Pollution Caused by Potentially Toxic Elements Present in Road Dust from Industrial Areas in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area
2.2. Road Dust Sampling
2.3. Particle Size and Magnetic Susceptibility Analysis
2.4. Potentially Toxic Metal Analysis
2.5. Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of PTEs Concentrations
3.2. PTEs Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessments
3.3. RD as a Potential Pollution Source for Coastal Environments and Atmosphere
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gabarrón, M.; Faz, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J.A. Assessment of metals behaviour in industrial soil using sequential extraction, multivariable analysis and a geostatistical approach. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 172, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziemska, M.; Bęś, A.; Gusiatin, Z.M.; Majewski, G.; Mazur, Z.; Bilgin, A.; Jaskulska, I.; Brtnický, M. Immobilization of potentially toxic elements (PTE) by mineral-based amendments: Remediation of contaminated soils in post-industrial sites. Minerals 2020, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srarfi, F.; Rachdi, R.; Bol, R.; Gocke, M.I.; Brahim, N.; SlimShimi, N. Stream sediments geochemistry and the influence of flood phosphate mud in mining area, Metlaoui, Western south of Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Duan, M.; Li, Y.; Nwankwegu, A.S.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, J. Concentration and pollution assessment of heavy metals within surface sediments of the Raohe Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielyan, A.V.; Shahnazaryan, G.; Minasyan, S. Distribution and identification of sources of heavy metals in the Voghji River Basin impacted by mining activities (Armenia). J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 7172426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Heavy metal contents of road-deposited sediment along the urban-rural gradient around Beijing and its potential contribution to runoff pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7120–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lim, J.; Ra, K. Heavy metal pollution by road-deposited sediments and its contribution to total suspended solids in rainfall runoff from intensive industrial areas. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, E.S.; Ra, K.; Lee, S.Y. Sediment quality assessment for heavy metals in streams around the Shihwa Lake. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Energy 2016, 19, 25–36, (in Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E.; Argyraki, A.; Chrastny, V.; Botsou, F.; Skordas, K.; Komarek, M.; Fouskas, A. Metal(loid) and isotopic tracing of Pb in soils, road and house dusts from the industrial area of Volos (central Greece). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Kang, H.M.; Ko, S.O. Reduction of non-point source contaminants associated with road-deposited sediments by sweeping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 1192–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Ye, B. Impacts of lead/zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q.; Peng, J.; Rong, G.; Tong, Z.; Liu, X. Pollution, sources and human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in different land use types under the background of industrial cities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W. Sources of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a rapidly industrializing area in the Yangtze Delta of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.Y.; Cai, D.J.; Yan, H. Soil Cd pollution and research progress of treatment techniques. Henan Chem. Ind. 2013, 30, 17–22. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Liang, L.; Yuan, C.; He, B.; Jiang, G. Methylmercury and total mercury in sediments collected from the East China Sea. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wei, D.; Zhu, Y.G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z. PM10 and PM2.5 and health risk assessment for heavy metals in a typical factory for Cathode Ray tube television recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12469–12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Chiang, H.C.; Chen, M.J.; Chuang, C.Y.; Tsen, C.M.; Fang, G.C.; Tsai, Y.I.; Chen, N.T.; Lin, T.Y.; Lin, S.L.; et al. Ambient PM2.5 in the residential area near industrial complexes: Spatiotemporal variation, source apportionment, and health impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 590–591, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Cheng, S.; Yao, S.; Xu, T.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Duan, W. Emission characteristics and chemical components of size-segregated particulate matter in iron and steel industry. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Shao, L.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, S. Mineralogical and geochemical composition of particulate matter (PM10) in coal and non-coal industrial cities of Henan Province, North China. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Yao, J.; Borthwick, A.G.L. Vanadium contamination and associated health risk of farmland soil near smelters throughout China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczynski, J.; Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Jablonska, M. The release of trace elements in the process of coal coking. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Liu, L.; Ii, D.; Guan, Y. Characterizing heavy metal build-up on urban road surfaces: Implication for stormwater reuse. