Intracellular Inclusions Induced by Patient-Derived and Amplified α-Synuclein Aggregates Are Morphologically Indistinguishable
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples
2.2. Preparation of Postmortem Brain Tissue Insoluble Fractions
2.3. Preparation of α-Syn Monomer
2.4. α-Syn Seed Amplification Assay
2.5. Proteinase K Digestion of α-Syn Aggregates Amplified by SAA
2.6. Negative Stain Electron Microscopy Imaging
2.7. Synuclein Biosensor Cells
2.8. FRET Seeding Assay
2.9. Confocal Microscopy Imaging
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
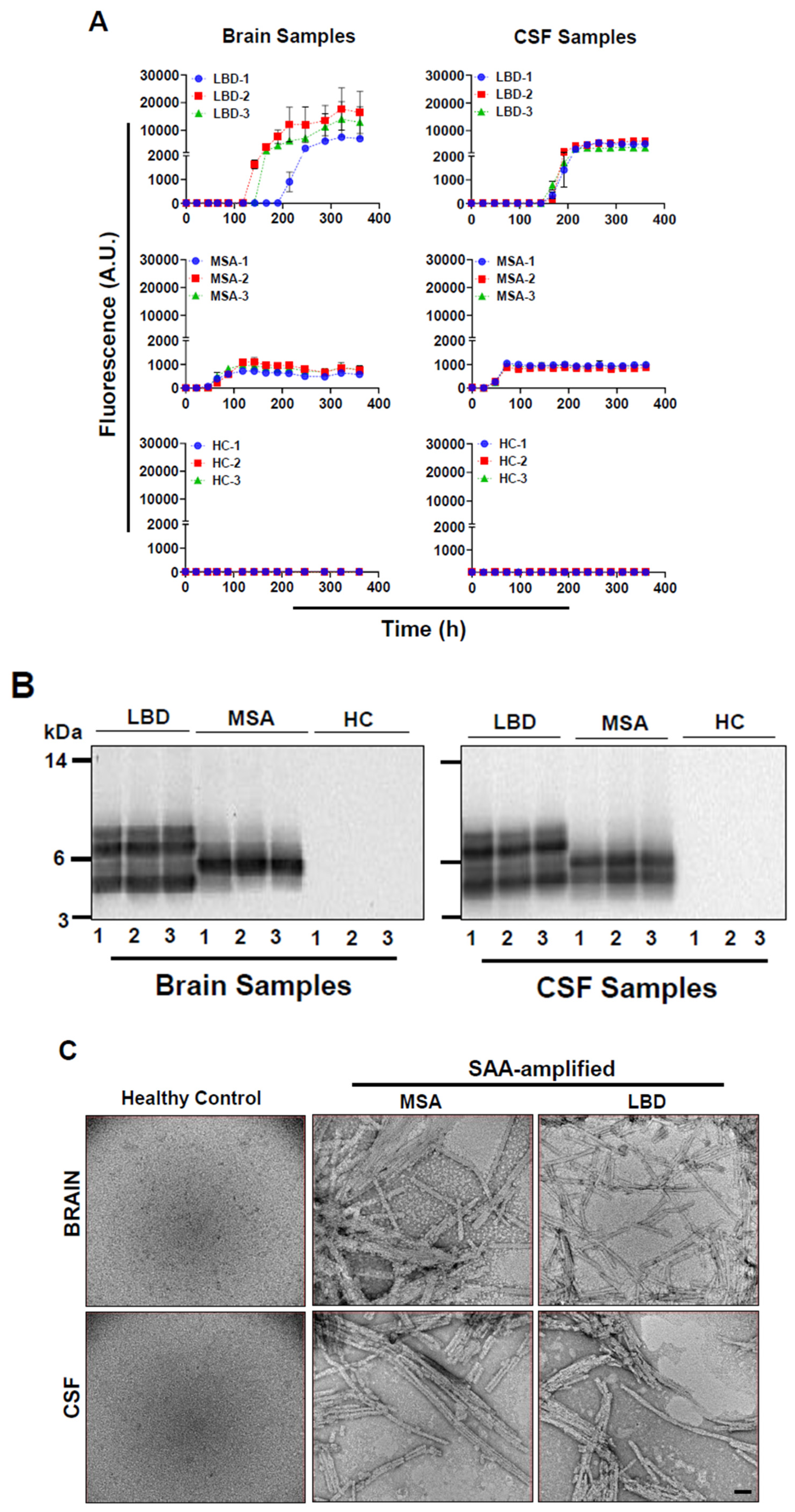
3.1. Amplification of α-Syn Aggregates from Patients’ Brains and CSF Samples and Their Characterization
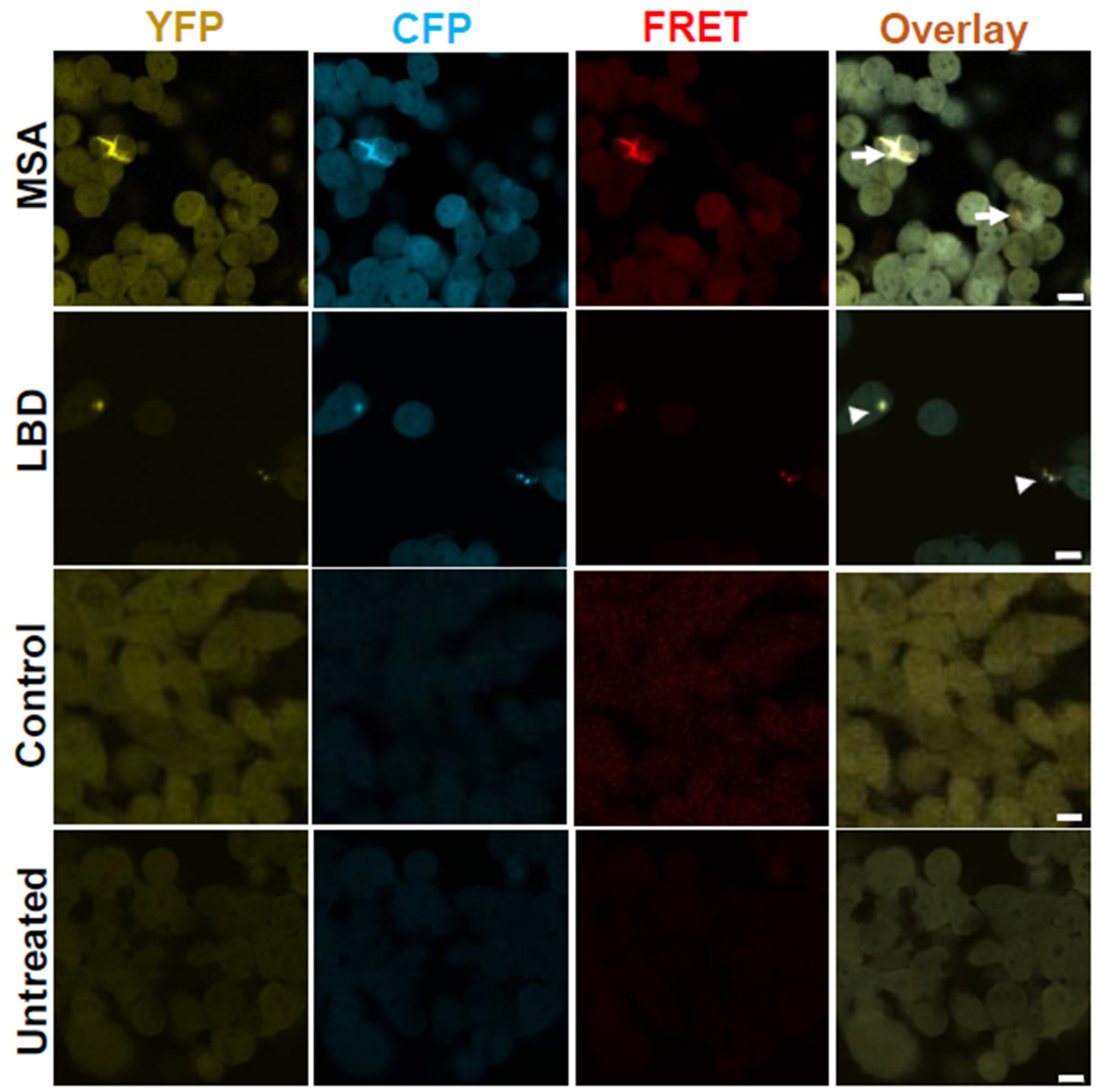
3.2. Brain Homogenates of LBD and MSA Patients Induce Intracellular α-Syn Inclusions with Distinct Morphologies
3.3. Morphologies of α-Syn Inclusions Induced with Un-Amplified and SAA-Amplified LBD and MSA Brain Homogenates Are Similar
3.4. SAA-Amplified LBD and MSA CSF Samples Induce the Formation of α-Syn Aggregates with Similar Morphologies to SAA-Amplified and Un-Amplified Brain Samples
3.5. MSA Samples Are More Seeding-Competent than LBD Samples
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M. Lewy body diseases and multiple system atrophy as α-synucleinopathies. Mol. Psychiatry 1998, 3, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Schmidt, M.; Lee, V.; Trojanowski, J.; Spillantini, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Cairns, N.J.; Lantos, P.L.; Goedert, M. Filamentous α-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 251, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Neurodegeneration and the ordered assembly of α-synuclein. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G. The synucleinopathies: Twenty years on. J. Park. Dis. 2017, 7, S51–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Yoshimoto, M.; Tsuji, S.; Takahashi, H. α-Synuclein immunoreactivity in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 249, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.I.; Lee, J.; Monteiro, O.; Woerman, A.L.; Lazar, A.A.; Condello, C.; Paras, N.A.; Prusiner, S.B. Different α-synuclein prion strains cause dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113489119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desplats, P.; Lee, H.-J.; Bae, E.-J.; Patrick, C.; Rockenstein, E.; Crews, L.; Spencer, B.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.-J. Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of α-synuclein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13010–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: The prion concept in relation to assembled Aβ, tau, and α-synuclein. Science 2015, 349, 1255555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Angot, E.; Bergström, A.