Ozone Layer Evolution in the Early 20th Century
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
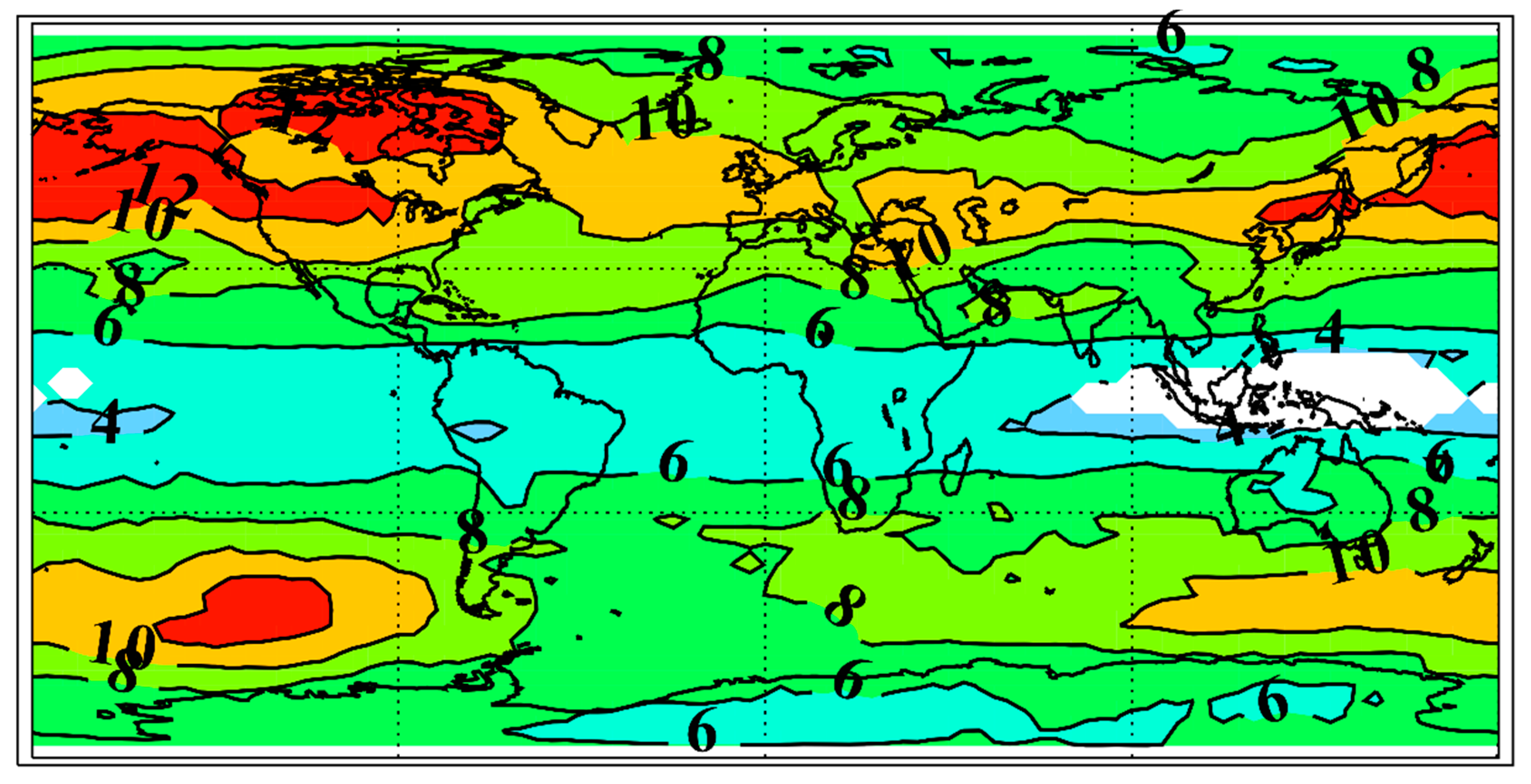
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Ozone Layer Evolution Drivers
3.1.1. Active Hydrogen Oxides
3.1.2. Nitrogen Oxides
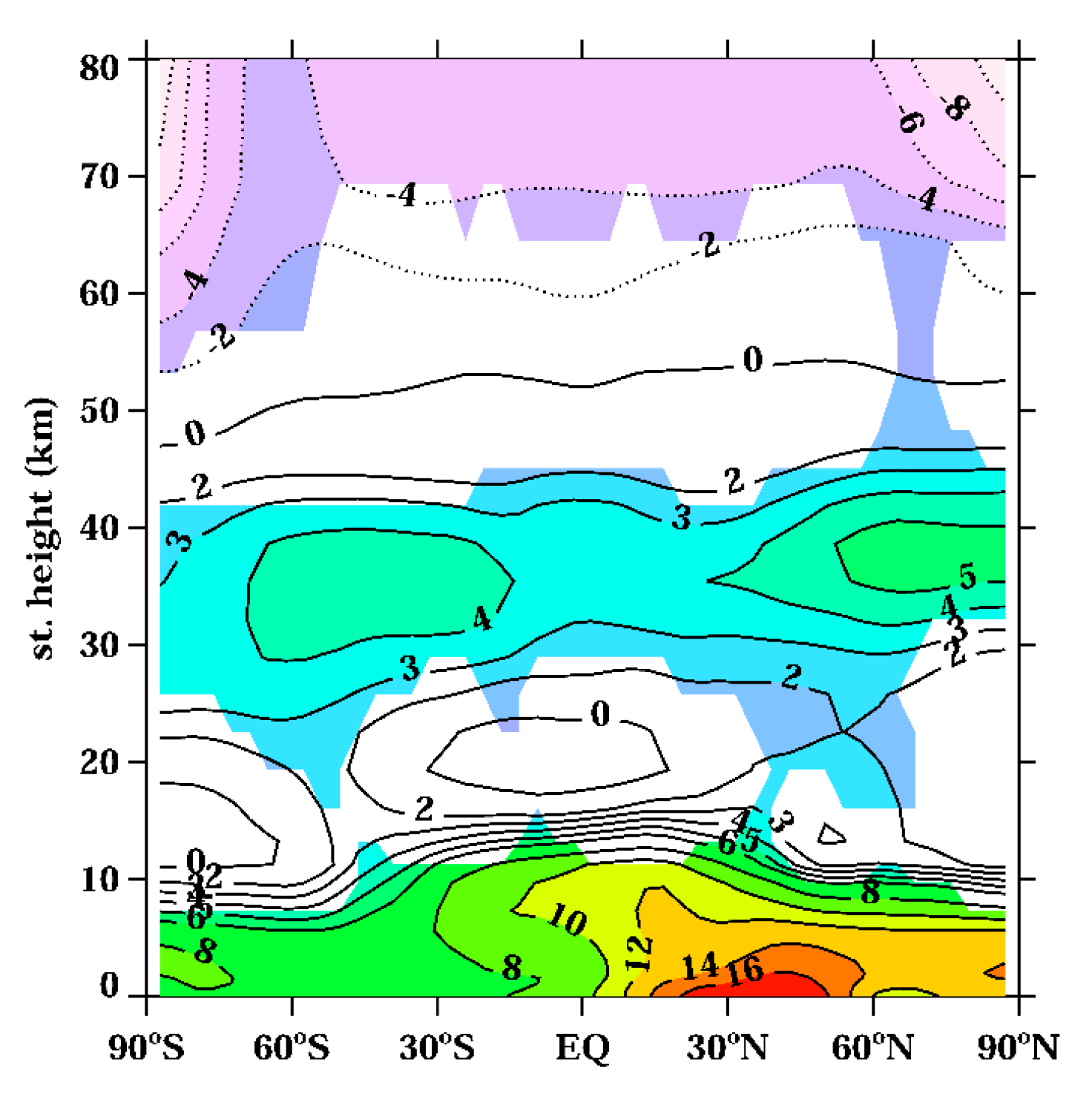
3.1.3. Temperature
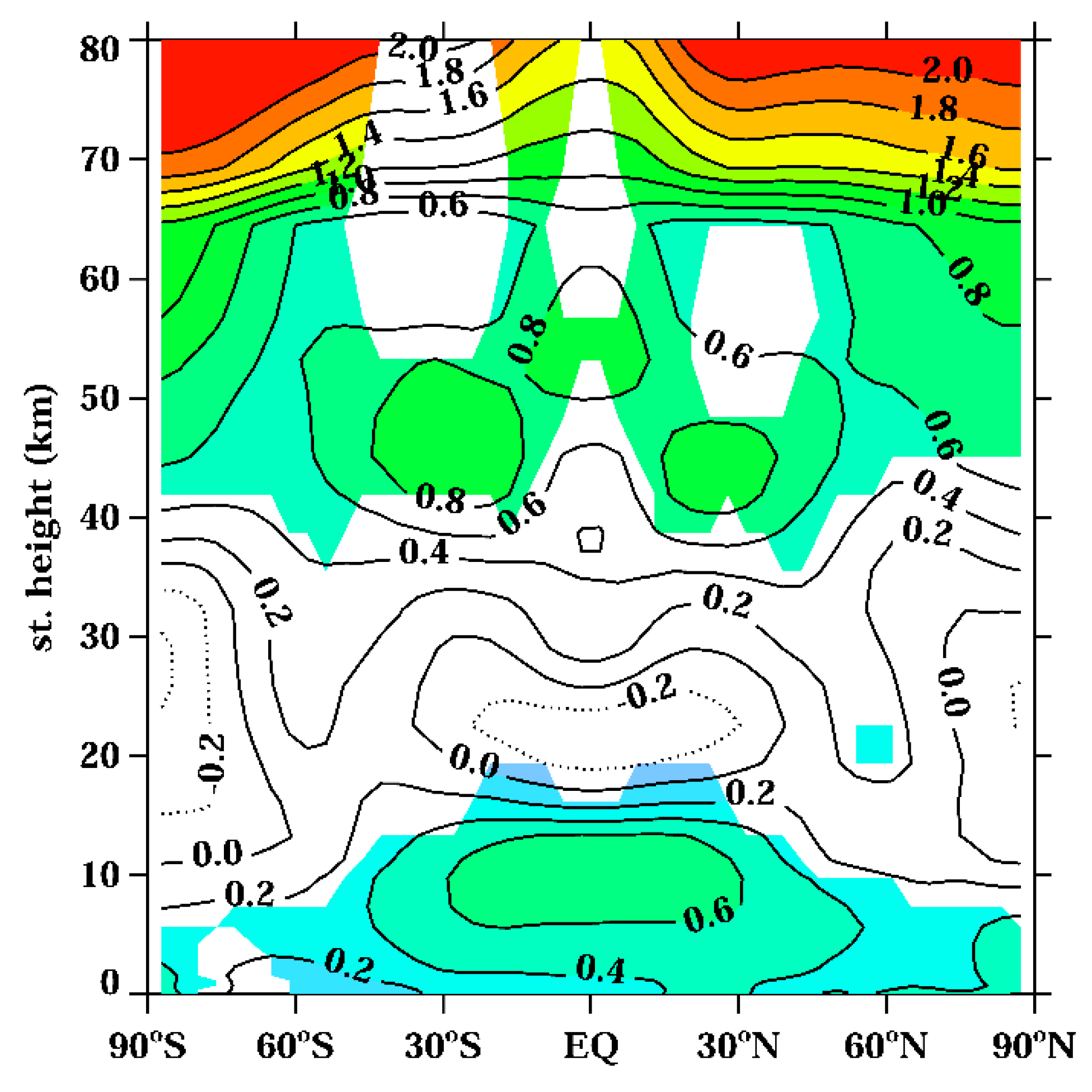
3.2. Analysis of the Ozone Layer Evolution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bais, A.F.; Lucas, R.M.; Bornman, J.F.; Williamson, C.E.; Sulzberger, B.; Austin, A.T.; Wilson, S.R.; Andrady, A.L.; Bernhard, G.; McKenzie, R.L.; et al. Environmental effects of ozone depletion, UV radiation and interactions with climate change: UNEP Environmental Effects Assessment Panel, update 2017. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 17, 127–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häder, D.-P.; Barnes, P.W. Comparing the impacts of climate change on the responses and linkages between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WMO (World Meteorological Organization). Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2018; Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project—Report No. 58; WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; 588p. [Google Scholar]
- Volz, A.; Kley, D. Evaluation of the Montsouris series of ozone measurements made in the nineteenth century. Nature 1988, 332, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenco, A.; Gouget, H.; Nedelec, P.; Pages, J.-P. Evidence of a long-term increase in tropospheric ozone from Pic du Midi data series: Consequences: Positive radiative forcing. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 16617–16632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauglustaine, D.A.; Brasseur, G.P. Evolution of tropospheric ozone under anthropogenic activities and associated radiative forcing of climate. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 32337–32360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalita, S.; Hauglustaine, D.A.; Letreut, H.; Müller, J.-F. Radiative forcing due to increased tropospheric ozone concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickley, L.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Rind, D. Uncertainty in preindustrial abundance of tropospheric ozone: Implications for radiative forcing calculations. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 3389–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindell, D.T.; Faluvegi, G.; Bell, N. Preindustrial-to-present-day radiative forcing by tropospheric ozone from improved simulations with the GISS chemistry-climate GCM. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 1675–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarque, J.-F.; Hess, P.; Emmons, L.; Buja, L.; Washington, W.; Granier, C. Tropospheric ozone evolution between 1890 and 1990. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 110, D08304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrella, J.P.; Jacob, D.J.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Mickley, L.J.; Miller, B.F.; Evans, M.J.; Yang, X.; Pyle, J.A.; Theys, N.; et al. Tropospheric bromine chemistry: implications for present and pre-industrial ozone and mercury. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 6723–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.J.; Archibald, A.T.; Bowman, K.W.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Naik, V.; Stevenson, D.S.; Tilmes, S.; Voulgarakis, A.; Wild, O.; Bergmann, D. Pre-industrial to end 21st century projections of tropospheric ozone from the Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Model Intercomparison Project (ACCMIP). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2063–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reader, M.C.; Plummer, D.A.; Scinocca, J.F.; Shepherd, T.G. Contributions to twentieth century total column ozone change from halocarbons, tropospheric ozone precursors, and climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 6276–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hollaway, M.J.; Arnold, S.R.; Collins, W.J.; Folberth, G.; Rap, A. Sensitivity of midnineteenth century tropospheric ozone to atmospheric chemistry-vegetation interactions. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 122, 2452–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, E.L.; Jackman, C.H.; Stolarski, R.S.; Douglass, A.R. A model study of the impact of source gas changes on the stratosphere for 1850–2100. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8515–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, J. Evolution of Total Atmospheric Ozone from 1900 to 2100 Estimated with Statistical Models. