Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Air Temperature Near the Ground Surface in the Central Baltic Area from 2005 to 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
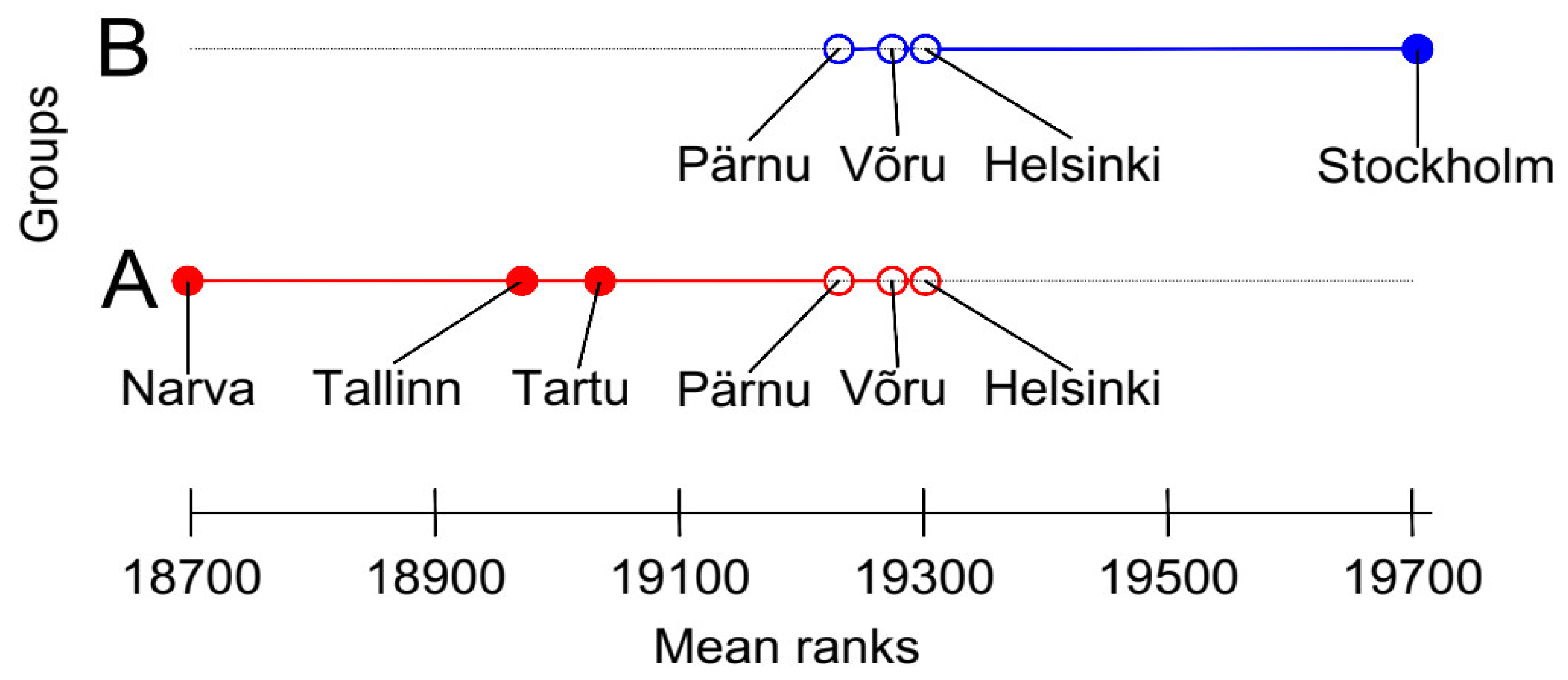
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Average Daily Surface Air Temperatures
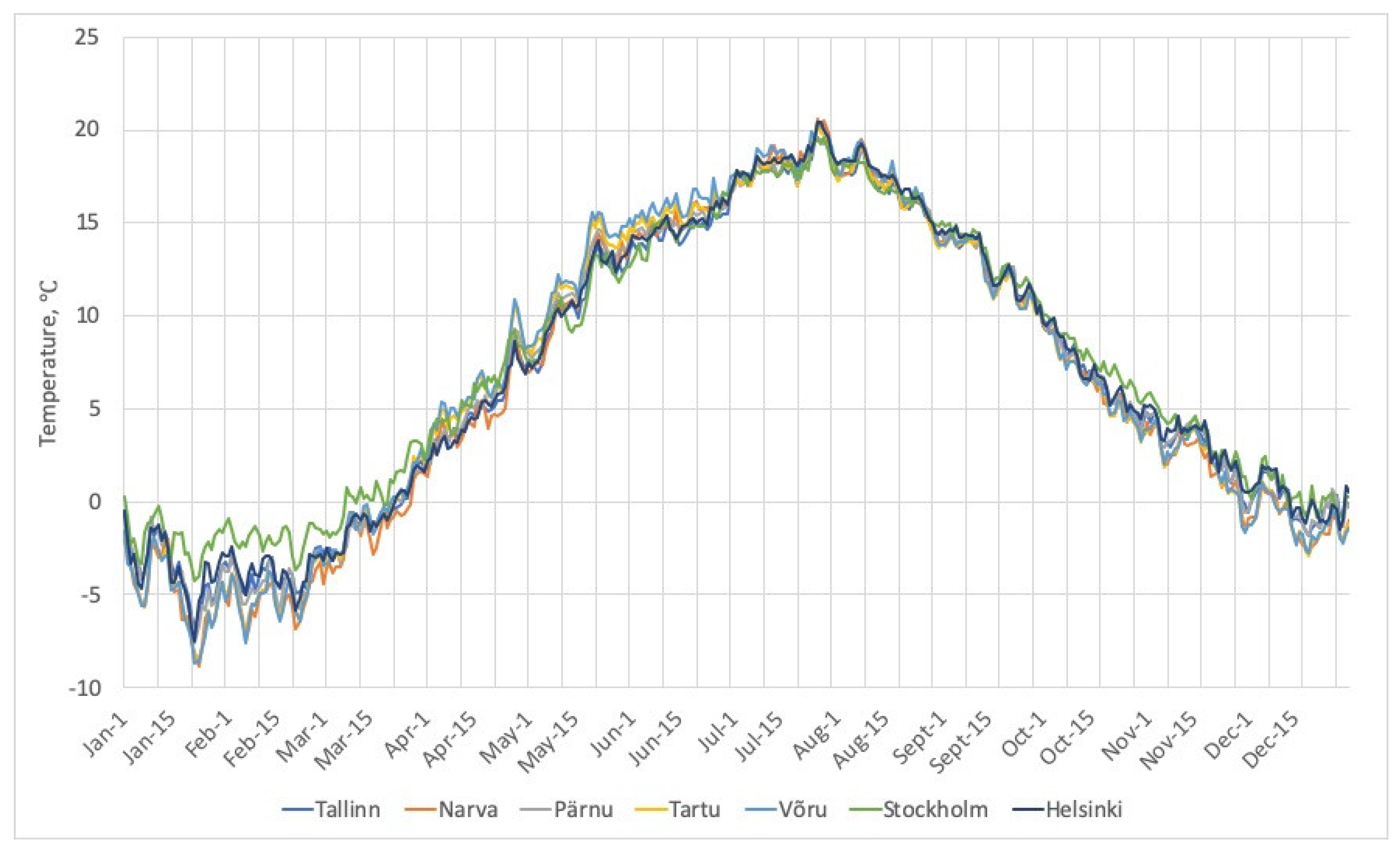
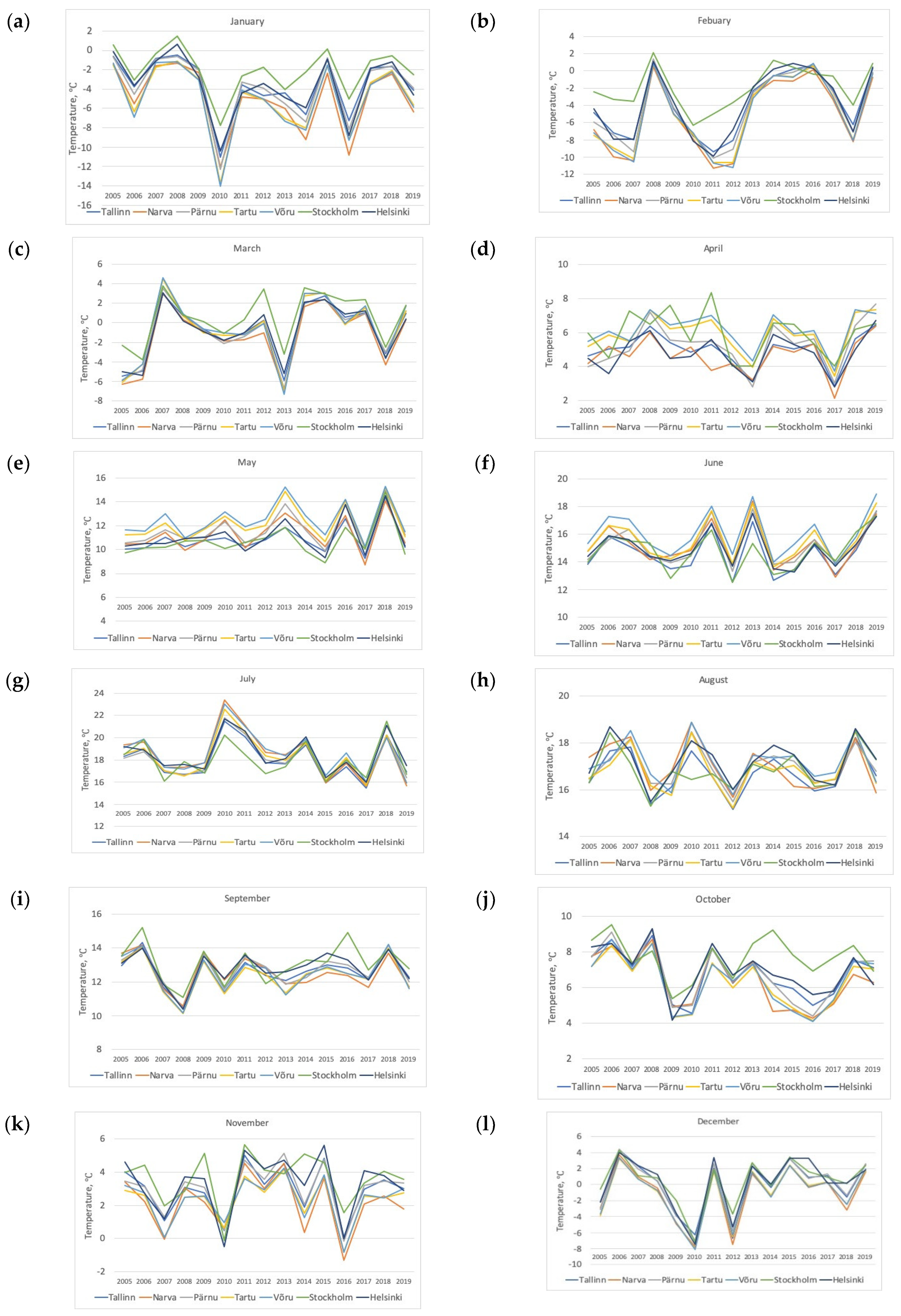
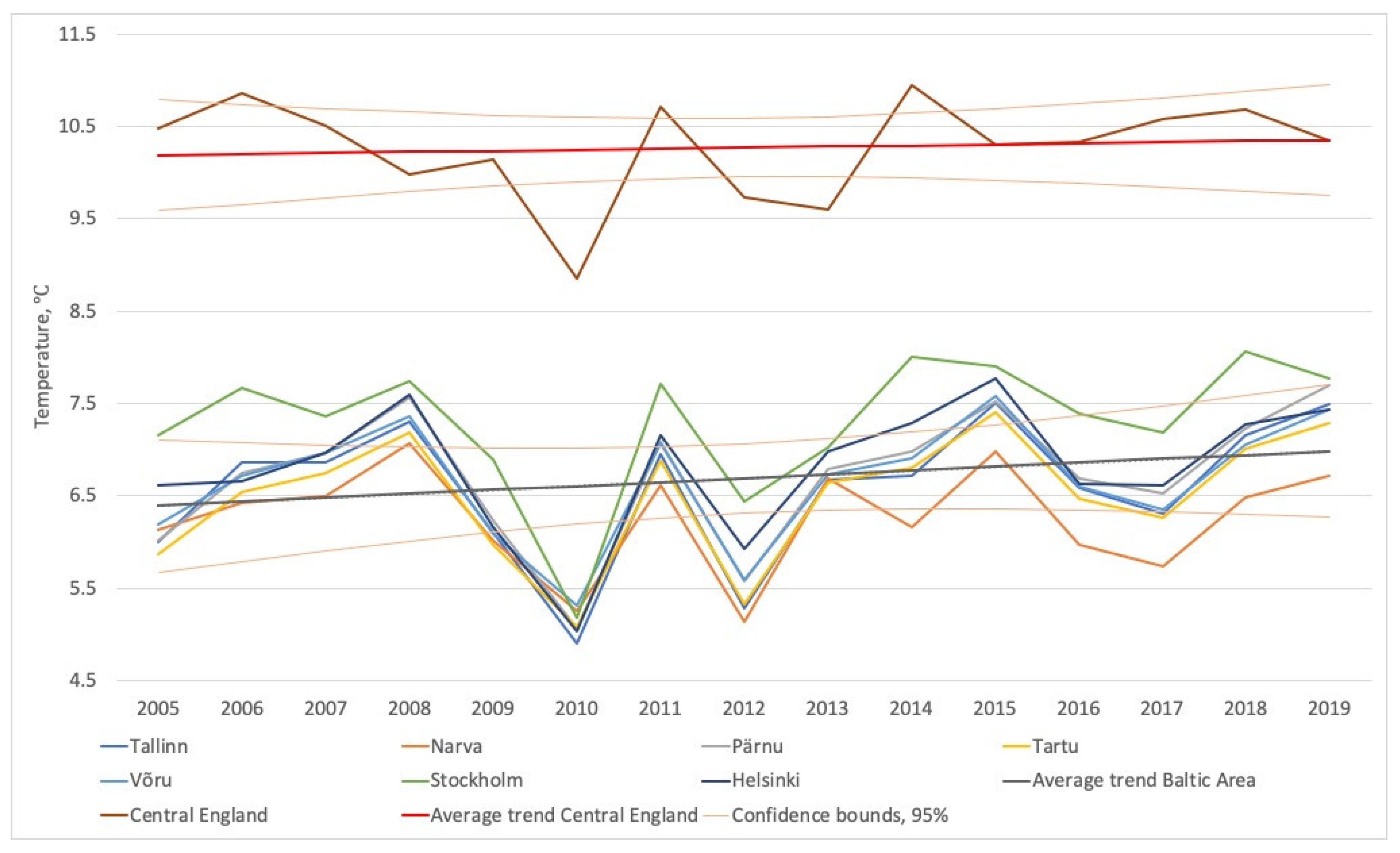
3.1.1. Annual Changes in Average Daily Surface Air Temperatures
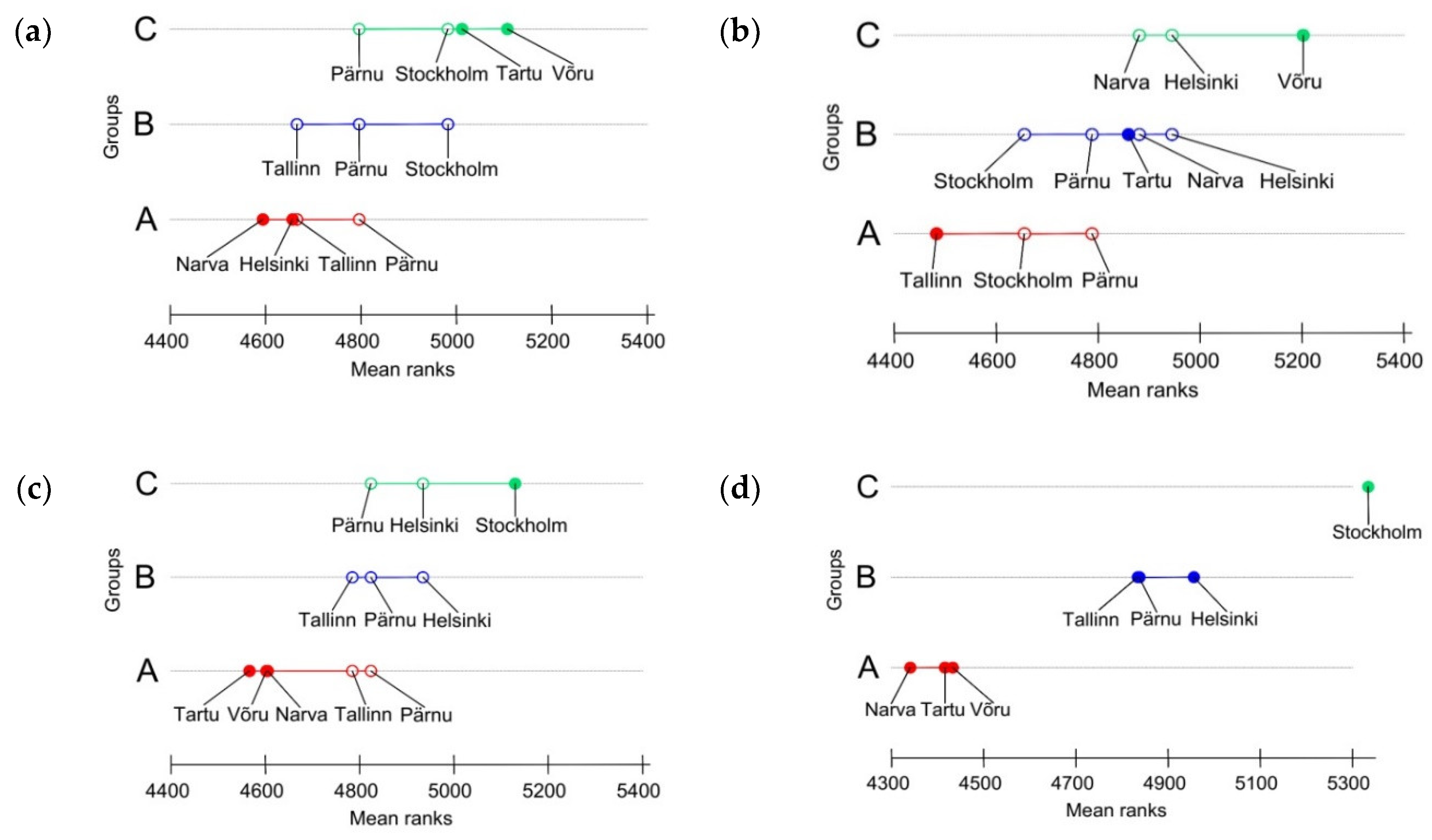
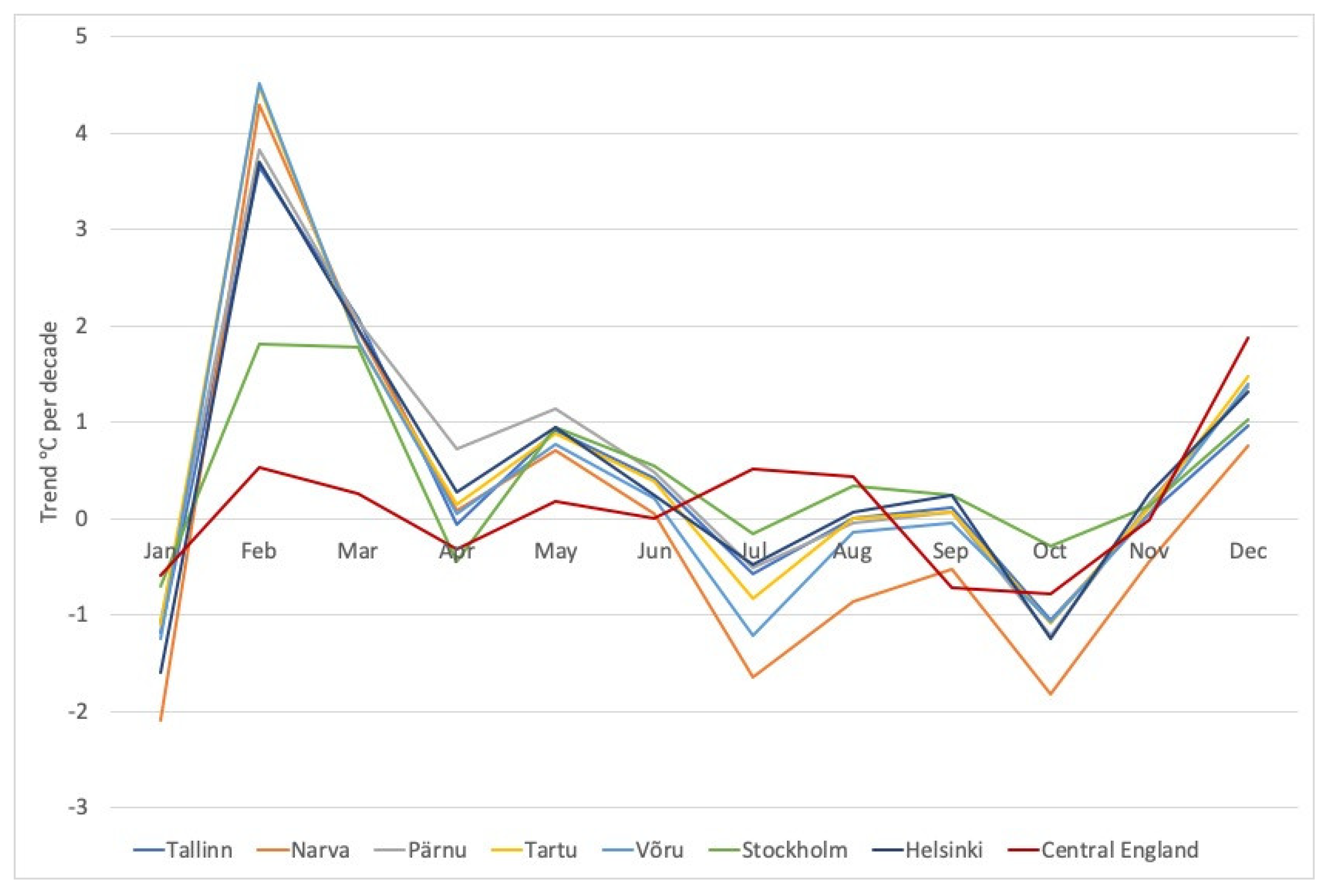
