Implicit Definition of Flow Patterns in Street Canyons—Recirculation Zone—Using Exploratory Quantitative and Qualitative Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
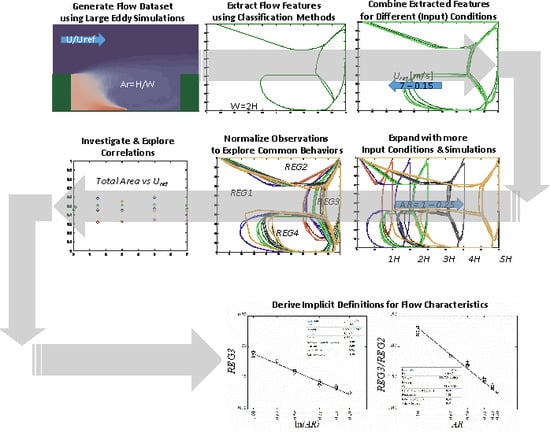
2. Methodology
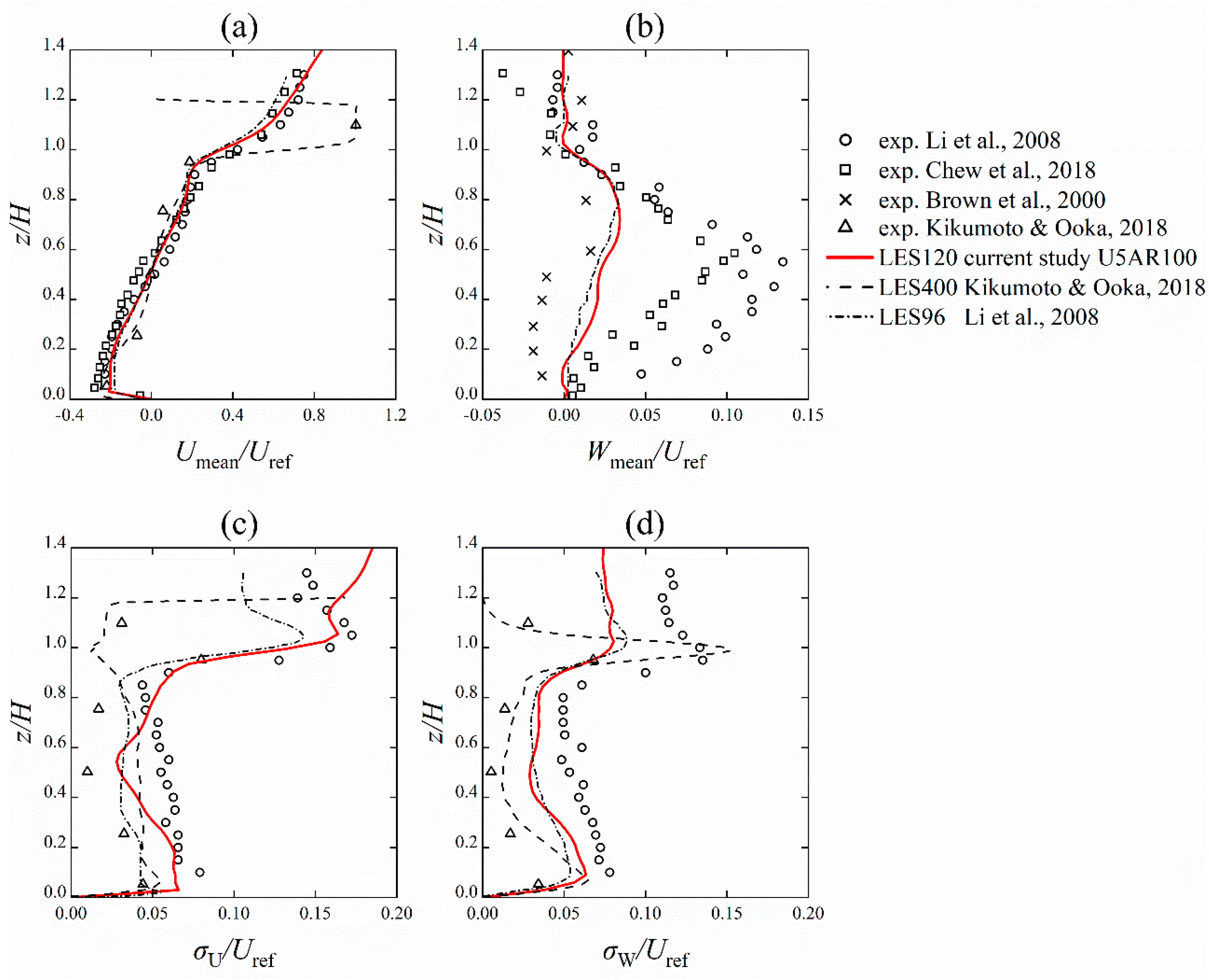
2.1. Simulation Set-up
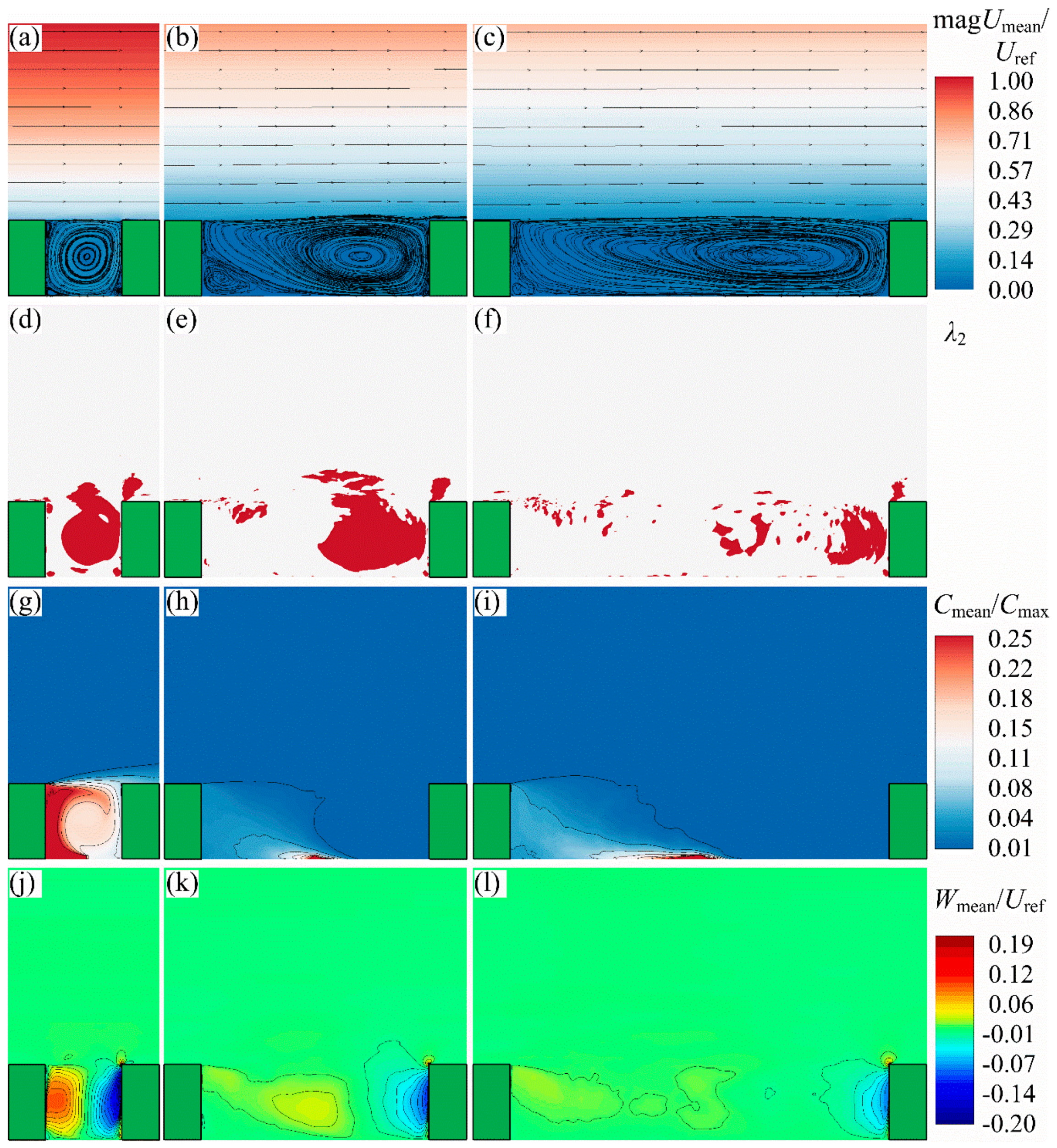
2.2. Vortex Visualisation
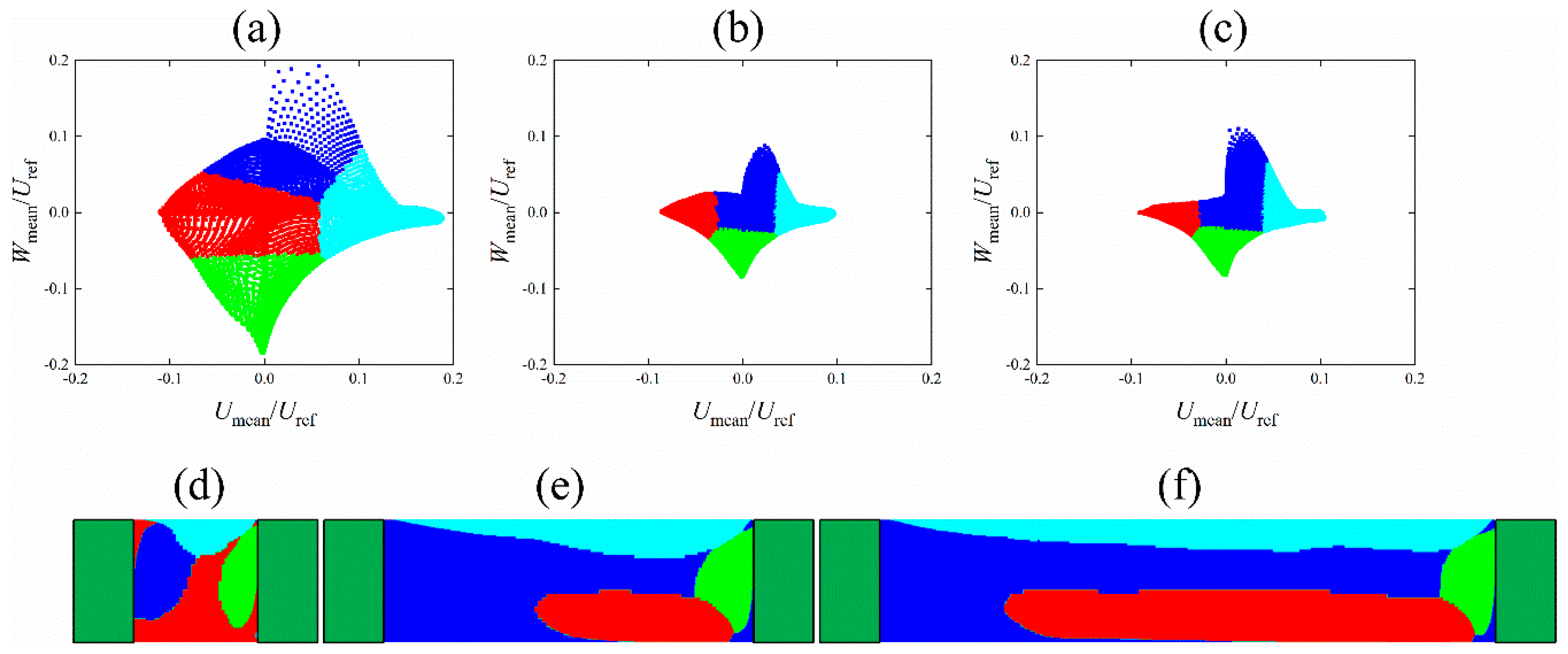
2.3. K-means Clustering
3. Results
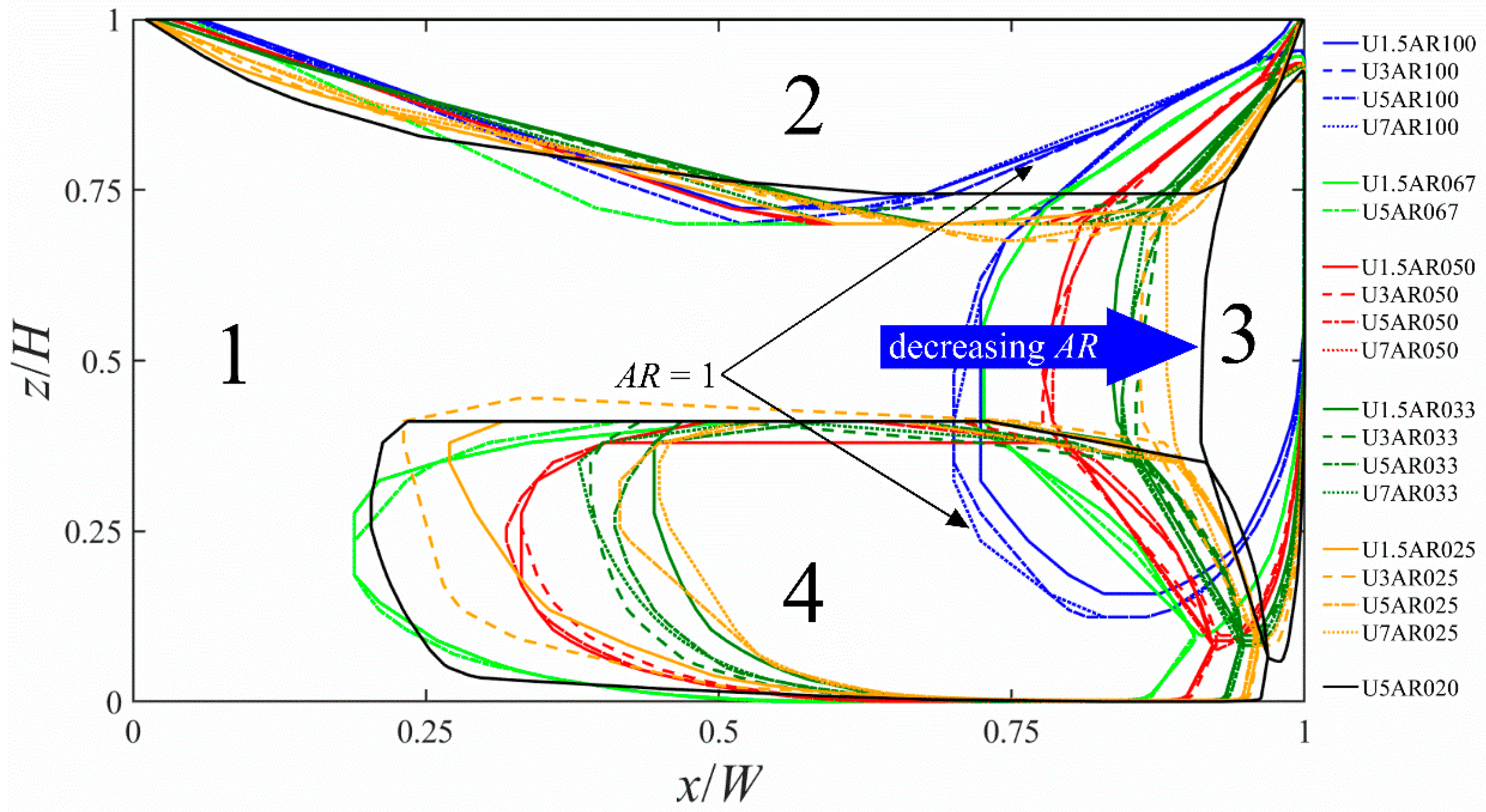
3.1. Vortex Visualisation
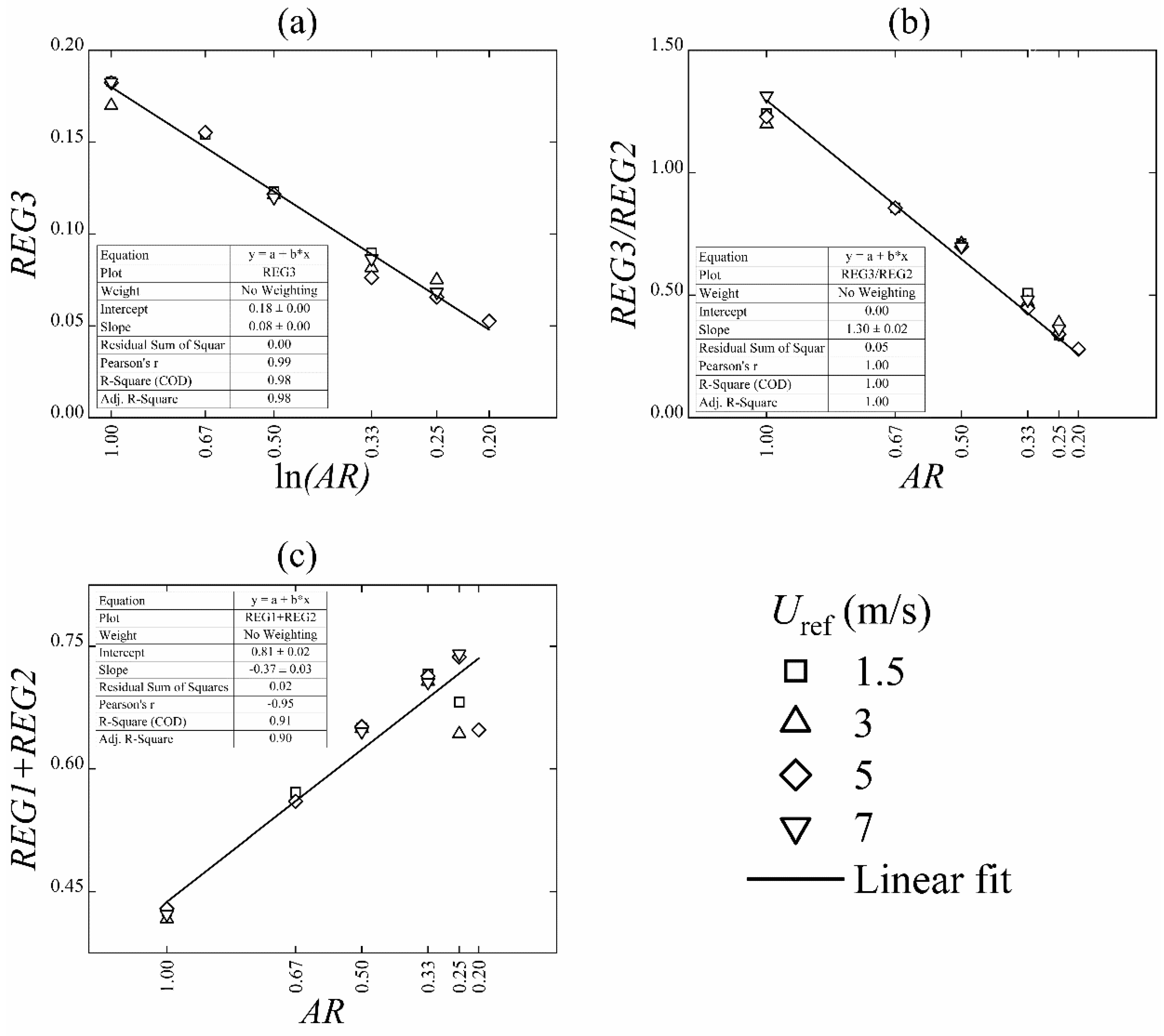
3.2. K-means Clustering
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Requia, W.J.; Adams, M.D.; Arain, A.; Papatheodorou, S.; Koutrakis, P.; Mahmoud, M. Global Association of Air Pollution and Cardiorespiratory Diseases: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Investigation of Modifier Variables. Am. J. Public Health 2018, 108, S123–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, F.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Pham, L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. FIne particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. JAMA 2006, 295, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowatte, G.; Lodge, C.; Lowe, A.J.; Erbas, B.; Perret, J.; Abramson, M.J.; Matheson, M.; Dharmage, S.C. The influence of childhood traffic-related air pollution exposure on asthma, allergy and sensitization: A systematic review and a meta-analysis of birth cohort studies. Allergy 2015, 70, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Beelen, R.; Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: Prospective analyses from the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beelen, R.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Wolf, K.; Samoli, E.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; et al. Effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on natural-cause mortality: An analysis of 22 European cohorts within the multicentre ESCAPE project. Lancet 2014, 383, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahiyuddin, R.; Sahani, M.; Aripin, R.; Latif, M.T.; Thach, T.-Q.; Wong, C.-M. Short-term effects of daily air pollution on mortality. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 65, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. 7 Million Premature Deaths Annually Linked to Air Pollution. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2014/air-pollution/en/ (accessed on 12 October 2018).
