Abstract
Considering the wide range of variability of all aerosol characteristics (especially in the near-ground layer of the atmosphere near industrial centers), when creating a realistic empirical model of optical and microphysical characteristics, the optimal dividing of the total data array according to some multifactor signs is needed. In this paper, we analyze the main states of “dry” aerosol on the basis of the results of long-term regular measurements in the near-ground layer of the atmosphere near the city of Tomsk in 2000–2017. The following parameters were considered: aerosol number concentration and size distribution function, total and angular scattering coefficients, including the small-angle range 1.2° to 20°, mass concentration and size distribution of absorbing substances (equivalent black carbon), characteristics of the aerosol hygroscopic properties, and spectral aerosol extinction of radiation on an open long path in the wavelength range 0.45 to 3.9 µm. In our comprehensive study, we first proposed and developed an original approach (classification) to study the optical and microphysical properties of atmospheric aerosol of various physicochemical origins (background, smoke, smog, anthropogenic, etc.) based on dividing the entire data array into characteristic subarrays (types of aerosol weather), which differ from each other in a different combination of scattering and absorbing properties of particles. To divide the total data array into types of aerosol weather including “Background”, “Haze-S”, “Smog”, and “Smoke haze”, the values of the scattering coefficient of the dry aerosol matter σd(λ = 0.51 μm) = 100 Mm−1 and the ratio of the mass concentration of the absorbing substance to the mass concentration of submicron aerosol P = 0.05. The results showed that most of the seasonal average values of the aerosol parameters analyzed in the paper are statistically significantly different when comparing various characteristic types of scattering and absorbing atmospheric aerosol. The results of the research indicate that the application of the developed classification of types of aerosol weather for the analyzed optical and microphysical parameters of aerosol particles is quite effective and reasonable.
1. Introduction
It is known that knowledge of the optical characteristics of atmospheric aerosols is needed to solve a wide range of fundamental and applied problems (see, for example, [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]). Due to the observed modern changes in the Earth’s climate system, one of the most complicated problems is to assess the role of atmospheric particles in the formation of the radiation regime [3,8].
This requires detailed information about aerosol scatter and absorption properties in the optical wavelength range [9,10,11]. Obviously, it is impossible to provide the necessary accuracy when specifying the optical and microphysical characteristics of atmospheric particles in modern climate models without carrying out measurements at various spatial scales (local, regional, global).
The aerosol state at a given time, at a particular observation site, depends both on the history of the air masses (in which, as they move in space, the aerosol composition is formed under the influence of many sources and processes of natural and anthropogenic origins), and on relatively quickly occurring processes directly in the period measurements. When creating approaches to the development of dynamic models based on the measurement results, an important step is to determine the optimal number of aerosol states that are most often realized at the observation point, similar to that usually used to describe weather and climate in a particular geophysical region. Gorchakov [12] introduced the term “optical weather” for continental conditions. The types of optical weather (haze, fog haze, drizzle haze) were separated based on the scattering properties. Continuing research, it became clear that only the scattering properties are not enough to identify the state of aerosol particles in the atmosphere. The absorption properties of the particles also must be considered. Then, the term “aerosol weather” was introduced [13]. This refers to the aerosol state at a given time at a particular observation site, which can be represented as a combination of its principal characteristics: concentration, chemical composition, particle size distribution function, growth factor, etc. Obviously, the most variable are the aerosol characteristics in the near-ground layer of the atmosphere and those at observation sites near large industrial centers. Here, in addition to the effects of large-scale processes (alternating air masses, etc.), the intrinsic rhythms of anthropogenic impact are superimposed (industrial and motor transport pollution types that have their own seasonal and diurnal cycles, which in turn depend largely on weather conditions). Considering the wide range of variability of all aerosol characteristics, when creating an empirical model, first of all, a certain typification of the total data array according to some criteria is necessary. In [14], in order to select the main states of the complex of optical and microphysical characteristics of the “dry” aerosol measured in the suburbs of Tomsk in all season, we proposed a version of the classification according to the types of “aerosol weather”. At the first stage, it was found that in all seasons, the main types of “aerosol weather” are reliably different in terms of the ratio of the content of submicron and coarse particles. Based on these encouraging results, in the present study, we analyze the whole complex of aerosol characteristics measured by our instruments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Measurement Site
Measurements of aerosol parameters (mass concentrations of the aerosol and absorbing substance (soot), particle size spectrum) have been carried out at the Aerosol station of the Institute of Atmospheric Optics of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (IAO SB RAS) [15], located in the southeastern suburb of Tomsk (56°28′ N, 85°05′ E, the southeast of the West Siberian Plain) every hour since 1997.
The region of Tomsk is characterized by continental climate (continental cyclonic type) with cold winter (temperature can be below −40 °C) and hot summer (up to 35 °C). The mean temperature in January is about −20 °C, and in July, it is about 20 °C. Winter lasts from November until March, and summer is from June until August. Snow lays on average 181 days a year. Its average maximum height is observed in March and is approximately 70 cm. South and southwest winds prevail in winter, spring, and autumn. In summer, the winds of northern and eastern directions often occur in the region.
In Tomsk region there are vast forests and wetlands, which are the main sources of natural aerosol. Significant sources of secondary aerosol are photochemical reactions in the atmosphere. A part of the aerosol is brought to the atmosphere of Tomsk under the influence of long-range transport. In particular, in summer, the Tomsk region is often influenced by smoke plumes of remote forest wildfires in Eastern Siberia.
In addition, the nearby industrial center also is a source of anthropogenic aerosol. The main urban sources are motor vehicles, state district power plants, and in winter, stove heating. In winter, there are often temperature inversions, which favor aerosol accumulation in the near-surface air layer.
2.2. Instrumentation and Techniques
Daily measurements of the dependences of the coefficient of aerosol scattering on the relative humidity of the air (hygrograms) were started in 1998. They allow one to study the hygroscopic properties of the particles. Round-the-clock, every-hour measurements of the angular scattering coefficients I(φ) in the small-angle range ϕ = 1.2°–20° at the wavelength of 0.65 µm were started in 2010, and those of the size distribution of the absorbing substance (soot) began in 2013. Measurements of the spectral transparency of the atmosphere on an along path are carried out mainly in the warm period of the year from March until October with a periodicity of 1–3 h. The following parameters of the atmospheric aerosol “dry matter” were used for analysis: the size distribution of aerosol particles, scattering coefficients σd (λ = 0.51 μm) (where the index “d” means “dry”), mass concentration and size distribution of the absorbing substance in the submicron aerosol fraction, angular scattering coefficients in the small-angle range I(φ), characteristics of the aerosol hygroscopic properties, and the results of measurements of the spectral transmission of the atmosphere in the wavelength range 0.45–3.9 µm on a near-ground long path.
The particle size distribution function was measured in the diameter range d = 0.4 to 10 µm by means of optical counters (in different years: AZ-5, AZ-10, and an instrument for Industrial Control – Gases, Tubes, Aerosol, Russian abbreviation is PKGTA) [16].
Investigations of the absorbing substance in the aerosol composition were carried out using an aethalometer (absorption photometer). The aethalometer was calibrated by a gravimetric method using pure soot (black carbon). Therefore, in this article, we also use the terms “soot” and “black carbon” (BC) to describe the properties of the absorbing substance of an aerosol, keeping in mind that we are talking about the absorbing component as a whole. The parameters related to the absorbing fraction are marked by the index “BC”. Measurements of the absorbing substance size distribution were carried out by means of a diffuse spectrometer of soot [17,18], which is a combination of a selector of particles (eight-stage diffuse battery of a grid type) and a Multiwavelength Differential Aethalometer (MDA) designed at IAO SB RAS [18]. The method provides for measurements of the size distribution of the mass concentration of soot in the size range 10 to 1000 nm.
