Abstract
Coal is China’s dominant energy source, among which bituminous coal is the most extensive and plentiful. Using bituminous coal resources to design a low-emission household fuel is very important for rural poverty areas. In this work, a new type of bituminous coal pellet (BCP) fuel using an automatic prototype pellet stove was designed for the first time. This study mainly shows the emission characteristic results of BCPs and some comparisons with other commercial solid fuels. Fuel property, PM2.5 morphology, and ash characteristics of the novel fuel were also assessed. In terms of fuel properties, BCPs had a cold compressive strength of 637.2 N, a heating value of 22.26 MJ/kg, and many fine pores in the cross-section for air entry. The real-time emissions of BCPs were stable during combustion. The emission factors of PM2.5 and CO of BCPs were 1.36–2.29 g/kg and 11.1–18.0 g/kg, which were significantly lower than those of bituminous chunk and bituminous briquette (p < 0.05). PM2.5 and CO reduced emissions by 83–90% and 61–76%, respectively, compared with raw coal chunk. According to the chemical composition and morphological characteristics, the PM2.5 from BCP combustion can be divided into fine particulates, molten char particles, and char fragmentation. The ash from BCPs had a higher melting temperature (over 1300 °C), with removable ash agglomeration. Overall, the results presented in this study highlight that turning bituminous coal into pellets and burning them in automatic stoves could noticeably reduce PM2.5 and CO emissions, effectively improving rural air quality.
1. Introduction
In 2019, coal consumption in China was equivalent to 2804 million tons of standard coal [1], accounting for more than half of global consumption [2]. Compared with anthracite coal and semi-coke, bituminous coal is widely used in rural China due to its large reserves, low price, and ease of ignition and burning. More than 1500 million tons of bituminous raw coal chunk are used annually for rural heating [3], accounting for 60% of residential energy consumption [4]. The burning of coal in inefficient stoves creates products of incomplete combustion (PICs) such as carbon monoxide (CO) and fine particulates (PM2.5) [5,6]. These PICs result in significant air pollution and human health problems in many developing countries [7,8,9]. Research has documented that household air pollution associated with solid fuel combustion causes about 1.15 million premature deaths every year in China [10]. The Chinese government is attempting to replace traditional solid fuel with cleaner fuel. In some poverty-stricken areas, clean heating intervention remains a challenge [11]. According to field surveys, interventions have resulted in high costs beyond the affordability of most rural households [12,13]; therefore, most residents opt to continue using raw bituminous coal. This result indicates that coal consumption is hard to replace because bituminous has a cost advantage. Hence, this rural energy structure dominated by bituminous coal is likely to persist for the next few years, and it will remain the primary source of household cooking and heating energy in many developing countries, including China [14,15]. Finding a pragmatic, affordable solution is of the highest priority in order to decrease emissions from the burning of solid fuel for cooking and heating among rural households.
In an effort to reduce the negative impacts of coal use in households, coal briquette has been introduced in rural China as a clean heating intervention. Coal briquettes are mainly made from coal, with additives that act as emission-reducing agents [16,17]. Zhang et al. reported a 37.5% reduction in PM2.5 emissions by using red mud additive in bituminous briquettes [16]. Han et al. found that coal briquettes with sulfur-reducing agents could effectively reduce SO2 emissions to the atmosphere [18]. However, adding many additives to the fuel will increase its cost, while the emission reduction effects are barely noticeable. Therefore, this research explores other acceptable ways to achieve the effect of reducing emissions.
Pelletized fuels appear to be an excellent alternative to ordinary fuels in rural households based on their emission reduction potential [19]. Meanwhile, half-ellipsoidal and cylindrical briquettes have also been shown to have higher thermal efficiency than spherical briquettes [20]. Pelletized biomass fuels and clean automatic stoves have been widely promoted in China because of the observed significant emissions reduction [19,21], but many areas lack biomass resources, and problems of severe slagging and low heating value for agricultural waste combustion are inevitable. Owing to the abundant sources and thermal properties of bituminous coal, we designed a novel bituminous coal pellet (BCP) as an alternative fuel source for households and assessed its emission reduction potential in this study.
In our current research, we preliminarily developed a type of bituminous coal pellet (BCP) and analyzed its capacity to reduce emissions during combustion in an automatic stove (Figure 1). This study mainly focused on (1) evaluating the properties of the self-made bituminous coal pellet and (2) recording the performance and emission characteristics of PM2.5, CO, NOX, and SO2 from burning BCPs and comparing the results with those from commercial biomass pellets and coal fuels. This study provides a novel clean heating solution to replace raw coal and information on the development of coal briquettes for household use.
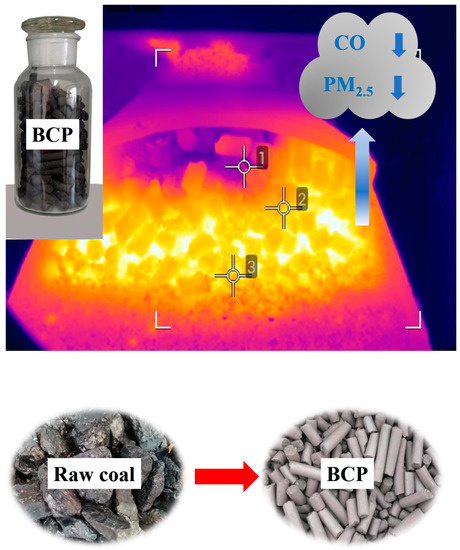

Figure 1.
Bituminous coal pellet and its burning phenomenon.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement System
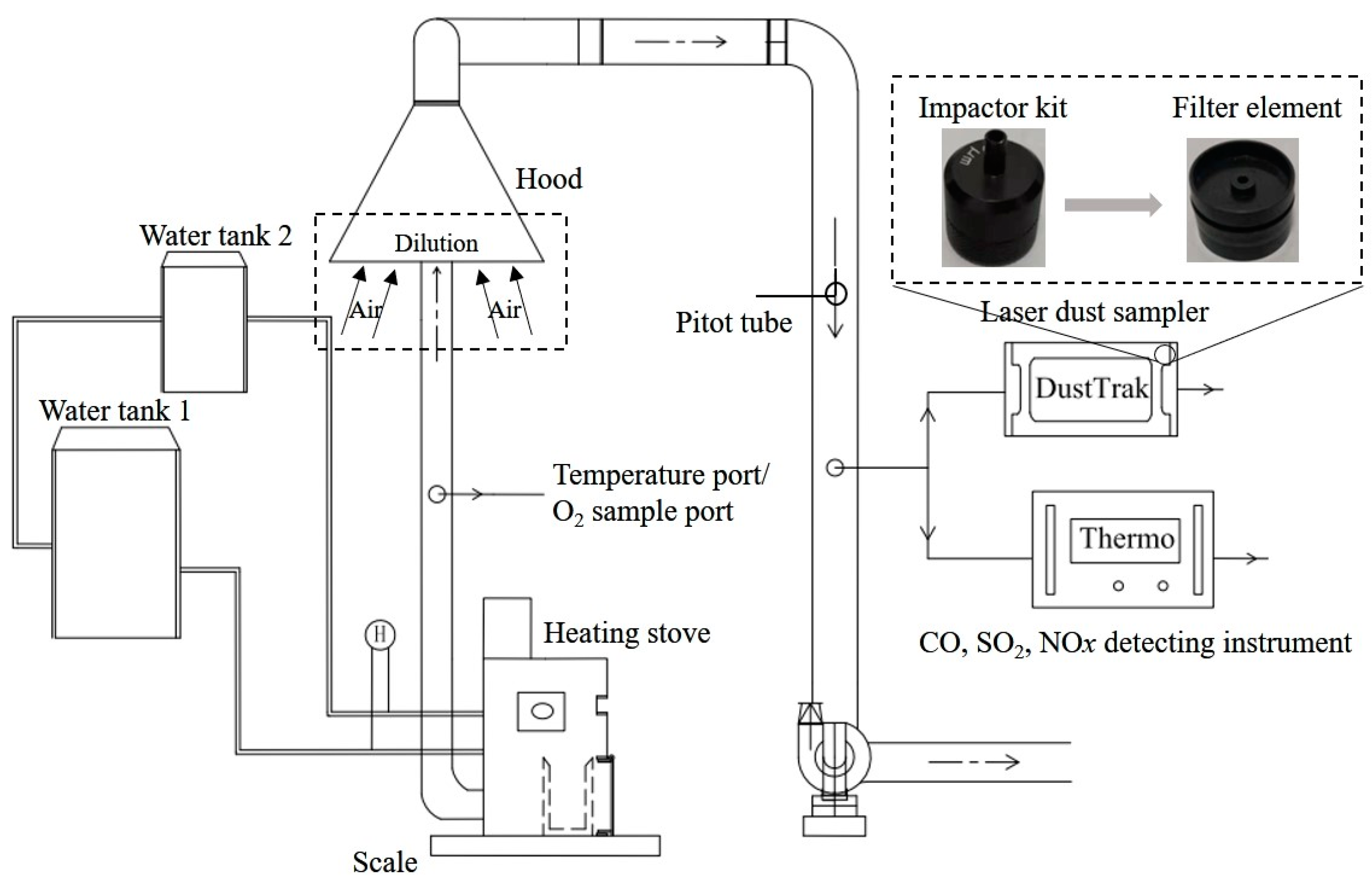
This study used a dynamic real-time pollutant emission monitoring system (Figure 2) following ISO standards (ISO/FDIS 19867-1, Clean cookstoves and clean cooking solutions—Harmonized laboratory test protocols) [22]. A hood (3400 mm high) was used to collect flue gas. Flue gas temperature and pollutant concentration were reduced through dilution with fresh air. Pollutants were sampled using the fixed source test method in a dilution tunnel. The collected flue gas mixed with dilution air was then drawn into a circular pipe (219 mm in diameter) with a flow rate of 1000 m3/h. A pitot tube was used to measure the flow rate of the diluted flue gas. A thermometer and hygrometer were installed in the pipe to correct the airflow rate by monitoring the real-time temperature and humidity, respectively, in the tunnel. The system also had an electronic scale, a calorimeter, and a thermocouple (K type), which were used to monitor the change in fuel mass during combustion, the heat load of the different combustion stages, and the stove combustion temperature, respectively.
