Aqueous Reactions of Sulfate Radical-Anions with Nitrophenols in Atmospheric Context
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Chemicals
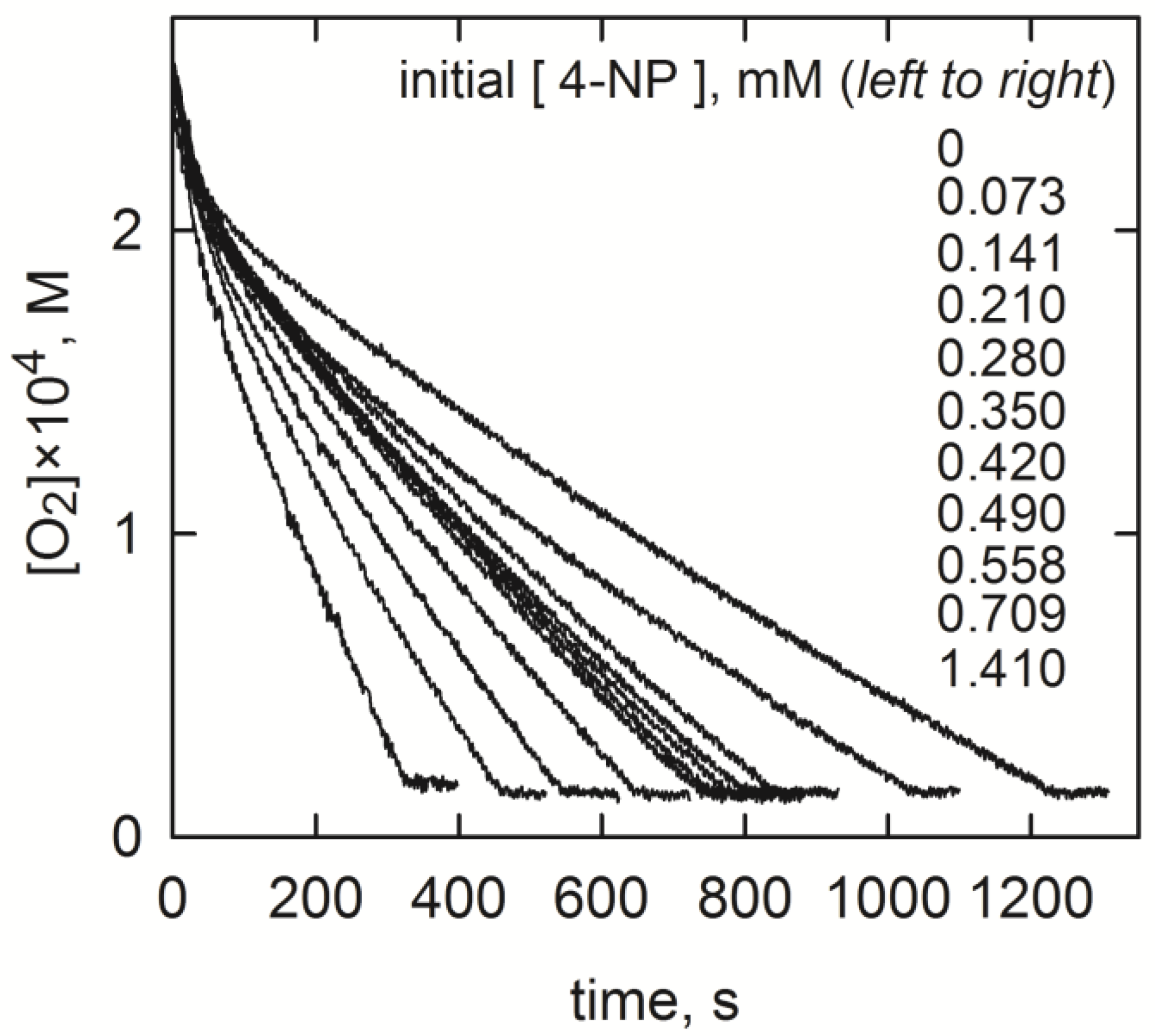
2.2. Estimation of the Rate Constants
2.3. Experimental Runs
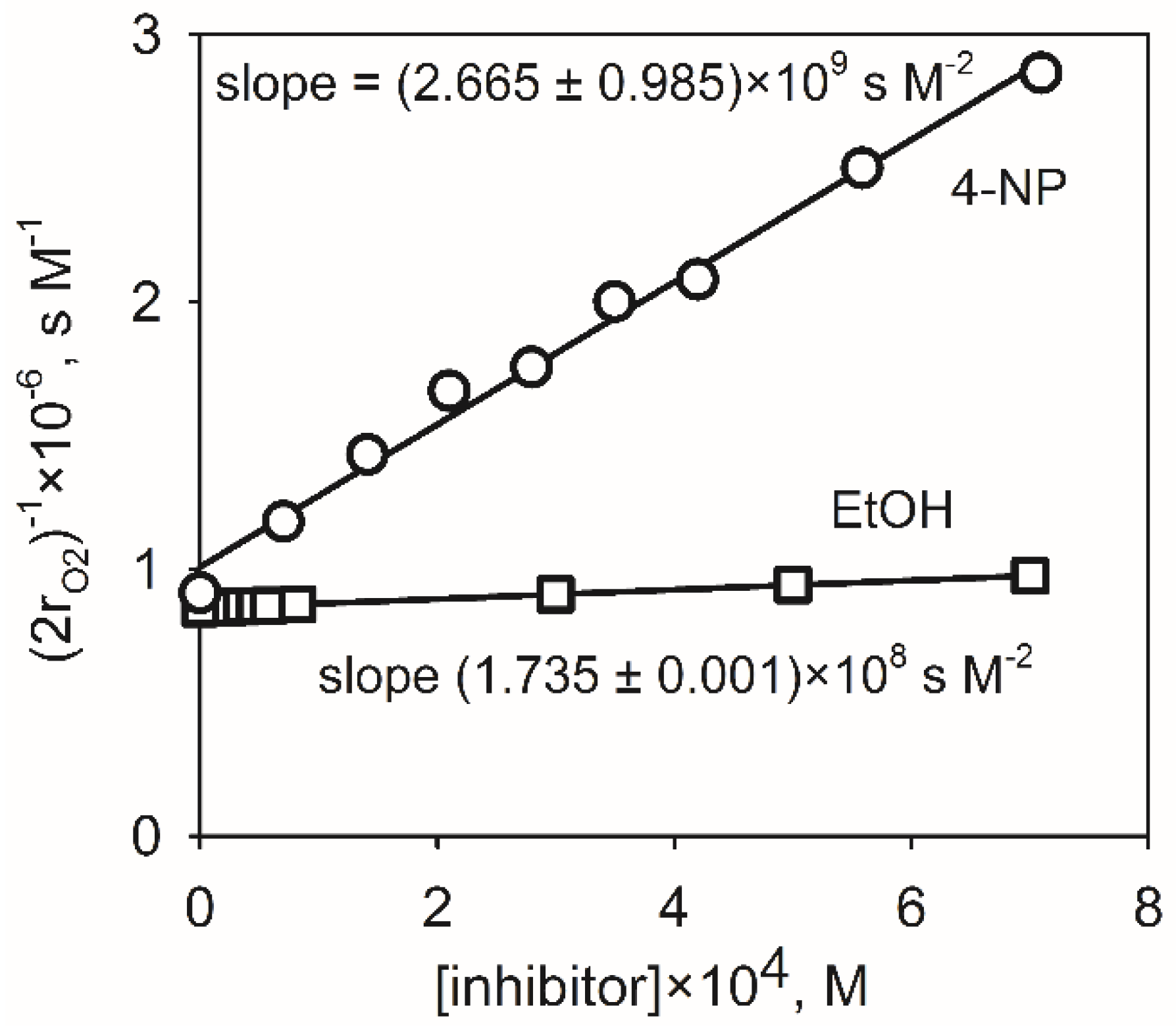
2.4. Correction of the Diffusional Limitations of the Rate Constants
3. Results
4. Discussion
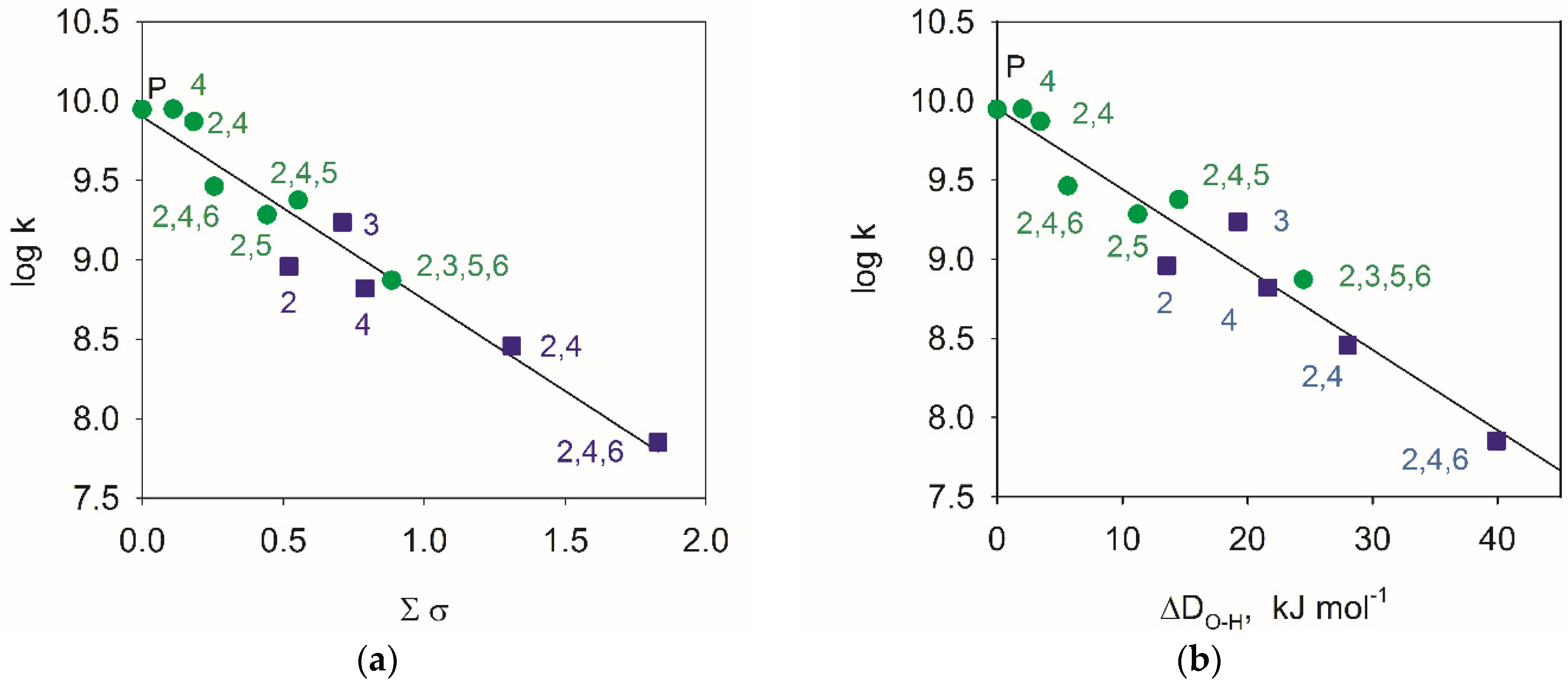
4.1. Hammett’s Correlations
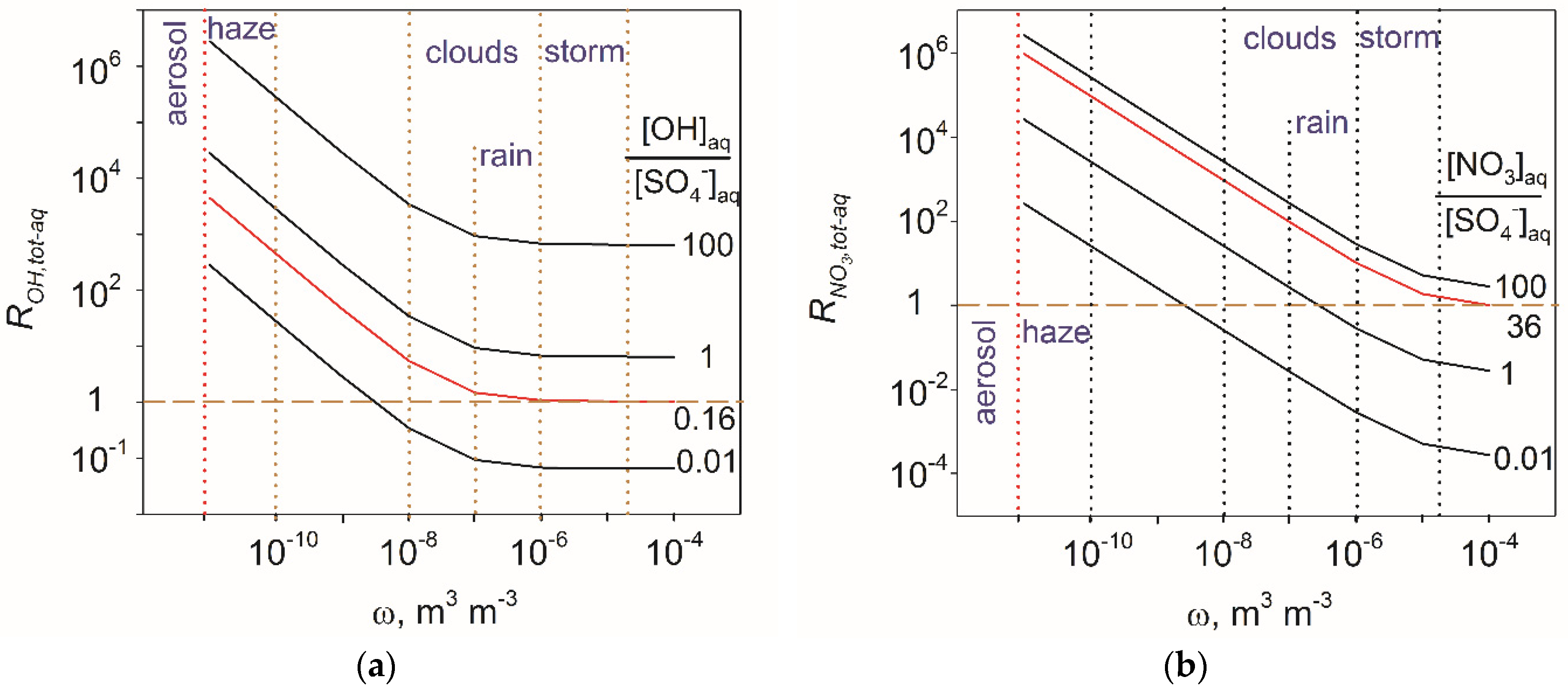
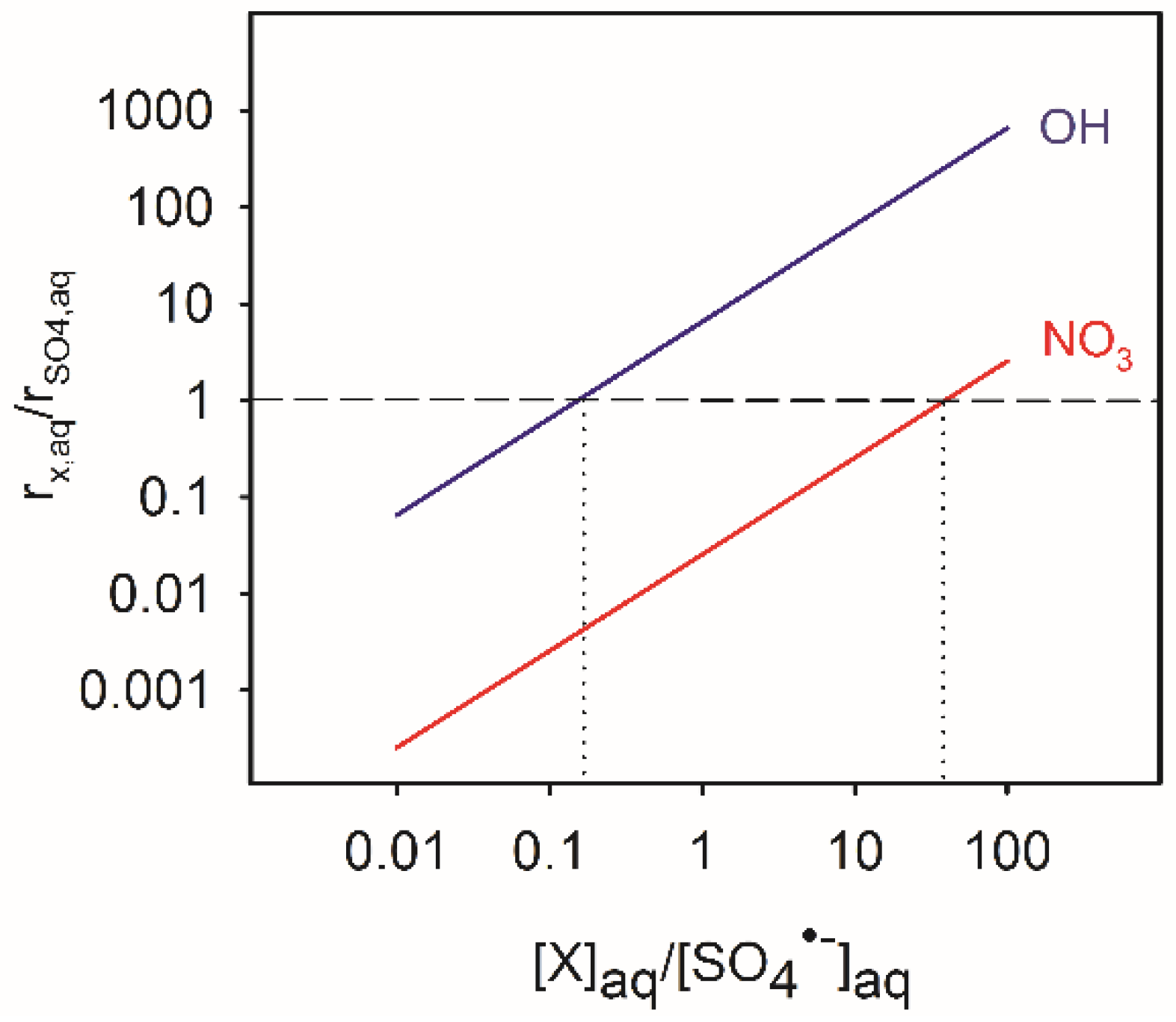
4.2. Atmospheric Significance
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, M.A.J.; Barra, S.; Borghesi, D.; Vione, D.; Arsene, C.; Iulian Olariu, R. Nitrated phenols in the atmosphere: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowicz, J.; Duda, W. Phenols—Sources and Toxicity. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 347–362. [Google Scholar]
- Belloli, R.; Bolzacchini, E.; Clerici, L.; Rindone, B.; Sesana, G.; Librando, V. Nitrophenols in air and rainwater. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 23, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhomme, O.; Morville, S.; Millet, M. Seasonal and diurnal variations of atmospheric concentrations of phenols and nitrophenols measured in the Strasbourg area, France. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2010, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morville, S.; Scheyer, A.; Mirabel, P.; Millet, M. A multiresidue method for the analysis of phenols and nitrophenols in the atmosphere. J. Environ. Monit. 2004, 6, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morville, S.; Scheyer, A.; Mirabel, P.; Millet, M. Spatial and geographical variations of urban, suburban and rural atmospheric concentrations of phenols and nitrophenols. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2006, 13, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, R.; Chan, Y.C.; Gardner, T.; Shaw, G.; Chapman, H. Characterisation of atmospheric deposition as a source of contaminants in urban rainwater tanks. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, F.; Schummer, C.; Al Chami, J.; Mirabel, P.; Millet, M. Solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry for analysis of phenols and nitrophenols in rainwater, as their t-butyldimethylsilyl derivatives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asman, W.A.H.; Jørgensen, A.; Bossi, R.; Vejrup, K.V.; Bügel Mogensen, B.; Glasius, M. Wet deposition of pesticides and nitrophenols at two sites in Denmark: Measurements and contributions from regional sources. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.; Hartmann, F.; Herrmann, H. Analysis of nitrophenols in cloud water with a miniaturized light-phase rotary perforator and HPLC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boris, A.J.; Lee, T.; Park, T.; Choi, J.; Seo, S.J.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Fog composition at Baengnyeong Island in the eastern Yellow Sea: Detecting markers of aqueous atmospheric oxidations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.S.; Huang, X.H.H.; Yu, J.Z. Quantification of nitroaromatic compounds in atmospheric fine particulate matter in Hong Kong over 3 years: Field measurement evidence for secondary formation derived from biomass burning emissions. Environ. Chem. 2016, 13, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.; Kadokami, K.; Trinh, H.T.; Phan, T.Q.; Le, G.T.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, D.T. Target screening analysis of 970 semi-volatile organic compounds adsorbed on atmospheric particulate matter in Hanoi, Vietnam. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, L.T.; Lin, P.; Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Weltman, R.; Edwards, R.D.; Arora, N.K.; Yadav, A.; Meinardi, S.; Blake, D.R.; et al. Molecular composition of particulate matter emissions from dung and brushwood burning household cookstoves in Haryana, India. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2461–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorio, C.; Bortolini, C.; Kourtchev, I.; Tapparo, A.; Bogialli, S.; Kalberer, M. Direct target and non-target analysis of urban aerosol sample extracts using atmospheric pressure photoionisation high-resolution mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irei, S.; Stupak, J.; Gong, X.; Chan, T.-W.; Cox, M.; McLaren, R.; Rudolph, J. Molecular marker study of particulate organic matter in Southern Ontario air. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitanovski, Z.; Grgic, I.; Vermeylen, R.; Claeys, M.; Maenhaut, W. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for characterization of monoaromatic nitro-compounds in atmospheric particulate matter. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1268, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitanovski, Z.; Shahpoury, P.; Samara, C.; Voliotis, A.; Lammel, G. Composition and mass size distribution of nitrated and oxygenated aromatic compounds in ambient particulate matter from southern and central Europe—implications for origin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 2019, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivácsy, Z.; Gelencsér, A.; Kiss, G.; Mészáros, E.; Molnár, Á.; Hoffer, A.; Mészáros, T.; Sárvári, Z.; Temesi, D.; Varga, B.; et al. Study on the chemical character of water soluble organic compounds in fine atmospheric aerosol at the Jungfraujoch. J. Atmos. Chem. 2001, 39, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Hoa, L.P.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, T.; Yang, X.; Iinuma, Y.; Chen, J.; Herrmann, H. Size distribution of particle-phase sugar and nitrophenol tracers during severe urban haze episodes in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OÖzel, M.Z.; Hamilton, J.F.; Lewis, A.C. New sensitive and quantitative analysis method for organic nitrogen compounds in urban aerosol samples. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teich, M.; Pinxteren, D.; Herrmann, H. Determination of nitrophenolic compounds from atmospheric particles using hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction and capillary electrophoresis/mass spectrometry analysis. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Gu, R.; Wang, H.; Yao, L.; Wen, L.; Zhu, F.; Wang, W.; Xue, L.; Yang, L.; et al. Observations of fine particulate nitrated phenols in four sites in northern China: Concentrations, source apportionment, and secondary formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.J.; Goldstein, A.H.; Kreisberg, N.M.; Hering, S.V.; Worsnop, D.R.; Ulbrich, I.M.; Docherty, K.S.; Jimenez, J.L. Major components of atmospheric organic aerosol in southern California as determined by hourly measurements of source marker compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11577–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Müller, L.; Winterhalter, R.; Moortgat, G.K.; Hoffmann, T.; Pöschl, U. Seasonal cycle and temperature dependence of pinene oxidation products, dicarboxylic acids and nitrophenols in fine and coarse air particulate matter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7859–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristanti, R.A.; Kanbe, M.; Toyama, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, X.; Mori, K. Accelerated biodegradation of nitrophenols in the rhizosphere of Spirodela polyrrhiza. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozňáková, Z.; Podehradská, J.; Kohličková, M. Determination of nitrophenols in soil. Chemosphere 1996, 33, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, S.; Minero, C.; Vione, D. Occurrence of 2,4-dichlorophenol and of 2,4-dichloro-6-nitrophenol in the Rhone River Delta (Southern France). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Khim, J.; Chung, S.; Seo, D.; Son, Y. Occurrence of micropollutants in four major rivers in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 491–492, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musilová, J.; Barek, J.; Pecková, K. Determination of nitrophenols in drinking and river water by differential pulse voltammetry at boron-doped diamond film electrode. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Bäumler, K.; Heberer, T.; Stan, H.-J. Occurrence and distribution of organic contaminants in the aquatic system in Berlin.Part II: Substituted phenols in Berlin surface water. Acta Hydroch. Hydrob. 1999, 27, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Balamurugan, T.S.T.; Chen, S.-M.; Chen, T.-W. Simplistic synthesis of ultrafine CoMnO3 nanosheets: An excellent electrocatalyst for highly sensitive detection of toxic 4-nitrophenol in environmental water samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, K.; Stieglitz, L. Identification and quantification of volatile organic components in emissions of waste incineration plants. Chemosphere 1995, 30, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goi, A.; Trapido, M. Comparison of advanced oxidation processes for the destruction of 2,4-dinitrophenol. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. Chem. 2001, 50, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Inomata, S.; Fushimi, A.; Sato, K.; Fujitani, Y.; Yamada, H. 4-Nitrophenol, 1-nitropyrene, and 9-nitroanthracene emissions in exhaust particles from diesel vehicles with different exhaust gas treatments. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 110, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xue, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Emissions of fine particulate nitrated phenols from various on-road vehicles in China. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, M.A.; Bustamante, P.; Vásquez, P. Atmospheric phenolic derivatives as tracers in an urban area. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2019, 64, 4407–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Interim Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Methyl Parathion, Case No. 0153; Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances, Ed.; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 20460.