-L.; Steiner, J.A.; Pieri, L.; Paul, G.; Outeiro, T.F.; Melki, R.; Kallunki, P.; Fog, K. α-Synuclein propagates from mouse brain to grafted dopaminergic neurons and seeds aggregation in cultured human cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordower, J.H.; Chu, Y.; Hauser, R.A.; Freeman, T.B.; Olanow, C.W. Lewy body–like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-Y.; Englund, E.; Holton, J.L.; Soulet, D.; Hagell, P.; Lees, A.J.; Lashley, T.; Quinn, N.P.; Rehncrona, S.; Björklund, A. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Englund, E.; Widner, H.; Mattsson, B.; van Westen, D.; Lätt, J.; Rehncrona, S.; Brundin, P.; Björklund, A.; Lindvall, O. Extensive graft-derived dopaminergic innervation is maintained 24 years after transplantation in the degenerating parkinsonian brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6544–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melki, R. Role of different alpha-synuclein strains in synucleinopathies, similarities with other neurodegenerative diseases. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.A.; Lavenir, I.; Fan, J.; Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Passarella, D.; DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein filaments from transgenic mouse and human synucleinopathy-containing brains are major seed-competent species. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6652–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelaerts, W.; Bousset, L.; Van der Perren, A.; Moskalyuk, A.; Pulizzi, R.; Giugliano, M.; Van den Haute, C.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 2015, 522, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Covell, D.J.; Medellin, C.; Stieber, A.; Robinson, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Pitkin, R.M.; Olufemi, M.F.; Luk, K.C. Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological α-synuclein strains in α-synucleinopathies. Nature 2018, 557, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N. Evidence for α-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimozawa, A.; Ono, M.; Takahara, D.; Tarutani, A.; Imura, S.; Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Higuchi, M.; Yanai, K.; Hisanaga, S.-i.; Hasegawa, M. Propagation of pathological α-synuclein in marmoset brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofaris, G.K.; Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G. The transcellular propagation and intracellular trafficking of α-synuclein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a024380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, J.C.; Giles, K.; Oehler, A.; Middleton, L.; Dexter, D.T.; Gentleman, S.M.; DeArmond, S.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Transmission of multiple system atrophy prions to transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19555–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerman, A.L.; Stöhr, J.; Aoyagi, A.; Rampersaud, R.; Krejciova, Z.; Watts, J.C.; Ohyama, T.; Patel, S.; Widjaja, K.; Oehler, A. Propagation of prions causing synucleinopathies in cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4949–E4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerman, A.L.; Watts, J.C.; Aoyagi, A.; Giles, K.; Middleton, L.T.; Prusiner, S.B. α-Synuclein: Multiple system atrophy prions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a024588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.R.; Holmes, B.B.; Furman, J.L.; Dhavale, D.D.; Su, B.W.; Song, E.