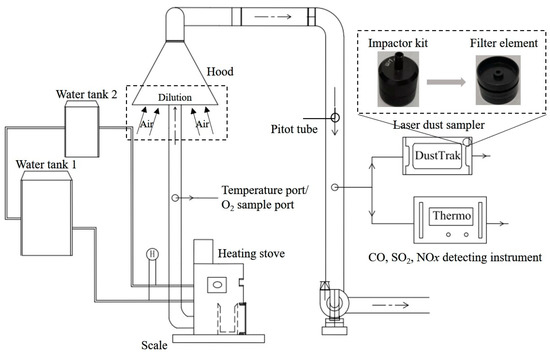
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of dynamic sampling system.
The pollutant monitoring equipment used in this experimental system included a CO analyzer (Model 48i; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), an SO2 analyzer (Model 43i; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), an NOX analyzer (Model 42i; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and a laser dust sampler (Dust Trak8533; TSI Inc., Saint Paul, MN, USA). The data on emissions were recorded every 30 s, and all instruments were calibrated with the help of engineers before the continuous test began. A 37 mm Teflon filter membrane was used to test particulate matter for gravimetric analysis. In addition, a high-definition thermal imaging camera (T1010; Wilsonville, OR, USA) was used to observe the surface temperature of the fuel.
2.2. Fuel and Stove
BCPs were made from low-sulfur coal (main raw material) and semi-coke powder (auxiliary raw material) in a ratio of 4:1. The raw material powder (prepared using the hammer pulverization system) was mixed in a high-speed dry–wet mixer with 3% pre-gelatinized starch and 15% water. In the novel fuel, 7% calcium-based fixation agents were added to the pellets to reduce SO2 emissions. The bituminous coal pellets were produced from the mixture using a screw briquette machine. Then they were air-dried for approximately 3 days until the moisture was below 8%, then stored in a warehouse at room temperature (25 °C) before the combustion experiment.
In general, the main raw materials used for commercial biomass pellets are wood residues, such as sawdust, wood shavings, and wood chips, as well as agricultural waste, such as straw, and waste products of the food industry and fuel crops. Nowadays, most biomass pellets are produced in pellet mills of the ring die type.
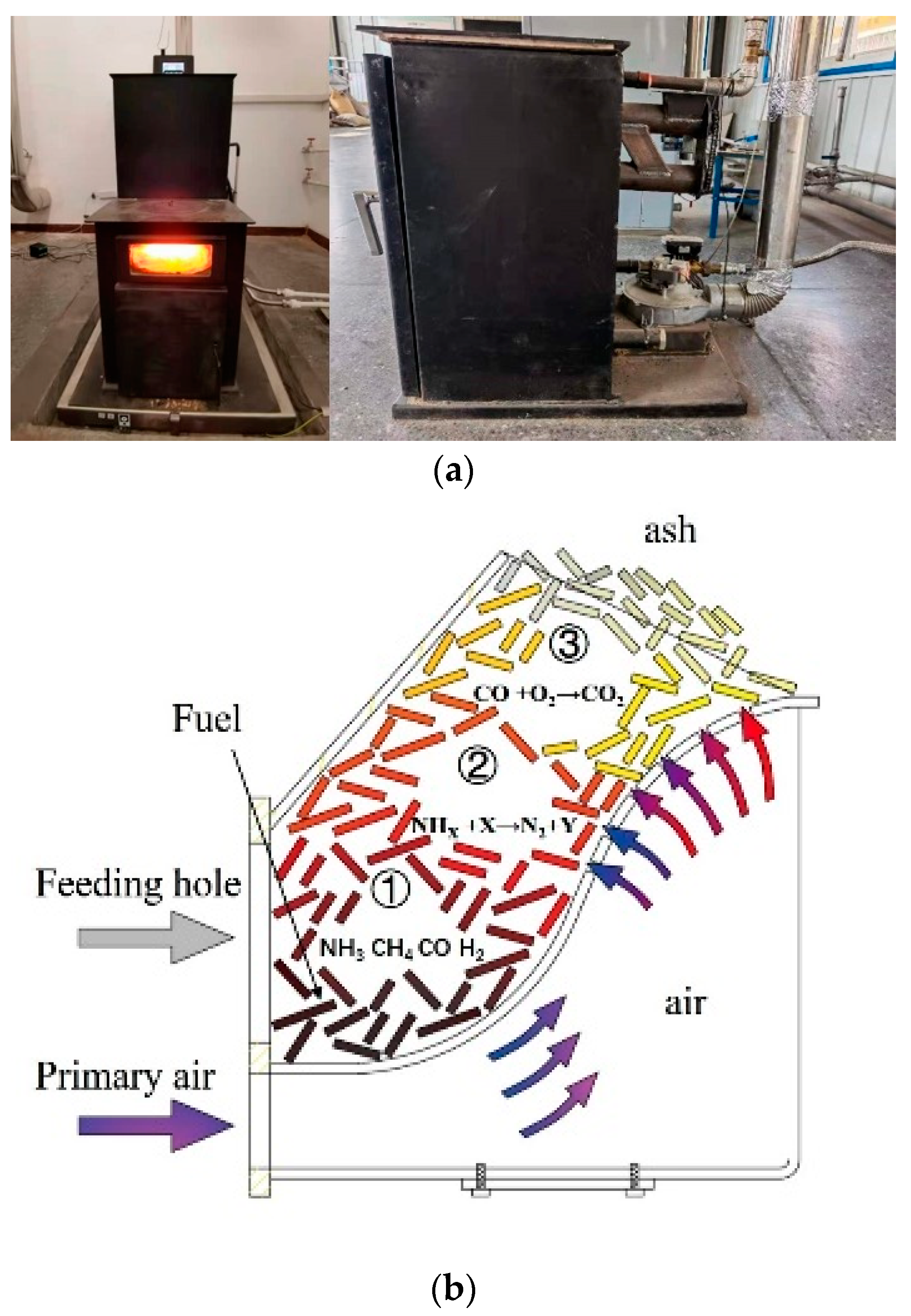
For this study, an automatic pellet stove prototype was designed with three combustion zones (Figure 3): pyrolysis, reduction, and burning, shown in Figure 3b as zones 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The following is based on BCP combustion under high power: (1) The pyrolysis zone is an oxygen-poor environment. The oxygen content in the pyrolysis process is 0 to 6%, and the temperature is 200 to 900 °C. The concave air distribution plate prevents the escape of flue gas and increases the time of BCP combustion. (2) The reduction zone has less than 10% oxygen content and a temperature below 1100 °C, and the contact combustion time of volatile matter and charcoal is more than 2 s. (3) The combustion zone has an oxygen content of less than 15% and a temperature below 1400 °C, and the residence time of volatile matter in the combustion zone is more than 2 s. Oxygen content and temperature in the ash zone are less than 15% and 1000 °C, respectively, with a residence time of more than 2 s for volatile matter. Other design features include an automatic ignition device and an automatic loading system.
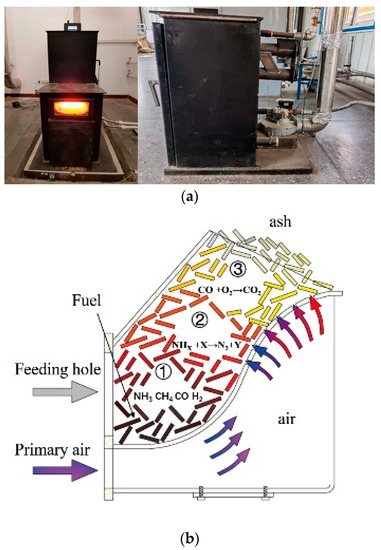
Figure 3.
(a) Photographs of new automatic pellet stove prototype. (b) Profile of combustor: ① pyrolysis zone, ② reduction zone, ③ burning zone.
2.3. Testing Procedure
Pellet stove users in rural China ignite the stoves infrequently (only once every one or two weeks) and rarely operate them at the maximum power. They control stove fuel consumption rates somewhat by adjusting the fuel feeding mode. Therefore, this study tested the automatic heating stove at high, medium, and low power modes, corresponding to a fuel loading rate for 5 s at 2, 4, and 6 s intervals, respectively. In this study, power ranges under the three loading conditions were obtained through multiple tests (Table S1).
The fuel sample was ignited by an automatic ignition device until a stable flame was observed to avoid any variabilities associated with user habits during ignition. Measurement started when sharp power fluctuations were no longer observed after igniting, and the ignition stage lasted approximately 20 to 30 min. Similarly, the period of power fluctuation, which was caused by the change of the loading and lasted about 10 to 30 min, was also excluded in the test stage. After the stove achieved stable combustion and the quantity of fuel consumed in the process was recorded, a 2-h measurement of stove emissions was performed in each of the three stages. To ensure accuracy, tests were carried out in triplicate for each power mode.