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 1956–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, T.; Schmutz, W.; Rozanov, E.; Shapiro, A.I.; Usoskin, I.; Beer, J.; Tagirov, R.V.; Peter, T. Revised historical solar irradiance forcing. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 615, A85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegerl, G.C.; Brönnimann, S.; Schurer, A.; Cowan, T. The early 20th century warming: anomalies, causes, and consequences. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, T.; Rozanov, E.; Arsenovic, P.; Peter, T.; Schmutz, W. Contributions of Natural and Anthropogenic Forcing Agents to the Early 20th Century Warming. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthers, S.; Anet, J.G.; Stenke, A.; Raible, C.C.; Rozanov, E.; Brönnimann, S.; Peter, T.; Arfeuille, F.X.; Shapiro, A.I.; Beer, J.; et al. The coupled atmosphere-chemistry-ocean model SOCOL MPIOM. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2014, 7, 2157–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenovic, P.; Rozanov, E.; Anet, J.; Stenke, A.; Peter, T. Implications of potential future grand solar minimum for ozone layer and climate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3469–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenke, A.; Schraner, M.; Rozanov, E.; Egorova, T.; Luo, B.; Peter, T. The SOCOL version 3.0 chemistry–climate model: description, evaluation, and implications from an advanced transport algorithm. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2013, 6, 1407–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeckner, E.; Bäuml, G.; Bonaventura, L.; Brokopf, R.; Esch, M.; Giorgetta, M.; Hagemann, S.; Kirchner, I.; Kornblueh, L.; Manzini, E.; et al. The Atmospheric General Circulation Model ECHAM5. Part I: Model Description; Report No. 349; Max Planck Institute for Meteorology: Hamburg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rozanov, E.V.; Zubov, V.; Schlesinger, M.E.; Yang, F.; Andronova, N.G. The UIUC three-dimensional stratospheric chemical transport model: description and evaluation of the simulated source gases and ozone. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 11755–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, T.; Rozanov, E.; Zubov, V.; Karol, I. Model for investigating ozone trends (MEZON). Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2003, 39, 277–292. [Google Scholar]
- Marsland, S.J.; Haak, H.; Jungclaus, J.H.; Latif, M. The Max-Planck-Institute global ocean/sea ice model with orthogonal curvilinear coordinates. Ocean Model. 2003, 5, 91–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungclaus, J.H.; Keenlyside, N.; Botzet, M.; Haak, H.; Luo, J.-J.; Latif, M.; Marotzke, J.; Mikolajewicz, U.; Roeckner, E. Ocean Circulation and Tropical Variability in the Coupled Model ECHAM5/MPI-OM. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3952–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.I.; Schmutz, W.; Rozanov, E.; Schoell, M.; Haberreiter, M.; Shapiro, A.V.; Nyeki, S. A new approach to the long-term reconstruction of the solar irradiance leads to large historical solar forcing. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 529, A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhodolov, T.; Rozanov, E.; Shapiro, A.I.; Anet, J.; Cagnazzo, C.; Peter, T.; Schmutz, W. Evaluation of the ECHAM family radiation codes performance in representation of the solar signal. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2014, 7, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthes, K.; Funke, B.; Andersson, M.E.; Barnard, L.; Beer, J.; Charbonneau, P.; Clilverd, M.A.; de Wit, T.D.; Haberreiter, M.; Hendry, A.; et al. Solar forcing for CMIP6 (v3. 2). Geosci. Model. Dev. 2017, 10, 2247–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinshausen, M.; Smith, S.J.; Calvin, K.; Daniel, J.S.; Kainuma, M.L.T.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Matsumoto, K.; Montzka, S.A.; Raper, S.C.B.; Riahi, K.; et al. The RCP greenhouse gas concentrations and their extensions from 1765 to 2300. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.J.; Beer, J.; Geller, M.; Haigh, J.D.; Lockwood, M.; Matthes, K.; Cubasch, U.; Fleitmann, D.; Harrison, R.G.; Hood, L.; et al. Solar influence on climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, G.P.; Solomon, S. Aeronomy of the Middle Atmosphere: Chemistry and Physics of the Stratosphere and Mesosphere; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 32, p. 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larin, I. On the chain length and rate of ozone depletion in the main stratospheric cycles. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2013, 3, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, I.A.; Aplin, K.L.; Arnold, F.; Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Harrison, R.G.; Krivolutsky, A.A.; Nicoll, K.A.; Rozanov, E.V.; Turunen, E.; Usoskin, I.G. Energetic