Aerosol Light Absorption at 1064 nm: Pollution Sources, Meteorological Parameters and Gas Pollutants in Qingdao Coastal Area, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
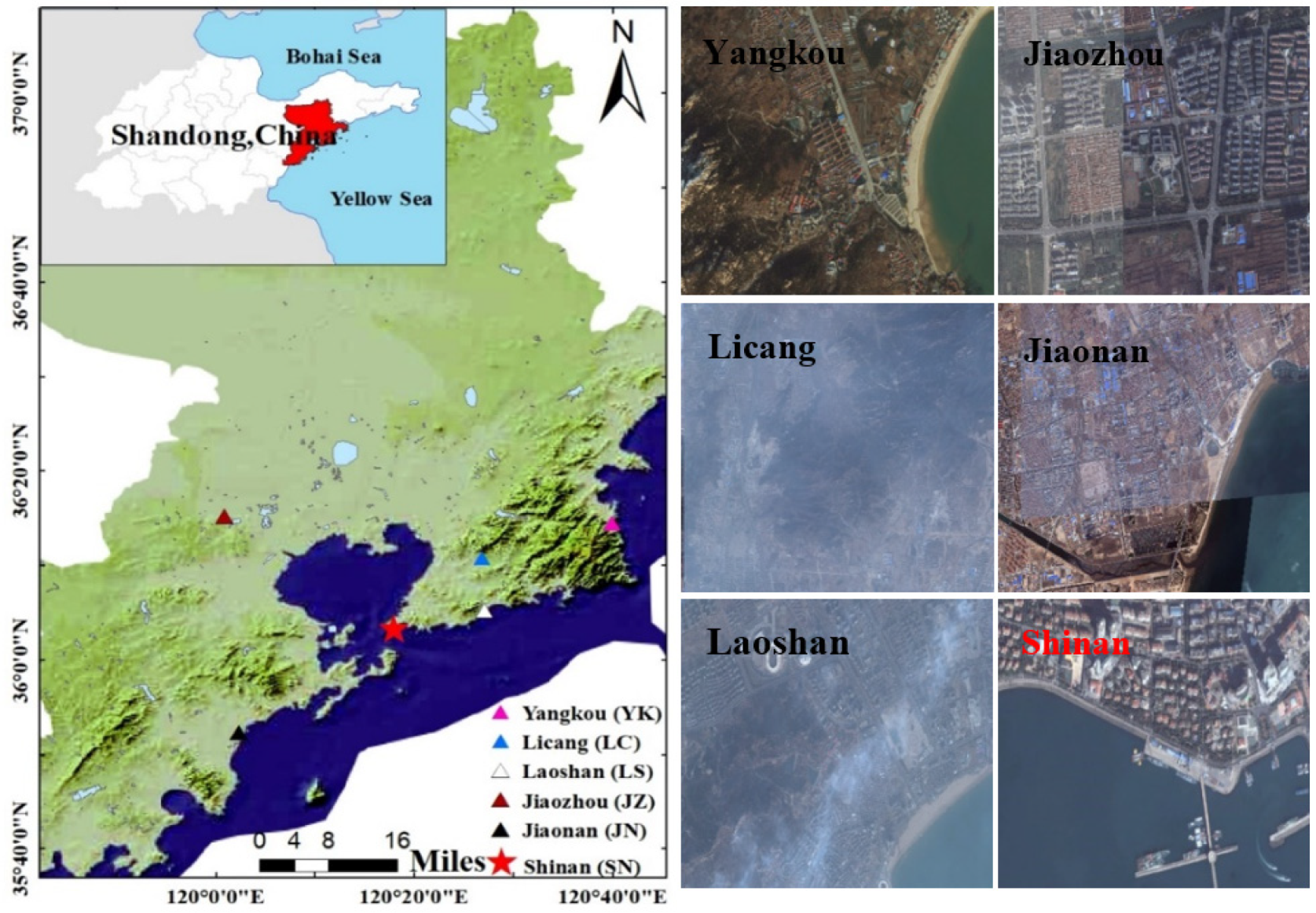
2.1. Measurement Site
2.2. Instrumentation Deployment and Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
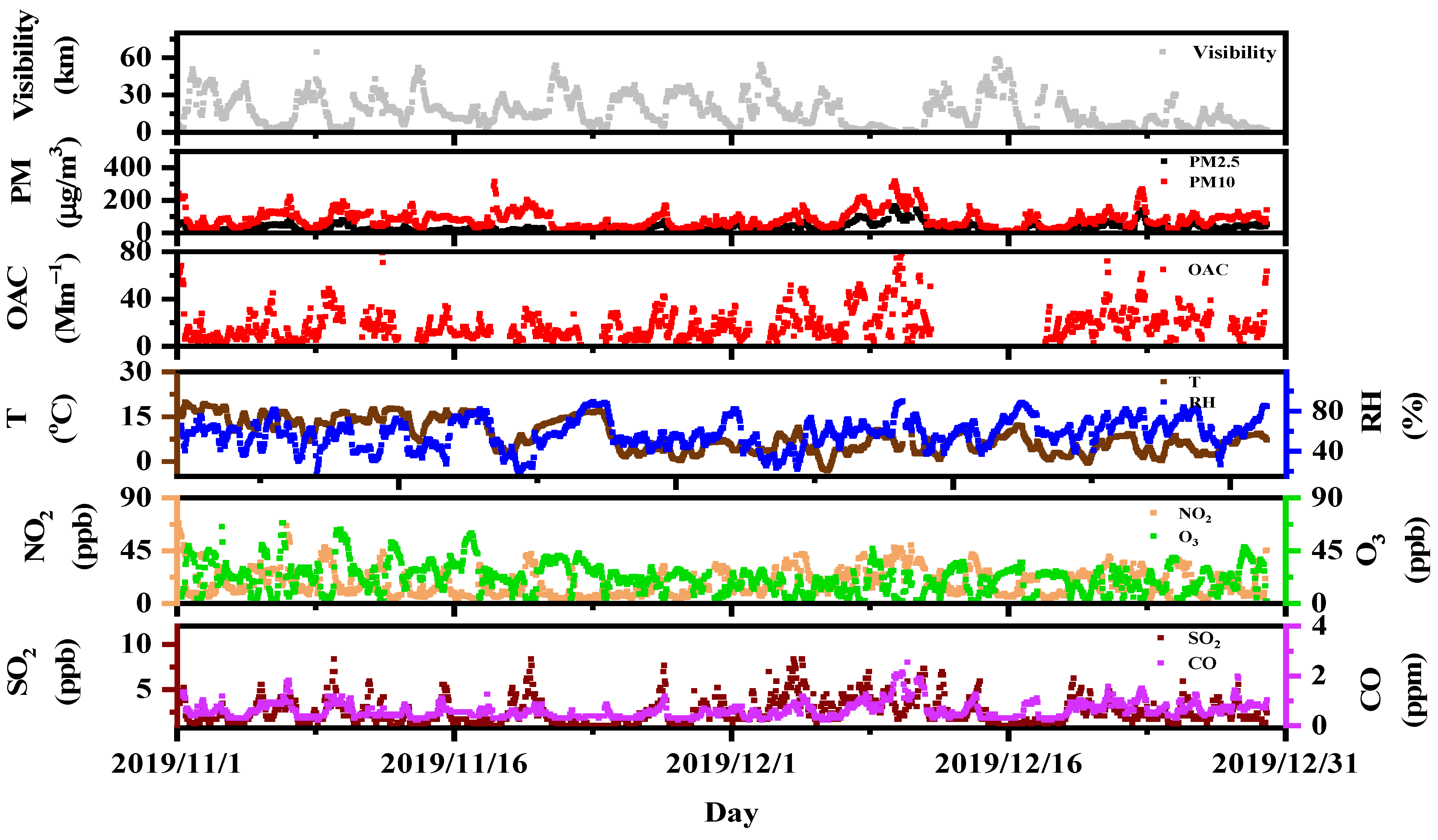
3.1. Regional Source
3.2. Wind Dependence of Local Gas Pollutants
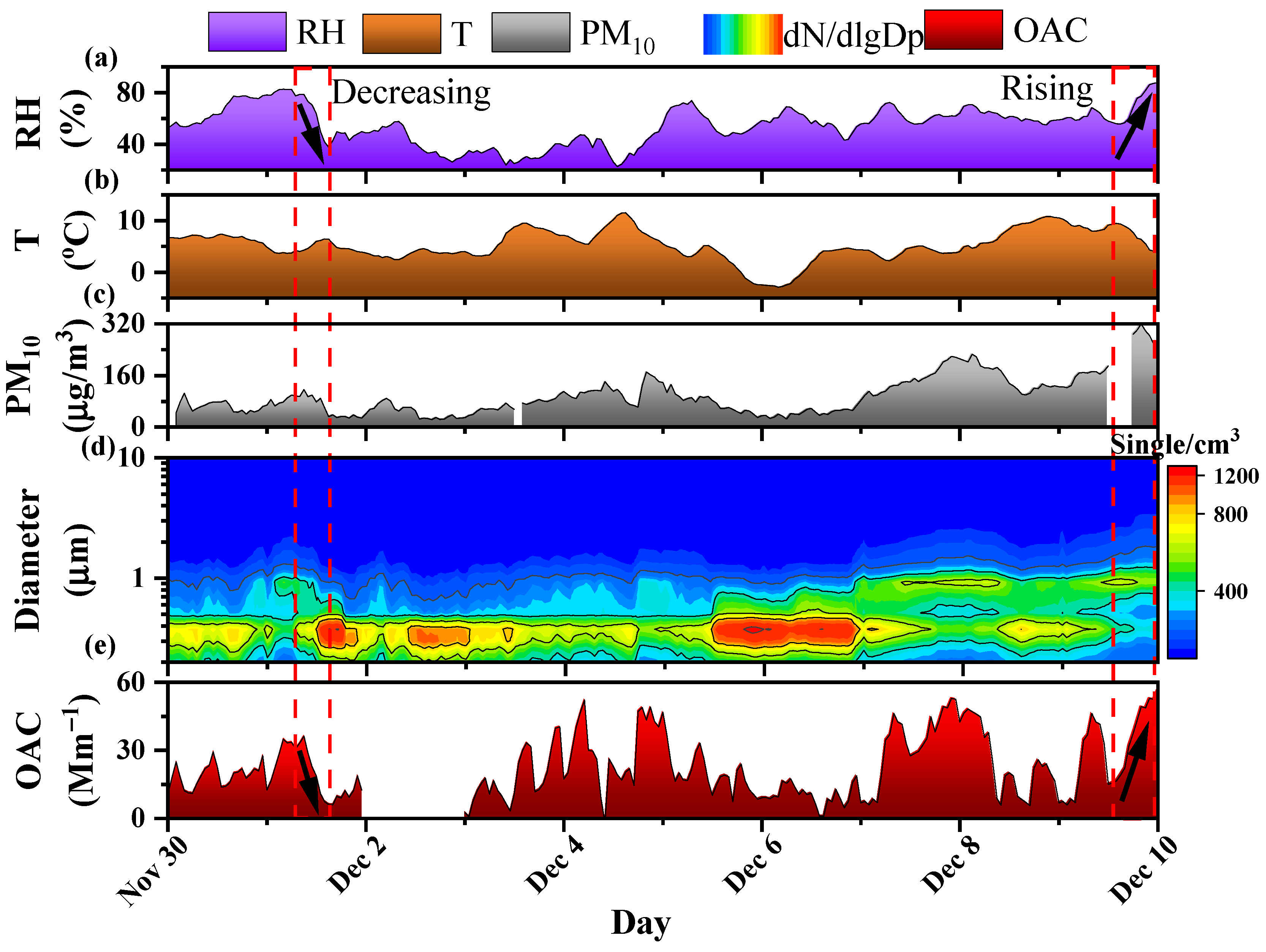
3.3. Meteorological Influence on OAC: Relative Humidity
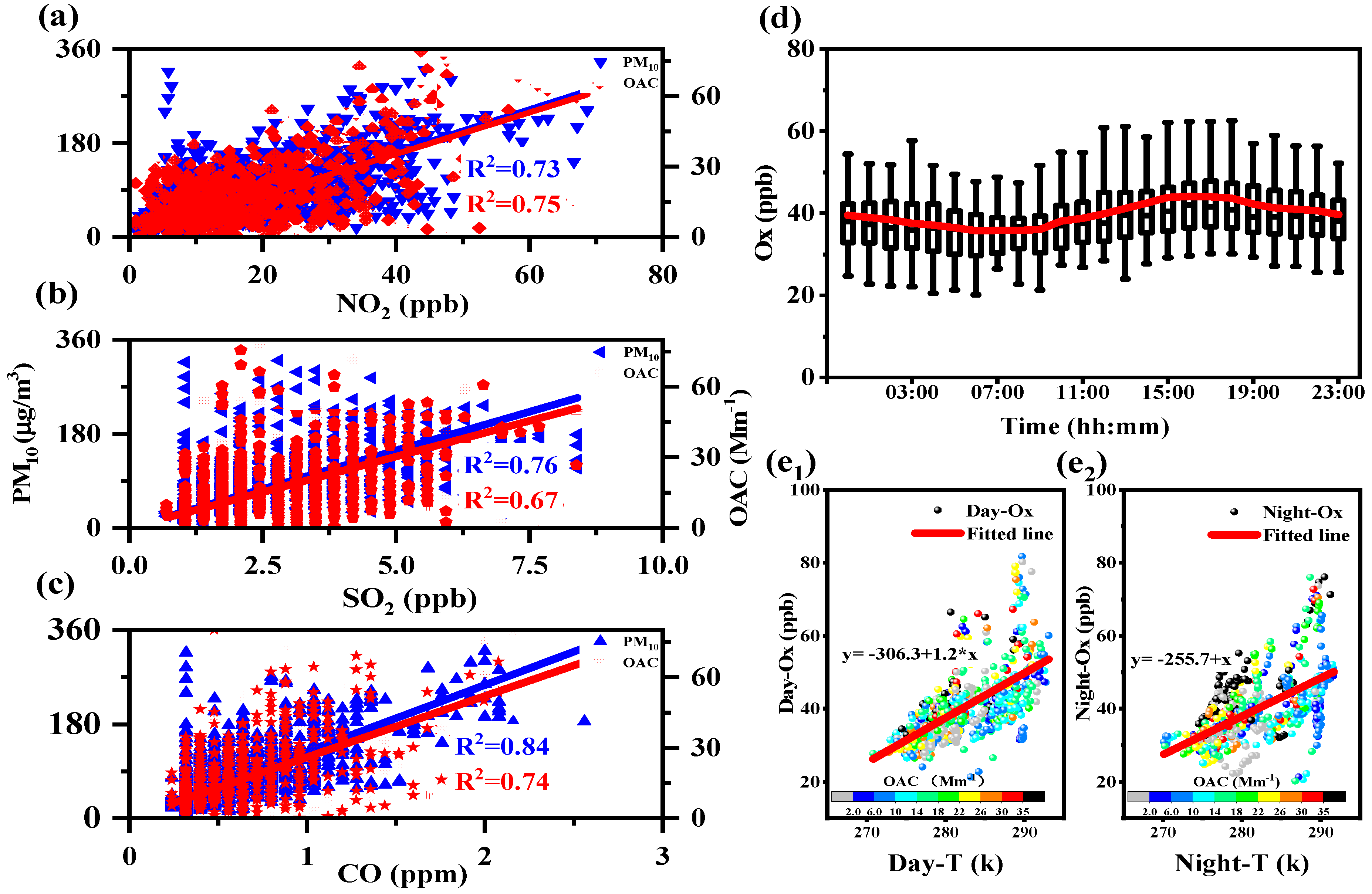
3.4. Trace Gases and Photochemical Oxidants on OACs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hegg, D.A.; Covert, D.S.; Rood, M.J.; Hobbs, P.V. Measurements of aerosol optical properties in marine air. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1996, 101, 12893–12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira, G.R.; Pinto, W.T.A.; Lima, E.E.P.; Andrade, C. Vertical distribution of marine aerosol salinity in a Brazilian coastal area—The influence of wind speed and the impact on chloride accumulation into concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, S.; Cuevas, E.; González, Y.; Ramos, R.; Romero, P.M.; Pérez, N.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Influence of sea breeze circulation and road traffic emissions on the relationship between particle number, black carbon, PM1, PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 concentrations in a coastal city. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6523–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Lyu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeren, Y.; Zou, S.; Ling, Z. Photochemical evolution of continental air masses and their influence on ozone formation over the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Pathak, V.; Bisht, D.S.; Tiwari, S. Surface solar radiation and its association with aerosol characteristics at an urban station in the Indo-Gangetic Basin: Implication to radiative effect. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 193, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Andreae, M.O.; Asmi, A.; Chin, M.; de Leeuw, G.; Donovan, D.P.; Kahn, R.; Kinne, S.; Kivekäs, N.; Kulmala, M.; et al. Global observations of aerosol-cloud-precipitation-climate interactions. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 750–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brem, B.T.; Mena Gonzalez, F.C.; Meyers, S.R.; Bond, T.C.; Rood, M.J. Laboratory-Measured Optical Properties of Inor-ganic and Organic Aerosols at Relative Humidities up to 95%. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, M.; Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, R.; et al. Chemical composition, water content and size distribution of aerosols during different development stages of regional haze episodes over the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tian, P.; Tao, J.; Huang, R.-J.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.; Han, Z.; et al. Effect of source variation on the size and mixing state of black carbon aerosol in urban Beijing from 2013 to 2019: Implication on light absorption. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanian, E.; Mousavi, A.; Taghvaee, S.; Shafer, M.M.; Sioutas, C. Impact of secondary and primary particulate matter (PM) sources on the enhanced light absorption by brown carbon (BrC) particles in central Los Angeles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Asutosh, A.; Sabu, P.; Anilkumar, N. Investigation of Black Carbon characteristics over southern ocean: Contribution of fossil fuel and biomass burning. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, X.; Brasseur, G.P.; Zhao, C.; Granier, C.; Massie, S.; Qin, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, G.; Yang, P.; Richter, A. Chemical characterization of air pollution in Eastern China and the Eastern United States. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2607–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Haywood, J.; Reddy, M.S. Global estimate of aerosol direct radiative forcing from satellite measurements. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 438, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, M.; Chu, A.; Levy, R.; Remer, L.; Kaufman, Y.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.; Ginoux, P.; Gao, Q. Aerosol distribution in the Northern Hemisphere during ACE-Asia: Results from global model, satellite observations, and Sun photometer measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Koren, L.A.; Remer, D.; Tanre, D.; Ginoux, P.; Fan, S. Dust transport and deposition observed from the Terra-Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) spacecraft over the Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D10S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, T.A.; Christopher, S.A. MODIS derived fine mode fraction characteristics of marine, dust, and anthropogenic aerosols over the ocean, constrained by GOCART, MOPITT, and TOMS. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112, D22204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. From air pollution to climate change. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 1998, 1326. [Google Scholar]
