Mathematical Modeling of the Biogas Production in MSW Landfills. Impact of the Implementation of Organic Matter and Food Waste Selective Collection Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
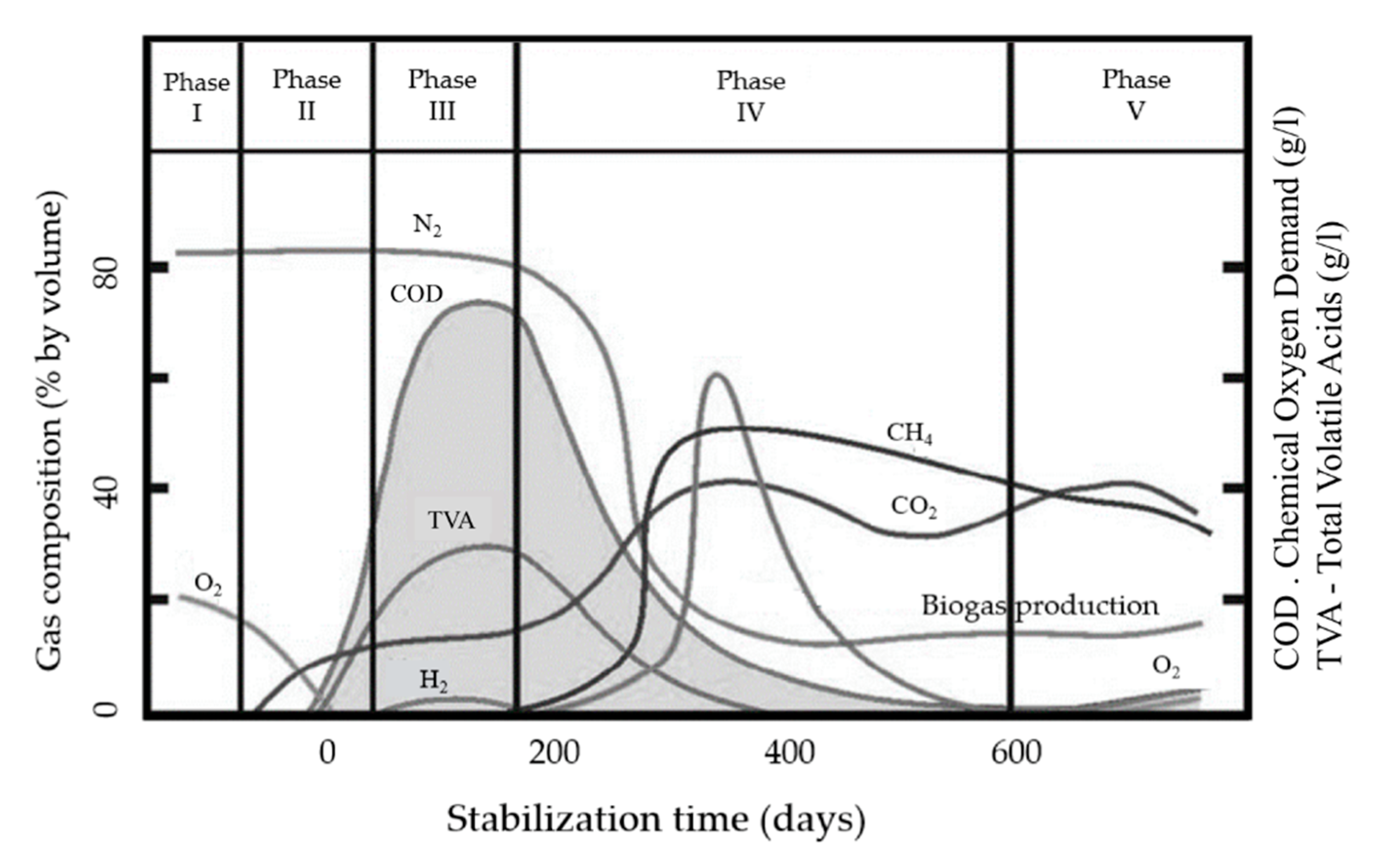
2. Landfill Biogas Production
2.1. Parameters That Control Biogas Production
2.1.1. Stoichiometric Equations
2.1.2. Reaction Kinetics
2.2. Biogas Production Models
3. Materials and Methods
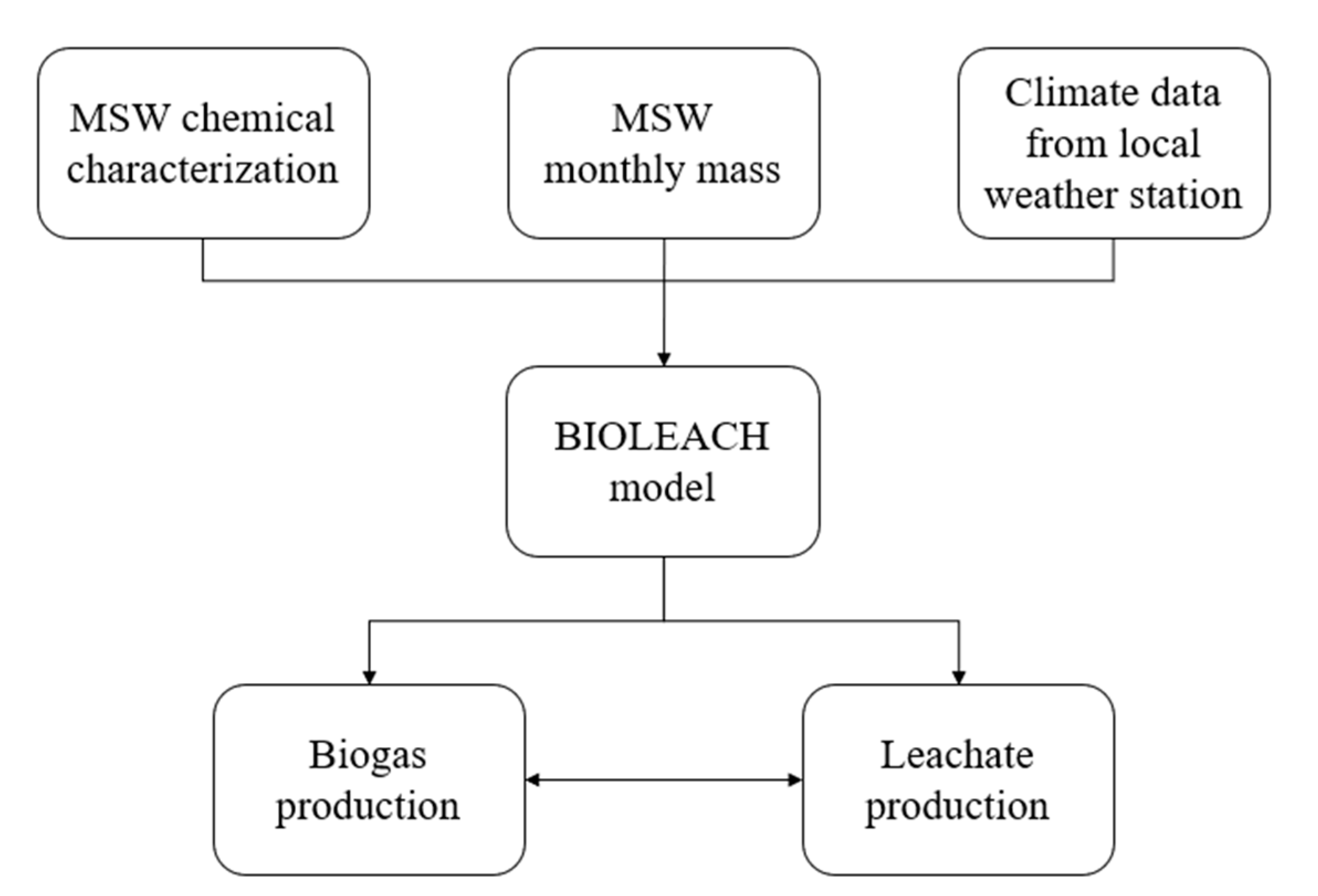
3.1. BIOLEACH Model
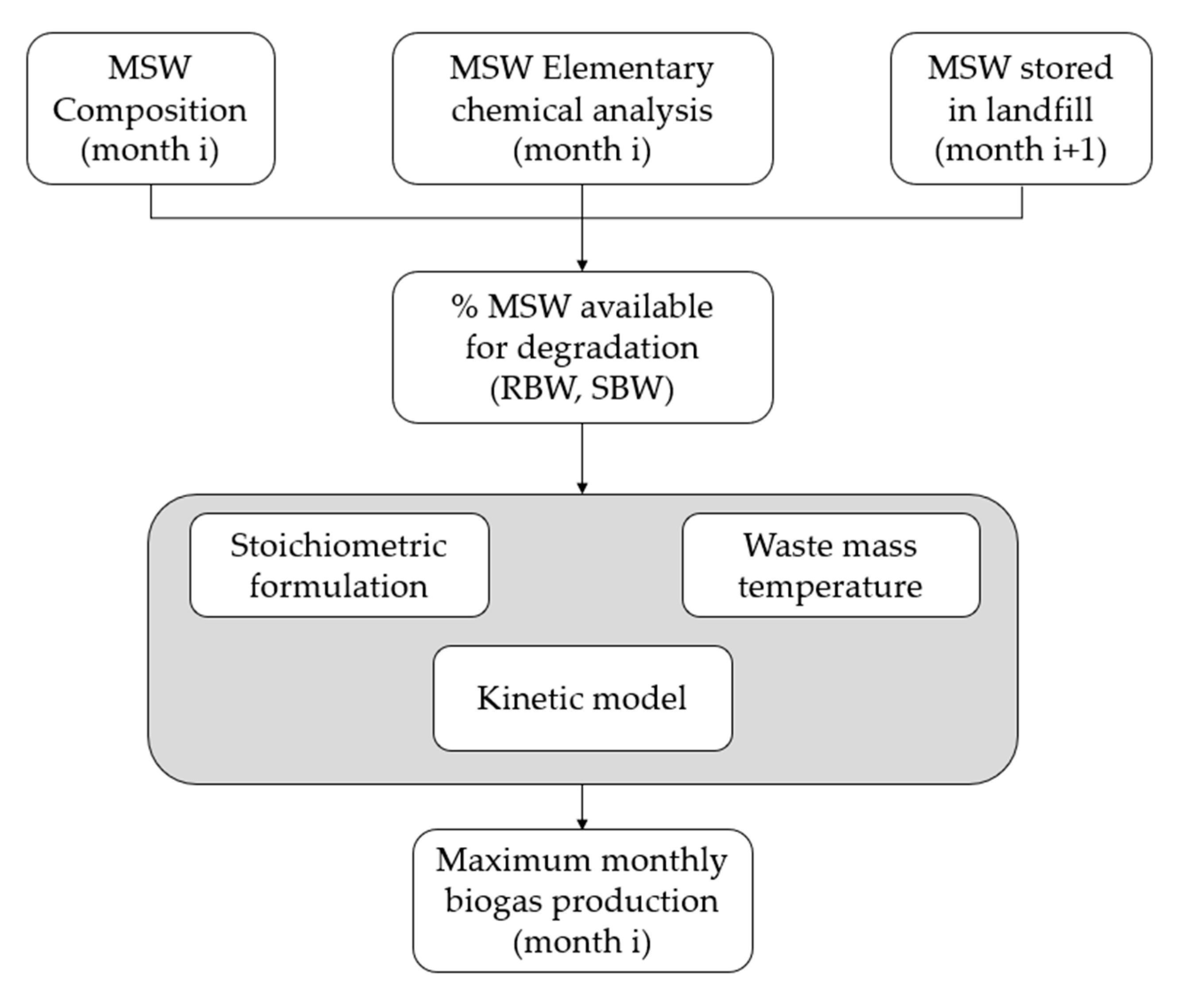
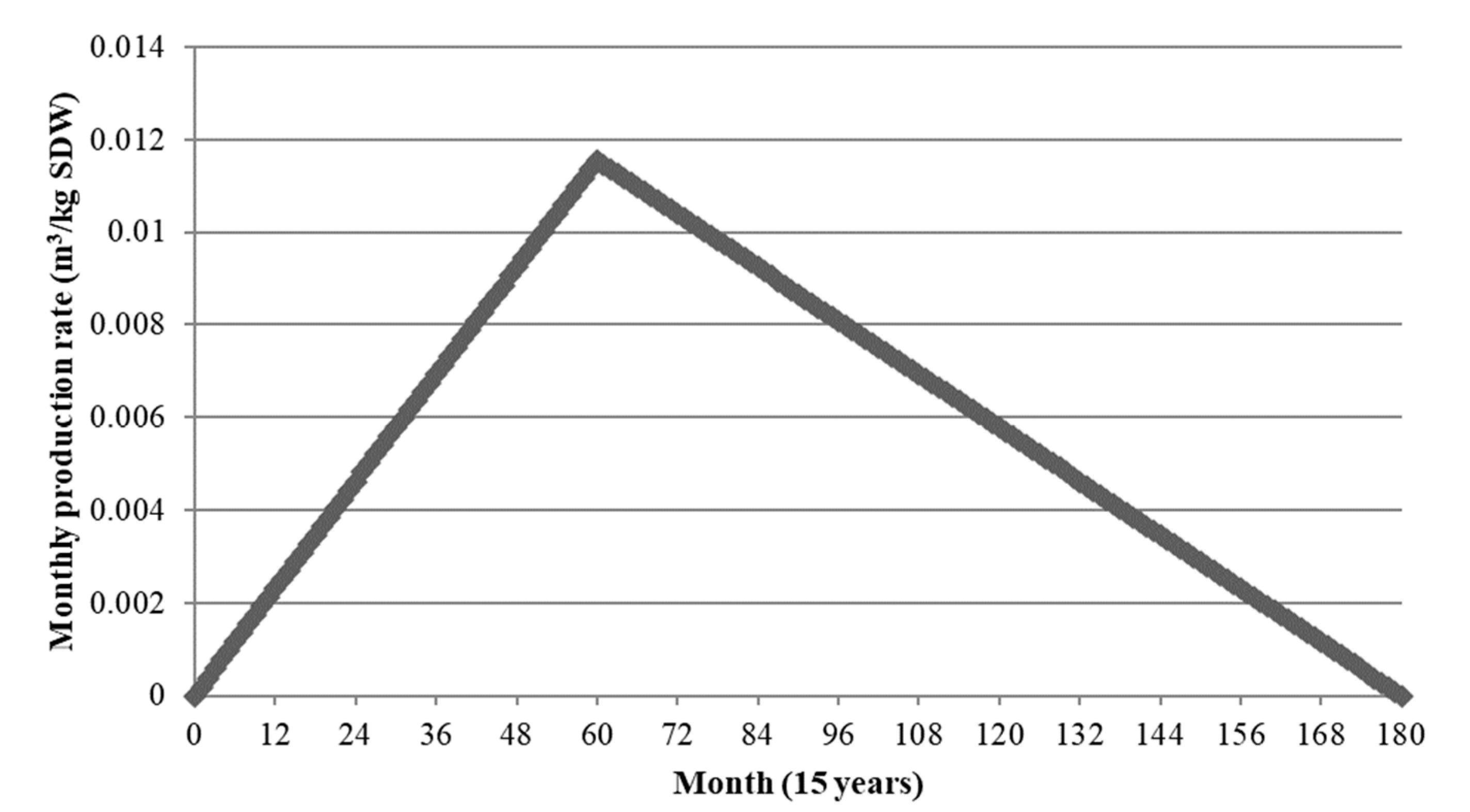
3.2. Optimal Monthly Biogas Production Calculation
4. Application of the BIOLEACH Model to the Estimation of the Biogas Production on a MSW Landfill
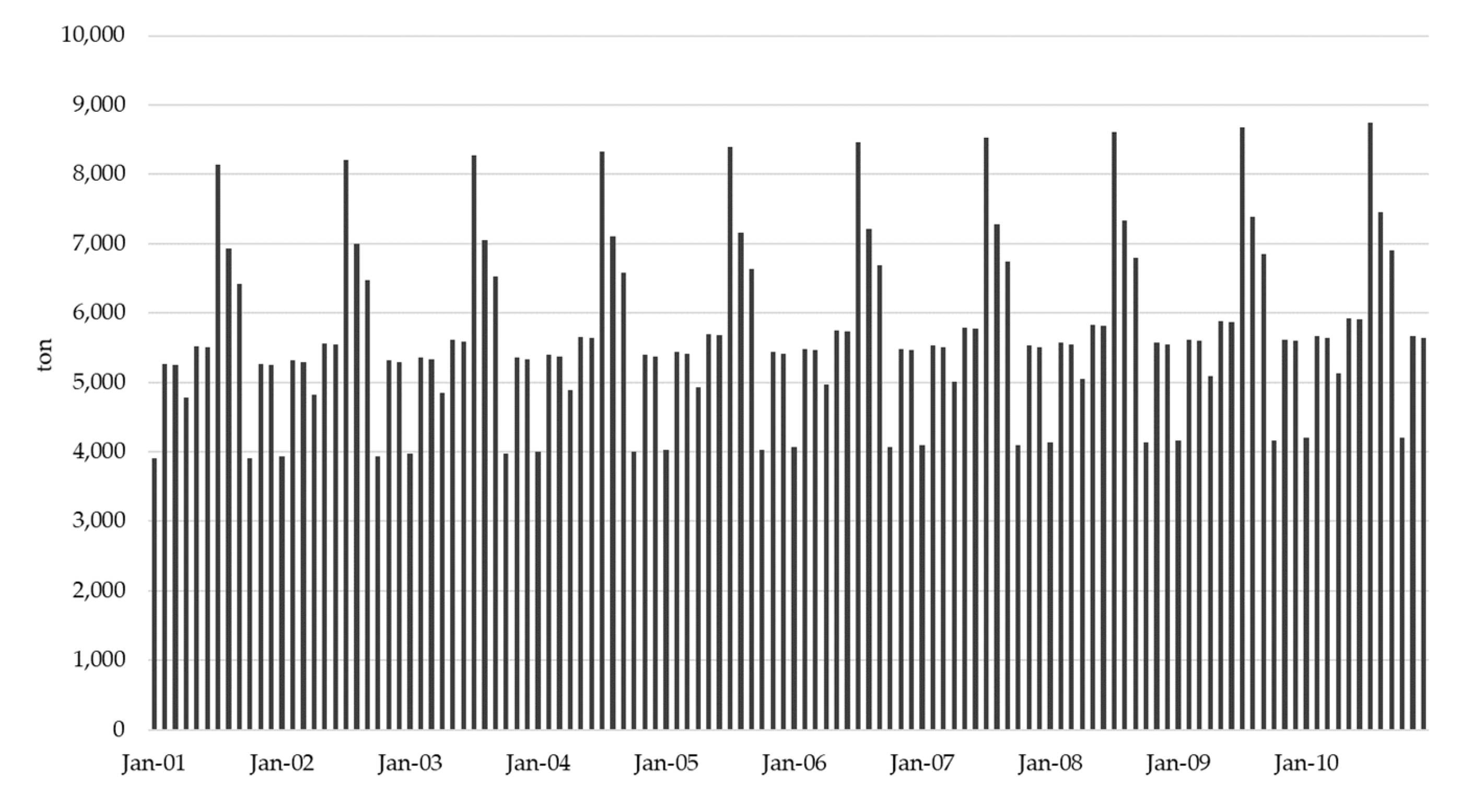
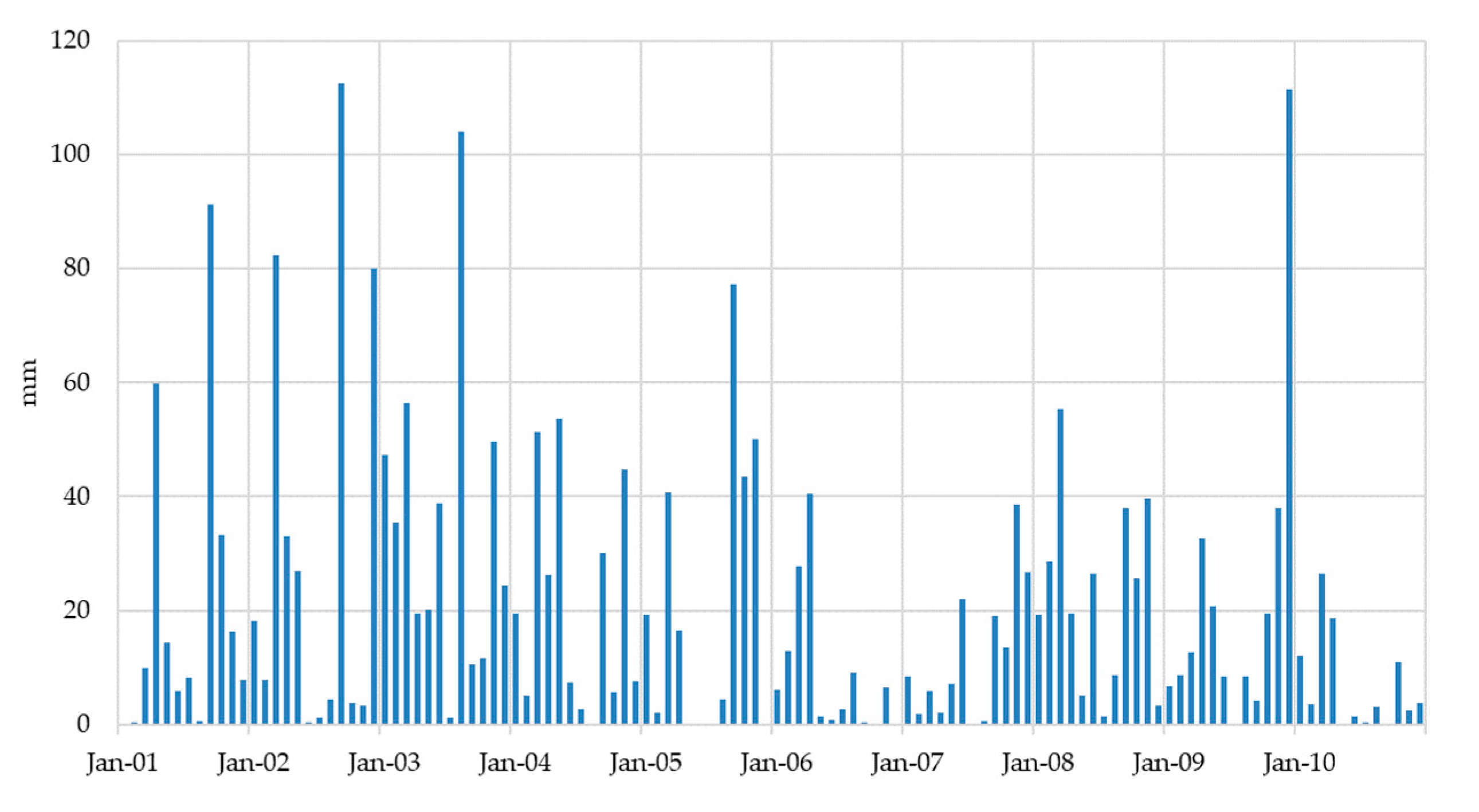
4.1. Input Data
4.2. Simulation Scenarios
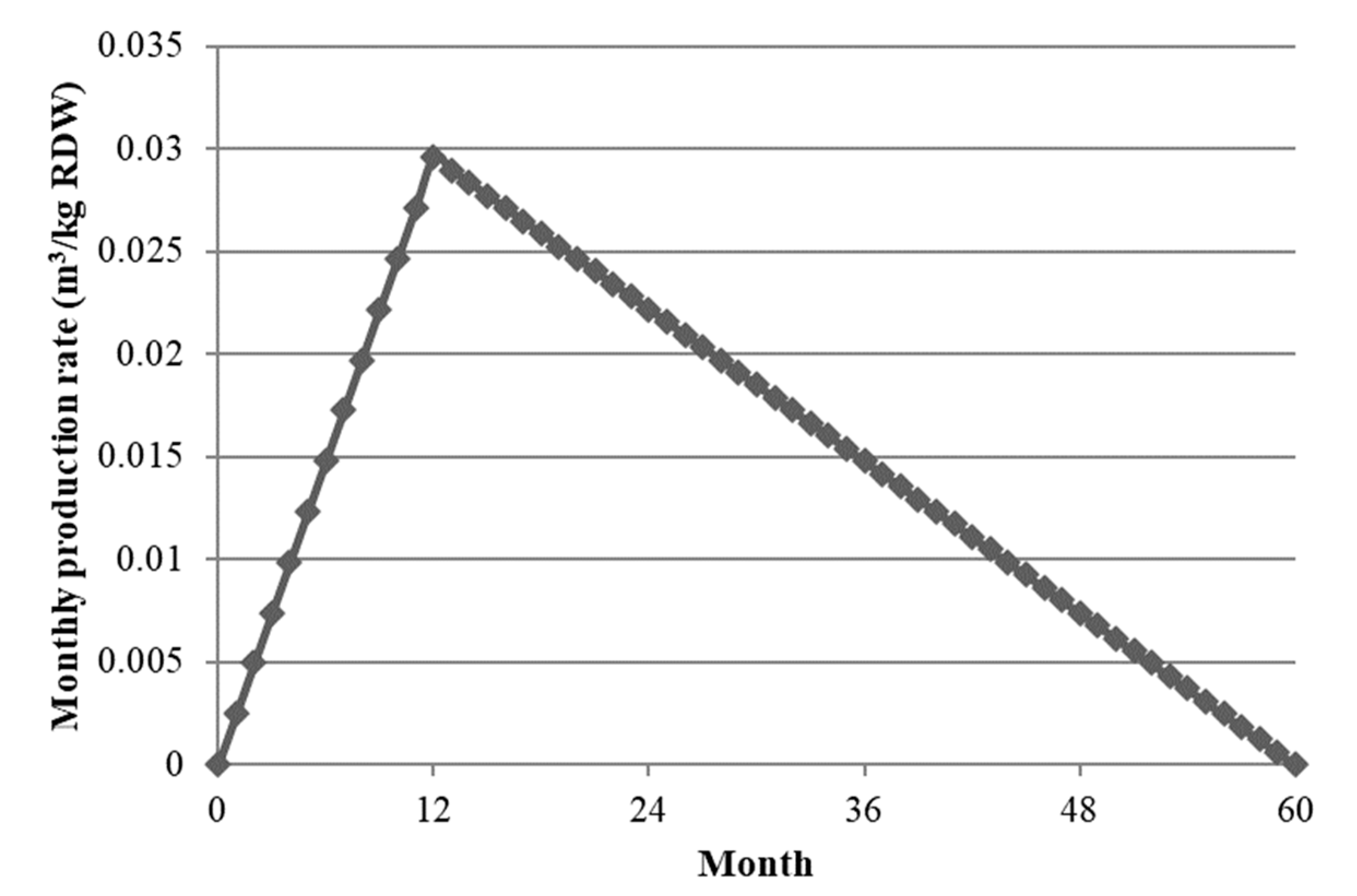
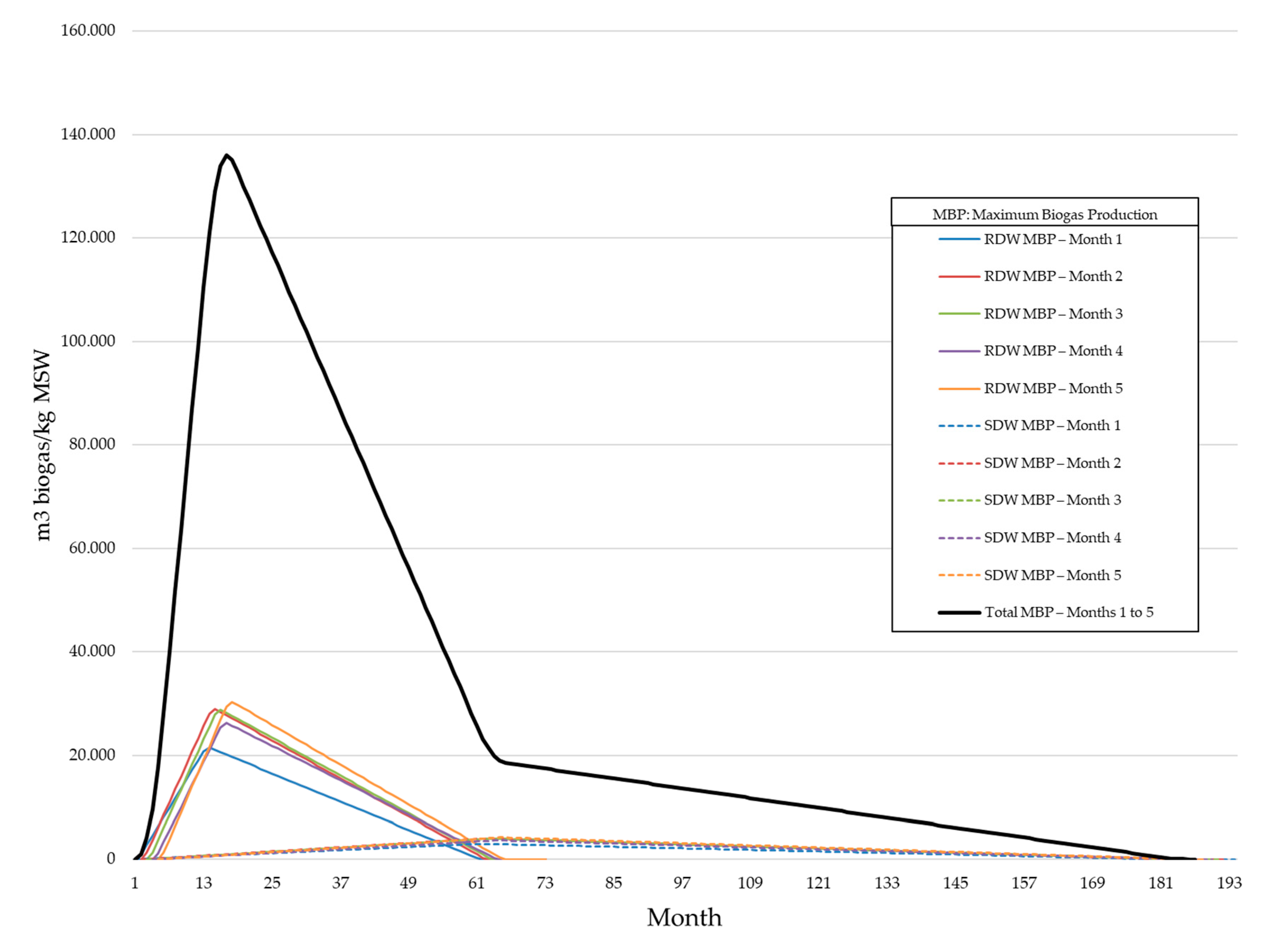
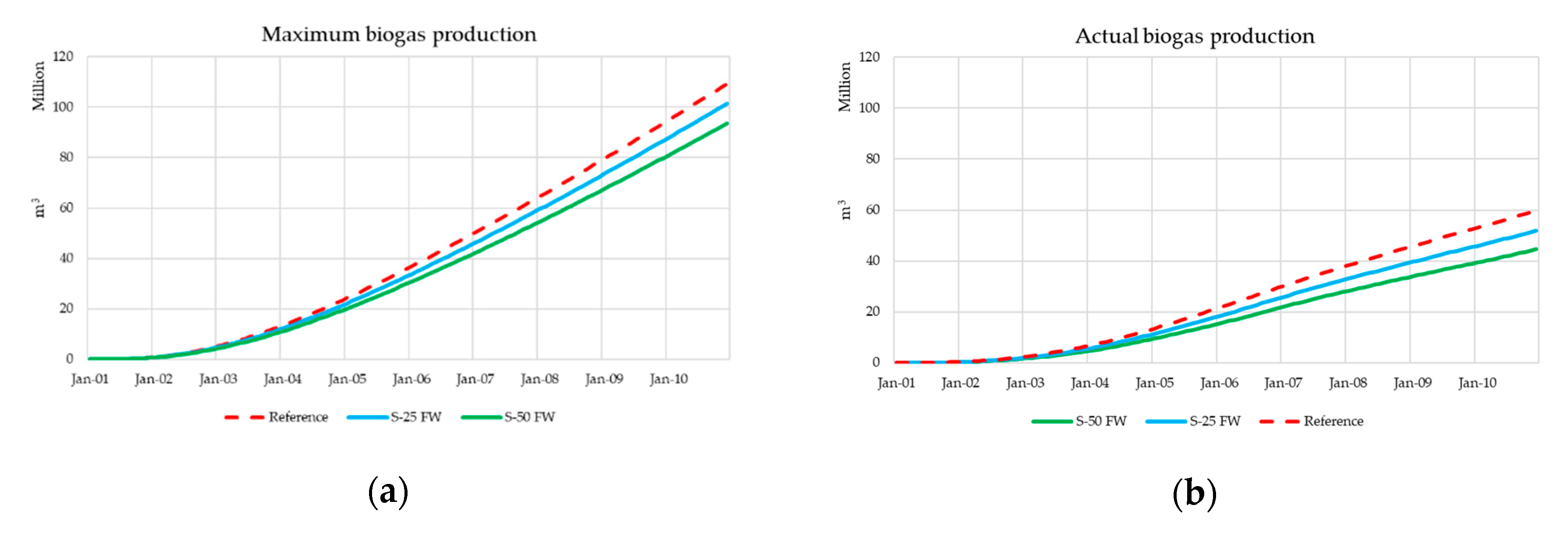
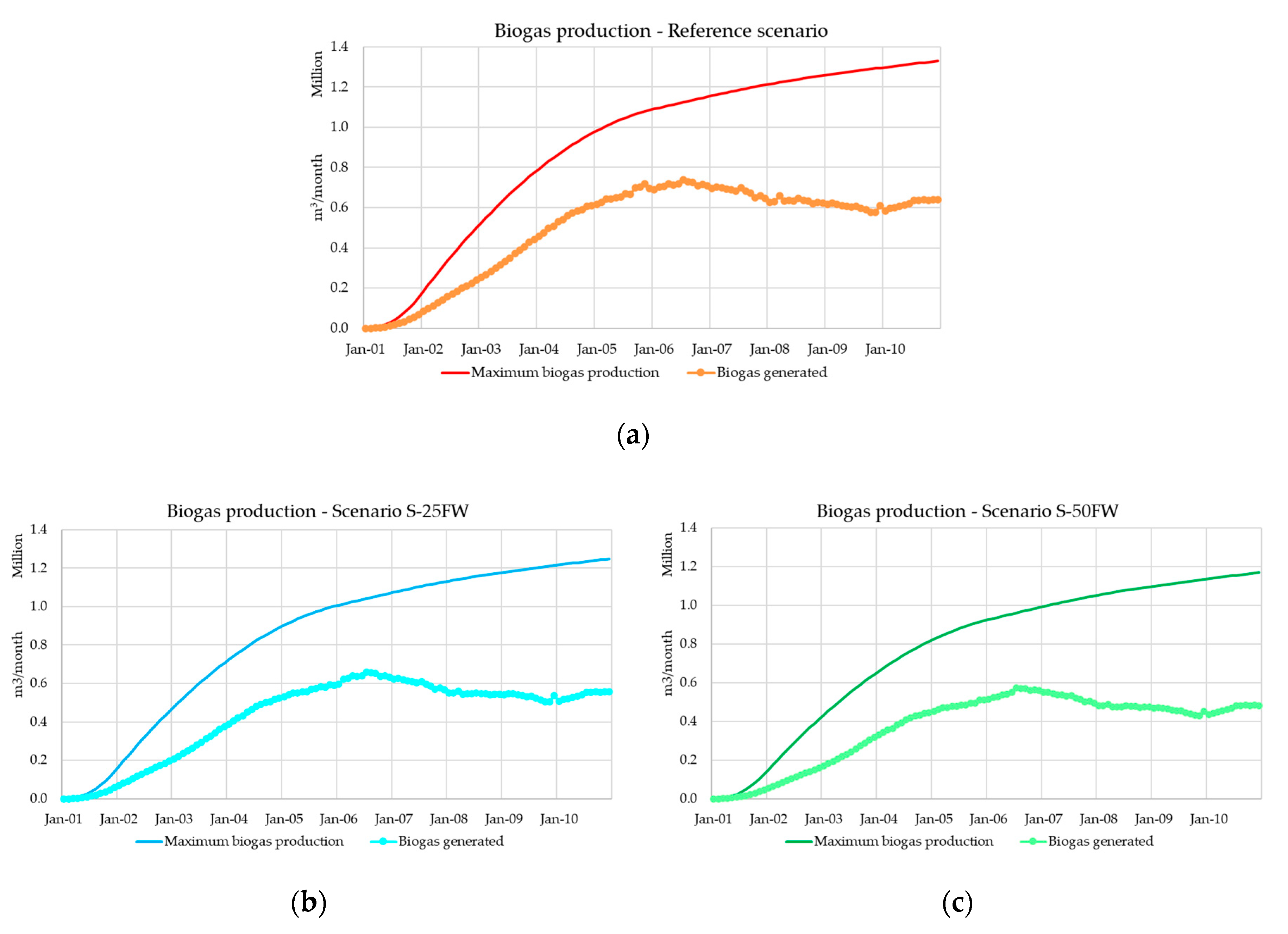
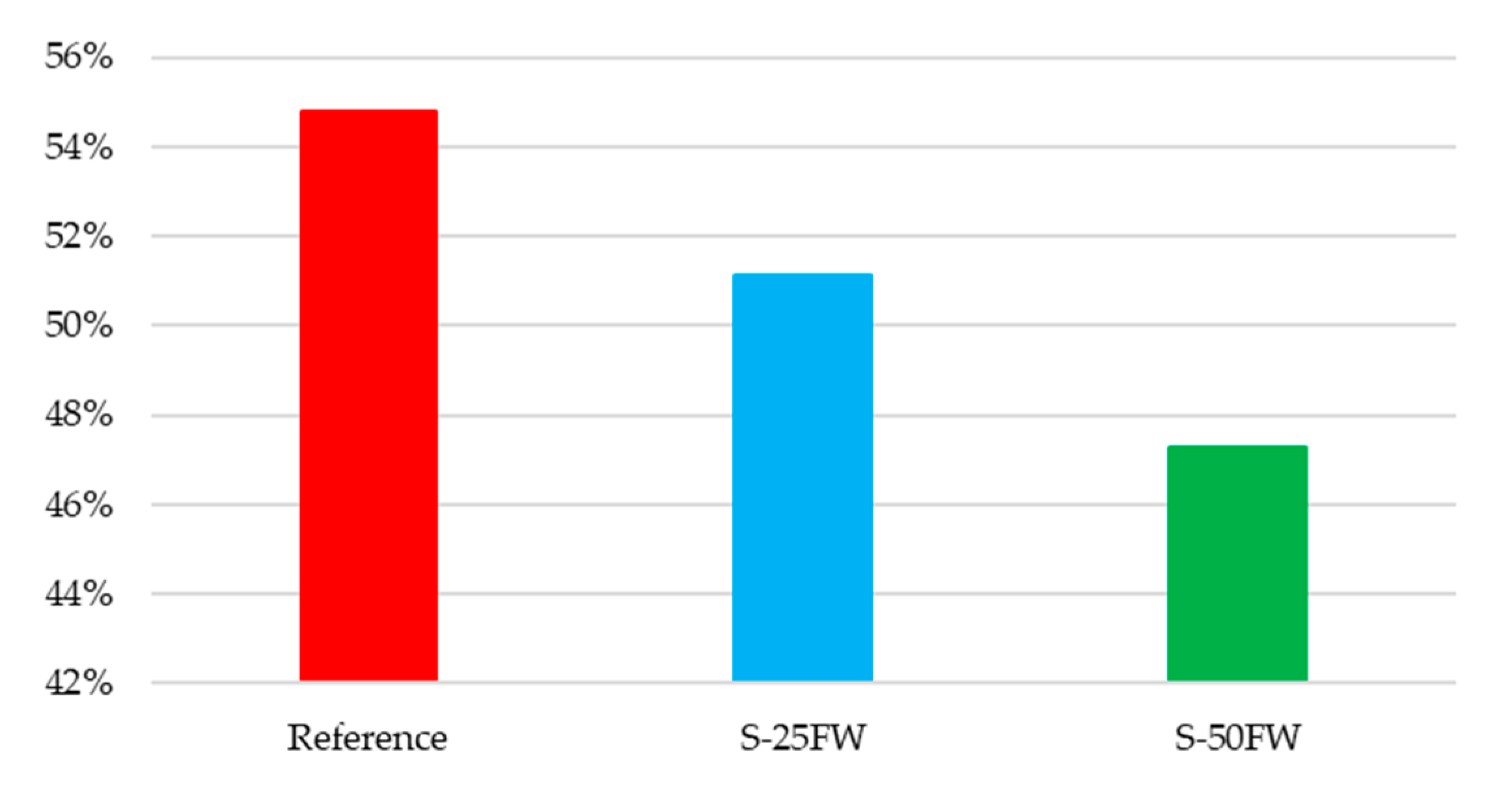
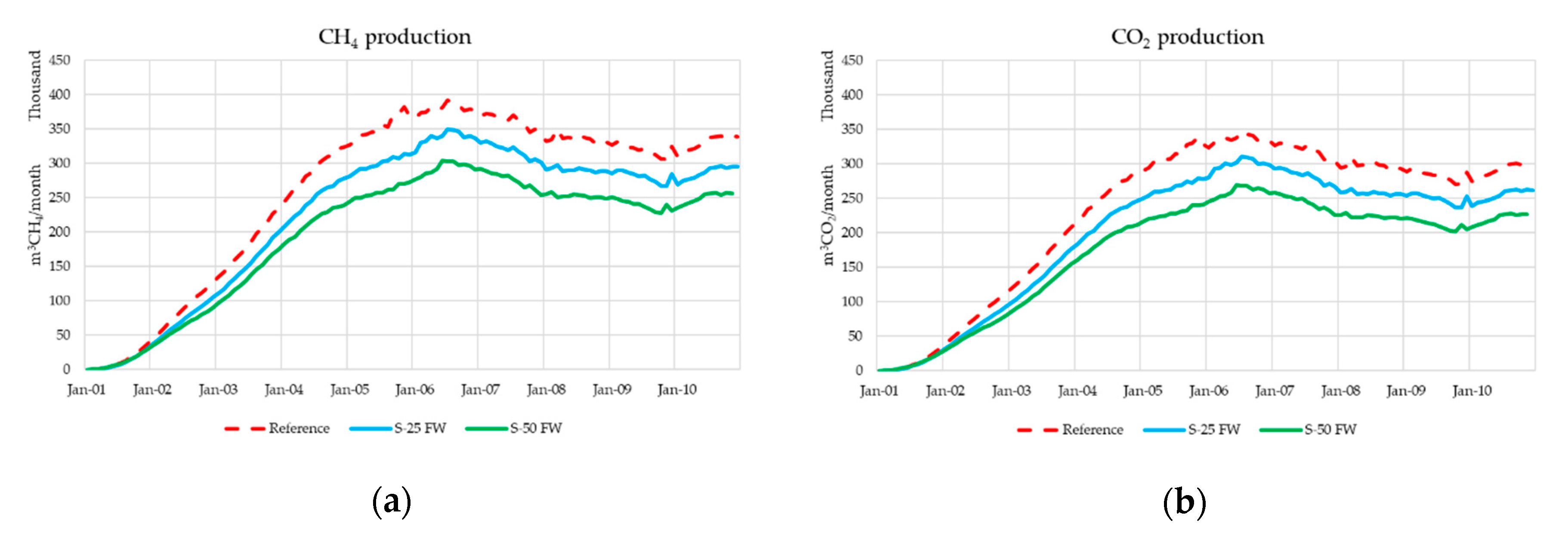
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oonk, H. Landfill Gas Formation, Recovery and Emission in The Netherlands. In Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gases; Ham, J., van Janssen, J.H.M., Swart, R.J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Atabi, F.; Ehyaei, M.A.; Ahmadi, M.H. Calculation of CH4 and CO2 Emission Rate in Kahrizak Landfill Site THROUGH LandGEM Mathematical Model. In Proceedings of the 4th World Sustainability Forum. 2014. Available online: https://sciforum.net/conference/wsf-4 (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Krause, M.J.; Chickering, G.W.; Townsend, T.G.; Reinhart, D.R. Critical review of the methane generation potential of municipal solid waste. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 1117–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Braithwaite, A.; Hills, C.C. Trace organic compounds in landfill gas at seven U.K. waste disposal sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, B.; Anderson, E.P.; Walker, B.L.; Burrows, D.B. Characterization of landfill gas composition at the Fresh Kills municipal solid-waste landfill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettenberger, G.; Stegmann, R. Landfilling Gas Components. In Landfilling of Waste: Biogas; Christensen, T.H., Cossu, R., Stegmann, R., Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1996; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, M.D.; Font, R.; Aracil, I. Biogas from MSW landfill: Composition and determination of chlorine content with the AOX (adsorbable organically bound halogens) technique. Energy 2013, 63, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Gámez, A.F. Caracterización Hidrogeológica y Estudio del Biogás en Vertederos de la Provincia de Málaga. Bases Para su Gestión Medioambiental. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Málaga, Málaga, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Edenhofer, O., Pichs-Madruga, R., Sokona, Y., Farahani, E., Kadner, S., Seyboth, K., Adler, A., Baum, I., Brunner, S., Eickemeier, P., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Harborth, P.; Fuss, R.; Münnich, K.; Flessa, H.; Fricke, K. Spatial variability of nitrous oxide and methane emissions from an MBT landfill in operation: Strong N2O hotspots at working face. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.A.; Maunder, D.H. Exploitation of Landfill Gas: A UK Perspective. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 30, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonk, H.; Weenk, A.; Coops, O.; Luning, L. Validation of landfill gas formation models. In Studies in Environmental Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, T.; Tauseef, S.M.; Abbasi, S.A. Capture of Biogas from Landfills. In Biogas Energy; Springer Briefs in Environmental Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US-EPA. LFG Energy Project Development Handbook; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kreith, F.; Tchobanoglous, G. Handbook of Solid Waste Management; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- El-Fadel, M.; Findikakis, A.N.; Leckie, J.O. Environmental Impacts of Solid Waste Landfilling. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 50, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, D.R.; Townsend, T.G. Landfill Bioreactor Design & Operation; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Levis, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. Is biodegradability a desirable attribute for discarded solid waste? Perspectives from a national landfill greenhouse gas inventory model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5470–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment Agency (EA) & Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA). Guidance on the Management of Landfill Gas; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Martín González, S. Producción y Recuperación del Biogás en Vertederos Controlados de Residuos Sólidos Urbanos: Análisis de Variables y Modelización. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cheremisinoff, N.P. Handbook of Solid Waste Management and Waste Minimization Technologies; Butterworth-Heinemann: Burlington, VT, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Uriarte, J.; Carreras, J.; Solano, M.L. Management of biogas generated in sanitary landfills. Electrical autogeneration in Artigas sanitary landfill. In Biomass for Energy, Industry and Environment, Proceedings of the 6th EC Conference, Athens, Greece, 22–26 April 1991; Grassi, G., Collina, A., Zibetta, H., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 590–594. [Google Scholar]
- Varnero-Moreno, M.T. Manual de Biogás; FAO: Santiago de Chile, Chile, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Karanjekar, R.V. An Improved Model for Predicting Methane Emissions from Landfills Based on Rainfall, Ambient Temperature, and Waste Composition. Ph.D Thesis, The University Of Texas, Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pohland, F.G.; Harper, S.R. Critical Review and Summary of Leachate and Gas Production from Landfills; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P. Basic biochemical processes in landfill. In Sanitary Landfilling: Process, Technology and Environmental Impact; Christensen, T.H., Cossu, R., Stegmann, R., Eds.; Academic Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1989; pp. 29–49. [Google Scholar]
- Nastev, M. Modeling Landfill Gas Generation and Migration in Sanitary Landfills and Geological Formations. Ph.D Thesis, Université Laval, Québec, QC, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Lindhardt, B. Gas-Generating Processes in Landfill. In Landfilling of Waste: Biogas; Christensen, T.H., Cossu, R., Segmann, R., Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1996; pp. 27–50. [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar, G.J.; Rovers, F.A. Gas production during refuse decomposition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1973, 2, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlaz, M.A.; Ham, R.K. Leachate and gas generation. In Geotechnical Practice for Waste Disposal; Daniel, D.E., Ed.; Springer: Boston, UK, 1993; pp. 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, J.F. Optimisation of methane production and refuse decomposition in landfills by temperature control. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1980, 30, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasali, G.B.; Senior, E.; Watson-Craik, I.A. Solid state refuse promotion methanogenic fermentation: Control and promotion by water addition. Appl. Microbiol. 