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 515–516, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, R.; Beecham, S.; Sarkar, B.; Chong, M.N.; Kinsela, A.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S. Readily wash-off road dust and associated heavy metals on motorways. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 228, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Shim, W.J.; Kim, Y.O.; Ra, K. Characterization of the contribution of road deposited sediments to the contamination of the close marine environment with trace metals: Case of the port city of Busan (South Korea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, K.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, J.Y. Assessment of heavy metal contamination and its ecological risk in the surface sediments along the coast of Korea. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Johansson, C.; Karlsson, H.; Hansson, H.C. Factors affecting non-tailpipe aerosol particle emissions from paved roads: On-road measurements in Stockholm, Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Ren, L. Determination of road dust loading and chemical characteristics using resuspension. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 1693–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, J.; Bao, X. Heavy metals and lead isotopes in soils, road dust and leafy vegetables and health risks via vegetable consumption in the industrial areas of Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Gallent, N. Industrial park development and planning in South Korea. Reg. Stud. 1997, 31, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S. A study on problems of environmental facilities in industrial complexes and some policy recommendations. J. Korean Urban Manag. Assoc. 2009, 22, 117–144. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Ra, K.; Kim, J.K.; Hong, S.H.; Yim, U.H.; Shim, W.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.O.; Lim, J.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, K.T. Assessment of pollution and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Ulsan Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2014, 49, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.W.; Kim, M.J.; Baek, K.M.; Seo, Y.K.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.S.; Baek, S.O. A study on the concentration distribution of airborne heavy metals in major industrial complexes in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 34, 269–280, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundawardena, J.; Ziyath, A.M.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Mathematical relationships for metal build-up on urban road surfaces based on traffic and land use characteristics. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, V.; Chesters, G. Handbook of Nonpoint Pollution Sources and Management; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company: New York, NY, USA, 1981; p. 255. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, T.S.; Park, J.G.; Chung, I.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H. Evaluation on natural background of the soil heavy metals in Korea. J. Soil Groundw. Environ. 2009, 14, 32–39. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, R.I.; Gao, S. Composition of the continental crust. Treatise Geochem. 2003, 3, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water. Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tian, H.; Hua, S.; Zhu, C.; Gao, J.; Xue, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J. A comprehensive emission inventory of multiple air pollutants from iron and steel industry in China: Temporal trends and spatial variation characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Ra, K. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in road dust from urban areas: Comparison by land use types. J. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2020, 23, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, J.; Ziyath, A.M.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Sources and transport pathways of common heavy metals to urban road surfaces. Ecol. Engin. 2015, 77, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mummullage, S.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Use of physiochemical signatures to assess the sources of metals in urban road dust. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 541, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, N.; Zhu, P.; Liu, A.; Zhao, X.; Guan, Y. Using an innovative flag element ratio approach to tracking potential source of heavy metals on urban road surfaces. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.; Ra, K. Assessment of metal pollution of road-deposited sediments and marine sediments around Gwangyang Bay, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2020, 25, 42–53. (in Korean). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.M.; Fiala, M.J.; Park, D.; Wade, T.L. Review of pollutants in urban road dust and stormwater runoff: Part 1. Heavy metals released from vehicles. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2016, 20, 334–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmreich, B.; Hilliges, R.; Schriewer, A.; Horn, H. Runoff pollutants of a highly trafficked urban road-Correlation analysis and seasonal influences. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Welker, A.; Helmreich, B. Critical review of heavy metal pollution of traffic area runoff: Occurrence influencing factors and partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 895–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sere, P.R.; Deya, C.; Elsner, C.I.; Di Sarli, A.R. Corrosion of painted galvanneal steel. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Ma, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, R.; Shen, X.; Zhang, T.; Hong, J. Environmental impact assessment of galvanized sheet production: A case study in Shandong Province, China. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.G.; Bai, S.Q.; Xue, Q.F. Magnetic properties as indicators of heavy metals pollution in urban topsoils: A case study from the city of Luoyang, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 171, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Appel, E.; Hu, S.; Yin, G.; Lin, H.; Rosler, W. Magnetic response to air pollution recorded by soil and dust-loaded leaves in a changing industrial environment. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, S.T.A.; Chen, L.Z.; Younas, H.; Ahmad, N. Heavy metals pollution assessment in correlation with magnetic susceptibility in topsoils of Shanghai. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brempong, F.; Mariam, Q.; Preko, K. The use of magnetic susceptibility measurements to determine pollution of agricultural soils in road proximity. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- NYSDEC (New York State Department of Environmental Conservation). Screening and Assessment of Contaminated Sediment; Division of Fish, Wildlife and Marine Resources: Albany, NY, USA, 2014; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Tian, D. Grain size distribution of road-deposited sediment and its contribution to heavy metal pollution in urban runoff in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzerstorfer, C. Heavy metals in the finest size fractions of road-deposited sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Youn, J.S.; Jung, Y.W. Characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 source profiles for resuspended road dust collected using mobile sampling methodology. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3343–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.S.; Kumar, R.V.; Chaudhuri, P.; Chanda, S.; Santra, S.C.; Sudarshan, M.; Chakraborty, A. Physico-chemical characterization of street dust and re-suspended dust on plant canopies: An approach for fingerprinting the urban environment. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.A.; Evtyugina, M.G.; Vicente, A.M.P.; Vicente, E.; Nunes, T.; Silva, P.M.A.; Duarte, M.A.C.; Pio, C.A.; Amato, F.; Querol, X. Chemical profiling of PM10 from urban road dust. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 434, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzerstorfer, C. Toward more intercomparable road dust studies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1737472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, V.C.; Tian, L.; Ho, K.F. Particulate matter from re-suspended mineral dust and emergency cause-specific respiratory hospitalizations in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Askariyeh, M.H.; Venugopal, M.; Khreis, H.; Birt, A.; Zietsman, J. Near-road traffic-related air pollution: Resuspended PM2.5 from highways and arterials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, F.; Zeng, G.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, H.; Gu, Y.; Li, X.; He, X.; et al. Integrating hierarchical bioavailability and population distribution into potential eco-risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust: A case study in Xiandao District, Changsha City, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Dzakpasu, M.; Chang, N.; Wang, X. Transferral of HMs pollution from road-deposited sediments to stormwater runoff during transport processes. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X. Risk assessment of metals in road-deposited sediment along an urban-rural gradient. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 174, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Ra, K. Heavy metal pollution assessment in stream sediments from urban and different types of industrial areas in South Korea. Soil Sediment Contam. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Pant, P.; Harrison, R.M. Estimation of the contribution of road traffic emissions to particulate matter concentrations from field measurements: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotto, G.; Rampazzo, G.; Visin, F.; Bonella, F.; Cattaruzza, E.; Slisenti, A.; Formenton, G.; Tieppo, P. Environmental and traffic related parameters affecting road dust composition: A multi-technique approach applied to Venice area (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexeis, M.; Hausberger, S. Trend of vehicle emission levels until 2020—Prognosis based on current vehicle measurements and future emission legislation. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4689–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.W.; Han, S.; Won, K.H.; Jang, K.W.; Hong, J.H. Present status of emission estimation methods of resuspended dusts from paved roads. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2006, 28, 1126–1132, (in Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, E.C.; Dou, W.G.; Cho, J.G. Study for the control of re-suspend dust from paved road. Annu. Rep. Busan Metropolitan City Inst. Health. Environ. 2009, 19, 177–186, (In Korean with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- MOLIT (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport). National Traffic Survey in 2017 (Freight Transport Surveys); MOLIT: Sejong City, Korea, 2017; p. 328.
