Molecular Insights into Outer Dynein Arm Defects in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Involvement of ZMYND10 and GRP78 †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Public and Patient Involvement Statement
2.3. Physical Examination
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. High-Speed Video Microscopy (HSVM)
2.6. Immunofluorescence (IF) Labeling
2.7. Proteomics and Metabolomics
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features
3.2. HSVM Findings
3.3. Genetic Characteristics of Individuals
3.4. Immunofluorescence (IF) Analysis
3.4.1. DNAH5
3.4.2. ZMYND10
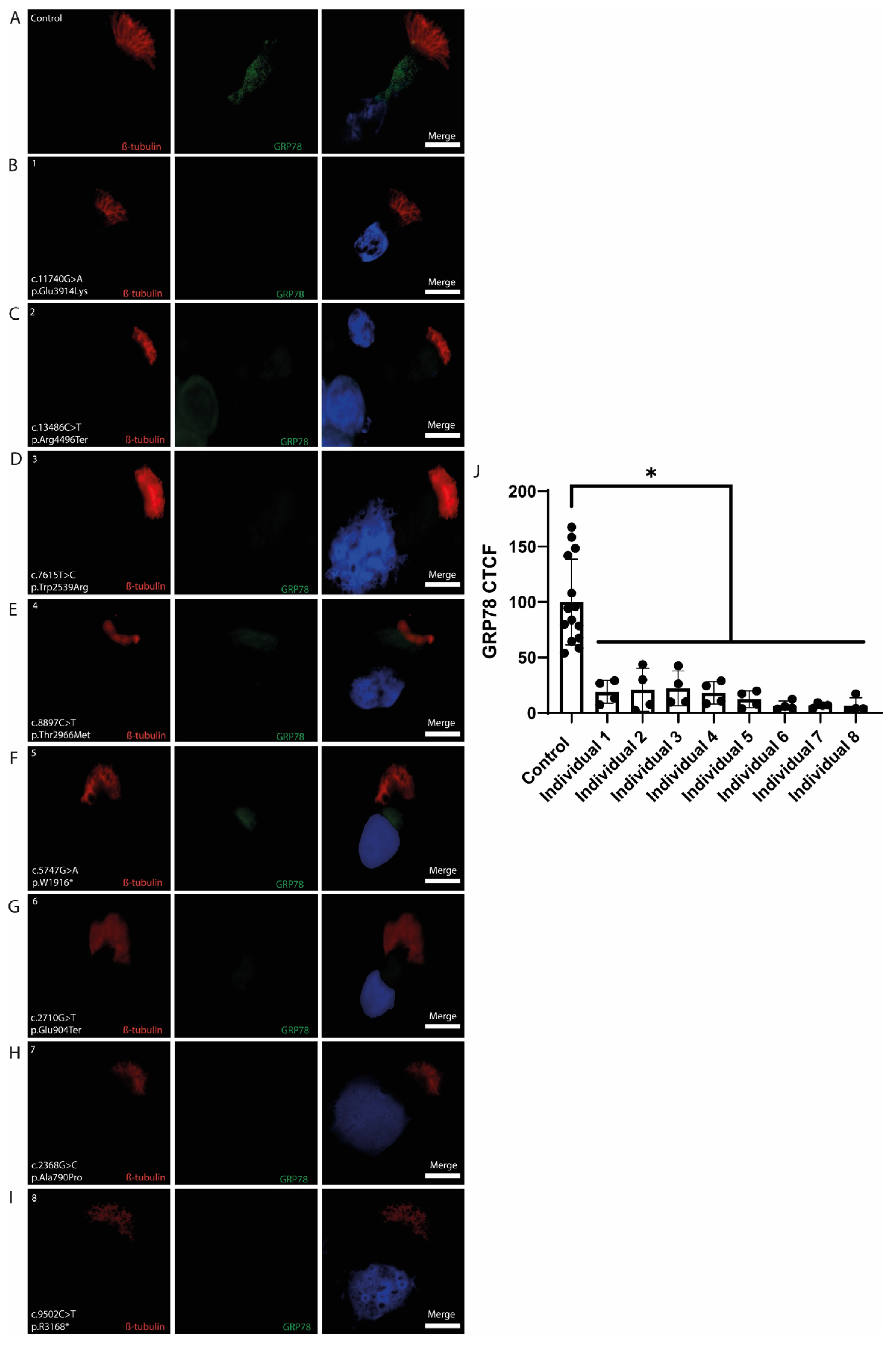
3.4.3. GRP78
3.5. Proteomics and Metabolomics Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Findings
4.2. DNAH5 Immunolabeling Showed Variety in DNAH5-Mutant Individuals
4.3. ZMYND10 Expression Is Altered in DNAH5-Related PCD
4.4. GRP78 Downregulation Indicates ER Stress in PCD Epithelium
4.5. Serum Proteomics and Metabolomics Support Systemic Stress Pathways
4.6. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leigh, M.W.; Ferkol, T.W.; Davis, S.D.; Lee, H.S.; Rosenfeld, M.; Dell, S.D.; Sagel, S.D.; Milla, C.; Olivier, K.N.; Sullivan, K.M.; et al. Clinical Features and Associated Likelihood of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Children and Adolescents. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Davis, S.D.; Ferkol, T.; Dell, S.D.; Rosenfeld, M.; Olivier, K.N.; Sagel, S.D.; Milla, C.; Zariwala, M.A.; Wolf, W.; et al. Laterality Defects Other Than Situs Inversus Totalis in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Chest 2014, 146, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Shoemark, A.; MacNeill, S.J.; Bhaludin, B.; Rogers, A.; Bilton, D.; Hansell, D.M.; Wilson, R.; Loebinger, M.R. A Longitudinal Study Characterising a Large Adult Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Population. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raidt, J.; Riepenhausen, S.; Pennekamp, P.; Olbrich, H.; Amirav, I.; Athanazio, R.A.; Aviram, M.; Balinotti, J.E.; Bar-On, O.; Bode, S.F.N.; et al. Analyses of 1236 Genotyped Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Individuals Identify Regional Clusters of Distinct DNA Variants and Significant Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2301769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Yang, Q.; Wan, X.; Wu, Y. Lrrc56 Deletion Causes Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in Mice Characterized by Dynein Arms Defects. Biol. Open 2025, 14, bio061846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiralioglu, N.; Karadag, B.; Ozcelik, H.U. Quality of Life Questionnaire for Turkish Patients with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Turk. Thorac. J. 2017, 18, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witman, G.B.; Leszyk, J.; Agrin, N.; Pazour, G.J. Proteomic Analysis of a Eukaryotic Cilium. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 170, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zariwala, M.; Lobo, J.; Noone, P. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, J.S.; Davis, S.D.; Omran, H.; Shoemark, A. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in the Genomics Age. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.; Ross, W.P. Histology, a Text and Atlas with Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology, 7th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T. Axoneme Structure from Motile Cilia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Stoyanova, M.; Rademacher, G.; Dutcher, S.K.; Brown, A.; Zhang, R. Structure of the Decorated Ciliary Doublet Microtubule. Cell 2019, 179, 909–922.e912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Shi, F.; Yang, Q.; Xie, L.; Lu, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Multiomics Analysis of a Dnah5-Mutated Pcd Organoid Model Revealed the Key Role of the Tgf-Beta/Bmp and Notch Pathways in Epithelial Differentiation and the Immune Response in Dnah5-Mutated Patients. Cells 2022, 11, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Shi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, J.; He, L.; Song, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, R.; Li, J.; Jia, N. Genetic Spectrum and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Dnah5-Mutated Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: A Systematic Review. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2025, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.T.; Gupta, A.; Bove, K.E.; Szabo, S.; Xu, F.; Krentz, A.; Shillington, A.L. Novel Pathogenic Dnah5 Variants in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Association with Visceral Heterotaxia and Neonatal Cholestasis. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2023, 12, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, A.K.; Wang, H.; Katayama, A.; Aihara, M.S.; Allen, R.D. 22s Axonemal Dynein Is Preassembled and Functional Prior to Being Transported to and Attached on the Axonemes. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 1994, 29, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, M.E.; Mitchell, D.R. The Role of Preassembled Cytoplasmic Complexes in Assembly of Flagellar Dynein Subunits. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.T.; Gao, C.; Lucker, B.F.; Cole, D.G.; Mitchell, D.R. Oda16 Aids Axonemal Outer Row Dynein Assembly through an Interaction with the Intraflagellar Transport Machinery. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, H.; Kobayashi, D.; Olbrich, H.; Tsukahara, T.; Loges, N.T.; Hagiwara, H.; Zhang, Q.; Leblond, G.; O’Toole, E.; Hara, C.; et al. Ktu/Pf13 Is Required for Cytoplasmic Pre-Assembly of Axonemal Dyneins. Nature 2008, 456, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchison, H.M.; Schmidts, M.; Loges, N.T.; Freshour, J.; Dritsoula, A.; Hirst, R.A.; O’Callaghan, C.; Blau, H.; Al Dabbagh, M.; Olbrich, H.; et al. Mutations in Axonemal Dynein Assembly Factor Dnaaf3 Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.J.; Noh, S.H.; Han, S.M.; Choi, W.I.; Kim, H.Y.; Yu, S.; Lee, J.S.; Rim, J.H.; Lee, M.G.; Hildebrandt, F.; et al. Zmynd10 Stabilizes Intermediate Chain Proteins in the Cytoplasmic Pre-Assembly of Dynein Arms. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horani, A.; Druley, T.E.; Zariwala, M.A.; Patel, A.C.; Levinson, B.T.; Van Arendonk, L.G.; Thornton, K.C.; Giacalone, J.C.; Albee, A.J.; Wilson, K.S.; et al. Whole-Exome Capture and Sequencing Identifies Heatr2 Mutation as a Cause of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarkar, A.; Loges, N.T.; Slagle, C.E.; Francis, R.; Dougherty, G.W.; Tamayo, J.V.; Shook, B.; Cantino, M.; Schwartz, D.; Jahnke, C.; et al. Dyx1c1 Is Required for Axonemal Dynein Assembly and Ciliary Motility. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zariwala, M.A.; Gee, H.Y.; Kurkowiak, M.; Al-Mutairi, D.A.; Leigh, M.W.; Hurd, T.W.; Hjeij, R.; Dell, S.D.; Chaki, M.; Dougherty, G.W.; et al. Zmynd10 Is Mutated in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Interacts with Lrrc6. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kott, E.; Duquesnoy, P.; Copin, B.; Legendre, M.; Dastot-Le Moal, F.; Montantin, G.; Jeanson, L.; Tamalet, A.; Papon, J.F.; Siffroi, J.P.; et al. Loss-of-Function Mutations in Lrrc6, a Gene Essential for Proper Axonemal Assembly of Inner and Outer Dynein Arms, Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horani, A.; Ferkol, T.W.; Shoseyov, D.; Wasserman, M.G.; Oren, Y.S.; Kerem, B.; Amirav, I.; Cohen-Cymberknoh, M.; Dutcher, S.K.; Brody, S.L.; et al. Lrrc6 Mutation Causes Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia with Dynein Arm Defects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.M.; Abdelmalek, D.H.; Elfiky, A.A. Grp78: A Cell’s Response to Stress. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashho, B.; Rumman, N.; Lucas, J.; Halaweh, H. Active Cycle of Breathing Technique Versus Oscillating Positive Expiratory Pressure Therapy: Effect on Lung Function in Children with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia; a Feasibility Study. Chronic Respir. Dis. 2025, 22, 14799731251314872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoc, E.; Hjeij, R.; Kaya, Z.B.; Emiralioglu, N.; Ademhan Tural, D.; Atilla, P.; Ozcelik, U.; Omran, H. Diagnostic Role of Immunofluorescence Analysis in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia-Suspected Individuals. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Barbosa, T.; Gales, L.; Oliveira, E.; Santos, R.; Oliveira, J.; Sousa, M. Clinical and Genetic Analysis of Children with Kartagener Syndrome. Cells 2019, 8, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, A.; Hoben, I.M.; Wolter, A.; Loges, N.T.; Olbrich, H.; Aprea, I.; Dworniczak, B.; Raidt, J.; Omran, H. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Associated Disease-Causing Variants in Ccdc39 and Ccdc40 Cause Axonemal Absence of Inner Dynein Arm Heavy Chains Dnah1, Dnah6, and Dnah7. Cells 2024, 13, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutaki, M.; Shoemark, A. Diagnosis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Clin. Chest Med. 2022, 43, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Meng, X.; Meng, F.; Gao, M. Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations of Dnah5 Identified in a Pediatric Patient with Kartagener Syndrome: Case Report and Literature Review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothe-Menchen, T.; Wallmeier, J.; Pennekamp, P.; Hoben, I.M.; Olbrich, H.; Loges, N.T.; Raidt, J.; Dougherty, G.W.; Hjeij, R.; Dworniczak, B.; et al. Randomization of Left-Right Asymmetry and Congenital Heart Defects: The Role of Dnah5 in Humans and Mice. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mutairi, D.A.; Alsabah, B.H.; Pennekamp, P.; Omran, H. Novel Pathogenic Variants of Dnah5 Associated with Clinical and Genetic Spectra of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia in an Arab Population. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1396797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horani, A.; Ferkol, T.W.; Dutcher, S.K.; Brody, S.L. Genetics and Biology of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2016, 18, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemark, A.; Frost, E.; Dixon, M.; Ollosson, S.; Kilpin, K.; Patel, M.; Scully, J.; Rogers, A.V.; Mitchison, H.M.; Bush, A.; et al. Accuracy of Immunofluorescence in the Diagnosis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, I.L.; Daniş, A.; Nayir Büyükşahin, H.; Emiralioğlu, N.; Kaya, Z.B.; Özçelik, U.; Atilla, P.; Bilgiç, E. A Histologıcal Approach to a Patıent Wıth Prımary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Cilium Preassembly Proteins in the Presence of the Outer Dynein Arm Defect. In Proceedings of the 15th National–1st International Congress of Histology and Embryology (NICHE 2022), Online, 26–28 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mali, G.R.; Yeyati, P.L.; Mizuno, S.; Dodd, D.O.; Tennant, P.A.; Keighren, M.A.; Zur Lage, P.; Shoemark, A.; Garcia-Munoz, A.; Shimada, A.; et al. Zmynd10 Functions in a Chaperone Relay During Axonemal Dynein Assembly. eLife 2018, 7, e34389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Ha, D.P.; Wang, J.; Xiong, M.; Lee, A.S. Er Chaperone Grp78/Bip Translocates to the Nucleus under Stress and Acts as a Transcriptional Regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303448120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, I.L.; Danis, A.; Buyuksahin, H.N.; Emiralioglu, N.; Kaya, Z.B.; Ozcelik, U.; Atilla, P.; Eylem, C.C.; Nemutlu, E.; Bilgic, E. Examining the Connection between Dnah5 Abnormalities and Preassembly Proteins in Patients with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (Pcd): May Be Accompanied with Potential Organelle Dysfunctions. In EMBO Cilia 2022; EMBO: Cologne, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rollet-Cohen, V.; Bourderioux, M.; Lipecka, J.; Chhuon, C.; Jung, V.A.; Mesbahi, M.; Nguyen-Khoa, T.; Guerin-Pfyffer, S.; Schmitt, A.; Edelman, A.; et al. Comparative Proteomics of Respiratory Exosomes in Cystic Fibrosis, Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Asthma. J. Proteom. 2018, 185, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horani, A.; Gupta, D.K.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.; Del Carmen Puga-Molina, L.; Santi, C.M.; Ramagiri, S.; Brennen, S.K.; Pan, J.; Huang, T.; et al. The Effect of Dnaaf5 Gene Dosage on Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Phenotypes. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e168836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Clinical Statistics | Valid Percent | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender Female Male | n 5 3 | 62.5 37.5 | |
| Age median (min–max) | 17.5 (14–22) | ||
| nNO median (min–max) | 7.5 (5–10) | ||
| Consanguinity, n | 4 (3 females; 1 male) | 50 | |
| Sinusitis, n | 5 (3 females; 2 males) | 62.5 | |
| Bronchiectasis, n | 7 (5 females; 2 males) | 87.5 | |