3.1.2. Changes in Average Daily Surface Air Temperatures in Different Seasons
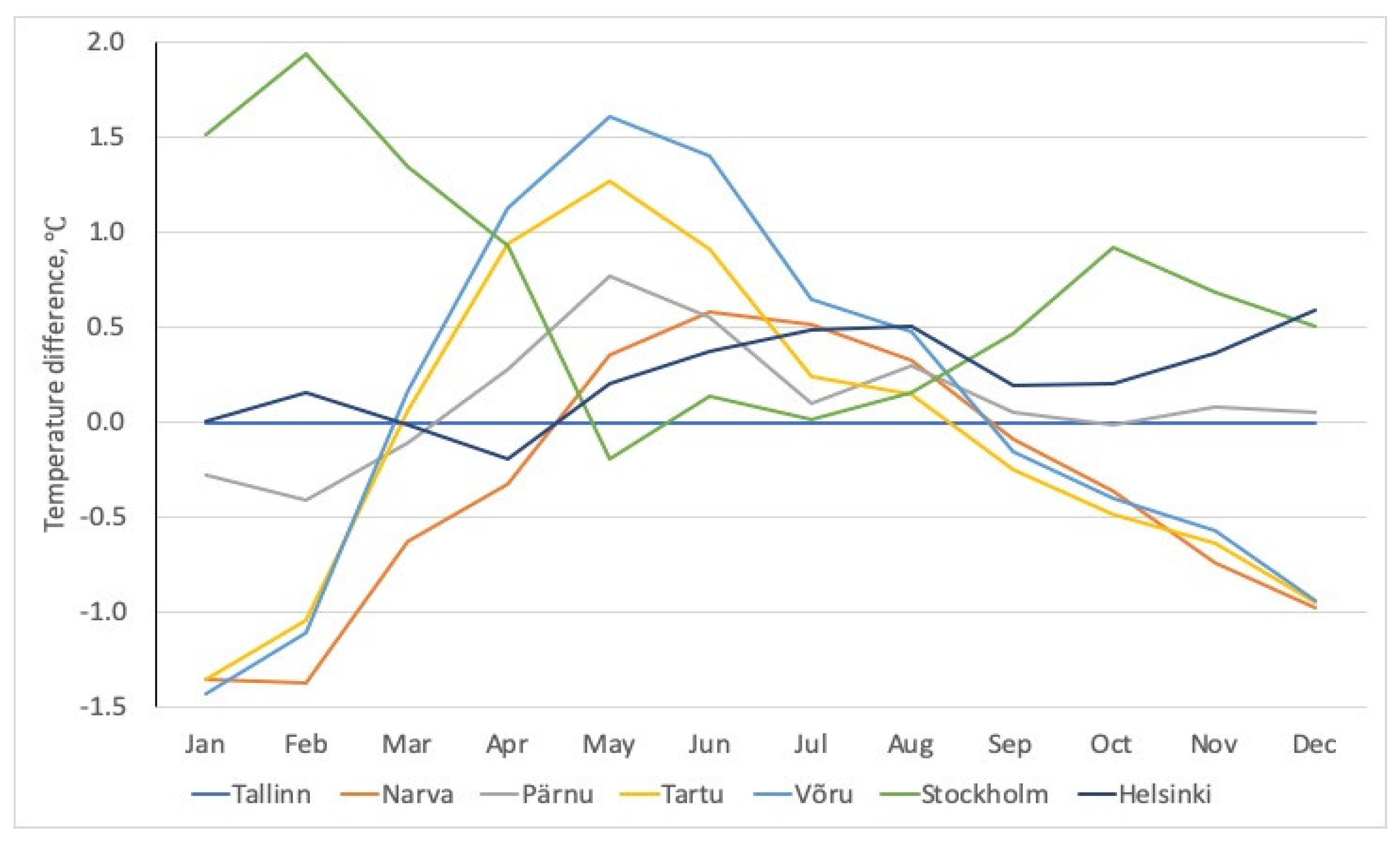
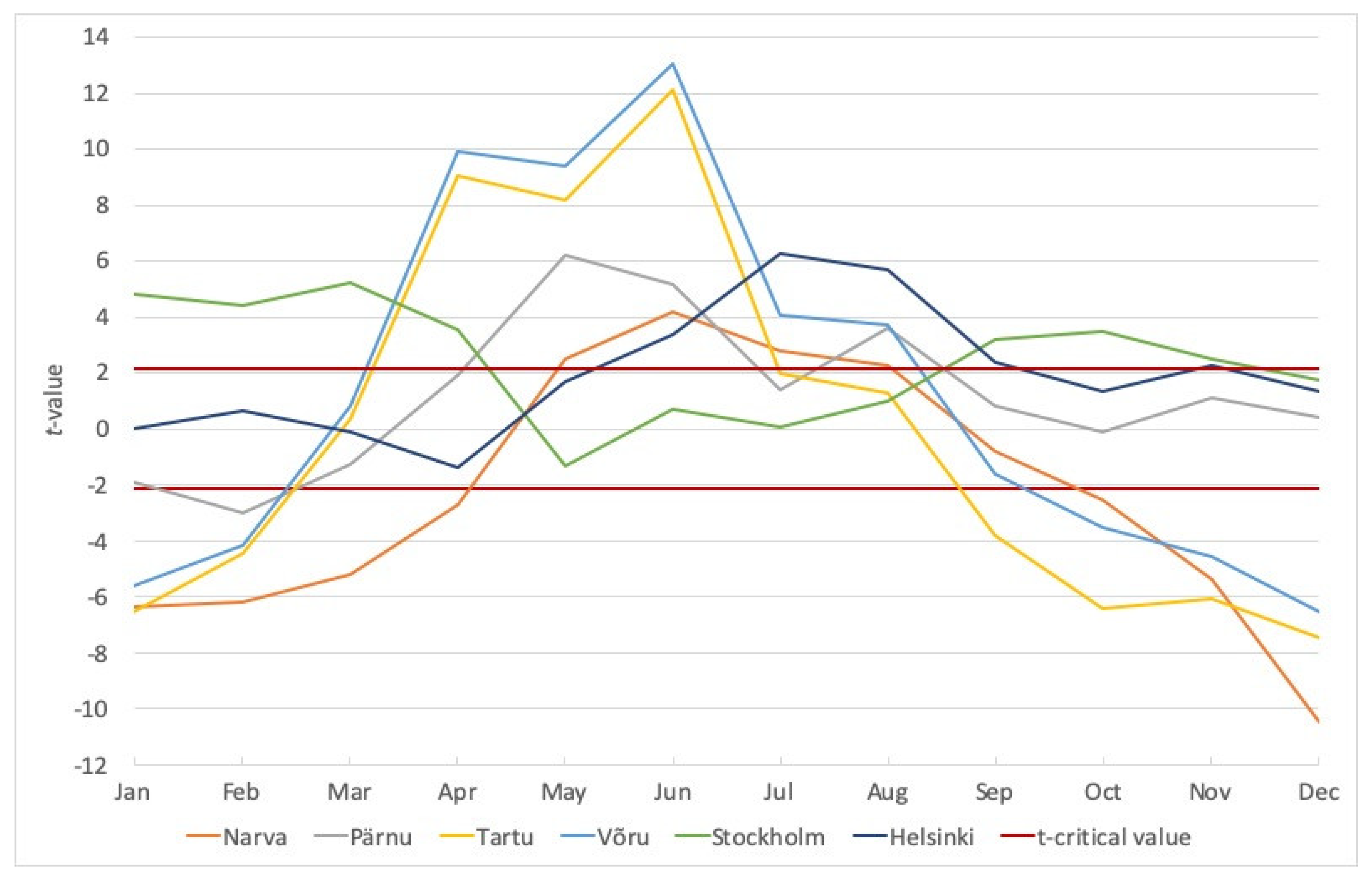
3.2. Changes in Average Monthly and Annual Air Temperatures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potter, T.D.; Colman, B.R. (Eds.) The Handbook of Weather, Climate, and Water: Dynamics, Climate, Physical Meteorology, Weather Systems, and Measurements; Wiley & Sons Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; 973p. [Google Scholar]
