Aerosol Particle and Black Carbon Emission Factors of Vehicular Fleet in Manila, Philippines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Measurement Set-Up
2.1. Street Configuration at Taft Avenue
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Estimation of Emission Factors (EF)
2.3.1. Determination of Curbside Contribution
2.3.2. Dilution and Emission Factors
3. Results and Discussion
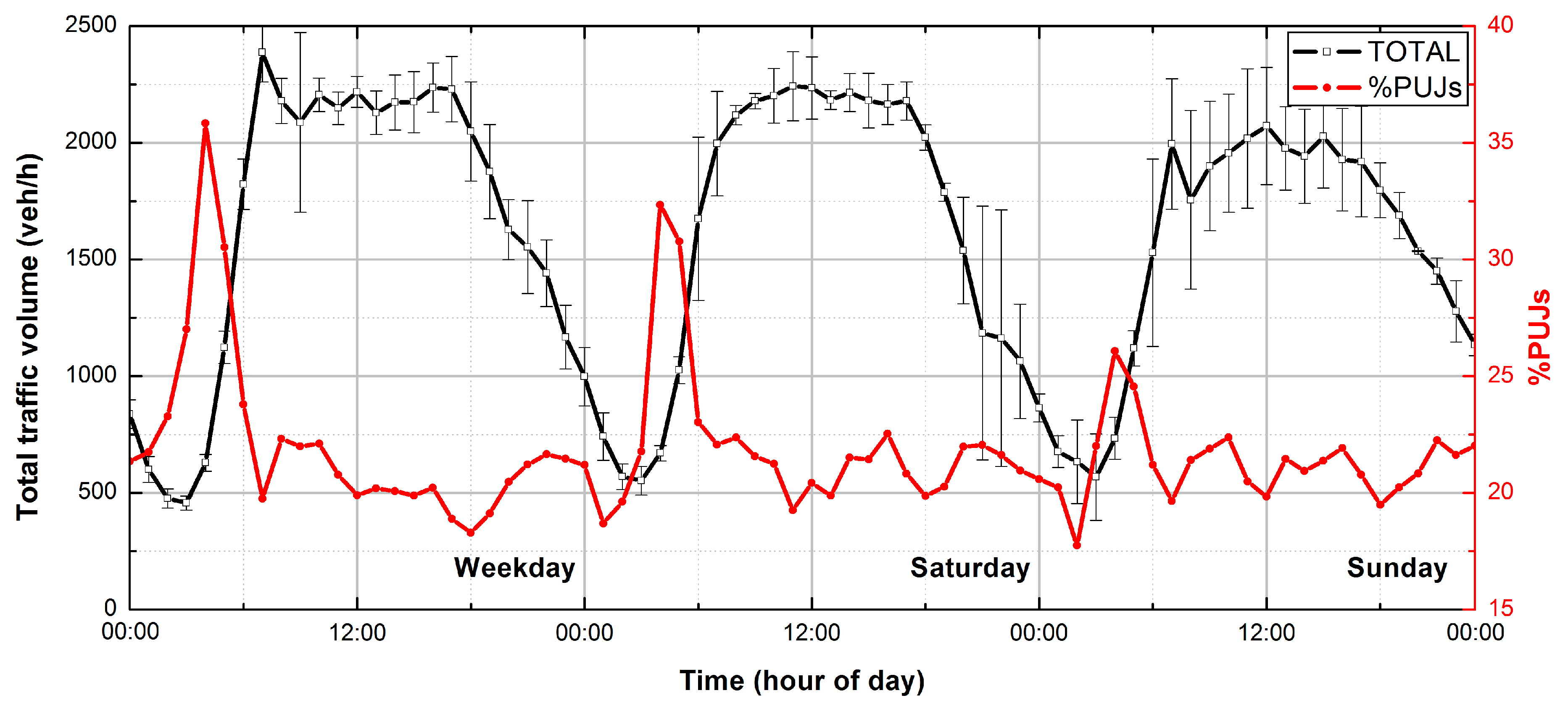
3.1. Traffic Conditions
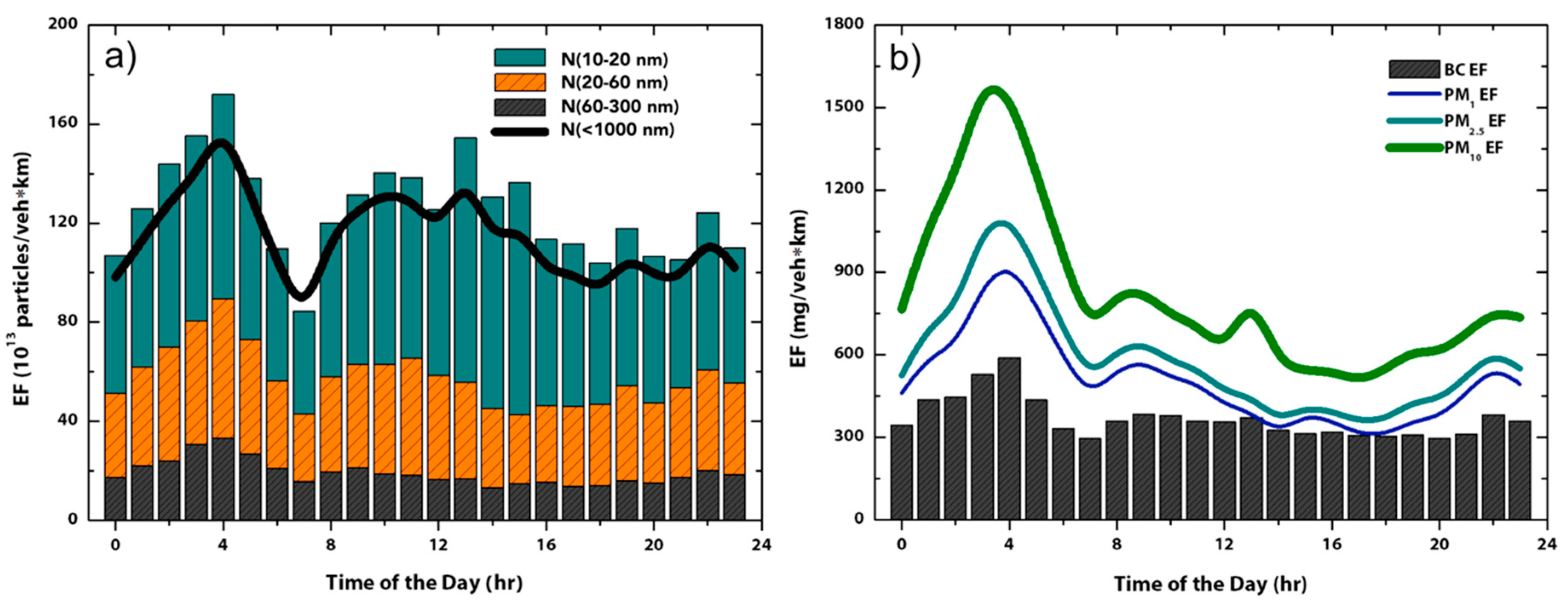
3.2. Mixed Fleet Emission Factor
3.3. Vehicle Segregated Emission Factor
4. Study Limitations
4.1. Measurements of Black Carbon Mass Concentration and Particle Number Size Distributions
4.2. Estimating Emission Factor with OSPM
5. Summary and Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oanh, N.T.K.; Upadhyay, N.; Zhuang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Murthy, D.; Lestari, P.; Villarin, J.; Chengchua, K.; Co, H.; Dung, N. Particulate Air Pollution in Six Asian Cities: Spatial and Temporal Distributions, and Associated Sources. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3367–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, A.; Godden, D.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K. Particulate Air Pollution and Acute Health Effects. Lancet 1995, 345, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlwein, S.; Kappeler, R.; Kutlar Joss, M.; Künzli, N.; Hoffmann, B. Health Effects of Ultrafine Particles: A Systematic Literature Review Update of Epidemiological Evidence. Int. J. Public Health. 2019, 64, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weingartner, E.; Keller, C.; Stahel, W.; Burtscher, H.; Baltensperger, U. Aerosol Emission in a Road Tunnel. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.; Wehner, B.; Ketzel, M.; Engler, C.; Voigtländer, J.; Tuch, T.; Wiedensohler, A. Atmospheric Number Size Distributions of Soot Particles and Estimation of Emission Factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Selzle, K.; Pöschl, U. Hazardous Components and Health Effects of Atmospheric Aerosol Particles: Reactive Oxygen Species, Soot, Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds and Allergenic Proteins. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecl, P.; Johansson, C.; Targino, A.; Ström, J.; Burman, L. Trends in Black Carbon and Size-Resolved Particle Number Concentrations and Vehicle Emission Factors Under Real-World Conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, S.; Birmili, W.; Voigtländer, J.; Tuch, T.; Wehner, B.; Wiedensohler, A.; Ketzel, M. Particle Number Emissions of Motor Traffic Derived from Street Canyon Measurements in A Central European City. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3763–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, C.; Harrison, R.; Querol, X. Review of The Efficacy of Low Emission Zones to Improve Urban Air Quality in European Cities. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 111, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Boltze, M.; Groer, S.; Scheuvens, D. Impacts of Low Emission Zones in Germany on Air Pollution Levels. Transp. Res. Procedia. 2017, 25, 3370–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oanh, N.T.K.; Van, H.H. Comparative Assessment of Traffic Fleets in Asian Cities for Emission Inventory and Analysis of Co-benefit from Faster Vehicle Intrusion. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Emission Inventory Conference: “Air Quality Challenges: Tackling the Changing Face of Emissions”, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–16 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowicz, R.; Hertel, O.; Sørensen, N.N.; Michelsen, J.A. Modelling air pollution from traffic in urban areas. In Flow and Dispersion Through Groups of Obstacles; Perkins, R.J., Belcher, S.E., Eds.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, S.; Berkowicz, R.; Sten Hansen, H.; Hertel, O. A Danish Decision-Support GIS Tool for Management of Urban Air Quality and Human Exposures. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2001, 6, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, H.; Beving, D.; Ziemann, P.; Sakurai, H.; Zuk, M.; McMurry, P.; Zarling, D.; Waytulonis, R.; Kittelson, D. Chemical Analysis of Diesel Engine Nanoparticles Using A Nano-DMA/Thermal Desorption Particle Beam Mass Spectrometer. Environ. Sci Technol. 2001, 35, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ketzel, M.; Ellermann, T.; Wåhlin, P.; Jensen, S.S.; Fang, D.; Massling, A. Particle number, particle mass and NOx emission factors at a highway and an urban street in Copenhagen. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geller, M.; Sardar, S.; Phuleria, H.; Fine, P.; Sioutas, C. Measurements of Particle Number and Mass Concentrations and Size Distributions in A Tunnel Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8653–8663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, D.; Ferreira, L.; Morawska, L. Development of A Particle Number and Particle Mass Vehicle Emissions Inventory for An Urban Fleet. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdahl, D.; Wang, X.; Pan, X.; Zhang, K. Characterization of On-Road Vehicle Emission Factors and Microenvironmental Air Quality in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ketzel, M.; Vardoulakis, S.; Pirjola, L.; Britter, R. Dynamics and Dispersion Modelling of Nanoparticles from Road Traffic in The Urban Atmospheric Environment—A Review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 580–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecorius, S.; Madueño, L.; Vallar, E.; Alas, H.; Betito, G.; Birmili, W.; Cambaliza, M.; Catipay, G.; Gonzaga-Cayetano, M.; Galvez, M.; et al. Aerosol Particle Mixing State, Refractory Particle Number Size Distributions And Emission Factors in a Polluted Urban Environment: Case Study Of Metro Manila, Philippines. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alas, H.; Müller, T.; Birmili, W.; Kecorius, S.; Cambaliza, M.; Simpas, J.; Cayetano, M.; Weinhold, K.; Vallar, E.; Galvez, M.; et al. Spatial Characterization Of Black Carbon Mass Concentration In The Atmosphere Of A Southeast Asian Megacity: An Air Quality Case Study For Metro Manila, Philippines. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2301–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Fisher, B.; Pericleous, K.; Gonzalez-Flesca, N. Modelling Air Quality in Street Canyons: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuch, T.; Haudek, A.; Müller, T.; Nowak, A.; Wex, H.; Wiedensohler, A. Design and Performance of An Automatic Regenerating Adsorption Aerosol Dryer for Continuous Operation at Monitoring Sites. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2009, 2, 1143–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedensohler, A.; Birmili, W.; Nowak, A.; Sonntag, A.; Weinhold, K.; Merkel, M.; Wehner, B.; Tuch, T.; Pfeifer, S.; Fiebig, M.; et al. Mobility particle size spectrometers: Harmonization of technical standards and data structure to facilitate high quality long-term observations of atmospheric particle number size distributions. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 657–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedensohler, A.; Wiesner, A.; Weinhold, K.; Birmili, W.; Hermann, M.; Merkel, M.; Müller, T.; Pfeifer, S.; Schmidt, A.; Tuch, T.; et al. Mobility Particle Size Spectrometers: Calibration Procedures and Measurement Uncertainties. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 2018, 52, 146–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, S.; Müller, T.; Weinhold, K.; Zikova, N.; Martins dos Santos, S.; Marinoni, A.; Bischof, O.; Kykal, C.; Ries, L.; Meinhardt, F.; et al. Intercomparison of 15 Aerodynamic Particle Size Spectrometers (APS 3321): Uncertainties in Particle Sizing and Number Size Distribution. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, S.; Birmili, W.; Schladitz, A.; Müller, T.; Nowak, A.; Wiedensohler, A. A Fast and Easy-To-Implement Inversion Algorithm for Mobility Particle Size Spectrometers Considering Particle Number Size Distribution Information Outside of The Detection Range. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Kittelson, D.; McMurry, P. Structural Properties of Diesel Exhaust Particles Measured by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM): Relationships to Particle Mass and Mobility. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 2004, 38, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, R.; Olfert, J. Coating Mass Dependence of Soot Aggregate Restructuring Due to Coatings of Oleic Acid and Dioctyl Sebacate. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 2013, 47, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmili, W.; Tomsche, L.; Sonntag, A.; Opelt, C.; Weinhold, K.; Nordmann, S.; Schmidt, W. Variability of Aerosol Particles in The Urban Atmosphere of Dresden (Germany): Effects of Spatial Scale and Particle Size. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Schönlinner, M. Multi-Angle Absorption Photometry—A New Method for The Measurement of Aerosol Light Absorption and Atmospheric Black Carbon. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketzel, M.; Wåhlin, P.; Berkowicz, R.; Palmgren, F. Particle and Trace Gas Emission Factors Under Urban Driving Conditions in Copenhagen Based on Street and Roof-Level Observations. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2735–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakosimos, K.; Hertel, O.; Ketzel, M.; Berkowicz, R. Operational Street Pollution Model (OSPM)—A Review of Performed Application and Validation Studies, And Future Prospects. Environ. Chem. 2010, 7, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizio, E.; Genon, G.; Borsarelli, S. PM Emissions in a Urban Context. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 3, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y. Temporal Environmental Traffic Capacity for Urban Streets. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, USA, August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, N.; Ketzel, M.; Jensen, S.; Oanh, N. Air Pollution Modeling At Road Sides Using the Operational Street Pollution Model—A Case Study in Hanoi, Vietnam. J. Air Waste Manag. Associ. 2010, 60, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowicz, R.; Ketzel, M.; Jensen, S.; Hvidberg, M.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. Evaluation and Application of OSPM For Traffic Pollution Assessment for A Large Number of Street Locations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, D.; Weingartner, E.; Ordóñez, C.; Gehrig, R.; Hill, M.; Buchmann, B.; Baltensperger, U. Real-World Emission Factors of Fine and Ultrafine Aerosol Particles for Different Traffic Situations in Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2005, 39, 8341–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühlwein, J.; Rexeis, M.; Luz, R.; Hausberger, S. Update of Emission Factors for EURO 5 and EURO 6 Passenger Cars for the HBEFA Version 3.2; Report No. I-31/2013/ Rex EM-I 2011/20/679; Graz University of Technology: Graz, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Wang, H.; Larson, T.; Kelp, M.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Marshall, J. On-Highway Vehicle Emission Factors, And Spatial Patterns, Based on Mobile Monitoring and Absolute Principal Component Score. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Ccoyllo, O.; Ynoue, R.; Martins, L.; Astolfo, R.; Miranda, R.; Freitas, E.; Borges, A.; Fornaro, A.; Freitas, H.; Moreira, A.; et al. Vehicular Particulate Matter Emissions in Road Tunnels in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 149, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecl, P.; Targino, A.; Landi, T.; Ketzel, M. Determination of Black Carbon, PM2.5, Particle Number and Nox Emission Factors from Roadside Measurements and Their Implications for Emission Inventory Development. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 186, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R.; Perez-Martinez, P.; de Fatima Andrade, M.; Ribeiro, F. Relationship Between Black Carbon (BC) and Heavy Traffic in São Paulo, Brazil. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 68, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Harrison, R. Estimation of the Emission Factors of Particle Number and Mass Fractions from Traffic at A Site Where Mean Vehicle Speeds Vary Over Short Distances. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7125–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birmili, W.; Alaviippola, B.; Hinneburg, D.; Knoth, O.; Tuch, T.; Kleefeld-Borken, J.; Schacht, A. Dispersion of Traffic-Related Exhaust Particles Near the Berlin Urban Motorway: Estimation of Fleet Emission Factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2009, 8, 15537–15594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaud Coen, M.; Weingartner, E.; Apituley, A.; Ceburnis, D.; Fierz-Schmidhauser, R.; Flentje, H.; Henzing, J.S.; Jennings, S.G.; Moerman, M.; Petzold, A.; et al. Minimizing light absorption measurement artifacts of the Aethalometer: Evaluation of five correction algorithms. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Henzing, J.S.; de Leeuw, G.; Wiedensohler, A.; Alastuey, A.; Angelov, H.; Bizjak, M.; Collaud Coen, M.; Engström, J.E.; Gruening, C.; et al. Characterization and intercomparison of aerosol absorption photometers: Result of two intercomparison workshops. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, S.; Birmili, W.; Weinhold, K.; Müller, K.; Spindler, G.; Wiedensohler, A. Measurements of the mass absorption cross section of atmospheric soot particles using Raman spectroscopy. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 12–075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurry, P.H.; Wang, X.; Park, K.; Ehara, K. The relationship between mass and mobility for atmospheric particles: A new technique for measuring particle density. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 2002, 36, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.T.; Bañaga, P.A.; Betito, G.; Braun, R.A.; Stahl, C.; Aghdam, M.A.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Dadashazar, H.; Hilario, M.R.; Lorenzo, G.R.; et al. Size-resolved composition and morphology of particulate matter during the southwest monsoon in Metro Manila, Philippines. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10675–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, S.; Cornford, D.; Bastin, L. How good are citizen weather stations? Addressing a biased opinion. Weather 2015, 70, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisler, J.; Kube, M.; Stocker, C.; Grüter, E. Quality Assessment Using Meteo-Cert: The Meteoswiss Classification Procedure for Automatic Weather Stations. Available online: https://www.wmo.int (accessed on 18 September 2019).
