Abstract
Understanding the wake characteristics between two in-line vehicles is essential for improving and developing new strategies for reducing in-cabin air pollution. In this study, Ahmed bodies are used to investigate the effects of the rear slant angle of a leading vehicle on the mean flow and turbulent statistics between two vehicles. The experiments were conducted with a particle image velocimetry at a fixed Reynolds number, , and inter-vehicle spacing distance of , where and are the height and length of the model. The rear slant angles investigated were a reference square back, high-drag angle () and low-drag angle (). The mean velocities, Reynolds stresses, production of turbulent kinetic energy and instantaneous swirling strength are used to provide physical insight into the wake dynamics between the two bodies. The results indicate that the recirculation region behind the square back Ahmed body increases while those behind the slant rear-end bodies decreases in the presence of a follower. For the square back models, the dominant motion in the wake region is a strong upwash of jet-like flow away from the road but increasing the rear slant angle induces a stronger downwash flow that suppresses the upwash and dominates the wake region.
1. Introduction
Air pollution inside and outside the cabin of passenger vehicles is a global concern because of the high level of exposure to gaseous and particulate pollutants from the exhaust of other vehicles and the associated health risks to the occupants, pedestrians and bicycle commuters [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The increased level of exposure is attributed to the increased number of hours spent every day in vehicles in traffic congestion and highway platooning [6,7,8]. Under these conditions, the pollutants in the exhaust of the leading vehicle are transported into the cabin of the following vehicle due to the relatively short inter-vehicle distance and the low intake point of the ventilation systems [9,10,11,12]. Since the transport of the pollutant between the vehicles is also influenced by the wake characteristics, a good understanding of the mean flow and turbulent characteristics between two in-line vehicles is essential for developing effective flow control strategies for minimizing in-cabin air pollution.
The Ahmed body is a simplified car model that has been used extensively to study the flow around ground vehicles [13,14,15,16]. The model, as shown in Figure 1a, consists of a fore end with rounded edges to minimize flow separation, a rectangular mid-section with sharp edges, and a rear end with varying slant angles (). The structure of the wake behind the Ahmed body is very complex as it involves unsteady three-dimensional (3D) interactions of three salient features: a recirculation bubble on the rear slanted surface, a pair of counter-rotating longitudinal vortices (well-known as C-pillar vortices) formed from the roll up of the shear layers at the two slanted edges, and a pair of counter-rotating recirculation bubbles behind the vertical base of the body [13,15]. Previous experimental and numerical investigations have shown that the wake characteristics and the aerodynamic drag largely depend on the rear slant angle [13,17,18,19,20,21]. For the square back () Ahmed body, the flow separates at the rear end and the wake structure is nominally two dimensional (2D) without the occurrence of C-pillar vortices. At relatively small , the C-pillar vortices are generated, which contributes to drag and induces a downwash flow between them, thereby promoting the reattachment of the recirculation bubble on the slanted surface. Moreover, a pair of counter-rotating recirculation bubbles is formed behind the vertical base of the body. The minimum drag occurs from to , but this is followed by a rapid increase beyond to a maximum drag at . For , the vortices burst, and the recirculation bubble on the slanted surface fails to reattach on the body but connects with the recirculation bubbles behind the vertical base to form a fully separated flow behind the body. This leads to a reduction in drag. Therefore, the wake behind the Ahmed body is often divided into two distinct regimes: a low-drag regime for and a high-drag regime for [18].
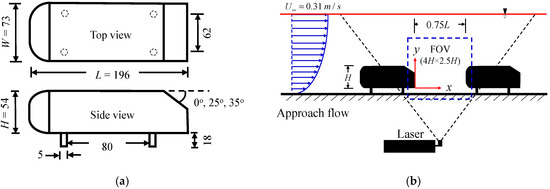
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of an Ahmed body with the nomenclature and dimension used in this study; (b) schematic of the experimental set up showing the two in-line Ahmed bodies and the position of the laser of the particle image velocimetry (PIV) system (Dimensions in mm).
Most of the previous investigations have focused on the wake characteristics behind a single Ahmed body. Wang et al. [21], for example, used particle image velocimetry (PIV) to investigate the effects of clearance (G/H, where G is the wall-normal distance from the ground to the base of the Ahmed body and H is the height of the body) on the wake structure behind an Ahmed body of and . The results of the mean velocity, Reynolds stresses and vorticity indicated that the salient features of the wake in the two flow regimes are significantly modified for an Ahmed body without a clearance (G/H = 0), as the upwash of flow beneath the body to form the lower recirculation bubble behind the vertical base is curtailed. Based on PIV, flow visualization and hotwire measurements, Zhang et al. [15] proposed a conceptual model that describes both the steady and unsteady wake structure around an Ahmed body in a high-drag flow regime. Several numerical investigations have also been conducted on the flow around an Ahmed body [16,19,22]. Krajnović and Davidson [22] used Large-Eddy Simulations (LES) to study the influence of floor motion on the flow around an Ahmed body () and found that the drag and lift are reduced by 16% and 8%, respectively for a moving floor compared with a stationary floor. Recently, Rao et al. [19] studied the influence of aspect ratio, defined as the ratio of the width of the model to that of the standard Ahmed body, and found that a lower aspect ratio promotes reattachment on the slanted surface while a larger aspect ratio induces a fully separated flow behind the body.