2.4. Characterization Method and Data Analysis
2.4.1. Characterization Method
Proximate and ultimate analyses were performed, and the calorific value of the pellet fuels was determined using an element analyzer (vario MACRO cube, Elementar, Hanau, Germany), automatic sulfur analyzer (5E-AS3200B; Kaiyuan, Changsha, China), industrial analyzer (WS-G606; Yuanguang, Changsha, China), and calorimeter (SDC5015; Shangde, Changsha, China). To evaluate the changes in thermal behavior during combustion, the samples were subjected to non-isothermal combustion experiments in a thermogravimetric analyzer (STA449-F5; NETZSCH, Selb, Bayern, Germany). In each experimental run, about 10 mg of the fuel was heated at a rate of 20 °C/min with an airflow rate of 100 mL/min up to a final temperature of 1300 °C.
The morphology of particle matter and pellet fuels was determined using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The elemental composition of particles was analyzed by an EDAX Apollo XP energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS). Specifically, part of the Teflon filter was attached to a small patch to observe the PM2.5 on its surface. High-resolution morphological characteristics of PM2.5 from fuel combustion were clarified using SEM (JSM-6701; JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
An X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF; S8 TIGER, Bruker, Ettlingen, Germany) was used to determine the main chemical composition of ash. Fusibility analysis was performed by an ash fusibility degerminator (AF700; LECO, San Jose, CA, USA). The ash fusibility temperatures, including deformation temperature (DT), softening temperature (ST), hemispherical temperature (HT), and flow temperature (FT), were determined within the given range (400 to 1500 °C). The mineral content of the raw coal was analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD; D8, Bruker, Ettlingen, Germany). The samples were scanned from 5 to 80° in the 2θ range.
2.4.2. Data Analysis
The emission factor of pollutants used in this study was calculated based on the mass of contaminants per kilogram of fuel. The calculation formula is shown in the following equation:
where EFm,i is the fuel–mass based pollutant emission factor (m is mass and i is fuel type; g/kg), Ci is the average concentration of pollutant i during the test (mg/m3), G is the average flow rate of the flue gas during the test (m3/h), H is the test duration (hours), and M is the mass of fuel consumed during the test (kg). In this study, the emission factor and dispersion degree for each type of power were calculated by three parallel tests.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. BCP Properties
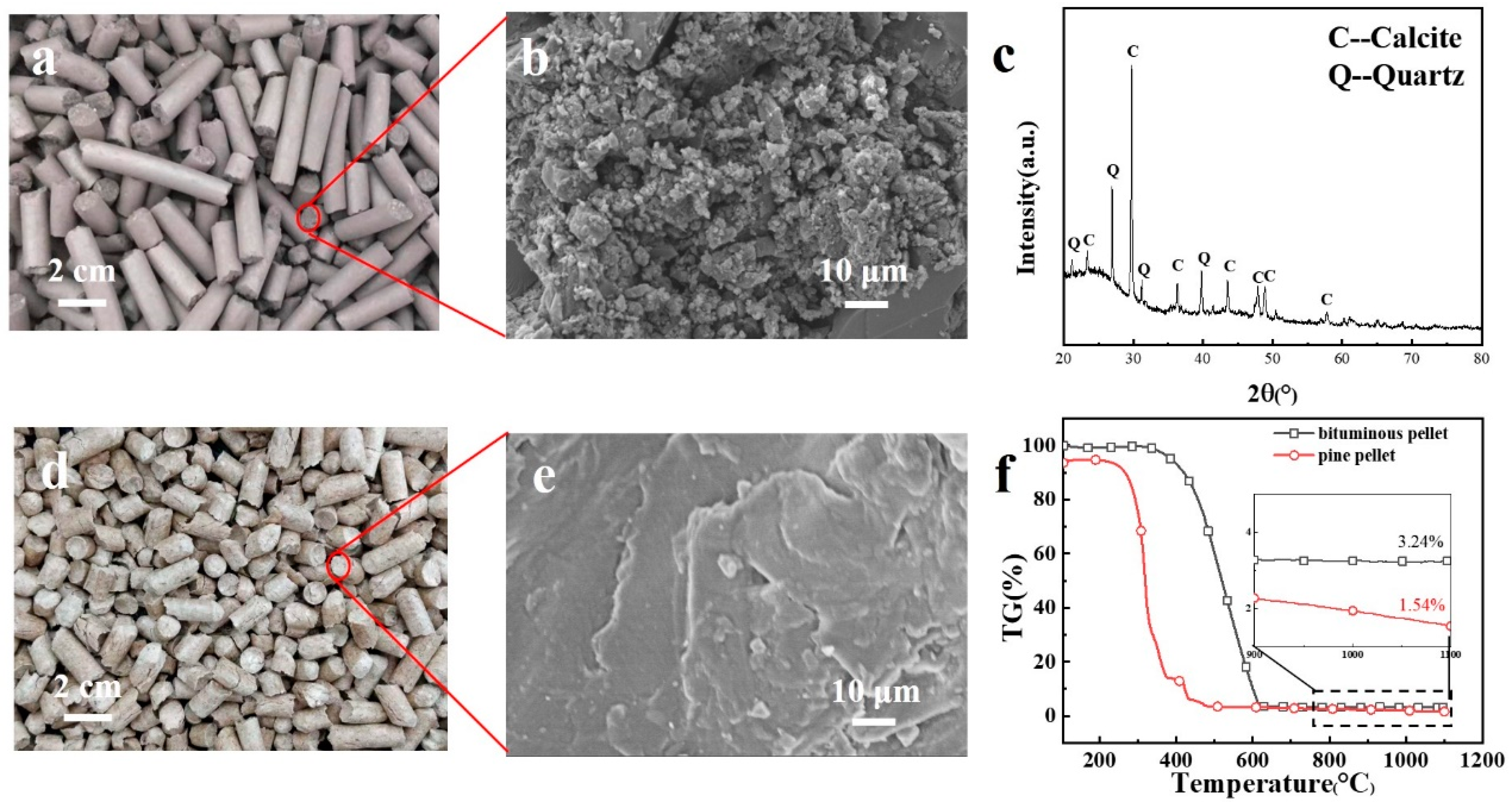
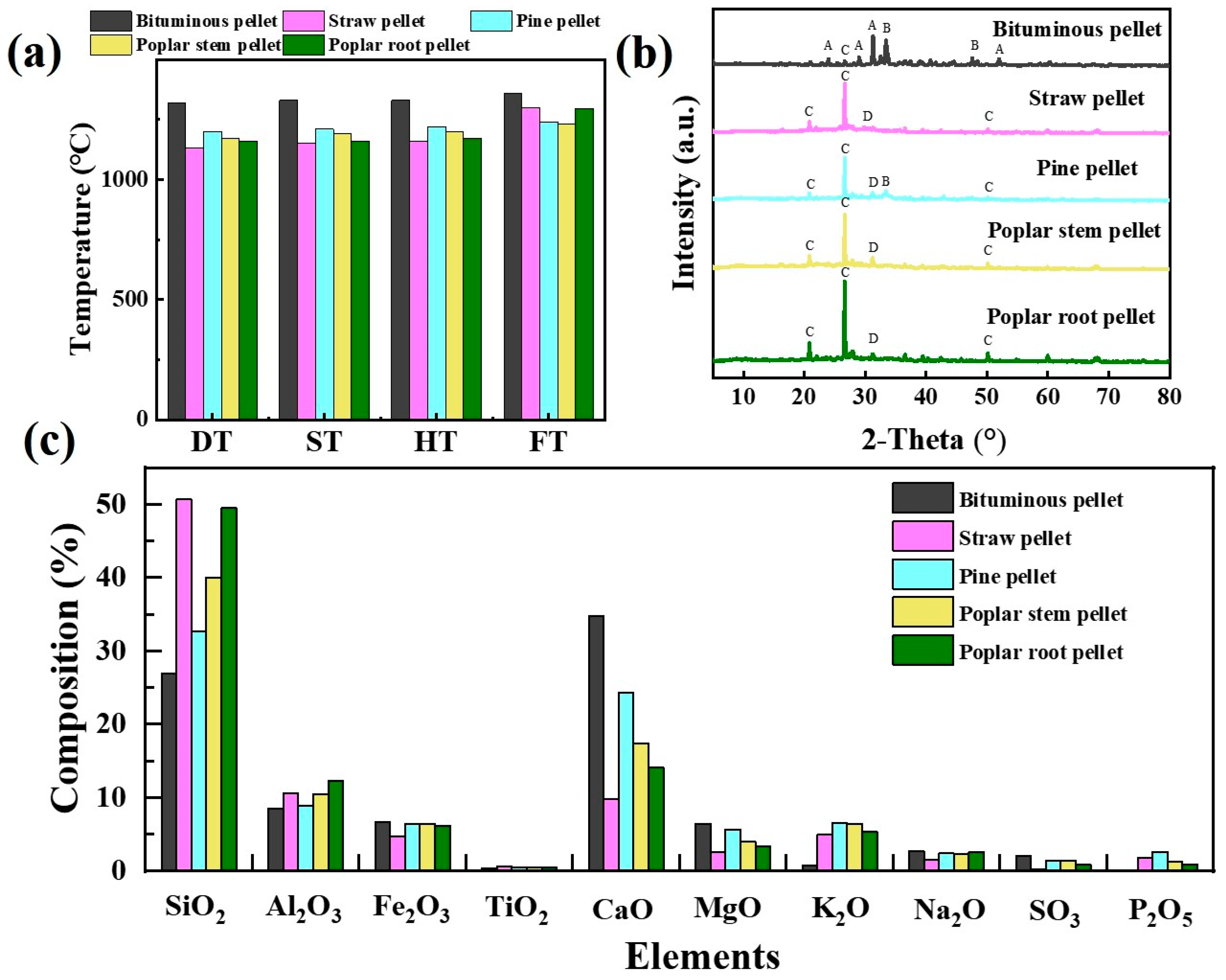
In order to have a better understanding of the novel fuel, the properties of BCPs were analyzed in this study. Figure 4a shows a photograph of the BCP sample. Results from the proximate and ultimate analyses are shown in Table 1. The physical properties of BCPs, shatter strength and cold compressive strength were found to be 99.2 ± 0.7% (>80%) and 637.2 ± 139.3 N (>400 N), respectively. These values conform with the Chinese commercial coal quality civil briquette standard (GB 34170-2017), which means that BCPs are strongly resistant to breakage. To compare the properties of other pellet fuels with those of BCPs, straw, pine, poplar stem, and poplar root pellets were purchased from a local market. Compared with the other pellet fuels (Table 1), BCPs have the highest heating value, meaning they will produce the highest amount of heat for the same fuel mass. They are more difficult to ignite than biomass pellets since they have a relatively low volatile matter content (29.1%). However, because BCPs are usually used in stoves with automatic ignition and loading, the difficulty in ignition caused by low volatile matter content has little effect during use. BCPs had the highest elemental sulfur content of all the fuels tested, leading to higher SO2 emissions [23].