Measurements of the spectral transparency of the atmosphere Т(λ) and determination of the aerosol extinction coefficients β(λ) in the wavelength range 0.45 to 3.9 μm have been carried out since 2000 on an 880-m long near-ground path by means of a two-channel multiwavelength photometer [19]. During 2000–2006, the random error δβ in determining the coefficients β(λ) was 8 to 14 Mm−1 in different years. In 2007, because of technical reasons, the path on which the extinction is measured was moved to another place. During 2007–2017, the error δβ was 37 to 54 Mm−1. Besides this, as the data show, its new location turned out to be under higher anthropogenic loading. The different quality levels of the data prevent combining them into one array. Considering the purpose of this work, an analysis was made of the 2000–2006 array, which was obtained in less polluted atmospheric conditions. In addition, the data on the spectral transparency of the atmosphere in winter are very few, so this parameter is analyzed for three warm seasons: spring, summer, and autumn.
To study the transformation of the optical and microphysical properties of aerosol under the effect of changing air humidity, a method was developed [20], which includes measuring the scattering coefficients of aerosol particles at zero relative humidity (in a real experiment, humidity values usually do not exceed 20–30%) and their changes during the process of artificial humidification.
Thus, the following time intervals were considered for the aerosol parameters:
- 2000–2017 for the angular scattering coefficient at the angle of 45°, the mass concentrations of aerosol and absorbing substance (soot, equivalent black carbon), the number, concentration, and particle size distribution function, the parameter of condensation activity;
- 2010–2017 for the angular scattering coefficients at small angles (1.2° to 20°);
- 2013–2017 for the size distribution of the absorbing substance (equivalent black carbon); and
- 2000–2006 for the aerosol extinction coefficients.
A summary table of the average values of the measured and calculated parameters and their standard deviations is given in Appendix A.
2.3. Aerosol Weather Classification Principle
A study of the factors of the formation of aerosol weather was begun in [13], and as the data accumulated, in 2019, an attempt was made to analyze the differences in the particle size distribution functions and the aureole scattering phase function in different types of aerosol weather [14].
In the framework of the proposed classification, the entire data array for each season was divided into four types of “aerosol weather”: “Background”, “Haze-S”, “Smog”, and “Smoke haze”. We call haze “Haze-S”, because the measurement site is located in a suburban area, and hence, we are dealing with suburban haze. Separation by types of “aerosol weather” was carried out in the coordinates “σd–P”, where σd is the scattering coefficient of the dry aerosol matter (λ = 0.51 μm), and P is the ratio of the mass concentration of the absorbing substance to the mass concentration of submicron particles [21]. Separation of the data array along the boundary σd = 100 Mm−1 was made based on knowledge of the properties of one-parameter models of surface hazes [22]. The allocation of situations according to P = MBC/MA, where MBC is the mass concentration of black carbon, and MA is the mass concentration of submicron aerosols (P-criterion), was carried out on the basis of information about the optical characteristics of the smoke of distant forest fires [21].
Figure 1 shows the percentages of different types of aerosol weather in the total data array (2000–2017) [14]. Let us note that when analyzing the specific parameters relating to each type of aerosol weather, the quantity of data may differ from that given in the general figure. In particular, measurements of angular scattering coefficients in the range ϕ = 1.2 to 20° were started in 2010, and measurements of the size distribution of absorbing substances were started in 2014.
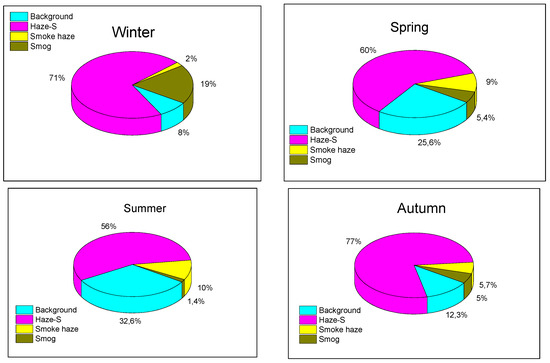
Figure 1.
Percentage of occurrences of aerosol weather types in different seasons according to the data set obtained in 2000–2017.
The figure shows that the total proportion of situations related to the class of “Haze” (“background” and “Haze-S”) in all seasons was 80–90%. The proportion of situations with high turbidity (“Smog” and “Smoke haze”) was much smaller (10–20%). These types of weather have their specific a priori sources of aerosol particles. In the first case, these are urban sources of pollution (boiler houses, state district power plants, motor vehicles); in the second case, these are smoke plumes from remote forest wildfires. Due to the specificity of the sources, it is clear that the aerosols in these types of weather will have chemical and morphological compositions characteristic of this type of weather only. Therefore, in addition to the formal division into types of aerosol weather, the other parameters in smog situations should noticeably differ from those for the class of hazes.
Considering the rather formal separation of the haze class (“Background” and “Haze-S”), one problem is to try to answer the question of whether such a separation is appropriate, or whether the haze class can be considered a single type of aerosol weather.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size Distribution Function
3.1.1. A Technique for Correcting the Optical Counter Data Using the Aureole Scattering Phase Function Data
Measurements of particle size distributions using optical counters are limited to a particle diameter range of 0.4 to 10 μm. Obviously, to retrieve the aerosol optical characteristics in the visible and infrared wavelength ranges, it is necessary to have information about the size distribution function from a few hundredths up to at least tens of microns. It is known that when approximating the size spectrum beyond the boundaries of the counters’ sensitivity, errors are unavoidable [16,23,24,25,26].
Earlier, when creating the tropospheric aerosol model, a procedure [27] was applied, where the particle size distribution was represented by a superposition of two lognormal distributions: submicron (i = sub–submicron) and coarse (i = c–coarse) particle fractions.
Here, r is the particle radius; ln2Si is the geometric standard deviation of the mode i; ri and Vi are the median radius and the volume concentration of mode i, respectively, and n = 2.
A comparison of the extinction coefficients reconstructed in the framework of the empirical model and the measured aerosol optical depth [14,27,28,29,30] showed that the representation of the distribution function with dispersion lnSsub = 0.8 is quite acceptable for wavelengths in the visible range and is consistent with the results of many researchers [31,32,33].
The greatest problems in the comparison were observed in the near IR region, where the correct data on the size distribution of coarse particles were obviously insufficient. Then, when approximating and correcting the size distribution in this range, the width of the submicron fraction lnSsub = 0.8 was fixed for all types of “aerosol weather” and seasons. The measured angular scattering coefficients I(φ) in the range of scattering angles φ = 1.2° to 20° provide data on particle sizes up to 10 to 15 μm [34,35].
The size spectrum was corrected in several stages. At the first stage, a formal approximation of the experimental data obtained in measurements by an optical counter of the form dV/dlnr of two lognormal functions Vsub and Vc was carried out. To estimate the ratios of the concentrations of submicron and coarse fractions, the volume concentration of the submicron fraction Vsub was taken to be equal to 1, and the volume concentration of the coarse fraction Vc was calculated from the ratio Vc/Vsub [25].