1990, 11, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurijala, K.R.; Suflita, J.M. Environmental factors influencing methanogenesis from refuse in landfill samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatmadari, N.; Sabour, M.R.; Kamalan, H.; Mansouri, A.; Abolfazlzadeh, M. Applying Simple Numerical Model to Predict Methane Emission from Landfill. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 7, 1511–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonk, H. Literature Review: Methane from Landfills: Methods to Quantify Generation, Oxidation and Emission; Sustainable Landfill Foundation: Assendelft, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- SCS Engineers. Comparison of Models for Predicting Landfill Methane Recovery; Institute for Environmental Management: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Peer, R.L.; Thorneloe, S.A.; Epperson, D.L. A comparison of methods for estimating global methane emissions from landfills. Chemosphere 1993, 26, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalan, H.; Sabour, M.R.; Shariatmadari, N. A review on available landfill gas models. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 4, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Q. Modelling of landfill gas generation: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, V.; Siddiqui, F.Z.; Khan, M.E. From Landfill Gas to Energy: Technologies and Challenges; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Canale, R.P. Biological Waste Treatment; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Buswell, A.M.; Mueller, H.F. Mechanism of methane fermentation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, G.E.; Buswell, A.M. The methane fermentation of carbohydrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, W.C. Energy Recovery from Sanitary Landfills—A Review. Microb. Energy Convers. 1977, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, L.G. Unit Processes of Environmental Sanitary; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- EMCON Associates. Methane Generation and Recovery from Landfills; Ann Arbor Science: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Augenstein, D.; Pacey, J. Modeling landfill methane generation. In Sardinia 91, Proceedings of the Third International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Cagliari, Italy, 14–18 October 1991; CISA, Environmental Sanitary