- Climate Indicators–Temperature. SMHI. Available online: https://www.smhi.se/en/climate/climate-indicators/climate-indicators-temperature-1.91472 (accessed on 18 February 2020).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Houghton, J.T., Ding, Y., Griggs, D.J., Noguer, N., van der Linden, P.J., Xiaosu, D., Maskell, K., Johnson, C.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; p. 881. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, D.L.; Tank, A.M.K.; Rusticucci, M.; Alexander, L.V.; Brönnimann, S.; Charabi, Y.A.R.; Dentener, F.J.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Easterling, D.R.; Kaplan, A.; et al. Observations: Atmosphere and surface. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 159–254. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.D.; New, M.; Parker, D.E.; Martin, S.; Rigor, I.G. Surface air temperature and its variations over the last 150 years. Rev. Geophys. 1999, 37, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Dool, H. A global monthly land surface air temperature analysis for 1948–present. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D01103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Ruedy, R.; Sato, M.; Lo, K. Global surface temperature change. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luterbacher, J.; Werner, J.P.; Smerdon, J.E.; Fernández-Donado, L.; González-Rouco, F.J.; Barriopedro, D.; Ljungqvist, F.C.; Büntgen, U.; Zorita, E.; Wagner, S.; et al. European summer temperatures since Roman times. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC Special Report Global Warming of 1.5 °C. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/sr15/ (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin; Regional Climate Studies. The BACC Author Team; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; 474p.