At the second stage, according to the Mie formulas, the angular scattering coefficients were calculated in the angular range φ = 1.2° to 20°. Then, the calculated and the measured scattering coefficients normalized to the value of the scattering coefficient at an angle of 10° were compared. The distribution parameters (the median radius, geometric standard deviations, and the volume concentration) were determined by an iterative technique (the library fit technique). The necessary number of iterations was chosen to ensure a minimum of discrepancy between the calculated and measured values of the angular scattering coefficients in the small-angle range. An example of the results of such a selection is presented in Figure 2. Here, the big hollow circles show the data of the measured angular scattering coefficient, and the small solid squares show the calculated data. The estimates show that the error in determining the scattering coefficients lies in the range of 3% to 11%.
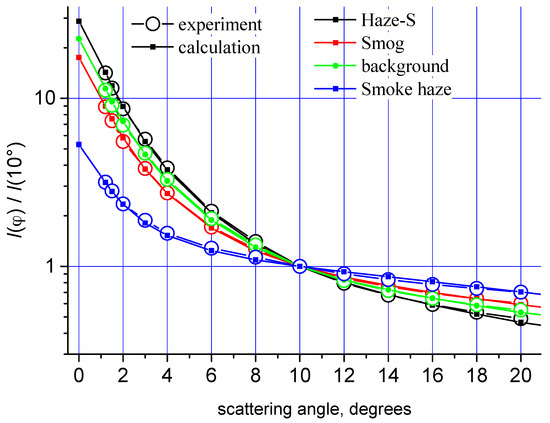
Figure 2.
An example of “fitting” the angular scattering coefficients calculated using the Mie formulas to the measured values in different types of aerosol weather for summer.
Differences in the shape of the aerosol particle size distribution function before and after correction in the size range of coarse particles using the data on the angular scattering coefficients in the range φ = 1.2° to 20° are shown in Figure 3.
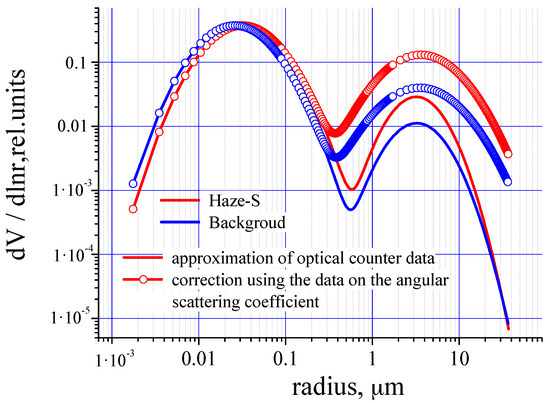
Figure 3.
Volume distributions obtained according to the data from the optical counter and corrected according to the data of the angular scattering coefficients (summer). The red lines indicate the “Haze-S” weather type, the blue lines indicate the “Background” type, the solid lines are the approximation of the data from the optical counter, and the circles show the distributions after correction using the angular scattering coefficients.
3.1.2. Analysis of The Parameters of The Particle Size Distributions in Different Types of Aerosol Weather
The values of the retrieved parameters of the distribution functions of the form given in Equation (1) are presented in Appendix A. As can be seen from the data, the trend of an increasing median radius of the submicron fraction rsub was observed for almost all seasons, from minimum values in the “Background” conditions to maximum values in the conditions of “Smoke haze”. Only in winter was the rsub value for “Smoke haze” slightly less than that for “Smog”, which is probably due to insufficient data for this situation (the total proportion of smog and smoke situations in different seasons did not exceed 10–20%). The maximum rsub values were observed in autumn in all types of aerosol weather, and the minimum values are realized in summer in “Background” and “Haze-S”. The maximum values of the median radius of the coarse fraction rc in the spring and summer are quite explainable by the effect of the emission of coarsely dispersed particles from the open ground surface. It is also quite obvious that the minimum values of rc in all types of aerosol weather are observed in the cold period, when the ground surface is covered with snow.
We note that the lnSc value characterizing the distribution width of the coarse fraction was quite stable in different types of aerosol weather. In summer, spring, and autumn, it was approximately the same and varied in the range of 0.87–0.95. In winter in all types of aerosol weather, this parameter takes on large values from 1.15 to 1.3.
3.2. Analysis of the Size Distribution of the Absorbing Substance (Equivalent Black Carbon) Concentration in Different Types of Aerosol Weather
Studying the distribution of the absorbing substance over the size spectrum of atmospheric aerosol is important for the development of correct models for calculating radiation-relevant optical characteristics, primarily the aerosol single scattering albedo in the visible wavelength range. This parameter determines the role of aerosols in the atmosphere as a cooling or warming factor, causing aerosol radiation forcing in the atmosphere and climate change [36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. Information about the equivalent black carbon (EBC) size distribution is also necessary for correct estimates of the mass of absorbing substances falling to the surface at various distances from remote sources of industrial pollution and smoke from wildfires, including in the Arctic region [38,43,44,45]. Detailed studies of the dynamics of the optical and microphysical properties of absorbing atmospheric aerosols are also important for the development of empirical aerosol models [27].
To study the peculiarities of the variability of the size distribution of the absorbing substance (EBC) in various types of aerosol weather, its content in a submicron aerosol was analyzed as a function of the diameter of aerosol particles in an approximation of a single-mode lognormal distribution [46]:
where D (nm) is the diameter of aerosol particles, VBC (µm3/cm3) is the volume concentration of the absorbing substance, DBC (nm) is the median diameter of EBC size distribution, and SBC is the geometric standard deviation. In this section, we analyze the dynamics of the absorbing substance size distribution in the form of the product of the volume concentration VBC and the normalized BC size distribution function dVBC/dlnDnorm:
dVBC/dlnD = VBC × (dVBC/dlnD)norm
This approach allows us to separately study the variability of the volume concentration of black carbon, which characterizes its content in a unit volume of air, and the normalized to volume concentration BC size distribution, characterizing qualitative changes in the distribution due to variation of the shape parameters DBC and SBC.
During the period of measurements, a data array was obtained containing 959 measurements of daily average size distributions of the absorbing substance. Based on these data, the average normalized size distributions were calculated for the four seasons and types of aerosol weather, and the main distribution parameters were determined: the average values of the volume concentration VBC, the median diameter DBC, and the standard deviations SBC. The average seasonal size distributions of the absorbing substance are shown in Figure 4, and their parameters are given in Appendix A. The figure also shows the number of measurements in each type of aerosol weather.
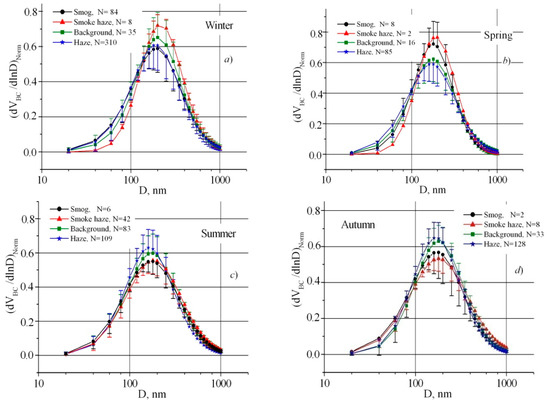
Figure 4.
Seasonal average normalized size distributions of the absorbing substance in the different types of aerosol weather in winter (a), spring (b), summer (c), and autumn (d).
