Estimation of CO2 Emissions from Wildfires Using OCO-2 Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) Data
2.2. Smoke Plumes and Burned Area Monitor Using Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Data
2.3. Multi-Angle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) Data and MISR Interactive Explorer (MINX) Software
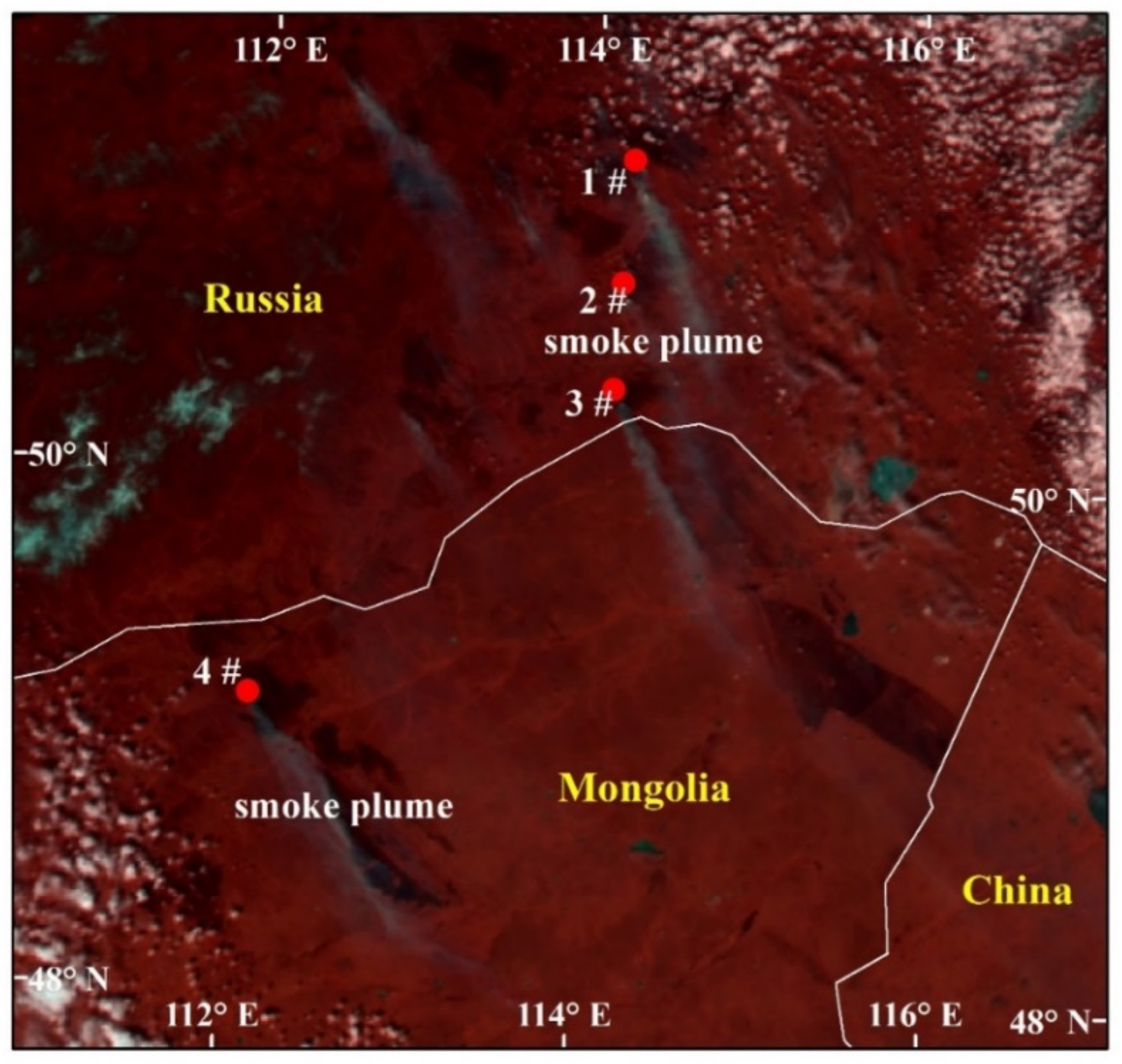
2.4. Wildfire Cases Selected in Boreal Forest
2.5. CO2 Emission Method (OCO-2 Model)
2.6. Biomass Burning Model (BBM)
3. Results
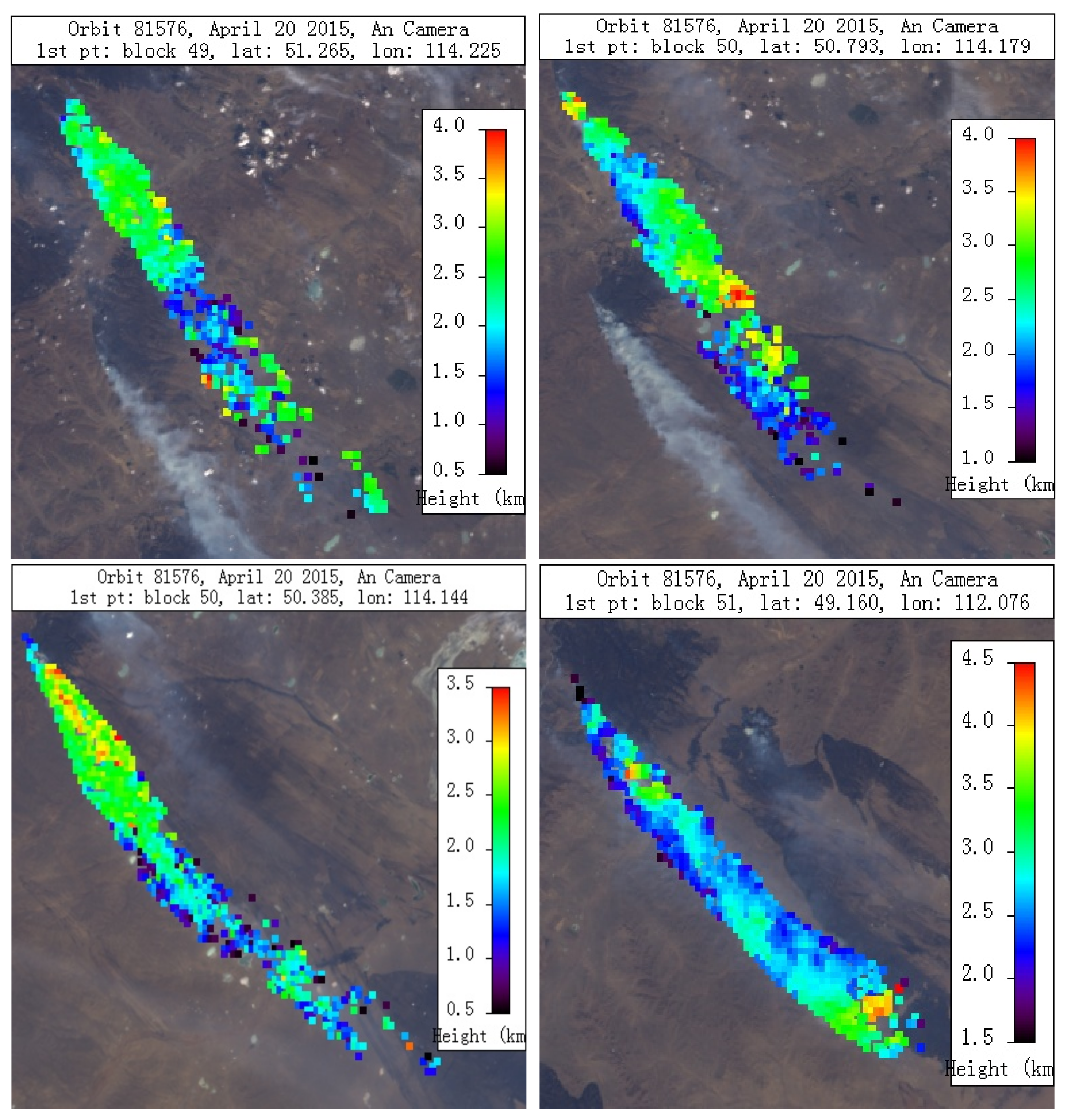
3.1. Smoke Plume Area Detection and Height Derivation
3.2. Burned Area Monitor
3.3. Model XCO2 from Smoke Plumes
3.4. CO2 Emission Calculation from OCO-2 Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Smoke Plume Height Estimation
4.2. CO2 Emissions by BBM
4.3. CO2 Emission Differences between the Two Models
4.4. Advantages and Limitations of the OCO-2 Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, C.A.; Gu, H.; MacLean, R.; Masek, J.G.; Collatz, G.J. Disturbance and the carbon balance of us forests: A quantitative review of impacts from harvests, fires, insects, and droughts. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 143, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boby, L.A.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Mack, M.C.; Verbyla, D.; Johnstone, J.F. Quantifying fire severity, carbon, and nitrogen emissions in Alaska’s boreal forest. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 1633–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Marle, M.J.E.; Kloster, S.; Magi, B.I.; Marlon, J.R.; Daniau, A.L.; Field, R.D.; Arneth, A.; Forrest, M.; Hantson, S.; Kehrwald, N.M.; et al. Historic global biomass burning emissions for CMIP6 (BB4CMIP) based on merging satellite observations with proxies and fire models (1750–2015). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 3329–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.; Muller, J.P.; Yershov, V.N. Automated stereo retrieval of smoke plume injection heights and retrieval of smoke plume masks from aatsr and their assessment with CALIPSO and MISR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner, A.; Siegert, F. Spatiotemporal fire occurrence in Borneo over a period of 10 years. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, H.D.; Mack, M.C. A canopy shift in interior Alaskan boreal forests: Consequences for above- and belowground carbon and nitrogen pools during post-fire succession. Ecosystems 2016, 19, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; He, H.; Wu, L. CO2 emissions from the 2010 russian wildfires using gosat data. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virkkula, A.; Levula, J.; Pohja, T.; Aalto, P.P.; Keronen, P.; Schobesberger, S.; Clements, C.B.; Pirjola, L.; Kieloaho, A.J.; Kulmala, L.; et al. Prescribed burning of logging slash in the boreal forest of Finland: Emissions and effects on meteorological quantities and soil properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4473–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, W.; Crutzen, P.J. Estimates of gross and net fluxes of carbon between the biosphere and the atmosphere from biomass burning. Clim. Chang. 