Ambient Mercury Observations near a Coal-Fired Power Plant in a Western U.S. Urban Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
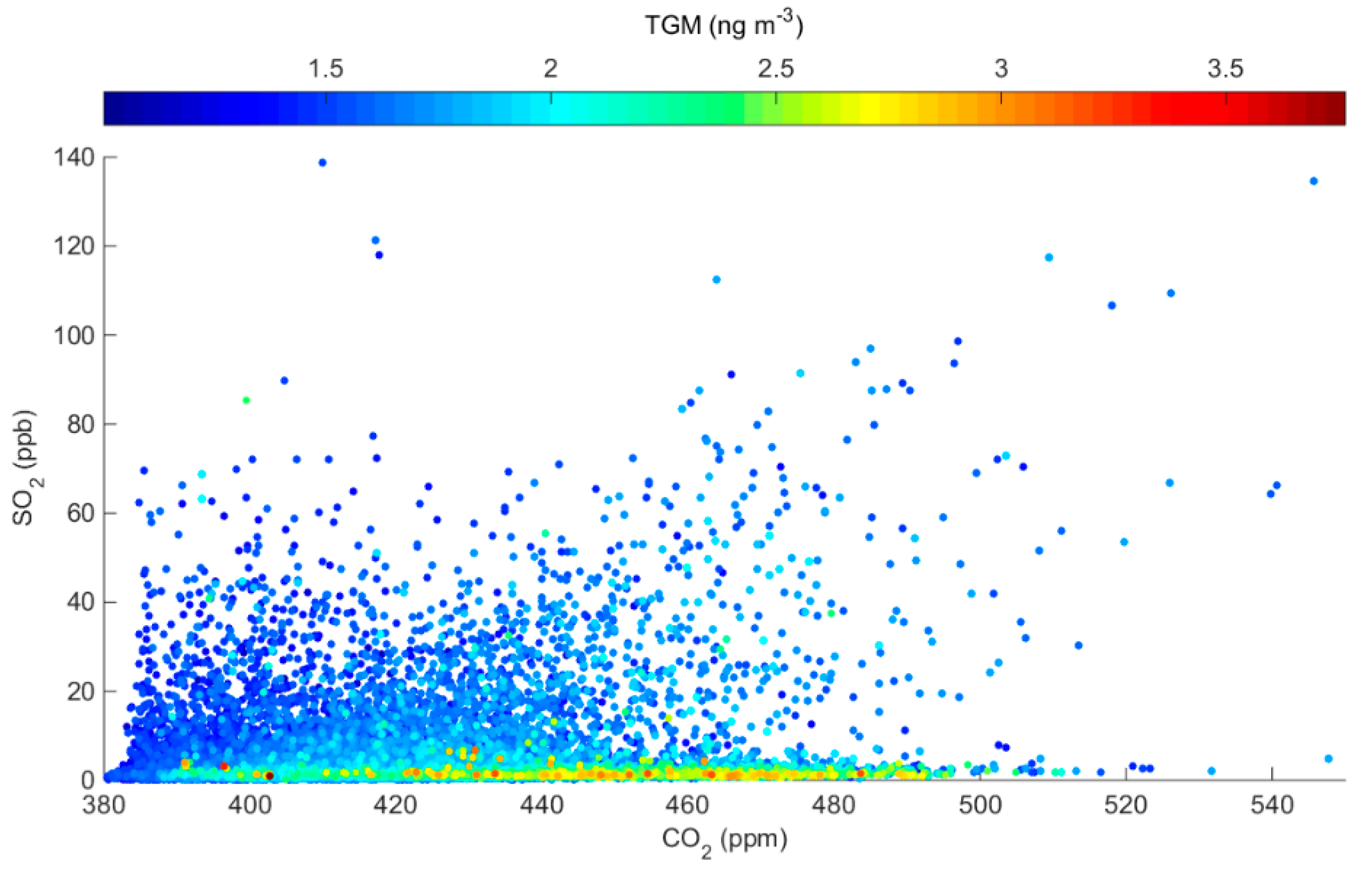
2.1. Summary of TGM and Ancillary Parameters
2.2. Directionality
2.3. Temporal Variability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
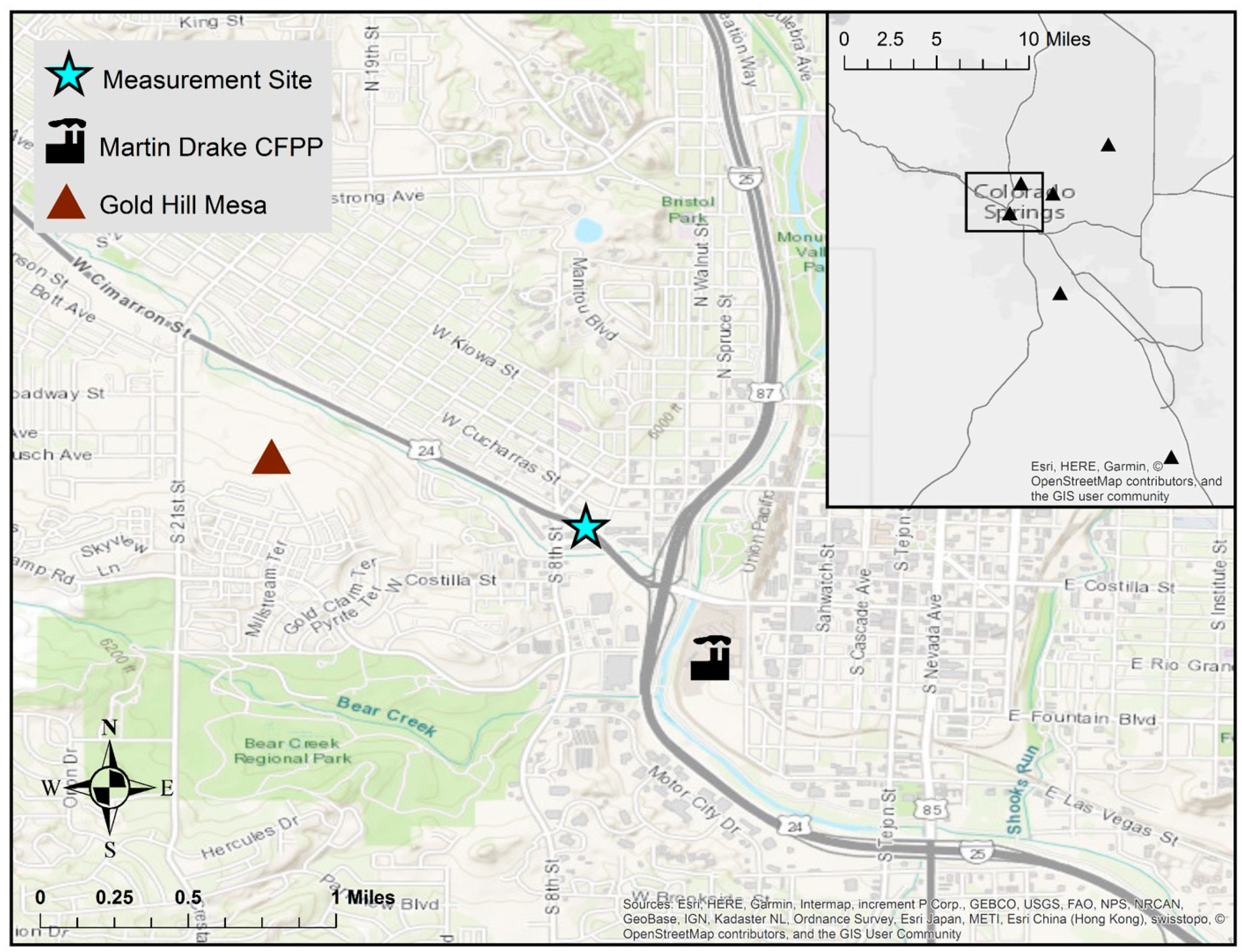
4.1. Site Description
4.2. Ambient Air Measurements
4.3. Data Analysis
4.4. HYSPLIT Plume Modeling
4.5. Mixing Height Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mergler, D.; Anderson, H.A.; Chan, L.H.; Mahaffey, K.R.; Murray, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Stern, A.H. Methylmercury exposure and health effects in humans: A worldwide concern. Ambio 2007, 36, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selin, N.E. Global Biogeochemical Cycling of Mercury: A Review. Ann. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y. Projections of Global Mercury in 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2983–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirrone, N.; Cinnirella, S.; Feng, X.; Finkelman, R.B.; Friedli, H.R.; Leaner, J.; Mason, R.; Mukherjee, A.B.; Stracher, G.B.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5951–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P. Mercury emissions from natural processes and their importance in the global mercury cycle. In Mercury Fate and Transport in the Global Atmosphere; Mason, R., Pirron, N., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 173–191. ISBN 978-0-387-93957-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mazur, M.; Mintz, R.; Lapalme, M.; Wiens, B. Ambient air total gaseous mercury concentrations in the vicinity of coal-fired power plants in Alberta, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.M.; Keeler, G.J.; Landis, M.S. Spatial Variability of Mercury Wet Deposition in Eastern Ohio: Summertime Meteorological Case Study Analysis of Local Source Influences. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4946–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckley, C.S.; Parsons, M.T.; Mintz, R.; Lapalme, M.; Mazur, M.; Tordon, R.; Elleman, R.; Graydon, J.A.; Blanchard, P.; St Louis, V. Impact of Closing Canada’s Largest Point-Source of Mercury Emissions on Local Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10339–10348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrist, D.; Kirk, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Sunderland, E.M.; Jiskra, M.; Selin, N. A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio 2018, 47, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Mercury Study Report to Congress, Volume II: An Inventory of Anthropogenic Mercury Emissions in the United States. EPA-452/R-97-004; 1997. Available online: https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/volume2.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2015 TRI National Analysis, Mercury Air Releases Trend. 2017. Available online: https://19january2017snapshot.epa.gov/trinationalanalysis/mercury-air-releases-trend-2015-tri-national-analysis_.html (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Register Vol. 77, No. 32, Rules and Regulations. National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants from Coal- and Oil-Fired Electric Utility Steam Generating Units and Standards of Performance for Fossil-Fuel-Fired Electric Utility, Industrial-Commercial-Institutional, and Small Industrial-Commercial-Institutional Steam Generating Units. 2012. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/airtoxics/utility/fr16fe12.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- U.S. Census Bureau, Population Division. 2017 population estimates for cities and towns. 2018. Available online: https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2017/demo/popest/total-cities-and-towns.html#tables (accessed on 19 March 2019).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2014 National Emissions Inventory version 2 Technical Support Document. Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards. 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/2014-national-emissions-inventory-nei-data (accessed on 23 September 2016).
- Colorado Springs Utilities, Martin Drake Power Plant Decommissioning. Available online: https://www.csu.org/Pages/martin-drake-r.aspx (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2011 National Emissions Inventory Technical Support Document. Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards. 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/2011-national-emissions-inventory-nei-data (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2008 National Emissions Inventory Technical Support Document. Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards. 2013. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/2008-national-emissions-inventory-nei-data (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Ambrose, J.L.; Gratz, L.E.; Jaffe, D.A.; Campos, T.; Flocke, F.M.; Knapp, D.J.; Stechman, D.M.; Stell, M.; Weinheimer, A.J.; Cantrell, C.A.; et al. Mercury Emission Ratios from Coal-Fired Power Plants in the Southeastern United States during NOMADSS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10389–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Air Markets Program Data (AMPD). Available online: http://ampd.epa.gov/ampd/ (accessed on 14 March 2019).