Then, we compared our data with the results of other researchers [43,44,45,47,48,49,50,51,52]. The obtained ranges of variations in the mean values of the median diameter DBC are in good agreement with the data of airborne measurements of the refractory BC (rBC) mass concentration using a single-particle soot photometer (SP2) in the Canadian Arctic, presented in [44], from flights at the altitudes from 0.1 to 5.5 km in the summer of 2014 and in the spring of 2015. In these flights, the BC median diameter varied from 160 in summer to 220 nm in spring. Close ranges of variation in DBC = 168 to 192 nm were obtained in [45] from marine measurements of black carbon in aerosol particles over the Arctic Ocean, Bering Sea, and North Pacific Ocean during September 2014. Let us note that according to the data obtained earlier in ground-based and airborne measurements in different geographical areas using different methods for selecting aerosol particles (impactor [45,49], electric mobility [52], and SP2, analysis of individual particles [51,52]), a soot concentration mode with DBC values in the range from 170 to 200 nm was regularly observed. In this case, the values DBC = 200 nm were observed in industrial city conditions [50].
An assessment of the significance of differences in the distribution parameters by Student’s test showed that statistical significance of the differences in the median diameter DBC in different weather types is mainly observed in winter and summer, and significant differences in the average SBC values were observed in summer and autumn (at a probability level of difference greater than 0.95).
To compare the distributions, let us consider in detail the situations related to the types of aerosol weather “Background” and “Haze-S”. We see that significant differences in the distributions can be observed both near the mode (the diameter range of D = 100–300 nm, in which the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) values are highest) and in the ranges of small (D < 100 nm) and large (D > 300 nm) particles. In winter, statistically significant differences in distributions were observed between all types of aerosol weather in almost the entire considered size range. In spring, differences were significant only when comparing situations of the haze class (“Background” and “Haze-S”) and the class of smog and smoke haze. It should be noted that in the summer and autumn, significant differences are observed between the distributions in aerosol weather types “Background” and “Haze-S” in the size range near the median radius.
3.3. Aerosol Hygroscopic Properties in Different Types of Aerosol Weather
Knowledge of the dynamics of aerosol optical parameters with changes in relative humidity is important for assessing radiative properties. Such information obtained experimentally is clearly not enough for the whole set of atmospheric–optical situations realized in the environment [53]. There have been attempts in the literature to connect aerosol properties, including hygroscopicity, with its chemical and disperse composition, type of air mass, and direction of its transfer [54,55,56,57]. Most studies of aerosol hygroscopic properties have been aimed at investigating the dynamics of size and optical constants of particles with changing humidity [57,58,59], and only a few works have been devoted to studying the actual optical and radiation-significant parameters [60,61,62,63,64].
Many researchers use the formula of the Kasten–Hänel type for a quantitative description of the dependence of the angular scattering coefficient on the relative humidity of air [65,66]:
where I is the angular aerosol scattering coefficient, RH is the relative humidity of air, and γ is the optical parameter of the aerosol condensation activity, which characterizes the change in the scattering coefficient with variation in the relative humidity.
I = I0(1 − RH)−γ
This formula is a one-parameter representation; the dependence becomes linear in the coordinates lnI–ln(1 − RH), and the parameter γ characterizes the slope of the obtained straight line [67]. This representation is especially convenient in the cases of when to study condensation activity, the drying method is used, and the scattering coefficient is measured at two values of relative humidity: ambient atmospheric (in situ) and close to zero [63,64]. In our investigations, we apply the technique of artificial humidification of the aerosol under study, which provided the possibility of detailed study of the dynamics of the aerosol optical characteristics in different ranges of relative humidity. The seasonal average values of the parameter γ in different types of aerosol weather are given in Appendix A.
The measurements showed that in the entire range of relative humidity under consideration, the one-parameter representation in Equation (4) is valid only in a limited number of realizations [65]; in other cases, at a certain humidity value, a dramatic increase in the scattering coefficient was observed due to the phase transition (dissolution) of the particle matter.
The seasonal features of the manifestation of the types of hygrograms were analyzed in [67,68], and the following notations was introduced there: G0 is the type of hygrogram without phase transition, i.e., the dependence is described by Equation (4) with the same condensation activity parameter throughout the entire range of relative humidity; G1 and G2 are the types of hygrograms with a phase transition, which is conventionally called by us “angle” and “step”. In the first case, at a certain humidity value, the rate of increase of the scattering coefficient changes, i.e., the two sections below and above the “threshold” humidity value are characterized by their own values of the parameter γ. In the second case, in addition to a changing rate of increase of the scattering coefficient with humidity, there is a dramatic increase in a narrow range of relative humidity (1–2% wide).
In each of the identified types of aerosol weather, the frequencies were determined for when a phase transition was recorded with an increase in relative humidity. The analysis showed that phase transitions were observed only during aerosol weather such as “Background” and “Haze-S”, i.e., in slightly turbid situations. In situations of the types, “Smog” and “Smoke haze”, a phase transition was recorded only in very few cases. Moreover, this, as a rule, was observed at a level of scattering coefficient of aerosol dry matter that only slightly exceeded the value σd = 100 Mm−1, which we chose as the “boundary” for the separation of aerosol weather types and is conditional. Therefore, detailed analysis of the aerosol hygroscopicity here was carried out only for atmospheric situations of the types “Background” and “Haze-S”.
Figure 5 shows the frequencies of each type for two kinds of aerosol weather: “Background” and “Haze-S”. It was found in [68] that hygrograms with phase transition appear only under conditions of σ < 100 Mm−1 (i.e., in the types of aerosol weather “Background” and “Haze-S”). Only these two types are shown in Figure 5, because there is only one type of hygrogram (G0) under conditions of “Smog” and “Smoke haze” [68]. As already noted in the analysis of the seasonal features of the appearance of various types of hygrograms [67,68], the phase transition most often occurred in spring, and in summer, their number is minimal. As the analysis showed, in the warm seasons (spring, summer, autumn), the frequencies of phase transition of the aerosol matter during humidification were almost the same in the “Background” and “Haze-S” types of aerosol weather. In winter, under “Background” conditions, the frequency of phase transitions was almost two times higher compared to that under to “Haze-S” conditions (43% and 20%, respectively).
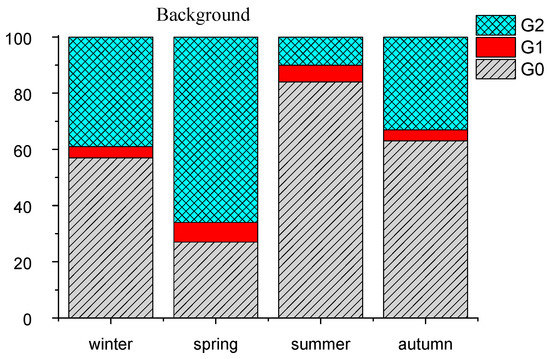
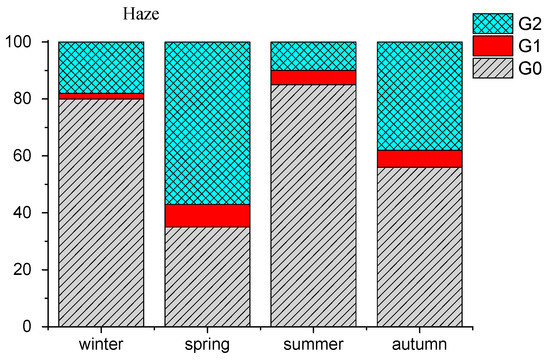
Figure 5.
Frequencies of occurrence of different types of hygrograms in types of aerosol weather “Background” and “Haze-S”.
To assess the differences in the condensation activity parameter in the “Background” and “Haze-S” arrays, the values γ were calculated in the relative humidity range of 30–90% without taking into account the presence or absence of a phase transition. In this case, for hygrograms of type G0, this is an experimentally observed parameter of condensation activity, and for dependences of types G1 and G2 (phase transition), it gives an idea of the average rate of increase of the angular scattering coefficient with increasing relative humidity from 30% to 90%.