Although considerable research efforts have been made to understand the flow around a single Ahmed body, our knowledge of the mean flow patterns and turbulent statistics between two Ahmed bodies interacting with each other is limited due to the lack of comprehensive experimental and numerical investigations. Watkins and Vino [23] conducted the earliest experimental study on the effects of spacing ratio ( where is the inter-vehicle distance and is the length of the Ahmed body) on the drag and lift coefficients behind two Ahmed bodies. The experiments were conducted in a wind tunnel at a fixed Reynolds number based on the approach velocity () and H, , and for . They found significant variations in the lift and drag coefficients, as spacing ratio increased from to 1.0. In particular, the drag of the leading body decreased considerably for the lowest spacing ratio (), but gradually increased to that of an isolated body as the spacing ratio increased to . On the other hand, the drag of the follower was significantly larger than that of the isolated body for . In the numerical simulations by Mirzaei et al. [24,25,26] both LES [24] and partially averaged Navier–Stokes (PANS) model [25,26] were used to investigate the influence of spacing ratio () on the flow structure between two Ahmed bodies. The simulations were conducted at for . They showed that the increase in drag of the follower of two in-line Ahmed bodies is due to significant changes in the wake structure between the bodies, as spacing ratio increased from 0.5 to 1.0. Gnatowska and Sosnowski [27] also made similar conclusions based on results from experiments and Reynolds Averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS)-based turbulence modelling. In a recent study, Murzyn et al. [10] performed detailed two-dimensional (2D) laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV) measurements of the wake structure between two Ahmed bodies using six spacing ratios ranging from 0.25 to 1.53 and three slant angles, and . It was shown that the length of the recirculation region (Lr) behind the leading model is independent of spacing ratio beyond a critical value that is sensitive to the slant angle. For a square back and , the critical spacing ratio was and the corresponding value for was . The study also investigated the dispersion of ultrafine particulate pollutants in the wake of a single Ahmed body and found that for and , the dispersion of the pollutants is mainly influenced by the recirculation region behind the body but for , the strong downwash induced by the C-pillars also contributes to the particle dispersion.
The objective of the present study is to investigate the effects of the rear slant angle on the wake characteristics between two in-line Ahmed bodies with the potential to improve our understanding of the transport or dispersion of air pollutants into the cabin of vehicles. The experiments were conducted with a planar PIV system at a fixed Reynolds number, , and inter-vehicle distance of and for three slant angles: a reference square back (), a high-drag rear angle of and a low-drag rear angle of . This study is the first of a research campaign on the effects of rear slant angle and spacing ratio on the wake characteristics between two Ahmed bodies.
2. Experiments
The experiments were carried out in a recirculating open water channel with a test section of length , width and depth . The walls of the test section were made of transparent acrylic plates to facilitate optical access. The test section is preceded with a flow conditioning section consisting of a series of hexagonal honeycomb and mesh screens. The water depth () in the test section was maintained at by means of a tailgate control installed at the end of the channel. A combination of small stone chips (average roughness height, ) and sand grains () was positioned at 1.0 and 2.5 m, respectively, from the inlet of the test section to trip the turbulent boundary layer. Figure 1b shows a schematic of the experimental setup of the Ahmed bodies. The model used is a scaled-down model of the standard Ahmed body [13] (Figure 1a) with height, , length, and width, . The models were placed on the floor of the channel and aligned with the mid-span of the test section. The streamwise distance from the second trip (sand grains) to the leading Ahmed body was 2.5 m and the clearance of the base of the models from the wall was (). The blockage ratio, defined as the ratio of the projected area of the model to the cross-sectional area of the channel, was 1.5%. The interaction between the two Ahmed bodies was investigated using a fixed inter-vehicle distance of and varying the slant angle of the leading model. Three rear slant angles were tested: a square back (), high-drag angle () and low-drag angle (). As shown in Figure 1b, the Cartesian coordinate system adopted has the origin located at the midpoint of the lower edge of the vertical base of the leading model, where x and y represent the streamwise and bottom wall-normal directions, respectively.
A planar PIV system was used to conduct velocity measurements in the wall-normal () mid-plane of the Ahmed bodies. The flow was seeded with silver-coated hollow glass spheres of specific gravity 1.1. The response time and Stokes number of the seeding particles were and , respectively. The relatively low Stokes number indicates that the particles followed the fluid motions faithfully. The flow field was illuminated from the bottom of the channel (Figure 1b) using an Nd:YAG double-pulsed laser at 50 mJ/pulse and 532 nm wavelength. The particle images were captured using a PowerViewPlus 8 MP charge-coupled device (CCD) camera with a resolution of 3320 pixels × 2500 pixels. The field of view (FOV) of the camera was set to × (× ) in the plane and the images were acquired at a sampling frequency of . The ratio of the separation time () between successive image pairs and the integral time scale, estimated as (where is the integral length scale and is the streamwise velocity fluctuation) in the approach flow and wake regions of the Ahmed body varied from . These values imply that the successive image pairs are statistically independent [28]. The acquisition time of 1380 s is also orders of magnitude larger than the integral time scales and was deemed sufficiently large for statistical convergence. Figure 2 shows a schematic representation of the measurement planes acquired around the Ahmed bodies. The reference test case, SB_0, was performed with an isolated or single square back model. Here, measurements were acquired both upstream (P1) and downstream (P2) of the model. The test cases performed using the two Ahmed bodies are denoted as DB_0, DB_25 and DB_35 for configurations with the leading model having a rear slant angle of and , respectively. The measurements were acquired only in the spacing between the models (P2) as shown in Figure 2b–d. Based on a convergence test, a sample size of 4000 instantaneous image pairs was acquired in each plane and post-processed using an adaptive multi-grid cross-correlation algorithm based on a multi-pass fast Fourier transform. The initial interrogation window size was set to 64 pixels × 64 pixels, with 50% overlap and the final interrogation window size was pixels × pixels, with 50% overlap in each direction. The resulting spatial resolution was in both directions.