- World Health Organization. Parathion in Drinking-Water; Background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bluvshtein, N.; Lin, P.; Flores, J.M.; Segev, L.; Mazar, Y.; Tas, E.; Snider, G.; Weagle, C.; Brown, S.S.; Laskin, A.; et al. Broadband optical properties of biomass-burning aerosol and identification of brown carbon chromophores. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 5441–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, M.; Le Breton, M.; Bannan, T.J.; Leather, K.E.; Bacak, A.; Reyes-Villegas, E.; De Vocht, F.; Shallcross, B.M.A.; Brazier, T.; Anwar Khan, M.; et al. Observations of Isocyanate, Amide, Nitrate, and Nitro Compounds From an Anthropogenic Biomass Burning Event Using a ToF-CIMS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 7687–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Chen, X.; Hays, M.D.; Holder, A.L. Composition and light absorption of N-containing aromatic compounds in organic aerosols from laboratory biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2899–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gu, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, W.; Xue, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, W. Emissions of fine particulate nitrated phenols from the burning of five common types of biomass. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinrichs, R.Z.; Buczek, P.; Trivedi, J.J. Solar Absorption by Aerosol-Bound Nitrophenols Compared to Aqueous and Gaseous Nitrophenols. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2016, 50, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Bluvshtein, N.; Rudich, Y.; Nizkorodov, S.A.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A. Molecular Chemistry of Atmospheric Brown Carbon Inferred from a Nationwide Biomass Burning Event. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2017, 51, 11561–11570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzaghi, P.; Herrmann, H. A mechanistic study of the oxidation of phenol by OH/NO2/NO3 in aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 3669–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heal, M.R.; Harrison, M.A.J.; Neil Cape, J. Aqueous-phase nitration of phenol by N2O5 and ClNO2. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3515–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Pelizzetti, E. Aqueous atmospheric chemistry: Formation of 2,4-dinitrophenol upon nitration of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol in solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7921–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Pelizzetti, E.; Harrison, M.A.J.; Olariu, R.; Arsene, C. Photochemical reactions in the tropospheric aqueous phase and on particulate matter. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Liggio, J.; Wentzell, J.; Li, S.M.; Stark, H.; Roberts, J.M.; Gilman, J.; Lerner, B.; Warneke, C.; Li, R.; et al. Secondary formation of nitrated phenols: Insights from observations during the Uintah Basin Winter Ozone Study (UBWOS) 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2139–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of organic compounds. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data Monogr. 1994, Monoghraph No. 2. 1–216. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, R.; Aschmann, S.M.; Arey, J. Reactions of hydroxyl and nitrogen trioxide radicals with phenol, cresols, and 2-nitrophenol at 296 ± 2 K. Environ. Sci.Technol. 1992, 26, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, F.; Bartels-Rausch, T.; De Laurentiis, E.; Ammann, M.; Brigante, M.; Mailhot, G.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Vione, D. Photochemical Formation of Nitrite and Nitrous Acid (HONO) upon Irradiation of Nitrophenols in Aqueous Solution and in Viscous Secondary Organic Aerosol Proxy. Environ. Sci.Technol. 2017, 51, 7486–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vione, D.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Duncianu, M.; Olariu, R.-I.; Arsene, C.; Sarakha, M.; Mailhot, G. Assessing the transformation kinetics of 2-and 4-nitrophenol in the atmospheric aqueous phase. Implications for the distribution of both nitroisomers in the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2321–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hems, R.F.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Aqueous Phase Photo-oxidation of Brown Carbon Nitrophenols: Reaction Kinetics, Mechanism, and Evolution of Light Absorption. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2018, 2, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Huang, D.D.; Cheung, H.Y.; Lee, A.K.Y.; Chan, C.K. Aqueous-phase photochemical oxidation and direct photolysis of vanillin—A model compound of methoxy phenols from biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2871–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Sun, J.; Mei, Q.; He, M. Mechanism and kinetic of nitrate radical-initiated atmospheric reactions of guaiacol (2-methoxyphenol). Comp. Theor. Chem. 2018, 1129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Smith, J.; Laskin, A.; Anastasio, C.; Laskin, J.; Zhang, Q. Chemical characterization of SOA formed from aqueous-phase reactions of phenols with the triplet excited state of carbonyl and hydroxyl radical. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13801–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Smith, J.; Laskin, A.; George, K.M.; Anastasio, C.; Laskin, J.; Dillner, A.M.; Zhang, Q. Molecular transformations of phenolic SOA during photochemical aging in the aqueous phase: Competition among oligomerization, functionalization, and fragmentation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4511–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litter, M.I. Introduction to Photochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment. In Environmental Photochemistry Part II; Boule, P., Bahnemann, D.W., Robertson, P.K.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 2, Pt M, pp. 325–366. [Google Scholar]