The seasonal average values of the parameter γ in different types of aerosol weather are given in Appendix A. The estimates showed that significant differences in the value of the parameter of condensation activity γ appeared in the data arrays “Background” and “Haze-S” only in spring.
3.4. Spectral Transparency of The Near-Ground Atmosphere
The average values and RMSDs of the aerosol extinction coefficients β(λ) at different wavelengths for different seasons and types of aerosol weather are presented in Appendix A.
To describe the spectral dependences of the total aerosol extinction coefficients β(λ) in the wavelength range 0.45–0.83 μm, the Angstrom formula was applied:
β(λ) = B∙λ−α
The parameter B denotes the extinction coefficient at the wavelength of 1 μm, and the exponent α characterizes the slope of the spectral dependence of the coefficients β(λ) in the considered wavelength range. The parameters α and B were calculated for each obtained realization β(λ); their average values and RMS deviations are also given in Appendix A. Estimation of the reliability of differences in the parameters α and B in different types of aerosol weather showed that in all seasons, the Angstrom exponent α and the parameter B in the arrays “Background” and “Haze-S” are different.
Let us note that on an open atmospheric path, there are almost always coarse aerosol particles of various origins (dust, organic matter, droplets of fog). For a correct analysis of the results, it is necessary to divide the total aerosol extinction of radiation into components due to submicron and coarse particles. To separate the coefficients β(λ) into components associated with submicron (sub) and coarse (c) aerosols, it was assumed that aerosol extinction at a wavelength of 3.9 μm is caused only by coarse aerosol, and that the spectral dependence of the extinction of radiation by the coarse aerosol fraction is not related to the wavelength. In this case, the aerosol extinction component due to submicron aerosol βsub(λ) can be represented as:
βsub(λ) = β(λ) − β(3.9)
Such an approach to the separation of the aerosol extinction into components was previously used when analyzing the results of measurements of aerosol optical depth [29,69].
For each spectral dependence obtained, the parameter CD = β(3.9)/β(0.55) was calculated, which is equal to the ratio of the aerosol extinction coefficients measured at wavelengths of 3.9 μm (characterizes extinction by the coarse fraction) and 0.55 μm (total extinction by submicron and coarse aerosols). This parameter corresponds to the fraction of extinction of radiation by a coarse aerosol at a wavelength of 0.55 μm. Figure 6 shows histograms of the distribution of the CD parameter for three seasons.
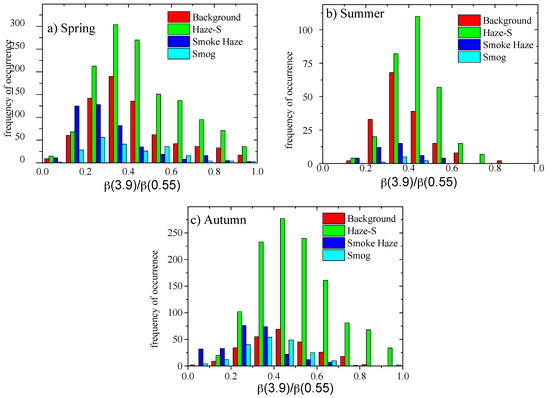
Figure 6.
Histograms of the distribution of the parameter CD = β (3.9)/β(0.55) in three seasons: spring (a), summer (b), and autumn (c).
A comparison of this parameter in the data arrays “Background” and “Haze-S” showed that the Angstrom exponent α and the parameter CD = β(3.9)/β(0.55) were different in all seasons (spring, summer, autumn).
3.5. General Remarks
Before proceeding to the analysis of the results obtained, let us note that the main purpose of our long-term comprehensive studies of the aerosol optical and microphysical characteristics is to create an empirical model of a regional scale, where an important step is to determine the optimal number of measured input parameters. Based on the experience of creating such models, it is obvious that the large range of variability of aerosol characteristics in the near-ground layer of the atmosphere will not allow us to find the minimum necessary set of parameters without a definite classification of their most typical realizations.
The classification considered in this paper (based to a certain extent on an intuitive definition of the boundaries) according to types of aerosol weather is only the first step to highlight the basic states of the optical and microphysical characteristics of the “dry” aerosol matter measured in the near-ground layer of the atmosphere in the suburbs of Tomsk. The analysis of the aerosol particle size distribution function, aerosol scattering coefficient σd (λ = 0.51 μm), mass concentration and size distribution of the absorbing substance in the submicron aerosol fraction, angular scattering coefficients in the small-angle range I(φ), characteristics of the aerosol hygroscopic properties, and the results of measurements of the spectral transmittance of the atmosphere in the wavelength range 0.45 to 3.9 μm on a long open near-ground path showed that for most of them, in each season, reliable differences in the various types of aerosol weather were observed. Obviously, the types “Smog” and “Smoke haze”, which we consider as separate classes, were observed in less than 30% of cases, differ a priori already in the given coordinates “σd–P”, and have well-defined aerosol sources. So, let us discuss in more detail the results obtained in the class of “Haze” (“Background” and “Haze-S”). To do this, let us consider Table 1, where an assessment of the level of significance of differences in the parameters between the aerosol weather types “Background” and “Haze-S” is presented.

Table 1.
Estimation of significance of differences between the aerosol weather types Background and Haze-S.
Let us emphasize that the proposed classification is based on analysis of the measurement data of the aerosol “dry matter” by means of various methods and instruments. Obviously, each of them most correctly represents the role of particles of only a limited size range. To construct an empirical model suitable for assessing the whole complex of aerosol optical characteristics, undoubtedly, a next stage of correction of the input parameters based on a comparison of the results of retrieval and measurements in the real atmosphere will be required.
Figure 7 shows an example of a comparison of model calculations (input parameters taken from Appendix A for summer, “Haze-S”) and the average values of the measured angular scattering coefficients and spectral extinction coefficients. The values of the angular scattering coefficients in absolute units in the small-angle range (Figure 7a) begin to differ only in the angular range < 3°, which is quite expected because of the large variability of the contribution of particles with size greater than 5 μm and do not go beyond the range of standard deviations of the measured I(φ). In turn, the data from direct calculation (Appendix A, summer, “Haze-S”) of the spectral behavior of the extinction coefficients in the visible wavelength range (Figure 7b) are approximately 30% lower than the measured average values. By increasing the total volume of the submicron fraction by 30%, we could achieve a very good agreement between the measured and retrieved values (Figure 7b).
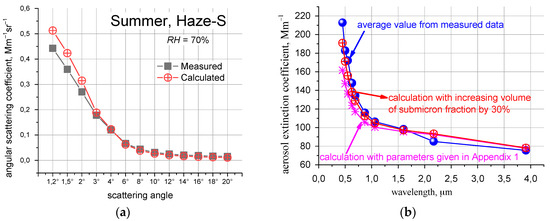
Figure 7.
Comparison of measured and calculated values of angular scattering coefficient (a) and spectral behavior of the extinction coefficients in the visible wavelength range (b).
The presented example illustrates the algorithm for further development of the empirical model and adequate correction of its input parameters, and the results obtained already at this stage inspire some optimism in the correctness of the chosen direction.
4. Conclusions
Summarizing the material presented, we can conclude that most of the aerosol characteristics in different types of aerosol weather significantly differ. However, it was shown that in the warm season, these arrays are not distinguishable on average by the condensation activity parameter, which apparently opens up the possibility of using the available measurement data when retrieving the dependence of the optical characteristics on the relative air humidity for the entire class of hazes as a whole.