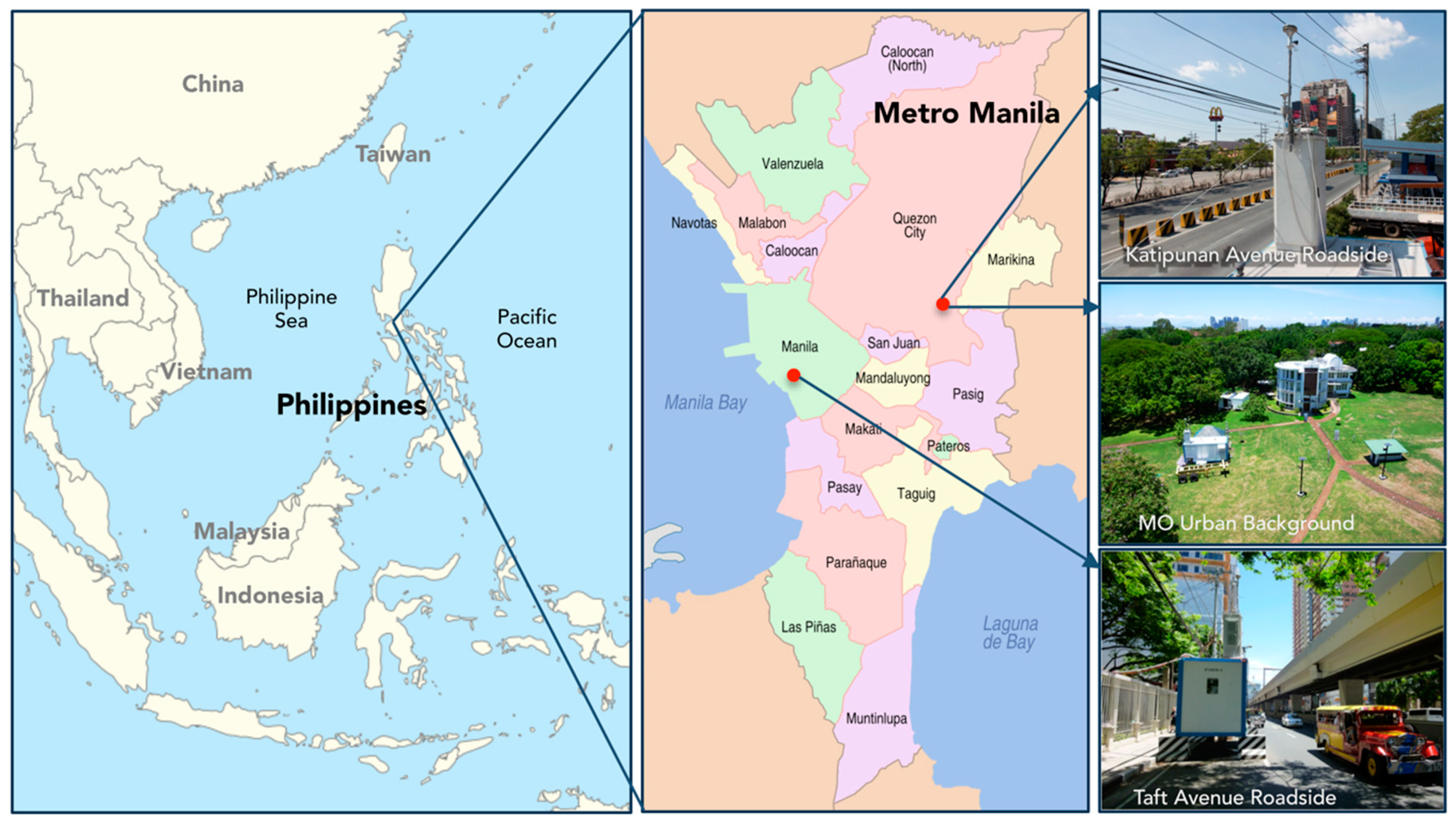

| Study | YoM | Site | Fleet | LDV | HDV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Emission Factor (mg/veh·km) | ||||||
| This study | 2015 | Urban | BC | 336 ± 4.2 | 179 ± 4.2 | 1260 ± 50 |
| Zurich, Switzerland [38] | 2002 | Urban | BC | 35 ± 3.0 | 10 ± 1.0 | 427 ± 33 |
| São Paolo, Brazil [41] | 2004 | Tunnel | BC | - | 16 ± 5 | 462 ± 112 |
| Beijing, China [18] | 2007 | Urban | BC | - | 26.6 | 1220 |
| Manila, Philippines [20] | 2015 | Urban | BC | 313 | 27 | 1620 |
| Londrina, Brazil [42] | 2016 | Urban | BC | - | 26 ± 12 | 691 ± 67 |
| São Paolo, Brazil [43] | 2015 | Highway | BC | - | 41 ± 63 | 170 ± 259 |
| Number Emission Factor (1013 particles/veh·km) | ||||||
| This study | 2015 | Urban | N10–20 | 53.5 ± 0.64 | 22.4 ± 4.3 | 137 ± 14 |
| N20–60 | 41.0 ± 0.43 | 24.2 ± 2.8 | 124 ± 9.7 | |||
| N60–300 | 17.6 ± 0.20 | 10.0 ± 1.3 | 65.9 ± 4.3 | |||
| N300–800 | 0.15 ± 0.003 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.64 ± 0.06 | |||
| N<1000 | 106 ± 1.1 | 55.6 ± 7.0 | 330 ± 24 | |||
| Copenhagen, Denmark [32] | 2001 | Urban | N10–700 | 28 | - | - |
| Zurich, Switzerland [38] | 2002 | Urban | N18–50 | 6.4 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | 73 ± 3 |
| N18–100 | 9.0 ± 0.5 | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 105 ± 3 | |||
| N18–300 | 11.2 ± 0.7 | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 132 ± 3 | |||
| N>7 | 38.6 ± 1.8 | 8.0 ± 0.9 | 550 ± 10 | |||
| London, UK [44] | 2003 | Urban | N11–437 | - | 5.8 | 63.6 |
| Berlin, Germany [45] | 2005 | Urban | N10–500 | 21 ± 2 | 2.4 ± 1.5 | 296 ± 35 |
| Leipzig, Germany [8] | 2006 | Urban | N4–800 | - | 54 ± 2 | 4300 ± 1700 |