Particle Influence on the Earth’s Atmosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 194, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarnato, B.; Staehelin, J.; Stübi, R.; Schill, H. Long-term total ozone observations at Arosa (Switzerland) with Dobson and Brewer instruments (1988–2007). J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozema, J.; van Geel, B.; Bjorn, L.O.; Lean, J.; Madronich, S. PALEOCLIMATE: Toward Solving the UV Puzzle. Science 2002, 296, 1621–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, D. Past UV-B flux from fossil pollen: Prospects for climate, environment and evolution. New Phytol. 2011, 192, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jardine, P.E.; Fraser, W.T.; Gosling, W.D.; Roberts, C.N.; Eastwood, W.J.; Lomax, B.H. Proxy reconstruction of ultraviolet-B irradiance at the Earth’s surface, and its relationship with solar activity and ozone thickness. Holocene 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, W.T.; Rozanov, E.; Alsing, J.; Marsh, D.R.; Tummon, F.; Mortlock, D.J.; Kinnison, D.; Haigh, J.D. The upper stratospheric solar cycle ozone response. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, L.Y.; Murray, L.T.; Martinerie, P.; Witrant, E.; Hu, H.; Banerjee, A.; Orsi, A.; Chappellaz, J. Isotopic constraint on the twentieth-century increase in tropospheric ozone. Nature 2019, 570, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubov, V.; Rozanov, E.; Egorova, T.; Karol, I.; Schmutz, W. Role of external factors in the evolution of the ozone layer and stratospheric circulation in 21st century. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4697–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