Author Contributions
Methodology: M.V.P.; Instrumentation maintenance: V.P.S.; Measurements: V.S.K., V.V.P. (Victor V. Polkin), V.V.P. (Vasily V. Polkin), D.G.C., S.A.T., V.N.U., E.P.Y.; Calculations: P.N.Z.; Analysis of results: M.V.P., V.S.K., V.V.P., V.V.P. (Vasily V. Polkin), S.A.T., V.N.U.; Writing and figures: M.V.P., V.S.K., V.V.P. (Victor V. Polkin), S.A.T., V.N.U.; Layout: S.A.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The long-term measurements were carried out within the framework of the state assignment for the project AAAA-A17-117021310142-5. Analysis of the aerosol characteristics in different types of aerosol weather in 2019 was made with the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation (Agreement No. 19-77-20092).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Average values and root mean square(rms) deviations (in parentheses) of the atmospheric aerosol parameters.
Table A1.
Average values and root mean square(rms) deviations (in parentheses) of the atmospheric aerosol parameters.
| Season | Type of Aerosol Weather | Particle Size Distribution Function | Ratio of Angular Scattering Coefficients | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rsub, μm | After Correction by Angular Scattering Coefficient | Before Correction | Nf/Nc | I(20°)/I(1.2°) | ||||||
| rc, μm | lnSc | Vc/Vsub | rc, μm | lnSc | Vc/Vsub | |||||
| Spring | Background | 0.03 (0.003) | 3.8 | 0.95 | 0.18 | 3.25 | 0.68 | 0.04 | 68 (50) | 0.068 (0.050) |
| Haze-S | 0.039 (0.001) | 3.9 | 0.95 | 0.45 | 3.76 | 0.71 | 0.11 | 64 (51) | 0.056 (0.040) | |
| Smoke haze | 0.05 (0.006) | 4.1 | 0.95 | 0.38 | 3.79 | 0.84 | 0.10 | 97 (57) | 0.116 (0.107) | |
| Smog | 0.036 (0.003) | 4.1 | 0.95 | 0.14 | 4.14 | 0.81 | 0.04 | 100 (43) | 0.114 (0.072) | |
| Summer | Background | 0.026 (0.005) | 3.5 | 0.90 | 0.12 | 3.24 | 0.64 | 0.024 | 60 (39) | 0.053 (0.023) |
| Haze-S | 0.032 (0.011) | 3.6 | 0.87 | 0.38 | 3.20 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 48 (34) | 0.039 (0.016) | |
| Smoke haze | 0.086 (0.012) | 3.3 | 0.90 | 0.16 | 2.53 | 0.62 | 0.313 | 93 (48) | 0.172 (0.106) | |
| Smog | 0.042 (0.005) | 3.3 | 0.90 | 0.25 | 2.96 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 71 (33) | 0.068 (0.047) | |
| Autumn | Background | 0.042 (0.003) | 3.2 | 0.90 | 0.26 | 2.79 | 0.60 | 0.06 | 83 (70) | 0.078 (0.035) |
| Haze-S | 0.047 (0.007) | 3.4 | 0.90 | 0.48 | 3.09 | 0.63 | 0.15 | 75 (65) | 0.066 (0.044) | |
| Smoke haze | 0.102 (0.02) | 2.8 | 0.95 | 0.28 | 3.58 | 0.93 | 0.35 | 96 (72) | 0.190 (0.078) | |
| Smog | 0.71 (0.011) | 3.2 | 0.90 | 0.55 | 3.24 | 0.66 | 0.29 | 78 (59) | 0.101 (0.078) | |
| Winter | Background | 0.035 (0.004) | 3.0 | 1.25 | 0.1 | 2.95 | 0.77 | 0.03 | 108 (86) | 0.150 (0.068) |
| Haze-S | 0.0435 (0.005) | 3.0 | 1.25 | 0.2 | 3.52 | 0.84 | 0.068 | 117 (128) | 0.135 (0.061) | |
| Smoke haze | 0.043 (0.010) | 3.0 | 1.15 | 0.12 | 3.25 | 0.80 | 0.053 | 107 (45) | 0.154 (0.062) | |
| Smog | 0.056 (0.008) | 3.1 | 1.3 | 0.19 | 3.61 | 0.93 | 0.094 | 131 (115) | 0.167 (0.047) | |

Table A2.
Table A1 continued.
Table A2.
Table A1 continued.
| Season | Type of Aerosol Weather | BC Size Distribution | Extinction Coefficients, Mm−1 | α | B | γ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBC, nm | SBC | λ = 0.45 | λ = 0.55 | λ = 0.69 | λ = 1.06 | λ = 3.9 | |||||
| Spring | Background | 175 (18.5) | 0.64 (0.16) | 204 (104) | 159 (78) | 122 (65) | 93 (56) | 69 (51) | 1,07 (0,45) | 96 (56) | 0.426 (0.12) |
| Haze-S | 167 (16) | 0.67 (0.13) | 227 (113) | 180 (89) | 140 (78) | 114 (70) | 89 (69) | 1,00 (0,42) | 115 (71) | 0.305 (0.14) | |
| Smoke haze | 192 (3.2) | 0.52 (0.05) | 367 (192) | 281 (148) | 204 (108) | 128 (67) | 78 (56) | 1,14 (0,36) | 161 (79) | 0.183 (0.040) | |
| Smog | 175 (17.7) | 0.56 (0.11) | 373 (145) | 289 (114) | 218 (92) | 152 (79) | 115 (79) | 1,31 (0,41) | 138 (70) | 0.130 (0.060) | |
| Summer | Background | 173 (18.1) | 0.66 (0.12) | 202 (76) | 166 (62) | 124 (52) | 95 (44) | 64 (26) | 1,02 (0,29) | 98 (45) | 0.230 (0.12) |
| Haze-S | 163 (14.4) | 0.63 (0.11) | 213 (71) | 172 (58) | 134 (47) | 106 (41) | 76 (31) | 0,90 (0,27) | 109 (41) | 0.215 (0.10) | |
| Smoke haze | 182 (20.4) | 0.71 (0.10) | 336 (129) | 268 (111) | 192 (77) | 135 (50) | 82 (28) | 1,15 (0,15) | 118 (28) | 0.066 (0.060) | |
| Smog | 170 (20.5) | 0.72 (0.08) | 276 (46) | 215 (36) | 158 (21) | 117 (32) | 75 (15) | 1,17 (0,32) | 139 (51) | – | |
| Autumn | Background | 169 (15.6) | 0.65 (0.09) | 237 (113) | 193 (85) | 150 (69) | 110 (62) | 85 (44) | 1,00 (0,38) | 116 (62) | 0.305 (0.16) |
| Haze-S | 168 (13.6) | 0.61 (0.08) | 225 (113) | 180 (90) | 146 (73) | 118 (64) | 90 (46) | 0,81 (0,40) | 122 (64) | 0.302 (0.12) | |
| Smoke haze | 178 (17.2) | 0.74 (0.10) | 434 (308) | 381 (295) | 283 (221) | 155 (92) | 86 (34) | 1,06 (0,33) | 175 (82) | 0.203 (0.063) | |
| Smog | 167 (36) | 0.69 (0.15) | 386 (184) | 310 (157) | 238 (121) | 164 (79) | 110 (51) | 1,21 (0,35) | 172 (108) | 0.222 (0.082) | |
| Winter | Background | 199 (24.8) | 0.60 (0.15) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.301 (0.11) |
| Haze-S | 186 (24) | 0.65 (0.15) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.285 (0.11) | |
| Smoke haze | 218 (7.10) | 0.55 (0.05) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.226 (0.061) | |
| Smog | 188 (29) | 0.67 (0.14) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.216 (0.079) | |
References
- Rosenberg, G.V. The properties of an atmospheric aerosol from optical data. Izv. Acad. Sci. USSR Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 1967, 3, 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Seinfield, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Haywood, J.; Boucher, O. Estimates of the direct and indirect radiative forcing due to tropospheric aerosols: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2000, 38, 513–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, E.; Sheridan, P.J.; Ogren, J.A. Seasonal differences in the vertical profiles of aerosol optical properties over rural Oklahoma. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10661–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenicke, R. Atmospheric aerosol and global climate. J. Aerosol Sci. 1980, 11, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC Fifth Assessment Report: Climate Change. 2013. Available online: http://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/ (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R.; Nazarenko, L.; Lacis, A.; Schmidt, G.A.; Russell, G.; Aleinov, I.; Bauer, M.; Bauer, S.; et al. Efficacy of climate forcings. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D18104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Yu, H.; Chin, Y.; Feingold, M.; Remer, G.; Anderson, L.; Balkanski, Y.; Bellouin, Y.; Boucher, O.; Christopher, S.; et al. A review of measurement based assessments of the aerosol direct radiative effect and forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 613–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, T.S.; Anderson, T.L.; Baynard, T.; Bond, T.; Boucher, O.; Carmichael, G.; Clarke, A.; Erlick, C.; Guo, H.; Horowitz, L.; et al. Aerosol direct radiative effects over the northwest Atlantic, northwest Pacific, and North Indian Oceans: Estimates based on in-situ chemical and optical measurements and chemical transport modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1657–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrtdinov, I.M.; Zhuravleva, T.B.; Chesnokova, T.Y. Estimation of direct radiative effects of background and smoke aerosol in the IR spectral region for Siberian summer conditions. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2018, 31, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorchakov, G.I. The light scattering matrix and types of optical weather. Izv. Acad. Sci. USSR Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 1973, 9, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Panchenko, M.V.; Pkhalagov, Y.A.; Rakhimov, R.F.; Sakerin, S.M.; Belan, B.D. Geophysical factors of the aerosol weather formation in the Western Siberia. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 1999, 12, 883–894. [Google Scholar]
