Emission Characteristics and Ozone Formation Potential Assessment of VOCs from Typical Metal Packaging Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. VOCs Analysis
2.3. OFP Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
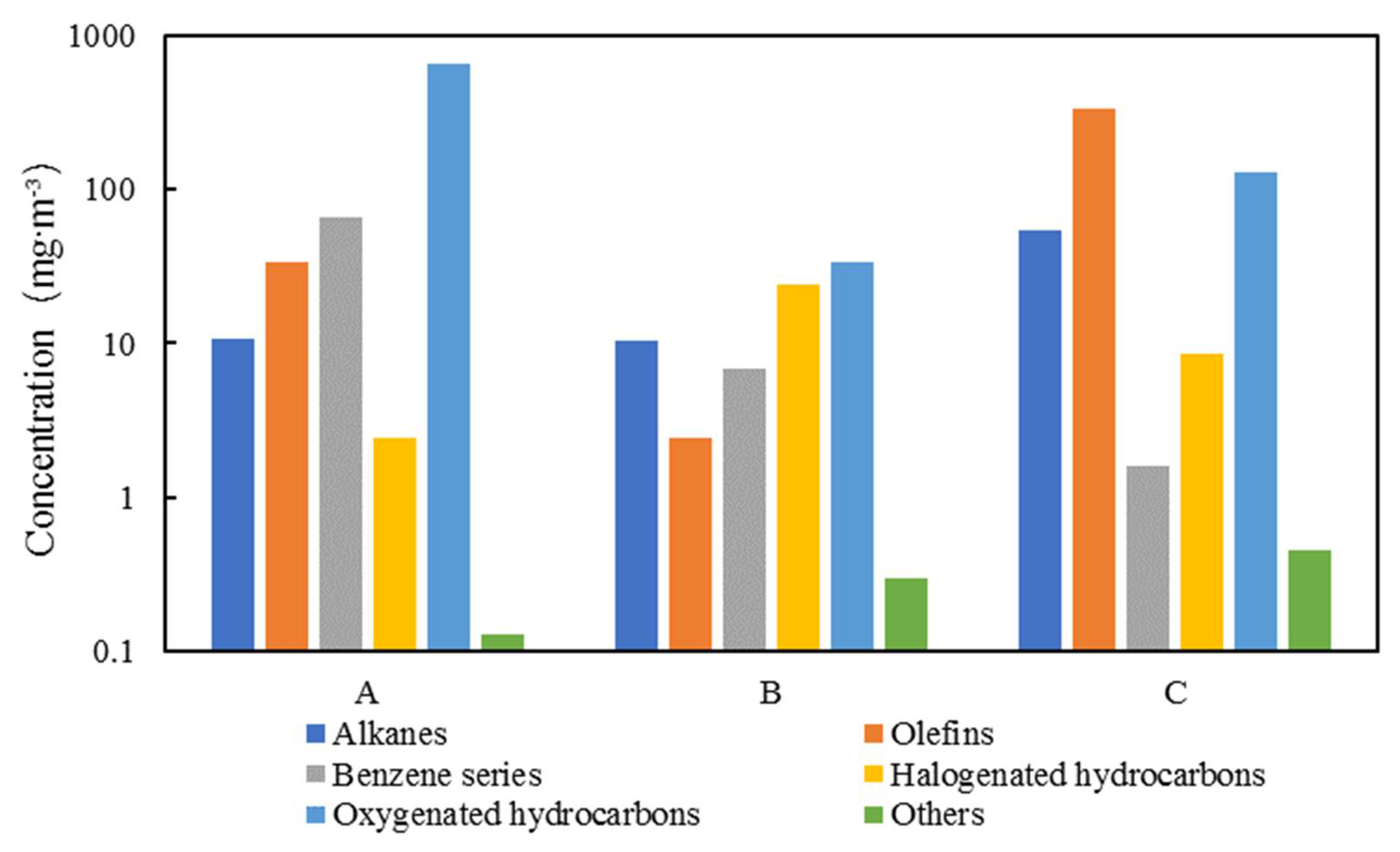
3.1. VOCs Emission Characteristics
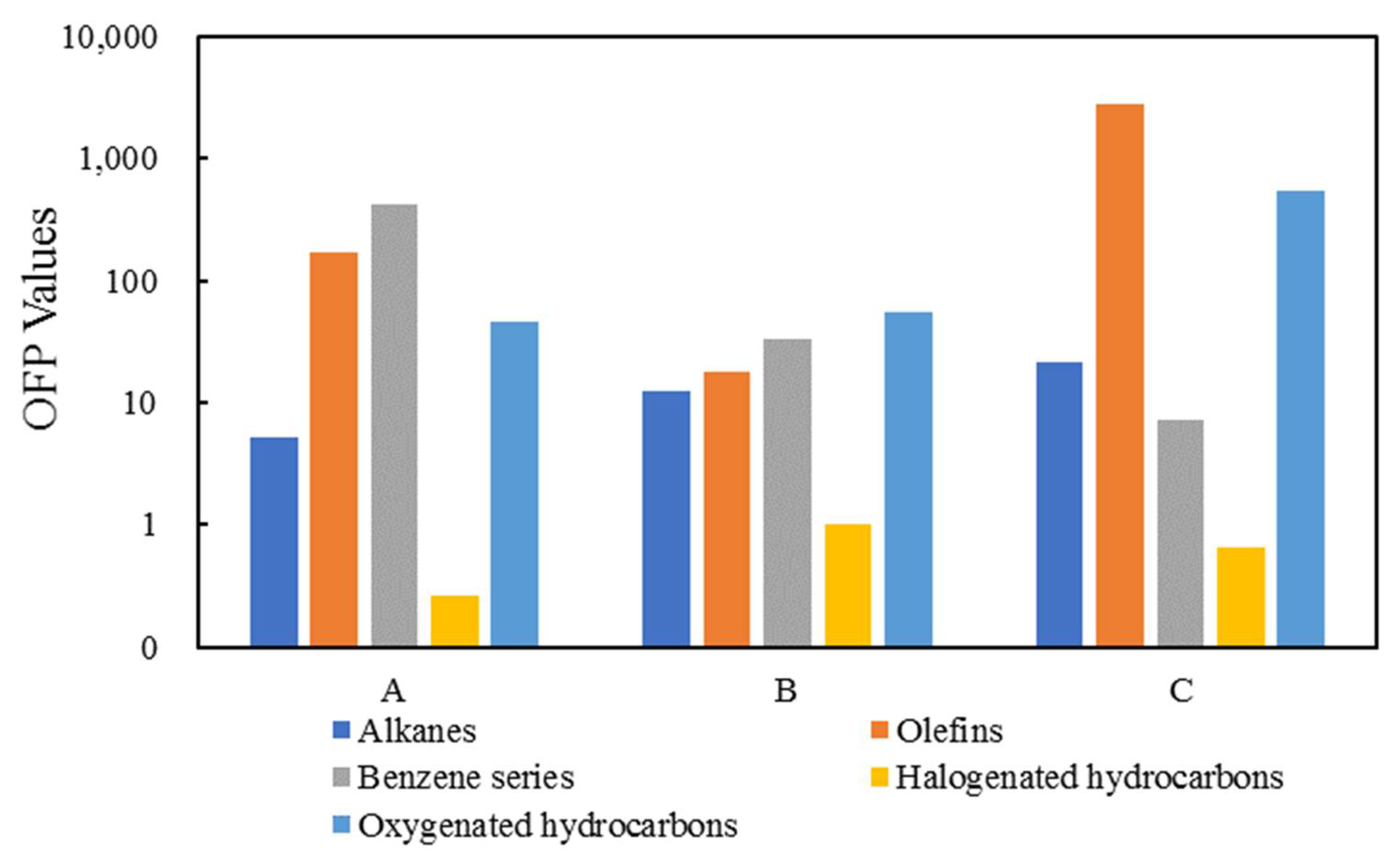
3.2. Assessment of Ozone Formation Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE, PRC). The 13th Five Year Plan for VOCs Pollution Prevention and Control. 2017. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bwj/201709/t20170919_421835.htm (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Masui, T.; Imadzu, H.; Matsuyama, N.; Imanaka, N. Total oxidation of toluene on Pt/CeO2-ZrO2-Bi2O3/γ-Al2O3 catalysts prepared in the presence of polyvinyl pyrrolidone. J. Hazard. Mater 2010, 176, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukul, P.; Schubert, J.K.; Oertel, P.; Kamysek, S.; Taunk, K.; Trefz, P.; Miekisch, W. FEV manoeuvre induced changes in breath VOC compositions: An unconventional view on lung function tests. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Ning, P.; Tian, S. Influence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on pulmonary surfactant monolayers at air-water interface: Implication for the pulmonary health. Colloid. Surf. A 2019, 562, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Garza, O.; Guo, L.; Byun, H.M.; Carrieri, M.; Bartolucci, G.B.; Barrón-Vivanco, B.S.; Baccarelli, A.A. Aberrant promoter methylation in genes related to hematopoietic malignancy in workers exposed to a VOC mixture. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 339, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, J.E.; Park, A.S.; Qiu, J.; Cockburn, M.; Ritz, B. Risk of leukemia in relation to exposure to ambient air toxics in pregnancy and early childhood. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.M.; Sun, X.B.; Xu, J.T.; Ye, D.Q.; Chen, L.G. Industrial volatile organic compounds(VOCs) emission inventory in China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4767–4775. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Nie, L.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhang, W.Q.; Dang, H.Y.; Shao, X.; Zhang, X.M. Pollution characteristics of volatile organic compounds emission from the metal packaging industry based on analysis of process. Environ.Sci. 2020, 41, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, D.X.; Yu, H.B.