- Favez, O.; Cachier, H.; Sciare, J.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Martinon, L. Evidence for a significant contribution of wood burning aerosols to PM2.5 during the winter season in Paris, France. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3640–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.-J.; Huang, X.-F.; Yu, K.-Y.; Sun, T.-L.; Zeng, L.-W.; Hu, M. Light absorption of black carbon aerosol and its en-hancement by mixing state in an urban atmosphere in South China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandradewi, J.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Szidat, S.; Perron, N.; Alfarra, M.R.; Lanz, V.A.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. Using Aerosol Light Absorption Measurements for the Quantitative Determination of Wood Burning and Traffic Emission Contributions to Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3316–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Liu, B.; Sun, J.Y.; Mao, X.; Yang, H.; Deng, T.; Song, L.; Li, M.; et al. Time-resolved black carbon aerosol vertical distribution measurements using a 356-m meteorological tower in Shenzhen. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2020, 140, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Utry, N.; Ajtai, T.; Filep, Á.; Pintér, M.; Török, Z.; Bozóki, Z.; Szabó, G. Correlations between absorption Angström ex-ponent (AAE) of wintertime ambient urban aerosol and its physical and chemical properties. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 91, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Fang, B.; Chen, W.; Venables, D.S.; Wang, X.; Pu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Optical properties of atmospheric fine particles near Beijing during the HOPE-J3A campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6421–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S. Optical properties and size distribution of dust aerosols over the Tengger Desert in Northern China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5971–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bergin, M.H.; Greenwald, R.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Jaffrezo, J.L.; Aymoz, G. Aerosol chemical, physical, and radiative characteristics near a desert source region of northwest China during ACE-Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2004, 109, D19S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellouin, N.; Quaas, J.; Morcrette, J.