Modes of Interaction of KMT2 Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferase/COMPASS Complexes with Chromatin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methylation of Histone H3 at Lysine 4
3. KMT2 Complexes Are Essential for Development and Are Affected in Diseases
4. Recruitment of KMT2 Complexes to Genes
4.1. Recruitment of KMT2 Complexes by Sequence-Specific Transcription Factors
4.2. Recruitment of KMT2 Complexes by lncRNAs
4.3. Direct DNA Binding
4.4. Interaction with Chromatin
5. Functional Consequences of H3K4 Methylation
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valentine, J.W.; Collins, A.G.; Meyer, C.P. Morphological Complexity Increase in Metazoans. Paleobiology 1994, 2, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, R.D. Structure of Chromatin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1977, 46, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Sabari, B.R.; Garcia, B.A.; Allis, C.D.; Zhao, Y. Snapshot: Histone Modifications. Cell 2014, 2, 458–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Garcia, B.A. Comprehensive Catalog of Currently Documented Histone Modifications. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 9, a025064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, M.S.; Boeke, J.D.; Wolberger, C. Regulated Nucleosome Mobility and the Histone Code. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, C.; Gurard-Levin, Z.A.; Almouzni, G.; Loyola, A. Histone Lysine Methylation and Chromatin Replication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 12, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, B.J.; Rall, N.A.; Ostwal, Y.; Kruitwagen, T.; Hiragami-Hamada, K.; Winkler, M.; Barral, Y.; Fischle, W.; Neumann, H. A Cascade of Histone Modifications Induces Chromatin Condensation in Mitosis. Science 2014, 6166, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, W.G. Biological Function and Regulation of Histone and Non-Histone Lysine Methylation in Response to DNA Damage. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 7, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, B.; Li, W.; Zhao, W.; Wang, R. Targeting Epigenetic Regulations in Cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 1, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R. Epigenetics in Autoimmune Diseases: Pathogenesis and Prospects for Therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 10, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgrave-Gomez, J.; Mercado-Gomez, O.; Guevara-Guzman, R. Epigenetic Mechanisms in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strahl, B.D.; Allis, C.D. The Language of Covalent Histone Modifications. Nature 2000, 6765, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encode Project Consortium. An Integrated Encyclopedia of DNA Elements in the Human Genome. Nature 2012, 7414, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, K. The Occurrence of Iε-N-Methyl Lysine in Histones. Biochemistry 1964, 3, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rea, S.; Eisenhaber, F.; O’Carroll, D.; Strahl, B.D.; Sun, Z.W.; Schmid, M.; Opravil, S.; Mechtler, K.; Ponting, C.P.; Allis, C.D.; et al. Regulation of Chromatin Structure by Site-Specific Histone H3 Methyltransferases. Nature 2000, 6796, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.G.; Tsukada, Y. The Discovery of Histone Demethylases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a017947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morera, L.; Lubbert, M.; Jung, M. Targeting Histone Methyltransferases and Demethylases in Clinical Trials for Cancer Therapy. Clin. Epigenet. 2016, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, E.; Turberfield, A.H.; Klose, R.J. Histone Demethylases in Chromatin Biology and Beyond. EMBO Rep. 2015, 12, 1620–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snowden, A.W.; Gregory, P.D.; Case, C.C.; Pabo, C.O. Gene-Specific Targeting of H3k9 Methylation is Sufficient for Initiating Repression In Vivo. Curr. Biol. 2002, 24, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Jones, R.S.; Zhang, Y. Role of Histone H3 Lysine 27 Methylation in Polycomb-Group Silencing. Science 2002, 5595, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, B.E.; Humphrey, E.L.; Erlich, R.L.; Schneider, R.; Bouman, P.; Liu, J.S.; Kouzarides, T.; Schreiber, S.L. Methylation of Histone H3 Lys 4 in Coding Regions of Active Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 13, 8695–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantalat, S.; Depaux, A.; Hery, P.; Barral, S.; Thuret, J.Y.; Dimitrov, S.; Gerard, M. Histone H3 Trimethylation at Lysine 36 Is Associated with Constitutive and Facultative Heterochromatin. Genome Res. 2011, 9, 1426–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allis, C.D.; Berger, S.L.; Cote, J.; Dent, S.; Jenuwien, T.; Kouzarides, T.; Pillus, L.; Reinberg, D.; Shi, Y.; Shiekhattar, R.; et al. New Nomenclature for Chromatin-Modifying Enzymes. Cell 2007, 4, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.; Krogan, N.J.; Dover, J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Johnston, M.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Shilatifard, A. Compass: A Complex of Proteins Associated with a Trithorax-Related Set Domain Protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 23, 12902–12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruthenburg, A.J.; Allis, C.D.; Wysocka, J. Methylation of Lysine 4 on Histone H3: Intricacy of Writing and Reading a Single Epigenetic Mark. Mol. Cell 2007, 1, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschiersch, B.; Hofmann, A.; Krauss, V.; Dorn, R.; Korge, G.; Reuter, G. The Protein Encoded by the Drosophila Position-Effect Variegation Suppressor Gene Su(Var)3-9 Combines Domains of Antagonistic Regulators of Homeotic Gene Complexes. EMBO J. 1994, 16, 3822–3831. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, H.L.; Blumenthal, R.M.; Cheng, X. Many Paths to Methyltransfer: A Chronicle of Convergence. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 6, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilatifard, A. The Compass Family of Histone H3k4 Methylases: Mechanisms of Regulation in Development and Disease Pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varier, R.A.; Timmers, H.T. Histone Lysine Methylation and Demethylation Pathways in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.C.; Dou, Y. Hijacked in Cancer: The Kmt2 (Mll) Family of Methyltransferases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 6, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, K.N.; Shearn, A. Ash1, a Drosophila Trithorax Group Protein, Is Required for Methylation of Lysine 4 Residues on Histone H3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 20, 11535–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, G.D.; Vakoc, C.R.; Rozovskaia, T.; Zheng, X.; Patel, S.; Nakamura, T.; Canaani, E.; Blobel, G.A. Mammalian Ash1l Is a Histone Methyltransferase That Occupies the Transcribed Region of Active Genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 24, 8466–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Xu, M.; Huang, C.; Liu, N.; Chen, S.; Zhu, B. H3k36 Methylation Antagonizes Prc2-Mediated H3k27 Methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 10, 7983–7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Yoshida, K.; Matsui, Y. A Histone H3 Methyltransferase Controls Epigenetic Events Required for Meiotic Prophase. Nature 2005, 7066, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segurel, L.; Leffler, E.M.; Przeworski, M. The Case of the Fickle Fingers: How the Prdm9 Zinc Finger Protein Specifies Meiotic Recombination Hotspots in Humans. PLoS Biol. 2011, 12, e1001211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhayalan, A.; Kudithipudi, S.; Rathert, P.; Jeltsch, A. Specificity Analysis-Based Identification of New Methylation Targets of the Set7/9 Protein Lysine Methyltransferase. Chem. Biol. 2011, 1, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellmon, N.; Holcomb, J.; Trescott, L.; Sirinupong, N.; Yang, Z. Structure and Function of Set and Mynd Domain-Containing Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 1, 1406–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakountis, A.; Moulos, P.; Sarris, M.E.; Hatzis, P.; Talianidis, I. Smyd3-Associated Regulatory Pathways in Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 42, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampranis, S.C.; Tsichlis, P.N. Histone Demethylases and Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2009, 102, 103–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alicea-Velazquez, N.L.; Shinsky, S.A.; Loh, D.M.; Lee, J.H.; Skalnik, D.G.; Cosgrove, M.S. Targeted Disruption of the Interaction between Wd-40 Repeat Protein 5 (Wdr5) and Mixed Lineage Leukemia (Mll)/Set1 Family Proteins Specifically Inhibits Mll1 and Setd1a Methyltransferase Complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 43, 22357–22372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Lin, C.; Smith, E.R.; Guo, H.; Sanderson, B.W.; Wu, M.; Gogol, M.; Alexander, T.; Seidel, C.; Wiedemann, L.M.; et al. Global Analysis of H3k4 Methylation Defines Mll Family Member Targets and Points to a Role for Mll1-Mediated H3k4 Methylation in the Regulation of Transcriptional Initiation by Rna Polymerase Ii. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 22, 6074–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreu-Vieyra, C.V.; Chen, R.; Agno, J.E.; Glaser, S.; Anastassiadis, K.; Stewart, A.F.; Matzuk, M.M. Mll2 Is Required in Oocytes for Bulk Histone 3 Lysine 4 Trimethylation and Transcriptional Silencing. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placek, K.; Hu, G.; Cui, K.; Zhang, D.; Ding, Y.; Lee, J.E.; Jang, Y.; Wang, C.; Konkel, J.E.; Song, J.; et al. Mll4 Prepares the Enhancer Landscape for Foxp3 Induction Via Chromatin Looping. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 9, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhuang, L.; Liu, C.; Ge, K. H3k4 Methyltransferase Activity Is Required for Mll4 Protein Stability. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 13, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bledau, A.S.; Schmidt, K.; Neumann, K.; Hill, U.; Ciotta, G.; Gupta, A.; Torres, D.C.; Fu, J.; Kranz, A.; Stewart, A.F.; et al. The H3k4 Methyltransferase Setd1a Is First Required at the Epiblast Stage, Whereas Setd1b Becomes Essential after Gastrulation. Development 2014, 5, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto, R.; Furukawa, Y.; Morita, M.; Iimura, Y.; Silva, F.P.; Li, M.; Yagyu, R.; Nakamura, Y. Smyd3 Encodes a Histone Methyltransferase Involved in the Proliferation of Cancer Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 8, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Cao, R.; Xia, L.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Borchers, C.; Tempst, P.; Zhang, Y. Purification and Functional Characterization of a Histone H3-Lysine 4-Specific Methyltransferase. Mol. Cell 2001, 6, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Kim, K.; Schmidt, T.; Punj, V.; Tucker, H.; Rice, J.C.; Ulmer, T.S.; An, W. Cooperation between Smyd3 and Pc4 Drives a Distinct Transcriptional Program in Cancer Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 18, 8868–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Sims, R.J., 3rd; Gottlieb, P.D.; Tucker, P.W. Identification and Characterization of Smyd2: A Split Set/Mynd Domain-Containing Histone H3 Lysine 36-Specific Methyltransferase That Interacts with the Sin3 Histone Deacetylase Complex. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nuland, R.; Smits, A.H.; Pallaki, P.; Jansen, P.W.; Vermeulen, M.; Timmers, H.T. Quantitative Dissection and Stoichiometry Determination of the Human Set1/Mll Histone Methyltransferase Complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 10, 2067–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, J.F.; Skiniotis, G. Assembling a Compass. Epigenetics 2013, 4, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Dharmarajan, V.; Vought, V.E.; Cosgrove, M.S. On the Mechanism of Multiple Lysine Methylation by the Human Mixed Lineage Leukemia Protein-1 (Mll1) Core Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 36, 24242–24256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southall, S.M.; Wong, P.S.; Odho, Z.; Roe, S.M.; Wilson, J.R. Structural Basis for the Requirement of Additional Factors for Mll1 Set Domain Activity and Recognition of Epigenetic Marks. Mol. Cell 2009, 2, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, M.; Timmers, H.T. Grasping Trimethylation of Histone H3 at Lysine 4. Epigenomics 2010, 3, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdic, V.; Zhang, P.; Lanouette, S.; Groulx, A.; Tremblay, V.; Brunzelle, J.; Couture, J.F. Structural and Biochemical Insights into Mll1 Core Complex Assembly. Structure 2011, 1, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chaturvedi, C.P.; Tremblay, V.; Cramet, M.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Skiniotis, G.; Brand, M.; Shilatifard, A.; Couture, J.F. A Phosphorylation Switch on Rbbp5 Regulates Histone H3 Lys4 Methylation. Genes Dev. 2015, 2, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Lee, H.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Couture, J.F. The Plasticity of Wdr5 Peptide-Binding Cleft Enables the Binding of the Set1 Family of Histone Methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 9, 4237–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steward, M.M.; Lee, J.S.; O’Donovan, A.; Wyatt, M.; Bernstein, B.E.; Shilatifard, A. Molecular Regulation of H3k4 Trimethylation by Ash2l, a Shared Subunit of Mll Complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 9, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Milne, T.A.; Ruthenburg, A.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.W.; Verdine, G.L.; Allis, C.D.; Roeder, R.G. Regulation of Mll1 H3k4 Methyltransferase Activity by Its Core Components. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 8, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Vought, V.E.; Dharmarajan, V.; Cosgrove, M.S. A Novel Non-Set Domain Multi-Subunit Methyltransferase Required for Sequential Nucleosomal Histone H3 Methylation by the Mixed Lineage Leukemia Protein-1 (Mll1) Core Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 5, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Shuai, J.; et al. Structural Basis for Activity Regulation of Mll Family Methyltransferases. Nature 2016, 7591, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, F.; Wan, B.; Dou, Y.; Lei, M. Structure of the Spry Domain of Human Ash2l and Its Interactions with Rbbp5 and Dpy30. Cell Res. 2012, 3, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odho, Z.; Southall, S.M.; Wilson, J.R. Characterization of a Novel Wdr5-Binding Site That Recruits Rbbp5 through a Conserved Motif to Enhance Methylation of Histone H3 Lysine 4 by Mixed Lineage Leukemia Protein-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 43, 32967–32976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.M.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Milne, T.A.; Copeland, T.D.; Levine, S.S.; Lee, J.C.; Hayes, D.N.; Shanmugam, K.S.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Biondi, C.A.; et al. Menin Associates with a Trithorax Family Histone Methyltransferase Complex and with the Hoxc8 Locus. Mol. Cell 2004, 4, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Cleary, M.L. Menin Critically Links Mll Proteins with Ledgf on Cancer-Associated Target Genes. Cancer Cell 2008, 1, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, M.J.; Pollock, J.; He, S.; Miao, H.; Purohit, T.; Yokom, A.; Hess, J.L.; Muntean, A.G.; Grembecka, J.; Cierpicki, T. The Same Site on the Integrase-Binding Domain of Lens Epithelium-Derived Growth Factor is a Therapeutic Target for Mll Leukemia and Hiv. Blood 2014, 25, 3730–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goo, Y.H.; Sohn, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, M.J.; Jung, D.J.; Kwak, E.; Barlev, N.A.; Berger, S.L.; Chow, V.T.; et al. Activating Signal Cointegrator 2 Belongs to a Novel Steady-State Complex That Contains a Subset of Trithorax Group Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 1, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.W.; Hong, T.; Hong, S.; Guo, H.; Yu, H.; Kim, D.; Guszczynski, T.; Dressler, G.R.; Copeland, T.D.; Kalkum, M.; et al. Ptip Associates with Mll3- and Mll4-Containing Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferase Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 28, 20395–20406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.R.; Kim, D.; Levitan, I.; Dressler, G.R. The Brct-Domain Containing Protein Ptip Links Pax2 to a Histone H3, Lysine 4 Methyltransferase Complex. Dev. Cell 2007, 4, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Tate, C.M.; You, J.S.; Skalnik, D.G. Identification and Characterization of the Human Set1b Histone H3-Lys4 Methyltransferase Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 18, 13419–13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, P.; Tee, W.W.; Reinberg, D. A Double Take on Bivalent Promoters. Genes Dev. 2013, 12, 1318–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Vought, V.E.; Dharmarajan, V.; Cosgrove, M.S. A Conserved Arginine-Containing Motif Crucial for the Assembly and Enzymatic Activity of the Mixed Lineage Leukemia Protein-1 Core Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 47, 32162–32175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ernst, P. Distinct Functions of Histone H3, Lysine 4 Methyltransferases in Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 4, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Cho, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Feng, X.; Baldridge, A.; Sartorelli, V.; Zhuang, L.; Peng, W.; et al. H3k4 Mono- and Di-Methyltransferase Mll4 Is Required for Enhancer Activation During Cell Differentiation. eLife 2013, 2, e01503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorighi, K.M.; Swigut, T.; Henriques, T.; Bhanu, N.V.; Scruggs, B.S.; Nady, N.; Still, C.D., 2nd; Garcia, B.A.; Adelman, K.; Wysocka, J. Mll3 and Mll4 Facilitate Enhancer Rna Synthesis and Transcription from Promoters Independently of H3k4 Monomethylation. Mol. Cell 2017, 4, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickels, R.; Herz, H.M.; Sze, C.C.; Cao, K.; Morgan, M.A.; Collings, C.K.; Gause, M.; Takahashi, Y.H.; Wang, L.; Rendleman, E.J.; et al. Histone H3k4 Monomethylation Catalyzed by Trr and Mammalian Compass-Like Proteins at Enhancers is Dispensable for Development and Viability. Nat. Genet. 2017, 11, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Chen, L.H.; Huang, Y.; Chang, C.C.; Wang, P.; Pirozzi, C.J.; Qin, X.; Bao, X.; Greer, P.K.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Kmt2d Maintains Neoplastic Cell Proliferation and Global Histone H3 Lysine 4 Monomethylation. Oncotarget 2013, 11, 2144–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herz, H.M.; Mohan, M.; Garruss, A.S.; Liang, K.; Takahashi, Y.H.; Mickey, K.; Voets, O.; Verrijzer, C.P.; Shilatifard, A. Enhancer-Associated H3k4 Monomethylation by Trithorax-Related, the Drosophila Homolog of Mammalian Mll3/Mll4. Genes Dev. 2012, 23, 2604–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Gao, X.; Morgan, M.A.; Herz, H.M.; Smith, E.R.; Shilatifard, A. The Mll3/Mll4 Branches of the Compass Family Function as Major Histone H3k4 Monomethylases at Enhancers. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 23, 4745–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wang, P.F.; Lee, J.S.; Martin-Brown, S.; Florens, L.; Washburn, M.; Shilatifard, A. Molecular Regulation of H3k4 Trimethylation by Wdr82, a Component of Human Set1/Compass. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 24, 7337–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Li, Y.; Liang, S.; Cui, K.; Salz, T.; Yang, H.; Tang, Z.; Gallagher, P.G.; Qiu, Y.; Roeder, R.; et al. Usf1 and Hset1a Mediated Epigenetic Modifications Regulate Lineage Differentiation and Hoxb4 Transcription. PLoS Genet. 