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, D. Analysis of VOCs pollution characteristics in packaging and printing industry. Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind. 2019, 39, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- China Business Intelligence Network. Market Scale Forecast and Competitive Landscape Analysisof China’s Foodand Beverage Metal Packaging Industry in 2019. 2019. Available online: http://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1620456506549370344&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Cheng, S.; Lu, F.; Peng, P.; Zheng, J. Emission characteristics and control scenario analysis of VOCs from heavy-duty diesel trucks. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, T.V.; Kim, S.Y.; Son, Y.S.; Choi, I.Y.; Park, S.R. Emission characteristics of VOCs emitted from consumer and commercial products and their ozone formation potential. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9345–9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, A.N.; Zhang, H.F.; Avilés, P.C.; Islam, A.; Yang, M. Emerging concerns of VOCs and SVOCs in coking wastewater treatment processes: Distribution profile, emission characteristics, and health risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. UV iron printing ink, an environmental pioneer in the metal packaging industry. Print China 2019, 3, 15–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE, PRC). Emission from Stationary Sources-Sampling of Volatile Organic Compounds-Bag Method. HJ 732-2014. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201501/t20150115_294220.shtml (accessed on 13 November 2021).
- Fang, L.; Liu, J.Y.; Nie, L.; He, L.J.; Wang, H.L. VOCs emission characteristics and ozone impact analysis of typical automobile repair enterprises in Beijing. Environ. Engrg. 2020, 38, 146–150, 155. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, W.P.L. Development of the SAPRC-07 chemical mechanism. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5324–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.W.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.R.; Nie, L.; Wang, M.Y. Emission characteristics and ozone formation potential of VOCs in printing enterprises in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 3942–3948. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.Y.; Yao, Z.L.; Shen, X.B.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, X. On-road emission characteristics of VOCs from light-duty gasoline vehicles in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.T.; Yue, X.; Chai, F.H.; Hu, J.N.; Lai, Y.T.; He, L.Q.; Zhu, R.C. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds(VOCs) from the evaporative emissions of modern passenger cars. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 151, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Plant | Manufacturing Types | VOCs-Containing Materials | Sampling Sites | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inks | Coatings | Varnish | |||
| A (116.6898N, 40.3510E) | three-piece can | solvent-based | solvent-based | water-based | end-pipe |
| B (116.7044N, 40.3680E) | two-piece can | water-based | water-based | water-based | end-pipe |
| C (116.6933N, 40.377745E) | two-piece can | solvent-based | water-based | water-based | end-pipe |
| Plant A | Plant B | Plant C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Components | Percentage (%) | Components | Percentage (%) | Components | Percentage (%) |
| 2-butanone | 82.67 | dichloromethane | 23.00 | ethylene | 36.67 |
| p- and m-xylene | 3.08 | butyraldehyde | 16.45 | acetaldehyde | 17.81 |
| o-xylene | 2.90 | acetaldehyde | 6.30 | acetylene | 9.06 |
| acetylene | 2.34 | isopentane | 5.23 | ethane | 8.72 |
| ethylbenzene | 2.26 | toluene | 4.92 | 1-butene | 8.29 |
| ethylene | 1.51 | propionaldehyde | 4.89 | propylene | 7.35 |
| ethane | 1.04 | isopropanol | 3.43 | acetone | 2.11 |
| acetaldehyde | 0.95 | acetone | 3.15 | butyraldehyde | 2.00 |
| 1-butene | 0.42 | 2-butanone | 2.04 | hexanal | 1.18 |
| butyraldehyde | 0.37 | n-hexane | 1.92 | 1,3-butadiene | 0.94 |
| isopropanol | 0.35 | hexanal | 1.63 | dichloromethane | 0.82 |
| acetone | 0.26 | crotonaldehyde | 0.99 | propane | 0.72 |
| dichloromethane | 0.23 | ethyl acetate | 0.98 | acrolein | 0.49 |
| propylene | 0.14 | propane | 0.97 | propionaldehyde | 0.40 |
| propane | 0.10 | 1-butene | 0.93 | n-hexane | 0.28 |
| cumene | 0.09 | ethane | 0.88 | carbon tetrachloride | 0.28 |
| p-diethylbenzene | 0.08 | ethylene | 0.85 | methyl chloride | 0.27 |
| toluene | 0.07 | acrolein | 0.80 | valeraldehyde | 0.23 |
| 1,3-butadiene | 0.07 | tetrahydrofuran | 0.79 | isopentane | 0.18 |
| benzene | 0.07 | p- and m-xylene | 0.76 | n-pentene | 0.18 |
| others | 0.97 | others | 12.71 | others | 2.01 |
| Components | MIR Coefficients | Components | MIR Coefficients |
|---|---|---|---|
| ethane | 0.28 | p-m-xylene | 7.79 |
| propane | 0.49 | o-xylene | 7.64 |
| butane | 1.15 | ethylbenzene | 3.04 |