-J.; Boucher, O. Estimates of aerosol radiative forcing from the MACC re-analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 2045–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AzadiAghdam, M.; Braun, R.A.; Edwards, E.-L.; Bañaga, P.A.; Cruz, M.T.; Betito, G.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Dadashazar, H.; Lorenzo, G.R.; Ma, L.; et al. On the nature of sea salt aerosol at a coastal megacity: Insights from Manila, Philippines in Southeast Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Seventh Population Census of the People’s Republic of China. 2021. Available online: https://www.jinan.gov.cn (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Chen, J.; Qian, X.M.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, J.J.; Zhu, W.Y.; Li, X.B. Research on Optical Absorption Characteristics of Atmospheric Aerosols at 1064 nm Wavelength. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, H.-H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.-S.; Cao, Z.-S.; Liu, K.; Chen, W.-D.; Gao, X.-M. Multi-wavelength meas-urements of aerosol optical absorption coefficients using a photoacoustic spectrometer. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 064205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Y. Aerosol absorption measurement at SWIR with water vapor interference using a differential photoacoustic spectrometer. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 23108–23116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Determination of the refractive index and size distribution of aerosol from du-al-scattering-angle optical particle counter measurements. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 3864–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Hu, H. New Method to Deduce Imaginary Part of Refractive Index of Aerosol with Double-Scattering Angles Laser Optical Particle Counter. Acta Opt. Sin. 2007, 27, 391–394. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, F.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, L.; Wang, L. An intensive study on aerosol optical properties and affecting factors in Nanjing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhao, P.S.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W.W.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Shi, Q.F. Analysis of a winter regional haze event and its formation mechanism in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Virkkula, A.; Gao, Y.; Lee, S.; Shen, Y.; Chi, X.; Nie, W.