- Panchenko, M.V.; Pol’kin, V.V.; Polkin, V.V.; Kozlov, V.S.; Yausheva, E.P.; Shmargunov, V.P. The size distribution of the “dry matter” of particles in the surface air layer in suburbs of Tomsk within the empirical classification of “aerosol weather” types. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2019, 32, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Online Monitoring Aerosol Station. Available online: http://aerosol.iao.ru (accessed on 11 November 2019).
- Panchenko, M.V.; Pol’kin, V.V. Microstructure of tropospheric aerosol in Siberia as judged from photoelectric particle-counter measurements. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2001, 14, 478–488. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov, V.S.; Shmargunov, V.P.; Panchenko, M.V.; Chernov, D.G.; Kozlov, A.S.; Malyshkin, S.B. Seasonal variability of Black Carbon size distribution in the atmospheric aerosol. Russ. Phys. J. 2016, 58, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, V.S.; Shmargunov, V.P.; Panchenko, M.V. Modified aethalometer for monitoring of black carbon concentration in atmospheric aerosol and technique for correction of the spot loading effect. Proceed. SPIE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pkhalagov, Y.A.; Uzhegov, V.N.; Shchelkanov, N.N. Automated multiwave meter of spectral transmission of the ground layer of the atmosphere. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 1992, 5, 423–425. [Google Scholar]
- Panchenko, M.V.; Sviridenkov, M.A.; Terpugova, S.A.; Kozlov, V.S. Active spectral nephelometry as a method for the study of submicrometer atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2004, 17, 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov, V.S.; Panchenko, M.V.; Yausheva, E.P. Mass fraction of Black Carbon in submicron aerosol as an indicator of influence of smokes from remote forest fires in Siberia. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorchakov, G.I.; Yemilenko, A.S.; Sviridenkov, M.A. One-parameter model of aerosol at the surface. Izv. Acad. Sci. USSR Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 1981, 17, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, D.; Kerker, M. Response calculations for light-scattering aerosol particle counters. Appl. Opt. 1975, 14, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecorius, S.; Madueño, L.; Vallar, E.; Alas, H.; Betito, G.; Birmili, W.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Catipay, G.; Gonzaga-Cayetano, M.; Galvez, M.C.; et al. Aerosol particle mixing state, refractory particle number size distributions and emission factors in a polluted urban environment: Case study of Metro Manila, Philippines. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol’kin, V.V.; Panchenko, M.V. Fitting of the particle size distributions by lognormal functions in the frameworks of empirical classification of the “aerosol weather” types. Proceed. SPIE 2019, 11208, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Strapp, J.W.; Leaitch, W.R.; Liu, P.S.K. Hydrated and dried aerosol size distribution measurements from the particle measuring systems FSSP-300 probe and the deiced PCASP-100X probe. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1992, 9, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, M.V.; Zhuravleva, T.B.; Terpugova, S.A.; Polkin, V.V.; Kozlov, V.S. An empirical model of optical and radiative characteristics of the tropospheric aerosol over West Siberia in summer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1513–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakerin, S.M.; Beresnev, S.A.; Gorda, S.Y.; Kabanov, D.M.; Kornienko, G.I.; Markelov, Y.I.; Mikhalev, A.V.; Nikolashkin, S.V.; Panchenko, M.V.; Poddubnyi, V.A.; et al. Characteristics of the annual behavior of the spectral aerosol optical depth of the atmosphere under conditions of Siberia. Atmos Ocean Opt. 2009, 22, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakerin, S.M.; Beresnev, S.A.; Kabanov, D.M.; Kornienko, G.I.; Nikolashkin, S.V.; Poddubny, V.A.; Tashchilin, M.A.; Turchinovich, Y.S.; Holben, B.N.; Smirnov, A. Analysis of Approaches to Modeling the Annual and Spectral Behaviors of Atmospheric Aerosol Optical Depth in Siberia and Primorye. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2015, 28, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, D.M.; Beresnev, S.A.; Gorda, S.Y.; Kornienko, G.I.; Nikolashkin, S.V.; Sakerin, S.M.; Tashchilin, M.A. Diurnal Behavior of Aerosol Optical Depth of the Atmosphere in a Few Regions of Asian Part of Russia. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2013, 26, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Byrne, D.M.; Herman, B.M.; Reagan, J.A. Aerosol size distributions obtained by inversion of spectral optical depth measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 1978, 35, 2153–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.R.; Jonsson, H.H.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Flagan, R.C.; Gasso, S.; Hegg, D.A.; Russell, P.B.; Schmid, B.; Livingston, J.M.; Ostrom, E.; et al. In-situ aerosol size distributions and clear column radiative closure during ACE-2. Tellus 2000, 498–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, J.; Francis, P.; Dubovik, O.; Glew, M.; Holben, B. Comparison of aerosol size distributions, radiative properties, and optical depths determined by aircraft observations and Sun photometers during SAFARI 2000. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol’kin, V.V.; Pol’kin, V.V.; Panchenko, M.V. Particle size distribution function of photoelectric counter and closed volume aureole photometer (seasonal variations and inter-annual differences). Proc. SPIE 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurton, T.; Renard, J.-B.; Vignelles, D.; Jeannot, M.; Akiki, R.; Mineau, J.-L.; Tonnelier, T. Light scattering at small angles by atmospheric irregular particles: Modeling and laboratory measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; Deangelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelencser, A. Carbonaceous Aerosol; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradova, A.A.; Vasileva, A.V. Black Carbon in air over northern regions of Russia: Sources and spatiotemporal variations. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2017, 30, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorchakov, G.I.; Karpov, A.V.; Vasiliev, A.V.; Gorchakova, I.A. Brown carbon and black carbon in megacity smogs. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2017, 30, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, R.P.; Beamesderfer, E.R.; Wagner, N.L.; Langridge, J.M.; Lack, D.A.; Jayarathne, T.; Stone, E.A.; Stockwell, C.E.; Yokelson, R.J.; Murphy, S.M. Relative importance of black carbon, brown carbon, and absorption enhancement from clear coatings in biomass burning emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5063–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.Z. Quantifying black carbon light absorption enhancement with a novel statistical approach. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semoutnikova, E.G.; Gorchakov, G.I.; Sitnov, S.A.; Kopeikin, V.M.; Karpov, A.V.; Gorchakova, I.A.; Ponomareva, T.Y.; Isakov, A.A.; Gushchin, R.A.; Datsenko, O.I.; et al. Siberian smoke haze over European territory of Russia in July 2016: Atmospheric pollution and radiative effects. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2018, 31, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.S.; Sharma, S.; Herber, A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Nelson, D.W. A characterization of Arctic aerosols on the basis of aerosol optical depth and black carbon measurements. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2014, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, H.; Zanatta, M.; Bozem, H.; Leaitch, W.R.; Herber, A.B.; Burkart, J.; Willis, M.D.; Kunkel, D.; Hoor, P.M.; Abbatt, J.P.D.; et al. High Arctic aircraft measurements characterising black carbon vertical variability in spring and summer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2361–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketani, F.; Miyakawa, T.; Takashima, H.; Komazaki, Y.; Pan, X.; Kanaya, Y.; Inoue, J. Shipborne observations of atmospheric black carbon aerosol particles over the Arctic Ocean, Bering Sea, and North Pacific Ocean during September 2014. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2016, 121, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, S.S.; College, B.; Charlson, R.J. An Introduction to Air Chemistry; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, P.J.; Arnott, W.P.; Ogren, J.A.; Andrews, E.; Atkinson, D.B.; Covert, D.S.; Moosmuller, H. The Reno Aerosol Optics Study: An evaluation of aerosol absorption measurement methods. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Liao, C.-W.; Liu, Z.-S.; Tsai, C.-J.; His, H.-C. A size-segregation method for monitoring the diurnal characteristics of atmospheric black carbon size distribution at urban traffic sites. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höller, R.; Tohno, S.; Kasahara, M.; Hitzenberger, R. Long–term characterization of carboneous aerosol in Uji, Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Chan, K.L.; Wong, K.C.; Westerdahl, D.; Mocnik, G.; Zhou, J.H.; Cheung, C.S. Black carbon mass size distributions of diesel exhaust and urban aerosols measured using differential mobility analyzer in tandem with Aethalometer. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Spackman, J.R.; Watts, L.A.; Thomson, D.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Ryerson, T.B.; Peischl, J.; Holloway, J.S.; Trainer, M.; et al. Measurement of the mixing state, mass, and optical size of individual black carbon particles in urban and biomass burning emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Sahu, L.; Moteki, N.; Khan, F.; Takegawa, N.; Liu, X.; Koike, M.; Miyakawa, T. Consistency and traceability of black carbon measurements made by laser-induced incandescence, thermal-optical transmittance, and filter-based photo-absorption techniques. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgievskiy, Y.S.; Rosenberg, G.V. Humidity as a factor in aerosol variability. Izv. Acad. Sci. USSR Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 1973, 9, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kabanov, D.M.; Kurbangaliev, T.R.; Rasskazchikova, T.M.; Sakerin, S.M.; Khutorova, O.G. The Influence of Synoptic Factors on Variations of Atmospheric Aerosol Optical Depth under Siberian Conditions. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2011, 24, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antokhina, O.Y.; Antokhin, P.N.; Arshinova, V.G.; Arshinov, M.Y.; Belan, B.D.; Davydov, D.K.; Dudorova, N.V.; Ivlev, G.A.; Kozlov, A.V.; Rasskazchikova, T.M.; et al. Study of Air Composition in Different Air Masses. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2019, 32, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklyadneva, T.K.; Belan, B.D.; Rasskazchikova, T.M.; Arshinova, V.G. Change in the Synoptic Regime of Tomsk in the Late 20th–Early 21st Centuries. Atmos. Oceanic Opt. 2019, 32, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryshkevich, T.I.; Mironov, G.N.; Mironova, S.Y.; Vlasenko, S.S.; Mikhailov, E.F.; Chi, X.; Andreae, M.O. Comparative analysis of hygroscopic properties of atmospheric aerosols at ZOTTO Siberian background station during summer and winter campaigns of 2011. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2015, 51, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jing, B.; Peng, C.; Tong, S.; Wang, W.; Ge, M. Hygroscopicity of internally mixed multi-component aerosol particles of atmospheric relevance. Atmosp. Environ. 2016, 125, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, N.; Mikhailov, E.F.; Pöschl, U.; Su, H. Dependence of the hygroscopicity parameter κ on particle size, humidity and solute concentration: Implications for laboratory experiments, field measurements and model studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D.B.; Radney, J.G.; Lum, J.; Kolesar, K.R.; Cappa, C.D.; Cziczo, D.J.; Pekour, M.S.; Zelenyuk, A.; Zhang, Q.; Setyan, A. Aerosol optical hygroscopicity measurements during the 2010 Cares campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4045–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovelli, G.; Miles, R.E.H.; Reid, J.P.; Clegg, S.L. Accurate measurements of aerosol hygroscopic growth over a wide range in relative humidity. J. Phys. Chem. 2016, 120, 4376–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasso, S.; Hegg, D.A.; Covert, D.S.; Noone, K.J.; Ostrom, E.; Schmid, B.; Russell, P.B.; Livingston, J.M.; Durkee, P.A.; Jonsson, H.H. Influence of humidity on the aerosol scattering coefficient and its effect on the upwelling radiance during ACE-2. Tellus 2000, 52B, 546–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, A.A.; Tikhonov, A.V. Relationship between aerosol parameters and air masses in central Russia. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2014, 27, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzdev, A.N.; Isakov, A.A.; Shukurova, L.M. Analysis of relationship between condensation activity of surface aerosol and its chemical composition and relative air humidity according to measurements at the Zvenigorod Scientific Station. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2014, 27, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, F. Visibility forecast in the phase of precondensation. Tellus 1969, 21, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänel, G. The properties of atmospheric aerosol particles as function of relative humidity at the thermodynamic equilibrium with surrounding moist air. Adv. Geophys. 1976, 19, 73–188. [Google Scholar]
- Terpugova, S.A.; Panchenko, M.V.; Sviridenkov, M.A.; Yausheva, E.P. Different types of dependence of aerosol properties upon relative humidity. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, S1043–S1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpugova, S.A.; Pol’kin, V.V.; Chernov, D.G.; Yausheva, E.P.; Pol’kin, V.V.; Kozlov, V.S. Aerosol condensation activity in the region of Tomsk in different types of “aerosol weather”. In Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Atmospheric and Ocean Optics: Atmospheric Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia, 30 June–5 July 2019; Romanovskii, O.A., Matvienko, G.G., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sakerin, S.M.; Kabanov, D.M. Fine and Coarse Components of Atmospheric Aerosol Optical Depth in Maritime and Polar Regions. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2015, 28, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).