RIAM-VASP Module Relays Integrin Complement Receptors in Outside-In Signaling Driving Particle Engulfment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Phagocytosis Assays
2.3. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Gene Silencing
2.6. Gene Knockout
2.7. VASP Overexpression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
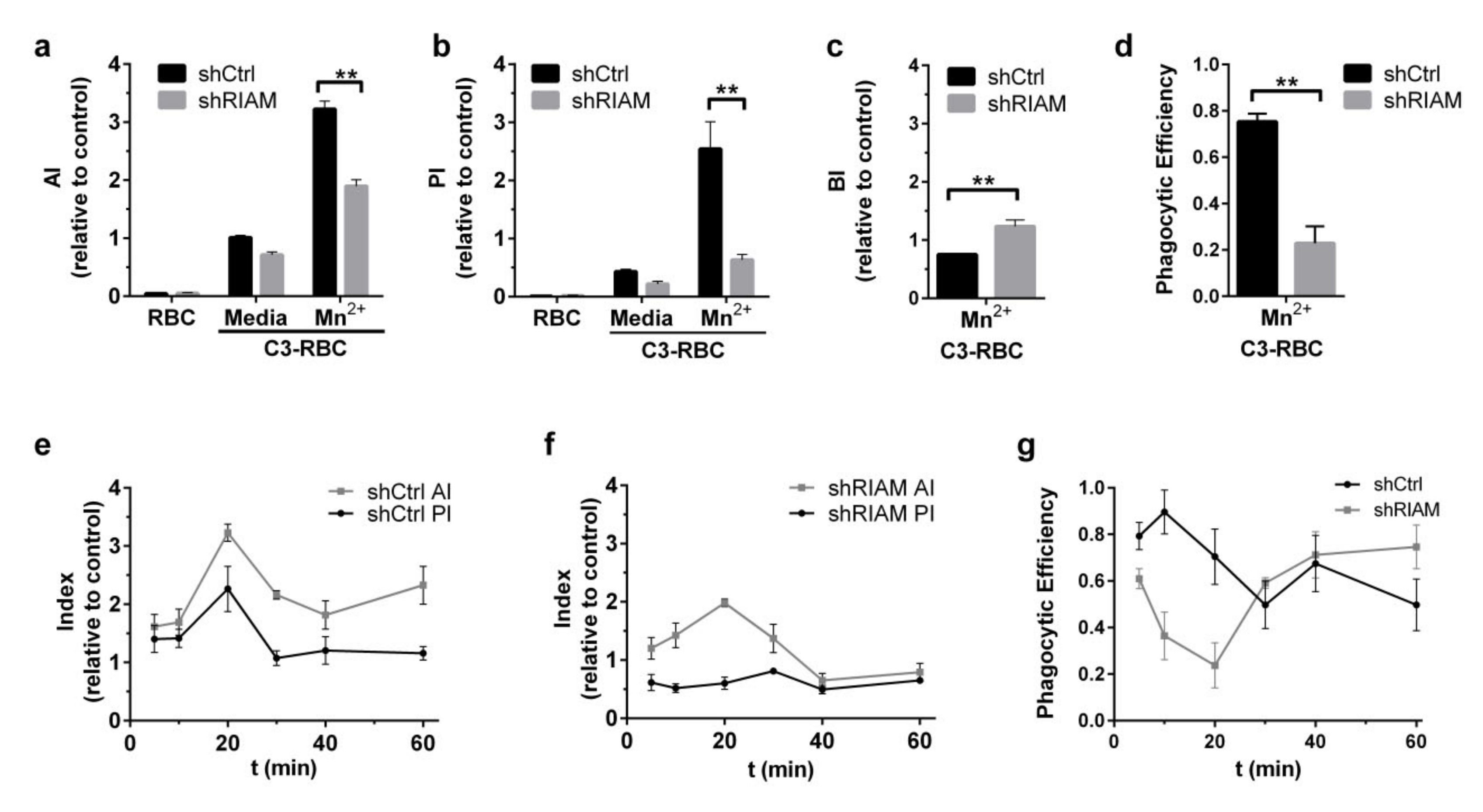
3.1. Efficient Particle Internalization during Complement-Mediated Phagocytosis Required RIAM
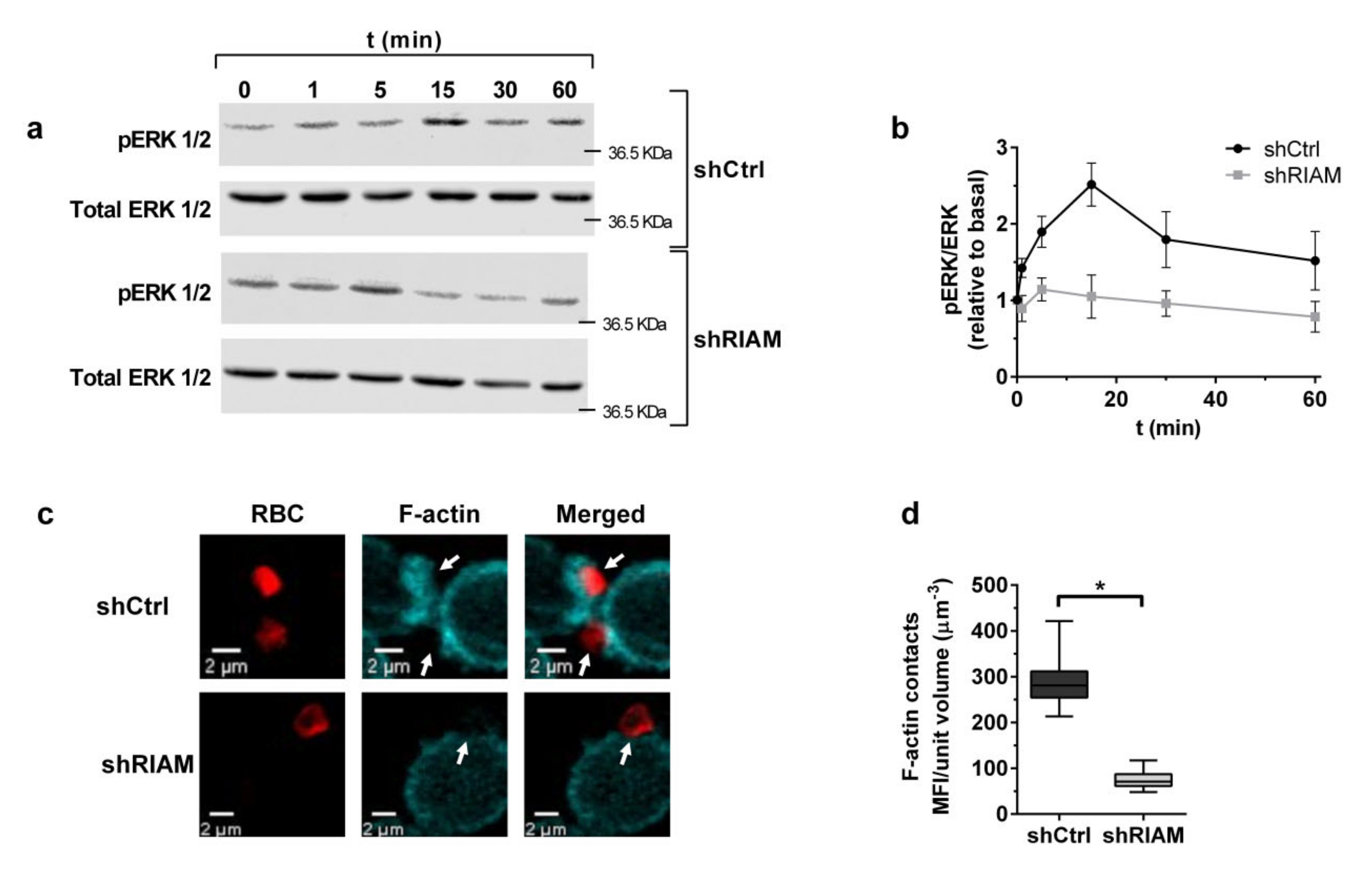
3.2. RIAM Knockdown Diminishes Downstream Signaling and F-Actin Enrichment at the Phagocytic Cup
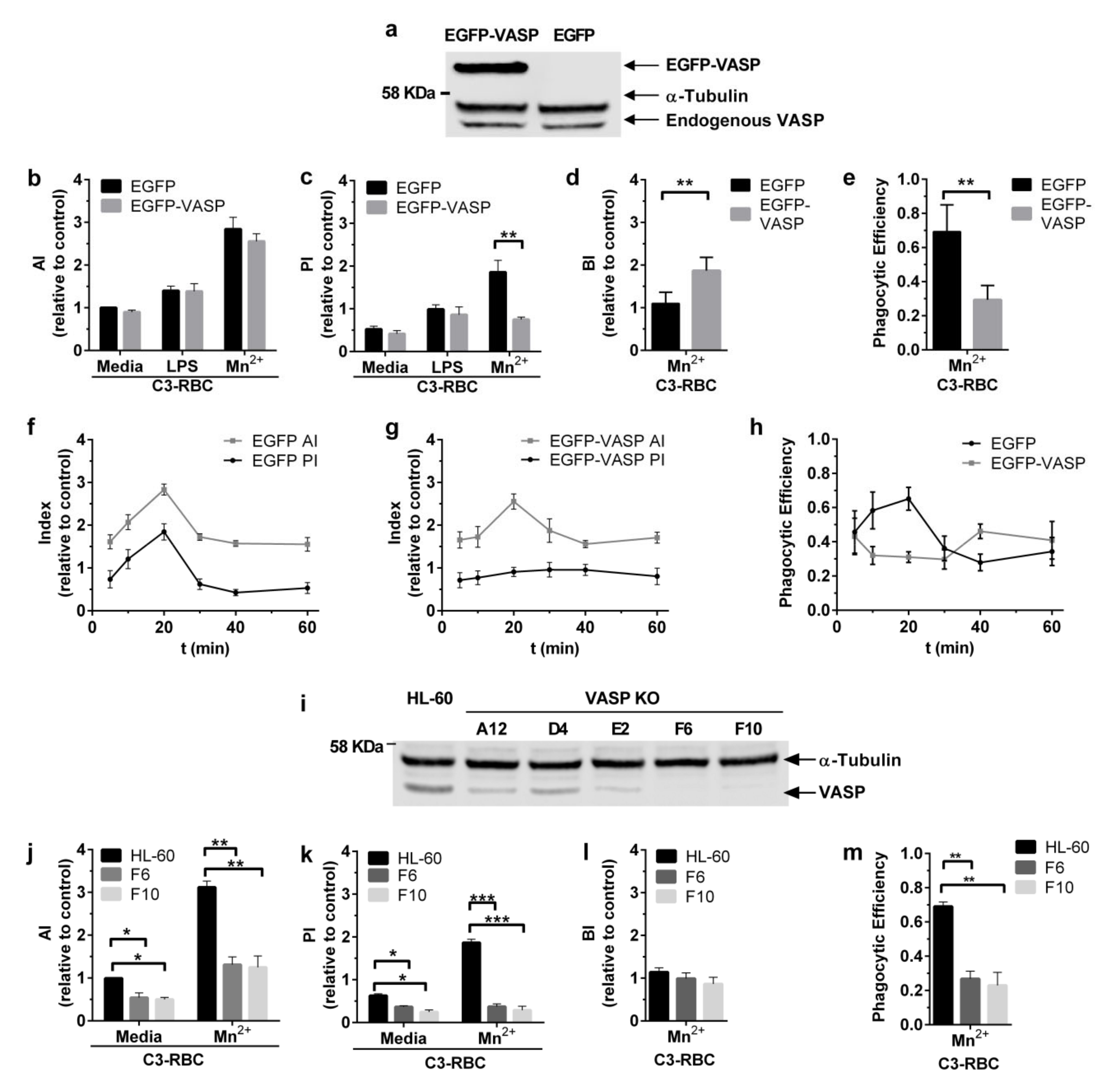
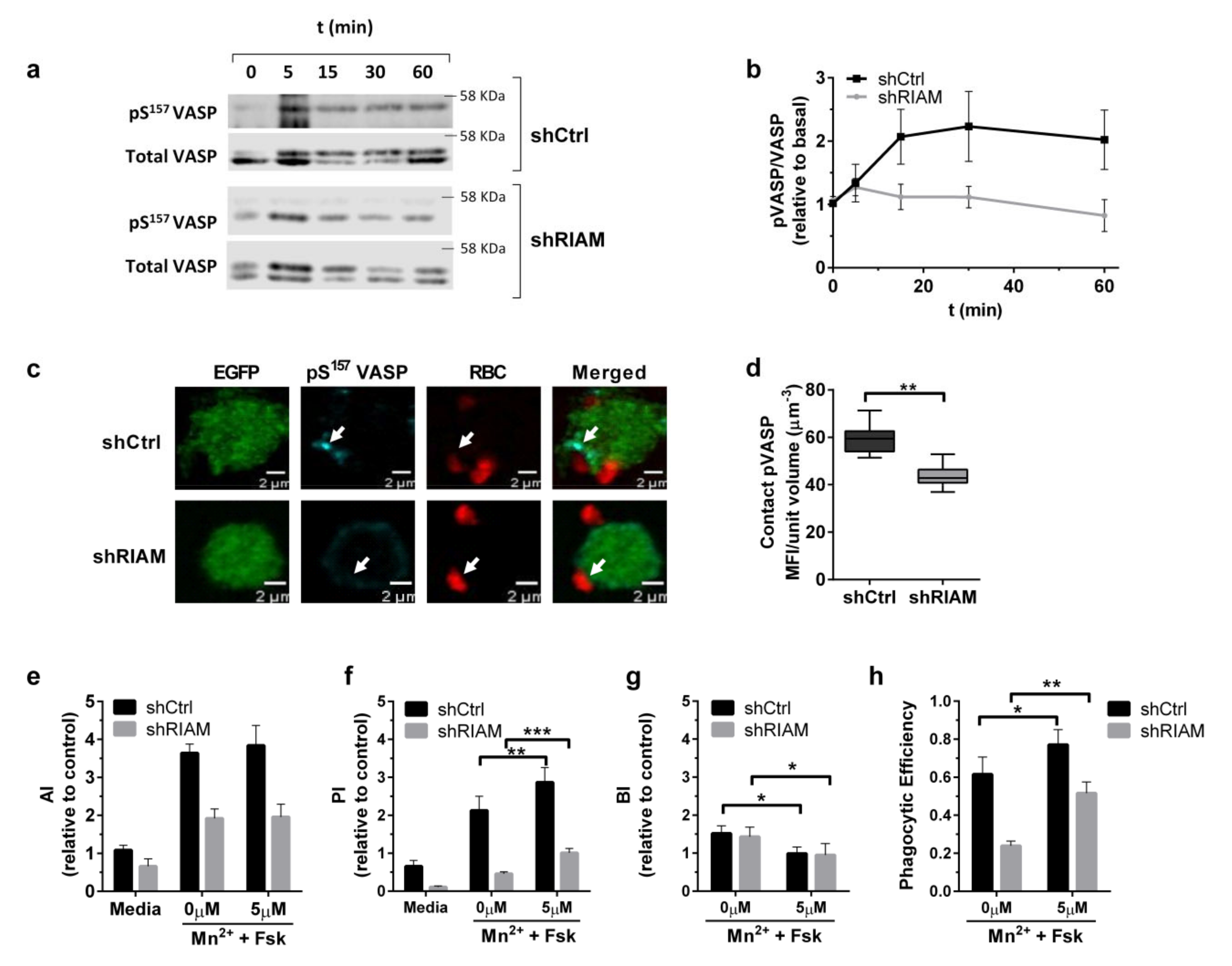
3.3. Efficient Particle Internalization during Complement-Dependent Phagocytosis Required VASP Expression
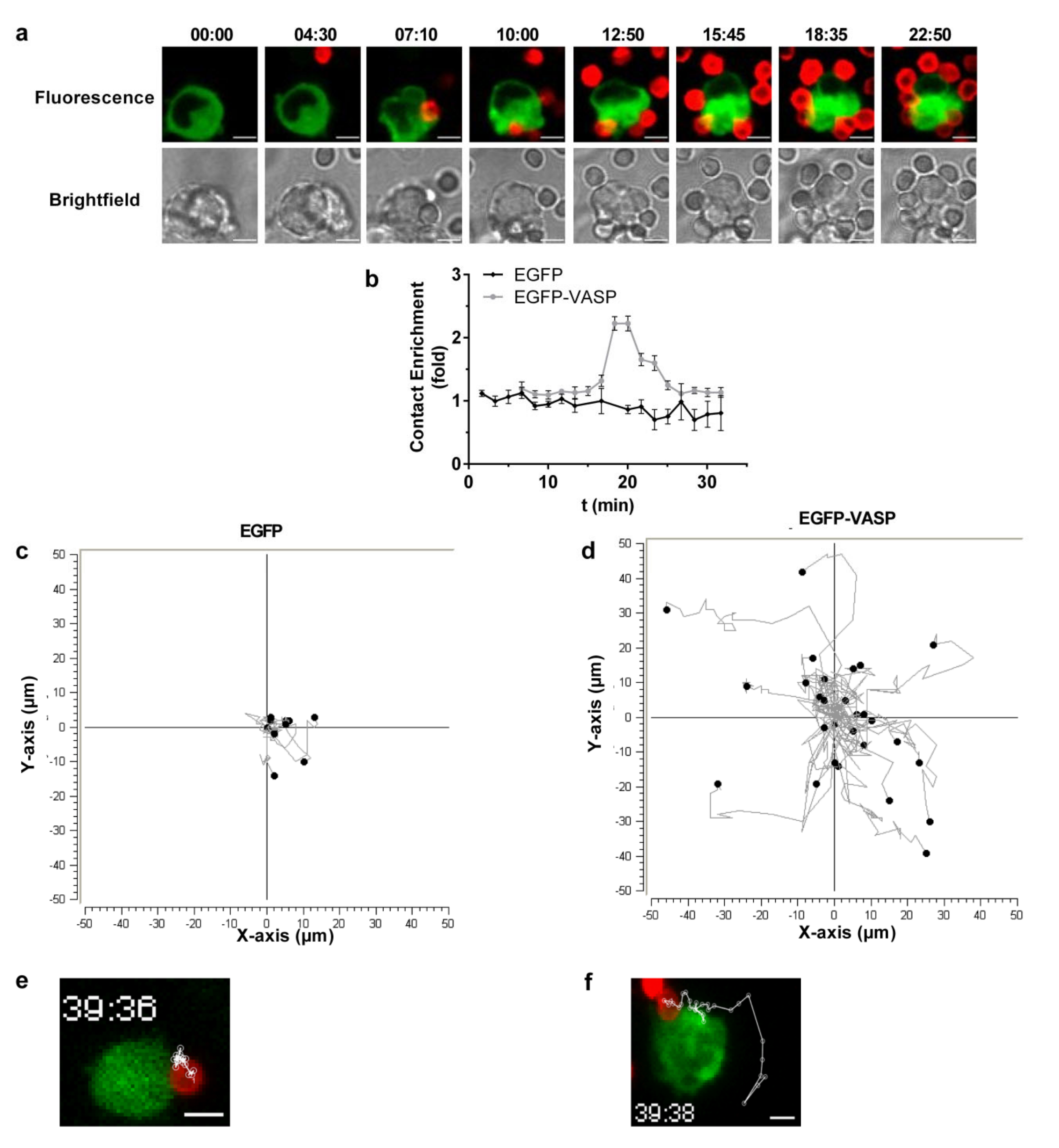
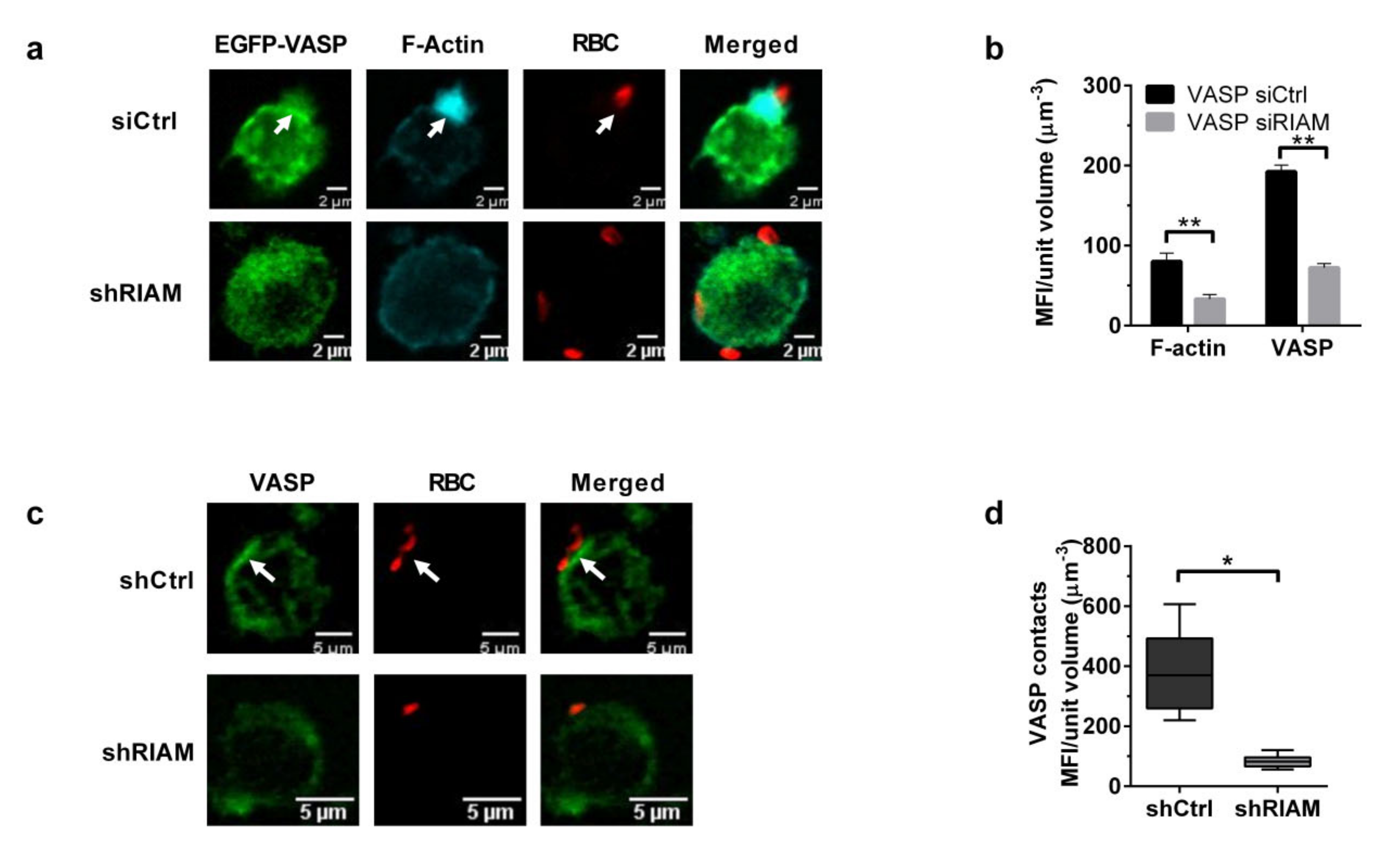
3.4. VASP Localized to Phagocytic Cups in a RIAM-Dependent Manner
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hogg, N.; Patzak, I.; Willenbrock, F. The insider’s guide to leukocyte integrin signalling and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herter, J.; Zarbock, A. Integrin regulation during leukocyte recruitment. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4451–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossaint, J.; Herter, J.M.; Van Aken, H.; Napirei, M.; Döring, Y.; Weber, C.; Soehnlein, O.; Zarbock, A. Synchronized integrin engagement and chemokine activation is crucial in neutrophil extracellular trap mediated sterile inflammation. Blood 2014, 123, 2573–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, D.F.; Faure, M.; Long, E.O. LFA-1 contributes an early signal for NK cell cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3653–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, E.; Dart, A.; Covarelli, V.; Caron, E. Molecular mechanisms of phagocytic uptake in mammalian cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1957–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, C.L.; Lowell, C.A. The ins and outs of leukocyte integrin signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, E.; Self, A.J.; Hall, A. The GTPase Rap1 controls functional activation of macrophage integrin alphaMbeta2 by LPS and other inflammatory mediators. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.A.; Grinstein, S. Phagocytosis: Receptors, signal integration, and the cytoskeleton. Immunol Rev. 2014, 262, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, E.; Martin, R.; Kwok, V.; Cherepanov, V.; Chow, C.-W.; Doerschuk, C.M.; Plumb, J.; Grinstein, S.; Downey, G.P. CD44-mediated phagocytosis induces inside-out activation of complement receptor-3 in murine macrophages. Blood 2007, 110, 4492–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderwood, D.A.; Campbell, I.D.; Critchley, D.R. Talins and kindlins: Partners in integrin-mediated adhesion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuy, A.G.; Caron, E. Integrin-dependent phagocytosis–spreading from microadhesion to new concepts. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Dupuy, A.G.; Critchley, D.R.; Caron, E. Rap1 controls activation of the αMβ2 integrin in a talin-dependent manner. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderwood, D.A. Integrin activation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, C.T.; Hyun, Y.-M.; Schultz, J.B.; Law, F.-Y.; Waugh, R.E.; Knauf, P.A.; Kim, M. Outside-in signal transmission by conformational changes in integrin Mac-1. J. Immunol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Wiedemann, A.; Tzircotis, G.; Monkley, S.J.; Critchley, D.R.; Caron, E. An essential role for talin during alpha(M)beta(2)-mediated phagocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafuente, E.M.; van Puijenbroek, A.A.; Krause, M.; Carman, C.V.; Freeman, G.J.; Berezovskaya, A.; Constantine, E.; Springer, T.A.; Gertler, F.B.; Boussiotis, V.A. RIAM, an Ena/VASP and