1980, 2, 207–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.I.; Coutinho, M.; Borrego, C. Forest fire emissions in Portugal: A contribution to global warming? Environ. Pollut. 1994, 83, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedinmyer, C.; Neff, J.C. Estimates of CO2 from fires in the United States: Implications for carbon management. Carbon Balance Manag. 2007, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, P.; Camia, A.; Kucera, J.; Libertà, G.; Palumbo, I.; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Schmuck, G. Chapter 8 Assessment of Forest Fire Impacts and Emissions in the European Union Based on the European Forest Fire Information System; Elsevier Science & Technology: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 197–208. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Collatz, G.J.; Mu, M.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Morton, D.C.; Defries, R.S.; Jin, Y.; Leeuwen, T.T.V. Global fire emissions and the contribution of deforestation, savanna, forest, agricultural, and peat fires (1997–2009). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 16153–16230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, I.M.D.; Pereira, J.M.C.; Tarantola, S. Atmospheric emissions from vegetation fires in Portugal (1990–2008): Estimates, uncertainty analysis, and sensitivity analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2625–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y. A high-resolution and multi-year emissions inventory for biomass burning in Southeast Asia during 2001–2010. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, C. A comprehensive biomass burning emission inventory with high spatial and temporal resolution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2839–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.; Freitas, S.R.; Moraes, E.C.; Ferreira, N.J.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Rao, V.B.; Longo, K.M. Estimating trace gas and aerosol emissions over South America: Relationship between fire radiative energy released and aerosol optical depth observations. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6388–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Yao, H.; Kang, Y.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Hu, M. Estimating emissions from agricultural fires in the North China Plain based on MODIS fire radiative power. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Freeborn, P.H.; Archibald, S.; Oppenheimer, C.; Roberts, G.J.; Smith, T.E.L.; Govender, N.; Burton, M.; Palumbo, I. Field determination of biomass burning emission ratios and factors via open-path ftir spectroscopy and fire radiative power assessment: Headfire, backfire and residual smouldering combustion in African savannahs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11591–11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.W.; Heil, A.; Andreae, M.O.; Benedetti, A.; Chubarova, N.; Jones, L.; Morcrette, J.J.; Razinger, M.; Schultz, M.G.; Suttie, M. Biomass burning emissions estimated with a global fire assimilation system based on observed fire radiative power. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, I.B.; Berezin, E.V.; Ciais, P.; Broquet, G.; Beekmann, M.; Hadjilazaro, J.; Clerbaux, C.; Andreae, M.O.; Kaiser, J.W.; Schulze, E.D. Constraining CO2 emissions from open biomass burning by satellite observations of co-emitted species: A method and its application to wildfires in Siberia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10383–10410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, I.B.; Beekmann, M.; Berezin, E.V.; Formenti, P.; Andreae, M.O. Probing into the aging dynamics of biomass burning aerosol by using satellite measurements of aerosol optical depth and carbon monoxide. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 17, 4513–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Randerson, J.T.; Van der Werf, G.R.; Giglio, L.; Kasibhatla, P.; Morton, D.; Collatz, G.J.; Defries, R.S.; Hyer, E.J.; Prins, E.M. Daily and 3-hourly variability in global fire emissions and consequences for atmospheric model predictions of carbon monoxide. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 24303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedinmyer, C.; Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Emmons, L.K. The Fire INventory from NCAR (FINN)—A high resolution global model to estimate the emissions from open burning. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2011, 3, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J.W.; Flemming, J.; Schultz, M.G.; Suttie, M.; Wooster, M.J. The MACC Global Fire Assimilation System: First emission products (GFASv0). ECMWF Tech. Memo. 2009, 596, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Arnett, J.T.; Coops, N.C.; Daniels, L.D.; Falls, R.W. Detecting forest damage after a low-severity fire using remote sensing at multiple scales. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 35, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, J.; Reuter, M.; Buchwitz, M.; Schneising, O.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P.; Massart, S.; Kaiser, J.W.; Crisp, D. CO2 emission of indonesian fires in 2015 estimated from satellite-derived atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, P.K.; Crisp, D.; Kaiser, J.W.; Wunch, D.; Saeki, T.; Ichii, K.; Sekiya, T.; Wennberg, P.O.; Feist, D.G.; Pollard, D.F. The orbiting carbon observatory (OCO-2) tracks 2–3 peta-gram increase in carbon release to the atmosphere during the 2014–2016 EI Nino. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, B.; Bösch, H.; McDuffie, J.; Taylor, T.; Fu, D.; Frankenberg, C.; O’Dell, C.; Payne, V.H.; Gunson, M.; Pollock, R.; et al. Quantification of uncertainties in OCO-2 measurements of XCO2: Simulations and linear error analysis. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5227–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunch, D.; Wennberg, P.O.; Osterman, G.; Fisher, B.; Naylor, B.; Roehl, C.M.; O’Dell, C.; Mandrake, L.; Viatte, C.; Kiel, M. Comparisons of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) XCO2 measurements with TCCON. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.; Pollock, H.; Rosenberg, R.; Chapsky, L.; Lee, R.; Oyafuso, F.; Frankenberg, C.; Dell, C.; Bruegge, C.; Doran, G.; et al. The on-orbit performance of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) instrument and its radiometrically calibrated products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, R.; Haring, R.E.; Holden, J.R.; Johnson, D.L.; Kapitanoff, A.; Mohlman, D.; Phillips, C.; Randall, D.; Rechsteiner, D.; Rivera, J.; et al. The orbiting carbon observatory instrument: Performance of the oco instrument and plans for the OCO-2 instrument. In Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, Toulouse, France, 13 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, P.; Rastogi, S.; Singh, R.P.; Panigrahy, S. Spectral modelling near the 1.6 μm window for satellite based estimation of CO2. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.A.M.; O’Dell, C.W.; Wunch, D.; Roehl, C.M.; Osterman, G.B.; Blavier, J.F.; Rosenberg, R.; Chapsky, L.; Frankenberg, C.; Hunyadi-Lay, S.L.; et al. Preflight spectral calibration of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.O.; O’Dell, C.W.; Pollock, R.; Bruegge, C.J.; Rider, D.; Crisp, D.; Miller, C.E. Preflight spectral calibration of the orbiting carbon observatory. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Next Generation Mobile Applications, Amman, Jordan, 27–29 July 2010; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberg, C.; Pollock, R.; Lee, R.A.M.; Rosenberg, R.; Blavier, J.F.; Crisp, D.; O’Dell, C.W.; Osterman, G.B.; Roehl, C.; Wennberg, P.O.; et al. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO-2): Spectrometer performance evaluation using pre-launch direct sun measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Ding, G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, R. A comparison and validation of atmosphere CO2 concentration OCO-2-based observations and tccon-based observations. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Singapore, 2016; Volume 645, pp. 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Eldering, A.; O’Dell, C.W.; Wennberg, P.O.; Crisp, D.; Gunson, M.R.; Viatte, C.; Avis, C.; Braverman, A.; Castano, R.; Chang, A.; et al. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2: First 18 months of science data products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrake, L.; Frankenberg, C.; O’Dell, C.W.; Osterman, G.; Wennberg, P.; Wunch, D. Semi-autonomous sounding selection for OCO-2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2851–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A. Gosat Measurements of Wildfire Emissions; University of London: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.N.; Wooster, M.J.; Boesch, H.; Parker, R. First satellite measurements of carbon dioxide and methane emission ratios in wildfire plumes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4098–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, T.R.K.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Murthy, M.S.R.; Rajshekhar, G.; Elvidge, C.D.; Tuttle, B.T. Active forest fire monitoring in Uttaranchal State, India using multi-temporal DMSP-OLS and MODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Li, J.; Sheng, C.; Xu, J.; Li, W. A review of wetland remote sensing. Sensors 2017, 17, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Descloitres, J.; Alleaume, S. The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 244–262. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.; Rogan, J.; Schneider, L.; Cochrane, M. Evaluating MODIS active fire products in subtropical yucatán forest. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 4, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Pereira, J.M.C.; Masiero, A.; Pirotti, F. Mapping fire regimes in China using MODIS active fire and burned area data. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 85, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, G.; Negro, C.D.; Fortuna, L.; Vicari, A. A tool for multi-platform remote sensing processing. Commun. Simai Congr. 2009, 3, 281. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Ng, D.; Dozier, J. Spectral emissivity measurements of land-surface materials and related radiative transfer simulations. Adv. Space Res. 1994, 14, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, D.; Logan, J.A.; Diner, D.; Kahn, R.; Tong, L.; Li, Q. A data-mining approach to associating MISR smoke plume heights with MODIS fire measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Moroney, C.M.; Gaitley, B.J.; Nelson, D.L.; Garay, M.J.; Mims, S.R. MISR stereo heights of grassland fire smoke plumes in Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, L.; Val Martin, M.; Kahn, R. Biomass burning smoke heights over the Amazon observed from space. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1685–16702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.L.; Garay, M.J.; Kahn, R.A.; Dunst, B.A. Stereoscopic height and wind retrievals for aerosol plumes with the MISR INteractive eXplorer (MINX). Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4593–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiev, M.; Ermakova, T.; Vankevich, R. Evaluation of the smoke-injection height from wild-land fires using remote-sensing data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 11, 27937–27966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Li, W.H.; Moroney, C.; Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Fishbein, E. Aerosol source plume physical characteristics from space-based multiangle imaging. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, Y.; Suzuki, S. Estimates of carbon emissions from forest fires in Japan, 1979–2008. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2013, 22, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Song, Y. Estimates of biomass burning emissions in tropical Asia based on satellite-derived data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2335–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. High-resolution mapping of biomass burning emissions in three tropical regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10806–10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Sasai, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. Spatio-temporal evaluation of carbon emissions from biomass burning in Southeast Asia during the period 2001–2010. Ecol. Model. 2014, 272, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Alvarado, M.J.; Reid, J.S.; Karl, T.; Crounse, J.D.; Wennberg, P.O. Emission factors for open and domestic biomass burning for use in atmospheric models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4039–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.; Ellicott, E.; Giglio, L.