- Colvile, R.N.; Hutchinson, E.J.; Mindell, J.S.; Warren, R.F. The transport sector as a source of air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1537–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasius, M.; Ketzel, M.; Wåhlin, P.; Jensen, B.; Mønster, J.; Berkowicz, R.; Palmgren, F. Impact of wood combustion on particle levels in a residential area in Denmark. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7115–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, X.; Li, G.; Bi, X.; Zhu, J.; Qin, H.; Dai, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, G. Distributions, sources and pollution status of 17 trace metal/metalloids in the street dust of a heavily industrialized city of central China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, C.; Abraham, M.; Hassan, H.; Ashraf, A.; Fthenou, E.; Sadoun, E.; Kakosimos, K. Modeling of PM10 and PM2.5 building infiltration during a dust event in Doha, Qatar. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Atmospheric Dust—DUST2016, Castellaneta Marina, Taranto, Italy, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, H. Air pollution in cities. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E. Policies and technical guidelines for urban planning of high-density cities – air ventilation assessment (AVA) of Hong Kong. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Xing, J.; Morawska, L.; Ding, A.; Kulmala, M.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Kujansuu, J.; et al. Particulate matter pollution over China and the effects of control policies. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 584-585, 426–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovar-Panskus, A.; Louka, P.; Sini, J.F.; Savory, E.; Czech, M.; Abdelqari, A.; Mestayer, P.G.; Toy, N. Influence of Geometry on the Mean Flow within Urban Street Canyons—A Comparison of Wind Tunnel Experiments and Numerical Simulations. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2002, 2, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallman, A.; Magnusson, S.; Britter, R.; Norford, L.; Entekhabi, D.; Fernando, H.J.S. Conditions for thermal circulation in urban street canyons. Build. Environ. 2014, 80, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraga, D.; Maggos, T.; Sadoun, E.; Fthenou, E.; Hassan, H.; Tsiouri, V.; Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, A.; Vasilakos, C.; Kakosimos, K. Chemical characterization of indoor and outdoor particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) in Doha, Qatar. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1156–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, C.D.; Hassan, H.; Kumar, P.; Kakosimos, K.E. Measurements and modelling of particulate matter building ingress during a severe dust storm event. Build. Environ. 2020, 167, 106441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, C.D.; Ashraf, A.M.; Markatos, N.C.; Kakosimos, K.E. Mathematical modelling and computer simulation of toxic gas building infiltration. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, C.D.; Elkhalifa, S.; Fthenou, E.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Andronopoulos, S.; Venetsanos, A.; Kovalets, I.V.; Kakosimos, K.E. Source reconstruction of airborne toxics based on acute health effects information. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, G.C.; Kovalets, I.V.; Argyropoulos, C.D.; Venetsanos, A.; Andronopoulos, S.; Kakosimos, K.E. Evaluation of an inverse modelling methodology for the prediction of a stationary point pollutant source in complex urban environments. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalets, I.V.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Andronopoulos, S.; Venetsanos, A.G.; Argyropoulos, C.D.; Kakosimos, K.E. Inverse identification of unknown finite-duration air pollutant release from a point source in urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 181, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Fisher, B.E.A.; Pericleous, K.; Gonzalez-Flesca, N. Modelling air quality in street canyons: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, N.S.; Morawska, L. A review of dispersion modelling and its application to the dispersion of particles: An overview of different dispersion models available. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5902–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, I. The use of climate knowledge in urban planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 48, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, T.; González Duque, J.A.; Bostenaru Dan, M. Urban planning with respect to environmental quality and human well-being. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Vardoulakis, S.; Zhang, F.; Pilot, E.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.; Krafft, T. Air Quality Strategies on Public Health and Health Equity in Europe-A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, J.; Belcher, S. A Wind Tunnel Model for Quantifying Fluxes in the Urban Boundary Layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol 2002, 104, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner-Klein, P.; Berkowicz, R.; Britter, R. The influence of street architecture on flow and dispersion in street canyons. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2004, 87, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.M.; Barlow, J.F.; Belcher, S.E. Dispersion and transfer of passive scalars in and above street canyons—Large-eddy simulations. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5885–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimichailidis, A.E.; Argyropoulos, C.D.; Assael, M.J.; Kakosimos, K.E. A formulation for the street canyon recirculation zone based on parametric analysis of large eddy simulations. In Proceedings of the HARMO 2017—18th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Bologna, Italy, 9–12 October 2017; pp. 455–459. [Google Scholar]
