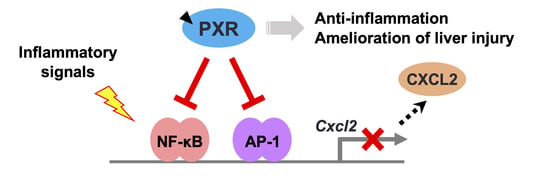
PXR Functionally Interacts with NF-κB and AP-1 to Downregulate the Inflammation-Induced Expression of Chemokine CXCL2 in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plasmid Preparation
2.3. Animal Experiments
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Liver Histology Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Reporter Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
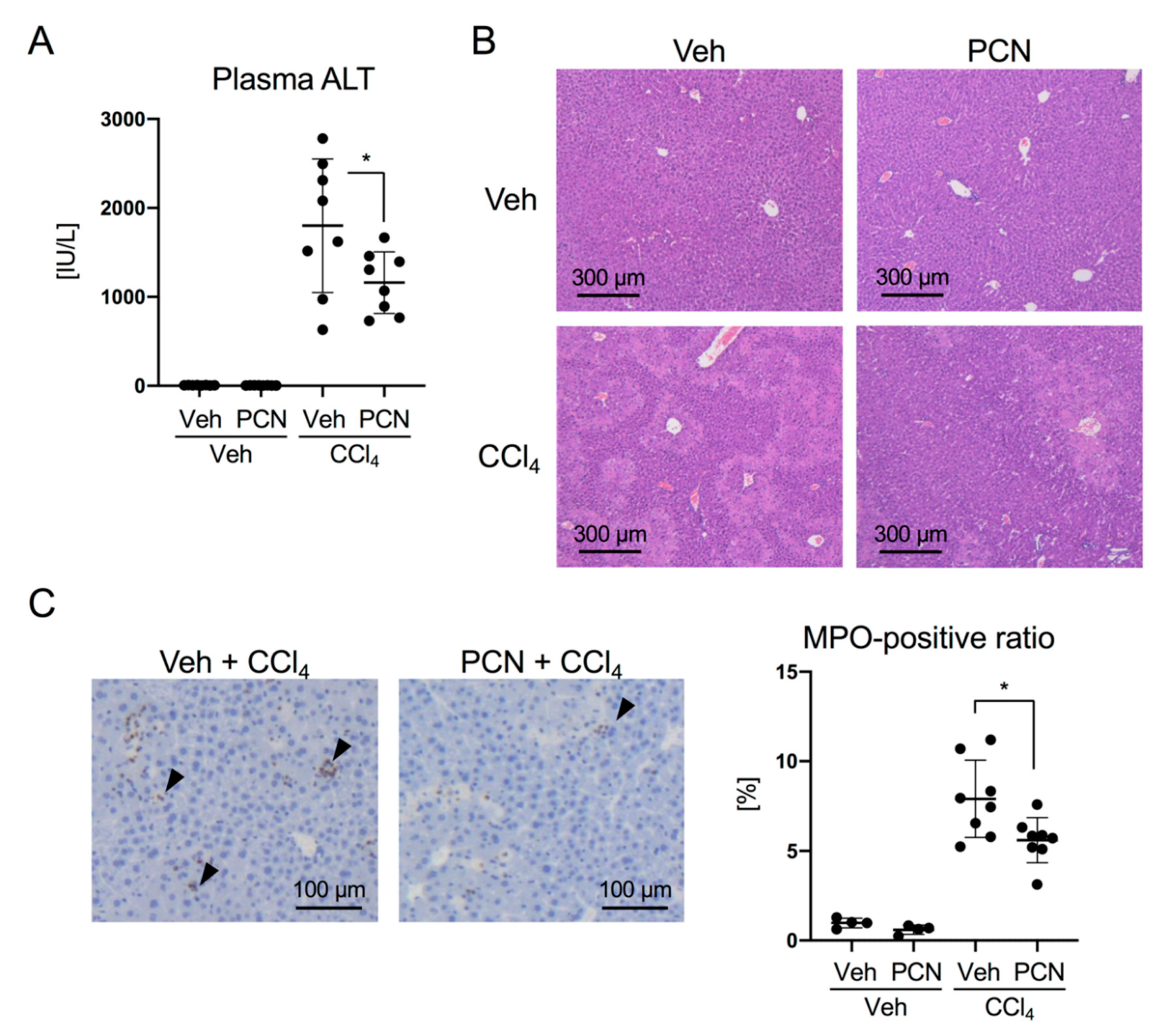
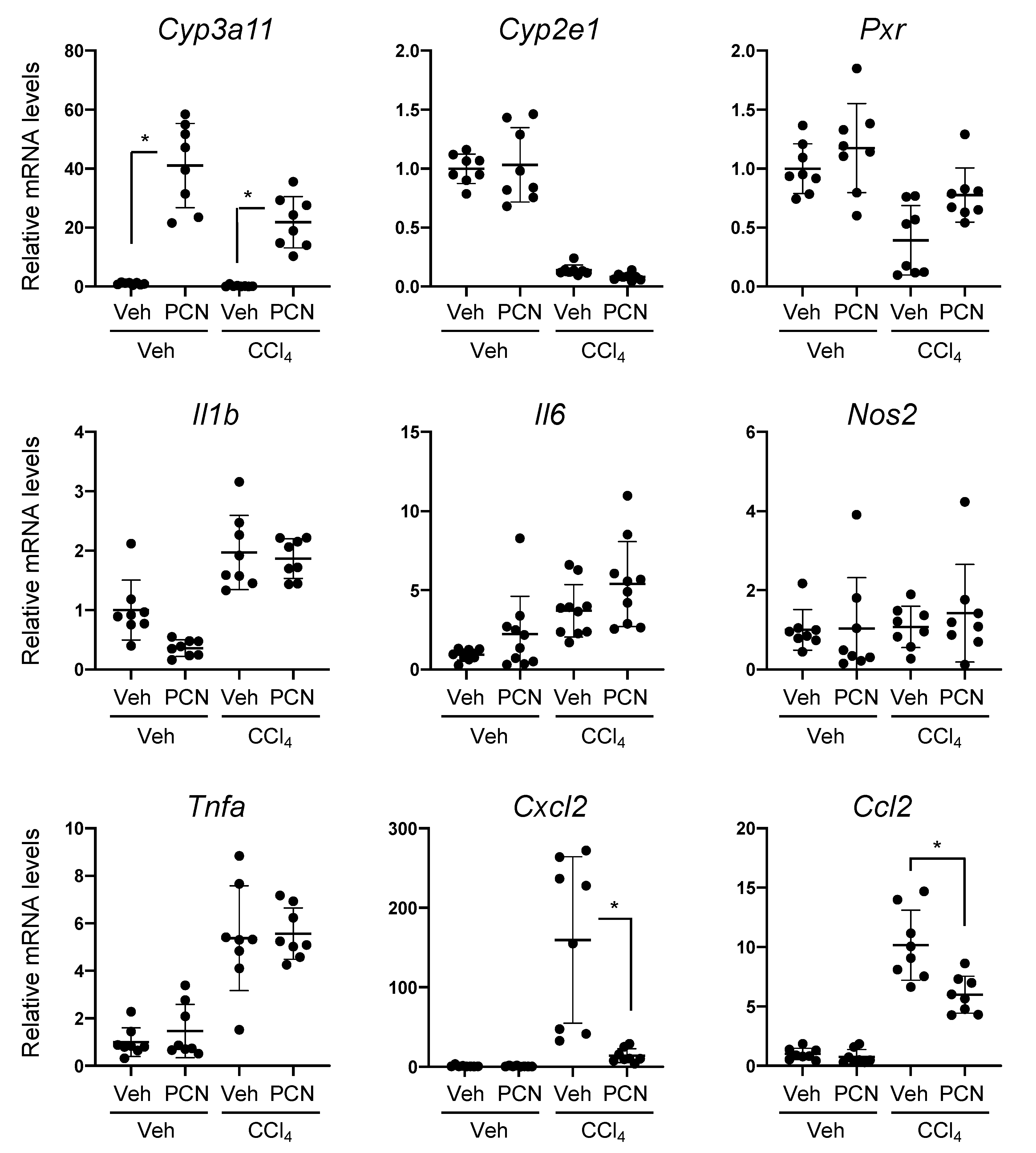
3.1. PCN Treatment Ameliorates Liver Injury-Induced Expression of Chemokines in Mice
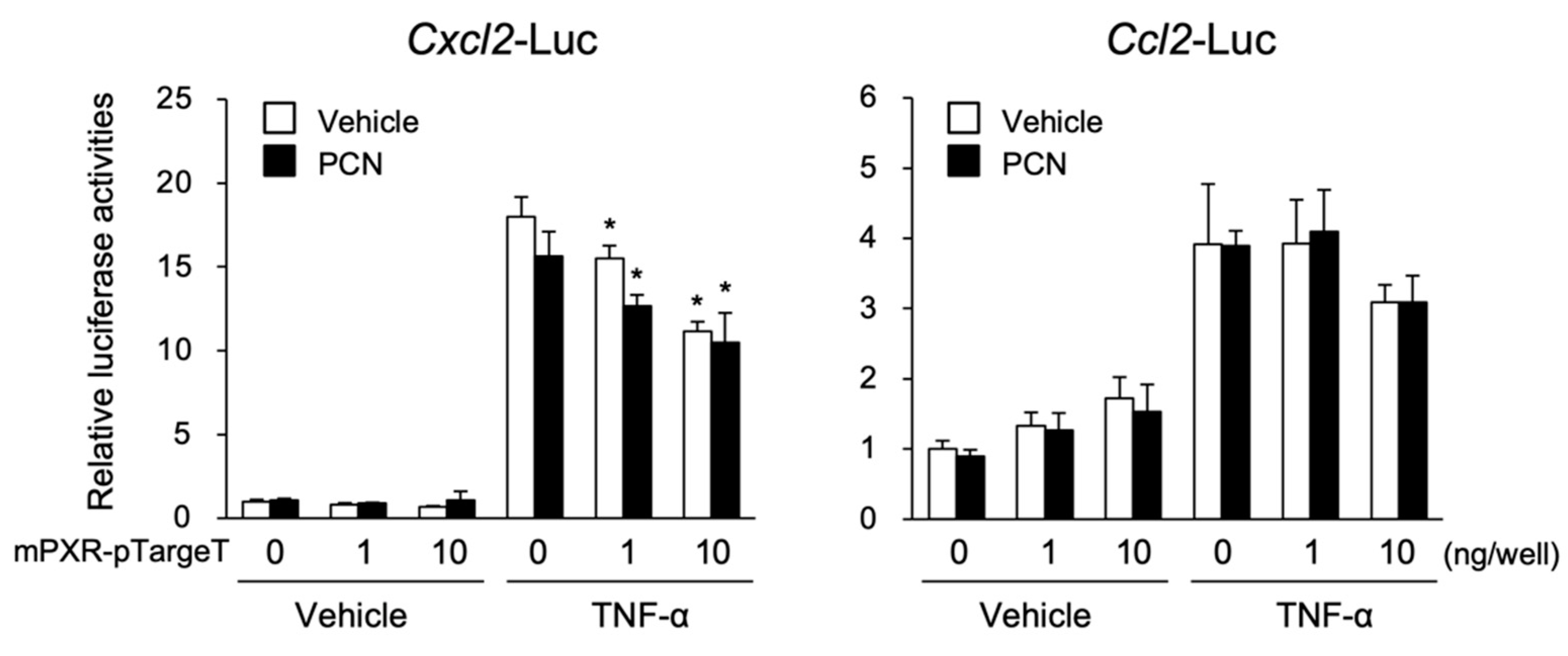
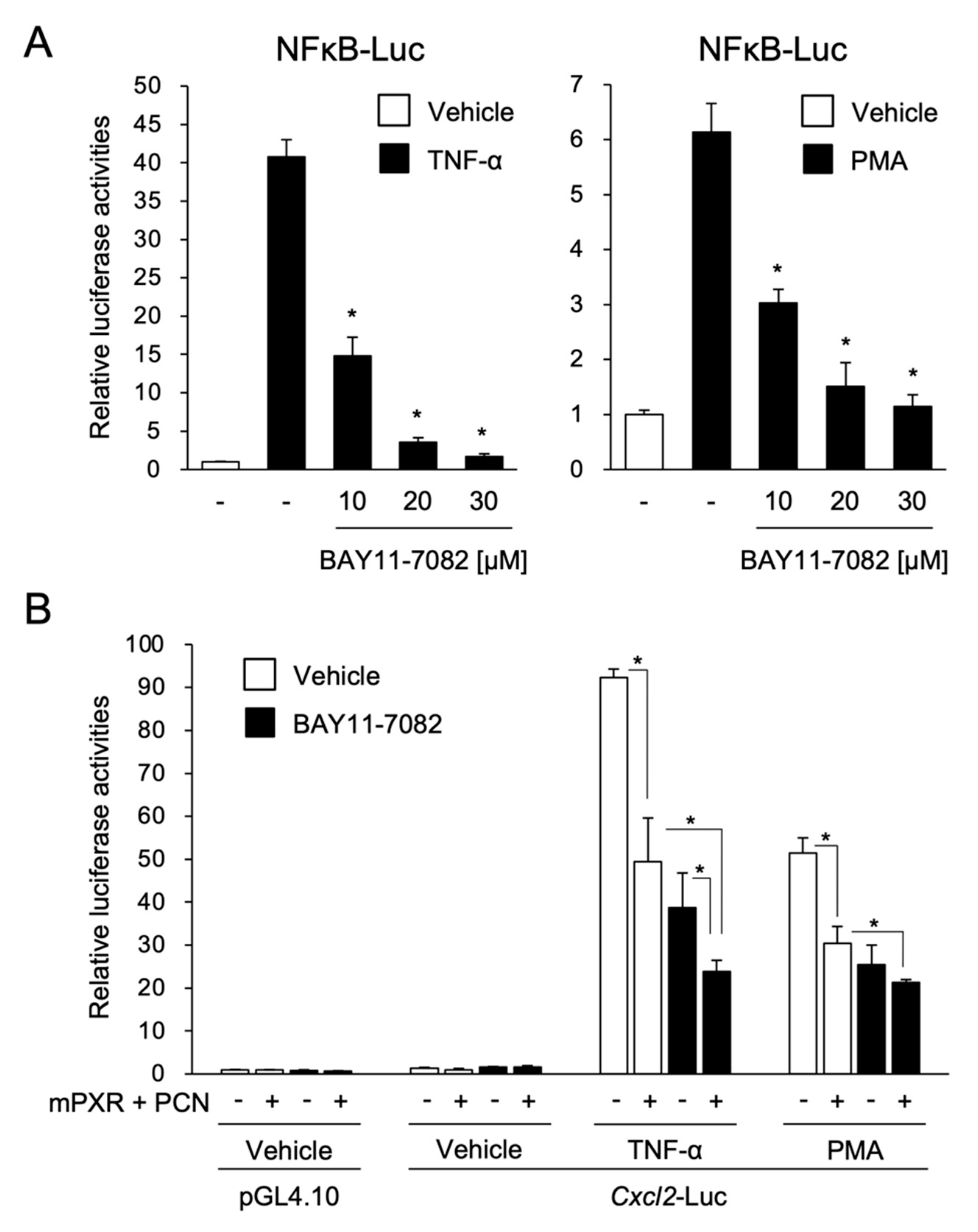
3.2. PXR Suppresses the NF-κB-Dependent Cxcl2 Expression
3.3. PXR Downregulates AP-1- and NF-κB-Dependent Cxcl2 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A. PXR, CAR and drug metabolism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, S.; Koike, C.; Negishi, M.; Yamamoto, Y. Nuclear receptors CAR and PXR cross talk with FOXO1 to regulate genes that encode drug-metabolizing and gluconeogenic enzymes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7931–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, S.; Negishi, M. Serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 2 determines drug-activated pregnane X receptor to induce gluconeogenesis in human liver cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 348, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, S.; Moore, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; Negishi, M. Human nuclear pregnane X receptor cross-talk with CREB to repress cAMP activation of the glucose-6-phosphatase gene. Biochem. J. 2007, 407, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shizu, R.; Abe, T.; Benoki, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kodama, S.; Miayata, M.; Matsuzawa, A.; Yoshinari, K. PXR stimulates growth factor-mediated hepatocyte proliferation by cross-talk with the FOXO transcription factor. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Shizu, R.; Sasaki, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Hosaka, T.; Kodama, S.; Matsuzawa, A.; Yoshinari, K. Functional interaction between pregnane X receptor and Yes-associated protein in xenobiotic-dependent liver hypertrophy and drug metabolism. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 371, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Feng, D.; Ma, X.; Fan, S.; Gao, Y.; Fu, K.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yao, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Pregnane X receptor regulates liver size and liver cell fate by Yes-associated protein activation in mice. Hepatology 2019, 69, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizu, R.; Yoshinari, K. Nuclear receptor CAR-mediated liver cancer and its species differences. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinari, K. Role of nuclear receptors PXR and CAR in xenobiotic-induced hepatocyte proliferation and chemical carcinogenesis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Xu, C.; Staudinger, J.L. Pregnane X receptor is SUMOylated to repress the inflammatory response. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencarelli, A.; Renga, B.; Palladino, G.; Claudio, D.; Ricci, P.; Distrutti, E.; Barbanti, M.; Baldelli, F.; Fiorucci, S. Inhibition of NF-kappaB by a PXR-dependent pathway mediates counter-regulatory activities of rifaximin on innate immunity in intestinal epithelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Cui, W.; Woody, S.K.; Staudinger, J.L. Pregnane X receptor modulates the inflammatory response in primary cultures of hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Tabb, M.M.; Nelson, E.L.; Grün, F.; Verma, S.; Sadatrafiei, A.; Lin, M.; Mallick, S.; Forman, B.M.; Thummel, K.E.; et