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Lau, W. Vegetation fires in the himalayan region—aerosol load, black carbon emissions and smoke plume heights. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cordero, L.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Smoke plume optical properties and transport observed by a multi-wavelength lidar, sunphotometer and satellite. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatchi, S.S.; Harris, N.L.; Brown, S.; Lefsky, M.; Mitchard, E.T.; Salas, W.; Zutta, B.R.; Buermann, W.; Lewis, S.L.; Hagen, S. Benchmark map of forest carbon stocks in tropical regions across three continents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, J.B.; Steele, M.D.; Cummings, D.L.; Jaramillo, V.J. Biomass dynamics associated with deforestation, fire, and conversion to cattle pasture in a Mexican tropical dry forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 176, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dell, C.W.; Connor, B.; Bösch, H.; O’Brien, D. The ACOS CO2 retrieval algorithm—Part 1: Description and validation against synthetic observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Yurganov, L.N.; Rakitin, V.; Dzhola, A.; August, T.; Fokeeva, E.; George, M.; Gorchakov, G.; Grechko, E.; Hannon, S.; Karpov, A. Satellite- and ground-based CO total column observations over 2010 Russian fires: Accuracy of top-down estimates based on thermal IR satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 7925–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Fire Point No. | Smoke Plume Area (103 km2) | Smoke Plume Height (km) | Base XCO2 (ppm) | T (K) | Ba (hPa) | CO2 Emission (103 Mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 2.48 | 2.29 | 399.786 | 281.59 | 906.97 | 156.25 (±4.85) |
| 2# | 2.41 | 2.38 | 122.21 (±4.87) | |||
| 3# | 2.50 | 1.99 | 122.84 (±4.21) | |||
| 4# | 6.48 | 2.61 | 288.70 (±14.33) |
| Fire Point No. | Burned Area (ha) | B × β (Mg/ha) | EF (kg/kg) | CO2 Emission (103 Mg) | Compared with OCO-2 Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 7100 | 38 | 1.489 (0.121) | 401.73 (±32.65) | +157.11% |
| 2# | 2700 | 153.69 (±12.41) | +25.76% | ||
| 3# | 4800 | 271.59 (±22.07) | +121.10% | ||
| 4# | 7500 | 424.37 (±34.49) | +46.99% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Li, J.; Wen, L.; Huang, S. Estimation of CO2 Emissions from Wildfires Using OCO-2 Data. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100581
Guo M, Li J, Wen L, Huang S. Estimation of CO2 Emissions from Wildfires Using OCO-2 Data. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(10):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100581
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Meng, Jing Li, Lixiang Wen, and Shubo Huang. 2019. "Estimation of CO2 Emissions from Wildfires Using OCO-2 Data" Atmosphere 10, no. 10: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100581
APA StyleGuo, M., Li, J., Wen, L., & Huang, S. (2019). Estimation of CO2 Emissions from Wildfires Using OCO-2 Data. Atmosphere, 10(10), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10100581