- Cole, A.S.; Steffen, A.; Eckley, C.S.; Narayan, J.; Pilote, M.; Tordon, R.; Graydon, J.A.; St Louis, V.L.; Xu, X.; Branfireun, B.A. A Survey of Mercury in Air and Precipitation across Canada: Patterns and Trends. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 635–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godish, T. Air Quality, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 1-56670-586-X. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey, R. Climate Change: Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide. National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration, News & Features. August 2018. Available online: https://www.climate.gov/news-features/understanding-climate/climate-change-atmospheric-carbon-dioxide (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- Novelli, P.C.; Masarie, K.A.; Lang, P.M.; Hall, B.M.; Myers, R.C.; Elkins, J.W. Reanalysis of tropospheric CO trends: Effects of the 1997-1998 wildfires. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, L.E.; Jaffe, D.J.; Hee, J.R. Causes of increasing ozone and decreasing carbon monoxide in springtime at the Mt. Bachelor Observatory from 2004 to 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 109, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, M.S.; Lewis, C.W.; Stevens, R.K.; Keeler, G.J.; Dvonch, J.T.; Tremblay, R.T. Ft. McHenry tunnel study: Source profiles and mercury emissions from diesel and gasoline powered vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8711–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, T.G. Mercury emissions from automobiles using gasoline, diesel, and LPG. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7547–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kellerhals, M.; Beauchamp, S.; Belzer, W.; Blanchard, P.; Froude, F.; Harvey, B.; McDonald, K.; Pilote, M.; Poissant, L.; Puckett, K.; et al. Temporal and spatial variability of total gaseous mercury in Canada: Results from the Canadian Atmospheric Mercury Measurement Network (CAMNet). Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss-Penzias, P.; Gustin, M.S.; Lyman, S.N. Observations of speciated atmospheric mercury at three sites in Nevada: Evidence for a free tropospheric source of reactive gaseous mercury. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, U.S.; Wu, Y.; Walters, J.; Jansen, J.; Edgerton, E.S. Diurnal and seasonal variation of mercury species at coastal-suburban, urban, and rural sites in the southeastern United States. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, L.E.; Keeler, G.J.; Marski, F.J.; Barres, J.A.; Dvonch, J.T. Atmospheric transport of speciated mercury across southern Lake Michigan: Influence from emission sources in the Chicago/Gary urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.B.; Shang, L.H.; Wang, S.F.; Tang, S.L.; Zheng, W. Temporal variation of total gaseous mercury in the air of Guiyang, China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2004, 109, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Xu, Z.C.; Ding, X.Y.; Zhang, W.D.; Huang, Y.M.; Fan, R.F.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Qian, D.; Feng, Y. Spatial trend and pollution assessment of total mercury and methylmercury pollution in the Pearl River Delta soil, South China. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, M.C.; Williamson, D.G.; Zhang, H.; Brooks, S.; Lindberg, S. Diurnal and seasonal trends in total gaseous mercury flux from three urban ground surfaces. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4269–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baya, A.P.; Van Heyst, B. Assessing the trends and effects of environmental parameters on the behavior of mercury in the lower atmosphere over cropped land over four seasons. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8617–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Resource Data System (MRDS). 2006. Available online: https://mrdata.usgs.gov/mrds/show-mrds.php?dep_id=10311068 (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- Miller, M.B.; Gustin, M.S. Gas-exchange chamber analysis of elemental mercury deposition/emission to alluvium, ore, and mine tailings. Chemosphere 2015, 131, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckley, C.S.; Branfireun, B. Gaseous mercury emissions from urban surfaces: Controls and spatiotemporal trends. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, E.; Tharumakulasingam, K.; Athar, M.; Yousaf, M.; Cheng, I.; Huang, Y.; Lu, J.; Yap, D. Source, concentration, and distribution of elemental mercury in the atmosphere in Toronto, Canada. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLagan, D.S.; Hussain, B.A.; Huang, H.Y.; Lei, Y.D.; Wania, F.; Mitchell, C.P.J. Identifying and evaluating urban mercury emission sources through passive sampler-based mapping of atmospheric concentration. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faïn, X.; Obrist, D.; Hallar, A.G.; Mccubbin, I.; Rahn, T. High levels of reactive gaseous mercury observed at a high elevation research laboratory in the Rocky Mountains. Atmos. Chem. Phys 2009, 9, 8049–8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, L.E.; Ambrose, J.L.; Jaffe, D.A.; Shah, V.; Jaeglé, L.; Stutz, J.; Festa, J.; Spolaor, M.; Tsai, C.; Selin, N.E.; et al. Oxidation of mercury by bromine in the subtropical free troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10494–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Jaeglé, L.; Gratz, L.E.; Ambrose, J.L.; Jaffe, D.A.; Selin, N.E.; Song, S.; Campos, T.L.; Flocke, F.M.; Reeves, M.; et al. Origin of Oxidized Mercury in the Summertime Free Troposphere over the Southeastern United States. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1511–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Fiore, A.M.; Cooper, O.R.; Horowitz, L.W.; Langford, A.O.; Levy, H., II; Johnson, B.J.; Naik, V.; Oltmans, S.; Senff, C.J. Springtime high surface ozone events over the western United States: Quantifying the role of stratospheric intrusions. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D00V22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzendruber, P.C.; Jaffe, D.A.; Finley, B. Improved fluorescence peak integration in the Tekran 2537 for applications with sub-optimal sample loadings. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3648–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, D.A.; Lyman, S.; Amos, H.M.; Gustin, M.S.; Huang, J.; Selin, N.E.; Levin, L.; Ter Schure, A.; Mason, R.P.; Talbot, R.; et al. Progress on Understanding Atmospheric Mercury Hampered by Uncertain Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7204–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, S.N.; Gustin, M.S.; Prestbo, E.M.; Marsik, F.J. Estimation of dry deposition of atmospheric mercury in Nevada by direct and indirect methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Zhang, L.; Blanchard, P. Regression modeling of gas-particle partitioning of atmospheric oxidized mercury from temperature data. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 11864–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2017 Air Quality Statistics by City, Released March 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-trends/air-quality-cities-and-counties (accessed on 12 March 2019).
- Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment. Air Pollution Control Division Technical Services Program Quality Assurance Project Plan. 30 July 2015. Available online: https://www.colorado.gov/airquality/tech_doc_repository.aspx?action=open&file=APCD_QAPP_07302015.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2019).
- Poissant, L.; Pilote, M.; Beauvais, C.; Constant, P.; Zhang, H.H. A year of continuous measurements of three atmospheric mercury species (GEM, RGM, and Hgp) in southern Quebec, Canada. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Keeler, G.J.; Dvonch, J.T.; Barres, J.A.; Lynam, M.M.; Marsik, F.J.; Taylor-Morgan, J. Temporal variability of mercury speciation in urban air. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Pollutant Emission Summary Files for Earlier NEIs (2005 NEI). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories/pollutant-emissions-summary-files-earlier-neis (accessed on 14 December 2017).




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gratz, L.E.; Eckley, C.S.; Schwantes, S.J.; Mattson, E. Ambient Mercury Observations near a Coal-Fired Power Plant in a Western U.S. Urban Area. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040176
Gratz LE, Eckley CS, Schwantes SJ, Mattson E. Ambient Mercury Observations near a Coal-Fired Power Plant in a Western U.S. Urban Area. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(4):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040176
Chicago/Turabian StyleGratz, Lynne E., Chris S. Eckley, Story J. Schwantes, and Erick Mattson. 2019. "Ambient Mercury Observations near a Coal-Fired Power Plant in a Western U.S. Urban Area" Atmosphere 10, no. 4: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040176
APA StyleGratz, L. E., Eckley, C. S., Schwantes, S. J., & Mattson, E. (2019). Ambient Mercury Observations near a Coal-Fired Power Plant in a Western U.S. Urban Area. Atmosphere, 10(4), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040176