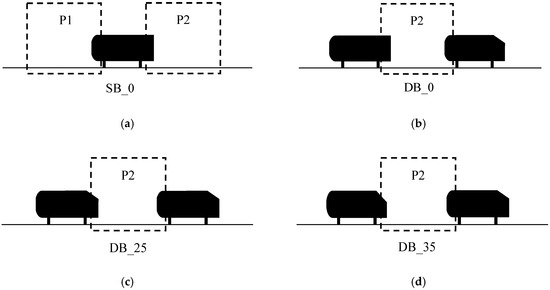
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the measurement planes around the (a) isolated square back, SB_0; and the two in-line Ahmed bodies with the leading model having a rear slant angle of (b) , DB_0; (c) , DB_25; and (d) , DB_35. P1 and P2 represent the measurement planes upstream and downstream of the leading model, respectively.
For each instantaneous flow field, the invalid velocity vectors in the area of interest was less than 5%, but these vectors were replaced using a Gaussian-weighted interpolation scheme. The mean and fluctuating velocity components were obtained from the instantaneous velocity vectors through Reynolds decomposition and ensemble averaging procedures. Following the AIAA uncertainty estimation procedure [29], the bias and precision errors were determined for the present measurements. For the mean velocity, the bias error was estimated as ( of the freestream velocity, ) and the precision error based on 6000 samples was ( of ). Therefore, the uncertainty in the mean velocity at the 95% confidence level is estimated as . The uncertainties in the turbulence intensities and Reynolds stresses are approximately and , respectively. From the convergence test, the mean velocities and Reynolds stresses attained statistical convergence, with the errors less than the measurement uncertainty, for sample sizes larger than 1000 and 2000 images, respectively. However, to improve the accuracy of the results, all the 4000 images were used to calculate the statistics reported herein.
3. Results
3.1. Approach Flow
Since the wake structure around the Ahmed bodies is influenced by the state of the approach turbulent boundary layer, it is important to perform a detailed characterization of the approach flow, which will also be useful for setting up inlet conditions for numerical simulations. In this study, measurement of the approach flow was performed before installing the Ahmed bodies in the channel. The open channel flow was fully developed () with a freestream velocity of . As summarized in Table 1, the Reynolds number based on and the boundary layer thickness () was , the Reynolds number based on and the momentum thickness was , and the Reynolds number based on and the height of the Ahmed body was . Figure 3a shows the profiles of the streamwise mean velocity () in inner (inset) and outer coordinates. The log law, (where and , where is the friction velocity and is the kinematic viscosity), is defined based on the classical constants, and [30]. The plot shows that the mean velocity profile matches the log law reasonably well in the region, . The skin friction coefficient, which provides a measure of the drag near the bottom wall, was evaluated as . The shape factor of the mean velocity profile is , where is the displacement thickness. The profiles of the streamwise and wall-normal Reynolds normal stresses and the Reynolds shear stress are presented in Figure 3b. The distributions of the Reynolds stresses agree reasonably well with results reported in previous smooth wall open channel studies [31,32,33,34].

Table 1.
Summary of approach flow conditions.
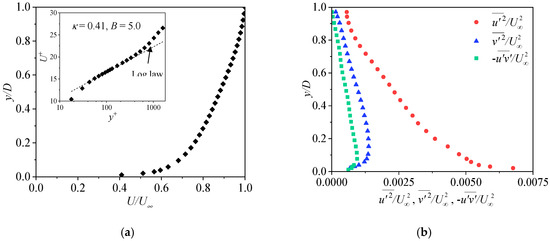
Figure 3.
The profiles of the approach flow. (a) streamwise mean velocity () in inner (inset) and outer coordinates; (b) streamwise () and wall-normal () Reynolds normal stresses and Reynolds shear stress () in outer coordinates.
Contours of the streamwise () and wall-normal () mean velocities upstream of the isolated Ahmed body are shown in Figure 4 to characterize the interaction of the approach flow with the fore end of the body. The streamlines are superimposed on the contours to reveal the flow pattern. The plots show that the oncoming boundary layer experiences a stagnation effect as it approaches the Ahmed body, but due to the rounded fore end, the flow bifurcates and deflects on either side of the body, leading to enhanced wall-normal mean velocity near the rounded edges. The stagnation or high-pressure point is determined as the location where the dividing streamline terminates on the front end of the body. This location is determined as (). In most vehicles, the air intake duct of the ventilation and air-conditioning system is located in the area of high pressure in front of the vehicle to force air into the system [35]. This implies that the area around the stagnation point of the present Ahmed body would correspond to the air intake point of the vehicle model. Therefore, investigating the flow dynamics upstream of the follower in the two in-line Ahmed body configurations is important for improving our understanding of the momentum and mass transport phenomena contributing to in-cabin air pollution.
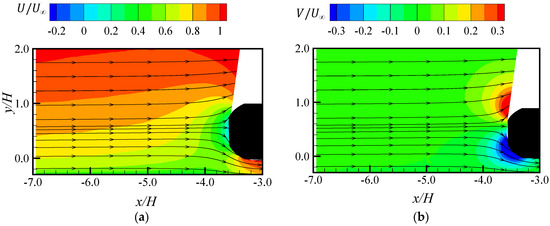
Figure 4.
Contours of (a) streamwise mean velocity (); and (b) wall-normal mean velocity () upstream of the isolated Ahmed body.