al. Mutual repression between steroid and xenobiotic receptor and NF-kappaB signaling pathways links xenobiotic metabolism and inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, S.; Shimura, T.; Kuribayashi, H.; Abe, T.; Yoshinari, K. Pregnenolone 16α-carbonitrile ameliorates concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice independent of the nuclear receptor PXR activation. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 271, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, J.; Angel, P.; Schorpp-Kistner, M. AP-1 subunits: Quarrel and harmony among siblings. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 5965–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Glass, C.K. Nuclear receptors and inflammation control: Molecular mechanisms and pathophysiological relevance. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, M.; Shizu, R.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshinari, K. Possible involvement of the competition for the transcriptional coactivator glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 in the inflammatory signal-dependent suppression of PXR-mediated CYP3A induction in vitro. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 34, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsley, R.N.; Sui, Y.; Ai, N.; Park, S.H.; Welsh, W.J.; Zhou, C. Pregnane X receptor mediates dyslipidemia induced by the HIV protease inhibitor amprenavir in mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Ke, S.; Liu, D.; Sheng, T.; Thomas, P.E.; Rabson, A.B.; Gallo, M.A.; Xie, W.; Tian, Y. Role of NF-kappaB in regulation of PXR-mediated gene expression: A mechanism for the suppression of cytochrome P-450 3A4 by proinflammatory agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17882–17889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Tian, Y. Xenobiotic receptor meets NF-kappaB, a collision in the small bowel. