Fluxes of Gaseous Elemental Mercury on a Mediterranean Coastal Grassland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling Instrumentation
2.3. Calibration of Mercury Analyzer
2.4. Data Processing
2.4.1. Aerodynamic Gradient Method (AGM)
2.4.2. Flux Footprint
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Summary of GEM Fluxes and Ancillary Parameters
3.2. Diurnal Cycles
3.3. Atmospheric Stability
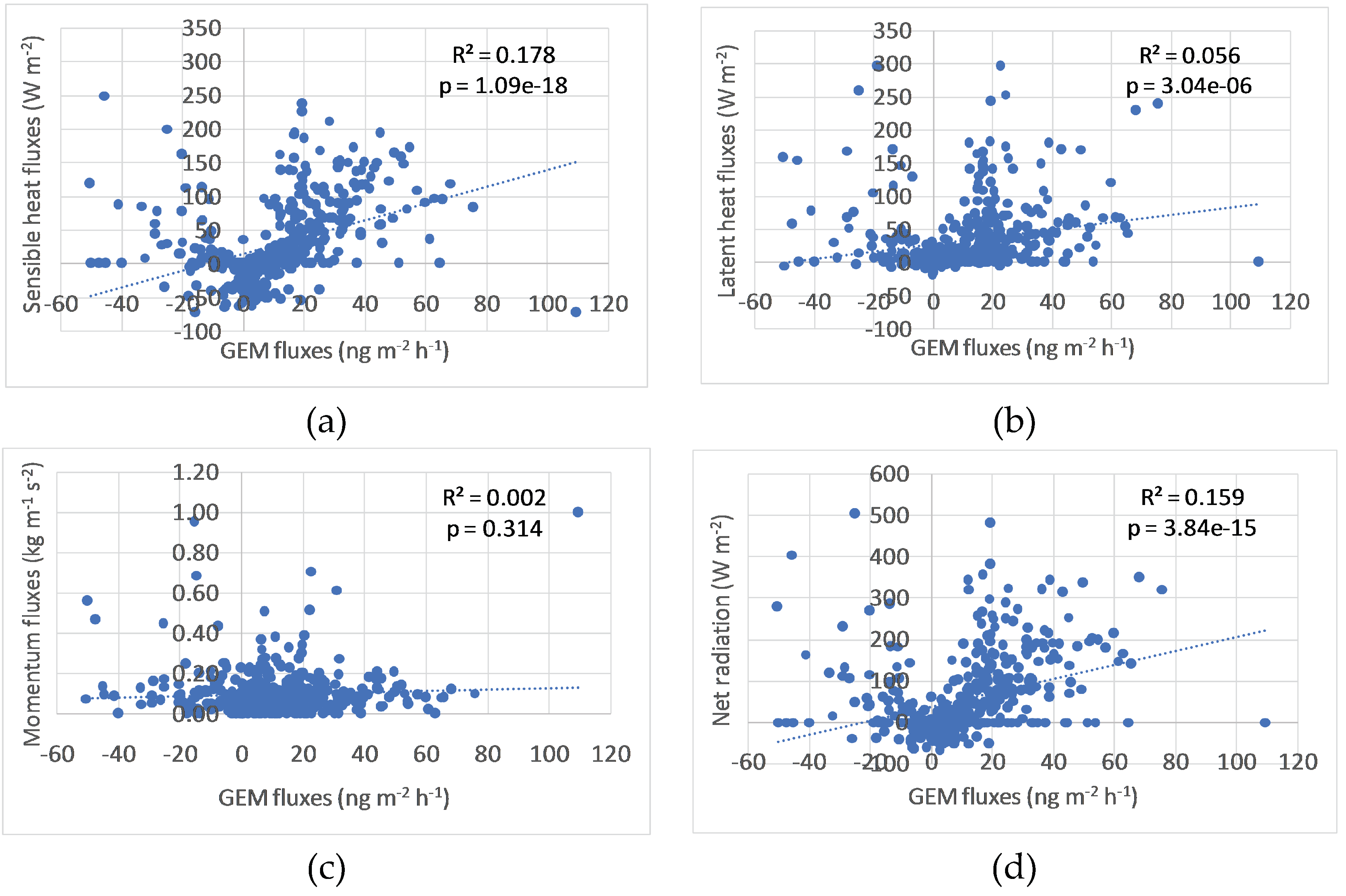
3.4. Correlation with Energy Fluxes
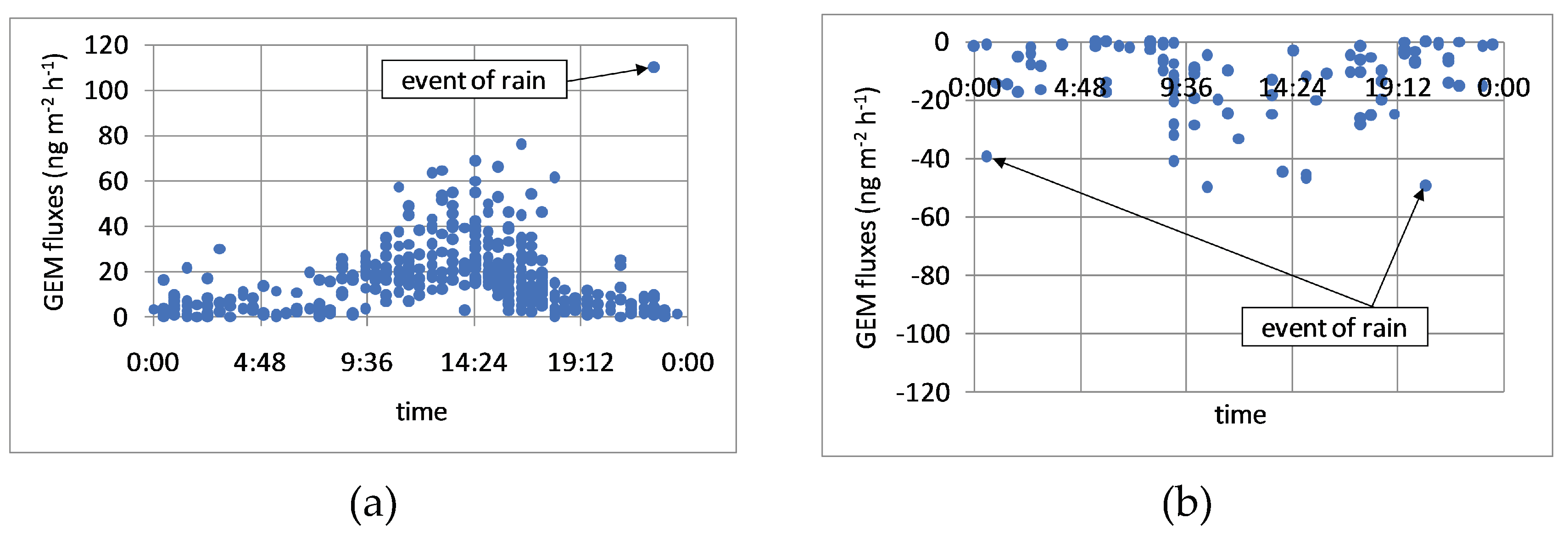
3.5. Effects of Rain Events
3.6. Contributing Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rapsomanikis, S.; Weber, J.H. Methyl transfer reactions of environmental significance involving naturally occurring and synthetic reagents. In Organometallic Compounds in the Environment; Longmans Group Ltd.: Essex, UK, 1986; pp. 279–307. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, R.; Rapsomanikis, S.; Andreae, M.O. Determination of methylmercury in fish samples using GC/AA and sodium tetraethylborate derivatization. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, R.G.; Rapsomanikis, S.; Andreae, M.O.; Baldi, F. Bioaccumulation of Methylmercury and Transformation of Inorganic Mercury by Macrofungi. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-J.; Pehkonen, S.O. The chemistry of atmospheric mercury: A review. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirrone, N.; Cinnirella, S.; Feng, X.; Finkelman, R.B.; Friedli, H.R.; Leaner, J.; Mason, R.; Mukherjee, A.B.; Stracher, G.B.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5951–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.H.; Munthe, J. Atmospheric mercury—An overview. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, M.S. Exchange of Mercury between the Atmosphere and Terrestrial Ecosystems. In Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology of Mercury; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 423–451. [Google Scholar]
- Sommar, J.; Zhu, W.; Lin, C.-J.; Feng, X. Field Approaches to Measure Hg Exchange Between Natural Surfaces and the Atmosphere—A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1657–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Sommar, J.; Lin, C.J.; Feng, X. Mercury vapor air–surface exchange measured by collocated micrometeorological and enclosure methods—Part I: Data comparability and method characteristics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 685–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gårdfeldt, K.; Sommar, J.; Ferrara, R.; Ceccarini, C.; Lanzillotta, E.; Munthe, J.; Wängberg, I.; Lindqvist, O.; Pirrone, N.; Sprovieri, F.; et al. Evasion of mercury from coastal and open waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37 (Suppl. 1), 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P.; Lawson, N.M.; Lawrence, A.L.; Leaner, J.J.; Lee, J.G.; Sheu, G.-R. Mercury in the Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Chem. 1999, 65, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.E.; Dong, W.; Chanton, J.; Qualls, R.G.; Meyers, T. A mechanism for bimodal emission of gaseous mercury from aquatic macrophytes. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissant, L.; Pilote, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Beauvais, C. Atmospheric mercury speciation and deposition in the Bay St. François wetlands. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.H.; Poissant, L.; Xu, X.; Pilote, M. Explorative and innovative dynamic flux bag method development and testing for mercury air–vegetation gas exchange fluxes. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7481–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.; Mazzolai, B. A dynamic flux chamber to measure mercury emission from aquatic systems. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 215, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Elemental mercury in coastal seawater of Yellow Sea, China: Temporal variation and air–sea exchange. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfhus, K.R.; Fitzgerald, W.F. The evasion and spatial/temporal distribution of mercury species in Long Island Sound, CT-NY. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, P.S.; Merlivat, L. Air-Sea Gas Exchange Rates: Introduction and Synthesis. In The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling; Buat-Ménard, P., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 113–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wanninkhof, R. Relationship Between Wind Speed and Gas Exchange Over the Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 7373–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.; Benoit, G.; Hu, X. Total gaseous mercury concentration and flux over a coastal saltmarsh vegetation in Connecticut, USA. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Reinfelder, J.R. Mercury volatilization from salt marsh sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepekli, A.; Loupa, G.; Rapsomanikis, S. Seasonal evapotranspiration, energy fluxes and turbulence variance characteristics of a Mediterranean coastal grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 226–227, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekran. Available online: https://www.tekran.com/products/ambient-air/tekran-model-2537-cvafs-automated-mercury-analyzer/ (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, M.-Y. The exchange of gaseous mercury across soil–air interface in a residential area of Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D. University of California, Berkeley, Biometeorology Lab, ESPM 228, Advanced Topics in Biometeorology and Micrometeorology: Lecture 2 on Micrometeorological Flux Measurement Methods/Flux-Gradient Theory. Available online: https://nature.berkeley.edu/biometlab/espm228/Lecture_2_Notes_ESPM_228_Flux_Gradient_Theory_v2016.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Wesely, M.L.; Hicks, B.B. A review of the current status of knowledge on dry deposition. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2261–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapsomanikis, S.; Trepekli, A.; Loupa, G.; Polyzou, C. Vertical Energy and Momentum Fluxes in the Centre of Athens, Greece During a Heatwave Period (Thermopolis 2009 Campaign). Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2015, 154, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. Boundary Layer Climates, 2nd ed.; University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987; 464p. [Google Scholar]
- Monin, A.S.; Obukhov, A.M. Basic Laws of Turbulent Mixing in the Atmosphere Near the Ground. Tr. Akad. Nauk SSSR Geoph. Inst. 1954, 24, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB and Statistics Toolbox Release 2010b; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2010.