Engineering Center: Sardinia, Italy, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cossu, R.; Andreottola, G.; Muntoni, A. Modelling of Landfill Gas. In Landfilling of Waste: Biogas; Christensen, T.H., Cossu, R., Segmann, R., Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1996; pp. 237–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, R.K. Recovery, Processing and Utilisation of Gas from Sanitary Landfill; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Lamborn, J.M.; Frecker, G.B. A review of landfill decomposition modelling. In Sardinia, Proceedings of the Ninth International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Cagliari, Italy, 6–10 October 2003; CISA, Environmental Sanitary Engineering Centre: Sardinia, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo García de Cortázar, A.; Tejero Monzón, I. MODUELO 2: A new version of an integrated simulation model for municipal solid waste landfills. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.K.; Beaven, R.P. Developments to a landfill processes model following its application to two landfill modelling challenges. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1969–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougall, J.R. A hydro-bio-mechanical model for settlement and other behavior in landfilled waste. Comput. Geotech. 2007, 34, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, L.K.; Richards, D.J.; Smallman, D.J. The longterm settlement of landfill waste. Waste Resour. Manag. 2008, 61, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bareither, C.A.; Benson, C.H.; Edil, T.B. Compression of municipal solid waste in bioreactor landfills: Mechanical creep and biocompression. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.F.; Xiong, J.H.; Feng, S.J.; Chen, H.X.; Bai, Z.B.; Fu, W.D.; Lü, F. A finite-volume numerical model for bio-hydro-mechanical behaviors of municipal solid waste in landfills. Comput. Geotech. 2019, 109, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Qian, X.; Hu, Y.; Peng, G. One-dimensional model for municipal solid waste (MSW) settlement considering coupled mechanical-hydraulic-gaseous effect and concise calculation. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, H.; Meegoda, J.; Hettiaratchi, P. Effects of gas and moisture on modeling of bioreactor landfill settlement. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhan, L. Analysis of solid-liquid-gas interactions in landfilled municipal solid waste by a bio-hydro-mechanical coupled model. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, M.J.; Gourc, J.P.; Drut, N.; Stolz, G.; Mansour, A.A. Large-scale bioreactor pilots for monitoring the long-term hydromechanics of MSW. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2013, 17, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.L.; Vilar, O.M.; Carvalho, M.F. Constitutive model for long term municipal solid waste mechanical behavior. Comput. Geotech. 2008, 35, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, C.H.; Meegoda, J.N.; Tavantzis, J.; Hettiaratchi, J.P.A. Numerical model to predict settlements coupled with landfill gas pressure in bioreactor landfills. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 139, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar Babu, G.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Chouksey, S.K.; Kulkarni, H.S. Prediction of long-term municipal solid waste landfill settlement using constitutive model. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. ASCE 2010, 14, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivella, S. Nonisothermal Multiphase Flow of Brine and Gas Throughsaline Media. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Cataluña, Barcelona, Spain, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, J.L.; Yesiller, N.; Onnen, M.T.; Liu, W.L.; Oettle, N.K.; Marinos, J.A. Development of numerical model for predicting heat generation and temperatures in MSW landfills. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawande, N.A.; Reinhart, D.R.; Yeh, G.T. Modeling microbiological and chemical processes in municipal solid waste bioreactor, part I: Development of a three-phase numerical model BIOKEMOD-3P. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholamifard, S.; Eymard, R.; Duquennoi, C. Modeling anaerobic bioreactor landfills in methanogenic phase: Long term and short-term behaviors. Water Resour. 2008, 42, 5061–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Achari, A. A comprehensive numerical model simulating gas, heat, and moisture transport in sanitary landfills and methane oxidation in final covers. Environ. Model. Assess. 2010, 15, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.-J.; Lu, S.-F.; Chen, H.X.; Fu, W.-D.; Lü, F. Three-dimensional modelling of coupled leachate and gas flow in bioreactor landfills. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 84, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grugnaletti, M.; Pantini, S.; Verginelli, I.; Lombardi, F. An easy-to-use tool for the evaluation of leachate production at landfill sites. Waste Manag. 