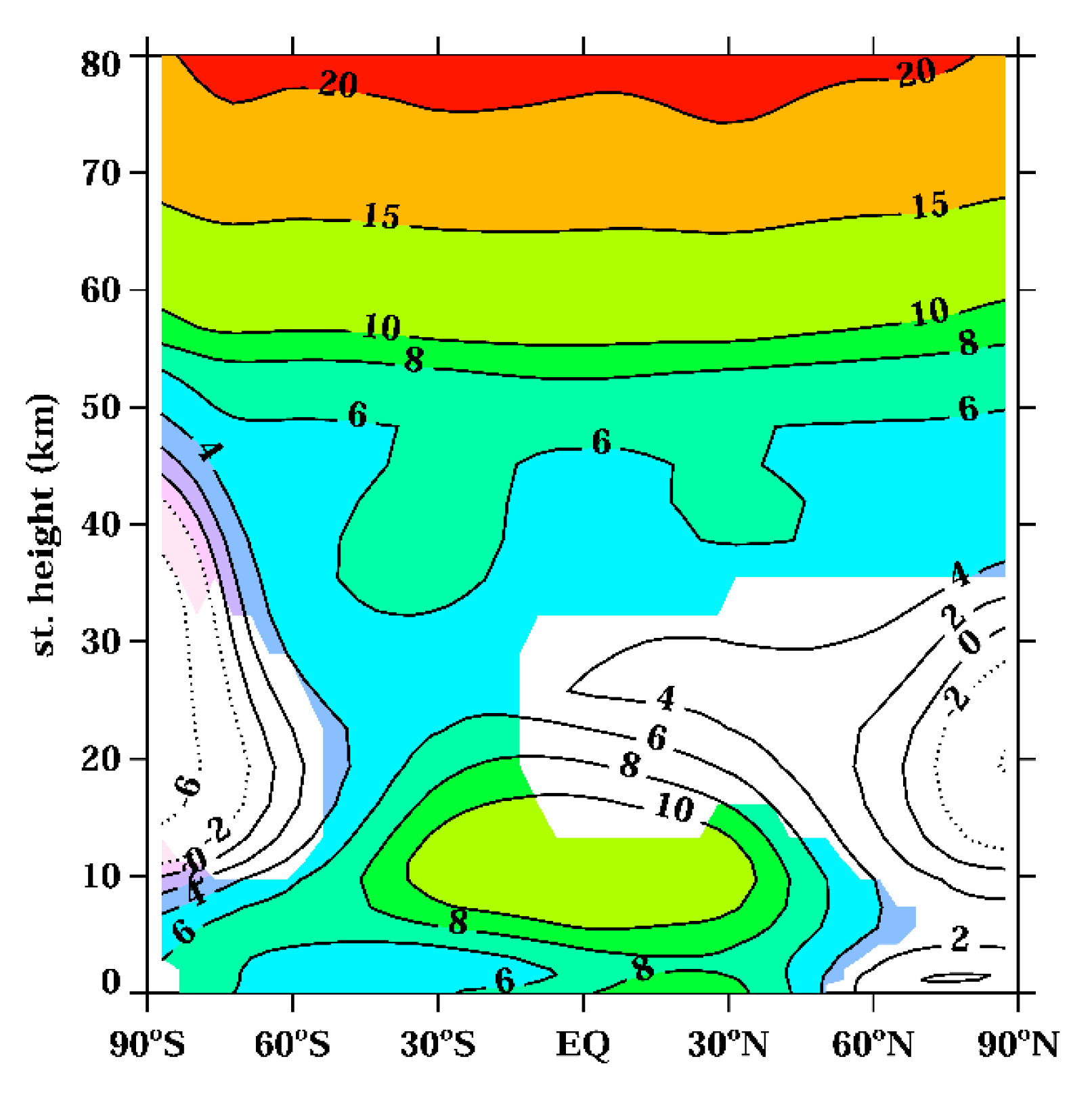
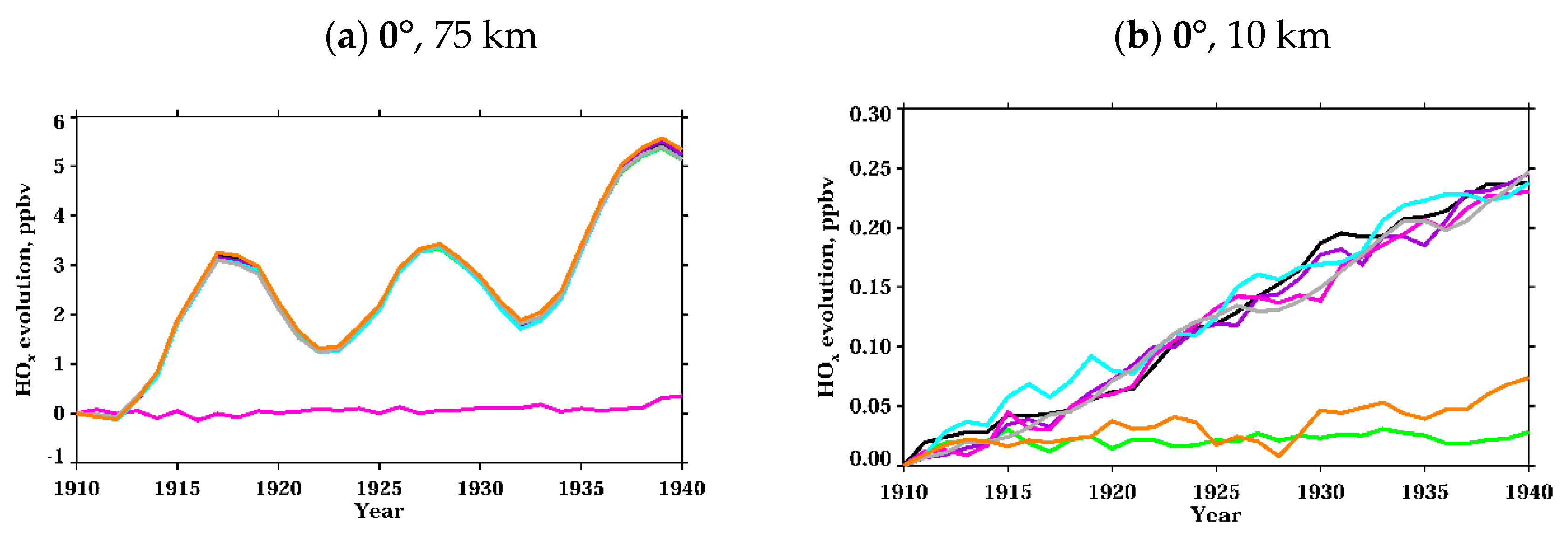
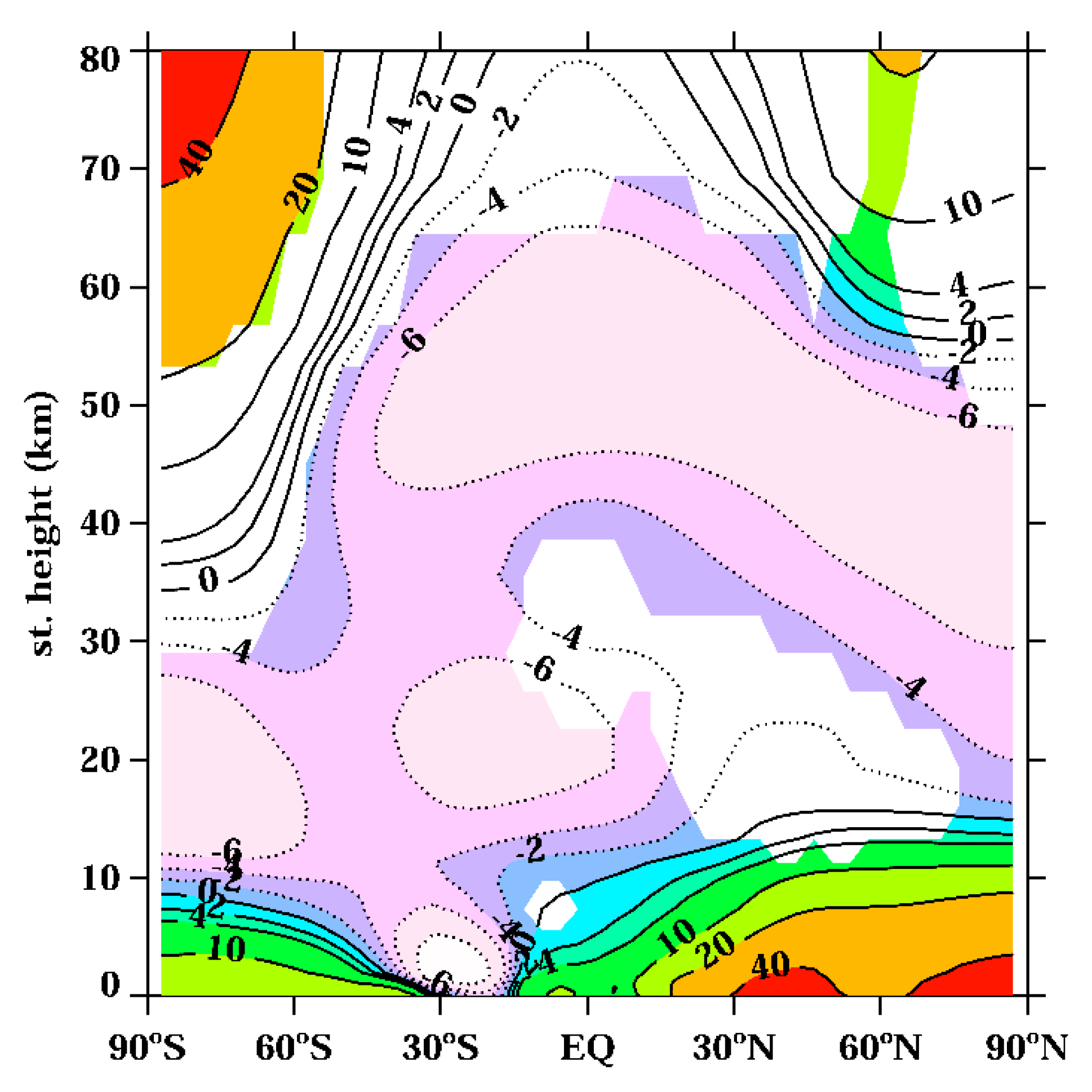
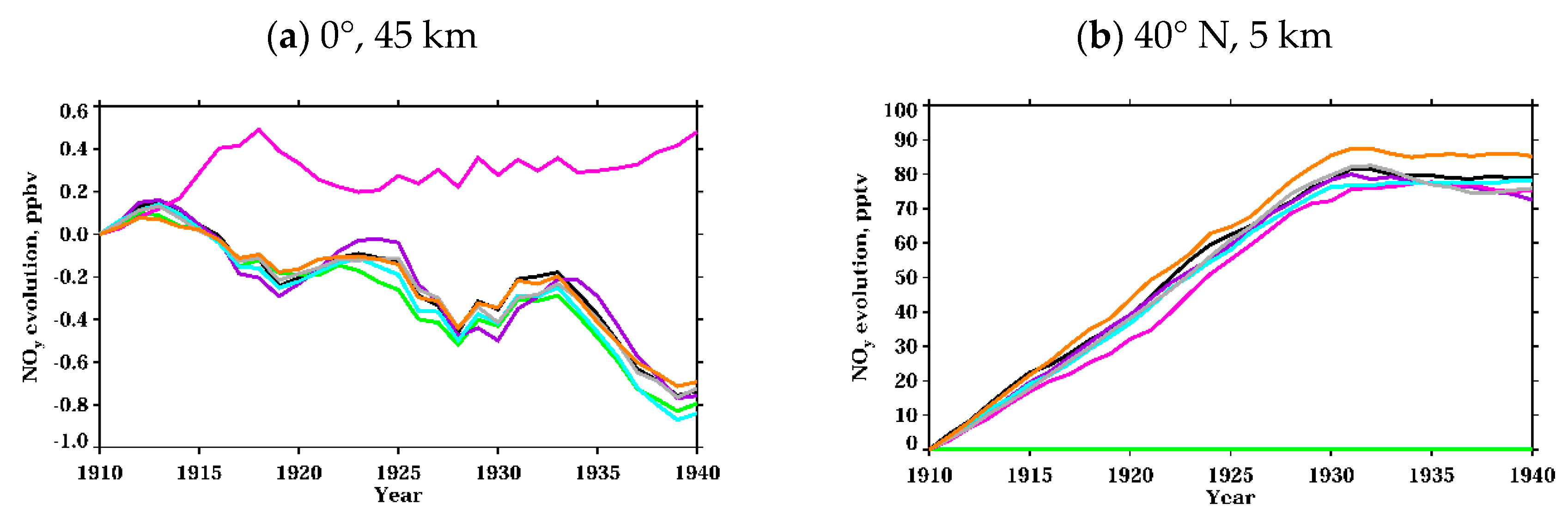
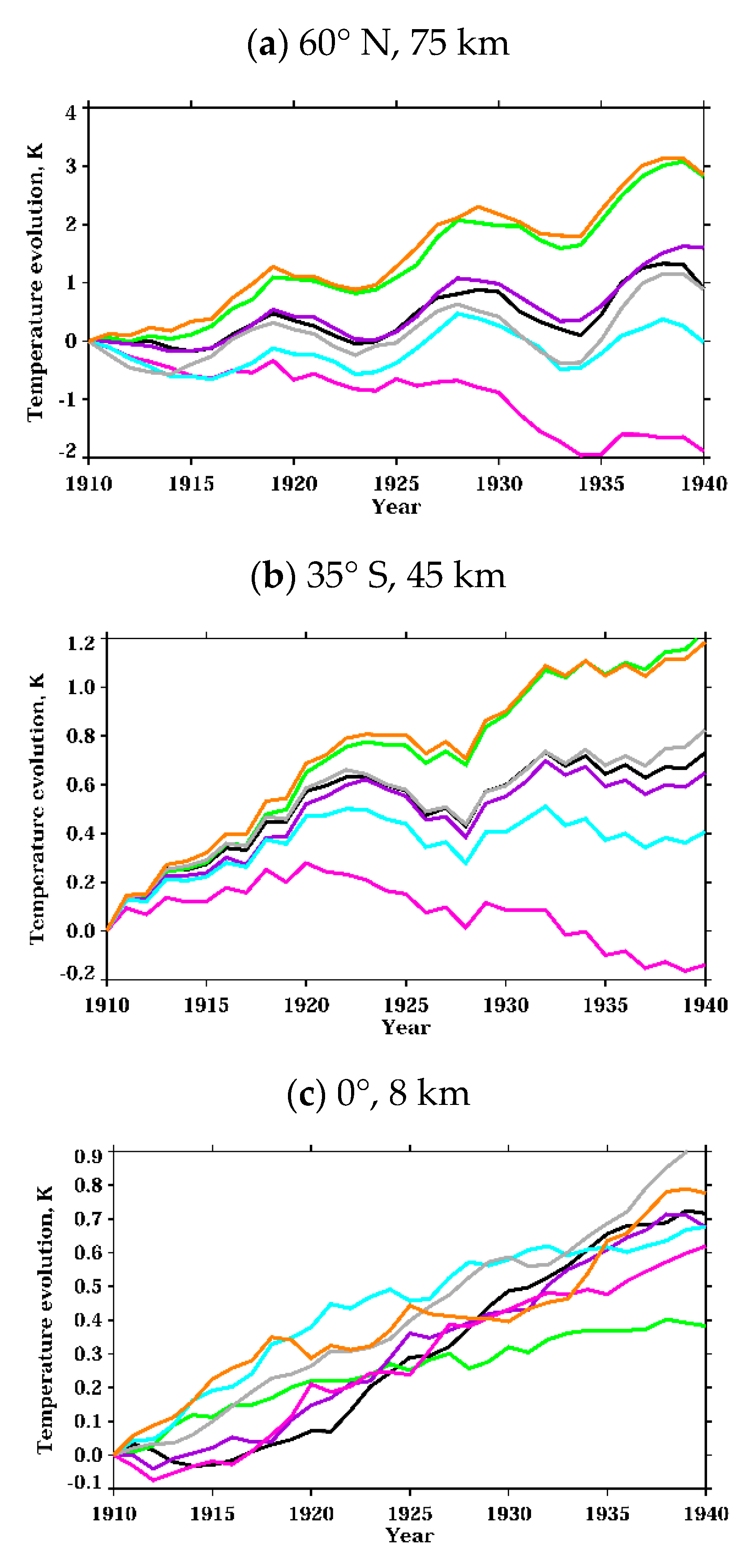
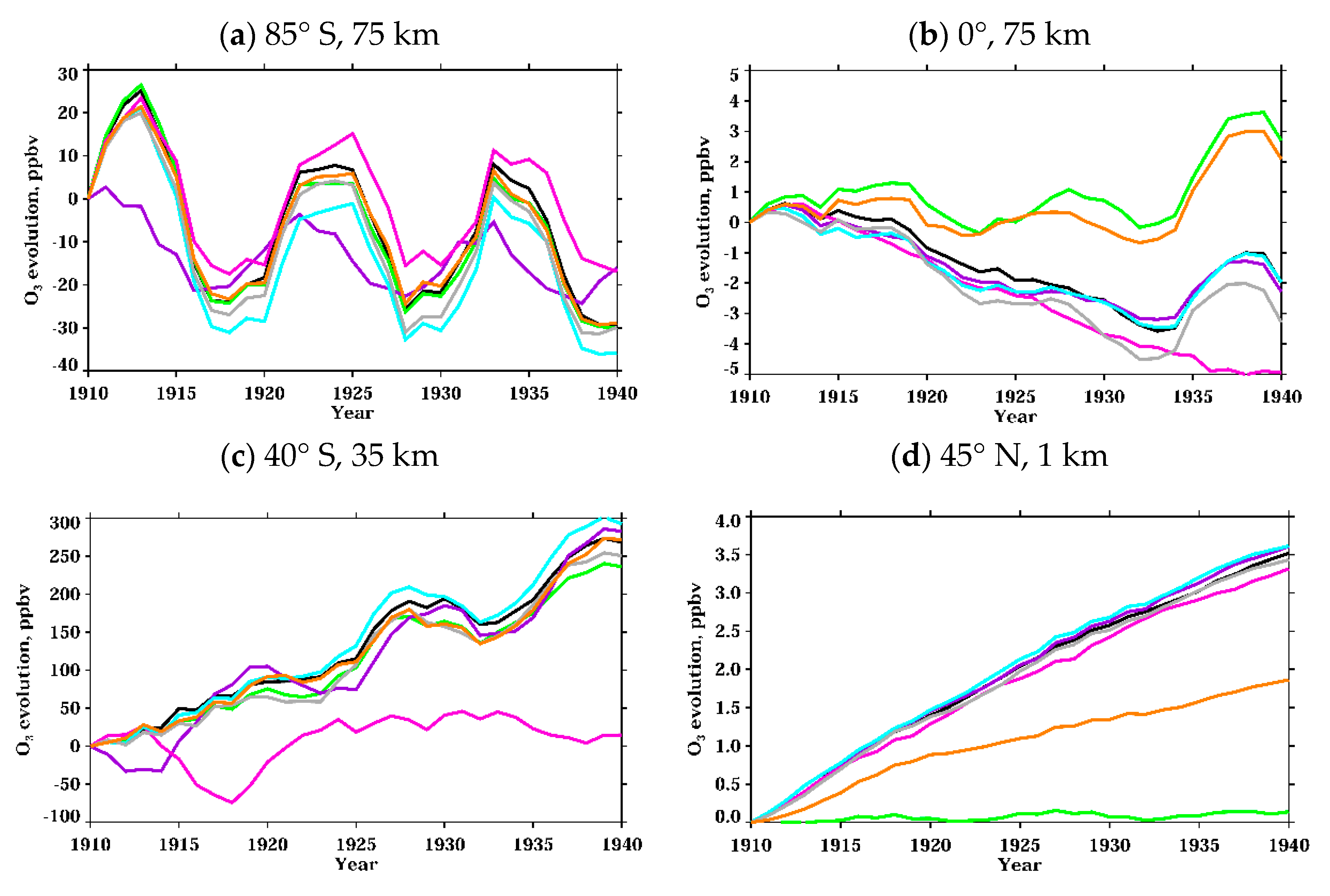
| Experiment Name | Fixed Forcing | Color Code for Evolution Plots |
|---|---|---|
| ALL | None | Black |
| noEPP | Energetic particles | Violet |
| fixUV | Solar UV irradiance (λ < 250 nm), extra heating, and photolysis rates | Magenta |
| fixVIS/IR | Solar visible and near infrared irradiance | Light blue |
| fixGHG | CO2, N2O, CH4, NOx, and CO emissions | Green |
| fixWMGHG | CO2, N2O, and CH4 | Orange |
| noVOL | Stratospheric sulfate aerosol | Grey |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Egorova, T.; Rozanov, E.; Arsenovic, P.; Sukhodolov, T. Ozone Layer Evolution in the Early 20th Century. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020169
Egorova T, Rozanov E, Arsenovic P, Sukhodolov T. Ozone Layer Evolution in the Early 20th Century. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleEgorova, Tatiana, Eugene Rozanov, Pavle Arsenovic, and Timofei Sukhodolov. 2020. "Ozone Layer Evolution in the Early 20th Century" Atmosphere 11, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020169
APA StyleEgorova, T., Rozanov, E., Arsenovic, P., & Sukhodolov, T. (2020). Ozone Layer Evolution in the Early 20th Century. Atmosphere, 11(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11020169