Profilin ligand, interacts with Rap1-GTP and mediates Rap1-induced adhesion. Dev. Cell. 2004, 7, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, J.P.; Wu, J.; Su, W.; Mor, A.; Patsoukis, N.; Boussiotis, V.A.; Hubbard, S.R.; Philips, M.R. Rap1-interacting adapter molecule (RIAM) associates with the plasma membrane via a proximity detector. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsoukis, N.; Bardhan, K.; Weaver, J.D.; Sari, D.; Torres-Gomez, A.; Li, L.; Strauss, L.; Lafuente, E.M.; Boussiotis, V.A. The adaptor molecule RIAM integrates signaling events critical for integrin-mediated control of immune function and cancer progression. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaam8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lim, C.J.; Watanabe, N.; Soriani, A.; Ratnikov, B.; Calderwood, D.A.; Puzon-McLaughlin, W.; Lafuente, E.M.; Boussiotis, V.A.; Shattil, S.J.; et al. Reconstructing and deconstructing agonist-induced activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Lim, C.J.; Puzon-McLaughlin, W.; Shattil, S.J.; Ginsberg, M.H. RIAM activates integrins by linking talin to ras GTPase membrane-targeting sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5119–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Hirbawi, J.; Fukuda, K.; Dwivedi, P.; Liu, J.; Byzova, T.; Plow, E.F.; Wu, J. Conformational activation of talin by RIAM triggers integrin-mediated cell adhesion. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménasché, G.; Kliche, S.; Chen, E.J.; Stradal, T.E.; Schraven, B.; Koretzky, G. RIAM links the ADAP/SKAP-55 signaling module to Rap1, facilitating T-cell-receptor-mediated integrin activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4070–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsoukis, N.; Lafuente, E.M.; Meraner, P.; Sub Kim, J.; Dombkowski, D.; Li, L.; Boussiotis, V.A. RIAM regulates the cytoskeletal distribution and activation of PLC-γ1 in T cells. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medraño-Fernandez, I.; Reyes, R.; Olazabal, I.; Rodriguez, E.; Sanchez-Madrid, F.; Boussiotis, V.A.; Reche, P.A.; Cabañas, C.; Lafuente, E.M. RIAM (Rap1-interacting adaptor molecule) regulates complement-dependent phagocytosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2395–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapproth, S.; Sperandio, M.; Pinheiro, E.M.; Prünster, M.; Soehnlein, O.; Gertler, F.B.; Fässler, R.; Moser, M. Loss of the Rap-1 effector RIAM results in leukocyte adhesion deficiency due to impaired β2 integrin function in mice. Blood 2015, 126, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougerie, P.; Miskolci, V.; Cox, D. Generation of membrane structures during phagocytosis and chemotaxis of macrophages: Role and regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 256, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.D.; Mullins, R.D. VASP is a processive actin polymerase that requires monomeric actin for barbed end association. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döppler, H.R.; Bastea, L.I.; Lewis-Tuffin, L.J.; Anastasiadis, P.Z.; Storz, P. Protein Kinase D1 mediated phosphorylations regulate vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) localization and cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, M113, 474676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, B.; Hüttelmaier, S.; Schlüter, K.; Jockusch, B.M.; Illenberger, S. Phosphorylation of the vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein regulates its interaction with actin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30817–30825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, P.M.; Blume, C.; Seifert, S.; Wilhelm, S.; Waschke, J.; Schuh, K.; Gertler, F.; Münzel, T.; Renné, T. Differential VASP phosphorylation controls remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3954–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, C. Role of VASP phosphorylation for