3.2. Streamwise and Wall-Normal Mean Velocities in the Wake Region
Figure 5 shows the mean streamlines and the contours of the streamwise mean velocity used to investigate the effects of rear slant angle on the mean flow pattern between the two Ahmed bodies. For each test case, the upper and lower recirculation bubbles behind the leading model are well-resolved (spatially) and the reverse flow region is indicated by the zero-contour line. The recirculation bubbles are asymmetric, and the direction of the streamlines shows a stable focus [36] at the center of each bubble. The location of the focus of each bubble are summarized in Table 2 along with other relevant parameters of the recirculation region: the length (), area () and centroid of the reverse flow region. The length of the reverse flow region, is determined as the streamwise distance from the rear end of the body to the furthest point on the zero-contour line. The area and centroid of the reverse flow region are computed based on the methodology outlined in Pearson et al. [37]. It should be noted that the computed reverse flow area for DB_25 and DB_35 does not account for the reverse flow on the slanted edges as observed in previous investigations [19,21]. The plots show that the maximum reverse velocity, is independent of the rear slant angle, although the area and centroid of the reverse flow region varies for each test case (Table 2).
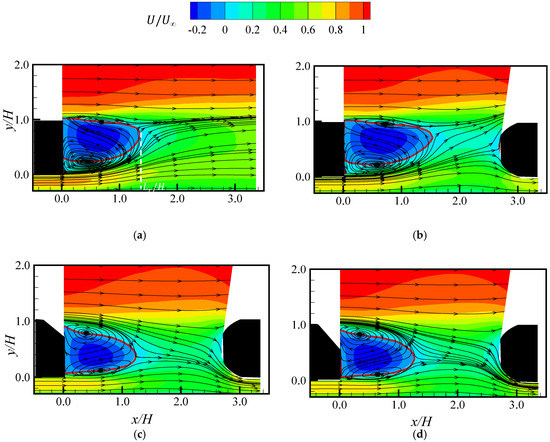
Figure 5.
Contours of streamwise mean velocity in the wake region of (a) SB_0; (b) DB_0; (c) DB_25; and (d) DB_35. The mean streamlines are superimposed on the contours. The line (red) represents the reverse flow region defined by the zero streamwise mean velocity contour line.

Table 2.
Statistics of the reverse flow region behind the leading Ahmed body.
The length of the reverse flow region behind the isolated square back model is . This value is comparable to reported in previous studies [10,38]. In the presence of a follower, the length of the reverse flow region behind the square back model () increased by 13%. However, the effect of rear slant angle decreased the values by and in the case of DB_25 and DB_35, respectively. Consequently, the mean reverse flow area,, is enhanced in the case of DB_0 (), but reduced in the case of DB_25 () and DB_35 () when compared to the area of the isolated model, SB_0 (). The values for DB_0 and DB_35 is comparable to values of 1.55 and 1.18, respectively reported by Murzyn et al. [10]. However, the corresponding value for DB_25 is larger (53%) than that of the previous study (0.58). The difference is attributed to the dynamic role of the C-pillar vortices that are dominant in the high-drag model. These C-pillar vortices are influenced by initial conditions such as Reynolds number and relative boundary layer thickness . The Reynolds number, , used in this study () is lower than used in the previous study. Moreover, the present Ahmed bodies were completely immersed in the turbulent boundary layer () but the previous study was conducted with a thin boundary layer thickness (). These differences in initial conditions contribute to the disparity in the values observed behind the high-drag model of the present study and that of Murzyn et al. [10].
The contours of the wall-normal mean velocity are presented in Figure 6. The contours and the streamlines demonstrate that the upwash of the jet-like flow beneath the square back model (SB_0) is stronger than the downwash from the upper edge. As a result, the size of the lower recirculation bubble is larger than that of the upper bubble, leading to a deflection of the flow further away from the bottom wall. The saddle point of the streamlines (marked as x) is, therefore, located closer to the upper edge (). At the presence of the second body (DB_0), the streamlines emanating from the upwash are bifurcated and deflected on either side of the follower, while the streamlines from the downwash are deflected over the upper edge of the follower. This leads to an enhanced region of wall-normal mean velocity near the upper rounded edge of the follower compared to the lower rounded edge. The stronger upwash from beneath the leading body would imply that pollutants from the vehicle exhaust may be carried into the air intake region of the follower, which may contribute to in-cabin air pollution. For the slanted rear-end models, the downwash is much stronger than the upwash due to the influence of the C-pillar vortices (DB_25) and the fully separated flow behind the leading model (DB_35). Consequently, the location of the saddle point is moved closer to the bottom wall () and the majority of the flow is deflected beneath the follower. This may suggest that in-cabin air pollution in a vehicle following a slanted rear-end vehicle may be reduced if the air intake point of the follower is farther away from the ground.
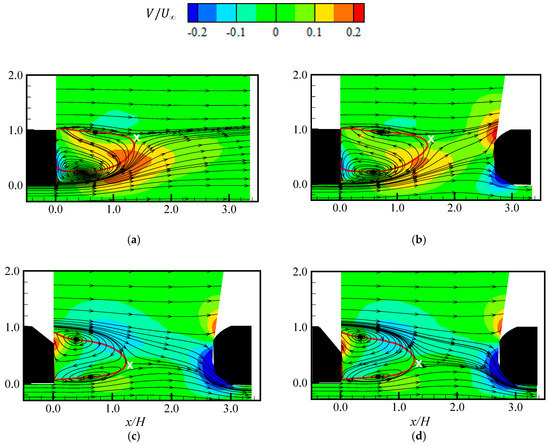
Figure 6.
Contours of wall-normal mean velocity in the wake region of (a) SB_0; (b) DB_0; (c) DB_25; and (d) DB_35. The mean streamlines are superimposed on the contours. The line (red) represents the reverse flow region defined by the zero streamwise mean velocity contour line. The mark x denotes the saddle point.