2016, 55, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Bing, L.; Qiang, X.; Ying, Z.; Chun, Y. The modelling of biochemical-thermal coupling effect on gas generation and transport in MSW landfill. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 46, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, C.M. T2LBM v.1: Landfill Bioreactor Model for TOUGH2; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharof, A.I.; Butler, A.P. Stochastic modelling of landfill leachate and biogas production incorporating waste heterogeneity. Model formulation and uncertainty analysis. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, S.; Chenu, D.; Quintard, M.; Lefebvre, X. A logistic model for the prediction of the influence of water on the solid waste methanization in landfills. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.; Fernandes, L.; Warith, M.A.; Rendra, S. A fuzzy logic model for biogas generation in bioreactor landfills. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 36, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Rodrigo-Clavero, M.E.; Cassiraga, E. BIOLEACH: A New Decision Support Model for the Real-Time Management of Municipal Solid Waste Bioreactor Landfills. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Component | Average Value (% Vol) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 (MOV) | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| CH4 | 63.8 | 88 | 40–60 | 45–60 | 35–60 | 60 | 63.4 |
| CO2 | 33.6 | 89.3 | 40–60 | 40–60 | 35–45 | 39.62 | 18 |
| O2 | 0.16 | 20.9 | - | 0–2.5 | 0.55 | 4.8 | |
| N2 | 2.4 | 87 | 5 | 2–5 | 0–20 | - | 13.8 |
| H | 0.05 | 21.1 | - | 0–0.2 | - | - | - |
| H2O | 1.8 | 4 | - | - | 1–10 | - | - |
| CO | - | - | 0.001 | 0–0.2 | - | 49.52 * | - |
| NH3 | - | - | 30 | 0–0.2 | - | - | - |
| H2S | - | - | 0.015 | 0–1 | 0–0.1 | 34.21 * | 11 |
| Model | Coupled Processes Considered by the Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal | Hydraulic | Mechanical | Biological | Biogas | |
| MODUELO [52] | x | x | x | x | |
| LDAT [53] | x | x | x | x | |
| [54] | x | x | x | x | |
| [55] | x | x | x | x | |
| [56] | x | x | x | x | |
| [57] | x | x | x | x | |
| [58] | x | x | x | x | |
| [59] | x | x | x | ||
| [60] | x | x | x | ||
| [61] | x | x | x | ||
| [62] | x | x | x | ||
| [63] | x | x | x | ||
| [64] | x | x | |||
| CODE_BRIGHT [65] | x | x | x | x | |
| [66] | x | x | x | ||
| BIOKEMOD-3P [67] | x | x | x | ||
| [68] | x | x | x | ||
| [69] | x | x | x | ||
| [70] | x | x | |||