- Tarand, A.; Eensaar, A. Air Temperature, Country Case Study on Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Assessments in the Republic of Estonia; Stockholm Environment Institute-Tallinn: Tallinn, Estonia, 1998; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Orviku, K.; Jaagus, J.; Kont, A.; Ratas, U.; Rivis, R. Increasing activity of coastal processes associated with climate change in Estonia. J. Coastal Res. 2003, 19, 364–375. [Google Scholar]
- Kont, A.; Jaagus, J.; Aunap, R. Climate change scenarios and the effect of sea-level rise for Estonia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eensaar, A. Analysis of Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations in the Ambient Air of the Industrial Cities of Northern Estonia. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 2, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Öğlü, B.; Möls, T.; Kaart, T.; Cremona, F.; Kangur, K. Parameterization of surface water temperature and long-term trends in Europe’s fourth largest lake shows recent and rapid warming in winter. Limnologica 2020, 82, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Change Adaption in Estonia. Estonian Environmental Research Centre. Available online: http://www.klab.ee/kohanemine/en/ (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Moberg, A.; Bergström, H.; Ruiz Krigsman, J.; Svanered, O. Daily air temperature and pressure series for Stockholm (1756–1998). Clim. Chang. 2002, 53, 171–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, A.; Alexandersson, H.; Bergström, H.; Jones, P.D. Were Southern Swedish summer temperatures before 1860 as warm as measured? Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1495–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarand, A.; Jaagus, J.; Kallis, A. Eesti Kliima Minevikus Ja Tänapäeval; Tartu Ülikooli Kirjastus: Tartu, Estonia, 2013; 631p. [Google Scholar]
- Tarand, A.; Nordli, P.Ø. The Tallinn temperature series reconstructed back half a millennium by use of proxy data. Clim. Chang. 2001, 48, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarand, A. Meteoroloogilised Vaatlused Eestis Enne 1850 Aastat; Teaduse ajaloo küsimusi Eestist: Tallinn, Estonia, 1992; pp. 30–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tarand, A. 200 Aastat Professor CL Carpovi Meteoroloogilistest Vaatlustest; EGS Aastaraamat: Tallinn, Estonia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Tarand, A. Tallinnas mõõdetud õhutemperatuuri aegrida. In Publicationes Geophysicales Universitatis Tartuensis; Tartu Ülikooli Kirjastus: Tartu, Estonia, 2003; Volume 93. [Google Scholar]
- Tietäväinen, H.; Tuomenvirta, H.; Venäläinen, A. Annual and seasonal mean temperatures in Finland during the last 160 years based on gridded temperature data. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivinen, S.; Sirpa, R.; Jylhä, K.; Laapas, M. Long-Term Climate Trends and Extreme Events in Northern Fennoscandia (1914–2013). Climate 2017, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The BACC II Author Team. Second Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin; Regional Climate Studies; Springer: Cham, Germany; Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2015; 501p. [Google Scholar]
- Männik, A.; Zirk, M.; Rõõm, R.; Luhamaa, A. Climate parameters of Estonia and the Baltic Sea region derived from the high-resolution reanalysis database BaltAn65+. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 122, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaagus, J.; Briede, A.; Rimkus, E.; Remm, K. Variability and trends in daily minimum and maximum temperatures and in the diurnal temperature range in Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia in 1951–2010. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 118, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kлимaт Taллинa (In Russian: Tallinn Climate); Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1982; 266p.
- Kлимaт Пярну (In Russian: Pärnu Climate); Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1986; 202p.
- Jaagus, J.; Mändla, K. Climate change scenarios for Estonia based on climate models from the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report. Est. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 63, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eensaar, A. Temporal and Spatial Variability of Air Temperatures in Estonia during 1756–2014. J. Climatol. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eensaar, A. Peculiarities of Long-Term Changes in Air Temperatures Near the Ground Surface in the Central Baltic Coastal Area. Climate 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løvsletten, O.; Rypdal, M. Statistics of Regional Surface Temperatures after 1900: Long-Range versus Short-Range Dependence and Significance of Warming Trends. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 4057–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzke, C. On the statistical significance of surface air temperature trends in the Eurasian Arctic region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L23705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaagus, J.; Ahas, R. Space-time variations of climatic seasons and their correlation with the phenological development of nature in Estonia. Clim. Res. 2000, 15, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karing, P. Õhutemperatuur Eestis; Valgus: Tallinn, Estonia, 1992; 78p. [Google Scholar]
- Jaagus, J. Climatic changes in Estonia during the second half of the 20th century in relationship with changes in large-scale atmospheric circulation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 83, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepp, M.; Jaagus, J. Frequency of circulation patterns and air temperature variations in Europe. Boreal Environ. Res. 2002, 7, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Jylhä, K.; Tuomenvirta, H.; Ruosteenoja, K. Climate change projections for Finland during the 21st century. Boreal Environ. Res. 2004, 9, 127–152. [Google Scholar]
- Jaagus, J. Climatic fluctuations and trends in Estonia in the 20th century and possible climate change scenarios. In Climate Change Studies in Estonia; Stockholm Environment Institute Tallinn Centre: Tallinn, Estonia, 1998; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lépy, É. Baltic Sea ice and environmental and societal implications from the comparative analysis of the Bay of Bothnia and the Gulf of Riga. Fennia 2012, 190, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrcz, C. Analysis of ice conditions in the Baltic Sea and in the Puck Bay. Sci. J. Pol. Nav. Acad. 2017, 210, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M. Sea Ice Concentration Analyses for the Baltic Sea and Their Impact on Numerical Weather Prediction. JAMC 2006, 45, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eesti Meteoroloogia Aastaraamat 2019, Tallinn, Eesti Keskkonnaagentuur. Available online: https://kaur.maps.arcgis.com/apps/MapSeries/index.html?appid=4f118ea1e3954d55ac418d124c0d8662 (accessed on 5 October 2020).
- Estonian Environment Agency. Estonian Weather Service. Available online: http://www.ilmateenistus.ee/teenused/teenuste-tellimine/ (accessed on 19 February 2020).
- Moberg, A. Stockholm Historical Weather Observations—Daily Mean Air Temperatures Since 1756. Available online: https://bolin.su.se/data/data/stockholm_daily_mean_temperature.csv (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Finnish Meteorological Institute. Available online: http://en.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/download-observations#!/ (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Parker, D.E.; Legg, T.P.; Folland, C.K. A new daily Central England Temperature Series, 1772–1991. Int. J. Climatol. 1992, 12, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Met Office Hadley Centre Central England Temperature Data. Available online: https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadcet/data/download.html (accessed on 25 December 2020).
