Toll-like Receptors in Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children: Diagnostic Potential and Therapeutic Frontiers—A Review of the Latest Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
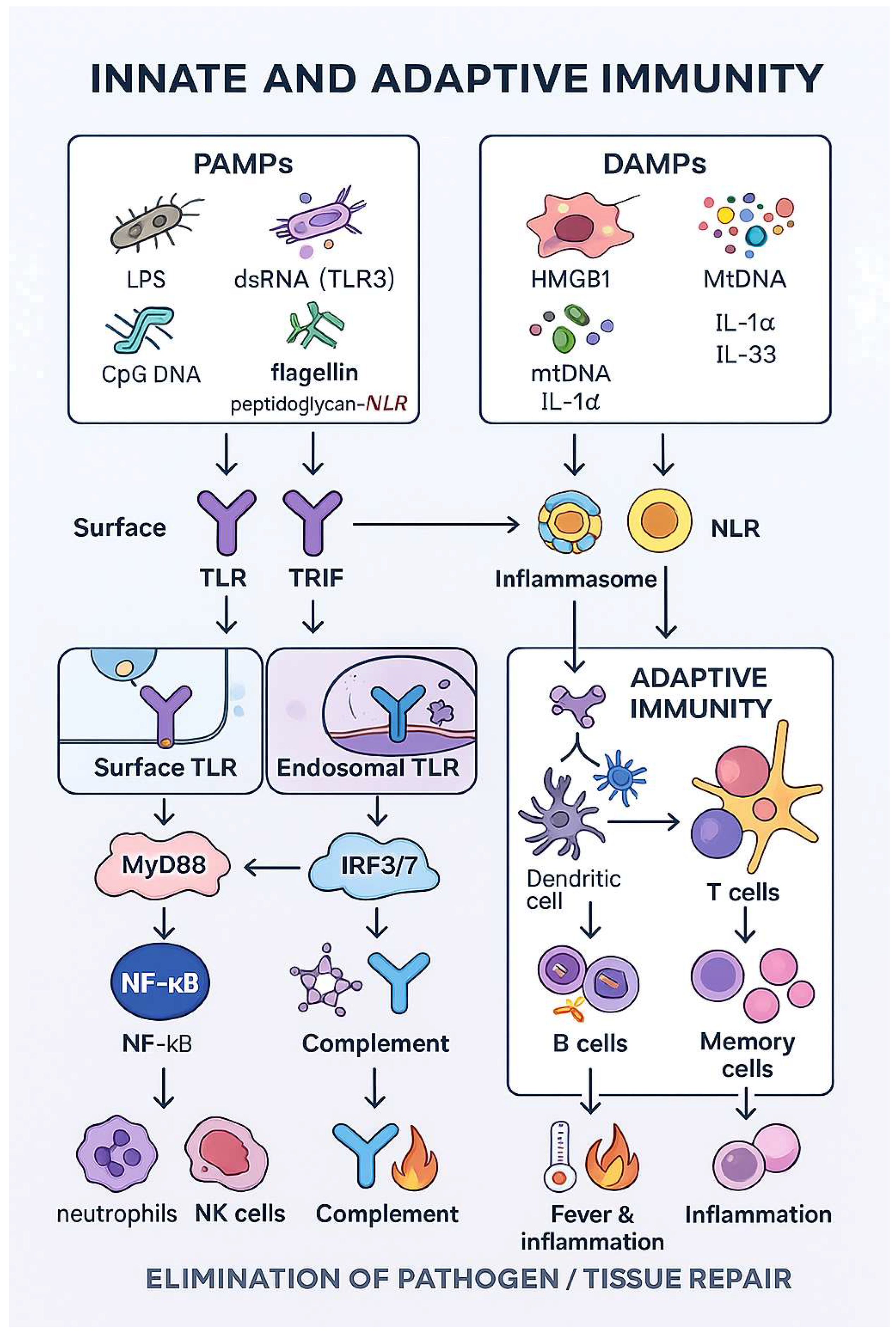
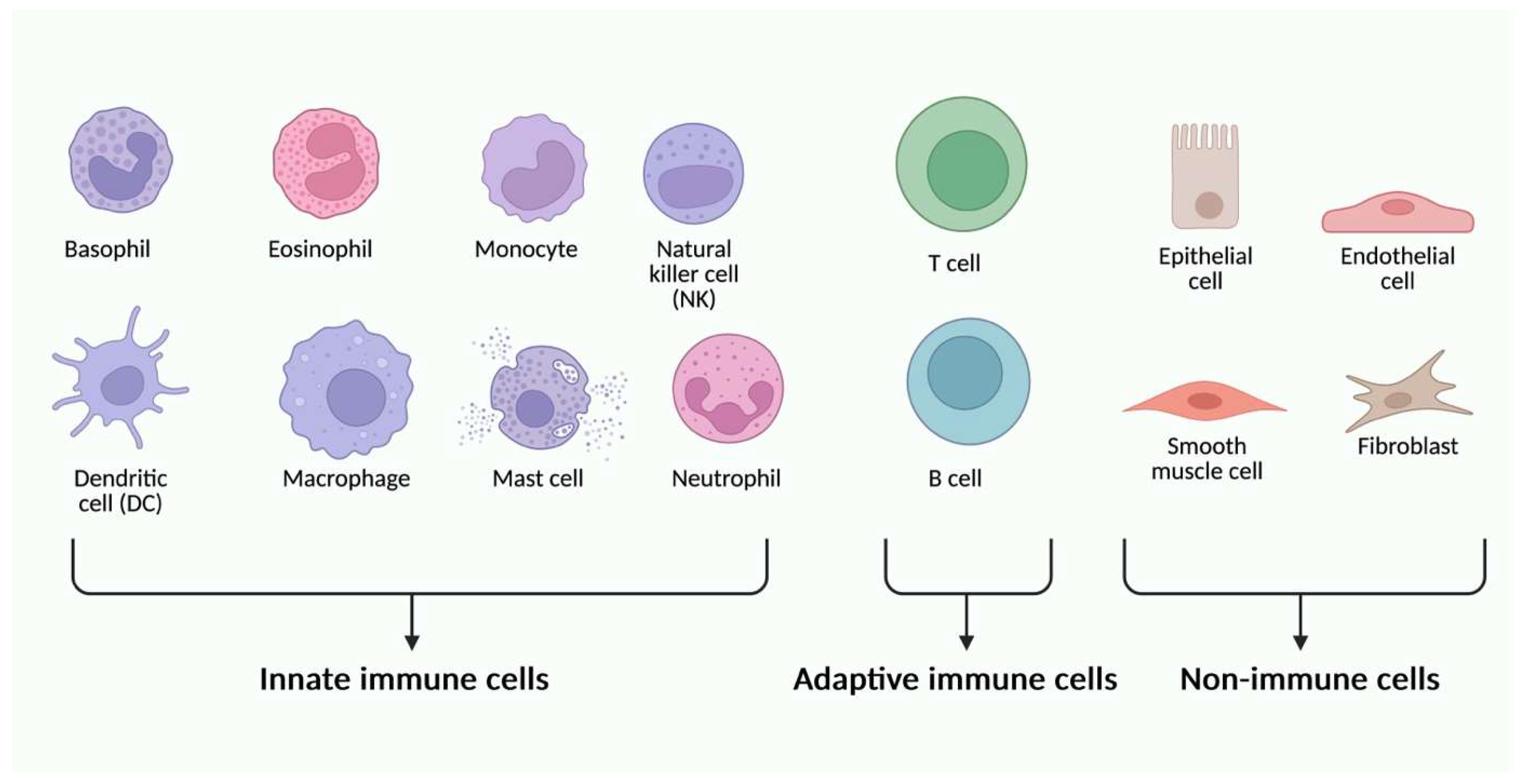
2. Mechanisms of Pathogen Recognition by the Immune System
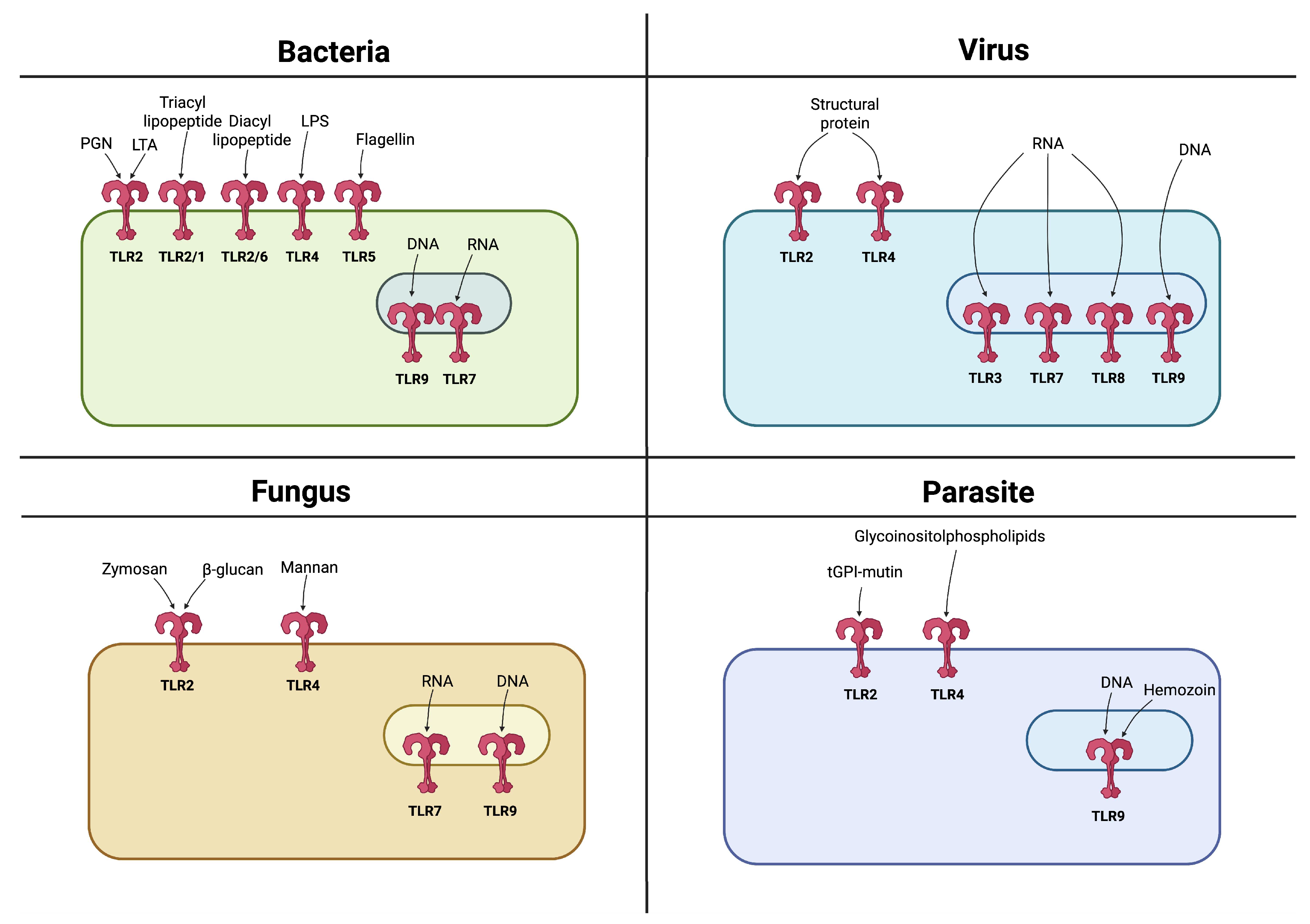
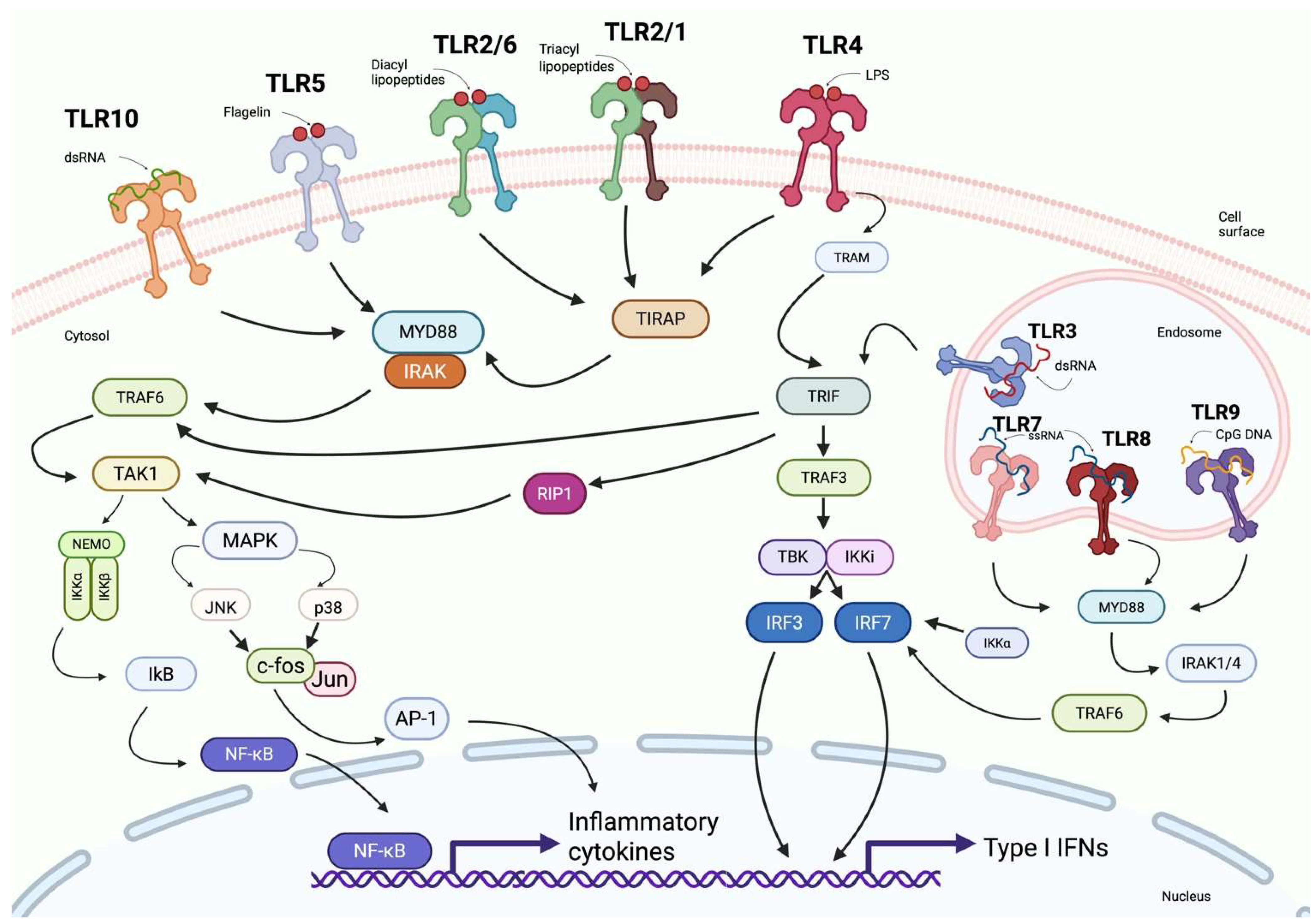
3. Toll-like Receptors
3.1. Types of Toll-like Receptors
3.2. TLRs Signaling Pathways
4. Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children
4.1. Dysfunction of TLR Signaling Pathways in IEIs
4.1.1. Genetic Defects Directly Affecting TLR Signaling Pathways
4.1.2. IEIs in Which TLRs Act as Modulators or Are Indirectly Involved
4.2. Epidemiology of TLR-Related Inborn Errors of Immunity
5. The Role of TLRs in the Diagnosis of IEIs
5.1. Functional Screening Tests for TLRs
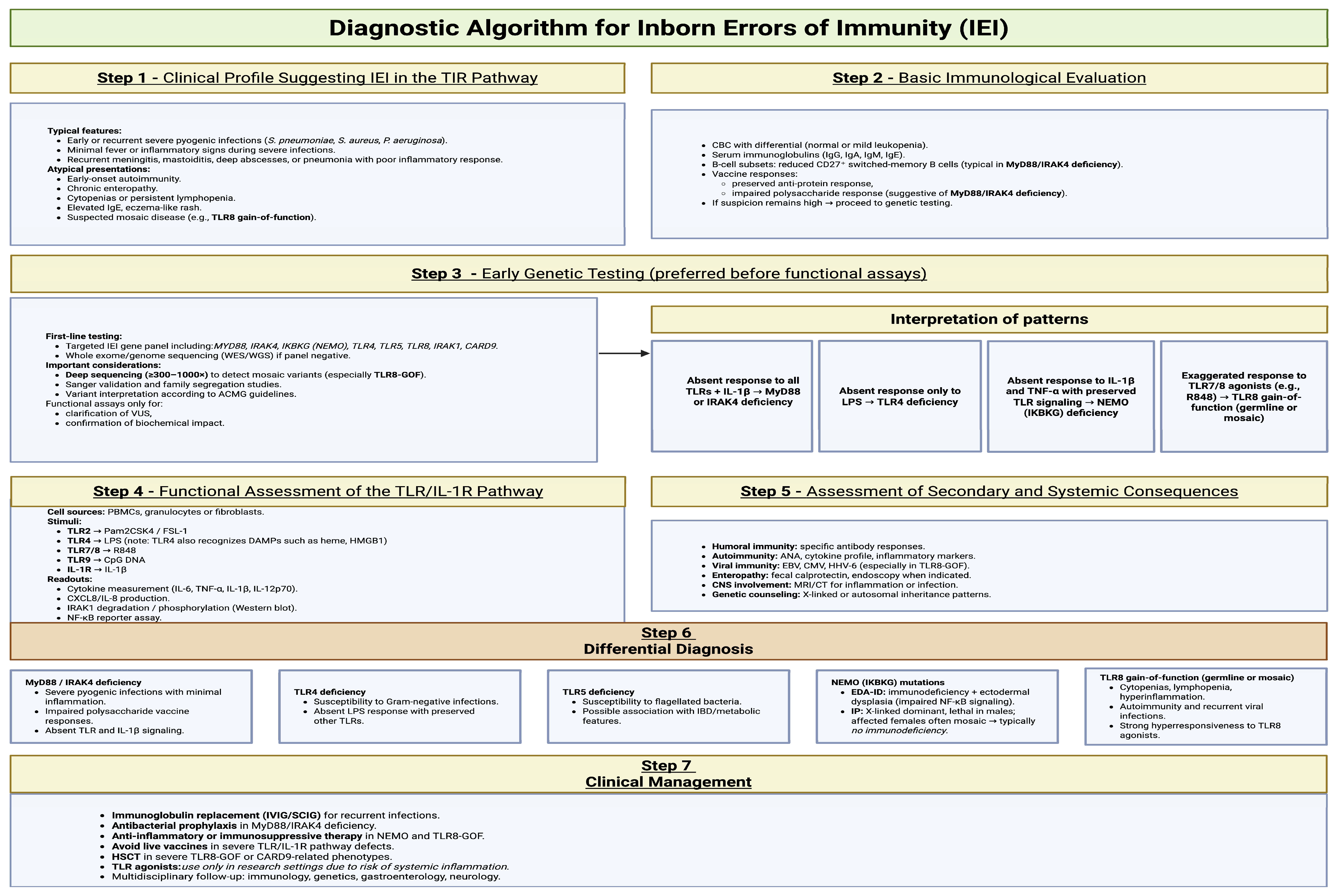
5.2. Proposed Diagnostic Algorithm
| Immunodeficiency/Syndrome | Associated Genetic Defects | Typical Age of Onset | Pathogen Susceptibility/Main Clinical Features | Inheritance | TLR Functional Response | Diagnostic Tests (Functional and Genetic) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRAK-4/MyD88 deficiency | Mutations in IRAK4 or MYD88 | Early childhood (<2 years) | Recurrent invasive bacterial infections (S. pneumoniae, S. aureus), absence of fever despite severe infection [15]. | Autosomal recessive | Markedly reduced TNF-α and IL-6 production after stimulation with TLR ligands (2/1, 2/6, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9). | Functional assays: IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α production after TLR and IL-1β stimulation. Genetic testing: sequencing of IRAK4 and MYD88 [15]. |
| TLR3 deficiency | Mutations in TLR3, UNC93B1, TRIF | Childhood or adulthood | Recurrent viral encephalitis (HSV-1, VZV, EV-A71) [12]. | Autosomal dominant or recessive | Reduced type I IFN (IFN-α, IFN-β) production in response to poly(I:C). | Functional assays: type I IFN induction after poly(I:C) stimulation. Genetic testing: sequencing of TLR3, UNC93B1 [16]. |
| UNC93B1 deficiency | Mutations in UNC93B1 | Childhood/adulthood | Severe HSV-1 infection (HSE), susceptibility to VZV and other viruses. | Autosomal recessive | Absent type I IFN response after stimulation via TLR3, 7, 8, 9. | Functional assays: IFN-α/β after stimulation via endosomal TLRs (3, 7, 8, 9). Genetic testing: sequencing of UNC93B1 [191]. |
| TLR5 deficiency | Mutations in TLR5 | From childhood to adulthood | Increased susceptibility to Salmonella, P. aeruginosa; recurrent pneumonia; possible metabolic and autoimmune comorbidities. | Autosomal recessive | Decreased response to flagellin (TLR5 agonist). | Functional assays: response to flagellin. Genetic testing: sequencing of TLR5 [133]. |
| TLR7/TLR8 deficiency | Mutations in TLR7 or TLR8 | Early childhood | Severe viral infections (RNA viruses, SARS-tCoV-2) or autoimmune diseases (SLE, autoimmune cytopenias). | X-linked | Diminished or excessive type I IFN production upon TLR7/8 stimulation. | Functional assays: IFN-α/β after R848 stimulation. Genetic testing: sequencing of TLR7, TLR8 [192]. |
| X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) | Mutations in BTK | Infancy | Severe bacterial, viral, and fungal infections [12]. | X-linked | Impaired TLR2, TLR4 signaling; in some studies, enhanced responses via TLR4, 7/8, 9. | Functional assays: stimulation with TLR ligands. Genetic testing: sequencing of BTK [193]. |
| Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) | Often unknown mutations | Adolescence/adulthood | Recurrent bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract. | Various (often sporadic) | Impaired B-cell and pDC responses to TLR7/9 stimulation; reduced IFN-α secretion. | Functional assays: IL-6 and IFN-α production after TLR7/9 stimulation. Genetic panel sequencing [194]. |
| Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) | Mutations in NADPH oxidase complex genes [12]. | Childhood | Bacterial and fungal infections (especially Aspergillus); granuloma formation. | Autosomal recessive or X-linked | Reduced responses via TLR2, TLR4; enhanced responses via TLR5, TLR9. | Functional assays: cytokine production after TLR stimulation; ROS measurement. Genetic testing: sequencing of NADPH oxidase genes [195]. |
| NEMO syndrome (IKBKG) | Mutations in IKBKG | Infancy/early childhood | Severe bacterial, viral, and fungal infections; often ectodermal dysplasia with anhidrosis (EDA). | X-linked | Impaired NF-κB activation upon IL-1β and TNF-α stimulation. | Functional assays: IκBα degradation and NF-κB activation. Genetic testing: sequencing of IKBKG [196]. |
| TRIAP1 deficiency | Mutations in TRIAP1 | Not specified | Severe neutropenia, myelodysplastic syndrome. | Autosomal recessive | Not determined. | Genetic testing: sequencing of TRIAP1 [197]. |
6. Therapeutic Strategies Based on TLRs
6.1. TLR Agonists as Potential Adjuvants and Therapeutics
6.2. Gene Therapy and Other Treatment Approaches
6.3. Clinical Trials in Children
7. Knowledge Gaps and Future Perspectives
7.1. Unmet Research Needs
7.2. Development Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bousfiha, A.A.; Jeddane, L.; Moundir, A.; Poli, M.C.; Aksentijevich, I.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Hambleton, S.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Picard, C.; et al. The 2024 Update of IUIS Phenotypic Classification of Human Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Hum. Immun. 2025, 1, e20250002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, M.C.; Aksentijevich, I.; Bousfiha, A.A.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Hambleton, S.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Picard, C.; Puel, A.; Rezaei, N.; et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2024 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Hum. Immun. 2025, 1, e20250003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Frange, P.; Blanche, S.; Casanova, J.-L. Pathogenesis of Infections in HIV-Infected Individuals: Insights from Primary Immunodeficiencies. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 48, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seminario, G.; Gonzalez-Serrano, M.E.; Aranda, C.S.; Grumach, A.S.; Segundo, G.R.S.; Regairaz, L.; Cardona, A.A.; LASID Registry Group; Becerra, J.C.A.; Poli, C.; et al. The Latin American Society for Immunodeficiencies Registry. J. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 45, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaad, M.J.; Zainal, M.; Al-Herz, W. Frequency and Manifestations of Autoimmunity Among Children Registered in the Kuwait National Primary Immunodeficiency Registry. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mousa, H.; Barbouche, M.-R. Genetics of Inborn Errors of Immunity in Highly Consanguineous Middle Eastern and North African Populations. Semin. Immunol. 2023, 67, 101763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, Z.; Pappalardo, A.; Schwartz, A.; Antoon, J.W. Prevalence and Outcomes of Primary Immunodeficiency in Hospitalized Children in the United States. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1705–1710.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, H.M.; Musekwa, E.M.; Glashoff, R.H.; Esser, M.; Zunza, M.; Abraham, D.R.; Chapanduka, Z.C. Peripheral-Blood Cytopenia, an Early Indicator of Inborn Errors of Immunity. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.J.; Nino, G.; Sun, D.; Restrepo-Gualteros, S.; Sadreameli, S.C.; Fiorino, E.K.; Wu, E.; Vece, T.; Hagood, J.S.; Maglione, P.J.; et al. The Lung in Inborn Errors of Immunity: From Clinical Disease Patterns to Molecular Pathogenesis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiri, A.; Masetti, R.; Conti, F.; Tignanelli, A.; Turrini, E.; Bertolini, P.; Esposito, S.; Pession, A. Inborn Errors of Immunity and Cancer. Biology 2021, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.; Chua, G.T.; Mondragon, A.V.; Zhong, Y.; Nguyen-Ngoc-Quynh, L.; Imai, K.; Vignesh, P.; Suratannon, N.; Mao, H.; Lee, W.