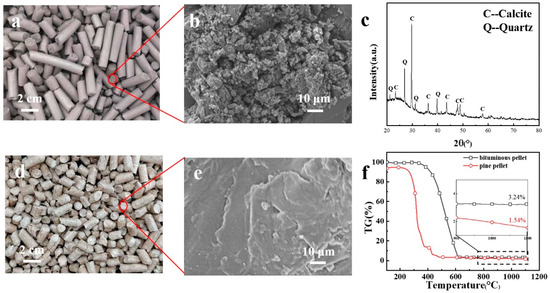
Figure 4.
Morphology, composition, and thermal behavior of pellets: (a) appearance of BCPs; (b) SEM image of BCP cross-section; (c) XRD result of BCPs; (d) appearance of pine pellets; (e) SEM image of pine pellet cross-section; (f) TGA curves of BCPs and pine pellets.

Table 1.
Proximate and ultimate analysis of fuels. All contents are in weight percent (%) on a dry fuel basis.
It is generally believed that wood pellets tend to have better performance [19,24]. Therefore, pine pellets, as shown in Figure 4d, were selected for morphology and thermal behavior analysis. Details on the other pellet fuels are shown in Figures S1 and S2. The cross-section of BCPs had more pore spaces than the pine pellets, as observed in Figure 4b,e. This phenomenon means sufficient oxygen can enter the BCPs via the pore spaces, leading to complete combustion and more energy release. Figure 4c shows that the two main minerals found in BCPs were quartz (peak Q) and calcite (peak C). Zhang et al. found similar results with their tests on bituminous coal produced in Shaanxi by XRD [25], which means there is more calcium (Ca) in BCPs. To understand the thermal behavior of pellet fuels, thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) curves of BCPs and pine pellets under air atmosphere were obtained (Figure 4f). Compared to pine pellets, BCPs started reducing weight and ignited at a higher temperature over a longer burning time. The unburned parts of the two fuels accounted for 3.24 and 1.54% of the total fuel, respectively. In general, BCPs released more energy when burned and lasted longer than other pellet fuels available on the market.
3.2. Emission Characteristics
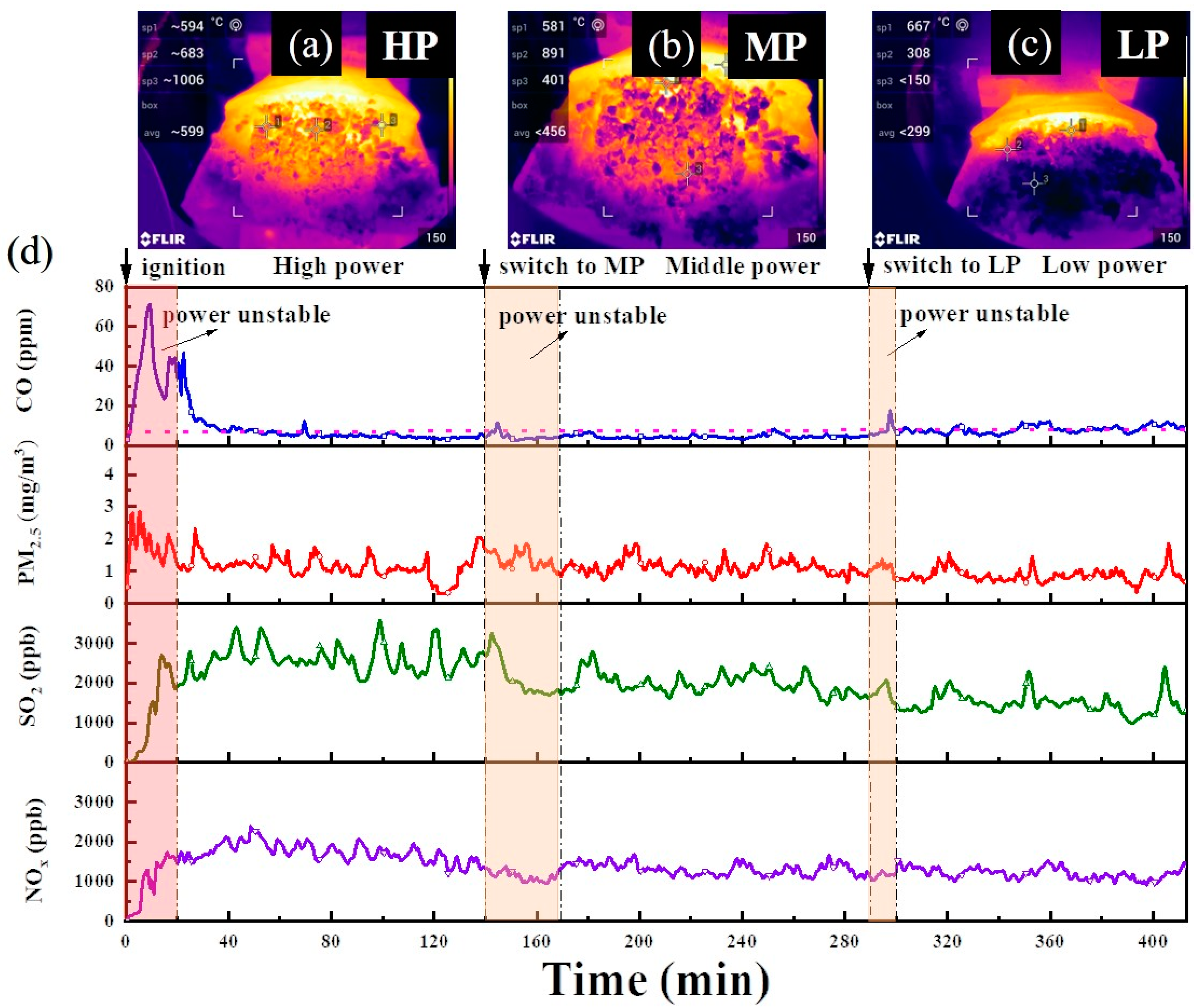
The typical real-time PM2.5, CO, SO2, and NOX concentrations selected in the three parallel tests and the furnace body temperature from BCPs burning in an automatic stove are illustrated in Figure 5, and the amount of pollutants per minute is shown in Table S2. Because the sampling spot was at the back end of the gas collector dilution, the concentration can only represent the relative change trend. Generally, the emission of air pollutants varies dramatically in the combustion process due to frequent fuel addition for traditional stoves and raw coal [26]. Lower variations and fluctuations existed throughout the overall combustion compared with those observed for traditional fuels in our earlier studies [26,27]. These results are consistent with previous research on pellet stoves [28,29]. The contributing factor for this phenomenon is the combustion of BCPs occurring through a continuous loading process and air supply, showing a weaker distinction between de-volatilization and flaming phases.
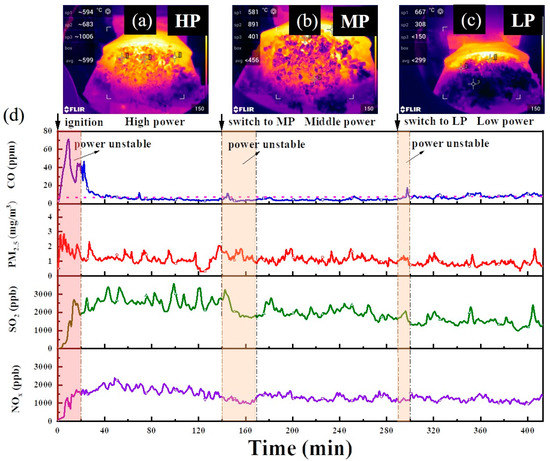
Figure 5.
Trend of CO, PM2.5, SO2, and NOX emissions and infrared thermal images of stove from BCP combustion: (a–c) infrared thermal images; (d) emission characteristics.
With regard to the emission trend, there was a significant increase in PM2.5, CO, SO2, and NOX in the ignition phase due to a sharp rise in temperature (Figure S3). This phenomenon occurred due to incomplete combustion and the low temperature of the furnace during cold start. Fortunately, as mentioned in Section 2.3, residents do not frequently perform ignition operations over the whole heating season, so a short-term increase in emissions may not have much impact on the environment. In the power unstable stage, the trend of CO showed slight growth after a sudden change in loading rate, but it was able to descend and stabilize rapidly. Other pollutants also showed fluctuations and promptly transitioned into stable combustion (1–2 min). This was most likely caused by the dropping of ash from the top of the stove, allowing adequate oxygen to approach the pellet fuel. Figure 5a–c shows the continual growth of the amount of ash accumulated from high to low power, and the average surface temperature reached 599, 456, and 299 °C, respectively. The ash rose above the furnace, thereby obstructing oxygen to create incomplete combustion, which may have contributed to the increase in PM2.5 and CO. Moreover, the highest SO2 emission in the high-temperature stage is caused by the release from sulfur fixation product (CaSO4) over 1100 °C.