- Montgomery, D.C.; Runge, R.G. Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.J. Statistical Analysis Handbook; A Comprehensive Handbook of Statistical Concepts, Techniques and Software Tools, 2018 ed.; Issue Version: 2018-3; The Winchelsea Press, Drumlin Publications: Edinburgh, UK, 2018; 631p. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, R. Concepts and Applications of Inferential Statistics. Online Statistic Textbook. 2008. Available online: http://faculty.vassar.edu/lowry/webtext.html (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Sprent, P.; Smeeton, N. Applied Nonparametric Statistical Methods, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; 480p. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple comparisons among means. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1961, 56, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demšar, J. Statistical Comparisons of Classifiers over Multiple Data Sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
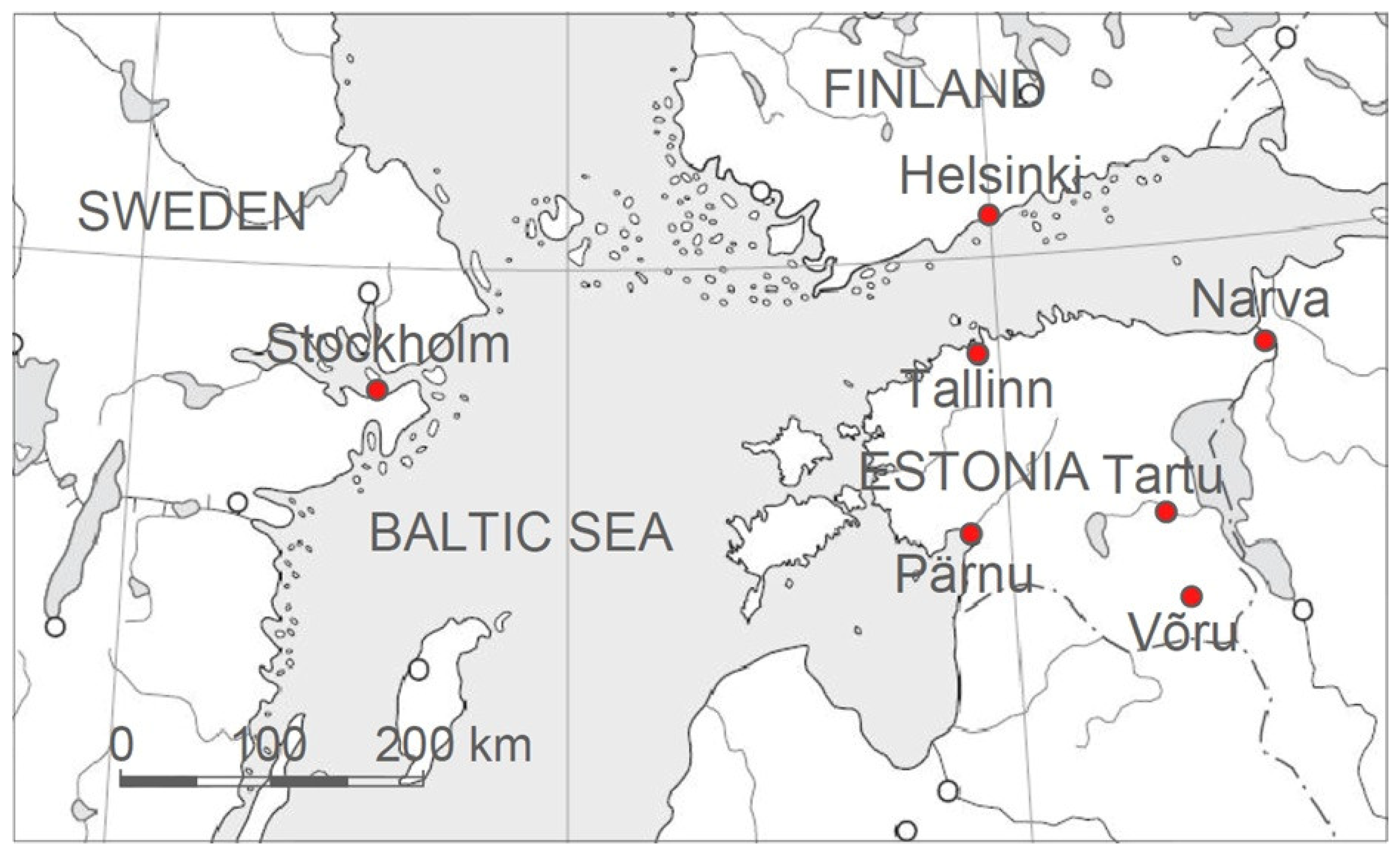


| Meteorological Station | Country | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|
| Tallinn–Harku | Estonia | 59°24′ N; 24°36′ E |
| Narva | Estonia | 59°23′ N; 28°07′ E |
| Pärnu | Estonia | 58°23′ N; 24°29′ E |
| Tartu–Tõravere | Estonia | 59°24′ N; 24°36′ E |
| Võru | Estonia | 57°51′ N; 27°01′ E |
| Stockholm | Sweden | 59°21′ N; 18°03′ E |
| Helsinki–Kaisaniemi | Finland | 60°12′ N; 24°57′ E |
| Tallinn | Narva | Pärnu | Tartu | Võru | Stockholm | Helsinki | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | 27.3 | 28.1 | 26.4 | 27.1 | 28.5 | 25.9 | 26.4 |
| Minimum | −23.7 | −27.3 | −25.1 | −27.2 | −28.1 | −18.0 | −22.7 |
| Average | 6.7 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 7.4 | 6.9 |
| SD | 8.5 | 9.2 | 8.8 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 7.8 | 8.6 |
| Narva | Pärnu | Tartu | Võru | Stockholm | Helsinki | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
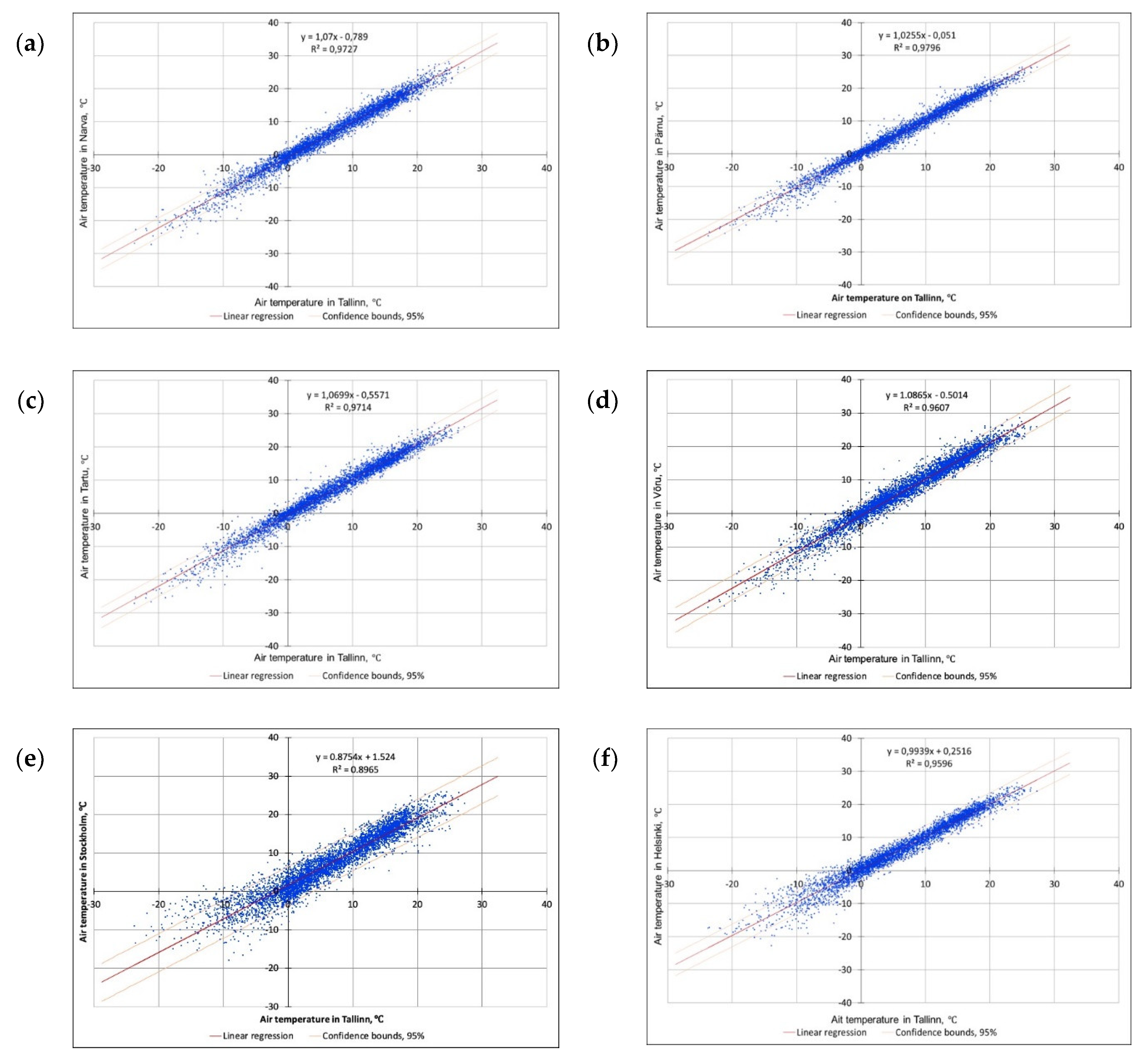
| Pearson correlation | 0.9862 | 0.9897 | 0.9856 | 0.9801 | 0.9468 | 0.9796 |
| Coefficient of determination | 0.9726 | 0.9796 | 0.9714 | 0.9607 | 0.8965 | 0.9596 |
| Standard error | 1.5231 | 1.2556 | 1.5555 | 1.8642 | 2.5219 | 1.7301 |
| Parameter | Value | Standard Error | t-Statistic | P-Value | Lower 95% | Upper 95% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narva | Slope a | 1.0699 | 0.0024 | 440.76 | 0.0000 | 1.0652 | 1.0747 |
| Intercept b | −0.7887 | 0.0262 | −30.15 | 0.0000 | −0.8400 | −0.7375 | |
| Pärnu | Slope a | 1.0255 | 0.0020 | 512.47 | 0.0000 | 1.0216 | 1.0294 |
| Intercept b | −0.0509 | 0.0216 | −2.36 | 0.0183 | −0.0932 | −0.0086 | |