-S.; Cairns, N.J.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Diamond, M.I. Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy have distinct α-synuclein seed characteristics. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.I.; Brooks, M.M.; Rutherford, N.J.; Howard, J.K.; Sorrentino, Z.A.; Riffe, C.J.; Giasson, B.I. Robust central nervous system pathology in transgenic mice following peripheral injection of α-Synuclein Fibrils. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02095-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breid, S.; Bernis, M.E.; Babila, J.T.; Garza, M.C.; Wille, H.; Tamgüney, G. Neuroinvasion of α-synuclein prionoids after intraperitoneal and intraglossal inoculation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9182–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, S.; Chutna, O.; Bousset, L.; Aldrin-Kirk, P.; Li, W.; Björklund, T.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Roybon, L.; Melki, R.; Li, J.-Y. Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, S.-H.; Kam, T.-I.; Panicker, N.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.R.; Kook, M.; Foss, C.A. Transneuronal propagation of pathologic α-synuclein from the gut to the brain models Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 2019, 103, 627–641.e627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Kehm, V.M.; Zhang, B.; O’Brien, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Intracerebral inoculation of pathological α-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative α-synucleinopathy in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Kehm, V.; Carroll, J.; Zhang, B.; O’Brien, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y. Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 2012, 338, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Nonaka, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Oikawa, T.; Arai, T.; Akiyama, H.; Mann, D.M.; Hasegawa, M. Prion-like spreading of pathological α-synuclein in brain. Brain 2013, 136, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterberg, V.R.; Spinelli, K.J.; Weston, L.J.; Luk, K.C.; Woltjer, R.L.; Unni, V.K. Progressive aggregation of alpha-synuclein and selective degeneration of lewy inclusion-bearing neurons in a mouse model of parkinsonism. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recasens, A.; Dehay, B.; Bové, J.; Carballo-Carbajal, I.; Dovero, S.; Pérez-Villalba, A.; Fernagut, P.O.; Blesa, J.; Parent, A.; Perier, C. Lewy body extracts from Parkinson disease brains trigger α-synuclein pathology and neurodegeneration in mice and monkeys. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacino, A.N.; Brooks, M.; Thomas, M.A.; McKinney, A.B.; Lee, S.; Regenhardt, R.W.; McGarvey, N.H.; Ayers, J.I.; Notterpek, L.; Borchelt, D.R. Intramuscular injection of α-synuclein induces CNS α-synuclein pathology and a rapid-onset motor phenotype in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10732–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, U.J.; Boehme, A.K.; Fairfoul, G.; Shahnawaz, M.; Ma, T.C.; Hutten, S.J.; Green, A.; Soto, C. Comparative study of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein seeding aggregation assays for diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Tokuda, T.; Waragai, M.; Mendez, N.; Ishii, R.; Trenkwalder, C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Soto, C. Development of a biochemical diagnosis of Parkinson disease by detection of α-synuclein misfolded aggregates in cerebrospinal fluid. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G. Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, W.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Shahnawaz, M.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Boeve, B.F.; Sletten, D.M.; Gehrking, T.L.; Gehrking, J.A.; Olson, A.D.; Savica, R. Alpha-synuclein oligomers and neurofilament light chain in spinal fluid differentiate multiple system atrophy from Lewy body synucleinopathies. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövestam, S.; Schweighauser, M.; Matsubara, T.; Murayama, S.; Tomita, T.; Ando, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Yoshida, M.; Tarutani, A.; Hasegawa, M. Seeded assembly in vitro does not replicate the structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerman, A.L.; Patel, S.; Kazmi, S.A.; Oehler, A.; Lee, J.; Mordes, D.A.; Olson, S.H.; Prusiner, S.B. Kinetics of α-synuclein prions preceding neuropathological inclusions in multiple system atrophy. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, V.; Shani, T.; Katzman, B.; Vyazmensky, M.; Papo, N.; Israelson, A.; Engel, S. Superoxide Dismutase 1 (SOD1)-Derived Peptide Inhibits Amyloid Aggregation of Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis SOD1 Mutants. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, B.B.; Furman, J.L.; Mahan, T.E.; Yamasaki, T.R.; Mirbaha, H.; Eades, W.C.; Belaygorod, L.; Cairns, N.J.; Holtzman, D.M.; Diamond, M.I. Proteopathic tau seeding predicts tauopathy in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4376–E4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweighauser, M.; Shi, Y.; Tarutani, A.; Kametani, F.; Murzin, A.G.; Ghetti, B.; Matsubara, T.; Tomita, T.; Ando, T.; Hasegawa, K. Structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 585, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Schweighauser, M.; Zhang, X.; Kotecha, A.; Murzin, A.G.; Garringer, H.J.; Cullinane, P.W.; Saito, Y.; Foroud, T. Cryo-EM structures of α-synuclein filaments from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Biorxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Schweighauser, M.; Zhang, X.; Kotecha, A.; Murzin, A.G.; Garringer, H.J.; Cullinane, P.W.; Saito, Y.; Foroud, T. Structures of α-synuclein filaments from human brains with Lewy pathology. Nature 2022, 610, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Perren, A.; Gelders, G.; Fenyi, A.; Bousset, L.; Brito, F.; Peelaerts, W.; Van den Haute, C.; Gentleman, S.