2013, 6, e1003524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Skalnik, D.G.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. H3k4 Methyltransferase Set1a Is a Key Oct4 Coactivator Essential for Generation of Oct4 Positive Inner Cell Mass. Stem Cells 2016, 3, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaikkonen, M.U.; Spann, N.J.; Heinz, S.; Romanoski, C.E.; Allison, K.A.; Stender, J.D.; Chun, H.B.; Tough, D.F.; Prinjha, R.K.; Benner, C.; et al. Remodeling of the Enhancer Landscape During Macrophage Activation is Coupled to Enhancer Transcription. Mol. Cell 2013, 3, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulger, M.; Groudine, M. Functional and Mechanistic Diversity of Distal Transcription Enhancers. Cell 2011, 3, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentner, G.E.; Scacheri, P.C. The Chromatin Fingerprint of Gene Enhancer Elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 37, 30888–30896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Blum, R.; Bowman, C.; Hu, D.; Shilatifard, A.; Shen, S.; Dynlacht, B.D. A Role for H3k4 Monomethylation in Gene Repression and Partitioning of Chromatin Readers. Mol. Cell 2014, 6, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.; Agger, K.; Cloos, P.A.; Pasini, D.; Rose, S.; Sennels, L.; Rappsilber, J.; Hansen, K.H.; Salcini, A.E.; Helin, K. Rbp2 Belongs to a Family of Demethylases, Specific for Tri-and Dimethylated Lysine 4 on Histone 3. Cell 2007, 6, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klose, R.J.; Kallin, E.M.; Zhang, Y. Jmjc-Domain-Containing Proteins and Histone Demethylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 9, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klose, R.J.; Yan, Q.; Tothova, Z.; Yamane, K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Gilliland, D.G.; Zhang, Y.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. The Retinoblastoma Binding Protein Rbp2 Is an H3k4 Demethylase. Cell 2007, 5, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Zhang, J.; Klose, R.J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Jones, R.S.; Zhang, Y. The Trithorax-Group Protein Lid Is a Histone H3 Trimethyl-Lys4 Demethylase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 4, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, T.; Yonezawa, M.; Lein, S.; Heidrich, K.; Kubicek, S.; Schafer, C.; Phalke, S.; Walther, M.; Schmidt, A.; Jenuwein, T.; et al. Heterochromatin Formation in Drosophila Is Initiated through Active Removal of H3k4 Methylation by the Lsd1 Homolog Su(Var)3-3. Mol. Cell 2007, 1, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissmann, M.; Yin, N.; Muller, J.M.; Greschik, H.; Fodor, B.D.; Jenuwein, T.; Vogler, C.; Schneider, R.; Gunther, T.; Buettner, R.; et al. Cooperative Demethylation by Jmjd2c and Lsd1 Promotes Androgen Receptor-Dependent Gene Expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 3, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, K.; Tateishi, K.; Klose, R.J.; Fang, J.; Fabrizio, L.A.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; Tempst, P.; Zhang, Y. Plu-1 is an H3k4 Demethylase Involved in Transcriptional Repression and Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell 2007, 6, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, H.; Deguchi, K.; Aono, A.; Tani, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Komori, T. “Growth Disturbance in Fetal Liver Hematopoiesis of Mll-Mutant Mice”. Blood 1998, 1, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.D.; Hess, J.L.; Horning, S.E.; Brown, G.A.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Altered Hox Expression and Segmental Identity in Mll-Mutant Mice. Nature 1995, 6556, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ernst, P. Set/Mll Family Proteins in Hematopoiesis and Leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, T.; Jude, C.D.; Zaffuto, K.; Ernst, P. Developmentally Induced Mll1 Loss Reveals Defects in Postnatal Haematopoiesis. Leukemia 2010, 10, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, P.; Fisher, J.K.; Avery, W.; Wade, S.; Foy, D.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Definitive Hematopoiesis Requires the Mixed-Lineage Leukemia Gene. Dev. Cell 2004, 3, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jude, C.D.; Climer, L.; Xu, D.; Artinger, E.; Fisher, J.K.; Ernst, P. Unique and Independent Roles for Mll in Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 3, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, K.A.; Hiew, S.Y.; Hadjur, S.; Veiga-Fernandes, H.; Menzel, U.; Price, A.J.; Kioussis, D.; Williams, O.; Brady, H.J. Mll Has a Critical Role in Fetal and Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 3, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, S.; Schaft, J.; Lubitz, S.; Vintersten, K.; van der Hoeven, F.; Tufteland, K.R.; Aasland, R.; Anastassiadis, K.; Ang, S.L.; Stewart, A.F. Multiple Epigenetic Maintenance Factors Implicated by the Loss of Mll2 in Mouse Development. Development 2006, 8, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, S.; Lubitz, S.; Loveland, K.L.; Ohbo, K.; Robb, L.; Schwenk, F.; Seibler, J.; Roellig, D.; Kranz, A.; Anastassiadis, K.; et al. The Histone 3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferase, Mll2, Is Only Required Briefly in Development and Spermatogenesis. Epigenet. Chromatin 2009, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoller, J.Z.; Huang, L.; Tan, C.C.; Huang, F.; Zhou, D.D.; Yang, J.; Gelb, B.D.; Epstein, J.A. Ash2l Interacts with Tbx1 and Is Required During Early Embryogenesis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 5, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.L.; Luscher-Firzlaff, J.; Ullius, A.; Schneider, U.; Longerich, T.; Luscher, B. Loss of the Epigenetic Regulator Ash2l Results in Desintegration of Hepatocytes and Liver Failure. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 5, 5167–5175. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Shah, K.; Khodadadi-Jamayran, A.; Jiang, H. Dpy30 Is Critical for Maintaining the Identity and Function of Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 11, 2349–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Metzger, E.; Schule, R.; Kirfel, J.; Buettner, R. Epigenetic Regulation of Cancer Growth by Histone Demethylases. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 9, 1991–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Hofmann, J.; Burmeister, T.; Groger, D.; Park, T.S.; Emerenciano, M.; de Oliveira, M.P.; Renneville, A.; Villarese, P.; Macintyre, E.; et al. The Mll Recombinome of Acute Leukemias in 2013. Leukemia 2013, 11, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, C.M.; Karemaker, D.; van Leeuwen, F.I. The Emerging Roles of Dot1l in Leukemia and Normal Development. Leukemia 2014, 11, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivtsov, A.V.; Hoshii, T.; Armstrong, S.A. Mixed-Lineage Leukemia Fusions and Chromatin in Leukemia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a026658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Lin, C.; Shilatifard, A. The Super Elongation Complex (Sec) Family in Transcriptional Control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 9, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, A.C.; Bernt, K.M. Mll-Rearranged Leukemias-an Update on Science and Clinical Approaches. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, W.D.; Dafou, D.; McEntagart, M.; Woollard, W.J.; Elmslie, F.V.; Holder-Espinasse, M.; Irving, M.; Saggar, A.K.; Smithson, S.; Trembath, R.C.; et al. De Novo Mutations in Mll Cause Wiedemann-Steiner Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 2, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strom, S.P.; Lozano, R.; Lee, H.; Dorrani, N.; Mann, J.; O’Lague, P.F.; Mans, N.; Deignan, J.L.; Vilain, E.; Nelson, S.F.; et al. De Novo Variants in the Kmt2a (Mll) Gene Causing Atypical Wiedemann-Steiner Syndrome in Two Unrelated Individuals Identified by Clinical Exome Sequencing. BMC Med. Genet. 2014, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, B.A.; Pronold, M.; Long, R.; Smaoui, N.; Slavotinek, A.M. Advanced Bone Age in a Girl with Wiedemann-Steiner Syndrome and an Exonic Deletion in Kmt2a (Mll). Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 8, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Rappaport, A.R.; Kitzing, T.; Schultz, N.; Zhao, Z.; Shroff, A.S.; Dickins, R.A.; Vakoc, C.R.; Bradner, J.E.; et al. Mll3 Is a Haploinsufficient 7q Tumor Suppressor in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2014, 5, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, T.J.; Weeraratne, S.D.; Archer, T.C.; Krummel, D.A.P.; Auclair, D.; Bochicchio, J.; Carneiro, M.O.; Carter, S.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Erlich, R.L.; et al. Medulloblastoma Exome Sequencing Uncovers Subtype-Specific Somatic Mutations. Nature 2012, 7409, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Lan, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, F.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ye, T.; Sun, H.; Lu, F.; et al. Lsd1 Regulates Pluripotency of Embryonic Stem/Carcinoma Cells through Histone Deacetylase 1-Mediated Deacetylation of Histone H4 at Lysine 16. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 2, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, Y.; Freese, L.; Manz, J.; Zoll, B.; Volter, C.; Brockmann, K.; Bogershausen, N.; Becker, J.; Wollnik, B.; Pauli, S. Charge and Kabuki Syndromes: A Phenotypic and Molecular Link. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 16, 4396–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreijerink, K.M.; JHoppener, W.; Timmers, H.M.; Lips, C.J. Mechanisms of Disease: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1-Relation to Chromatin Modifications and Transcription Regulation. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. MeTab. 