| Tartu | Slope a | 1.0699 | 0.0025 | 431.55 | 0.0000 | 1.0650 | 1.0747 |
| Intercept b | −0.5571 | 0.0267 | −20.85 | 0.0000 | −0.6095 | −0.5047 | |
| Võru | Slope a | 1.0865 | 0.0030 | 365.71 | 0.0000 | 1.0807 | 1.0924 |
| Intercept b | −0.5014 | 0.0320 | −15.66 | 0.0000 | −0.5641 | −0.4386 | |
| Stockholm | Slope a | 0.8754 | 0.0040 | 217.81 | 0.0000 | 0.8676 | 0.8833 |
| Intercept b | 1.5240 | 0.0433 | 35.19 | 0.0000 | 1.4391 | 1.6089 | |
| Helsinki | Slope a | 0.9939 | 0.0028 | 360.45 | 0.0000 | 0.9885 | 0.9993 |
| Intercept b | 0.2516 | 0.0297 | 8.47 | 0.0000 | 0.1933 | 0.3098 |
| Month | Tallinn | Narva | Pärnu | Tartu | Võru | Stockholm | Helsinki |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | −3.6 | −4.9 | −3.8 | −4.9 | −5.0 | −2.0 | −3.6 |
| February | −3.9 | −5.3 | −4.3 | −5.0 | −5.0 | −2.0 | −3.8 |
| March | −0.8 | −1.4 | −0.9 | −0.7 | −0.6 | 0.6 | −0.8 |
| April | 5.0 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 4.8 |
| May | 10.9 | 11.2 | 11.6 | 12.1 | 12.5 | 10.7 | 11.1 |
| June | 14.6 | 15.2 | 15.2 | 15.6 | 16.1 | 14.8 | 15.0 |
| July | 18.0 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 18.2 | 18.6 | 18.0 | 18.5 |
| August | 16.7 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 16.8 | 17.2 | 16.8 | 17.2 |
| September | 12.6 | 12.5 | 12.7 | 12.4 | 12.5 | 13.1 | 12.8 |
| October | 6.8 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 6.3 | 6.4 | 7.7 | 7.0 |
| November | 2.9 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 3.6 | 3.3 |
| December | −0.1 | −1.1 | −0.1 | −1.1 | −1.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Year | 6.7 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 6.6 | 6.7 | 7.4 | 6.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eensaar, A. Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Air Temperature Near the Ground Surface in the Central Baltic Area from 2005 to 2019. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010060
Eensaar A. Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Air Temperature Near the Ground Surface in the Central Baltic Area from 2005 to 2019. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleEensaar, Agu. 2021. "Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Air Temperature Near the Ground Surface in the Central Baltic Area from 2005 to 2019" Atmosphere 12, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010060
APA StyleEensaar, A. (2021). Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Variability of Air Temperature Near the Ground Surface in the Central Baltic Area from 2005 to 2019. Atmosphere, 12(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12010060




