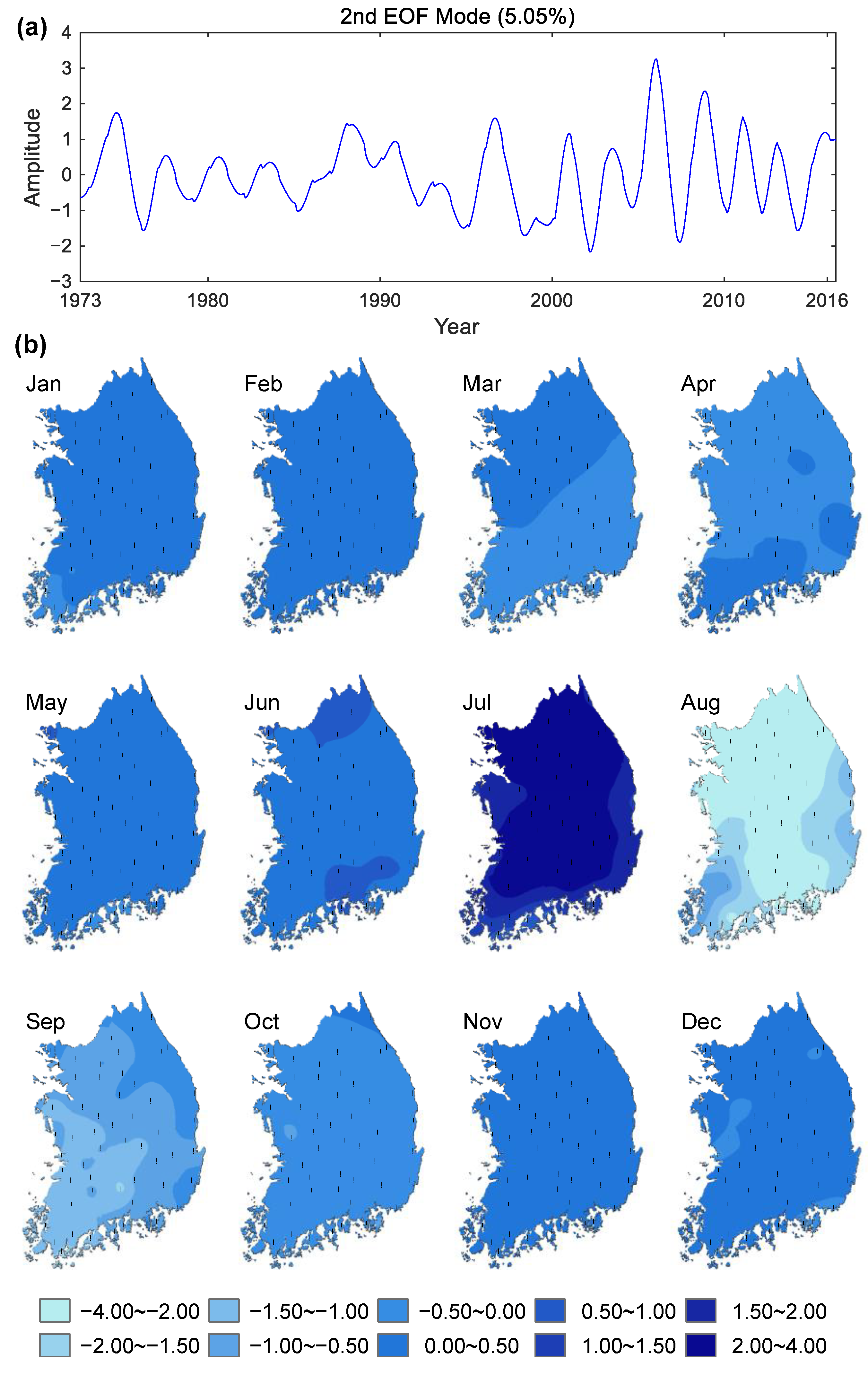
2.2.2. Cyclostationary Empirical Orthogonal Function
2.2.3. Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)
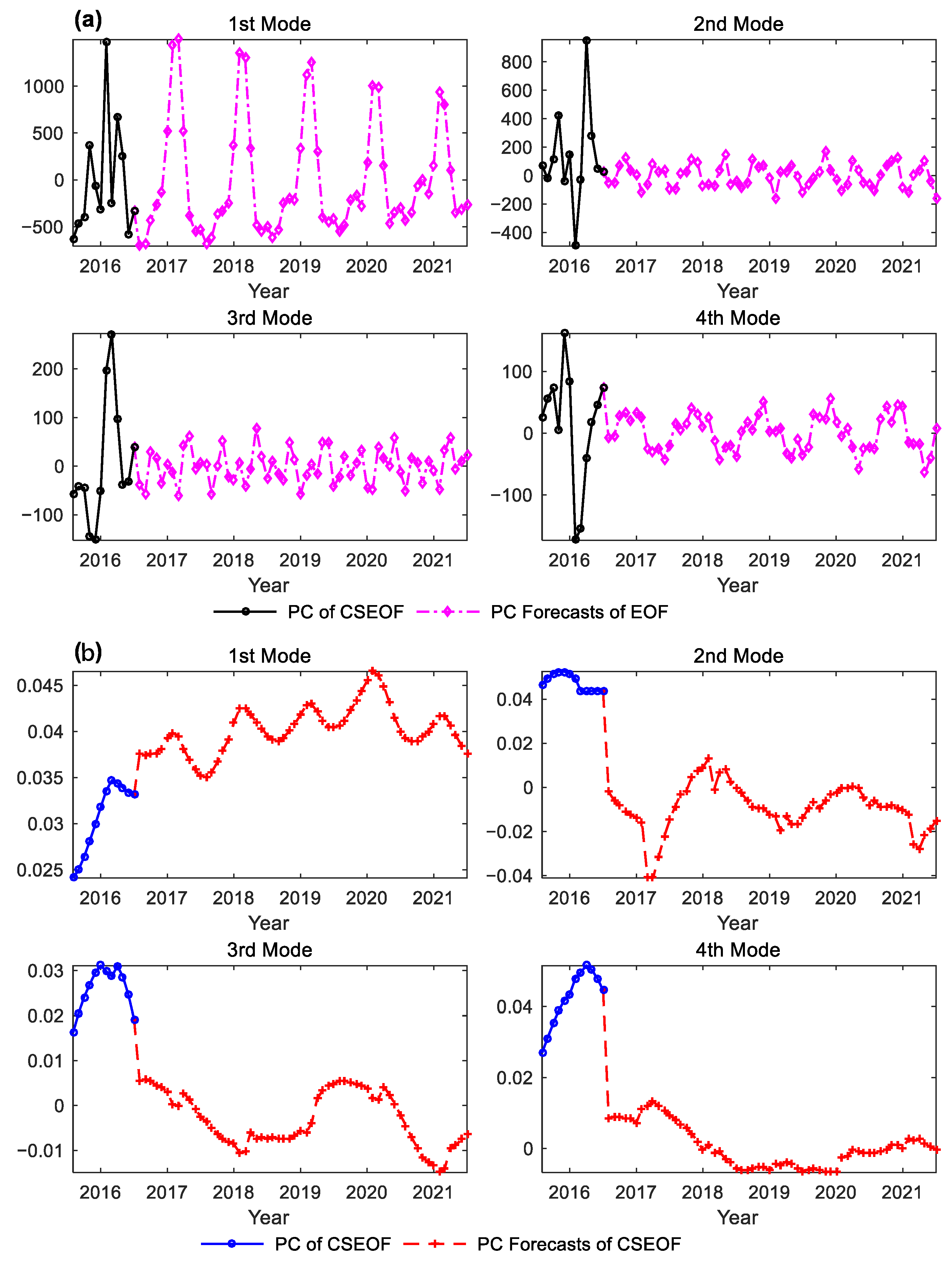
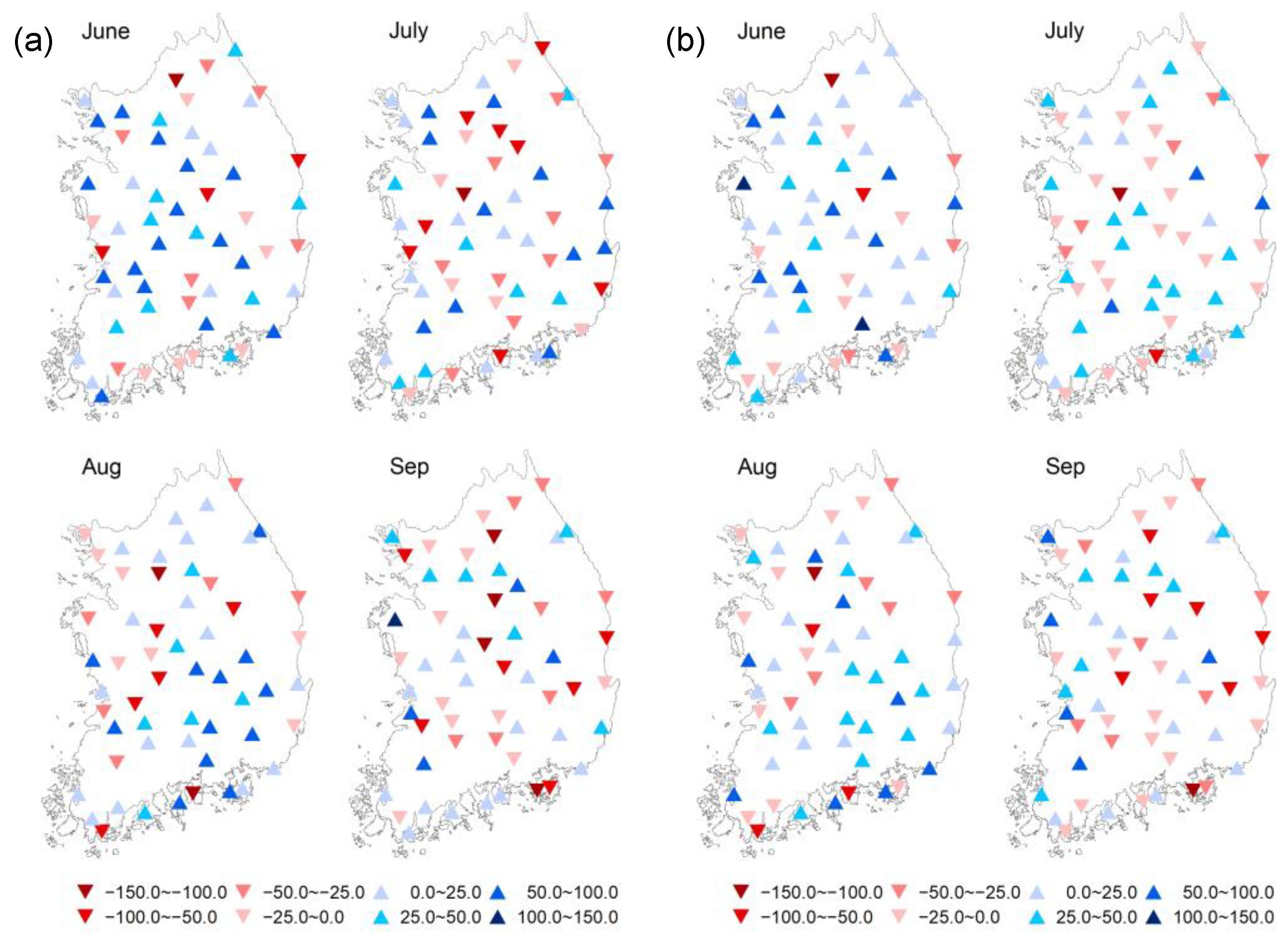
3. Results and Discussion
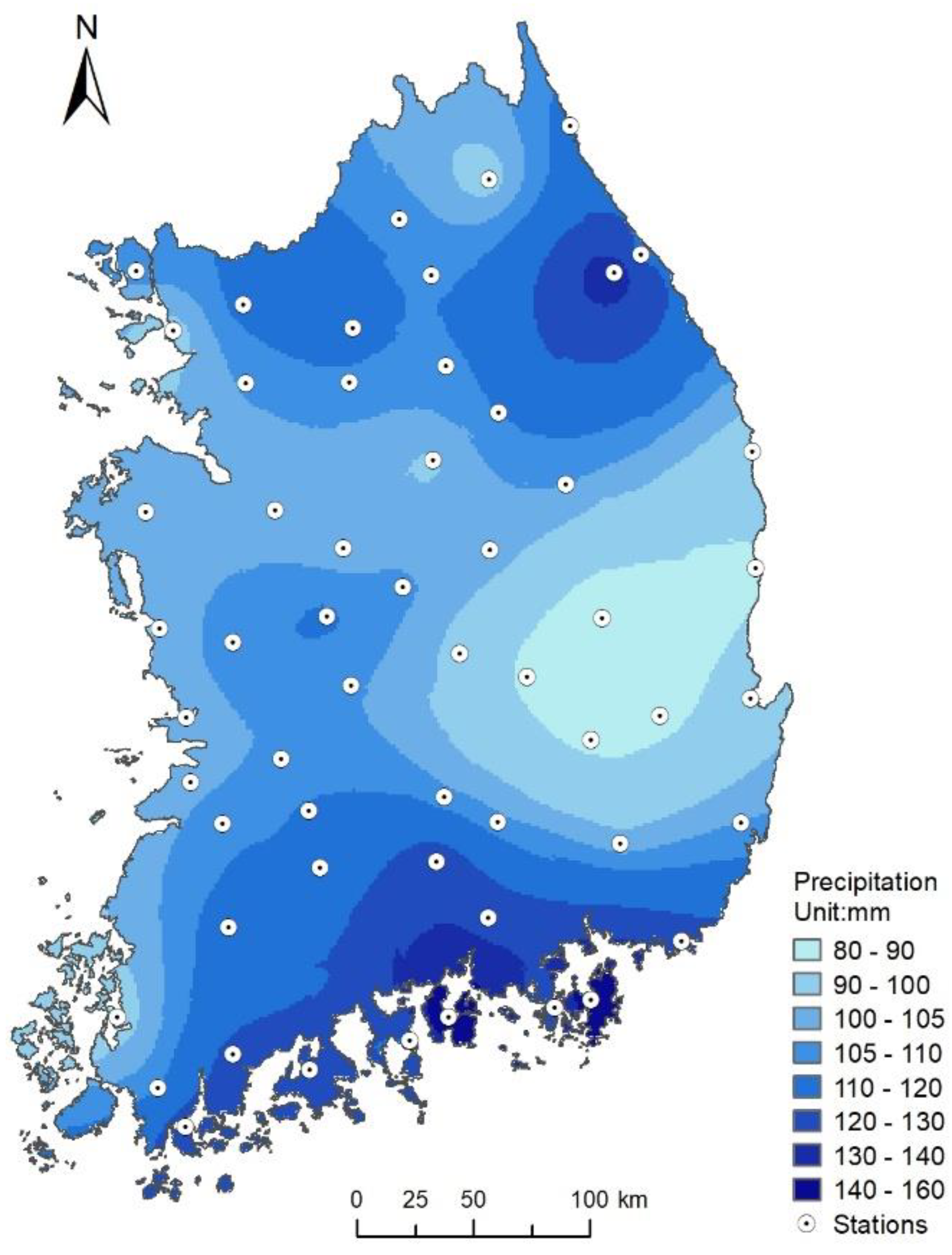
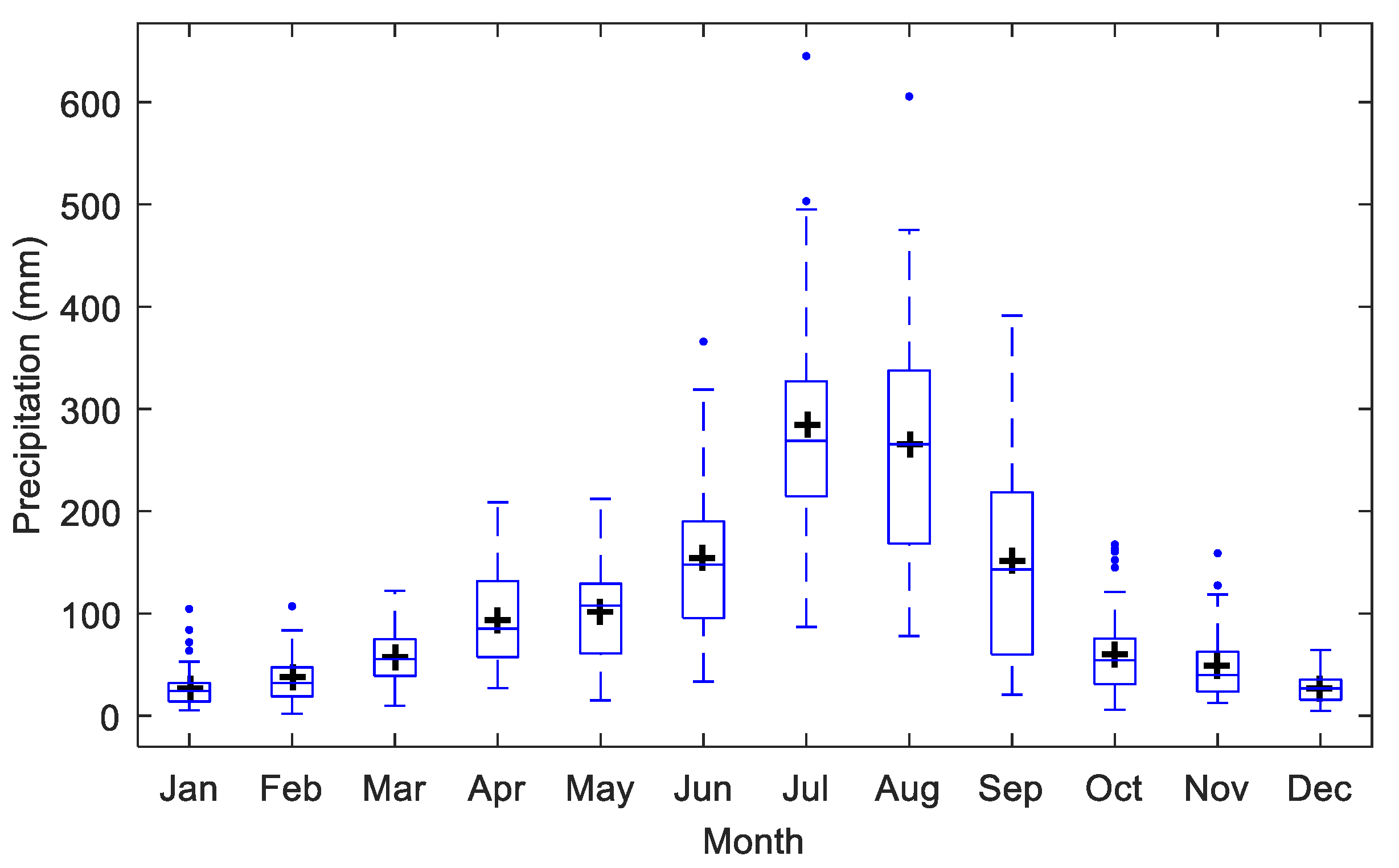
3.1. Seasonal Cycle of Precipitation
3.2. Forecasting of Precipitation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trenberth, K.E. Recent Observed Interdecadal Climate Changes in the Northern Hemisphere. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1990, 71, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alijanian, M.; Rakhshandehroo, G.R.; Mishra, A.K.; Dehghani, M. Evaluation of satellite rainfall climatology using CMORPH, PERSIANN-CDR, PERSIANN, TRMM, MSWEP over Iran. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4896–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, L. Evaluation of multiple gridded precipitation datasets for the arid region of northwestern China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T.G. Evidence for intensification of the global water cycle: Review and synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, N.; Alexander, L. Has the climate become more variable or extreme? Progress 1992–2006. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2007, 31, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Gemmer, M.; Jiang, T. Spatiotemporal analysis of precipitation trends in the Yangtze River catchment. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2006, 20, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.K.; Kim, K.Y. A New Perspective on the Climate Prediction of Asian Summer Monsoon Precipitation. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4840–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.T.; Wang, H. Relationship between the boreal spring Hadley circulation and the summer precipitation in the Yangtze River valley. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Miller, N.L.; Farrara, J.D.; Hong, S.Y. A Seasonal Precipitation and Stream Flow Hindcast and Prediction Study in the Western United States during the 1997/98 Winter Season Using a Dynamic Downscaling System. J. Hydrometeorol. 2000, 1, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, R.W.; Kim, H.K.; Unger, D. Long-Lead Seasonal Temperature and Precipitation Prediction Using Tropical Pacific SST Consolidation Forecasts. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3398–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ting, M.; Ji, M. Prediction of seasonal mean United States precipitation based on El Niño sea surface temperatures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, D.; Dracup, J.A. Artificial Neural Networks and Long-Range Precipitation Prediction in California. J. Appl. Meteor 2010, 39, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, P.; Rajagopalan, B. Interannual Variability and Ensemble Forecast of Upper Blue Nile Basin Kiremt Season Precipitation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peel, S.; Wilson, L.J. A Diagnostic Verification of the Precipitation Forecasts Produced by the Canadian Ensemble Prediction System. Weather. Forecast. 2008, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Kwon, W.T. Spatial variations of summer precipitation trends in South Korea, 1973–2005. Environ. Res. Lett. 2007, 2, 45012–45019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Y.H.; Kawamura, A.; Jinno, K.; Berndtsson, R. Detection of ENSO-influence on the monthly precipitation in South Korea. Hydrol. Processes 2005, 19, 4081–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, Y.Y. Investigation of tropical Pacific upper-ocean variability using cyclostationary EOFs of assimilated data. Ocean Dyn. 2004, 54, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Ding, Q.; Jhun, J.G. Trends in Seoul (1778–2004) summer precipitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aghakouchak, A. Evaluation of satellite-retrieved extreme precipitation rates across the central United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampoulis, D.; Anagnostou, E.N. Evaluation of Global Satellite Rainfall Products over Continental Europe. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona, M.; Overeem, A.; Brasjen, A.M.; Meirink, J.F.; Leijnse, H.; Uijlenhoet, R. Evaluation of Rainfall Products Derived From Satellites and Microwave Links for The Netherlands. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6849–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnston, A.G.; He, Y.; Glantz, M.H. Predictive Skill of Statistical and Dynamical Climate Models in SST Forecasts during the 1997–98 El Niño Episode and the 1998 La Niña Onset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vautard, R.; Plaut, G.; Wang, R.; Brunet, G. Seasonal Prediction of North American Surface Air Temperatures Using Space-Time Principal Components. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.E.; Jones, C.; Schemm, J.K.E.; Graham, N.E. A Statistical Extended-Range Tropical Forecast Model Based on the Slow Evolution of the Madden-Julian Oscillation. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1918–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waliser, D.E.; Lau, K.M.; Stern, W.; Jones, C. Potential Predictability of the Madden-Julian Oscillation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cahalan, R.F.; Wharton, L.E.; Wu, M.L. Empirical orthogonal functions of monthly precipitation and temperature over the United States and homogeneous stochastic models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 26309–26318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.V. Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) analysis of monsoon rainfall and satellite-observed outgoing long-wave radiation for Indian monsoon: A comparative study. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2004, 85, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, C. Empirical Orthogonal Function Analysis of Daily Rainfall in the Upper Reaches of the Huai River Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1999, 62, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Empirical Orthogonal Functions and Statistical Weather Prediction; Scientific Report No. 1; MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1956; pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hannachi, A.; Jolliffe, I.T.; Stephenson, D.B. Empirical orthogonal functions and related techniques in atmospheric science: A review. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 1119–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; North, G.R.; Huang, J. EOFs of One-Dimensional Cyclostationary Time Series: Computations, Examples, and Stochastic Modeling. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; North, G.R. EOFs of Harmonizable Cyclostationary Processes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Chung, C. On the Evolution of the Annual Cycle in the Tropical Pacific. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Wu, Q. A Comparison Study of EOF Techniques: Analysis of Nonstationary Data with Periodic Statistics. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Roh, J. Physical Mechanisms of the Wintertime Surface Air Temperature Variability in South Korea and the near-7Day Oscillations. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2197–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, K.-Y.; Kim, B.-M. Physical mechanisms of European winter snow cover variability and its relationship to the NAO. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; Holden-Day: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, G.R.; Bell, T.L.; Cahalan, R.F.; Moeng, F.J. Sampling Errors in the Estimation of Empirical Orthogonal Functions. Mon. Weather Rev. 1982, 110, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, A.; So, J.-M.; Bae, D.-H. Precipitation Forecast Contribution Assessment in the Coupled Meteo-Hydrological Models. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jee, J.B.; Ki, S. Sensitivity Study on High-Resolution WRF Precipitation Forecast for a Heavy Rainfall Event. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Nam, K.-Y.; Chang, K.; Oh, S. The Operational Very Short Range Forecast of Precipitation and its Hydrological Applications in South Korea. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Radar Meteorology, Cairns, Australia, 5–10 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.K.; Kang, I.S.; Park, C.K.; Kim, K.M. Superensemble prediction of regional precipitation over Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Kim, G. Quantitative Monthly Precipitation Forecasting Using Cyclostationary Empirical Orthogonal Function and Canonical Correlation Analysis. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Lim, Y.; Lee, J.; Kang, H.S.; Oh, H.S. Bayesian regression model for seasonal forecast of precipitation over Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 48, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

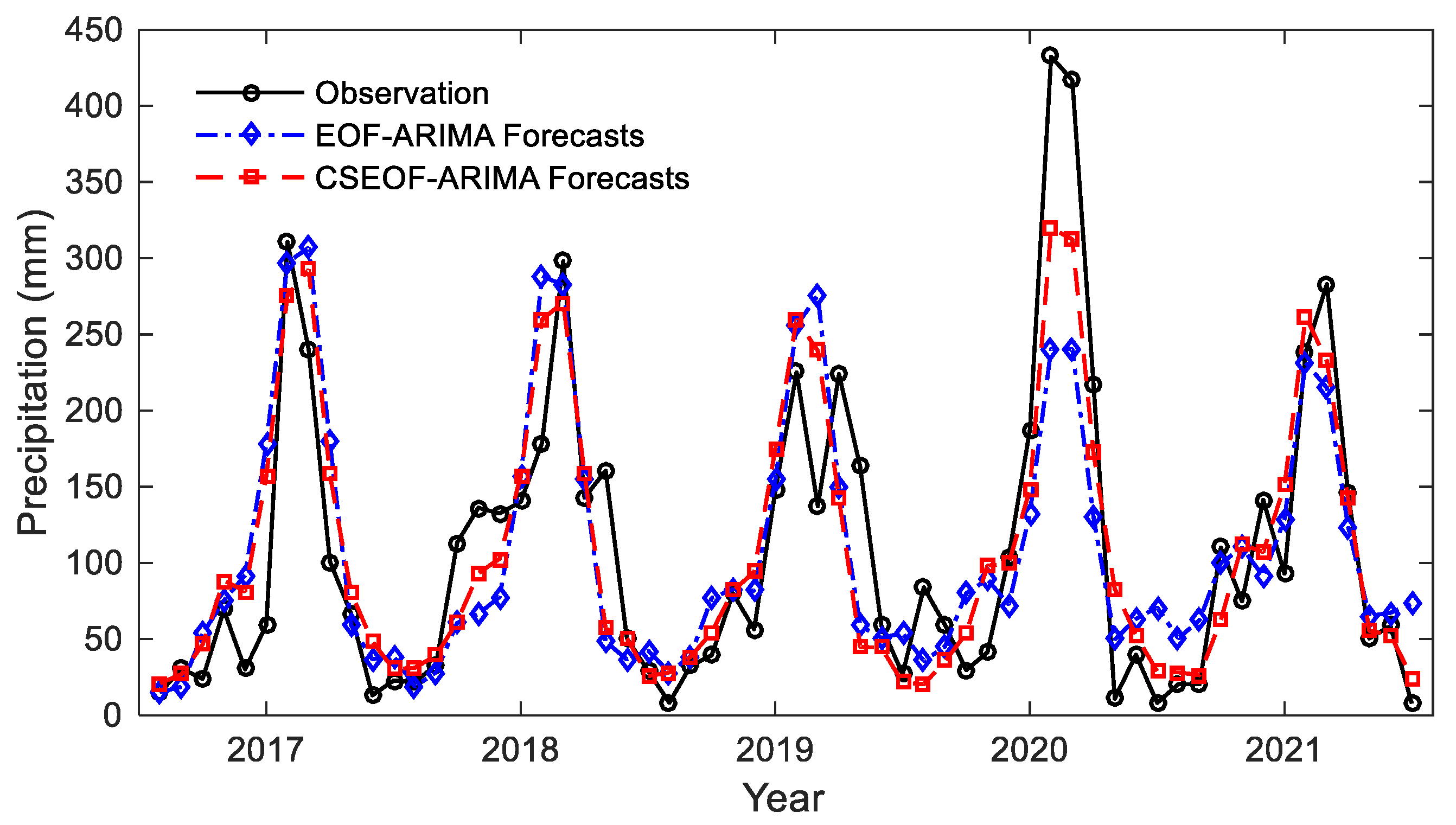
| Index | MAE (mm) | RMSE (mm) | R2 | CC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOF–ARIMA | 57.86 | 74.44 | 0.79 | 0.68 |
| CSEOF–ARIMA | 49.41 | 67.71 | 0.87 | 0.76 |
| Model or System | Study Area | Precipitation Source Type | Predictor | Time Scale | Time Period | Performance Evaluation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | CC | R2 | ||||||
| Bayesian Regression Models [47] | Over South Korea | Stations and Grids | GDAPS | Monthly (Average JJA) | 1979–2007 | 1.09 | - | - |
| Meteorological Model of WRF [42] | Imjin River Basin of Korea peninsula | Stations and Grids | - | 6 h | 2007–2011 | 59.67–212.80 | - | - |
| WRF Model [43] | Seoul & suburban in South Korea | Grids | SST Data | 3 h | 26–29 July 2011 | 2.54–13.18 | 0.2–0.59 | - |
| VSRF model [44] | Kyoungan River basin of South Korea | Stations and Radar Reflectivity | - | Hourly | 5.77–7.67 | - | 0.7–0.8 | |
| SVDA and CCA [45] | Over South Korea | Stations | SLP Data | Monthly | 1954–2003 | - | 0.11–0.87 | - |
| Cyclostationary EOF and CCA [46] | Over South Korea | Stations | SST | Monthly | 1973–2013 | 54.17–63.85 | 0.69–0.73 | 0.55–0.67 |
| Cyclostationary EOF and ARIMA | Over South Korea | Stations | Precipitation | Monthly | 1973–2021 | 67.71–74.44 | 0.79–0.87 | 0.68–0.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Kim, G.; Lei, K.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of Technology for the Analysis and Forecasting of Precipitation Using Cyclostationary EOF and Regression Method. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030500
Sun M, Kim G, Lei K, Wang Y. Evaluation of Technology for the Analysis and Forecasting of Precipitation Using Cyclostationary EOF and Regression Method. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(3):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030500
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mingdong, Gwangseob Kim, Kun Lei, and Yan Wang. 2022. "Evaluation of Technology for the Analysis and Forecasting of Precipitation Using Cyclostationary EOF and Regression Method" Atmosphere 13, no. 3: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030500
APA StyleSun, M., Kim, G., Lei, K., & Wang, Y. (2022). Evaluation of Technology for the Analysis and Forecasting of Precipitation Using Cyclostationary EOF and Regression Method. Atmosphere, 13(3), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030500