the regulation of microglia chemotaxis via the regulation of focal adhesion formation/maturation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2009, 42, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Gunst, S.J. Vasodilator Stimulated Phosphoprotein (VASP) Regulates Actin Polymerization and Contraction in Airway Smooth Muscle by a Vinculin-dependent Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, M115, 645788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Smith, X.; Wu, Z.; Strebhardt, K.; Ladbury, J.E.; Rudd, C.E. T Cell Receptor “Inside-Out” Pathway via Signaling Module SKAP1-RapL Regulates T Cell Motility and Interactions in Lymph Nodes. Immunity 2010, 32, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnemann, S.C.; Silverstein, R.L. Differential roles of CD36 and alphavbeta5 integrin in photoreceptor phagocytosis by the retinal pigment epithelium. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.D.; Scott, D.A.; Weinstein, J.A.; Ran, F.A.; Konermann, S.; Agarwala, V.; Li, Y.; Fine, E.J.; Wu, X.; Shalem, O. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppolino, M.G.; Krause, M.; Hagendorff, P.; Monner, D.A.; Trimble, W.; Grinstein, S.; Wehland, J.; Sechi, A.S. Evidence for a molecular complex consisting of Fyb/SLAP, SLP-76, Nck, VASP and WASP that links the actin cytoskeleton to Fcγ receptor signalling during phagocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4307–4318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lagarrigue, F.; Anekal, P.V.; Lee, H.-S.; Bachir, A.I.; Ablack, J.N.; Horwitz, A.F.; Ginsberg, M.H. A RIAM/lamellipodin-talin-integrin complex forms the tip of sticky fingers that guide cell migration. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coló, G.P.; Hernández-Varas, P.; Lock, J.; Bartolomé, R.A.; Arellano-Sánchez, N.; Strömblad, S.; Teixidó, J. Focal adhesion disassembly is regulated by a RIAM to MEK-1 pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5338–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, A.; Bruck, J.; Sternberg, P.W. Scaffold proteins may biphasically affect the levels of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and reduce its threshold properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5818–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.A.; Asthagiri, A.R. Quantitative effect of scaffold abundance on signal propagation. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2009, 5, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzel, F.; Maddison, L.; Blüthgen, N. How scaffolds shape MAPK signaling: What we know and opportunities for systems approaches. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortum, R.L.; Lewis, R.E. The Molecular Scaffold KSR1 Regulates the Proliferative and Oncogenic Potential of Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 4407–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Wynne, J.; Pinheiro, E.M.; Strazza, M.; Mor, A.; Montenont, E.; Berger, J.; Paul, D.S.; Bergmeier, W.; Gertler, F.B.; et al. Rap1 and its effector riam are required for lymphocyte trafficking. Blood 2015, 126, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.J.; Brindle, N.P.J. Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is involved in stress-fiber and membrane ruffle formation in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, J.E.; Loureiro, J.J.; Libova, I.; Fässler, R.; Wehland, J.; Gertler, F.B. Negative Regulation of Fibroblast Motility by Ena/VASP Proteins. Cell 2000, 101, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.E.; Svitkina, T.M.; Krause, M.; Schafer, D.A.; Loureiro, J.J.; Strasser, G.A.; Maly, I.V.; Chaga, O.Y.; Cooper, J.A.; Borisy, G.G.; et al. Antagonism between Ena/VASP Proteins and Actin Filament Capping Regulates Fibroblast Motility. Cell 2002, 109, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galler, A.B.; Arguinzonis, M.I.G.; Baumgartner, W.; Kuhn, M.; Smolenski, A.; Simm, A.; Reinhard, M. VASP-dependent regulation of actin cytoskeleton rigidity, cell adhesion, and detachment. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 125, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotty, J.D.; Bear, J.E. Competition and collaboration between different actin assembly pathways allows for homeostatic control of the actin cytoskeleton. Bioarchitecture 2015, 5, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci-Guyon, E.; Niedergang, F.; Wallar, B.J.; Peng, J.; Alberts, A.S.; Chavrier, P. A role for mammalian diaphanous-related formins in complement receptor (CR3)-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewkowicz, E.; Herit, F.; Le Clainche, C.; Bourdoncle, P.; Perez, F.; Niedergang, F. The microtubule-binding protein CLIP-170 coordinates mDia1 and actin reorganization during CR3-mediated phagocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilancia, C.G.; Winkelman, J.D.; Tsygankov, D.; Nowotarski, S.H.; Sees, J.A.; Comber, K.; Evans, I.; Lakhani, V.; Wood, W.; Elston, T.C. Enabled negatively regulates diaphanous-driven actin dynamics in vitro and in vivo. Dev. Cell 2014, 28, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaumouillé, V.; Cartagena-Rivera, A.X.; Waterman, C.M. Coupling of β2 integrins to actin by a mechanosensitive molecular clutch drives complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Elliott, H.L.; Oak, Y.; Zee, C.T.; Groisman, A.; Tytell, J.D.; Danuser, G. Functional hierarchy of redundant actin assembly factors revealed by fine-grained registration of intrinsic image fluctuations. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döppler, H.; Storz, P. Regulation of VASP by phosphorylation. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worth, D.C.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.; Robinson, S.D.; King, S.J.; Morton, P.E.; Gertler, F.B.; Humphries, M.J.; Parsons, M. αvβ3 integrin spatially regulates VASP and RIAM to control adhesion dynamics and migration. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 189, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.; Leslie, J.D.; Stewart, M.; Lafuente, E.M.; Valderrama, F.; Jagannathan, R.; Strasser, G.A.; Rubinson, D.A.; Liu, H.; Way, M.; et al. Lamellipodin, an Ena/VASP ligand, is implicated in the regulation of lamellipodial dynamics. Dev. Cell. 2004, 7, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.D.; Mullins, R.D. Lamellipodin promotes actin assembly by clustering Ena/VASP proteins and tethering them to actin filaments. Elife 2015, 4, e06585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Gomez, A.; Sanchez-Trincado, J.L.; Toribio, V.; Torres-Ruiz, R.; Rodríguez-Perales, S.; Yáñez-Mó, M.; Reche, P.A.; Cabañas, C.; Lafuente, E.M. RIAM-VASP Module Relays Integrin Complement Receptors in Outside-In Signaling Driving Particle Engulfment. Cells 2020, 9, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051166
Torres-Gomez A, Sanchez-Trincado JL, Toribio V, Torres-Ruiz R, Rodríguez-Perales S, Yáñez-Mó M, Reche PA, Cabañas C, Lafuente EM. RIAM-VASP Module Relays Integrin Complement Receptors in Outside-In Signaling Driving Particle Engulfment. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051166
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Gomez, Alvaro, Jose Luis Sanchez-Trincado, Víctor Toribio, Raul Torres-Ruiz, Sandra Rodríguez-Perales, María Yáñez-Mó, Pedro A. Reche, Carlos Cabañas, and Esther M. Lafuente. 2020. "RIAM-VASP Module Relays Integrin Complement Receptors in Outside-In Signaling Driving Particle Engulfment" Cells 9, no. 5: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051166
APA StyleTorres-Gomez, A., Sanchez-Trincado, J. L., Toribio, V., Torres-Ruiz, R., Rodríguez-Perales, S., Yáñez-Mó, M., Reche, P. A., Cabañas, C., & Lafuente, E. M. (2020). RIAM-VASP Module Relays Integrin Complement Receptors in Outside-In Signaling Driving Particle Engulfment. Cells, 9(5), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051166