-I.; et al. Current Perspectives and Unmet Needs of Primary Immunodeficiency Care in Asia Pacific. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaati, N.; Grier, A.; Ochfeld, E.; McClory, S.; Heimall, J. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Primary Immunodeficiency. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2024, 45, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kagan, J.C. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, M. Pattern Recognition Receptors in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Wu, K.-H.; Wu, H.-P. Unraveling the Complexities of Toll-like Receptors: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Ikegawa, M.; Ori, D.; Akira, S. Decoding Toll-like Receptors: Recent Insights and Perspectives in Innate Immunity. Immunity 2024, 57, 649–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Control of Adaptive Immunity by the Innate Immune System. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla, F.A.; Oettgen, H.C. Adaptive Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S33–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A.; Medzhitov, R. Innate Immune Recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeway—Immunobiology—9th ed. 2017. Online Book Share. Available online: https://epage.pub/doc/janeway-immunobiology-9-ed-2017-y1752rvvxy (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Janeway, C.A. Approaching the Asymptote? Evolution and Revolution in Immunology. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1989, 54 Pt 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Chiang, C.; Gack, M.U. Endogenous Nucleic Acid Recognition by RIG-I-Like Receptors and cGAS. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKernan, D.P. Pattern Recognition Receptors as Potential Drug Targets in Inflammatory Disorders. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2020, 119, 65–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Ding, S. Regulation of cGAS/STING Signaling and Corresponding Immune Escape Strategies of Viruses. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 954581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, C.; Hudson, K.L.; Anderson, K.V. The Toll Gene of Drosophila, Required for Dorsal-Ventral Embryonic Polarity, Appears to Encode a Transmembrane Protein. Cell 1988, 52, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, B.; Nicolas, E.; Michaut, L.; Reichhart, J.-M.; Hoffmann, J.A. The Dorsoventral Regulatory Gene Cassette Spätzle/Toll/Cactus Controls the Potent Antifungal Response in Drosophila Adults. Cell 1996, 86, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, S.; Beyaert, R. Role of Toll-like Receptors in Pathogen Recognition. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzówka, M.; Bagrowska, W.; Góra, A. Recent Advances in Studying Toll-like Receptors with the Use of Computational Methods. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 3669–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Yin, H.; Wang, X. Small-Molecule Modulators of Toll-like Receptors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, P.; García-Perdomo, H.A.; Karpiński, T.M. Toll-Like Receptors: General Molecular and Structural Biology. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9914854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zayat, S.R.; Sibaii, H.; Mannaa, F.A. Toll-like Receptors Activation, Signaling, and Targeting: An Overview. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The Role of Pattern-Recognition Receptors in Innate Immunity: Update on Toll-like Receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Dong, G. The Synergism of PGN, LTA and LPS in Inducing Transcriptome Changes, Inflammatory Responses and a Decrease in Lactation as Well as the Associated Epigenetic Mechanisms in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2020, 12, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Brinkmann, M.M.; Paquet, M.-E.; Ploegh, H.L. UNC93B1 Delivers Nucleotide-Sensing Toll-like Receptors to Endolysosomes. Nature 2008, 452, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabeta, K.; Hoebe, K.; Janssen, E.M.; Du, X.; Georgel, P.; Crozat, K.; Mudd, S.; Mann, N.; Sovath, S.; Goode, J.; et al. The Unc93b1 Mutation 3d Disrupts Exogenous Antigen Presentation and Signaling via Toll-like Receptors 3, 7 and 9. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Du, Y.; Xing, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, R.-F. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling and Its Role in Cell-Mediated Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Latz, E.; Mills, K.H.G.; Natoli, G.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; O’Neill, L.A.J.; Xavier, R.J. Trained Immunity: A Program of Innate Immune Memory in Health and Disease. Science 2016, 352, aaf1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like Receptor Signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.; Janssens, S.; Brissoni, B.; Olivos, N.; Beyaert, R.; Tschopp, J. Inhibition of Interleukin 1 Receptor/Toll-like Receptor Signaling through the Alternatively Spliced, Short Form of MyD88 Is Due to Its Failure to Recruit IRAK-4. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, N.J.; O’Neill, L.A. Mal, More than a Bridge to MyD88. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goligorsky, M.S. TLR4 and HMGB1: Partners in Crime? Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmich, N.N.; Sivak, K.V.; Chubarev, V.N.; Porozov, Y.B.; Savateeva-Lyubimova, T.N.; Peri, F. TLR4 Signaling Pathway Modulators as Potential Therapeutics in Inflammation and Sepsis. Vaccines 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, C.E.; Symmons, M.; Gay, N.J. Toll-like Receptor Signalling through Macromolecular Protein Complexes. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettrick, A.F.; Brint, E.K.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Rowe, D.C.; Golenbock, D.T.; Gay, N.J.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; O’Neill, L.A.J. Trif-Related Adapter Molecule Is Phosphorylated by PKC{epsilon} during Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9196–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, S.; Bowie, A.G. The Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinases: Critical Regulators of Innate Immune Signalling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.-C.; Xu, W.-D.; Huang, A.-F. IRAK Family in Inflammatory Autoimmune Diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkov, E.; Stamp, A.; Dimaio, F.; Baker, D.; Verstak, B.; Roversi, P.; Kellie, S.; Sweet, M.J.; Mansell, A.; Gay, N.J.; et al. Crystal Structure of Toll-like Receptor Adaptor MAL/TIRAP Reveals the Molecular Basis for Signal Transduction and Disease Protection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14879–14884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-C.; Lo, Y.-C.; Wu, H. Helical Assembly in the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 Complex in TLR/IL-1R Signalling. Nature 2010, 465, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motshwene, P.G.; Moncrieffe, M.C.; Grossmann, J.G.; Kao, C.; Ayaluru, M.; Sandercock, A.M.; Robinson, C.V.; Latz, E.; Gay, N.J. An Oligomeric Signaling Platform Formed by the Toll-like Receptor Signal Transducers MyD88 and IRAK-4. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25404–25411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Qiao, Q.; Ferrao, R.; Shen, C.; Hatcher, J.M.; Buhrlage, S.J.; Gray, N.S.; Wu, H. Crystal Structure of Human IRAK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13507–13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagoe, T.; Sato, S.; Matsushita, K.; Kato, H.; Matsui, K.; Kumagai, Y.; Saitoh, T.; Kawai, T.