2006, 10, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matkar, S.; Thiel, A.; Hua, X. Menin: A Scaffold Protein That Controls Gene Expression and Cell Signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luscher-Firzlaff, J.; Gawlista, I.; Vervoorts, J.; Kapelle, K.; Braunschweig, T.; Walsemann, G.; Rodgarkia-Schamberger, C.; Schuchlautz, H.; Dreschers, S.; Kremmer, E.; et al. The Human Trithorax Protein Hash2 Functions as an Oncoprotein. Cancer Res. 2008, 3, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magerl, C.; Ellinger, J.; Braunschweig, T.; Kremmer, E.; Koch, L.K.; Holler, T.; Buttner, R.; Luscher, B.; Gutgemann, I. H3k4 Dimethylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Rare Compared with Other Hepatobiliary and Gastrointestinal Carcinomas and Correlates with Expression of the Methylase Ash2 and the Demethylase Lsd1. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 2, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.S.; Qiu, Y.H.; Zhang, N.; Yoo, S.Y.; Coombes, K.R.; Dent, S.Y.; Kornblau, S.M. Low Expression of Ash2l Protein Correlates with a Favorable Outcome in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 5, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Song, E.J.; Kawasawa, Y.I.; Li, J.; Dovat, S.; Song, C. Wdr5 High Expression and Its Effect on Tumorigenesis in Leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 25, 37740–37754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhilber, D.; Marschalek, R. How to Effectively Treat Acute Leukemia Patients Bearing Mll-Rearrangements ? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 147, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebien, F.; Vedadi, M.; Getlik, M.; Giambruno, R.; Grover, A.; Avellino, R.; Skucha, A.; Vittori, S.; Kuznetsova, E.; Smil, D.; et al. Pharmacological Targeting of the Wdr5-Mll Interaction in C/Ebpalpha N-Terminal Leukemia. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 8, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senisterra, G.; Wu, H.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Wasney, G.A.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Dombrovski, L.; Dong, A.; Nguyen, K.T.; Smil, D.; Bolshan, Y.; et al. Small-Molecule Inhibition of Mll Activity by Disruption of Its Interaction with Wdr5. Biochem. J. 2013, 1, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.W.; Armstrong, S.A. Designed to Kill: Novel Menin-Mll Inhibitors Target Mll-Rearranged Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015, 4, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkin, D.; He, S.; Miao, H.; Kempinska, K.; Pollock, J.; Chase, J.; Purohit, T.; Malik, B.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; et al. Pharmacologic Inhibition of the Menin-Mll Interaction Blocks Progression of Mll Leukemia In Vivo. Cancer Cell 2015, 4, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brondfield, S.; Umesh, S.; Corella, A.; Zuber, J.; Rappaport, A.R.; Gaillard, C.; Lowe, S.W.; Goga, A.; Kogan, S.C. Direct and Indirect Targeting of Myc to Treat Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 1, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, S.R.; Olhava, E.J.; Therkelsen, C.A.; Basavapathruni, A.; Jin, L.; Boriack-Sjodin, P.A.; Allain, C.J.; Klaus, C.R.; Raimondi, A.; Scott, M.P.; et al. Potent Inhibition of Dot1l as Treatment of Mll-Fusion Leukemia. Blood 2013, 6, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Deng, L.; Song, Y.; Redell, M. Dot1l Inhibition Sensitizes Mll-Rearranged Aml to Chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2014, 5, e98270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, C.; Chen, F.; Wu, F.; Wei, L.; Liu, W.; Dong, S.; Redell, M.; Mo, Q.; et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Lsd1 for the Treatment of Mll-Rearranged Leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, M.A.; Prinjha, R.K.; Dittmann, A.; Giotopoulos, G.; Bantscheff, M.; Chan, W.I.; Robson, S.C.; Chung, C.W.; Hopf, C.; Savitski, M.M.; et al. Inhibition of Bet Recruitment to Chromatin as an Effective Treatment for Mll-Fusion Leukaemia. Nature 2011, 7370, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.; Volk, A.G.; Haug, J.S.; Marshall, S.A.; Woodfin, A.R.; Bartom, E.T.; Gilmore, J.M.; Florens, L.; Washburn, M.P.; Sullivan, K.D.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of Mll Degradation Pathways in Mll-Rearranged Leukemia. Cell 2017, 168, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhofer, N.; Metzeler, K.H.; Rothenberg, M.; Herold, T.; Tiedt, S.; Groiss, V.; Carlet, M.; Walter, G.; Hinrichsen, T.; Wachter, O.; et al. Dual Pi3k/Mtor Inhibition Shows Antileukemic Activity in Mll-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 4, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Chang, C.C.; Wortham, M.; Chen, L.H.; Kernagis, D.N.; Qin, X.; Cho, Y.W.; Chi, J.T.; Grant, G.A.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Global Identification of Mll2-Targeted Loci Reveals Mll2’s Role in Diverse Signaling Pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 43, 17603–17608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Carey, M.; Workman, J.L. The Role of Chromatin During Transcription. Cell 2007, 4, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, E.A.; Frey, B.L.; Smith, L.M.; Auble, D.T. Formaldehyde Crosslinking: A Tool for the Study of Chromatin Complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 44, 26404–26411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, Y.S.; Tsai, S.Y.; Lee, D.F.; Monk, J.; Su, J.; Ratnakumar, K.; Ding, J.; Ge, Y.; Darr, H.; Chang, B.; et al. Wdr5 Mediates Self-Renewal and Reprogramming Via the Embryonic Stem Cell Core Transcriptional Network. Cell 2011, 2, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Augustin, J.; Hu, J.; Jiang, H. Physical Interactions and Functional Coordination between the Core Subunits of Set1/Mll Complexes and the Reprogramming Factors. PLoS ONE 2015, 12, e0145336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertero, A.; Madrigal, P.; Galli, A.; Hubner, N.C.; Moreno, I.; Burks, D.; Brown, S.; Pedersen, R.A.; Gaffney, D.; Mendjan, S.; et al. Activin/Nodal Signaling and Nanog Orchestrate Human Embryonic Stem Cell Fate Decisions by Controlling the H3k4me3 Chromatin Mark. Genes Dev. 2015, 7, 702–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullius, A.; Luscher-Firzlaff, J.; Costa, I.G.; Walsemann, G.; Forst, A.H.; Gusmao, E.G.; Kapelle, K.; Kleine, H.; Kremmer, E.; Vervoorts, J.; et al. The Interaction of Myc with the Trithorax Protein Ash2l Promotes Gene Transcription by Regulating H3k27 Modification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 11, 6901–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.R.; Wang, Q.; Grieb, B.C.; Phan, J.; Foshage, A.M.; Sun, Q.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Clark, T.; Dey, S.; Lorey, S.; et al. Interaction with Wdr5 Promotes Target Gene Recognition and Tumorigenesis by Myc. Mol. Cell 2015, 3, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampalli, S.; Li, L.; Mak, E.; Ge, K.; Brand, M.; Tapscott, S.J.; Dilworth, F.J. P38 Mapk Signaling Regulates Recruitment of Ash2l-Containing Methyltransferase Complexes to Specific Genes During Differentiation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 12, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L.; Loffler, K.A.; Chen, D.; Stallcup, M.R.; Muscat, G.E. The Coactivator-Associated Arginine Methyltransferase Is Necessary for Muscle Differentiation: Carm1 Coactivates Myocyte Enhancer Factor-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 6, 4324–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Pan, W.S.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.H.; Shen, Y.F. Carm1 Activates Myogenin Gene Via Pcaf in the Early Differentiation of Tpa-Induced Rhabdomyosarcoma-Derived Cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2010, 1, 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe, Y.; Wang, Y.X.; McKinnell, I.W.; Bedford, M.T.; Rudnicki, M.A. Carm1 Regulates Pax7 Transcriptional Activity through Mll1/2 Recruitment During Asymmetric Satellite Stem Cell Divisions. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 3, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossati, A.; Dolfini, D.; Donati, G.; Mantovani, R. Nf-Y Recruits Ash2l to Impart H3k4 Trimethylation on Ccaat Promoters. PLoS ONE 2011, 3, e17220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, A.; Song, S.H.; Brand, M.; Dean, A. Nucleosome and Transcription Activator Antagonism at Human Beta-Globin Locus Control Region Dnase I Hypersensitive Sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 17, 5831–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers, C.; Chaturvedi, C.P.; Ranish, J.A.; Juban, G.; Lai, P.; Morle, F.; Aebersold, R.; Dilworth, F.J.; Groudine, M.; Brand, M. Activator-Mediated Recruitment of the Mll2 Methyltransferase Complex to the Beta-Globin Locus. Mol. Cell 2007, 4, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Monckton, E.A.; Godbout, R. Ectopic Expression of Transcription Factor Ap-2delta in Developing Retina: Effect on Psa-Ncam and Axon Routing. J. Neurochem. 2014, 1, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.C.; Sindhu, K.V.; Li, S.; Nishio, H.; Stoller, J.Z.; Oishi, K.; Puttreddy, S.; Lee, T.J.; Epstein, J.A.; Walsh, M.J.; et al. Transcription Factor Ap2delta Associates with Ash2l and Alr, a Trithorax Family Histone Methyltransferase, to Activate Hoxc8 Transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 21, 7472–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.C.; Walsh, M.J.; Gelb, B.D. Fgfr3 Is a Transcriptional Target of Ap2delta and Ash2l-Containing Histone Methyltransferase Complexes. PLoS ONE 2009, 12, e8535. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, K.R.; Patel, S.R.; Dressler, G.R. Role of Ptip in Class Switch Recombination and Long-Range Chromatin Interactions at the Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Locus. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 7, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McManus, S.; Ebert, A.; Salvagiotto, G.; Medvedovic, J.; Sun, Q.; Tamir, I.; Jaritz, M.; Tagoh, H.; Busslinger, M. The Transcription Factor Pax5 Regulates Its Target Genes by Recruiting Chromatin-Modifying Proteins in Committed B Cells. EMBO J. 2011, 12, 2388–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D.K.; Dou, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.; Kwak, E.; Kong, Y.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Roeder, R.G.; Lee, J.W. Coactivator as a Target Gene Specificity Determinant for Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 42, 15392–15397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthanarayanan, M.; Li, Y.; Surapureddi, S.; Balasubramaniyan, N.; Ahn, J.; Goldstein, J.A.; Suchy, F.J. Histone H3k4 Trimethylation by Mll3 as Part of Ascom Complex Is Critical for Nr Activation of Bile Acid Transporter Genes and Is Downregulated in Cholestasis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 5, G771–G781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Scoville, D.W.; Cyphert, H.A.; Liao, L.; Xu, J.; Reynolds, A.; Guo, S.; Stein, R. Mll3 and Mll4 Methyltransferases Bind to the Mafa and Mafb Transcription Factors to Regulate Islet Beta-Cell Function. Diabetes 2015, 11, 3772–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.; Yang, Q.H.; Lee, D.K.; Lee, S.K.; Roeder, R.G.; Lee, J.W. A Tumor Suppressive Coactivator Complex of P53 Containing Asc-2 and Histone H3-Lysine-4 Methyltransferase Mll3 or Its Paralogue Mll4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 21, 8513–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Chen, W.Y.; Shimada, M.; Nguyen, U.T.; Kim, J.; Sun, X.J.; Sengoku, T.; McGinty, R.K.; Fernandez, J.P.; Muir, T.W.; et al. Set1 and P300 Act Synergistically, through Coupled Histone Modifications, in Transcriptional Activation by P53. Cell 2013, 2, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Milne, T.A.; Tackett, A.J.; Smith, E.R.; Fukuda, A.; Wysocka, J.; Allis, C.D.; Chait, B.T.; Hess, J.L.; Roeder, R.G. Physical Association and Coordinate Function of the H3 K4 Methyltransferase Mll1 and the H4 K16 Acetyltransferase Mof. Cell 2005, 6, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mungamuri, S.K.; Wang, S.; Manfredi, J.J.; Gu, W.; Aaronson, S.A. Ash2l Enables P53-Dependent Apoptosis by Favoring Stable Transcription Pre-Initiation Complex Formation on Its Pro-Apoptotic Target Promoters. Oncogene 2015, 19, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, R.; Rao, S.M.; Zhu, Y.J. Identification of the Mll2 Complex as a Coactivator for Estrogen Receptor Alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 23, 15714–15720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, K.I.; Hussain, I.; Shrestha, B.; Kasiri, S.; Mandal, S.S. Hoxc6 Is Transcriptionally Regulated Via Coordination of Mll Histone Methylase and Estrogen Receptor in an Estrogen Environment. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 2, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, K.I.; Shrestha, B.; Hussain, I.; Kasiri, S.; Mandal, S.S. Histone Methylases Mll1 and Mll3 Coordinate with Estrogen Receptors in Estrogen-Mediated Hoxb9 Expression. Biochemistry 2011, 17, 3517–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, K.I.; Kasiri, S.; Hussain, I.; Bobzean, S.A.; Perrotti, L.I.; Mandal, S.S. Mll Histone Methylases Regulate Expression of Hdlr-Sr-B1 in Presence of Estrogen and Control Plasma Cholesterol In Vivo. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreijerink, K.M.; Mulder, K.W.; Winkler, G.S.; Hoppener, J.W.; Lips, C.J.; Timmers, H.T. Menin Links Estrogen Receptor Activation to Histone H3k4 Trimethylation. Cancer Res. 2006, 9, 4929–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imachi, H.; Murao, K.; Dobashi, H.; Bhuyan, M.M.; Cao, X.; Kontani, K.; Niki, S.; Murazawa, C.; Nakajima, H.; Kohno, N.; et al. Menin, a Product of the Meni Gene, Binds to Estrogen Receptor to Enhance Its Activity in Breast Cancer Cells: Possibility of a Novel Predictive Factor for Tamoxifen Resistance. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 2, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Zhao, H.; Yi, Y.; Nakata, Y.; Kalota, A.; Gewirtz, A.M. C-Myb Binds Mll through Menin in Human Leukemia Cells and Is an Important Driver of Mll-Associated Leukemogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 2, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Huo, L.; Zhu, Y.T.; Zhu, Y.J. Absent, Small or Homeotic 2-Like Protein (Ash2l) Enhances the Transcription of the Estrogen Receptor Alpha Gene through Gata-Binding Protein 3 (Gata3). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 45, 31373–31381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, J.S.; Liu, X.S.; Brodsky, A.S.; Li, W.; Meyer, C.A.; Szary, A.J.; Eeckhoute, J.; Shao, W.; Hestermann, E.V.; Geistlinger, T.R.; et al. Chromosome-Wide Mapping of Estrogen Receptor Binding Reveals Long-Range Regulation Requiring the Forkhead Protein Foxa1. Cell 2005, 1, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jozwik, K.M.; Chernukhin, I.; Serandour, A.A.; Nagarajan, S.; Carroll, J.S. Foxa1 Directs H3k4 Monomethylation at Enhancers Via Recruitment of the Methyltransferase Mll3. Cell Rep. 2016, 10, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.; Muller, G.A. Cell Cycle Transcription Control: Dream/Muvb and Rb-E2f Complexes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 6, 638–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, S.; Chabes, A.L.; Wysocka, J.; Herr, W. E2f Activation of S Phase Promoters Via Association with Hcf-1 and the Mll Family of Histone H3k4 Methyltransferases. Mol. Cell 2007, 1, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Chen, D.Y.; Westergard, T.D.; Fisher, J.K.; Rubens, J.A.; Sasagawa, S.; Kan, J.T.; Korsmeyer, S.J.; Cheng, E.H.; Hsieh, J.J. Proteolysis of Mll Family Proteins Is Essential for Taspase1-Orchestrated Cell Cycle Progression. Genes Dev. 2006, 17, 2397–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussouar, F.; Jamshidikia, M.; Morozumi, Y.; Rousseaux, S.; Khochbin, S. Malignant Genome Reprogramming by Atad2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 10, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revenko, A.S.; Kalashnikova, E.V.; Gemo, A.T.; Zou, J.X.; Chen, H.W. Chromatin Loading of E2f-Mll Complex by Cancer-Associated Coregulator Ancca Via Reading a Specific Histone Mark. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 22, 5260–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, S.; Herr, W. E2f1 Mediates DNA Damage and Apoptosis through Hcf-1 and the Mll Family of Histone Methyltransferases. EMBO J. 2009, 20, 3185–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaret, K.S. Pioneering the Chromatin Landscape. Nat. Genet. 2018, 2, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Skalnik, D.G. Wdr82 Is a C-Terminal Domain-Binding Protein That Recruits the Setd1a Histone H3-Lys4 Methyltransferase Complex to Transcription Start Sites of Transcribed Human Genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 2, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Shibata, Y.; Rao, B.; Laribee, R.N.; O’Rourke, R.; Buck, M.J.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Krogan, N.J.; Lieb, J.D.; Strahl, B.D. The Rna Polymerase Ii Kinase Ctk1 Regulates Positioning of a 5′ Histone Methylation Boundary Along Genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 2, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, K.; Deb, S.; Moniaux, N.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Batra, S.K. Human Rna Polymerase Ii-Associated Factor Complex: Dysregulation in Cancer. Oncogene 2007, 54, 7499–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntean, A.G.; Tan, J.; Sitwala, K.; Huang, Y.; Bronstein, J.; Connelly, J.A.; Basrur, V.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Hess, J.L. The Paf Complex Synergizes with Mll Fusion Proteins at Hox Loci to Promote Leukemogenesis. Cancer Cell 2010, 6, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, L.M.; He, P.C.; Chun, Y.; Suh, H.; Kim, T.; Buratowski, S. Determinants of Histone H3k4 Methylation Patterns. Mol. Cell 2017, 4, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladopoulos, V.; Hofemeister, H.; Hoogenkamp, M.; Riggs, A.D.; Stewart, A.F.; Bonifer, C. The Histone Methyltransferase Kmt2b Is Required for Rna Polymerase Ii Association and Protection from DNA Methylation at the Magohb Cpg Island Promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 7, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z. Global and Cell-Type Specific Properties of Lincrnas with Ribosome Occupancy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 5, 2786–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, F.P.; Raimondi, I.; Huarte, M. The Multidimensional Mechanisms of Long Noncoding Rna Function. Genome Biol. 2017, 1, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonasio, R.; Shiekhattar, R. Regulation of Transcription by Long Noncoding Rnas. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2014, 48, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Dominguez, J.R.; Lodish, H.F. Emerging Mechanisms of Long Noncoding Rna Function During Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis. Blood 2017, 18, 1965–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding Rnas in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 4, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Caffrey, D.R. Long Noncoding Rnas in Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Youmans, D.T.; Cech, T.R. How Do Lncrnas Regulate Transcription? Sci. Adv. 2017, 9, eaao2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chedin, F. Nascent Connections: R-Loops and Chromatin Patterning. Trends Genet. 