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X.; et al. Observations of aerosol optical properties at a coastal site in Hong Kong, South China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 2653–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, P.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Mao, J.T.; Zhou, X.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhou, H.G. The measurement of aerosol optical properties at a rural site in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2007, 7, 13001–13033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garland, R.M.; Yang, H.; Schmid, O.; Rose, D.; Nowak, A.; Achtert, P.; Wiedensohler, A.; Takegawa, N.; Kita, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; et al. Aerosol optical properties in a rural environment near the mega-city Guangzhou, China: Implications for regional air pollution, radiative forcing and remote sensing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2008, 8, 5161–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Wu, C.; Liao, B.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Li, F.; Tan, H.; Deng, T.; Li, H.; Jiang, D.; et al. Black carbon over the South China Sea and in various continental locations in South China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 12257–12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.; Stein, A. Source term estimation using air concentration measurements and a Lagrangian dispersion model—Experiments with pseudo and real cesium-137 observations from the Fukushima nuclear accident. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Z.; Dan, T.; Meng, L.; Fei, L.; Chaopeng, H.; Guannan, G.; Haiyan, L.; Xin, L.; Liqun, P.; Ji, Q. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Xu, X.; Ge, B.; Liu, X. Gaseous pollutants in Beijing urban area during the heating period 2007–2008: Variability, sources, meteorological, and chemical impacts. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 8157–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.; Lau, A.K.; Li, F.; Tan, H.; Yuan, Z.; Ng, W.M.; Deng, T.; Wu, C.; et al. Characterization of secondary aerosol and its extinction effects on visibility over the Pearl River Delta Region, China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ma, J.; An, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Cui, H. Impacts of meteorological condition and aerosol chemical compositions on visibility impairment in Nanjing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Cohen, J.B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, M.