| isobutane | 1.23 | cumene | 2.03 |
| 2,2-dimethylbutane | 1.17 | n-propyl benzene | 2.03 |
| 2,3-dimethylbutane | 0.97 | m-ethyl toluene | 7.39 |
| pentane | 1.31 | p-ethyl toluene | 4.44 |
| isopentane | 1.45 | o-ethyl toluene | 5.59 |
| 2-methylpentane | 1.5 | m-diethylbenzene | 7.1 |
| 3-methylpentane | 1.8 | p-diethylbenzene | 4.43 |
| 2,4-dimethylpentane | 1.55 | 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene | 11.97 |
| 2,2,4-trimethylpentane | 1.26 | 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene | 8.87 |
| 2,3,4-trimethylpentane | 1.03 | 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene | 11.76 |
| cyclopentane | 2.39 | styrene | 1.73 |
| methylcyclopentane | 2.19 | naphthalene | 4.58 |
| n-hexane | 1.24 | chloroform | 0.038 |
| 2-methylhexane | 1.19 | dichloromethane | 0.041 |
| 3-methylhexane | 1.61 | 1,2-dichloroethane | 0.21 |
| cyclohexane | 1.25 | trichloroethylene | 0.64 |
| methylcyclohexane | 1.7 | tetrachloroethylene | 0.031 |
| heptane | 1.07 | chlorobenzene | 0.32 |
| 3-methylheptane | 1.24 | 1,3-dichlorobenzene | 0.178 |
| octane | 0.9 | formaldehyde | 7.2 |
| nonane | 0.78 | acetaldehyde | 5.5 |
| decane | 0.68 | acetone | 0.56 |
| undecane | 0.61 | propionaldehyde | 6.5 |
| dodecane | 0.55 | isopropyl alcohol | 0.54 |
| acetylene | 0.95 | n-pentene | 7.21 |
| ethylene | 9 | trans-2-pentene | 10.56 |
| propylene | 11.66 | cis-2-pentene | 10.38 |
| 1-butene | 9.73 | n-hexene | 5.49 |
| 1,3-butadiene | 12.61 | benzene | 0.72 |
| trans-2-butene | 15.16 | toluene | 4 |
| cis-2-butene | 14.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Xue, S.; Hao, R.; Fang, L.; Nie, L. Emission Characteristics and Ozone Formation Potential Assessment of VOCs from Typical Metal Packaging Plants. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010057
Wang H, Xue S, Hao R, Fang L, Nie L. Emission Characteristics and Ozone Formation Potential Assessment of VOCs from Typical Metal Packaging Plants. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hailin, Song Xue, Run Hao, Li Fang, and Lei Nie. 2022. "Emission Characteristics and Ozone Formation Potential Assessment of VOCs from Typical Metal Packaging Plants" Atmosphere 13, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010057
APA StyleWang, H., Xue, S., Hao, R., Fang, L., & Nie, L. (2022). Emission Characteristics and Ozone Formation Potential Assessment of VOCs from Typical Metal Packaging Plants. Atmosphere, 13(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010057