- Bian, B.; Lin, C.; Wu, H.S. Contamination and risk assessment of metals in road-deposited sediments in a medium-sized city of China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2015, 112, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamiec, E.; Jarosz-Krzeminska, E. Human Health risk assessment associated with contaminants in the finest fraction of sidewalk dust collected in proximity to trafficked roads. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
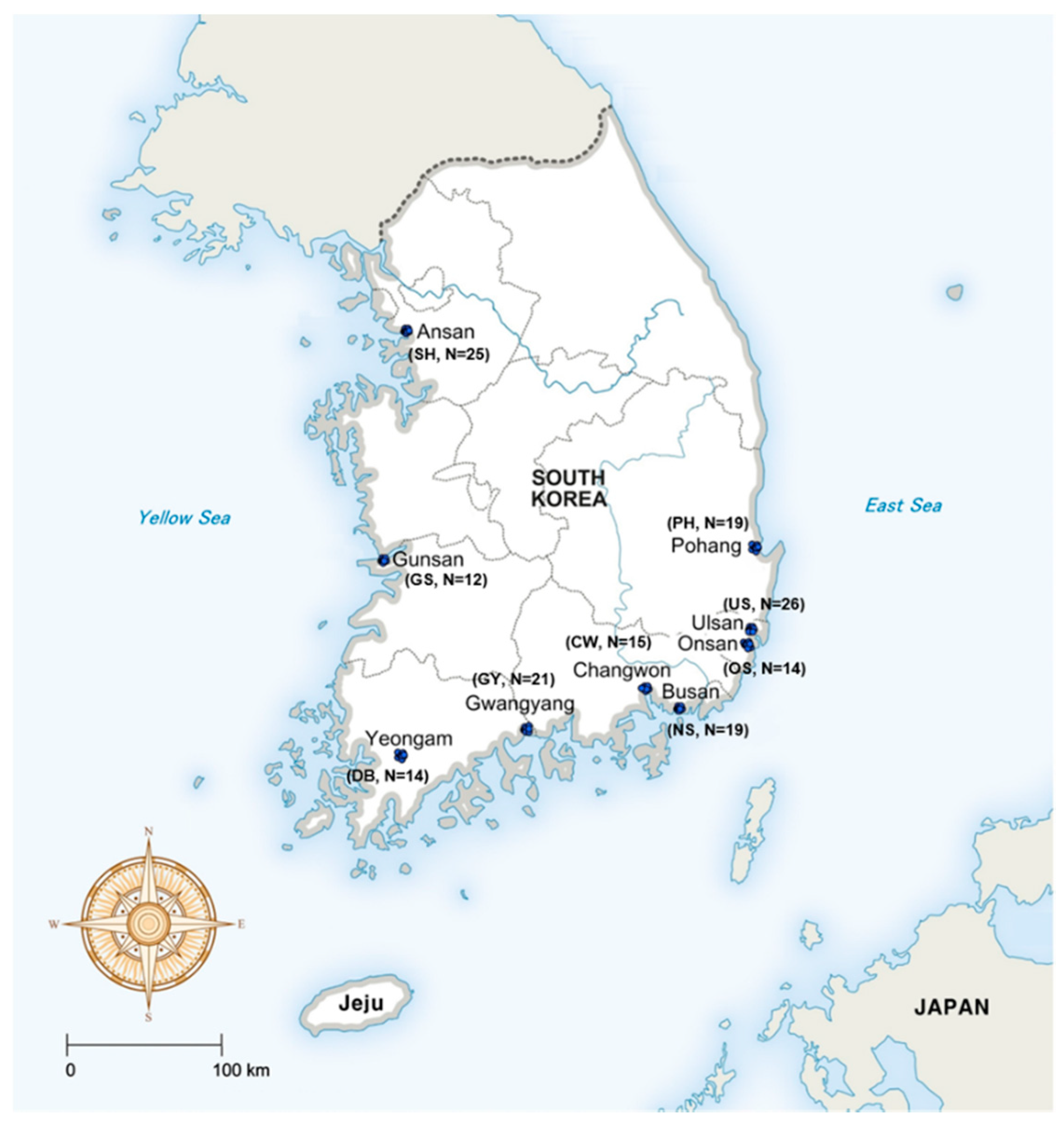
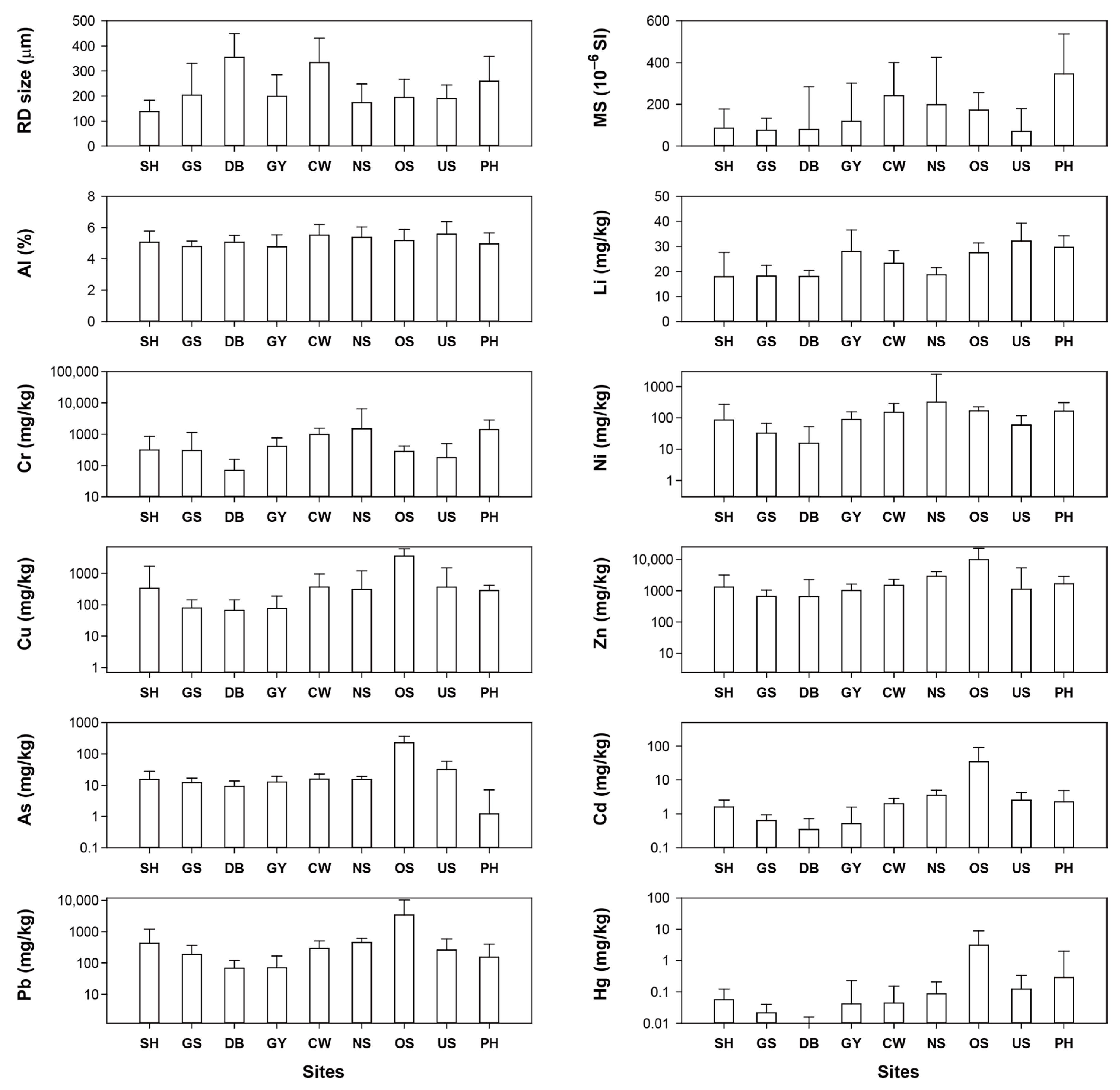

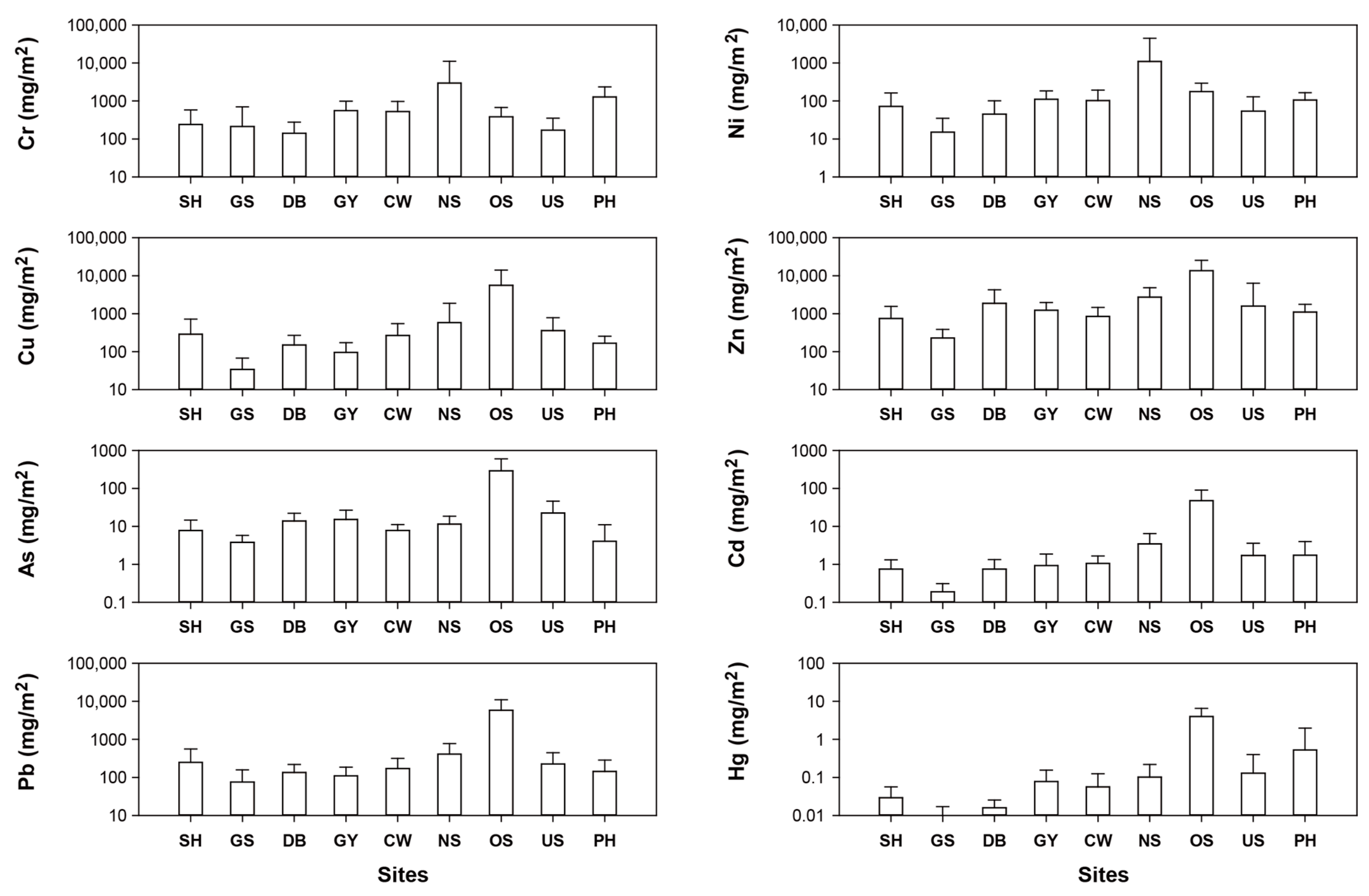
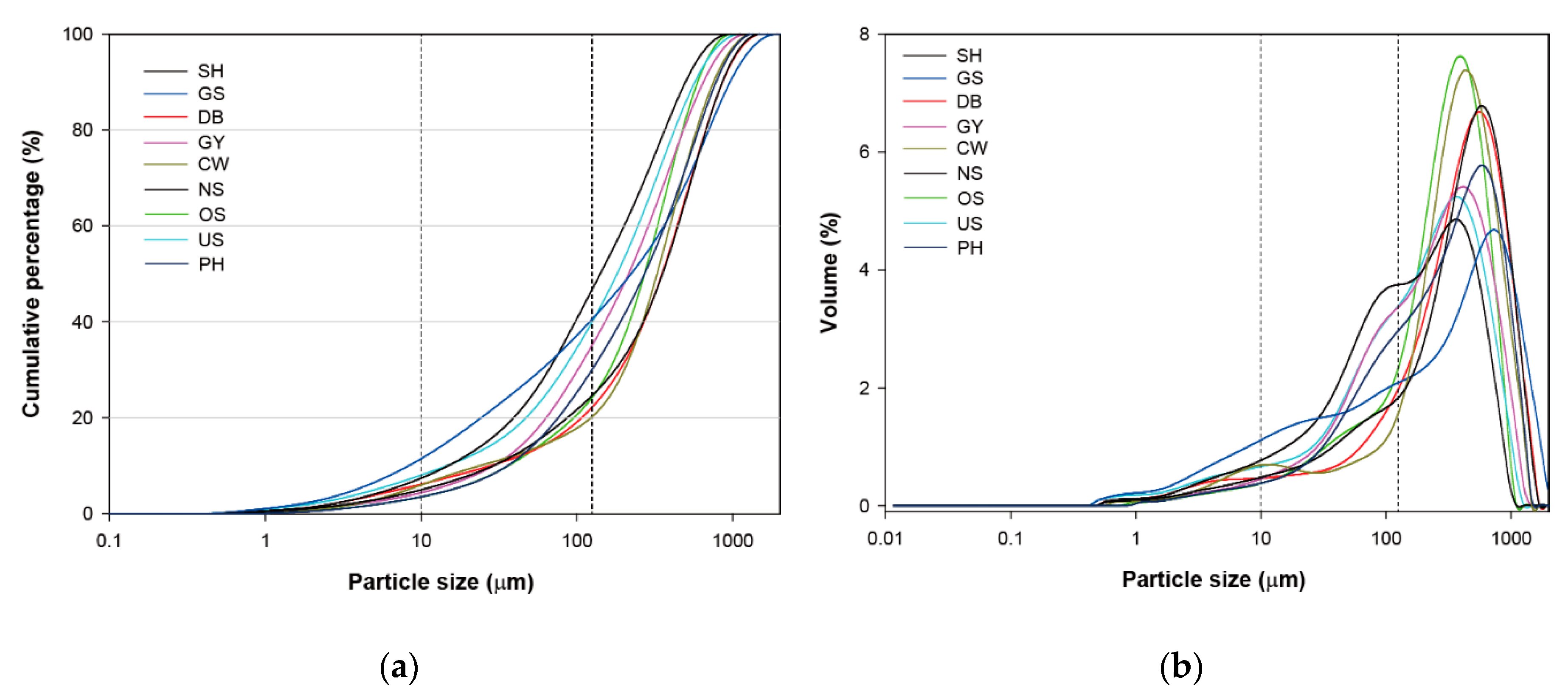
| Region | No. of Facilities (N) | Designated Area (km2) | No. of Employees (N) | No. of Residents (N) | No. of Sampling (N) | Major Industrial Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ansan (Shihwa; SH) | 18,809 | 30.8 | 292,070 | 650,918 | 25 | Assembled metal, metal processing, electronics components |