- Foken, T. Micrometeorology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg Germany, 2008; p. 308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Sommar, J.; Lin, C.J.; Feng, X. Mercury vapor air–surface exchange measured by collocated micrometeorological and enclosure methods—Part II: Bias and uncertainty analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5359–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-I.; Katul, G.; Chi, T.-W. An approximate analytical model for footprint estimation of scalar fluxes in thermally stratified atmospheric flows. Adv. Water Resour. 2000, 23, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gårdfeldt, K.; Feng, X.; Sommar, J.; Lindqvist, O. Total gaseous mercury exchange between air and water at river and sea surfaces in Swedish coastal regions. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3027–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.; Mazzolai, B.; Lanzillotta, E.; Nucaro, E.; Pirrone, N. Temporal trends in gaseous mercury evasion from the Mediterranean seawaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 259, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Lindberg, S.E.; Meyers, T.P. Micrometeorological measurements of mercury vapor fluxes over background forest soils in eastern Tennessee. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, M.T.; Van Heyst, B.J.; Schroeder, W.H. Modelling of mercury emissions from background soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 304, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariya, P.A.; Amyot, M.; Dastoor, A.; Deeds, D.; Feinberg, A.; Kos, G.; Poulain, A.; Ryjkov, A.; Semeniuk, K.; Subir, M.; et al. Mercury Physicochemical and Biogeochemical Transformation in the Atmosphere and at Atmospheric Interfaces: A Review and Future Directions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3760–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Van Heyst, B. Volatilization of mercury from soils in response to simulated precipitation. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7494–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.E.; Zhang, H.; Gustin, M.; Vette, A.; Marsik, F.; Owens, J.; Casimir, A.; Ebinghaus, R.; Edwards, G.; Fitzgerald, C.; et al. Increases in mercury emissions from desert soils in response to rainfall and irrigation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 21879–21888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, J.; Sprovieri, F.; Ogrinc, N.; Horvat, M.; Pirrone, N. Mercury in the Mediterranean, part I: Spatial and temporal trends. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 4063–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, S.E.; Meyers, T.P. Development of an automated micrometeorological method for measuring the emission of mercury vapor from wetland vegetation. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 9, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canário, J.; Poissant, L.; Pilote, M.; Caetano, M.; Hintelmann, H.; O’Driscoll, N.J. Salt-marsh plants as potential sources of Hg0 into the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencarelli, C.N.; De Simone, F.; Hedgecock, I.M.; Sprovieri, F.; Yang, X.; Pirrone, N. European and Mediterranean mercury modelling: Local and long-range contributions to the deposition flux. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 117, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marumoto, K.; Imai, S. Determination of dissolved gaseous mercury in seawater of Minamata Bay and estimation for mercury exchange across air–sea interface. Mar. Chem. 2015, 168, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, P.S.; Slater, P.G. Flux of Gases across the Air-Sea Interface. Nature 1974, 247, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Elemental mercury (Hg(0)) in air and surface water of the Yellow Sea during late spring and late fall 2012: Concentration, spatial-temporal distribution and air/sea flux. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ci, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Air-sea exchange of gaseous mercury in the East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.E.; Sommar, J.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Jutterström, S. Air–sea exchange of volatile mercury in the North Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Chem. 2011, 125, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Time Period | n | GEM Fluxes (ng m−2 h−1) | Emissions–GEM Fluxes (ng m−2 h−1) | Deposition–GEM Fluxes (ng m−2 h−1) | Sensible Heat Fluxes (W m−2) | Latent Heat Fluxes (W m−2) | Momentum Fluxes (kg m−1 s−2) | Net Radiation (W m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| all data | 463 | 10.50 ± 19.14 | 17.09 | −11.98 | 31.26 | 38.48 | 0.11 | 68.00 |
| August 2014 | 88 | 6.36 ± 24.73 | 22.16 | −14.43 | 42.73 | 79.66 | 0.08 | 116.72 |
| September 2014 | 33 | 12.84 ± 20.06 | 21.19 | −13.25 | 93.04 | 94.26 | 0.09 | 180.13 |
| October 2014 | 258 | 11.51 ± 17.96 | 16.53 | −9.89 | 21.32 | 21.20 | 0.13 | 41.97 |
| November 2014 | 63 | 11.27 ± 14.28 | 13.63 | −11.11 | 28.60 | 17.65 | 0.06 | 46.23 |
| January 2015 | 21 | 9.45 ± 16.94 | 14.73 | −12.99 | ||||
| day (7:00–19:00) | 320 | 14.35 | 21.43 | −14.53 | 53.51 | 51.03 | 0.10 | 101.84 |
| night (19:00–7:00) | 143 | 1.89 | 6.07 | −7.25 | −22.37 | 7.23 | 0.12 | −15.43 |
| GEM Fluxes (Emissions) in (ng m−2 h−1) | |||
| Unstable | Neutral | Stable | |
| mean | 23.55 | 20.72 | 4.40 |
| min | 2.92 | 3.08 | 0.07 |
| max | 75.71 | 109.69 | 30.17 |
| daytime mean | 23.91 | 13.00 | 3.54 |
| nightime mean | 5.92 | 27.15 | 6.07 |
| GEM Fluxes (Depositions) in (ng m−2 h−1) | |||
| Unstable | Neutral | Stable | |
| mean | −19.93 | −15.25 | −5.85 |
| min | −50.30 | −16.35 | −49.81 |
| max | −4.98 | −13.69 | −0.01 |
| daytime mean | −19.93 | − | −2.90 |
| nightime mean | − | −15.25 | −8.15 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polyzou, C.; Loupa, G.; Trepekli, A.; Rapsomanikis, S. Fluxes of Gaseous Elemental Mercury on a Mediterranean Coastal Grassland. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090485
Polyzou C, Loupa G, Trepekli A, Rapsomanikis S. Fluxes of Gaseous Elemental Mercury on a Mediterranean Coastal Grassland. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(9):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090485
Chicago/Turabian StylePolyzou, Christiana, Glykeria Loupa, Aikaterini Trepekli, and Spyridon Rapsomanikis. 2019. "Fluxes of Gaseous Elemental Mercury on a Mediterranean Coastal Grassland" Atmosphere 10, no. 9: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090485
APA StylePolyzou, C., Loupa, G., Trepekli, A., & Rapsomanikis, S. (2019). Fluxes of Gaseous Elemental Mercury on a Mediterranean Coastal Grassland. Atmosphere, 10(9), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10090485