One-dimensional plots of the streamwise and wall-normal mean velocities at the selected streamwise location in the recirculation region (), the downstream wake () and at the front end of the follower () for the single and double Ahmed bodies are shown in Figure 7. The profiles are normalized by the local maximum mean velocity, and the height of the model. In the recirculation region and the wake, the profiles for the square back Ahmed bodies (SB_0 and DB_0) are in reasonable agreement with each other. However, the blockage by the follower (DB_0) significantly reduces the streamwise mean velocity but enhances the wall-normal mean velocity at the front end of the follower compared to the profiles of the isolated body. For the slanted rear-end Ahmed bodies, the profiles of the mean velocities are less sensitive to the differences in slant angle ( and ), although the distributions of the profiles are significantly different from that of the square back. For example, the streamwise mean velocity near the wall for the slanted rear-end models is reduced compared to those of the square backs, while the downwash of the flow (negative wall-normal mean velocity) at the front end of the follower is much stronger for the slanted rear-end models than the square backs.
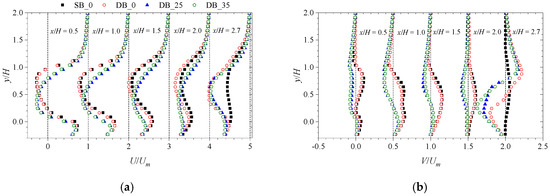
Figure 7.
Profiles (a) streamwise () and (b) wall-normal () mean velocities. The profiles of are offset at an interval of 1.0 and those of are offset at an interval of 0.5.
3.3. Reynolds Stresses and Turbulent Production in the Wake Region
The Reynolds stresses are used to investigate the effects of rear slant angle on the turbulent interaction between the Ahmed bodies. Figure 8 shows the contours of the streamwise Reynolds normal stress in the wake of the Ahmed bodies. For each test case, the contours show two main regions of concentrated on either side of the reverse flow region. These regions are associated with the upper and lower shear layers of the wake downstream of the leading model. For the square back models (SB_0 and DB_0), is significantly enhanced in the upper shear layer but reduced in the lower shear layer. The asymmetry of is attributed to the skewness of the mean flow away from the wall due to the strong upwash of the jet-like flow beneath the leading model. Consequently, the mean shear near the lower edge of the leading model is reduced while the shear near the upper edge is enhanced, leading to the high level of in the upper shear layer. Further downstream, decreases in both the upper and lower shear layers, however, the reduction is much slower for DB_0 due to the presence of the follower. Unlike the square back models, the contours of for DB_25 and DB_35 show the opposite trend where is enhanced in the lower shear layer and decreased in the upper shear layer. This should be expected, since the mean shear in the upper layer is reduced while that in the lower layer is enhanced due to the strong downwash of the mean flow.
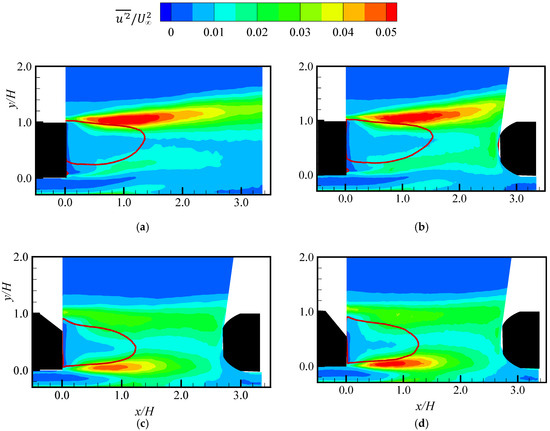
Figure 8.
Contours of streamwise Reynolds normal stress in the wake region of (a) SB_0; (b) DB_0; (c) DB_25; and (d) DB_35. The line (red) represents the reverse flow region defined by the zero streamwise mean velocity contour line.
Contours of the wall-normal Reynolds normal stress and the Reynolds shear stress are presented in Figure 9 and Figure 10, respectively. Similar to , the spatial distributions and intensities of and exhibit asymmetry which is influenced by the wall effect and the rear slant angle. The presence of the follower also restricts the outward growth of and in the shear layers of each test case. It is worth noting that the intensities and spatial distributions of the Reynolds stresses are in good agreement with results reported in the wake region of a single [20,39] and double Ahmed bodies [10]. Figure 11 shows contours of the production term of the turbulent kinetic energy () transport equation used to examine the effect of the rear slant angle on the turbulence energy source. Since the spanwise velocity component was not measured, the production of turbulence was evaluated based on the streamwise and wall-normal components as follows:
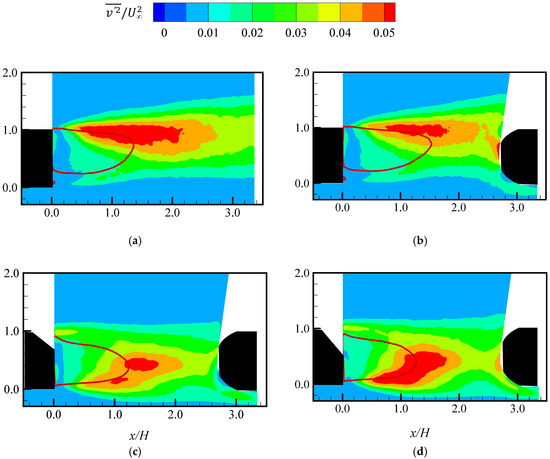
Figure 9.
Contours of wall-normal Reynolds normal stress in the wake region of (a) SB_0; (b) DB_0; (c) DB_25; and (d) DB_35. The line (red) represents the reverse flow region defined by the zero streamwise mean velocity contour line.