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ling, Z.; et al. Chemical Composition of PM2.5 and its Impact on Visibility in Guangzhou, Southern China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2349–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Chakrabarty, R.; Arnott, W. Aerosol light absorption and its measurement: A review. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 844–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhuang, G.; Lin, Y.; Fu, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, C.; Fu, Q.; et al. Typical types and formation mechanisms of haze in an Eastern Asia megacity, Shanghai. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeCarlo, P.F.; Slowik, J.G.; Worsnop, D.R.; Davidovits, P.; Jimenez, J.L. Particle Morphology and Density Characteriza-tion by Combined Mobility and Aerodynamic Diameter Measurements. Part 1: Theory. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1185–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petzold, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Fiebig, M.; Laj, P.; Li, S.M.; Baltensperger, U.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Kinne, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. Recommendations for reporting “black carbon” measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8365–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaur, A.; Tripathi, S.N.; Kanawade, V.P.; Tare, V.; Shukla, S.P. Four-year measurements of trace gases (SO2, NOx, CO, and O3) at an urban location, Kanpur, in Northern India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2014, 71, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton-Walsh, C.; Jones, N.; Wilson, S.; Meier, A.; Deutscher, N.; Griffith, D.; Mitchell, R.; Campbell, S. Trace gas emissions from biomass burning inferred from aerosol optical depth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L05116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichler, H.; Cheng, Y.F.; Birmili, W.; Nowak, A.; Wiedensohler, A.; Brüggemann, E.; Gnauk, T.; Herrmann, H.; Althausen, D.; Ansmann, A. Hygroscopic properties and extinction of aerosol particles at ambient relative humidity in South-Eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6321–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Morino, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yu, P.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Ge, B.; Tang, G.; et al. Investigating the evolution of summertime secondary atmospheric pollutants in urban Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, D.J.; Logan, J.A.; Yevich, R.M.; Gardner, G.M.; Spivakovsky, C.M.; Wofsy, S.C.; Munger, J.W.; Sillman, S.; Prather, M.J.; Rodgers, M.O.; et al. Simulation of summertime ozone over North America. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1993, 98, 14797–14816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Location | Observation Time | Λ (nm) | Instrumentation | OAC (Mm−1) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingdao (urban, coastal) | November to December 2019 | 1064 | PAS | 18.52 ± 13.31 | This study |
| Shenzhen (urban) | 26 August to 20 September 2011 | 450 532 781 | PASS-3 | 37.1 ± 28.1 25.4 ± 19.0 17.6± 12.9 | [19] |
| Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei (urban) | 14 to 23 November 2010 | 532 | AE31 | 37 ± 43 | [35] |
| Hok Tsui (rural, coastal) | February 2012 to February 2015 | 550 | AE31 | 8.3 ± 6.1 | [36] |
| Nanjing (urban) | 14 to 28 November 2012 | 405 532 781 | PASS-3 | 68.4 ± 53.5 41.6 ± 18.7 28.0 ± 18.7 | [34] |
| Shangdianzi (Beijing, rural background station) | September 2003 to January 2005 | 525 | AE31 | 17.54 ± 13.44 | [37] |
| Guangzhou, (rural) | July 2006 | 532 | PAS | 34.3 ± 26.5 | [38] |
| Yulin (Gobi Desert) | April 2001 | 565 | PASP | 6 ± 11 | [25] |
| Yongxing Island (oceanic, rural) | May to June 2008 December 2008 to January 2009 | 532 | AE31 | 7.21 ± 5.23 | [39] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Q.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Yang, T.; Xu, Q. Aerosol Light Absorption at 1064 nm: Pollution Sources, Meteorological Parameters and Gas Pollutants in Qingdao Coastal Area, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121553
Chen J, Zhu W, Liu Q, Qian X, Li X, Zheng J, Yang T, Xu Q. Aerosol Light Absorption at 1064 nm: Pollution Sources, Meteorological Parameters and Gas Pollutants in Qingdao Coastal Area, China. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(12):1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121553
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie, Wenyue Zhu, Qiang Liu, Xianmei Qian, Xuebin Li, Jianjie Zheng, Tao Yang, and Qiuyi Xu. 2021. "Aerosol Light Absorption at 1064 nm: Pollution Sources, Meteorological Parameters and Gas Pollutants in Qingdao Coastal Area, China" Atmosphere 12, no. 12: 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121553
APA StyleChen, J., Zhu, W., Liu, Q., Qian, X., Li, X., Zheng, J., Yang, T., & Xu, Q. (2021). Aerosol Light Absorption at 1064 nm: Pollution Sources, Meteorological Parameters and Gas Pollutants in Qingdao Coastal Area, China. Atmosphere, 12(12), 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12121553