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Sequential Control of Toll-like Receptor-Dependent Responses by IRAK1 and IRAK2. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziczak-Holbro, M.; Joyce, C.; Glück, A.; Kinzel, B.; Müller, M.; Tschopp, C.; Mathison, J.C.; Davis, C.N.; Gram, H. IRAK-4 Kinase Activity Is Required for Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Receptor- and Toll-like Receptor 7-Mediated Signaling and Gene Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13552–13560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lye, E.; Mirtsos, C.; Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, S.; Yeh, W.-C. The Role of Interleukin 1 Receptor-Associated Kinase-4 (IRAK-4) Kinase Activity in IRAK-4-Mediated Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40653–40658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Commane, M.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Li, X. IRAK-Mediated Translocation of TRAF6 and TAB2 in the Interleukin-1-Induced Activation of NFkappa B. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41661–41667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, A.; Carpenter, S.; Brikos, C.; Gray, P.; Strelow, A.; Wesche, H.; Morrice, N.; O’Neill, L.A.J. IRAK1 and IRAK4 Promote Phosphorylation, Ubiquitination, and Degradation of MyD88 Adaptor-like (Mal). J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18276–18282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Bowie, A.G.; Jefferies, C.A.; Mansell, A.S.; Brady, G.; Brint, E.; Dunne, A.; Gray, P.; Harte, M.T.; et al. Mal (MyD88-Adapter-like) Is Required for Toll-like Receptor-4 Signal Transduction. Nature 2001, 413, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horng, T.; Barton, G.M.; Medzhitov, R. TIRAP: An Adapter Molecule in the Toll Signaling Pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaesu, G.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Kishida, S.; Li, X.; Stark, G.R.; Matsumoto, K. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Receptor-Associated Kinase Leads to Activation of TAK1 by Inducing TAB2 Translocation in the IL-1 Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, E.; Agathangelidis, A.; Reverberi, D.; Ntoufa, S.; Scarfò, L.; Ranghetti, P.; Cutrona, G.; Tedeschi, A.; Xochelli, A.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Stimulation in Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma Can Modulate Cell Signaling, Activation and Proliferation. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson Kvarnhammar, A.; Tengroth, L.; Adner, M.; Cardell, L.-O. Innate Immune Receptors in Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells: Activation by TLR1/2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR7 and NOD1 Agonists. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Ii, M.; Kitazaki, T.; Iizawa, Y.; Kimura, H. TAK-242 Selectively Suppresses Toll-like Receptor 4-Signaling Mediated by the Intracellular Domain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 584, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Levy, O.; Dowling, D.J. The TLR5 Agonist Flagellin Shapes Phenotypical and Functional Activation of Lung Mucosal Antigen Presenting Cells in Neonatal Mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.K.; Seppänen, M.; Hautala, T.; Ciancanelli, M.J.; Itan, Y.; Lafaille, F.G.; Dell, W.; Lorenzo, L.; Byun, M.; Pauwels, E.; et al. TLR3 Deficiency in Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: High Allelic Heterogeneity and Recurrence Risk. Neurology 2014, 83, 1888–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, M.C.; Achek, A.; Kim, G.-Y.; Panneerselvam, S.; Shin, H.-J.; Baek, W.-Y.; Lee, W.H.; Sung, J.; Jeong, U.; Cho, E.-Y.; et al. A Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Endosomal TLRs Reduces Inflammation and Alleviates Autoimmune Disease Symptoms in Murine Models. Cells 2020, 9, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.N.; Pisetsky, D.S.; Schwartz, D.A. Toll-like Receptors in the Pathogenesis of Human Disease. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.R.; Shupe, J.; Nickerson, K.; Kashgarian, M.; Flavell, R.A.; Shlomchik, M.J. Toll-like Receptor 7 and TLR9 Dictate Autoantibody Specificity and Have Opposing Inflammatory and Regulatory Roles in a Murine Model of Lupus. Immunity 2006, 25, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.; Fan, H.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Chu, C.-Q.; Shi, X. Toll-like Receptors 7 and 9 Regulate the Proliferation and Differentiation of B Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1093208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, C.; Lim, E.L.; Mokhtari, M.; Kind, B.; Odainic, A.; Lara-Villacanas, E.; Koss, S.; Mages, S.; Menzel, K.; Engel, K.; et al. UNC93B1 Variants Underlie TLR7-Dependent Autoimmunity. Sci. Immunol. 2024, 9, eadi9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Song, G.G. Associations of Toll-like Receptor Polymorphisms with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, F.G.; Midwood, K.S. Intrinsic Danger: Activation of Toll-like Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-Q.; Pope, R.M. Role of toll like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2009, 11, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racke, M.K.; Drew, P.D. Toll-Like Receptors in Multiple Sclerosis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 336, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, S.; Han, J.; Li, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, J.; Jin, T. Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Neuroimmune Diseases: Therapeutic Targets and Problems. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 777606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahromi, A.S.; Erfanian, S.; Jahromi, M.S.S.; Roustazadeh, A. Association of Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Gene Polymorphism with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) in Iranian Patients. Acta Neurol. Taiwanica 2024, 33, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, J.; van der Made, C.I.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Coughlan, E.; Asselta, R.; Löscher, B.-S.; Valenti, L.V.C.; de Cid, R.; Bujanda, L.; Julià, A.; et al. Stratified Analyses Refine Association between TLR7 Rare Variants and Severe COVID-19. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2024, 5, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-H.; Liu, Z.; Bastard, P.; Khobrekar, N.; Hutchison, K.M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Fan, Q.; Matuozzo, D.; Harschnitz, O.; Kerrouche, N.; et al. Human TMEFF1 Is a Restriction Factor for Herpes Simplex Virus in the Brain. Nature 2024, 632, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, A.; Pérez de Diego, R.; Flores, C.; Rinchai, D.; Solé-Violán, J.; Deyà-Martínez, À.; García-Solis, B.; Lorenzo-Salazar, J.M.; Hernández-Brito, E.; Lanz, A.-L.; et al. Humans with Inherited MyD88 and IRAK-4 Deficiencies Are Predisposed to Hypoxemic COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20220170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Patra, R.; Behzadi, P.; Masotti, A.; Paolini, A.; Sarshar, M. Toll-like Receptor-Guided Therapeutic Intervention of Human Cancers: Molecular and Immunological Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1244345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, A.M.; Hagström, J.; Mustonen, H.; Seppänen, H.; Haglund, C. The Expression and Prognostic Value of Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) in Pancreatic Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Therapy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.J.A.; Figueira, L.R.T.; Sardinha, D.M.; Costa da Cruz, E.; Andrade, N.C.O.; Bispo, S.K.D.S.; Augusto Ferreira Dos Anjos, T.; Dos Santos, E.C.; Garcia, A.J.P.; Lima, L.N.G.C. Analyses of Haplotypes of TLR2 and TLR3 Genes for COVID-19 Prognosis in a Cohort of Professionals Who Worked in the First Pandemic Wave in Belém-PA, Brazil. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1659269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.S.; Bentes, A.A.; Diniz, L.M.; Carvalho, S.H.; Kroon, E.G.; Campos, M.A. Association Between Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 3 (Tlr3), Tlr7, Tlr8 and Tirap Genes with Severe Symptoms in Children Presenting COVID-19. Viruses 2024, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, E.R.; Elshennawy, S.I.; Elhakeem, H.; Saleh, R.A.M.; Elsawy, S.B.; Salama, K.S.M.; Mohamed, M.F.; Bahi, R.H.; Mansour, H.H.; Kasim Mahmoud, S.A.; et al. The Association of Toll-like Receptor-9 Gene Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism and AK155(IL-26) Serum Levels with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbation Risk: A Case-Controlled Study with Bioinformatics Analysis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Kim, T.H.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.-A.; Jung, J.-Y.; Choi, I.A.; Lee, K.E. Association of TLR 9 Gene Polymorphisms with Remission in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving TNF-α Inhibitors and Development of Machine Learning Models. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglione, P.J.; Simchoni, N.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Toll-like Receptor Signaling in Primary Immune Deficiencies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1356, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, V.H.D.; Upton, J.E.M.; Derfalvi, B.; Hildebrand, K.J.; McCusker, C. Inborn Errors of Immunity (Primary Immunodeficiencies). Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2025, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmonte, O.M.; Castagnoli, R.; Calzoni, E.; Notarangelo, L.D. Inborn Errors of Immunity With Immune Dysregulation: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, J.-L. Human Immunity. J. Hum. Immun. 2025, 1, e20250001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarangelo, L.D.; Bacchetta, R.; Casanova, J.-L.; Su, H.C. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: An Expanding Universe. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabb1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IJspeert, H.; Edwards, E.S.J.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Dalm, V.A.S.H.; van Zelm, M.C. Update on Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025, 155, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurabielle, C.; LaFlam, T.N.; Gearing, M.; Ye, C.J. Functional Genomics in Inborn Errors of Immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 322, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulis, M.W.; Williams, K.W. Keeping up with Recent Developments in Immunodeficiency. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025, 134, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Yin, J.; Xiong, J.; Xu, M.; Qi, Q.; Yang, W. Diagnostic Yield of Next-Generation Sequencing in Suspect Primary Immunodeficiencies Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merico, D.; Sharfe, N.; Dadi, H.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; de Rijke, J.; Dahi, Z.; Zarrei, M.; Al Ghamdi, A.; Al Shaqaq, A.; Vong, L.; et al. Pre-T Cell Receptor-α Immunodeficiency Detected Exclusively Using Whole Genome Sequencing. npj Genom. Med. 2025, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, Z.H.; Frangieh, C.J.; Kothapalli, N.; Levy, J.; Heck, C.K.; Melms, J.C.; Gejman, R.S.; Shah, P.; Pollard, J.M.; Naik, A.; et al. Scalable Generation and Functional Classification of Genetic Variants in Inborn Errors of Immunity to Accelerate Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment. Cell 2025, 188, 4861–4879.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott de Bruin, L.M.; Lankester, A.C.; Staal, F.J.T. Advances in Gene Therapy for Inborn Errors of Immunity. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 23, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciol, G.; Moens, L.; Bosch, B.; Bossuyt, X.; Casanova, J.-L.; Puel, A.; Meyts, I. Lessons Learned from the Study of Human Inborn Errors of Innate Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyts, I.; Bosch, B.; Bolze, A.; Boisson, B.; Itan, Y.; Belkadi, A.; Pedergnana, V.; Moens, L.; Picard, C.; Cobat, A.; et al. Exome and Genome Sequencing for Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, C.; Fischer, A. Contribution of High-Throughput DNA Sequencing to the Study of Primary Immunodeficiencies. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangye, S.G.; Al-Herz, W.; Bousfiha, A.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; Klein, C.; Morio, T.; Oksenhendler, E.; Picard, C.; et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2022 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1473–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, G.; Ramirez-Alejo, N.; Seeleuthner, Y.; Yang, R.; Ogishi, M.; Cobat, A.; Patin, E.; Quintana-Murci, L.; Boisson-Dupuis, S.; Casanova, J.-L.; et al. Homozygosity for TYK2 P1104A Underlies Tuberculosis in about 1% of Patients in a Cohort of European Ancestry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10430–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, M.; Abhyankar, A.; Lelarge, V.; Plancoulaine, S.; Palanduz, A.; Telhan, L.; Boisson, B.; Picard, C.; Dewell, S.; Zhao, C.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing-Based Discovery of STIM1 Deficiency in a Child with Fatal Classic Kaposi Sarcoma. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsina, L.; Israelsson, E.; Altman, M.C.; Dang, K.K.; Ghandil, P.; Israel, L.; Von Bernuth, H.; Baldwin, N.; Qin, H.; Jin, Z.; et al. A Narrow Repertoire of Transcriptional Modules Responsive to Pyogenic Bacteria Is Impaired in Patients Carrying Loss-of-Function Mutations in MYD88 or IRAK4. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sipos, F.; Műzes, G. Good’s Syndrome: Brief Overview of an Enigmatic Immune Deficiency. APMIS 2023, 131, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrnbecher, T.; Russo, A.; Rohde, G. Correction: A Survey of Diagnosis and Therapy of Inborn Errors of Immunity among Practice-Based Physicians and Clinic-Based Pneumologists and Hemato-Oncologists. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1597635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousfiha, A.; Jeddane, L.; Picard, C.; Al-Herz, W.; Ailal, F.; Chatila, T.; Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Etzioni, A.; Franco, J.L.; Holland, S.M.; et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2019 Update of the IUIS Phenotypical Classification. J. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 40, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham-Rundles, C.; Radigan, L.; Knight, A.K.; Zhang, L.; Bauer, L.; Nakazawa, A. TLR9 Activation Is Defective in Common Variable Immune Deficiency. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertowska, P.; Smolak, K.; Mertowski, S.; Grywalska, E. Unraveling the Role of Toll-like Receptors in the Immunopathogenesis of Selected Primary and Secondary Immunodeficiencies. Cells 2023, 12, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.V.; Neves, J.F. Precision Medicine: The Use of Tailored Therapy in Primary Immunodeficiencies. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1029560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, A.K.; Bolanos, L.C.; Dexheimer, P.J.; Karns, R.A.; Aronow, B.J.; Komurov, K.; Jegga, A.G.; Casper, K.A.; Patil, Y.J.; Wilson, K.M.; et al. IRAK1 Is a Novel DEK Transcriptional Target and Is Essential for Head and Neck Cancer Cell Survival. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 43395–43407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Jouanguy, E.; Ugolini, S.; Smahi, A.; Elain, G.; Romero, P.; Segal, D.; Sancho-Shimizu, V.; Lorenzo, L.; Puel, A.; et al. TLR3 Deficiency in Patients with Herpes Simplex Encephalitis. Science 2007, 317, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.J.; Currie, A.J.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Brown, K.L.; Rosenberger, C.M.; Ma, R.C.; Bylund, J.; Campsall, P.A.; Puel, A.; Picard, C.; et al. IRAK-4 Mutation (Q293X): Rapid Detection and Characterization of Defective Post-Transcriptional TLR/IL-1R Responses in Human Myeloid and Non-Myeloid Cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8202–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, C.; von Bernuth, H.; Ghandil, P.; Chrabieh, M.; Levy, O.; Arkwright, P.D.; McDonald, D.; Geha, R.S.; Takada, H.; Krause, J.C.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcome of Patients with IRAK-4 and MyD88 Deficiency. Medicine 2010, 89, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohnishi, H.; Moriya, K.; Tsumura, M.; Sakata, S.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Takada, H.; Kato, Z.; Sancho-Shimizu, V.; et al. IRAK4 Deficiency Presenting with Anti-NMDAR Encephalitis and HHV6 Reactivation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, C.; Casanova, J.-L.; Puel, A. Infectious Diseases in Patients with IRAK-4, MyD88, NEMO, or IκBα Deficiency. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, S.; Price-Kuehne, F.; Hong, Y.; Omoyinmi, E.; Burleigh, A.; Gilmour, K.C.; Ahmad, B.; Choi, S.; Bahar, M.W.; Torpiano, P.; et al. Neuroinflammation, Autoinflammation, Splenomegaly and Anemia Caused by Bi-Allelic Mutations in IRAK4. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1231749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Tadros, S.; Bahal, S.; Lowe, D.M.; Burns, S.O. Case of Fatal Meningitis in an Adult Patient with IRAK4 Deficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 1137–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bernuth, H.; Picard, C.; Jin, Z.; Pankla, R.; Xiao, H.; Ku, C.-L.; Chrabieh, M.; Mustapha, I.B.; Ghandil, P.; Camcioglu, Y.; et al. Pyogenic Bacterial Infections in Humans with MyD88 Deficiency. Science 2008, 321, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Pandey, S.N.; Mishra, A.; Srivastava, R. Suppression of TLR Signaling by IRAK-1 and -4 Dual Inhibitor Decreases TPF-Resistance-Induced pro-Oncogenic Effects in HNSCC. 3 Biotech. 2023, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczanowska, S.; Joseph, A.M.; Davila, E. TLR Agonists: Our Best Frenemy in Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, F.; Altamura, S.; Frosali, S.; Conti, P. Key Role of DAMP in Inflammation, Cancer, and Tissue Repair. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-Stimulated Genes: A Complex Web of Host Defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Audry, M.; Ciancanelli, M.; Alsina, L.; Azevedo, J.; Herman, M.; Anguiano, E.; Sancho-Shimizu, V.; Lorenzo, L.; Pauwels, E.; et al. Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis in a Patient with Complete TLR3 Deficiency: TLR3 Is Otherwise Redundant in Protective Immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2083–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Casanova, J.-L. Inborn Errors Underlying Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: From TLR3 to IRF3. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1342–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casrouge, A.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Eidenschenk, C.; Jouanguy, E.; Puel, A.; Yang, K.; Alcais, A.; Picard, C.; Mahfoufi, N.; Nicolas, N.; et al. Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis in Human UNC-93B Deficiency. Science 2006, 314, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Shimizu, V.; Pérez de Diego, R.; Lorenzo, L.; Halwani, R.; Alangari, A.; Israelsson, E.; Fabrega, S.; Cardon, A.; Maluenda, J.; Tatematsu, M.; et al. Herpes Simplex Encephalitis in Children with Autosomal Recessive and Dominant TRIF Deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4889–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.L.; Mørk, N.; Reinert, L.S.; Kofod-Olsen, E.; Narita, R.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Skipper, K.A.; Höning, K.; Gad, H.H.; Østergaard, L.; et al. Functional IRF3 Deficiency in a Patient with Herpes Simplex Encephalitis. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.H.; Yu, W.; Menden, H.; Xia, S.; Schreck, C.F.; Gibson, M.; Louiselle, D.; Pastinen, T.; Raje, N.; Sampath, V. IRF7 and UNC93B1 Variants in an Infant with Recurrent Herpes Simplex Virus Infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e154016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiu, J.H.C.; Chan, K.-S.; Cheung, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fung, W.W.L.; Cai, J.; Cheung, S.W.M.; Dorweiler, B.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Associated Activation of TLR5 Induces Apolipoprotein A1 Production in the Liver. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1236–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leifer, C.A.; McConkey, C.; Li, S.; Chassaing, B.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Ley, R.E. Linking Genetic Variation in Human Toll-like Receptor 5 Genes to the Gut Microbiome’s Potential to Cause Inflammation. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawn, T.R.; Verbon, A.; Lettinga, K.D.; Zhao, L.P.; Li, S.S.; Laws, R.J.; Skerrett, S.J.; Beutler, B.; Schroeder, L.; Nachman, A.; et al. A Common Dominant TLR5 Stop Codon Polymorphism Abolishes Flagellin Signaling and Is Associated with Susceptibility to Legionnaires’ Disease. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.Y.; Tan, J.E.; Hee, E.W.; Yong, D.W.X.; Heng, Y.S.; Low, W.X.; Wu, X.H.; Cletus, C.; Kumar Chellappan, D.; Aung, K.; et al. Human Genetic Variation Influences Enteric Fever Progression. Cells 2021, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassaing, B.; Ley, R.E.; Gewirtz, A.T. Intestinal Epithelial Cell Toll-like Receptor 5 Regulates the Intestinal Microbiota to Prevent Low-Grade Inflammation and Metabolic Syndrome in Mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1363–1377.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Koury, J.; Kaul, M. Innate Immune Sensing of Viruses and Its Consequences for the Central Nervous System. Viruses 2021, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, E.A.; Tremblay, N.; Al-Balushi, M.S.; Al-Jabri, A.A.; Lamarre, D. Viruses Seen by Our Cells: The Role of Viral RNA Sensors. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 9480497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiering, A.E.; de Vries, T.J. Why Females Do Better: The X Chromosomal TLR7 Gene-Dose Effect in COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 756262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, S.; Daga, S.; Fallerini, C.; Baldassarri, M.; Benetti, E.; Picchiotti, N.; Fava, F.; Gallì, A.; Zibellini, S.; Bruttini, M.; et al. Rare Variants in Toll-like Receptor 7 Results in Functional Impairment and Downregulation of Cytokine-Mediated Signaling in COVID-19 Patients. Genes Immun. 2022, 23, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youness, A.; Cenac, C.; Faz-López, B.; Grunenwald, S.; Barrat, F.J.; Chaumeil, J.; Mejía, J.E.; Guéry, J.-C. TLR8 Escapes X Chromosome Inactivation in Human Monocytes and CD4+ T Cells. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2023, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Boisson, B.; Onodi, F.; Matuozzo, D.; Moncada-Velez, M.; Maglorius Renkilaraj, M.R.L.; Zhang, P.; Meertens, L.; Bolze, A.; Materna, M.; et al. X-Linked Recessive TLR7 Deficiency in ~1% of Men under 60 Years Old with Life-Threatening COVID-19. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabl4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Made, C.I.; Simons, A.; Schuurs-Hoeijmakers, J.; van den Heuvel, G.; Mantere, T.; Kersten, S.; van Deuren, R.C.; Steehouwer, M.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Jaeger, M.; et al. Presence of Genetic Variants Among Young Men with Severe COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluri, J.; Bach, A.; Kaviany, S.; Chiquetto Paracatu, L.; Kitcharoensakkul, M.; Walkiewicz, M.A.; Putnam, C.D.; Shinawi, M.; Saucier, N.; Rizzi, E.M.; et al. Immunodeficiency and Bone Marrow Failure with Mosaic and Germline TLR8 Gain of Function. Blood 2021, 137, 2450–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleesing, J. Gain-of-Function Defects in Toll-like Receptor 8 Shed Light on the Interface between Immune System and Bone Marrow Failure Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 935321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Wan, Y.; Gao, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; et al. Erythroid-Intrinsic Activation of TLR8 Impairs Erythropoiesis in Inherited Anemia. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannoy, V.; Côté-Biron, A.; Asselin, C.; Rivard, N. TIRAP, TRAM, and Toll-Like Receptors: The Untold Story. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 2899271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpoot, S.; Wary, K.K.; Ibbott, R.; Liu, D.; Saqib, U.; Thurston, T.L.M.; Baig, M.S. TIRAP in the Mechanism of Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 697588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, L.; Wang, Y.; Bulek, K.; Della Mina, E.; Zhang, Z.; Pedergnana, V.; Chrabieh, M.; Lemmens, N.A.; Sancho-Shimizu, V.; Descatoire, M.; et al. Human Adaptive Immunity Rescues an Inborn Error of Innate Immunity. Cell 2017, 168, 789–800.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, K.; Plantinga, T.S.; Wong, J.; Monks, B.G.; Gay, N.J.; Netea, M.G.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Golenbock, D.T. A TIR Domain Variant of MyD88 Adapter-like (Mal)/TIRAP Results in Loss of MyD88 Binding and Reduced TLR2/TLR4 Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25742–25748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, J.C.; Medzhitov, R. Phosphoinositide-Mediated Adaptor Recruitment Controls Toll-like Receptor Signaling. Cell 2006, 125, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, K.; Lou, H.; Zhou, L.; An, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ding, Y. Clinical Relevance of Loss-of-Function Mutations of NEMO/IKBKG. Genes Dis. 2025, 12, 101531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonana, J.; Elder, M.E.; Schneider, L.C.; Orlow, S.J.; Moss, C.; Golabi, M.; Shapira, S.K.; Farndon, P.A.; Wara, D.W.; Emmal, S.A.; et al. A Novel X-Linked Disorder of Immune Deficiency and Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Is Allelic to Incontinentia Pigmenti and Due to Mutations in IKK-Gamma (NEMO). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, H.; Kishimoto, Y.; Taguchi, T.; Kawamoto, N.; Nakama, M.; Kawai, T.; Nakayama, M.; Ohara, O.; Orii, K.; Fukao, T. Immunodeficiency in Two Female Patients with Incontinentia Pigmenti with Heterozygous NEMO Mutation Diagnosed by LPS Unresponsiveness. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Romano, F.; Nieddu, F.; Picard, C.; Azzari, C. OL-EDA-ID Syndrome: A Novel Hypomorphic NEMO Mutation Associated with a Severe Clinical Presentation and Transient HLH. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, F.; Pescatore, A.; Conte, M.I.; Mirabelli, P.; Paciolla, M.; Esposito, E.; Lioi, M.B.; Ursini, M.V. EDA-ID and IP, Two Faces of the Same Coin: How the Same IKBKG/NEMO Mutation Affecting the NF-κB Pathway Can Cause Immunodeficiency and/or Inflammation. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 34, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.R.; Arno, G.; Robson, A.G.; Fakin, A.; Pontikos, N.; Mohamed, M.D.; Bird, A.C.; Moore, A.T.; Michaelides, M.; Webster, A.R.; et al. The X-Linked Retinopathies: Physiological Insights, Pathogenic Mechanisms, Phenotypic Features and Novel Therapies. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 82, 100898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrakasan, S.; Marsh, R.A.; Uzel, G.; Holland, S.M.; Shah, K.N.; Bleesing, J. Outcome of Patients with NEMO Deficiency Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1040–1043.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fevang, B. Treatment of Inflammatory Complications in Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID): Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañero-Navalon, M.D.; Garcia-Bustos, V.; Nuñez-Beltran, M.; Císcar Fernández, P.; Mateu, L.; Solanich, X.; Carrillo-Linares, J.L.; Robles-Marhuenda, Á.; Puchades-Gimeno, F.; Pelaez Ballesta, A.; et al. Current Clinical Spectrum of Common Variable Immunodeficiency in Spain: The Multicentric Nationwide GTEM-SEMI-CVID Registry. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1033666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Provot, J.; Jais, J.-P.; Alcais, A.; Mahlaoui, N.; members of the CEREDIH French PID study group. Autoimmune and Inflammatory Manifestations Occur Frequently in Patients with Primary Immunodeficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1388–1393.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gathmann, B.; Mahlaoui, N.; CEREDIH; Gérard, L.; Oksenhendler, E.; Warnatz, K.; Schulze, I.; Kindle, G.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Dutch, W.I.D.; et al. Clinical Picture and Treatment of 2212 Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, H.-E.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. Non-Infectious Complications of Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Updated Clinical Spectrum, Sequelae, and Insights to Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Valles-Ibáñez, G.; Esteve-Solé, A.; Piquer, M.; González-Navarro, E.A.; Hernandez-Rodriguez, J.; Laayouni, H.; González-Roca, E.; Plaza-Martin, A.M.; Deyà-Martínez, Á.; Martín-Nalda, A.; et al. Evaluating the Genetics of Common Variable Immunodeficiency: Monogenetic Model and Beyond. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, A.; Qin, S.; Fallert Junecko, B.A.; Nisato, R.E.; Pepper, M.S.; Reinhart, T.A. Human Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Express Multiple Functional TLRs. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, L.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Rezaei, N.; Yazdani, R.; Rezaei, F.; Bokaie, S.; Zavareh, F.T.; Kiaee, F.; Kamali, A.N.; Azizi, G.; et al. Interleukin-1β and Interleukin-6 in Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Their Association with Subtypes of B Cells and Response to the Pneumovax-23 Vaccine. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2019, 30, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, N.L.; Onai, N.; Lanzavecchia, A. A Role for Toll-like Receptors in Acquired Immunity: Up-Regulation of TLR9 by BCR Triggering in Naive B Cells and Constitutive Expression in Memory B Cells. Blood 2003, 101, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, E.; Bosisio, D.; Golay, J.; Polentarutti, N.; Mantovani, A. The Toll-like Receptor Repertoire of Human B Lymphocytes: Inducible and Selective Expression of TLR9 and TLR10 in Normal and Transformed Cells. Blood 2003, 102, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traggiai, E.; Puzone, R.; Lanzavecchia, A. Antigen Dependent and Independent Mechanisms That Sustain Serum Antibody Levels. Vaccine 2003, 21 (Suppl. 2), S35–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.E. New Primary Immunodeficiencies 2023 Update. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2024, 36, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczawinska-Poplonyk, A.; Schwartzmann, E.; Bukowska-Olech, E.; Biernat, M.; Gattner, S.; Korobacz, T.; Nowicki, F.; Wiczuk-Wiczewska, M. The Pediatric Common Variable Immunodeficiency—From Genetics to Therapy: A Review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartl, D.; Lehmann, N.; Hoffmann, F.; Jansson, A.; Hector, A.; Notheis, G.; Roos, D.