In short, except for the large fluctuations in the ignition stage lasting 20 min, the emission tendency showed barely noticeable variation. Since the ignition stage took a small proportion in the heating season, the impact of this fluctuation is limited.
3.3. Emission Factors
3.3.1. Emission Factors in This Study
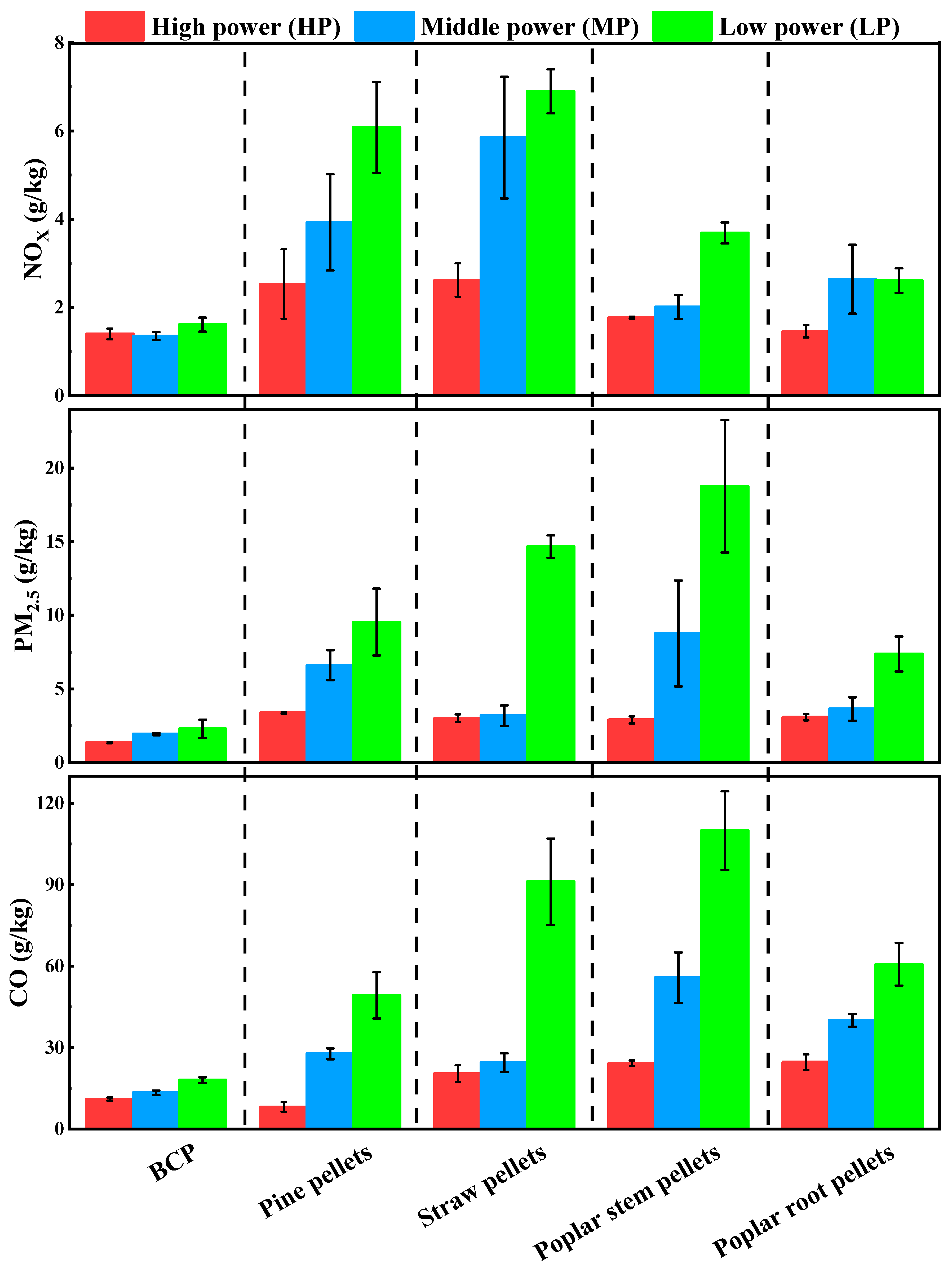
As seen in Figure 6 and Table S3, the emission factors varied significantly between the various fuels and at different firepower. Due to PM associated with incomplete combustion, the EFPM2.5 from BCPs showed an increasing tendency from 1.36 ± 0.04 to 2.29 ± 0.62 g/kg as the loading rate decreased. This was mainly caused by the slow speed in fuel feeding, which resulted in discontinuous combustion. The ash from the burned BCPs interfered with the fuel–oxygen contact, which led to incomplete combustion. EFCO showed the same trend as that observed in PM2.5, increasing from 11.1 ± 0.6 to 18.0 ± 1.1 g/kg. There is often a strong correlation between CO and PM2.5, as CO is also caused by incomplete combustion [30,31].
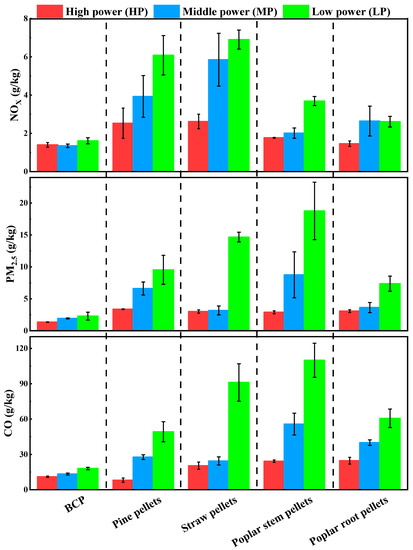
Figure 6.
EFs of CO, CO2, SO2, NOX, and PM2.5 for different types of biomass pellet fuel.
Different from EFCO and EFPM2.5, EFNOx and EFSO2 did not show an obvious upward or downward trend. Several studies have revealed that NOX emission is often affected by fuel nitrogen content and the reducing conditions in the combustion chamber [32,33]. Due to the instability of reduction, NOX emissions showed fluctuations. The EFNOx at the three power stages was 1.40 ± 0.12, 1.35 ± 0.09, and 1.61 ± 0.16 g/kg, respectively. Sulfur-reducing agents were added during BCP production to reduce SO2 emissions. Though CaO is used as a sulfur fixation agent, CaO and sulfur-containing gas (SO2, H2S) react with O2 to form CaSO4 [16,34]. As mentioned in the literature review, 800–1000 °C is the best temperature range for sulfur fixation by Ca-based fixation agents [16]. When the combustion temperature exceeds 1100 °C, the sulfur fixation product (CaSO4) decomposes and increases SO2 emissions [35]. Thus, the EFs of SO2 fluctuated between 3.88 and 4.26 g/kg, as shown in Figure S4. The coefficient of variation (COV, defined as the standard deviation divided by the mean) was less than 6% for all pollutants in this study. Because the combustion process in the automatic heating stoves was relatively stable, COV did not show much variation.
In addition, the same test procedure was carried out on four kinds of commercial biomass pellets, and the results are shown in Figure 6 and Figure S5. By testing the biomass pellets, as shown in Figure 6, it was found that all EFs of biomass pellets were higher than those of BCPs, except for the EFCO of pine pellets during the high-power stage. The EFCO of pine pellets was 8.15 ± 1.79 g/kg, which means that pine pellets can significantly reduce CO emissions. Shen et al. also found that the EFCO of pine pellets was at a relatively low level [19]. The results from Figure 6 show that the emission factors of CO, PM2.5, and NOX at low power were higher than those at high power for the four types of biomass pellets. The slowdown of the loading rate resulted in the deterioration of combustion continuity, which caused the phenomenon. Because the sulfur content of biomass fuels has always been significantly lower than that of coal [36], the SO2 emission from biomass combustion was not compared with BCPs in this study.
The results in this section indicate that the EFs of PM2.5 and NOX for BCPs were significantly lower than those for biomass pellets (p < 0.01), and the EFs of CO for BCPs were lower than those for straw pellets.
3.3.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
A few studies in China measured pollutant emissions from residential solid fuel combustion, among which CO and PM2.5 are the two most commonly tested pollutants [19,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45]. Because laboratory and simulated kitchen tests are carried out using standard testing protocols under controlled environments, emission factors in this condition are dependable regardless of user behavior.