| LAST [71] | x | x | |||
| [72] | x | x | x | ||
| T2LBM [73] | x | x | x | ||
| [74] | x | x | x | ||
| [75] | x | x | x | ||
| FLS [76] | x | x | x | ||
| BIOLEACH [77] | x | x | x | ||
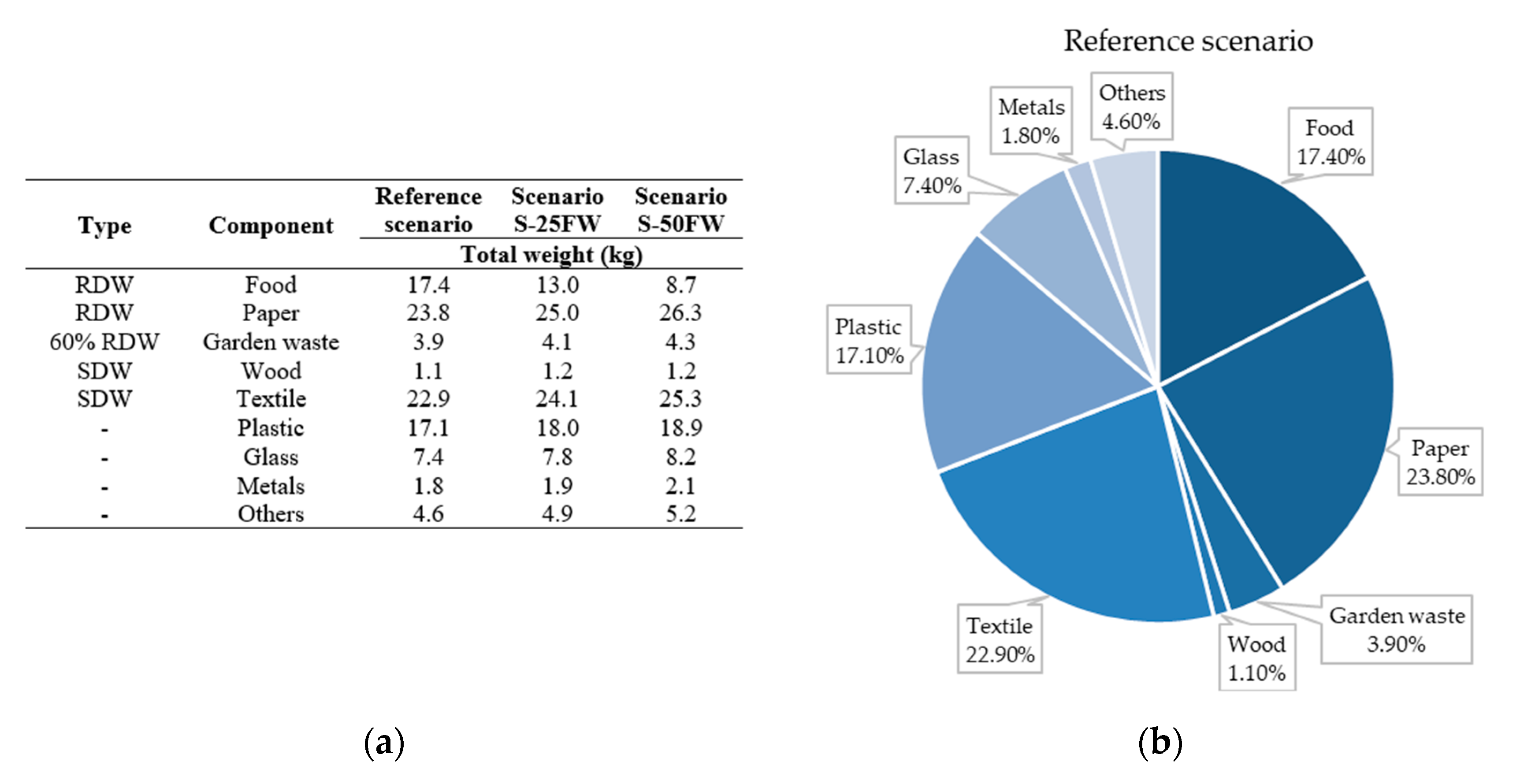
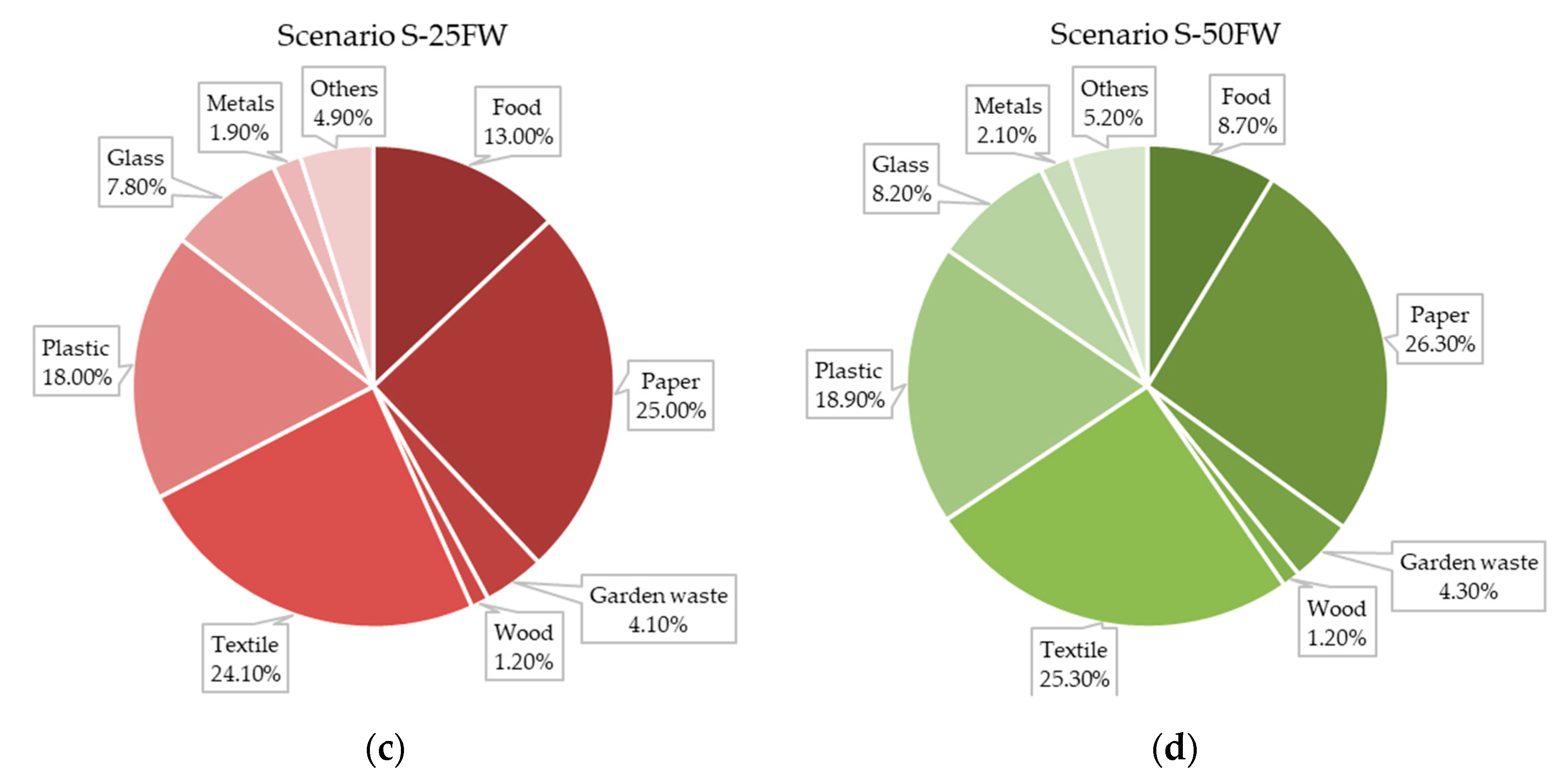
| Type | Component | Total Weight (kg) | Water Content (%) | C | H | O | N | S | Ashes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDW | Food | 17.4 | 50 | 48.0 | 6.4 | 37.6 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 5.0 |
| RDW | Paper | 23.8 | 5 | 43.5 | 6.0 | 44.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 6.0 |
| 60% RDW | Garden waste | 3.9 | 30 | 47.8 | 6.0 | 38.0 | 3.4 | 0.3 | 4.5 |
| SDW | Wood | 1.1 | 20 | 49.5 | 6.0 | 42.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.5 |
| SDW | Textile | 22.9 | 8 | 55.0 | 6.6 | 31.2 | 4.6 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| - | Plastic | 17.1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | Glass | 7.4 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | Metals | 1.8 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | Others | 4.6 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RDW | Food | 17.4 | 50 | 48.0 | 6.4 | 37.6 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 5.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Rodrigo-Clavero, M.-E. Mathematical Modeling of the Biogas Production in MSW Landfills. Impact of the Implementation of Organic Matter and Food Waste Selective Collection Systems. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121306
Rodrigo-Ilarri J, Rodrigo-Clavero M-E. Mathematical Modeling of the Biogas Production in MSW Landfills. Impact of the Implementation of Organic Matter and Food Waste Selective Collection Systems. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(12):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121306
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigo-Ilarri, Javier, and María-Elena Rodrigo-Clavero. 2020. "Mathematical Modeling of the Biogas Production in MSW Landfills. Impact of the Implementation of Organic Matter and Food Waste Selective Collection Systems" Atmosphere 11, no. 12: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121306
APA StyleRodrigo-Ilarri, J., & Rodrigo-Clavero, M.-E. (2020). Mathematical Modeling of the Biogas Production in MSW Landfills. Impact of the Implementation of Organic Matter and Food Waste Selective Collection Systems. Atmosphere, 11(12), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11121306