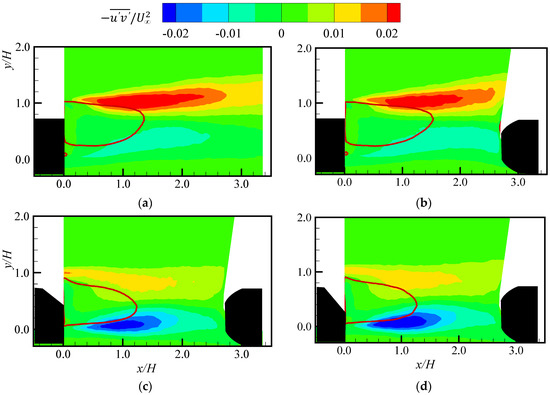
Figure 10.
Contours of Reynolds shear stress in the wake region of (a) SB_0; (b) DB_0; (c) DB_25; and (d) DB_35. The line (red) represents the reverse flow region defined by the zero streamwise mean velocity contour line.
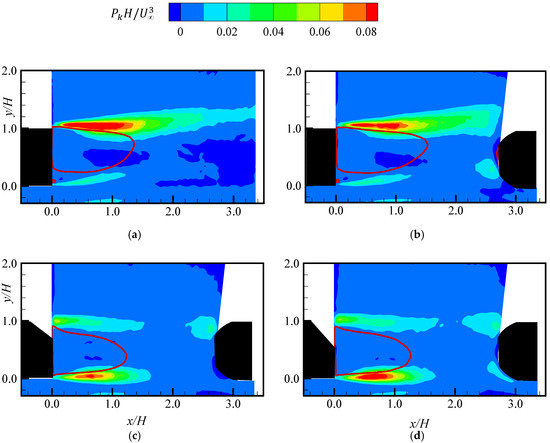
Figure 11.
Contours of production of turbulent kinetic energy in the wake region of (a) SB_0; (b) DB_0; (c) DB_25; and (d) DB_35. The line (red) represents the reverse flow region defined by the zero streamwise mean velocity contour line.
For each test case, the production of turbulence is enhanced in the shear layers on either side of the reverse flow region due to the large mean shear and Reynolds shear stress. In agreement with the contours of the Reynolds stresses, the turbulence production is more intense in the upper shear layer of the square back test cases and persists further downstream than in the lower shear layer. On the other hand, the turbulence production is larger in the lower shear layer of DB_25 and DB_35 but decays much faster, leaving clusters near the rounded edges of the follower. The break between the high-production region and the clusters near the follower is attributed to the strong downwash in the wake region of these test cases (Figure 5 and Figure 6).
To perform a more quantitative comparison between the single and double Ahmed bodies, the profiles of the Reynolds stresses and the production term of the turbulent kinetic energy () transport equation are shown in Figure 12. The profiles of the Reynolds stresses for SB_0 and DB_0 collapse reasonably well on each other at each streamwise location. This indicates that, for the present spacing ratio, the Reynolds stresses behind the square back Ahmed body are less sensitive to the effects of blockage by the follower. For DB_25 and DB_35, the Reynolds stresses are enhanced in the region near the wall, which contrasts with the profiles for SB_0 and DB_0. Throughout the wake region, the profiles for DB_25 and DB_35 are in good agreement, except at the front end of the follower where is larger in the case of DB_35. The production of turbulence (Figure 12d) is locally highest immediately downstream of the rear edges of the leading model but decreases to negligible values farther downstream due to the diminishing mean shear. Moreover, the turbulence production attains peak values in the upper shear layer of SB_0 and DB_0 and near the wall for DB_25 and DB_35. However, the peak values of the profiles for DB_25 and DB_35 diminish faster than those of the square back Ahmed bodies.
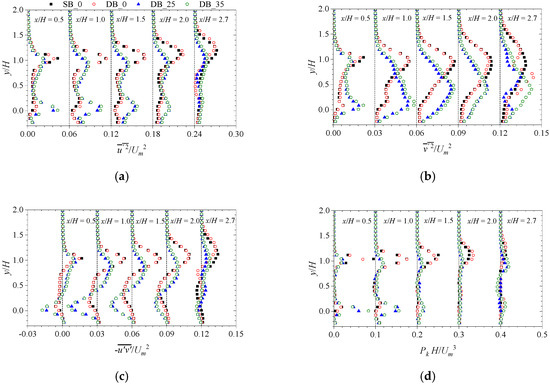
Figure 12.
The profiles of (a) streamwise and (b) wall-normal Reynolds normal stresses; (c) Reynolds shear stress; and (d) production of turbulent kinetic energy . The profiles of , and are offset at an interval of 0.06, 0.03, 0.03 and 0.1, respectively.
3.4. Instantaneous Flow Structures
The evolution of vortical structures shed from the rear end of the Ahmed body plays a significant role in the transport of momentum and mass downstream of the body. This can be used to provide insight into the influence of rear slant angle on pollutant transport between the two vehicles. Figure 13 shows contours of instantaneous swirling strength used to extract the vortical structures in the wake of the four test cases, SB_0, DB_0, DB_25 and DB_35. The swirling strength, is the magnitude of the imaginary part of the complex eigenvalues of the local velocity gradient tensor [40]. Since the swirling strength is always positive, the local vorticity fluctuation is used to sign the swirls to provide insight into the rotational direction of the vortices as follows [41]:
where is the signed swirling strength, is the spanwise vorticity fluctuations and represent the absolute value. The positive swirls () are known as retrogrades (counter-clockwise rotating structures), while the negative swirls () are known as progrades (clockwise rotating structures). Superimposed on the contours are the Galilean decomposition of the instantaneous flow fields which augments the vortices revealed by the swirling strength. Here, the small-scale vortices are displayed as “circular” patterns of the velocity vectors. Based on a sensitivity test, the convection velocity used for the Galilean decomposition was and for SB_0, DB_0, DB_25 and DB_35, respectively. To demarcate the reverse flow region () behind the leading body, the contour line representing the zero streamwise mean velocity is added to each plot.