| Recurrent lung infection, n | 6 (4 females; 2 males) | 75 | |
| Hearing defect, n | 2 (1 female; 1 male) | 25 | |
| Situs inversus, n | 3 (3 females) | 37.5 | |
| Rhinitis, n | 3 (1 female and 2 males) | 37.5 | |
| Individual ID | Sex | Age | Symptoms | Bronchiectasis | Situs Inversus | Consanguinity | Lobectomy | Nasal NO (ppb) | HSVM | Genetic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 21 y | Rhinitis, sinusitis | yes | no | no | no | 5 ppb | Almost immotile cilia, only minimal residual ciliary movements | DNAH5 het: c.11740G>A; p.Glu3914Lys |
| 2 | F | 17 y | Recurrent lung infection, rhinitis, recurrent sinusitis | yes | no | yes | no | 6 ppb | Almost immotile cilia, only minimal residual ciliary movements | DNAH5 hom: c.13486C>T; p.Arg4496Ter |
| 3 | F | 22 y | Recurrent lung infection, sinusitis | yes | yes | yes | no | 8 ppb | Slightly reduced amplitude | DNAH5 hom: c.7615T>C; p.Trp2539Arg |
| 4 | F | 18 y | Recurrent lung infection | yes | yes | yes | no | 6 ppb | Almost immotile cilia, only minimal residual ciliary movements | DNAH5 hom: c.8897C>T; p.Thr2966Met |
| 5 | F | 19 y | Recurrent lung infection, sinusitis, hearing defect | yes | yes | no | no | 10 ppb | Almost immotile cilia, only minimal residual ciliary movements | DNAH5 het: c.5747G>A; p.W1916 * |
| 6 | M | 16 y | Recurrent lung infection | yes | no | no | yes | 7 ppb | Almost immotile cilia, only minimal residual ciliary movements | DNAH5 hom: c.2710G>T; p.Glu904Ter |
| 7 | F | 16 y | Recurrent lung infection, sinusitis, | yes | no | no | yes | 9 ppb | Slightly reduced amplitude | DNAH5 hom: c.2368G>C; p.Ala790Pro |
| 8 | M | 14 y | Rhinitis, hearing defect | no | no | yes | no | 8 ppb | NA | DNAH5 hom: c.9502C>T; p.R3168 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erdem, İ.L.; Kaya, Z.B.; Atilla, P.; Emiralioğlu, N.; Eylem, C.C.; Nemutlu, E.; Özçelik, U.; Büyükşahin, H.N.; Daniş, A.; Karakoç, E. Molecular Insights into Outer Dynein Arm Defects in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Involvement of ZMYND10 and GRP78. Cells 2025, 14, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120916
Erdem İL, Kaya ZB, Atilla P, Emiralioğlu N, Eylem CC, Nemutlu E, Özçelik U, Büyükşahin HN, Daniş A, Karakoç E. Molecular Insights into Outer Dynein Arm Defects in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Involvement of ZMYND10 and GRP78. Cells. 2025; 14(12):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120916
Chicago/Turabian StyleErdem, İlker Levent, Zeynep Bengisu Kaya, Pergin Atilla, Nagehan Emiralioğlu, Cemil Can Eylem, Emirhan Nemutlu, Uğur Özçelik, Halime Nayır Büyükşahin, Ayşenur Daniş, and Elif Karakoç. 2025. "Molecular Insights into Outer Dynein Arm Defects in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Involvement of ZMYND10 and GRP78" Cells 14, no. 12: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120916
APA StyleErdem, İ. L., Kaya, Z. B., Atilla, P., Emiralioğlu, N., Eylem, C. C., Nemutlu, E., Özçelik, U., Büyükşahin, H. N., Daniş, A., & Karakoç, E. (2025). Molecular Insights into Outer Dynein Arm Defects in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: Involvement of ZMYND10 and GRP78. Cells, 14(12), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14120916