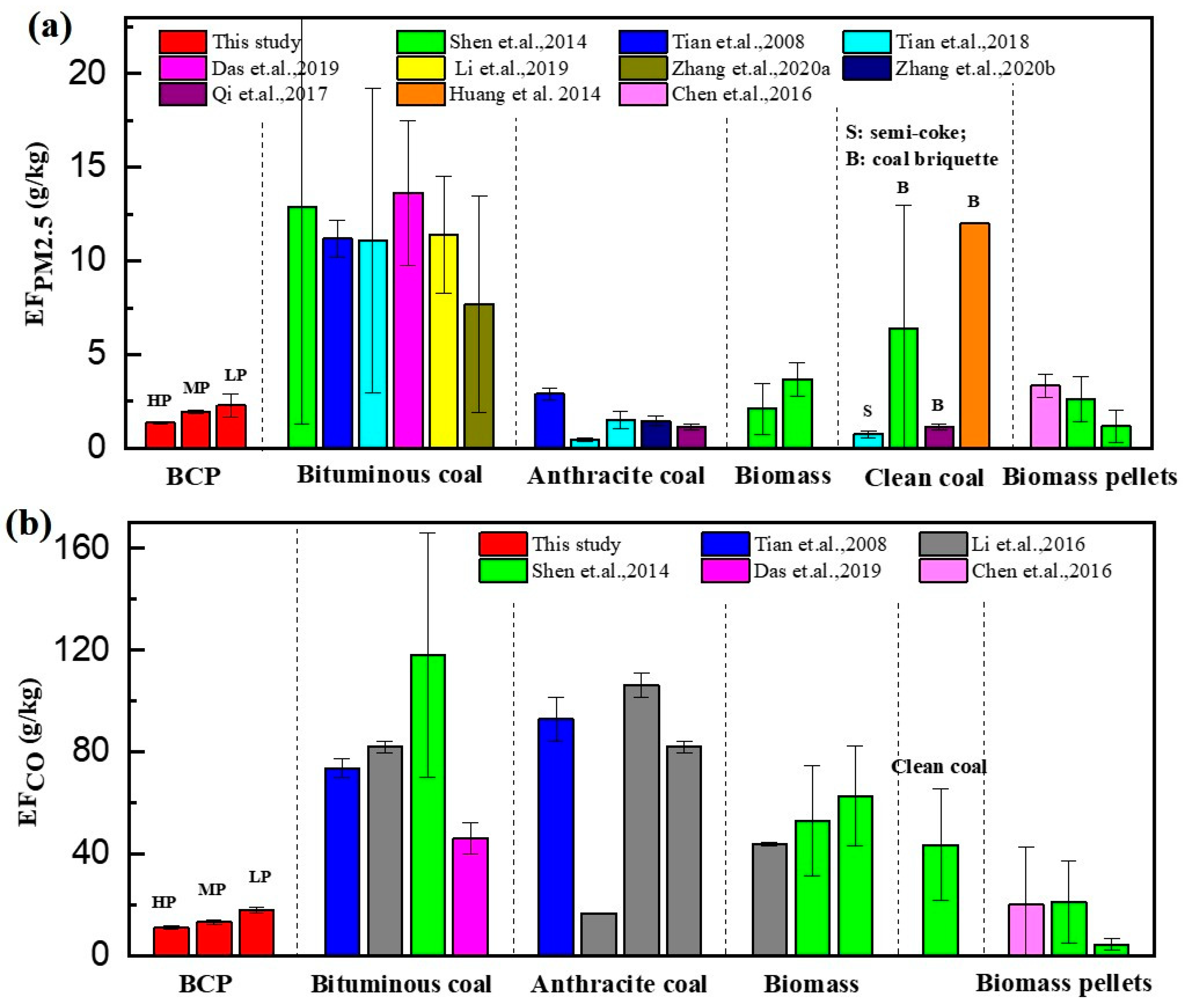
The EFCO and EFPM2.5 of solid fuel combustion in stoves from the previous literature were collected, and the results are shown in Figure 7 and Table S4. The EFPM2.5 for clean coal, biomass fuel, and bituminous coal ranged from 0.45–2.9, 1.17–3.69, and 1.13–13.64 g/kg, respectively. The EFPM2.5 of BCP at high power was lower than that of other bituminous coals and even lower than that of raw anthracite and raw biomass. Among all the fuel types shown in Figure 7, semi-coke showed the lowest EFPM2.5 and was identified as being more expensive than BCPs through our investigation. EFs of CO for clean coal, biomass fuel, and bituminous coal were in the range of 16.8–106, 4.38–62.8, and 43.6–118 g/kg, respectively. The EFPM2.5 of BCP was lower than that of other bituminous coals, anthracite, and straw pellets.
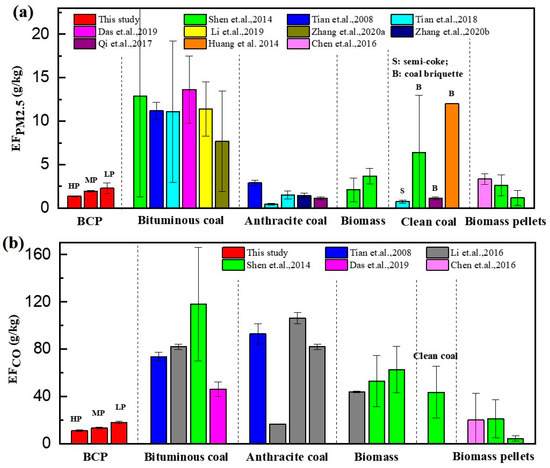
Figure 7.
Emission factors of (a) PM2.5 and (b) CO for BCP, AC, BF, and BC were measured in controlled conditions: A, anthracite; S, semi-coke; R, raw fuel (coal or biomass); P, pellet fuel; B, briquette fuel. (Data shown as arithmetic means and standard deviations.).
In comparison to other fuels, burning traditional bituminous coal yielded higher EFs of PM2.5 and CO (p < 0.05), yet BCPs settled these issues satisfactorily. It was evident that pollution emissions of bituminous coal follow this order: raw chunk > briquettes > pellets. The average EFPM2.5 for combustion of raw bituminous chunk and bituminous briquettes in controlled tests were 13.6 and 7.7 g/kg [38,44], approximately 10 and 5.7 times that of BCPs, respectively. Similar results were also found for EFCO, showing that the laboratory-based EFCO for raw bituminous chunk and bituminous briquette combustion was 46.1 and 43.6g/kg [19,38], around 4.2 and 4 times that of bituminous pellets, respectively. Pelletizing can effectively reduce emissions; Anca-Couce [33] reported similar results for biomass.
Pollutant emissions are affected by many other factors during combustion. For instance, airflow rates [46], oxidizing and reducing conditions [47], fuel characteristics [48], and user behaviors [21] vary among different residential stoves. Testing automated stoves in the laboratory and the field can be regarded as a combustion process with unified fuel loading and air supply conditions. Thus, from this study of BCPs, the emission results can avoid the effects of human operation in terms of combustion state.
3.4. PM2.5 Morphology
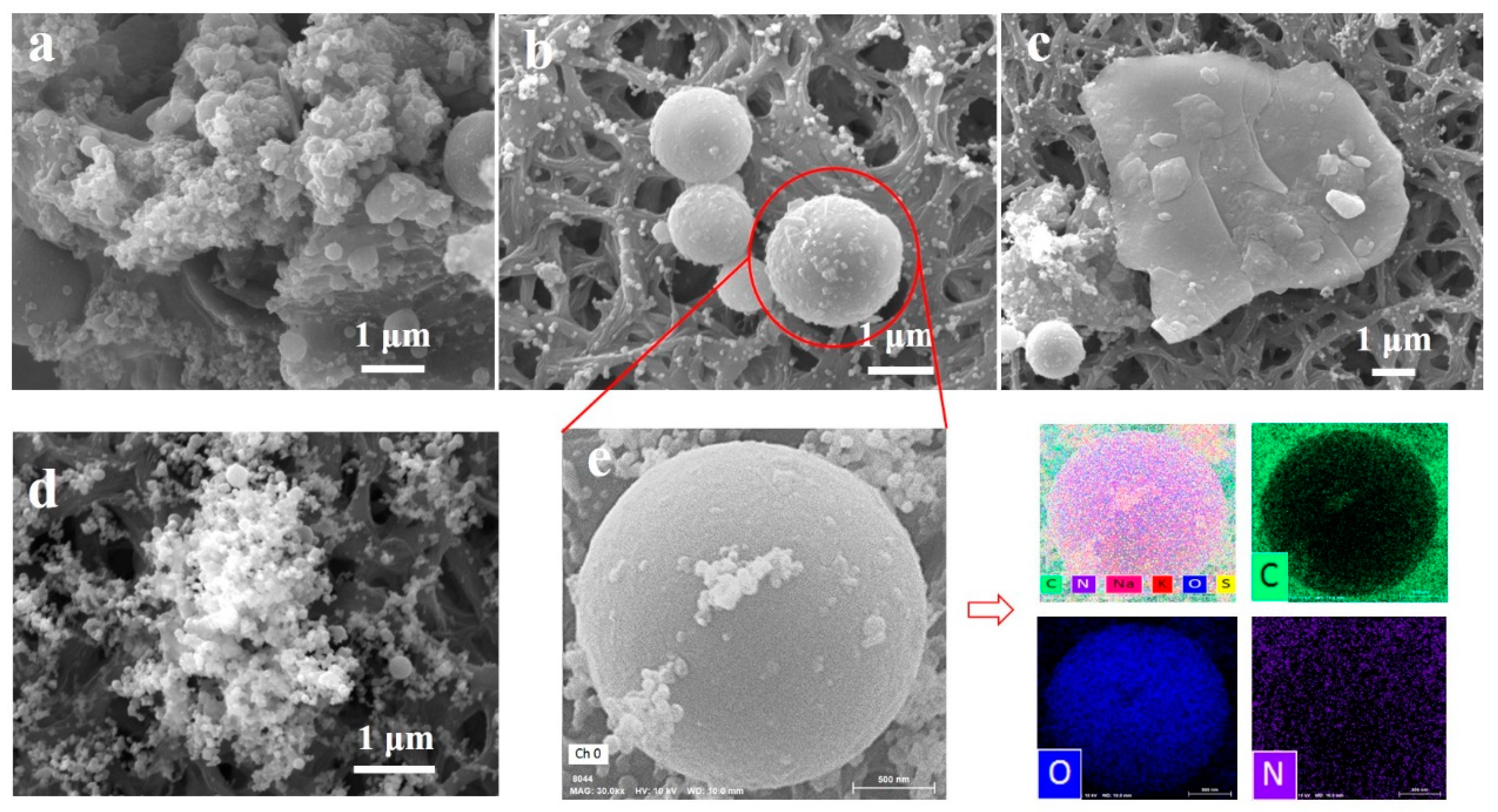
Figure 7a–d and Figure S6 present SEM images of particulate matter sampled on Teflon filters during BCP and pine pellet combustion. The PM2.5 morphology for the three different power levels of bituminous coal pellet combustion is shown in Figure S7. The solid particles in Figure 8a–c represent three kinds of typical particulate matter produced during combustion of BCPs: (a) fine particulates that tend to aggregate, forming a single large fragment (these fine particulates were always balls of congealed tar), (b) molten char particles, and (c) char fragments due to the high heating rate and volatile matter ejection. While the latter is more likely to occur during the reloading process, the first two are mostly found during the steady combustion phase [49]. As shown in Figure 8d, the surface of particulate matter from pine pellets is fractal-like and consists of plentiful fine particles forming agglomerates. Table S5 shows the elemental composition of the obtained particulate matter for BCPs and pine pellets. This result is consistent with the tar ball morphology obtained by Chakrabarty [50], and part of the soot particles may have been formed by the agglomeration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) clusters [51].