- Goi, A.; Trapido, M. Hydrogen peroxide photolysis, Fenton reagent and photo-Fenton for the degradation of nitrophenols: A comparative study. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, W.-Y.; Sheeley, S.A.; Rajh, T.; Cropek, D.M. Photocatalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol with arginine-modified titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 74, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Hassan, A.; Shabaan, S.; El-Nasser, K. Synthesis and characterization of composite catalysts Cr/ZSM-5 and their effects toward photocatalytic degradation of p-nitrophenol. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2106–S2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, M.H.; Madras, G. Kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of chlorophenol, nitrophenol, and their mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Y. Comparative study of the electrocatalytic oxidation and mechanism of nitrophenols at Bi-doped lead dioxide anodes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.A.; Egerton, T.A.; Kosa, S.A.M.; Tinlin, J.R.; Scott, K. The photoelectrocatalytic oxidation of aqueous nitrophenol using a novel reactor. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 35, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lei, L. An improved UV/Fe3+ process by combination with electrocatalysis for p-nitrophenol degradation. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolinário, Â.C.; Silva, A.M.T.; Machado, B.F.; Gomes, H.T.; Araújo, P.P.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L. Wet air oxidation of nitro-aromatic compounds: Reactivity on single-and multi-component systems and surface chemistry studies with a carbon xerogel. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 84, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, E.; Polo, A.M.; Mohedano, A.F.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. On the biodegradability of nitrophenols and their reaction products by catalytic hydrogenation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Gonzalez, M.A. Cobalt-Mediated Activation of Peroxymonosulfate and Sulfate Radical Attack on Phenolic Compounds. Implications of Chloride Ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. The Original List of Hazardous Air Pollutants. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/ttn/atw/188polls.html (accessed on 29 October 2014).
- EPA. Priority Pollutants. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/scitech/methods/cwa/pollutants.cfm (accessed on 27 October 2014).
- Keith, L.; Telliard, W. ES&T Special Report: Priority pollutants: I-a perspective view. Environ. Sci.Technol. 1979, 13, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P.; Santagostino, A.; Bolzacchini, E.; Rindone, B. Atmospheric monitoring, toxicology and QSAR modelling of nitrophenols. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2002, 11, 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Schafer, K.S.; Reeves, M.; Spitzer, S.; Kegley, S.E. Chemical Trespass Pesticides in our Bodies and Corporate Accountability; Pesticide Action Network North America: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.-P.; Wu, W.-L.; Long, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Yang, Z.-S. Voltammetric Behavior of o-Nitrophenol and Damage to DNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Salmon, G.A.; Williams, J.E. The reactivity of biogenic monoterpenes towards OH·and SO4− radicals in de-oxygenated acidic solution. J. Atmos. Chem. 2000, 36, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, C.L.; Huie, R.E. Rate constants for hydrogen abstraction reactions of the sulfate radical, SO4−. Alcohols. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1989, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, C.; Rassy, H.E.; Chovelon, J.M. Reactivity of selected volatile organic compounds (VOCs) toward the sulfate radical (SO4−). Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2001, 33, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Hoffmann, D.; Schaefer, T.; Bräuer, P.; Tilgner, A. Tropospheric Aqueous-Phase Free-Radical Chemistry: Radical Sources, Spectra, Reaction Kinetics and Prediction Tools. ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 3796–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzinski, K.J. Degradation of Isoprene in the Presence of Sulphoxy Radical Anions. J. Atmos. Chem. 2004, 48, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudziński, K.J.; Gmachowski, L.; Kuznietsova, I. Reactions of isoprene and sulphoxy radical-anions—A possible source of atmospheric organosulphites and organosulphates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajka, J.; Rudzinski, K. Autoxidation of S-IV inhibited by chlorophenols reacting with sulfate radicals. Environ. Chem. 2007, 4, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajka, J.; Pasiuk-Bronikowska, W. Autoxidation of sulphur dioxide in the presence of alcohols under conditions related to the tropospheric aqueous phase. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3913–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziajka, J.; Pasiuk-Bronikowska, W. Rate constants for atmospheric trace organics scavenging SO4− in the Fe-catalysed autoxidation of S(IV). Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgić, I.; Podkrajšek, B.; Barzaghi, P.; Herrmann, H. Scavenging of SO4− radical anions by mono-and dicarboxylic acids in the Mn(II)-catalyzed S(IV) oxidation in aqueous solution. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9187–9194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, A.J.; McCracken, D.R.; Buxton, G.V.; Wood, N.D. Estimation of rate constants for near-diffusion-controlled reactions in water at high temperatures. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1990, 86, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Nicovich, J.M.; Wine, P.H. Temperature-dependent kinetics studies of aqueous phase reactions of SO4− radicals with dimethylsulfoxide, dimethylsulfone, and methanesulfonate. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2003, 157, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, R.M. Effects of diffusion rates on chemical kinetics. In Progress in Reaction Kinetics; Porter, G., Stevens, B., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1961; Volume 1, pp. 129–160. [Google Scholar]
- North, A.M. The Collision Theory of Chemical Reactions in Liquids; Methuen: London, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Taft, R.W. A survey of Hammett substituent constants and resonance and field parameters. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.Y. Physical and Mechanistic Organic Chemistry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, M.; Lind, J.; Eriksen, T.E.; Merényi, G. O–H bond strengths and one-electron reduction potentials of multisubstituted phenols and phenoxyl radicals. Predictions using free energy relationships. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1993, 1567–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Schaefer, T.; Tilgner, A.; Styler, S.A.; Weller, C.; Teich, M.; Otto, T. Tropospheric aqueous-phase chemistry: Kinetics, mechanisms, and its coupling to a changing gas phase. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4259–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. Kinetics and mechanisms of the gas-phase reactions of the hydroxyl radical with organic compounds. Chem. Ref. 1989, Monograph No. 1. 1–246. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, H. Kinetics of Aqueous Phase Reactions Relevant for Atmospheric Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 4691–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Brimblecombe, P. Henry’s law constants of phenol and mononitrophenols in water and aqueous sulfuric acid. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | Abbreviation | Concentration Range, mM |
|---|---|---|
| 2-nitrophenol | 2-NP | 0.032–0.347 |
| 3-nitrophenol | 3-NP | 0.019–0.089 |
| 4-nitrophenol | 4-NP | 0.073–0.711 |
| 2,4-dinitrophenol | 2,4-DNP | 0.169–1.325 |
| 2,4,6-trinitrophenol | 2,4,6-TNP | 0.197–0.788 |
| HSO3− | 2 | |
| O2 | ~0.25 | |
| Fe(ClO4)3 | 0.01 |
| Compound | Slope, s M−2 | kobserved, M−1s−1 | kdiffusionA, M−1s−1 | kreaction, M−1s−1 | (kr − ko)/ko, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EtOH (reference) | (1.735 ± 0.001) × 108 | (4.30 ± 0.86) × 107 | |||
| 2-NP | (3.662 ± 0.235) × 109 | (9.08 ± 2.40) × 108 | 2.01 × 1010 | (9.50 ± 4.58) × 108 | 4.74 |
| 3-NP | (6.957 ± 0.277) × 109 | (1.72 ± 0.41) × 109 | 2.01 × 1010 | (1.89 ± 0,89) × 109 | 9.53 |
| 4-NP | (2.665 ± 0.985) × 109 | (6.60 ± 3.77) × 108 | 2.01 × 1010 | (6.83 ± 5.42) × 108 | 3.41 |
| 2,4-DNP | (1.154 ± 0.152) × 109 | (2.86 ± 0.95) × 108 | 2.13 × 1010 | (2.90 ± 1.58) × 108 | 1.51 |
| 2,4,6-TNP | (2.865 ± 0.180) × 108 | (7.10 ± 1.87) × 107 | 2.18 × 1010 | (7.12 ± 3.31) × 107 | 0.33 |
| Reaction X + NP | kX,g | kX,aq | HdX | HdNP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm3 molecule−1 s−1 | dm3 mol−1 s−1 | dm3 mol−1 s−1 | |||
| OH + 2-NP | 9.00 × 10−13 (a) | 5.42 × 108 | 5.90 × 109 (b) | 6.11 × 102 (d) | 5.17 × 103 (e) |
| NO3 + 2-NP | 2.00 × 10−14 (a) | 1.20 × 107 | 2.30 × 107 (c) | 1.47 × 101 (d) | |
| Gas Phase (a) | Aqueous Phase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OH | NO3 | OH | NO3 | SO4•− | [OH]/[SO4•−] | [NO3]/[SO4•−] | |
| molecule cm−3 | mol dm−3 | ||||||
| Minimal | 1.4 × 102 | 7.9 × 106 | 1.4 × 10−16 | 1.6 × 10−16 | 5 × 10−17 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 1.8 × 10−3 |
| Maximal | 6.6 × 103 | 1.2 × 107 | 8.0 × 10−12 | 3.0 × 10−13 | 9 × 10−13 | 1.6 × 105 | 6.0 × 103 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudziński, K.J.; Szmigielski, R. Aqueous Reactions of Sulfate Radical-Anions with Nitrophenols in Atmospheric Context. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120795
Rudziński KJ, Szmigielski R. Aqueous Reactions of Sulfate Radical-Anions with Nitrophenols in Atmospheric Context. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(12):795. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120795
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudziński, Krzysztof J., and Rafał Szmigielski. 2019. "Aqueous Reactions of Sulfate Radical-Anions with Nitrophenols in Atmospheric Context" Atmosphere 10, no. 12: 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120795
APA StyleRudziński, K. J., & Szmigielski, R. (2019). Aqueous Reactions of Sulfate Radical-Anions with Nitrophenols in Atmospheric Context. Atmosphere, 10(12), 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120795