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Wintergerst, U. Dysregulation of Innate Immune Receptors on Neutrophils in Chronic Granulomatous Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 375–382.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.L.; Bylund, J.; MacDonald, K.L.; Song-Zhao, G.X.; Elliott, M.R.; Falsafi, R.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Speert, D.P. ROS-Deficient Monocytes Have Aberrant Gene Expression That Correlates with Inflammatory Disorders of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 129, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Bhattad, S.; Singh, S. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Indian J. Pediatr. 2016, 83, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig-Mueller, N.; Hammad, R.; Elling, R.; Alzubi, J.; Timm, B.; Kolter, J.; Knelangen, N.; Bednarski, C.; Gläser, B.; Ammann, S.; et al. Modeling MyD88 Deficiency In Vitro Provides New Insights in Its Function. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 608802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson, B.; Casanova, J.-L. TLR8 Gain of Function: A Tall Surprise. Blood 2021, 137, 2420–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Nishikomori, R.; Heike, T. Diagnosis and Treatment in Anhidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Immunodeficiency. Allergol. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Allergol. 2012, 61, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klangkalya, N.; Fleisher, T.A.; Rosenzweig, S.D. Diagnostic Tests for Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders: Classic and Genetic Testing. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2024, 45, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Puel, A.; Zhang, S.; Eidenschenk, C.; Ku, C.-L.; Casrouge, A.; Picard, C.; von Bernuth, H.; Senechal, B.; Plancoulaine, S.; et al. Human TLR-7-, -8-, and -9-Mediated Induction of IFN-Alpha/Beta and -Lambda Is IRAK-4 Dependent and Redundant for Protective Immunity to Viruses. Immunity 2005, 23, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglione, P.J.; Simchoni, N.; Black, S.; Radigan, L.; Overbey, J.R.; Bagiella, E.; Bussel, J.B.; Bossuyt, X.; Casanova, J.-L.; Meyts, I.; et al. IRAK-4 and MyD88 Deficiencies Impair IgM Responses against T-Independent Bacterial Antigens. Blood 2014, 124, 3561–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frans, G.; Meyts, I.; Picard, C.; Puel, A.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Moens, L.; Wuyts, G.; Van der Werff Ten Bosch, J.; Casanova, J.-L.; Bossuyt, X. Addressing Diagnostic Challenges in Primary Immunodeficiencies: Laboratory Evaluation of Toll-like Receptor- and NF-κB-Mediated Immune Responses. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2014, 51, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, P.; Davis, M.M. Human Immune System Variation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deering, R.P.; Orange, J.S. Development of a Clinical Assay to Evaluate Toll-Like Receptor Function. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, K.; Hintermeyer, M.; Boisson, B.; Chrabieh, M.; Ghandil, P.; Puel, A.; Picard, C.; Casanova, J.-L.; Routes, J.; Verbsky, J. IRAK4 Deficiency in a Patient with Recurrent Pneumococcal Infections: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Karim, F.; Kiessu, E.; Cushing, L.; Lin, L.-L.; Ghandil, P.; Hoarau, C.; Casanova, J.-L.; Puel, A.; Rao, V.R. Mechanism of Dysfunction of Human Variants of the IRAK4 Kinase and a Role for Its Kinase Activity in Interleukin-1 Receptor Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15208–15220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitani, M.; Al-Shaibi, A.A.; Pandey, S.; Gartner, L.; Taylor, H.; Hubrack, S.Z.; Agrebi, N.; Al-Mohannadi, M.J.; Al Kaabi, S.; Vogl, T.; et al. Biallelic TLR4 Deficiency in Humans. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 783–790.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, R.; Rezaei, N.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Delbandi, A.-A.; Teimourian, S.; Yazdani, R.; Tavasolian, P.; Kiaee, F.; Tajik, N. Evaluation of the TLR Negative Regulatory Network in CVID Patients. Genes. Immun. 2019, 20, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.; Bednarski, J.; Warren, J.; Cooper, M. A Rare case of TLR8 gain of function in a female patient. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 133, S151–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altammar, F.; Alshamali, M.; Alqunaee, M.; Alali, A.J.; Elshafie, R.M.; Al-Herz, W. A Case Report of a Patient with Recurrent and Severe Infections Highlighting the Importance of Considering Inborn Errors of Immunity. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1340367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, V.; Heimall, J.R.; Chong, H.; Nandiwada, S.L.; Chen, K.; Lawrence, M.G.; Sadighi Akha, A.A.; Kumánovics, A.; Jyonouchi, S.; Ngo, S.Y.; et al. A Toolkit and Framework for Optimal Laboratory Evaluation of Individuals with Suspected Primary Immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3293–3307.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.S.; Freeman, A.F.; Fleisher, T.A. Inborn Errors of Immunity: A Role for Functional Testing and Flow Cytometry in Aiding Clinical Diagnosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluri, J.; Cooper, M.A.; Schuettpelz, L.G. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling in the Establishment and Function of the Immune System. Cells 2021, 10, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.M.; Moyer, A.M.; Hasadsri, L.; Abraham, R.S. Diagnostic Tools for Inborn Errors of Human Immunity (Primary Immunodeficiencies and Immune Dysregulatory Diseases). Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelka, K.; Bertheloot, D.; Reimer, E.; Phulphagar, K.; Schmidt, S.V.; Christ, A.; Stahl, R.; Watson, N.; Miyake, K.; Hacohen, N.; et al. The Chaperone UNC93B1 Regulates Toll-like Receptor Stability Independently of Endosomal TLR Transport. Immunity 2018, 48, 911–922.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Wang, K.; Lin, X.; Qian, W.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Z.F.; Cui, M. TLR7 Deficiency Leads to TLR8 Compensative Regulation of Immune Response against JEV in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, P.T.; Vihinen, M.; Smith, C.I. X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia (XLA): A Genetic Tyrosine Kinase (Btk) Disease. Bioessays 1996, 18, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.E.; Zhang, L.; Radigan, L.; Sanchez-Ramon, S.; Cunningham-Rundles, C. TLR-Mediated B Cell Defects and IFN-α in Common Variable Immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McLetchie, S.; Volpp, B.D.; Dinauer, M.C.; Blum, J.S. Hyper-Responsive Toll-like Receptor 7 and 9 Activation in NADPH Oxidase-Deficient B Lymphoblasts. Immunology 2015, 146, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolitz, E.; Chamseddin, B.; Son, R.; Vandergriff, T.; Hsu, A.P.; Holland, S.; Wang, R.C. A Novel NEMO/IKBKG Mutation Identified in a Primary Immunodeficiency Disorder with Recurrent Atypical Mycobacterial Infections. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 7, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.; Cazzanelli, G.; Rasul, S.; Hitchinson, B.; Hu, Y.; Coombes, R.C.; Raguz, S.; Yagüe, E. Apoptosis Inhibitor TRIAP1 Is a Novel Effector of Drug Resistance. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toll-Like Receptor Assay for Innate-Adaptive Immune Response. Available online: https://emea.eurofinsdiscovery.com/solution/toll-like-receptors (accessed on 28 October 2025).