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Verma, S.; Blumberg, B. The steroid and xenobiotic receptor (SXR), beyond xenobiotic metabolism. Nuclear Recept. Signal 2009, 7, e001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, J.W.; Schoenleber, R.; Jesmok, G.; Best, J.; Moore, S.A.; Collins, T.; Gerritsen, M.E. Novel inhibitors of cytokine-induced IκBα phosphorylation and endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression show anti-inflammatory effects in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21096–21103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-S.; Ho Han, J.; Kwon, H.-J. NF-κB and c-Jun-dependent regulation of macrophage inflammatory protein-2 gene expression in response to lipopolysaccharide in RAW 264.7 cells. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 40, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Y.M.; Ma, X.; Morimura, K.; Kim, I.; Gonzalez, F.J. Pregnane X receptor activation ameliorates DSS-induced inflammatory bowel disease via inhibition of NF-kappaB target gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1114–G1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrell, T.C.; Forbes, I.J. Depression of immune competence by phenytoin and carbamazepine. Studies in vivo and in vitro. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1975, 20, 273–285. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, E.; Sun, A.; Ding, L.; Chou, G.; Wang, Z.; Mani, S. Chrysin ameliorates chemically induced colitis in the mouse through modulation of a PXR/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 345, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Total synthesis and pharmacological characterization of solomonsterol A, a potent marine pregnane-X-receptor agonist endowed with anti-inflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 4590–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, I.M.E.