Figure 8.
SEM images of particulate matter for (a–c) BCPs and (d) pine pellets. (e) Element mappings (EDS results) of particulate matter for BCPs.
The results revealed that the compositions of fine and coarse particles were different. Coarse particles had more minerals and oxygen than fine particles but had less carbon, which indicated that the large particles were formed from mineral particles that combusted incompletely, while ultrafine particles were governed by the solid–vapor–particle process. A portion of mineral matter vaporized at high temperatures and was then converted into particles through homogeneous nucleation and heterogeneous condensation, followed by coagulation and agglomeration [52].
3.5. Chemical Compositions of Ash and Fusion Characteristics
It is widely accepted that most severe deposit formation, slagging, and fouling problems during thermochemical conversion result from low ash-melting temperature [53]. The fusion temperature of ash, which is crucial for predicting deposition on furnace walls, is directly related to the chemical composition of ash [54]. Figure 9 illustrates the fusion temperature of BCPs and four types of commercial biomass pellets. Softening temperature (ST) was an evaluation index used to analyze the ash fusion of coal. For biomass, deformation temperature (DT) was applied because of the lack of sensitivity of ST, hemispherical temperature (HT), and flow temperature (FT) of the elements present in biomass ash [55]. Thus, we tested ST, DT, HT, and FT for five types of fuel. A comparison of the results of ash melting for BCPs and the other four types of biomass pellets is shown in Figure 9a. The DTs of the five fuels decreased in the order of BCPs > pine pellets > poplar stem pellets > poplar root pellets > straw pellets. The deformation and softening temperatures of biomass ash were 1130–1200 and 1150–1210 °C, respectively, which were lower than those of BCPs due to their higher content of alkali (Figure 9c) such as potassium [24,56,57]. The lower deformation temperature of biomass particles caused more molten substances in the furnace to affect the contact between fuel and oxygen, which resulted in an incomplete combustion phenomenon, described in Section 3.3.1. The fusion temperature of BCP ash is higher than that of biomass pellets. As a result, when BCP combusts in a stove, it will be less likely to deposit.
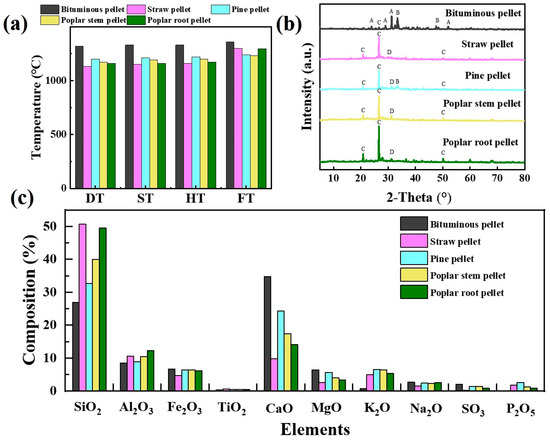
Figure 9.
Fusion temperature and chemical composition of ash: (a) fusion temperatures of pellet ash; (b) XRD patterns of pellets (A: AL0.41 Ca1.5Fe0.16 MgO0.39Na0.5O7Si2, akermanite; B: Ca3MgO8Si2, merwinite; C: SiO2, quartz; D: Al0.4Ca1.7K0.1Mg0.5Na0.2O7Si2, melilite); (c) chemical composition of pellet ash.
Meanwhile, the results of pellet ash composition were different according to XRD and XRF (Figure 9b,c), including SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, TiO2, CaO, MgO, K2O, Na2O, MnO, SO3, and P2O5. Due to the fusion of CaO and SiO2 in BCPs at high temperatures [58], the ash composition of BCPs is more complex. A large amount of calcite in raw coal and the addition of Ca-based fixation agents in the pelletizing process result in the highest calcium element composition compared with other pellets. Although the calcium content dramatically influences the melting temperature, low-temperature eutectics will hardly occur when the calcium is higher than 30% [59]. The melting temperature will increase as the calcium content increases. Liu et al. [60] noted that ash slag primarily consists of SiO2, and this echoes the findings presented in this study. In general, high concentrations of Si, K, and Na in ash may lead to the formation of low-melting-point eutectics for biomass pellets, which can cause slagging or bed agglomeration in combustors [24]. However, such an issue never emerged for BCPs.
3.6. Implications and Outlook
The development of novel bituminous coal pellets provides a new direction for clean heating intervention due to the significant reduction in emissions of PM2.5 and CO, with lower prices and higher calorific value. Though the laboratory test showed a significant advantage for emission reduction, the emission reduction effect of BCPs in residential buildings needs to be verified by field tests. In the next heating season, we propose to conduct a demonstration in northern China and evaluate the emission reduction effects during actual resident use. In addition, the results of solid fuel emissions are also affected by the characteristics of fuels and stoves. Thus, future research should include emissions from different bituminous coal pellets in various regions, characterization of coal combustion in other stoves, and indoor air pollution and its health effects on households. Furthermore, the characteristics of pellets produced from coal–biomass blends are worth studying. An assessment of production costs in different regions is vital in order to offer feasibility studies, which will ensure the suitability of BCPs for commercial applications.
4. Conclusions
The BCPs developed in this study can overcome the defects of coal chunk fuel, achieving stable combustion without dramatic fluctuations. BCPs could greatly reduce emissions of PM2.5 by 83–90% and CO by 61–76% in comparison to raw coal combustion in traditional stoves. The measured emission factors of PM2.5 and CO were 1.36 ± 0.04 and 11.1 ± 0.6 g/kg at high power, 1.93 ± 0.08 and 13.4 ± 0.9 g/kg at medium power, and 2. 29 ± 0.62 and 18.0 ± 1.1 g/kg at low power, respectively. BCPs exhibited the same emission reduction advantages as other commercial pellet fuels. Bituminous coal pellets, meanwhile, demonstrated higher fusion temperature (over 1300 °C), which implies that it is less susceptible to slag. Replacing existing domestic raw coal with BCP was found to be a practical method to improve the regional air quality in coal-rich areas.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13020159/s1, Figure S1: SEM images of (a) straw pellets (b) wood1 pellets (c) wood2 pellets.; Figure S2: TG curves of poplar stem pellets, poplar root pellets and straw pellets; Figure S3: The temperature trend during ignition stage; Figure S4: The EFs of SO2 for bituminous coal pellets in three different power levels; Figure S5: The furnace temperature distribution during the combustion of the four types of biomass pellets; Figure S6: The PM2.5 morphology from biomass pellets combustion (a) particle cluster system (b,c) particle dispersion system; Figure S7: PM2.5 morphology for the three different powers from bituminous coal pellets combustion; Table S1: Three different stage power; Table S2: (a) The amount of pollutants per minute (mg/min) of PM2.5, CO, NOX and SO2 from BCP combustion in different stages (b) Total amount of gas pollutants in different stages (one month); Table S3: Mass-based EFs (g/kg) of PM2.5, CO, NOX and SO2 from different fuel combustion; Table S4: Fuel information and mass-based EFs (g/kg) of CO and PM2.5 from fuel combustion in published data; Table S5: EDS results for PM2.5 from bituminous pellet.