- Owen, A.M.; Fults, J.B.; Patil, N.K.; Hernandez, A.; Bohannon, J.K. TLR Agonists as Mediators of Trained Immunity: Mechanistic Insight and Immunotherapeutic Potential to Combat Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 622614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veneziani, I.; Alicata, C.; Moretta, L.; Maggi, E. The Latest Approach of Immunotherapy with Endosomal TLR Agonists Improving NK Cell Function: An Overview. Biomedicines 2022, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segundo, G.R.S.; Condino-Neto, A. Treatment of Patients with Immunodeficiency: Medication, Gene Therapy, and Transplantation. J. Pediatr. 2020, 97, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanitsch, L.; Baumann, U.; Boztug, K.; Burkhard-Meier, U.; Fasshauer, M.; Habermehl, P.; Hauck, F.; Klock, G.; Liese, J.; Meyer, O.; et al. Treatment and Management of Primary Antibody Deficiency: German Interdisciplinary Evidence-Based Consensus Guideline. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 1432–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martuszewski, A.; Paluszkiewicz, P.; Sierżęga-Staykov, K.; Wawrzyniak-Dzierżek, E.; Salamonowicz-Bodzioch, M.; Frączkiewicz, J.; Janeczko-Czarnecka, M.; Mielcarek-Siedziuk, M.; Nowak, M.; Dąbrowska-Leonik, N.; et al. Successful Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Essential Modulator Deficiency Syndrome After Treosulfan-Based Conditioning: A Case Report. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejtkova, M.; Sukova, M.; Hlozkova, K.; Skvarova Kramarzova, K.; Rackova, M.; Jakubec, D.; Bakardjieva, M.; Bloomfield, M.; Klocperk, A.; Parackova, Z.; et al. TLR8/TLR7 Dysregulation Due to a Novel TLR8 Mutation Causes Severe Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Autoinflammation in Identical Twins. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, N.I.; Papoin, J.; Raparia, C.; Sun, Z.; Josselsohn, R.; Lu, A.; Katerji, H.; Syeda, M.M.; Polsky, D.; Paulson, R.; et al. Human TLR8 Induces Inflammatory Bone Marrow Erythromyeloblastic Islands and Anemia in SLE-Prone Mice. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202302241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Ye, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, X.; Zhuang, Z. Application of Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) and Their Agonists in Cancer Vaccines and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1227833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddineni, S.; Chen, M.; Baik, F.; Divi, V.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Finegersh, A. Toll-like Receptor Agonists Are Unlikely to Provide Benefits in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfo, C.; Giovannetti, E.; Martinez, P.; McCue, S.; Naing, A. Applications and Clinical Trial Landscape Using Toll-like Receptor Agonists to Reduce the Toll of Cancer. NPJ Precis. Onc. 2023, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.A.; Booth, C. Gene Therapy for Primary Immunodeficiencies. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagnoli, R.; Delmonte, O.M.; Calzoni, E.; Notarangelo, L.D. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A. Gene Therapy for Inborn Errors of Immunity: Past, Present and Future. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessach, I.M.; Notarangelo, L.D. Gene Therapy for Primary Immunodeficiencies: Looking Ahead, toward Gene Correction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohn, D.B.; Booth, C.; Kang, E.M.; Pai, S.-Y.; Shaw, K.L.; Santilli, G.; Armant, M.; Buckland, K.F.; Choi, U.; De Ravin, S.S.; et al. Lentiviral Gene Therapy for X-Linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepensky, P.; Keller, B.; Shamriz, O.; von Spee-Mayer, C.; Friedmann, D.; Shadur, B.; Unger, S.; Fuchs, S.; NaserEddin, A.; Rumman, N.; et al. T+ NK+ IL-2 Receptor γ Chain Mutation: A Challenging Diagnosis of Atypical Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-H.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chiang, B.-L. Chronic Granulomatous Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Clin. Rev. Allerg. Immunol. 2021, 61, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronsley, R.; Kariminia, A.; Ng, B.; Mostafavi, S.; Reid, G.; Subrt, P.; Hijiya, N.; Schultz, K. The TLR9 Agonist (GNKG168) Induces a Unique Immune Activation Pattern in Vivo in Children with Minimal Residual Disease Positive Acute Leukemia: Results of the TACL T2009-008 Phase I Study. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 36, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneichi, H.; Kanegane, H.; Sira, M.M.; Futatani, T.; Agematsu, K.; Sako, M.; Kaneko, H.; Kondo, N.; Kaisho, T.; Miyawaki, T. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Is Impaired in Dendritic Cells from Patients with X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.L.; Dai, D.; Modi, B.P.; Sara, R.; Garabedian, E.; Marsh, R.A.; Puck, J.; Secord, E.; Sullivan, K.E.; Turvey, S.E.; et al. Inborn Errors of Immunity Associated with Type 2 Inflammation in the USIDNET Registry. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 831279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindle, G.; Alligon, M.; Albert, M.H.; Buckland, M.; Edgar, J.D.; Gathmann, B.; Ghosh, S.; Gkantaras, A.; Nieters, A.; Pignata, C.; et al. Inborn Errors of Immunity: Manifestation, Treatment, and Outcome—An ESID Registry 1994–2024 Report on 30,628 Patients. J. Hum. Immun. 2025, 1, e20250007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M.G.; Kindle, G.; Gathmann, B.; Quinti, I.; Buckland, M.; van Montfrans, J.; Scheible, R.; Rusch, S.; Gasteiger, L.M.; Grimbacher, B.; et al. The European Society for Immunodeficiencies (ESID) Registry Working Definitions for the Clinical Diagnosis of Inborn Errors of Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2019, 7, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pediatric Gene Therapy Program—Children’s Health. Available online: https://www.childrens.com/specialties-services/specialty-centers-and-programs/genetics/gene-therapy (accessed on 28 October 2025).
| TLR | Localization | Main Ligand | Signaling Pathway | Functions and Example Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR1/2 | Cell surface | Triacylated lipopeptides (Pam3CSK4) | MyD88-dependent | Activation of immune response; potential applications in cancer and infectious disease therapy [28] |
| TLR2/6 | Cell surface | Lipopeptides | MyD88-dependent | Regulation of inflammatory processes and immune responses; potential therapies for allergic and autoimmune diseases [60] |
| TLR3 | Endosomes | Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) | TRIF-dependent | Antiviral response; applications as a vaccine adjuvant and in cancer immunotherapy; requires UNC93B1 [61] |
| TLR4 | Cell surface | Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), HMGB1; heme; saturated fatty acids; oxidized phospholipids; ECM fragments | MyD88- and TRIF-dependent | Regulation of inflammatory response; potential applications in treating infections and cancers; requires coactivator MD2 and CD14 [62] |
| TLR5 | Cell surface | Flagellin | MyD88-dependent | Recognizes bacterial flagellin, regulates gut homeostasis and microbiota; promotes mucosal immunity. Flagellin is used as a potent vaccine adjuvant and mucosal immunostimulant. Role in metabolic regulation and aging [63,64] |
| TLR7 | Endosomes | Single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) | MyD88-dependent | Antiviral response; regulation of autoimmune diseases such as lupus (SLE); type I IFN activation [65] |
| TLR8 | Endosomes | Single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) | MyD88-dependent | Antiviral and anticancer responses; therapeutic applications; similar role to TLR7; activates dendritic cells [65] |
| TLR9 | Endosomes | CpG DNA | MyD88-dependent | Antiviral response; applications as a vaccine adjuvant and in treatment of infections and cancers; requires proteolysis [60] |
| TLR10 | Cell surface | Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)—presumed | MyD88-dependent | Potential role in antiviral response and immune regulation; requires further research [60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jurczuk, A.; Bałdyga, P.; Płoński, A.; Jurczuk, M.; Garley, M. Toll-like Receptors in Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children: Diagnostic Potential and Therapeutic Frontiers—A Review of the Latest Data. Cells 2025, 14, 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231902
Jurczuk A, Bałdyga P, Płoński A, Jurczuk M, Garley M. Toll-like Receptors in Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children: Diagnostic Potential and Therapeutic Frontiers—A Review of the Latest Data. Cells. 2025; 14(23):1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231902
Chicago/Turabian StyleJurczuk, Aleksandra, Paulina Bałdyga, Adam Płoński, Maria Jurczuk, and Marzena Garley. 2025. "Toll-like Receptors in Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children: Diagnostic Potential and Therapeutic Frontiers—A Review of the Latest Data" Cells 14, no. 23: 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231902
APA StyleJurczuk, A., Bałdyga, P., Płoński, A., Jurczuk, M., & Garley, M. (2025). Toll-like Receptors in Inborn Errors of Immunity in Children: Diagnostic Potential and Therapeutic Frontiers—A Review of the Latest Data. Cells, 14(23), 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14231902