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Vermeulen, L.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Haegeman, G.; De Bosscher, K. Crosstalk in inflammation: The interplay of glucocorticoid receptor-based mechanisms and kinases and phosphatases. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 830–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, L.I.; Cidlowski, J.A. Molecular control of immune/inflammatory responses: Interactions between nuclear factor-kappa B and steroid receptor-signaling pathways. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 435–459. [Google Scholar]
- Na, S.Y.; Kang, B.Y.; Chung, S.W.; Han, S.J.; Ma, X.; Trinchieri, G.; Im, S.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, T.S. Retinoids inhibit interleukin-12 production in macrophages through physical associations of retinoid X receptor and NFkappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7674–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladimeji, P.; Cui, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, T. Regulation of PXR and CAR by protein-protein interaction and signaling crosstalk. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Na, S.Y.; Kim, T.S.; Choi, H.S.; Im, S.Y.; Lee, J.W. Steroid receptor coactivator-1 coactivates activating protein-1-mediated transactivations through interaction with the c-Jun and c-Fos subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16651–16654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Han, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Im, S.Y.; Lee, J.W. Steroid receptor coactivator-1 interacts with the p50 subunit and coactivates nuclear factor kappaB-mediated transactivations. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 10831–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Na, S.Y.; Jung, S.Y.; Choi, J.E.; Jhun, B.H.; Cheong, J.; Meltzer, P.S.