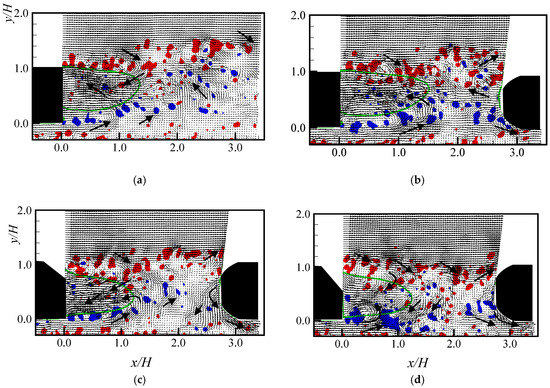
Figure 13.
Galilean decomposition of instantaneous velocity fields with superimposed positive (retrograde (red)) and negative (prograde (blue)) swirling strength contours for (a) SB_0; (b) DB_0; (c) DB_25; and (d) DB_35. The contour level of the swirling strength is and the line (green) represents the reverse flow region defined by the zero streamwise mean velocity contour line.
For each test case, the instantaneous velocity vectors demonstrate the downwash of the separated flow near the upper rear edge of the leading body and the upwash of the jet-like flow beneath the body. Part of the downwash and upwash flow are deflected backwards to form the reverse flow region. Near the follower (DB_0, DB_25 and DB_35), the downwash of the deflected flow beneath the body is more intense than the upwash over the upper rounded front end. For the isolated square back (SB_0), the progrades are shed from the lower rear edge of the body while the retrogrades are shed from the upper rear edge. These vortices are mostly located outside the reverse flow region, although a smaller number of vortices are found inside. The vortices appear to evolve further away into the freestream as the wake develops downstream. This observation may depict the dispersion pattern of particulate pollutants behind square back vehicles. Near the wall, the traces of retrogrades are generated by the interaction of the jet-like flow beneath the leading model with the bottom wall. With the presence of a follower (DB_0), the streamwise evolution of the vortices is restricted, leading to the congestion of the vortices in the spacing between the two bodies. For the high-drag model (DB_25), the vortices appear to show similar distribution as the isolated body, but the progrades decay faster, perhaps due to the blockage by the follower. On the other hand, the progrades and retrogrades behind the low-drag model (DB_35) are highly disorganized beyond the reverse flow region and appear to be washed down towards the bottom wall compared to the other cases. The downwash is attributed to the fully separated flow behind the low-drag Ahmed body [13,19]. The present observations support the notion that the rear slant angle has a significant influence on the dispersion of pollutants in the spacing between two passenger vehicles.
4. Conclusions
In this study, particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements were conducted around single and double in-line Ahmed bodies to investigate the effect of rear slant angle on the mean flow and turbulence statistics in the wake region of the Ahmed bodies. The experiments were conducted at a fixed Reynolds number, , and inter-vehicle spacing distance of , where and are the height and length of the model. Three rear slant angles of the leading Ahmed body were investigated: a reference square back (), high-drag angle () and low-drag angle (). The results showed that the presence of a follower behind a square back Ahmed body increased the length of the reverse flow region by 13%. However, increasing the rear slant angle of the leading model decreased the length of the reverse flow region by 7% and 10% for and , respectively.
The instantaneous velocity fields and the mean velocities showed that the changes to the reverse flow region and the wake characteristics between the two bodies are influenced by two dominant motions: a downwash of the separated flow near the upper rear edge of the leading body and an upwash of the jet-like flow near the lower rear edge. For the square back model, the upwash of the mean flow away from the wall was stronger than the downwash, while the downwash is much stronger than the upwash for the slanted rear-end models. As a result, the Reynolds stresses and the production of turbulent kinetic energy were enhanced in the upper shear layer behind the square back Ahmed bodies but reduced in the lower shear layer. On the other hand, these turbulent quantities were larger in the lower shear layer of the slanted rear-end bodies. The vortical structures examined using the instantaneous swirling strength showed that increasing the rear slant angle modifies the streamwise evolution of the structures in the wake region. The presence of the follower was also found to restrict the outward spread of the vortical structures, leading to their congestion in the spacing between the two bodies.