2016, 12, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Pereira, J.M.; Aguilera, A. R Loops: New Modulators of Genome Dynamics and Function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 10, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.C.; Yang, Y.W.; Liu, B.; Sanyal, A.; Corces-Zimmerman, R.; Chen, Y.; Lajoie, B.R.; Protacio, A.; Flynn, R.A.; Gupta, R.A.; et al. A Long Noncoding Rna Maintains Active Chromatin to Coordinate Homeotic Gene Expression. Nature 2011, 7341, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, R.; Gajula, R.P.; Williams, R.D.; Nghiem, B.; Simons, B.W.; Nugent, K.; Wang, H.; Taparra, K.; Lemtiri-Chlieh, G.; Yoon, A.R.; et al. Twist1-Wdr5-Hottip Regulates Hoxa9 Chromatin to Facilitate Prostate Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 12, 3181–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, M.G.; Jenner, R.G.; Chevalier, B.; Nakamura, T.; Croce, C.M.; Canaani, E.; Young, R.A. Global and Hox-Specific Roles for the Mll1 Methyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 24, 8603–8608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, S.; Ye, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Lncrna Hottip Modulates Cancer Stem Cell Properties in Human Pancreatic Cancer by Regulating Hoxa9. Cancer Lett. 2017, 410, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliata, L.; Matter, M.S.; Piscuoglio, S.; Arabi, L.; Ruiz, C.; Procino, A.; Kovac, M.; Moretti, F.; Makowska, Z.; Boldanova, T.; et al. Long Noncoding Rna Hottip/Hoxa13 Expression Is Associated with Disease Progression and Predicts Outcome in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Hepatology 2014, 3, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ye, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Song, Y.; Gao, W.; et al. The Long Non-Coding Rna Hottip Promotes Progression and Gemcitabine Resistance by Regulating Hoxa13 in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; Cai, Z.; Gong, H.; Xue, S.; Wu, D.; Wang, K. Hottip: A Critical Oncogenic Long Non-Coding Rna in Human Cancers. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 11, 3247–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cho, J.; Patel, B.; Terada, N.; Li, Y.Q.; Bungert, J.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, S.M. Hoxblinc Rna Recruits Set1/Mll Complexes to Activate Hox Gene Expression Patterns and Mesoderm Lineage Development. Cell Rep. 2016, 1, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, P.; Wittler, L.; Hendrix, D.; Koch, F.; Wahrisch, S.; Beisaw, A.; Macura, K.; Blass, G.; Kellis, M.; Werber, M.; et al. The Tissue-Specific Lncrna Fendrr Is an Essential Regulator of Heart and Body Wall Development in the Mouse. Dev. Cell 2013, 2, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Wen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lv, H.; Wang, G. Identification of Dysregulated Long Non-Coding Rnas/Micrornas/Mrnas in Tnm I Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 31, 51703–51718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.J.; Tang, R.X.; He, R.Q.; Li, D.Y.; Liang, L.; Zeng, J.H.; Hu, X.H.; Ma, J.; Li, S.K.; Chen, G. Clinical Roles of the Aberrantly Expressed Lncrnas in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Study Based on Rna-Sequencing and Microarray Data Mining. Oncotarget 2017, 37, 61282–61304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.P.; Huang, M.D.; Xia, R.; Liu, X.X.; Sun, M.; Yin, L.; Chen, W.M.; Han, L.; Zhang, E.B.; Kong, R.; et al. Decreased Expression of the Long Non-Coding Rna Fendrr Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Gastric Cancer and Fendrr Regulates Gastric Cancer Cell Metastasis by Affecting Fibronectin1 Expression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.M.; Guttman, M.; Huarte, M.; Garber, M.; Raj, A.; Morales, D.R.; Thomas, K.; Presser, A.; Bernstein, B.E.; van Oudenaarden, A.; et al. Many Human Large Intergenic Noncoding Rnas Associate with Chromatin-Modifying Complexes and Affect Gene Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 28, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.W.; Flynn, R.A.; Chen, Y.; Qu, K.; Wan, B.; Wang, K.C.; Lei, M.; Chang, H.Y. Essential Role of Lncrna Binding for Wdr5 Maintenance of Active Chromatin and Embryonic Stem Cell Pluripotency. eLife 2014, 3, e02046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Notani, D.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Enhancers as Non-Coding Rna Transcription Units: Recent Insights and Future Perspectives. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 4, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.; Lajoie, B.R.; Jain, G.; Dekker, J. The Long-Range Interaction Landscape of Gene Promoters. Nature 2012, 7414, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding Rna as Modular Scaffold of Histone Modification Complexes. Science 2010, 5992, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayou, C.; Millan-Zambrano, G.; Santos-Rosa, H.; Petfalski, E.; Robson, S.; Houseley, J.; Kouzarides, T.; Tollervey, D. Rna Binding by Histone Methyltransferases Set1 and Set2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00165-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.K.; Blackledge, N.P.; Klose, R.J. Zf-Cxxc Domain-Containing Proteins, Cpg Islands and the Chromatin Connection. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 3, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaton, A.M.; Bird, A. Cpg Islands and the Regulation of Transcription. Genes Dev. 2011, 10, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Cancer Epigenomics: DNA Methylomes and Histone-Modification Maps. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 4, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birke, M.; Schreiner, S.; Garcia-Cuellar, M.P.; Mahr, K.; Titgemeyer, F.; Slany, R.K. The Mt Domain of the Proto-Oncoprotein Mll Binds to Cpg-Containing DNA and Discriminates against Methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 4, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayton, P.M.; Chen, E.H.; Cleary, M.L. Binding to Nonmethylated Cpg DNA Is Essential for Target Recognition, Transactivation, and Myeloid Transformation by an Mll Oncoprotein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 23, 10470–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cierpicki, T.; Risner, L.E.; Grembecka, J.; Lukasik, S.M.; Popovic, R.; Omonkowska, M.; Shultis, D.D.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J.; Bushweller, J.H. Structure of the Mll Cxxc Domain-DNA Complex and Its Functional Role in Mll-Af9 Leukemia. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 1, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Gao, X.; Cao, K.; Morgan, M.A.; Mas, G.; Smith, E.R.; Volk, A.G.; Bartom, E.T.; Crispino, J.D.; di Croce, L.; et al. Not All H3k4 Methylations Are Created Equal: Mll2/Compass Dependency in Primordial Germ Cell Specification. Mol. Cell 2017, 3, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfurth, F.E.; Popovic, R.; Grembecka, J.; Cierpicki, T.; Theisler, C.; Xia, Z.B.; Stuart, T.; Diaz, M.O.; Bushweller, J.H.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J. Mll Protects Cpg Clusters from Methylation within the Hoxa9 Gene, Maintaining Transcript Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 21, 7517–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, R.; Beckerbauer, L. Hmgi/Y Proteins: Flexible Regulators of Transcription and Chromatin Structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1519, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benecke, A.G.; Eilebrecht, S. Rna-Mediated Regulation of Hmga1 Function. Biomolecules 2015, 2, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, M. Revised Nomenclature for High Mobility Group (Hmg) Chromosomal Proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 3, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, L.; Landsman, D. At-Hook Motifs Identified in a Wide Variety of DNA-Binding Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 19, 4413–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, J.R.; Bewley, C.A.; Nissen, M.S.; Evans, J.N.; Reeves, R.; Gronenborn, A.M.; Clore, G.M. The Solution Structure of an Hmg-I(Y)-DNA Complex Defines a New Architectural Minor Groove Binding Motif. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 8, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazda, V.; Laister, R.C.; Jagelska, E.B.; Arrowsmith, C. Cruciform Structures Are a Common DNA Feature Important for Regulating Biological Processes. BMC Mol. Biol. 2011, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham, H.E.; Thurman, R.E.; Fu, Y.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Noble, W.S.; Struhl, K.; Weng, Z. Nucleosome Positioning Signals in Genomic DNA. Genome Res. 2007, 8, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosschedl, R.; Giese, K.; Pagel, J. Hmg Domain Proteins: Architectural Elements in the Assembly of Nucleoprotein Structures. Trends Genet. 1994, 3, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvan, S.; Avdic, V.; Tremblay, V.; Chaturvedi, C.P.; Zhang, P.; Lanouette, S.; Blais, A.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Brand, M.; Couture, J.F. Crystal Structure of the Trithorax Group Protein Ash2l Reveals a Forkhead-Like DNA Binding Domain. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 7, 857–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wan, B.; Wang, K.C.; Cao, F.; Yang, Y.; Protacio, A.; Dou, Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Lei, M. Crystal Structure of the N-Terminal Region of Human Ash2l Shows a Winged-Helix Motif Involved in DNA Binding. EMBO Rep. 2011, 8, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Liang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; He, Q.; Yang, D.; Chen, R.; Liu, D.; et al. The Trithorax Group Protein Ash2l Is Essential for Pluripotency and Maintaining Open Chromatin in Embryonic Stem Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 7, 5039–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margueron, R.; Reinberg, D. The Polycomb Complex Prc2 and Its Mark in Life. Nature 2011, 7330, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turker, M.S. Gene Silencing in Mammalian Cells and the Spread of DNA Methylation. Oncogene 2002, 35, 5388–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, A. DNA Methylation Patterns and Epigenetic Memory. Genes Dev. 2002, 1, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, R.; Zhou, M.M. The Phd Finger: A Versatile Epigenome Reader. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 7, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, K.; Jeon, J.; Park, K.; Kim, J. Writing, Erasing and Reading Histone Lysine Methylations. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 4, e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, M.; Wu, J.; Workman, J.L.; Li, B. Readers of Histone Modifications. Cell Res. 2011, 4, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, S.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kan, P.Y.; Voigt, P.; Ma, L.; Shi, X.; Reinberg, D.; Lee, M.G. Trans-Tail Regulation of Mll4-Catalyzed H3k4 Methylation by H4r3 Symmetric Dimethylation Is Mediated by a Tandem Phd of Mll4. Genes Dev. 2012, 24, 2749–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fair, K.; Anderson, M.; Bulanova, E.; Mi, H.; Tropschug, M.; Diaz, M.O. Protein Interactions of the Mll Phd Fingers Modulate Mll Target Gene Regulation in Human Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 10, 3589–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Muntean, A.G.; Wu, L.; Hess, J.L. A Subset of Mixed Lineage Leukemia Proteins Has Plant Homeodomain (Phd)-Mediated E3 Ligase Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 52, 43410–43416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slany, R.K. The Molecular Mechanics of Mixed Lineage Leukemia. Oncogene 2016, 40, 5215–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntean, A.G.; Giannola, D.; Udager, A.M.; Hess, J.L. The Phd Fingers of Mll Block Mll Fusion Protein-Mediated Transformation. Blood 2008, 12, 4690–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Santillan, D.A.; Koonce, M.; Wei, W.; Luo, R.; Thirman, M.J.; Zeleznik-Le, N.J.; Diaz, M.O. Loss of Mll Phd Finger 3 Is Necessary for Mll-Enl-Induced Hematopoietic Stem Cell Immortalization. Cancer Res. 2008, 15, 6199–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Osmers, U.; Raman, G.; Schwantes, R.H.; Diaz, M.O.; Bushweller, J.H. The Phd3 Domain of Mll Acts as a Cyp33-Regulated Switch between Mll-Mediated Activation and Repression. Biochemistry 2010, 31, 6576–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberl, H.C.; Spruijt, C.G.; Kelstrup, C.D.; Vermeulen, M.; Mann, M. A Map of General and Specialized Chromatin Readers in Mouse Tissues Generated by Label-Free Interaction Proteomics. Mol. Cell 2013, 2, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, J.P.; Skene, P.J.; Selfridge, J.; Clouaire, T.; Guy, J.; Webb, S.; Kerr, A.R.; Deaton, A.; Andrews, R.; James, K.D.; et al. Cpg Islands Influence Chromatin Structure Via the Cpg-Binding Protein Cfp1. Nature 2010, 7291, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdin, E.; Ott, M. 50 Years of Protein Acetylation: From Gene Regulation to Epigenetics, Metabolism and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 4, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rack, J.G.; Lutter, T.; Bjerga, G.E.K.; Guder, C.; Ehrhardt, C.; Varv, S.; Ziegler, M.; Aasland, R. The Phd Finger of P300 Influences Its Ability to Acetylate Histone and Non-Histone Targets. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 24, 3960–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, J.D.; Reshmi, S.; Sobulo, O.; Musvee, T.; Anastasi, J.; Raimondi, S.; Schneider, N.R.; Barredo, J.C.; Cantu, E.S.; Schlegelberger, B.; et al. All Patients with the T(11;16)(Q23;P13.3) That Involves Mll and Cbp Have Treatment-Related Hematologic Disorders. Blood 1997, 2, 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Ida, K.; Kitabayashi, I.; Taki, T.; Taniwaki, M.; Noro, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Ohki, M.; Hayashi, Y. Adenoviral E1a-Associated Protein P300 Is Involved in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with T(11;22)(Q23;Q13). Blood 1997, 12, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar]
- Sugita, K.; Taki, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Shimaoka, H.; Kumazaki, H.; Inoue, H.; Konno, Y.; Taniwaki, M.; Kurosawa, H.; Eguchi, M. Mll-Cbp Fusion Transcript in a Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia with the T(11;16)(Q23;P13) Which Developed in an Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patient with Fanconi Anemia. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2000, 3, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, T.; Pattenden, S.G.; Workman, J.L. Diverse Functions of Wd40 Repeat Proteins in Histone Recognition. Genes Dev. 2008, 10, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliori, V.; Mapelli, M.; Guccione, E. On Wd40 Proteins: Propelling Our Knowledge of Transcriptional Control? Epigenetics 2012, 8, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocka, J.; Swigut, T.; Milne, T.A.; Dou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Burlingame, A.L.; Roeder, R.G.; Brivanlou, A.H.; Allis, C.D. Wdr5 Associates with Histone H3 Methylated at K4 and Is Essential for H3 K4 Methylation and Vertebrate Development. Cell 2005, 6, 859–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guccione, E.; Bassi, C.; Casadio, F.; Martinato, F.; Cesaroni, M.; Schuchlautz, H.; Luscher, B.; Amati, B. Methylation of Histone H3r2 by Prmt6 and H3k4 by an Mll Complex Are Mutually Exclusive. Nature 2007, 7164, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Deng, X.W.; Chai, J. Structural Basis for the Specific Recognition of Methylated Histone H3 Lysine 4 by the Wd-40 Protein Wdr5. Mol. Cell 2006, 1, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, J.F.; Collazo, E.; Trievel, R.C. Molecular Recognition of Histone H3 by the Wd40 Protein Wdr5. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 8, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmarajan, V.; Lee, J.H.; Patel, A.; Skalnik, D.G.; Cosgrove, M.S. Structural Basis for Wdr5 Interaction (Win) Motif Recognition in Human Set1 Family Histone Methyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 33, 27275–27289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.C.; Matthews, A.G.; Jin, Y.; Chen, C.F.; Chapman, B.A.; Ohsumi, T.K.; Glass, K.C.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Borowsky, M.L.; Struhl, K.; et al. Histone H3r2 Symmetric Dimethylation and Histone H3k4 Trimethylation Are Tightly Correlated in Eukaryotic Genomes. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.; Zielinska, A.E.; Shaaban, A.M.; Sanchez-Bailon, M.P.; Jarrold, J.; Clarke, T.L.; Zhang, J.; Francis, A.; Jones, L.J.; Smith, S.; et al. Prmt5 is a Critical Regulator of Breast Cancer Stem Cell Function Via Histone Methylation and Foxp1 Expression. Cell Rep. 2017, 12, 3498–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Banerjee, T.; Vinckevicius, A.; Luo, Q.; Parker, J.B.; Baker, M.R.; Radhakrishnan, I.; Wei, J.J.; Barish, G.D.; Chakravarti, D. A Role for Wdr5 in Integrating Threonine 11 Phosphorylation to Lysine 4 Methylation on Histone H3 During Androgen Signaling and in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cell 2014, 4, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, A.J.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; Marsh, D.J. Histone H2b Monoubiquitination: Roles to Play in Human Malignancy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 1, T19–T33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, G.; Oren, M. Writing and Reading H2b Monoubiquitylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 8, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Pham, A.D.; Mandal, S.S.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Reinberg, D. Monoubiquitination of Human Histone H2b: The Factors Involved and Their Roles in Hox Gene Regulation. Mol. Cell 2005, 4, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shema, E.; Tirosh, I.; Aylon, Y.; Huang, J.; Ye, C.; Moskovits, N.; Raver-Shapira, N.; Minsky, N.; Pirngruber, J.; Tarcic, G.; et al. The Histone H2b-Specific Ubiquitin Ligase Rnf20/Hbre1 Acts as a Putative Tumor Suppressor through Selective Regulation of Gene Expression. Genes Dev. 2008, 19, 2664–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minsky, N.; Shema, E.; Field, Y.; Schuster, M.; Segal, E.; Oren, M. Monoubiquitinated H2b Is Associated with the Transcribed Region of Highly Expressed Genes in Human Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 4, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.K.; Heath, C.; Hair, A.; West, A.G. Histone Crosstalk Directed by H2b Ubiquitination Is Required for Chromatin Boundary Integrity. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batta, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yen, K.; Goffman, D.B.; Pugh, B.F. Genome-Wide Function of H2b Ubiquitylation in Promoter and Genic Regions. Genes Dev. 2011, 21, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Guermah, M.; McGinty, R.K.; Lee, J.S.; Tang, Z.; Milne, T.A.; Shilatifard, A.; Muir, T.W.; Roeder, R.G. Rad6-Mediated Transcription-Coupled H2b Ubiquitylation Directly Stimulates H3k4 Methylation in Human Cells. Cell 2009, 3, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Lee, S.Y.; Zhou, B.; Nguyen, U.T.; Muir, T.W.; Tan, S.; Dou, Y. Ash2l Regulates Ubiquitylation Signaling to Mll: Trans-Regulation of H3 K4 Methylation in Higher Eukaryotes. Mol. Cell 2013, 6, 1108–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vethantham, V.; Yang, Y.; Bowman, C.; Asp, P.; Lee, J.H.; Skalnik, D.G.; Dynlacht, B.D. Dynamic Loss of H2b Ubiquitylation without Corresponding Changes in H3k4 Trimethylation During Myogenic Differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 6, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Daniel, J.; Espejo, A.; Lake, A.; Krishna, M.; Xia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Bedford, M.T. Tudor, Mbt and Chromo Domains Gauge the Degree of Lysine Methylation. EMBO Rep. 2006, 4, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.A.J.; Rickels, R.A.; Collings, C.K.; He, X.; Cao, K.; Herz, H.M.; Cozzolino, K.A.; Abshiru, N.A.; Marshall, S.A.; Rendleman, E.J.; et al. A Cryptic Tudor Domain Links Brwd2/Phip to Compass-Mediated Histone H3k4 Methylation. Genes Dev. 2017, 19, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.J.; Wang, Z. Readout of Epigenetic Modifications. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 81–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, M.; Mulder, K.W.; Denissov, S.; Pijnappel, W.W.; van Schaik, F.M.; Varier, R.A.; Baltissen, M.P.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Mann, M.; Timmers, H.T. Selective Anchoring of Tfiid to Nucleosomes by Trimethylation of Histone H3 Lysine 4. Cell 2007, 1, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales, E.; Patel, A.B.; Louder, R.K. Towards a Mechanistic Understanding of Core Promoter Recognition from Cryo-Em Studies of Human Tfiid. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 47, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R. Tbp-Associated Factors (Tafiis): Multiple, Selective Transcriptional Mediators in Common Complexes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 2, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ingen, H.; van Schaik, F.M.; Wienk, H.; Ballering, J.; Rehmann, H.; Dechesne, A.C.; Kruijzer, J.A.; Liskamp, R.M.; Timmers, H.T.; Boelens, R. Structural Insight into the Recognition of the H3k4me3 Mark by the Tfiid Subunit Taf3. Structure 2008, 8, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocka, J.; Swigut, T.; Xiao, H.; Milne, T.A.; Kwon, S.Y.; Landry, J.; Kauer, M.; Tackett, A.J.; Chait, B.T.; Badenhorst, P.; et al. A Phd Finger of Nurf Couples Histone H3 Lysine 4 Trimethylation with Chromatin Remodelling. Nature 2006, 7098, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhatib, S.G.; Landry, J.W. The Nucleosome Remodeling Factor. FEBS Lett. 2011, 20, 3197–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallen, G.; Riabowol, K. Keep-Ing Balance: Tumor Suppression by Epigenetic Regulation. FEBS Lett. 2014, 16, 2728–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, K.S.; Saksouk, N.; Pena, P.V.; Johnson, K.; Ullah, M.; Yang, X.J.; Cote, J.; Kutateladze, T.G. The Crystal Structure of the Ing5 Phd Finger in Complex with an H3k4me3 Histone Peptide. Proteins 2008, 4, 1371–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, P.V.; Davrazou, F.; Shi, X.; Walter, K.L.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Gozani, O.; Zhao, R.; Kutateladze, T.G. Molecular Mechanism of Histone H3k4me3 Recognition by Plant Homeodomain of Ing2. Nature 2006, 7098, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Hong, T.; Walter, K.L.; Ewalt, M.; Michishita, E.; Hung, T.; Carney, D.; Pena, P.; Lan, F.; Kaadige, M.R.; et al. Ing2 Phd Domain Links Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methylation to Active Gene Repression. Nature 2006, 7098, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyon, Y.; Cayrou, C.; Ullah, M.; Landry, A.J.; Cote, V.; Selleck, W.; Lane, W.S.; Tan, S.; Yang, X.J.; Cote, J. Ing Tumor Suppressor Proteins Are Critical Regulators of Chromatin Acetylation Required for Genome Expression and Perpetuation. Mol. Cell 2006, 1, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, A.; Moreno, A.; Oliveira, B.L.; Rivera, T.; Prieto, J.; Garcia, P.; Fernandez-Fernandez, M.R.; Bernado, P.; Palmero, I.; Blanco, F.J. The Dimeric Structure and the Bivalent Recognition of H3k4me3 by the Tumor Suppressor Ing4 Suggests a Mechanism for Enhanced Targeting of the Hbo1 Complex to Chromatin. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 4, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinkley, S.; Staege, H.; Mohrmann, G.; Rohaly, G.; Schaub, T.; Kremmer, E.; Winterpacht, A.; Will, H. Spoc1: A Novel Phd-Containing Protein Modulating Chromatin Structure and Mitotic Chromosome Condensation. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2946–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordlein, A.; Scherthan, H.; Nelkenbrecher, C.; Molter, T.; Bosl, M.R.; Dippold, C.; Birke, K.; Kinkley, S.; Staege, H.; Will, H.; et al. Spoc1 (Phf13) Is Required for Spermatogonial Stem Cell Differentiation and Sustained Spermatogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.R.; Xu, C.; Fuchs, A.; Mund, A.; Lange, M.; Staege, H.; Schubert, T.; Bian, C.; Dunkel, I.; Eberharter, A.; et al. Phf13 Is a Molecular Reader and Transcriptional Co-Regulator of H3k4me2/3. eLife 2016, 5, e10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, T.K.; Imhof, A. Fast Signals and Slow Marks: The Dynamics of Histone Modifications. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2010, 11, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Higgins, J.M. Histone Modifications and Mitosis: Countermarks, Landmarks, and Bookmarks. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 4, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oomen, M.E.; Dekker, J. Epigenetic Characteristics of the Mitotic Chromosome in 1d and 3d. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 2, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blobel, G.A.; Kadauke, S.; Wang, E.; Lau, A.W.; Zuber, J.; Chou, M.M.; Vakoc, C.R. A Reconfigured Pattern of Mll Occupancy within Mitotic Chromatin Promotes Rapid Transcriptional Reactivation Following Mitotic Exit. Mol. Cell 2009, 6, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palozola, K.C.; Donahue, G.; Liu, H.; Grant, G.R.; Becker, J.S.; Cote, A.; Yu, H.; Raj, A.; Zaret, K.S. Mitotic Transcription and Waves of Gene Reactivation During Mitotic Exit. Science 2017, 6359, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festuccia, N.; Gonzalez, I.; Owens, N.; Navarro, P. Mitotic Bookmarking in Development and Stem Cells. Development 2017, 20, 3633–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellhaus, A.K.; de Magistris, P.; Antonin, W. Nuclear Reformation at the End of Mitosis. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 1962–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raccaud, M.; Suter, D.M. Transcription Factor Retention on Mitotic Chromosomes: Regulatory Mechanisms and Impact on Cell Fate Decisions. FEBS Lett. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatchalian, J.; Gallardo, C.M.; Shinsky, S.A.; Ospina, R.R.; Liendo, A.M.; Krajewski, K.; Klein, B.J.; Andrews, F.H.; Strahl, B.D.; van Wely, M.; et al. Chromatin Condensation and Recruitment of Phd Finger Proteins to Histone H3k4me3 Are Mutually Exclusive. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 13, 6102–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Rincon-Arano, H.; Zhao, W.; Rothbart, S.B.; Tong, Q.; Parkhurst, S.M.; Strahl, B.D.; Deng, L.W.; Groudine, M.; Kutateladze, T.G. Molecular Basis for Chromatin Binding and Regulation of Mll5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 28, 11296–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Dai, J.; Daum, J.R.; Niedzialkowska, E.; Banerjee, B.; Stukenberg, P.T.; Gorbsky, G.J.; Higgins, J.M. Histone H3 Thr-3 Phosphorylation by Haspin Positions Aurora B at Centromeres in Mitosis. Science 2010, 6001, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varier, R.A.; Outchkourov, N.S.; de Graaf, P.; van Schaik, F.M.; Ensing, H.J.; Wang, F.; Higgins, J.M.; Kops, G.J.; Timmers, H.T. A Phospho/Methyl Switch at Histone H3 Regulates Tfiid Association with Mitotic Chromosomes. EMBO J. 2010, 23, 3967–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Yuan, Z.F.; Han, Y.; Marchione, D.M.; Garcia, B.A. Preferential Phosphorylation on Old Histones During Early Mitosis in Human Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 29, 15342–15357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
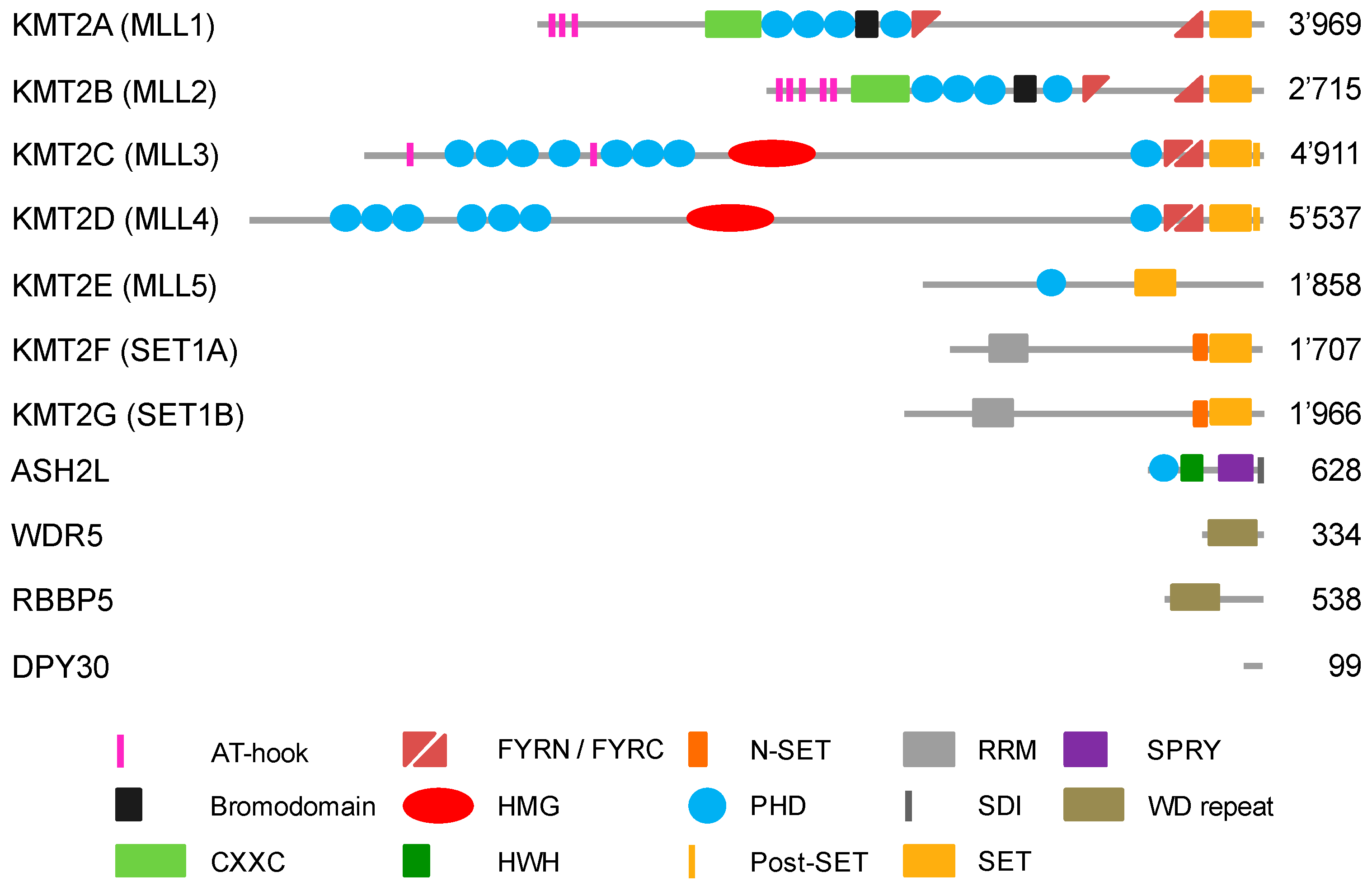
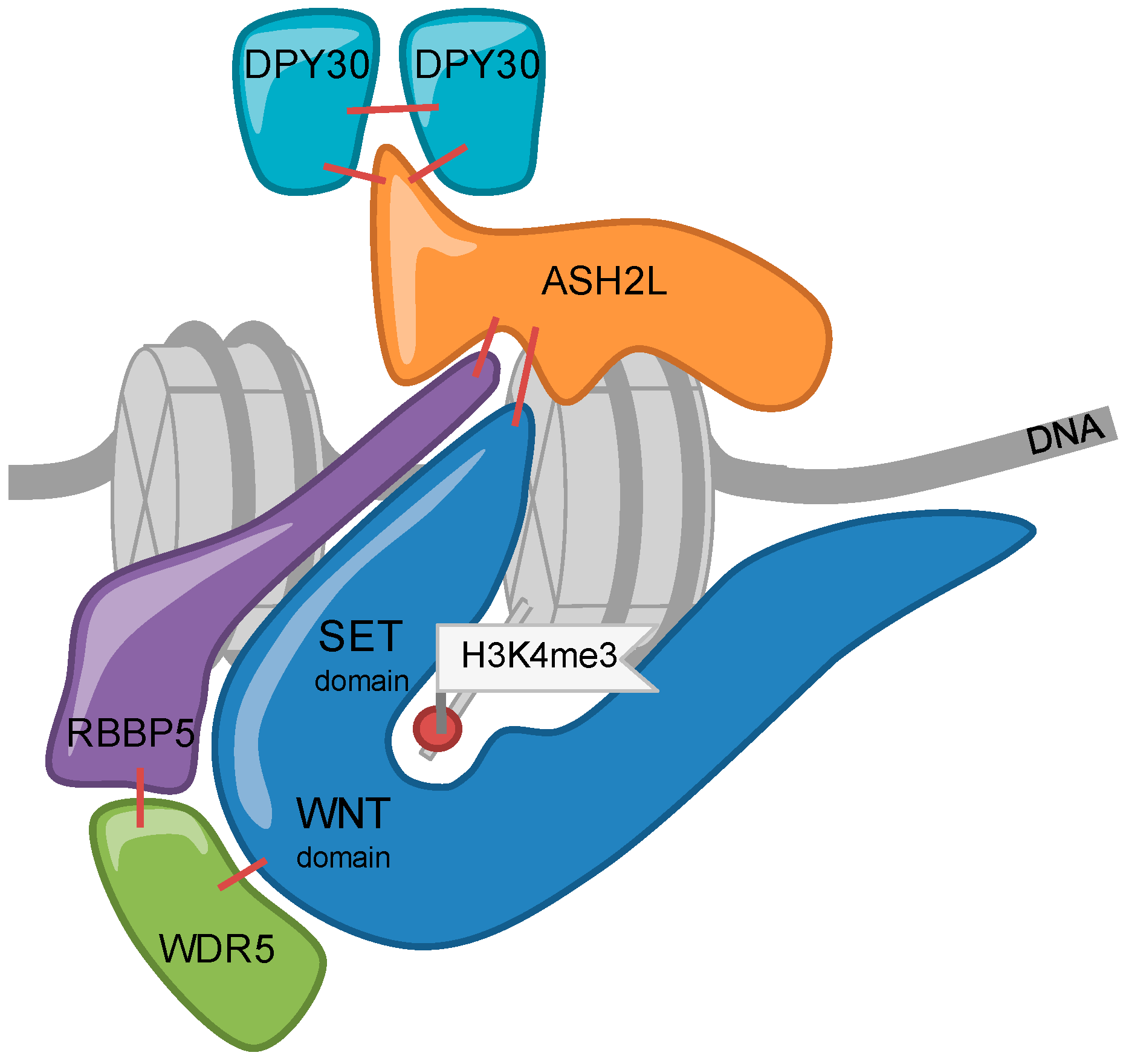
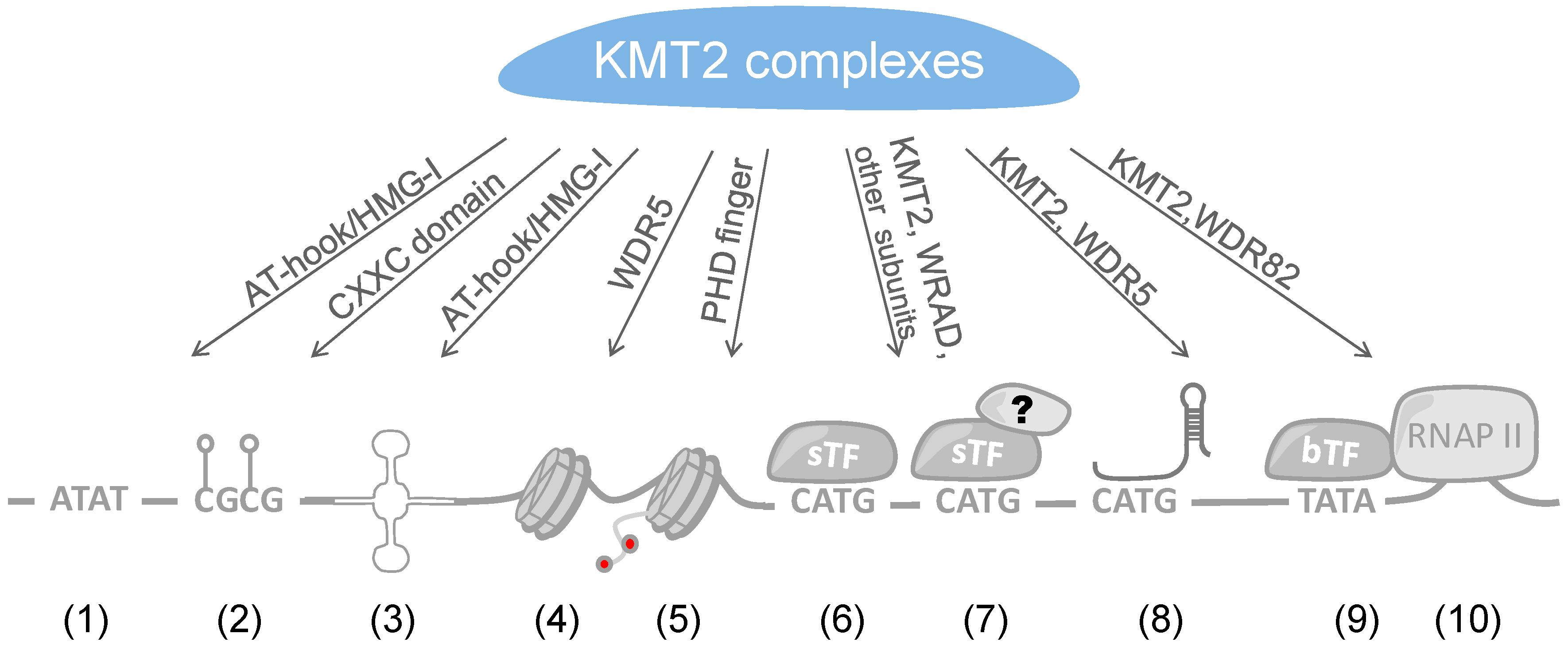
| Writers Able to Methylate H3K4 (Gene ID) | Me1 | Me2 | Me3 | Erasers Able to De-Methylate H3K4 (Gene ID) [39] | Me1 | Me2 | Me3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLL1 (KMT2A) (#4297) | [40] * | [41] | LSD1(KDM1A) (#23028) | |||||||
| MLL2 (KMT2B) (#9757) | [40] | [42] | LSD2 (KDM1B) (#221656) | |||||||
| MLL3 (KMT2C) (#58508) | [40] | [43] | JHDM1B (KDM2B) (#84678) | |||||||
| MLL4 (KMT2D) (#8085) | [40] | [44] | JARID1A (KDM5A) (#5927) | |||||||
| SET1A (KMT2F) (#9739) | [40] | [45] | JARID1B (KDM5B) (#10765) | |||||||
| SET1B (KMT2G) (#23067) | [40] | [45] | JARID1C (KDM5C) (#8242) | |||||||
| PRDM9 (Meisetz) (#56979) | [34] | [34] | JARID1D (KDM5D) (#8284) | |||||||
| SET7/9 (KMT7) (#80854) | [46,47] | |||||||||
| SMYD3 (KMT3E) (#64754) | [46] | [48] | ||||||||
| SMYD1/2 (#150572/56950) | [49] | |||||||||
| Transcription Factor | References |
|---|---|
| OCT4 | [140,141] |
| ANCCA/ATAD2 | [175,178,179] |
| Ap2delta | [152,153] |
| c-MYB | [170] |
| E2F | [175,176] |
| ERα | [164] |
| FOXA1 | [173] |
| FXR | [158] |
| MAFA and B | [159] |
| Mef2d | [140] |
| MYC/MAX | [143,144] |
| NANOG | [140] |
| NF-Y | [149] |
| NF-E2 | [150,151] |
| p53 | [160] |
| Pax2 and Pax5 | [50,68,69,155,156] |
| Pax7 | [148,173] |
| PRMT4 | [146,147] |
| SOX2 | [140,141] |
| USF1 | [81] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochyńska, A.; Lüscher-Firzlaff, J.; Lüscher, B. Modes of Interaction of KMT2 Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferase/COMPASS Complexes with Chromatin. Cells 2018, 7, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7030017
Bochyńska A, Lüscher-Firzlaff J, Lüscher B. Modes of Interaction of KMT2 Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferase/COMPASS Complexes with Chromatin. Cells. 2018; 7(3):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7030017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochyńska, Agnieszka, Juliane Lüscher-Firzlaff, and Bernhard Lüscher. 2018. "Modes of Interaction of KMT2 Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferase/COMPASS Complexes with Chromatin" Cells 7, no. 3: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7030017
APA StyleBochyńska, A., Lüscher-Firzlaff, J., & Lüscher, B. (2018). Modes of Interaction of KMT2 Histone H3 Lysine 4 Methyltransferase/COMPASS Complexes with Chromatin. Cells, 7(3), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7030017