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. The structural differences between patient-derived α-synuclein strains dictate characteristics of Parkinson’s disease, multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohäker, T.; Jung, B.C.; Liou, S.-H.; Fernandez, C.O.; Riedel, D.; Becker, S.; Halliday, G.M.; Bennati, M.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, S.-J. Structural heterogeneity of α-synuclein fibrils amplified from patient brain extracts. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarutani, A.; Suzuki, G.; Shimozawa, A.; Nonaka, T.; Akiyama, H.; Hisanaga, S.-i.; Hasegawa, M. The effect of fragmented pathogenic α-synuclein seeds on prion-like propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 18675–18688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulić, S.; Le, T.T.N.; Moda, F.; Abounit, S.; Corvaglia, S.; Casalis, L.; Gustincich, S.; Zurzolo, C.; Tagliavini, F.; Legname, G. Defined α-synuclein prion-like molecular assemblies spreading in cell culture. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CSF | BH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S/No | Clinical Diagnosis | Age/Sex | Disease Duration | S/No | Clinical Diagnosis | Brain Regions | Age/Sex | Disease Duration |
| 1 | LBD | 76/M | 11 | 1 | LBD | ENT | 84/F | 10 |
| 2 | LBD | 74/M | 1 | 2 | LBD | MB | 86/F | 8 |
| 3 | LBD | 63/M | 3 | 3 | LBD | MB | 87/M | 5 |
| 4 | MSA-P | 64/M | 1 | 4 | MSA-C | RFL | 61/M | 7 |
| 5 | MSA-C | 60/M | 6 | 5 | MSA-P | RFL | 60/M | 9 |
| 6 | MSA-C | 51/M | 2.5 | 6 | MSA-P | RFL | 71/F | 10 |
| 7 | Control | 59/F | NA | 7 | Control | RFL | 97/F | NA |
| 8 | Control | 69/M | NA | 8 | Control | RFL | 82/M | NA |
| 9 | Control | 67/M | NA | 9 | Control | RFL | 73/F | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Lahham, R.; Corkins, M.E.; Ishtikhar, M.; Rabadia, P.; Ramirez, S.; Banerjee, V.; Shahnawaz, M. Intracellular Inclusions Induced by Patient-Derived and Amplified α-Synuclein Aggregates Are Morphologically Indistinguishable. Cells 2025, 14, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100684
Al-Lahham R, Corkins ME, Ishtikhar M, Rabadia P, Ramirez S, Banerjee V, Shahnawaz M. Intracellular Inclusions Induced by Patient-Derived and Amplified α-Synuclein Aggregates Are Morphologically Indistinguishable. Cells. 2025; 14(10):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100684
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Lahham, Rabab, Mark E. Corkins, Mohd Ishtikhar, Prakruti Rabadia, Santiago Ramirez, Victor Banerjee, and Mohammad Shahnawaz. 2025. "Intracellular Inclusions Induced by Patient-Derived and Amplified α-Synuclein Aggregates Are Morphologically Indistinguishable" Cells 14, no. 10: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100684
APA StyleAl-Lahham, R., Corkins, M. E., Ishtikhar, M., Rabadia, P., Ramirez, S., Banerjee, V., & Shahnawaz, M. (2025). Intracellular Inclusions Induced by Patient-Derived and Amplified α-Synuclein Aggregates Are Morphologically Indistinguishable. Cells, 14(10), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100684