| Copenhagen, Denmark [15] | 2008 | Urban | N10–50 | 10.1 ± 0.24 | 3.9 ± 0.48 | 155 ± 10 |
| Urban | N50–100 | 4.70 ± 0.14 | 3.4 ± 0.31 | 33.5 ± 6.4 | ||
| Urban | N100–700 | 2.02 ± 0.11 | 0.86 ± 0.24 | 29.0 ± 0.50 | ||
| Urban | N10–700 | 18.7 ± 3.0 | 10 ± 0.6 | 221 ± 13 | ||
| Highway | N10–700 | 21.5 ± 0.53 | 8.1 ± 0.69 | 175 ± 6.8 | ||
| Londrina, Brazil [42] | 2016 | Urban | N<1000 | - | 92.5 ± 11 | 373 ± 58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madueño, L.; Kecorius, S.; Birmili, W.; Müller, T.; Simpas, J.; Vallar, E.; Galvez, M.C.; Cayetano, M.; Wiedensohler, A. Aerosol Particle and Black Carbon Emission Factors of Vehicular Fleet in Manila, Philippines. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100603
Madueño L, Kecorius S, Birmili W, Müller T, Simpas J, Vallar E, Galvez MC, Cayetano M, Wiedensohler A. Aerosol Particle and Black Carbon Emission Factors of Vehicular Fleet in Manila, Philippines. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(10):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100603
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadueño, Leizel, Simonas Kecorius, Wolfram Birmili, Thomas Müller, James Simpas, Edgar Vallar, Maria Cecilia Galvez, Mylene Cayetano, and Alfred Wiedensohler. 2019. "Aerosol Particle and Black Carbon Emission Factors of Vehicular Fleet in Manila, Philippines" Atmosphere 10, no. 10: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100603
APA StyleMadueño, L., Kecorius, S., Birmili, W., Müller, T., Simpas, J., Vallar, E., Galvez, M. C., Cayetano, M., & Wiedensohler, A. (2019). Aerosol Particle and Black Carbon Emission Factors of Vehicular Fleet in Manila, Philippines. Atmosphere, 10(10), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100603