| Gunsan (Gunsan; GS) | 519 | 19.2 | 9.573 | 270,131 | 12 | Manufacture of assembly metals related to automobiles |
| Yeongam (Daebul; DB) | 245 | 10.7 | 6.172 | 54,593 | 14 | Transportation equipment, steel, machinery manufacturing |
| Gwangyang (Gwangyang; GY) | 92 | 16.6 | 4.643 | 156,750 | 21 | Steel and steel-related works, container terminal |
| Changwon (Changwon; CW) | 2469 | 24.4 | 116.436 | 1,044,740 | 15 | Industrial machinery industry, electrical equipment, transportation machinery |
| Busan (Noksan; NS) | 1459 | 6.0 | 35.208 | 3,413,841 | 19 | Precision machinery manufacturing, assembled metal, automobile |
| Onsan (Onsan; OS) | 296 | 16.6 | 17.220 | 223,167 | 14 | Nonferrous metals processing, shipbuilding equipment, oil refining |
| Ulsan (Ulsan; US) | 757 | 37.1 | 106.075 | 1,148,019 | 26 | Petrochemicals, automobile and transportation equipment |
| Pohang (Pohang; PH) | 78 | 3.9 | 7.134 | 507,025 | 19 | Steel-related primary metal manufacturing industry |