- Oke, T.R. Street design and urban canopy layer climate. Energy Build. 1988, 11, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowicz, R.; Hertel, O.; Larsen, S.E.; Sorensen, N.N.; Nielsen, M. Modelling Traffic Pollution in Streets; National Environmental Research Institute: Roskilde, Denmark, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, W.B.; Ludwig, F.L.; Dabberdt, W.F.; Allen, R.J. An Urban Diffusion Simulation Model For Carbon Monoxide. J. Air Pollut. Control. Assoc. 1973, 23, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabberdt, W.F.; Ludwig, F.L.; Johnson, W.B., Jr. Validation and applications of an urban diffusion model for vehicular pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 1973, 7, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamartino, R.J.; Wiegand, G. Development and evaluation of simple models for the flow, turbulence and pollutant concentration fields within an urban street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 1986, 20, 2137–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Britter, R.; Norford, L.K. Effect of stable stratification on dispersion within urban street canyons: A large-eddy simulation. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegrini, J.; Dorer, V.; Carmeliet, J. Wind tunnel measurements of buoyant flows in street canyons. Build. Environ. 2013, 59, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.T.; Mak, C.M. CFD simulation of flow in a long street canyon under a perpendicular wind direction: Evaluation of three computational settings. Build. Environ. 2017, 114, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowicz, R. OSPM—A Parameterised Street Pollution Model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2000, 65, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, A.T. Validation of a Street Canyon Model in Two Cities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1998, 52, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, D.J.; Holroyd, R.J.; Hunt, J.C.R.; Weng, W.S.; Robins, A.G.; Apsley, D.D.; Thompson, D.J.; Smith, F.B. UK-ADMS: A new approach to modelling dispersion in the earth’s atmospheric boundary layer. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1994, 52, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherin, N.; Roustan, Y.; Musson-Genon, L.; Seigneur, C. Modelling atmospheric dry deposition in urban areas using an urban canopy approach. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, I.; Barlow, J.; Belcher, S. Scalar Fluxes from Urban Street Canyons Part II: Model. Bound.-Layer Meteorol 2004, 113, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shao, Y. A Scheme for Scalar Exchange in the Urban Boundary Layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol 2006, 120, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Cierco, F.X.; Perkins, R. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; part I, presentation of the model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7379–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Mejean, P.; Perkins, R.J. Modelling the transport and dispersion of pollutants in street canyons. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 16, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.M. Dispersion of a passive plume in an idealised urban convective boundary layer: A large-eddy simulation. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-X.; Liu, C.-H.; Leung, D.C. Large-Eddy Simulation of Flow and Pollutant Dispersion in High-Aspect-Ratio Urban Street Canyons with Wall Model. Bound.-Layer Meteorol 2008, 129, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Cai, X.-M.; Bloss, W.J. Modelling segregation effects of heterogeneous emissions on ozone levels in idealised urban street canyons: Using photochemical box models. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 188, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesieur, M.; Métais, O.; Comte, P. Large-Eddy Simulations of Turbulence; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, C.D.; Markatos, N.C. Recent advances on the numerical modelling of turbulent flows. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 693–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagaut, P. Large Eddy Simulation for Incompressible Flows: An Introduction; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa, A.; Horiuti, K. A statistically-derived subgrid-scale kinetic energy model for the large-eddy simulation of turbulent flows. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1985, 54, 2834–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, A. Subgrid-scale modeling with a variable length scale. Phys. Fluids A Fluid Dyn. 1989, 1, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Cai, X.-M.; Bloss, W.J. Modelling the dispersion and transport of reactive pollutants in a deep urban street canyon: Using large-eddy simulation. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Stathopoulos, T. Numerical simulation of dispersion around an isolated cubic building: Model evaluation of RANS and LES. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assael, M.J.; Kakosimos, K.E. Fires, Explosions, and Toxic Gas Dispersions: Effects Calculation and Risk Analysis; CRC Press: Florida, FA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Issa, R.I. Solution of the implicitly discretised fluid flow equations by operator-splitting. J. Comput. Phys. 1986, 62, 40–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, H. OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox User Guide; The OpenFOAM Foundation Ltd.: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, J.; Baklanov, A. Best Practice Guideline for the CFD Simulation of Flows in the urban Environment: COST Action 732 Quality Assurance and Improvement of Microscale Meteorological Models; Meteorologisches Institut Universitat Hamburg: Hamburg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lien, F.S.; Leschziner, M.A. Upstream monotonic interpolation for scalar transport with application to complex turbulent flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 1994, 19, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X. Effects of differential wall heating in street canyons on dispersion and ventilation characteristics of a passive scalar. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimichailidis, A.; Argyropoulos, C.; Assael, M.; Kakosimos, K. Qualitative and Quantitative Investigation of Multiple Large Eddy Simulation Aspects for Pollutant Dispersion in Street Canyons Using OpenFOAM. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Lawson, R.E.; Decroix, D.S.; Lee, R.L. Mean Flow and Turbulence Measurement around a 2-D Array of Buildings in a Wind Tunnel; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Li, X.-X.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Liu, C.-H.; Lam, K.M. Physical Modeling of Flow Field inside Urban Street Canyons. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, L.W.; Aliabadi, A.A.; Norford, L.K.J.E.F.M. Flows across high aspect ratio street canyons: Reynolds number independence revisited. Springer 2018, 18, 1275–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikumoto, H.; Ooka, R. Large-eddy simulation of pollutant dispersion in a cavity at fine grid resolutions. Build. Environ. 2018, 127, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatzmann, M. COST 732 Model Evaluation Case Studies: Approach and Results; Meteorological Institute: Hamburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, I.B.; Cehreli, Z.N.; Yavuz, I. Index of Resolution Quality for Large Eddy Simulations. J. Fluids Eng. 2005, 127, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Machiraju, R.; Thompson, D. Detection and visualization of vortices. In The Visualization Handbook; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 295–309. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, P.; Balachandar, S.; Adrian, R.J. On the relationships between local vortex identification schemes. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 535, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Hussain, F. On the identification of a vortex. J. Fluid Mech. 1995, 285, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.C.; Wray, A.; Moin, P. Eddies, streams, and convergence zones in turbulent flows. In Proceedings of the 1988 Summer Program, Stanford, CA, USA, 1 December 1988; 1988; CA, p. USA. [Google Scholar]
- Holmén, V. Methods for vortex identification. Master’s Theses, Mathematics (Faculty of Engineering), Sölvegatan, Lund, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Coceal, O.; Dobre, A.; Thomas, T.G.; Belcher, S.E. Structure of turbulent flow over regular arrays of cubical roughness. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 589, 375–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michioka, T.; Sato, A.; Takimoto, H.; Kanda, M. Large-Eddy Simulation for the Mechanism of Pollutant Removal from a Two-Dimensional Street Canyon. Bound.-Layer Meteorol 2011, 138, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellnerová, R.; Kukačka, L.; Jurčáková, K.; Uruba, V.; Jaňour, Z. PIV measurement of turbulent flow within a street canyon: Detection of coherent motion. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2012, 104–106, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsourakis, N.; Bartzis, J.G.; Efthimiou, G.C.; Venetsanos, A.G.; Tolias, I.C.; Markatos, N.C.; Hertwig, D.; Leitl, B. LES study of unsteady flow phenomena in an urban geometry – the need for special evaluation methods. In Proceedings of the HARMO 2016—17th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Varna, Bulgaria, 8–11 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brunton, S.L.; Noack, B.R.; Koumoutsakos, P. Machine learning for fluid mechanics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2019, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Peng, Z.-R.; Fu, Q. Investigating the relationship between air pollution variation and urban form. Build. Environ. 2019, 147, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Namdeo, A.; Bell, M. Classification of road traffic and roadside pollution concentrations for assessment of personal exposure. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, T.; Hussein, T.; Hämeri, K.; Vesala, T.; Kulmala, M.; Weber, S. Properties of aerosol signature size distributions in the urban environment as derived by cluster analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1967; pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.-P.; Sander, R.