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, J.W. Activating protein-1, nuclear factor-kappaB, and serum response factor as novel target molecules of the cancer-amplified transcription coactivator ASC-2. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Surapureddi, S.; Rana, R.; Goldstein, J.A. NCOA6 differentially regulates the expression of the CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 genes. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Nie, Y.; Zhong, X.B.; Kan, Q.; Zhang, L. Alterations of histone modifications contribute to pregnane X receptor-mediated induction of CYP3A4 by rifampicin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 92, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okamura, M.; Shizu, R.; Abe, T.; Kodama, S.; Hosaka, T.; Sasaki, T.; Yoshinari, K. PXR Functionally Interacts with NF-κB and AP-1 to Downregulate the Inflammation-Induced Expression of Chemokine CXCL2 in Mice. Cells 2020, 9, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102296
Okamura M, Shizu R, Abe T, Kodama S, Hosaka T, Sasaki T, Yoshinari K. PXR Functionally Interacts with NF-κB and AP-1 to Downregulate the Inflammation-Induced Expression of Chemokine CXCL2 in Mice. Cells. 2020; 9(10):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102296
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkamura, Maya, Ryota Shizu, Taiki Abe, Susumu Kodama, Takuomi Hosaka, Takamitsu Sasaki, and Kouichi Yoshinari. 2020. "PXR Functionally Interacts with NF-κB and AP-1 to Downregulate the Inflammation-Induced Expression of Chemokine CXCL2 in Mice" Cells 9, no. 10: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102296
APA StyleOkamura, M., Shizu, R., Abe, T., Kodama, S., Hosaka, T., Sasaki, T., & Yoshinari, K. (2020). PXR Functionally Interacts with NF-κB and AP-1 to Downregulate the Inflammation-Induced Expression of Chemokine CXCL2 in Mice. Cells, 9(10), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102296