| Parameter | Component | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
| Eigenvalue | 4.25 | 2.22 | 1.3 |
| Variance (%) | 35.5% | 18.5% | 10.9% |
| Particle size | −0.093 | −0.024 | −0.523 |
| Magnetic susceptibility | 0.063 | 0.504 | −0.383 |
| Al | −0.122 | −0.095 | 0.803 |
| Li | 0.057 | −0.070 | 0.538 |
| Cr | −0.051 | 0.962 | −0.022 |
| Ni | −0.001 | 0.947 | −0.006 |
| Cu | 0.797 | −0.002 | −0.079 |
| Zn | 0.890 | 0.036 | −0.111 |
| As | 0.774 | −0.044 | 0.238 |
| Cd | 0.929 | −0.015 | −0.014 |
| Pb | 0.938 | −0.013 | 0.010 |
| Hg | 0.671 | 0.032 | 0.106 |
| Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <Class A (% samples) | 6 (4%) | 16 (10%) | 6 (4%) | 0 (0%) | 43 (26%) | 61 (37%) | 4 (2%) | 117 (71%) |
| Class B (% samples) | 13 (8%) | 24 (15%) | 46 (28%) | 16 (10%) | 93 (56%) | 81 (49%) | 37 (22%) | 32 (19%) |
| >Class C (% samples) | 146 (88%) | 125 (76%) | 113 (68%) | 149 (90%) | 29 (18%) | 23 (14%) | 124 (75%) | 16 (10%) |