Given the influence of the wake dynamics on the transport of pollutants between two vehicles, the physical insight from this study can be adopted in the future development of reduced-order models for active closed-loop/feedback flow control strategies for minimizing in-cabin air pollution. Active feedback control systems with the aid of artificial intelligence (AI) in modern vehicles can be used to regulate the air intake and ventilation systems of vehicles to reduce in-cabin air pollution in congested traffic conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; methodology, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; software, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; validation, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; formal analysis, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; investigation, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; resources, R.B.; data curation, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; writing—original draft preparation, E.E. and S.D.; writing—review and editing, E.E. and R.B.; visualization, E.E., S.D. and R.B.; supervision, E.E. and R.B.; project administration, E.E. and R.B.; funding acquisition, E.E. and R.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada through NSERC Postdoctoral Fellowship for E.E. and NSERC Discovery Grant for R.B.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Knibbs, L.D.; de Dear, R.J. Exposure to ultrafine particles and PM2.5 in four Sydney transport modes. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3224–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhu, Y. Investigation on lowering commuters’ in-cabin exposure to ultrafine particles. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 18, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquier, A.; André, M. Considering criteria related to spatial variabilities for the assessment of air pollution from traffic. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 3354–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.Q.; Koehoorn, M.; Davies, H.W.; Demers, P.A.; Tamburic, L.; Brauer, M. Long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution and the risk of coronary heart disease hospitalization and mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, M.; Hoek, G.; Van Vliet, P.; Meliefste, K.; Fischer, P.H.; Wijga, A.; Koopman, L.P.; Neijens, H.J.; Gerritsen, J.; Kerkhof, M.; et al. Air pollution from traffic and the development of respiratory infections and asthmatic and allergic symptoms in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Morawska, L. A review of commuter exposure to ultrafine particles and its health effects. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rank, J.; Folke, J.; Homann Jespersen, P. Differences in cyclists and car drivers exposure to air pollution from traffic in the city of Copenhagen. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 279, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulliver, J.; Briggs, D.J. Personal exposure to particulate air pollution in transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Kostenidou, E.; Sioutas, C.; Delfino, R.J.; Fruin, S.A. Vehicle and driving characteristics that influence in-cabin particle number concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8691–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murzyn, F.; Fokoua, G.; Rodriguez, R.; Shen, C.; Larrarte, F.; Mehel, A. Car Wake Flows and Ultrafine Particle Dispersion: From Experiments to Modelling. Atmosphere 2019, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Colvile, R.N. Fine particulate matter and carbon monoxide exposure concentrations in urban street transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4781–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Esber, L.; El-Fadel, M. Indoor to outdoor air quality associations with self-pollution implications inside passenger car cabins. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Ramm, G.; Faltin, G. Some Salient Features of the Time -Averaged Ground Vehicle Wake. SAE Trans. 1984, 473–503. [Google Scholar]
- Minguez, M.; Pasquetti, R.; Serre, E. High-order large-eddy simulation of flow over the “Ahmed body” car model. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.F.; Zhou, Y.; To, S. Unsteady flow structures around a high-drag Ahmed body. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 777, 291–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnović, S. Large Eddy Simulation Exploration of Passive Flow Control Around an Ahmed Body. J. Fluids Eng. 2014, 136, 121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, J.F.; Aider, J.L. Drag and lift reduction of a 3D bluff body using flaps. Exp. Fluids 2008, 44, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hucho, W.-H.; Sovran, G. Aerodynamics of Road Vehicles. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1993, 25, 485–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Minelli, G.; Basara, B.; Krajnović, S. On the two flow states in the wake of a hatchback Ahmed body. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 173, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunay, T.; Sahin, B.; Ozbolat, V. Effects of rear slant angles on the flow characteristics of Ahmed body. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2014, 57, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Zhou, Y.; Pin, Y.F.; Chan, T.L. Turbulent near wake of an Ahmed vehicle model. Exp. Fluids 2013, 54, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnović, S.; Davidson, L. Influence of floor motions in wind tunnels on the aerodynamics of road vehicles. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2005, 93, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, S.; Vino, G. The effect of vehicle spacing on the aerodynamics of a representative car shape. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Krajnović, S. Large Eddy Simulations of Flow around Two Generic Vehicles in a Platoon. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Jets, Wakes and Separated Flows (ICJWSF2015), Stockholm, Sweden, 15–18 June 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, M.; Pavlenko, A. Experimental and Numerical Study of Flow Structures between Two Ahmed Bodies with Various Inter-Body Distances; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, M.; Krajnović, S. Numerical Study of Aerodynamic Interactions in a Homogeneous Multi-vehicle Formation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Jets, Wakes and Separated Flows (ICJWSF2015), Stockholm, Sweden, 15–18 June 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Gnatowska, R.; Sosnowski, M. The influence of distance between vehicles in platoon on aerodynamic parameters. EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 180, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, R.J.; Westerweel, J. Particle Image Velocimetry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, H.; Steele, W. Engineering application of experimental uncertainty analysis. AIAA J. 1995, 33, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Roussinova, V.; Biswas, N.; Balachandar, R. Revisiting turbulence in smooth uniform open channel flow. J. Hydraul. Res. 2008, 46, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, B.; Faruque, M.A.; Balachandar, R. Effect of Reynolds number, near-wall perturbation and turbulence on smooth open-channel flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 2009, 47, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezu, I.; Nakagawa, H. Turbulent Open-Channel Flows (IAHR Monograph); AA Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Tachie, M.F.; Balachandar, R.; Bergstrom, D.J. Low Reynolds number effects in open-channel turbulent boundary layers. Exp. Fluids 2003, 34, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S. Automotive Air Conditioning and Climate Control Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, A.E.; Steiner, T.R. Large-scale vortex structures in turbulent wakes behind bluff bodies. Part 1. Vortex formation processes. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 174, 233–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.S.; Goulart, P.J.; Ganapathisubramani, B. Turbulent separation upstream of a forward-facing step. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 724, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumejeau, B.; Delprat, S.; Keirsbulck, L.; Lippert, M.; Abassi, W. Ultra-local model-based control of the square-back Ahmed body wake flow. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 85103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandemange, M.; Gohlke, M.; Cadot, O. Turbulent wake past a three-dimensional blunt body. Part 1. Global modes and bi-stability. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 722, 51–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Adrian, R.J.; Balachandar, S.; Kendall, T.M. Mechanisms for generating coherent packets of hairpin vortices in channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 387, 353–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Christensen, K.T. Population trends of spanwise vortices in wall turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 568, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).