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters a density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, Oregon, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical Grouping to Optimize an Objective Function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Livny, M. BIRCH: An efficient data clustering method for very large databases. Proceedings of ACM Sigmod Record, Montreal, QC, Canada, 4–6 June 1996; pp. 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y. Mean Shift, Mode Seeking, and Clustering %J IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1995, 17, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Theodoridis, S.; Koutroumbas, K. Pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 2008, 19, 376. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.M.; Eckelmann, H.; Brodkey, R.S. The wall region in turbulent shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 54, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Uref | AR | Code |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 0.25 | U1.5AR025 |
| 1.5 | 0.33 | U1.5AR033 |
| 1.5 | 0.50 | U1.5AR050 |
| 1.5 | 0.67 | U1.5AR067 |
| 1.5 | 1.00 | U1.5AR100 |
| 3 | 0.25 | U3AR025 |
| 3 | 0.33 | U3AR033 |
| 3 | 0.50 | U3AR050 |
| 3 | 1.00 | U3AR100 |
| 5 | 0.20 | U5AR020 |
| 5 | 0.25 | U5AR025 |
| 5 | 0.33 | U5AR033 |
| 5 | 0.50 | U5AR050 |
| 5 | 0.67 | U5AR067 |
| 5 | 1.00 | U5AR100 |
| 7 | 0.25 | U7AR025 |
| 7 | 0.33 | U7AR033 |
| 7 | 0.50 | U7AR050 |
| 7 | 1.00 | U7AR100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatzimichailidis, A.E.; Argyropoulos, C.D.; Assael, M.J.; Kakosimos, K.E. Implicit Definition of Flow Patterns in Street Canyons—Recirculation Zone—Using Exploratory Quantitative and Qualitative Methods. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120794
Chatzimichailidis AE, Argyropoulos CD, Assael MJ, Kakosimos KE. Implicit Definition of Flow Patterns in Street Canyons—Recirculation Zone—Using Exploratory Quantitative and Qualitative Methods. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(12):794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120794
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatzimichailidis, Arsenios E., Christos D. Argyropoulos, Marc J. Assael, and Konstantinos E. Kakosimos. 2019. "Implicit Definition of Flow Patterns in Street Canyons—Recirculation Zone—Using Exploratory Quantitative and Qualitative Methods" Atmosphere 10, no. 12: 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120794
APA StyleChatzimichailidis, A. E., Argyropoulos, C. D., Assael, M. J., & Kakosimos, K. E. (2019). Implicit Definition of Flow Patterns in Street Canyons—Recirculation Zone—Using Exploratory Quantitative and Qualitative Methods. Atmosphere, 10(12), 794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120794