Author Contributions
M.J. designed the experiment, conducted the experiment, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript; M.Y. conducted the experiment and analyzed the data; H.S., H.W., Z.L. and Y.X. conducted the experiment; C.X. and G.L. supervised, reviewed, and edited; Y.L., S.K.M. and P.S. analyzed the data. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42175126) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2017YFC0211400).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors kindly acknowledge Guangjun Lu of Shanxi University and Yifan Wu of Tsinghua University for their suggestions. The authors sincerely thank Ni Wang from the Research Center of the Ministry of Education for High Gravity Engineering and Technology, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, for offering practical assistance with SEM. We would like to thank the editor and reviewers for constructive suggestions and valuable comments, helping us to improve this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). National Development and Reform Commission, People’s Republic of China, China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2019/indexch.htm (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Yuan, J. The future of coal in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispersed Coal Management Research Group. China Dispersed Coal Management Report 2020, Beijing, China. Available online: http://coalcap.nrdc.cn/Public/uploads/pdf/1600925110407138593.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Han, S.; Chen, H.; Long, R.; Cui, X. Peak coal in China: A literature review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.R.; Bruce, N.; Balakrishnan, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Balmes, J.; Chafe, Z.; Dherani, M.; Hosgood, H.D.; Mehta, S.; Pope, D.; et al. Millions Dead: How Do We Know and What Does It Mean? Methods Used in the Comparative Risk Assessment of Household Air Pollution. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2014, 35, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailis, R.; Drigo, R.; Ghilardi, A.; Masera, O. The carbon footprint of traditional woodfuels. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Yun, X.; Meng, W.; Xu, H.; Du, W.; Shen, G.; Cheng, H.; Ma, J.; Tao, S. Stacked Use and Transition Trends of Rural Household Energy in Mainland China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Rumchev, K.; Mead-Hunter, R.; Morawska, L.; Hao, J. Impacts of household coal and biomass combustion on indoor and ambient air quality in China: Current status and implication. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, X.; Shen, G.; Shen, H.; Meng, W.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Du, W.; Ma, J.; et al. Residential solid fuel emissions contribute significantly to air pollution and associated health impacts in China. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba7621. Available online: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/6/44/eaba7621 (accessed on 15 April 2021). [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; Yun, X.; Smith, K.R.; Li, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, J. Energy and air pollution benefits of household fuel policies in northern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16773–16780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, M.; Ma, R.; Lu, F.; Nie, Y.; Li, P.; Ding, X.; Yuan, Y.; Shan, M.; Yang, X. Techno-economic performances of clean heating solutions to replace raw coal for heating in Northern rural China. Energy Build. 2021, 240, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Lin, W.; Chen, Y.; Yue, D.; Liu, Z.; Yang, C. Factors influencing the adoption and sustainable use of clean fuels and cookstoves in China-a Chinese literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Luo, K. Household consumption of coal and related sulfur, arsenic, fluorine and mercury emissions in China. Energy Policy 2018, 112, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Li, P.; Ma, R.; Shan, M.; Yang, X. Air pollutant emission factors of solid fuel stoves and estimated emission amounts in rural Beijing. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Shen, Q.; Cheng, F. Sulfur fixation characteristics of single coal briquette particle during the process of combustion in different atmospheres. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhi, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Measurements of emission factors of PM2.5, OC, EC, and BC for household stoves of coal combustion in China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 109, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Gao, J.; Qi, J. The study of sulphur retention characteristics of biomass briquettes during combustion. Energy 2019, 186, 115788.1–115788.12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Xue, M. Comparison of Carbon Monoxide and Particulate Matter Emissions from Residential Burnings of Pelletized Biofuels and Traditional Solid Fuels. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 3933–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Xie, Z.; Shen, Y. Model study of carbonisation of low rank coal briquettes: Effect of briquettes shape. Powder Technol. 2021, 385, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Zhang, S.; Shan, M.; Li, J.; Baumgartner, J.; Carter, E.; Yang, X. The impact of cookstove operation on PM2.5 and CO emissions: A comparison of laboratory and field measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19867-1:2018; Clean Cookstoves and Clean Cooking Solutions e Harmonized Laboratory Test Protocols-Part 1: Standard Test Sequence for Emissions and Performance, Safety and Durability. International Standardization Organization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/66519.html7 (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Zhong, Q.; Shen, H.; Yun, X.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xu, H.; Shen, G.; Du, W.; Meng, J.; Li, W.; et al. Global Sulfur Dioxide Emissions and the Driving Forces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6508–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommersacher, P.; Brunner, T.; Obernberger, I. Fuel Indexes: A Novel Method for the Evaluation of Relevant Combustion Properties of New Biomass Fuels. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, N.; Wang, P.; Che, D. Experimental investigation on combustion and NO formation characteristics of semi-coke and bituminous coal blends. Fuel 2019, 247, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xue, C.; Liu, G. Air pollutant emissions and mitigation potential through the adoption of semi-coke coals and improved heating stoves: Field evaluation of a pilot intervention program in rural China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ye, K.; Mawusi, S.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Jiao, M.; Shrestha, P.; et al. A 24-h real-time emissions assessment of 41 uncontrolled household raw coal combustion stoves in four provinces of Northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 235, 117588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poláčik, J.; Sitek, T.; Pospíšil, J.; Šnajdárek, L.; Lisý, M. Emission of fine particles from residential combustion of wood: Comparison of automatic boiler, manual log feed stove and thermo-gravimetric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illerup, J.B.; Hansen, B.B.; Lin, W.; Nickelsen, J.; Pedersen, V.H.; Eskerod, B.; Dam-Johansen, K. Performance of an automatically controlled wood stove: Thermal efficiency and carbon monoxide emissions. Renew. Energy 2020, 151, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křůmal, K.; Mikuška, P.; Horák, J.; Hopan, F.; Kuboňová, L. Influence of boiler output and type on gaseous and particulate emissions from the combustion of coal for residential heating. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křůmal, K.; Mikuška, P.; Horák, J.; Hopan, F.; Krpec, K. Comparison of emissions of gaseous and particulate pollutants from the combustion of biomass and coal in modern and old-type boilers used for residential heating in the Czech Republic, Central Europe. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Torres-Rojas, D.; Burford, M.; Whitlow, T.H.; Lehmann, J.; Fisher, E.M. Fuel sensitivity of biomass cookstove performance. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anca-Couce, A.; Hochenauer, C.; Scharler, R. Bioenergy technologies, uses, market and future trends with Austria as a case study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lou, H.H.; Yang, F.; Cheng, F. Development and performance evaluation of a clean-burning stove. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 134, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Song, M.; Chen, D.; Cao, Y.; Meng, F.; Wei, Y. Retention of arsenic in coal combustion flue gas at high temperature in the presence of CaO. Fuel 2020, 259, 116249.1–116249.7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, E.; Ren, X.; Panahi, A.; Levendis, Y.A. Emissions of SO2, NOX, CO2, and HCl from Co-firing of coals with raw and torrefied biomass fuels. Fuel 2018, 211, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, G.; Su, S.; Du, W.; Huangfu, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Xing, B.; Smith, K.R.; Tao, S. Efficiencies and pollutant emissions from forced-draft biomass-pellet semi-gasifier stoves: Comparison of International and Chinese water boiling test protocols. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2016, 32, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Bhandarkar, U.; Sethi, V. Influence of the Inclusion of Ignition Stage Emissions in the Development of Emission Factors for Coal Cookstoves Used in India. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3149–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Qi, J.; Deng, J.; Yang, D.; Wu, J.; Duan, L.; Hao, J. Improving the Energy Efficiency of Stoves To Reduce Pollutant Emissions from Household Solid Fuel Combustion in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qi, J.; Jiang, J.; Wu, J.; Duan, L.; Wang, S.; Hao, J. Significant reduction in air pollutant emissions from household cooking stoves by replacing raw solid fuels with their carbonized products. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650 Pt 1, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J.; Miao, Z.; Li, D. Biocoal Briquettes Combusted in a Household Cooking Stove: Improved Thermal Efficiencies and Reduced Pollutant Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1886–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Lucas, D.; Fischer, S.L.; Lee, S.C.; Hammond, S.K.; Koshland, C.P. Particle and Gas Emissions from a Simulated Coal-Burning Household Fire Pit. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Ni, H.; Han, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Long, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J. Primary PM2.5 and trace gas emissions from residential coal combustion: Assessing semi-coke briquette for emission reduction in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, T. Carbonaceous aerosols emission reduction by using red mud additive in coal briquette. Fuel Proc. Technol. 2020, 199, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Bei, N.; Tian, J.; Wang, Q.; et al. Emission reduction effect on PM2.5, SO2 and NOX by using red mud as additive in clean coal briquetting. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryner, J.; Tillotson, J.W.; Baumgardner, M.E.; Mohr, J.T.; DeFoort, M.W.; Marchese, A.J. The Effects of Air Flow Rates, Secondary Air Inlet Geometry, Fuel Type, and Operating Mode on the Performance of Gasifier Cookstoves. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9754–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussbaumer, T. Combustion and co-combustion of biomass: Fundamentals, technologies, and primary measures for emission reduction. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanta, A.T.; Saiful Alam, M.; Nakaso, K.; Fukai, J.; Shimizu, M. Optimized combustion of biomass volatiles by varying O2 and CO2 levels: A numerical simulation using a highly detailed soot formation reaction mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Shang, T.; Zhuo, J.; Yao, Q. Study on the mechanisms of ultrafine particle formation during high-sodium coal combustion in a flat-flame burner. Fuel 2016, 181, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, R.K.; Moosmüller, H.; Chen, L.W.A.; Lewis, K.; Arnott, W.P.; Mazzoleni, C.; Dubey, M.K.; Wold, C.E.; Hao, W.M.; Kreidenweis, S.M. Brown carbon in tar balls from smoldering biomass combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6363–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, Y.; Li, X.; Teng, S.; Wang, K.; Pei, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhao, H. Development of a soot particle model with PAHs as precursors through simulations and experiments. Fuel 2016, 179, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yu, D.; Yao, H.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y. Coal combustion-generated aerosols: Formation and properties. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 1681–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Vassileva, C.G.; Vassilev, V.S. Advantages and disadvantages of composition and properties of biomass in comparison with coal: An overview. Fuel 2015, 158, 330–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvuka, D.; Kakaras, E. Ash properties and environmental impact of various biomass and coal fuels and their blends. Fuel Process Technol. 2011, 92, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.G.; Meng, A.H.; Li, L.; Li, G.X. Study on ash fusion temperature using original and simulated biomass ashes. Fuel Process Technol. 2013, 107, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmeier, S.; Wopienka, E.; Schwarz, M.; Schön, C.; Pfeifer, C. Applicability of Fuel Indexes for Small-Scale Biomass Combustion Technologies, Part 1: Slag Formation. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 10969–10977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H. Review on slagging evaluation methods of biomass fuel combustion. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklivaniti, V.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Katsiotis, N.S.; Velissariou, D.; Pistofidis, N.; Papageorgiou, D.; Beazi, M. Valorisation of woody biomass bottom ash in Portland cement: A characterization and hydration study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Wang, G.; Ning, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C. Effect of CaO mineral change on coal ash melting characteristics. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, H.; Yang, X.; Hu, W.; Liang, F.; Mi, B. Ash fusion characteristics of bamboo, wood and coal. Energy 2018, 161, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).