| Class A | <43 | <23 | <32 | <120 | <10 | <1 | <36 | <0.2 |
| Class B | 43–110 | 23–49 | 32–150 | 120–460 | 10–33 | 1–5 | 36–130 | 0.2–1 |
| Class C | >110 | >49 | >150 | >460 | >33 | >5 | >130 | >1 |
| SH | GS | DB | GY | CW | NS | OS | US | PH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 3.0 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 5.2 |
| Ni | 1.7 | 0.3 | −0.8 | 1.7 | 2.5 | 3.6 | 2.7 | 1.2 | 2.6 |
| Cu | 3.9 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 7.3 | 4.0 | 3.7 |
| Zn | 4.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 5.2 | 6.9 | 3.8 | 4.3 |
| As | 0.6 | 0.2 | −0.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 4.5 | 1.6 | −3.1 |
| Cd | 4.3 | 3.0 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 4.6 | 5.5 | 8.8 | 5.0 | 4.8 |
| Pb | 3.9 | 2.8 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 6.9 | 3.2 | 2.5 |
| Hg | −0.4 | −1.8 | −2.9 | −0.9 | −0.8 | 0.2 | 5.3 | 0.7 | 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Lim, J.; Ra, K. Pollution Caused by Potentially Toxic Elements Present in Road Dust from Industrial Areas in Korea. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121366
Jeong H, Choi JY, Lim J, Ra K. Pollution Caused by Potentially Toxic Elements Present in Road Dust from Industrial Areas in Korea. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(12):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121366
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Hyeryeong, Jin Young Choi, Jaesoo Lim, and Kongtae Ra. 2020. "Pollution Caused by Potentially Toxic Elements Present in Road Dust from Industrial Areas in Korea" Atmosphere 11, no. 12: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121366
APA StyleJeong, H., Choi, J. Y., Lim, J., & Ra, K. (2020). Pollution Caused by Potentially Toxic Elements Present in Road Dust from Industrial Areas in Korea. Atmosphere, 11(12), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121366






