CD40L Activates Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3 by Binding to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) in a KGD-Independent Manner and HIGM1 Mutations Are Clustered in the Integrin-Binding Sites of CD40L
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Synthesis of Recombinant sCD40L with No KGD Motif
2.2. Synthesis of Fibrinogen Fragments
2.3. Binding of Soluble αIIbβ3 to CD40L
2.4. Activation of Soluble αIIbβ3 by sCD40L
2.5. Activation of Cell-Surface αIIbβ3 on Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) Cells
2.6. Docking Simulation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
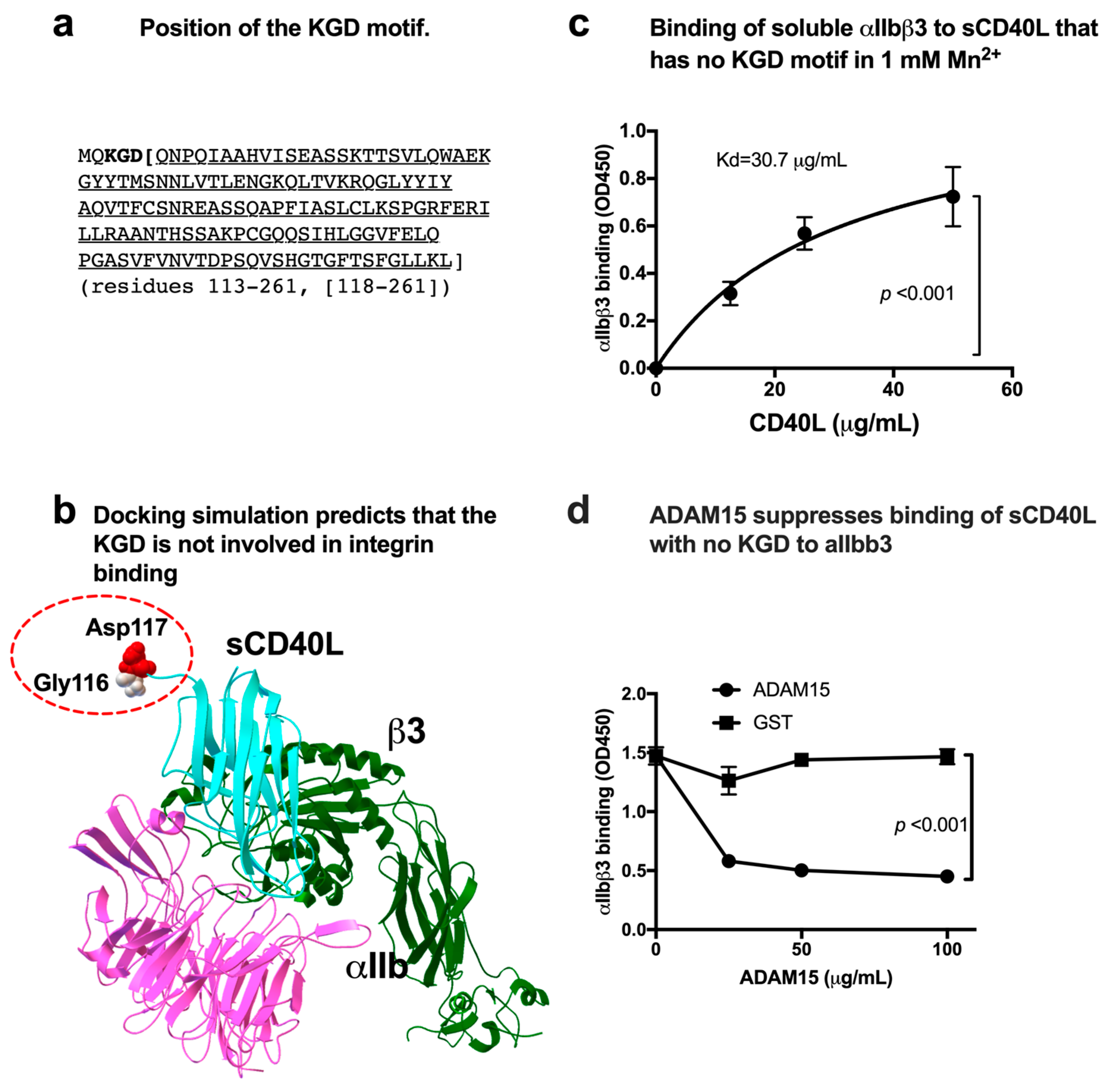
3.1. sCD40L Binds to Soluble αIIbβ3 in a KGD-Independent Manner
3.2. Effect of a Group of HIGM1 Mutations on the Binding of sCD40L to the Classical Ligand-Binding Site (Site 1) of αIIbβ3
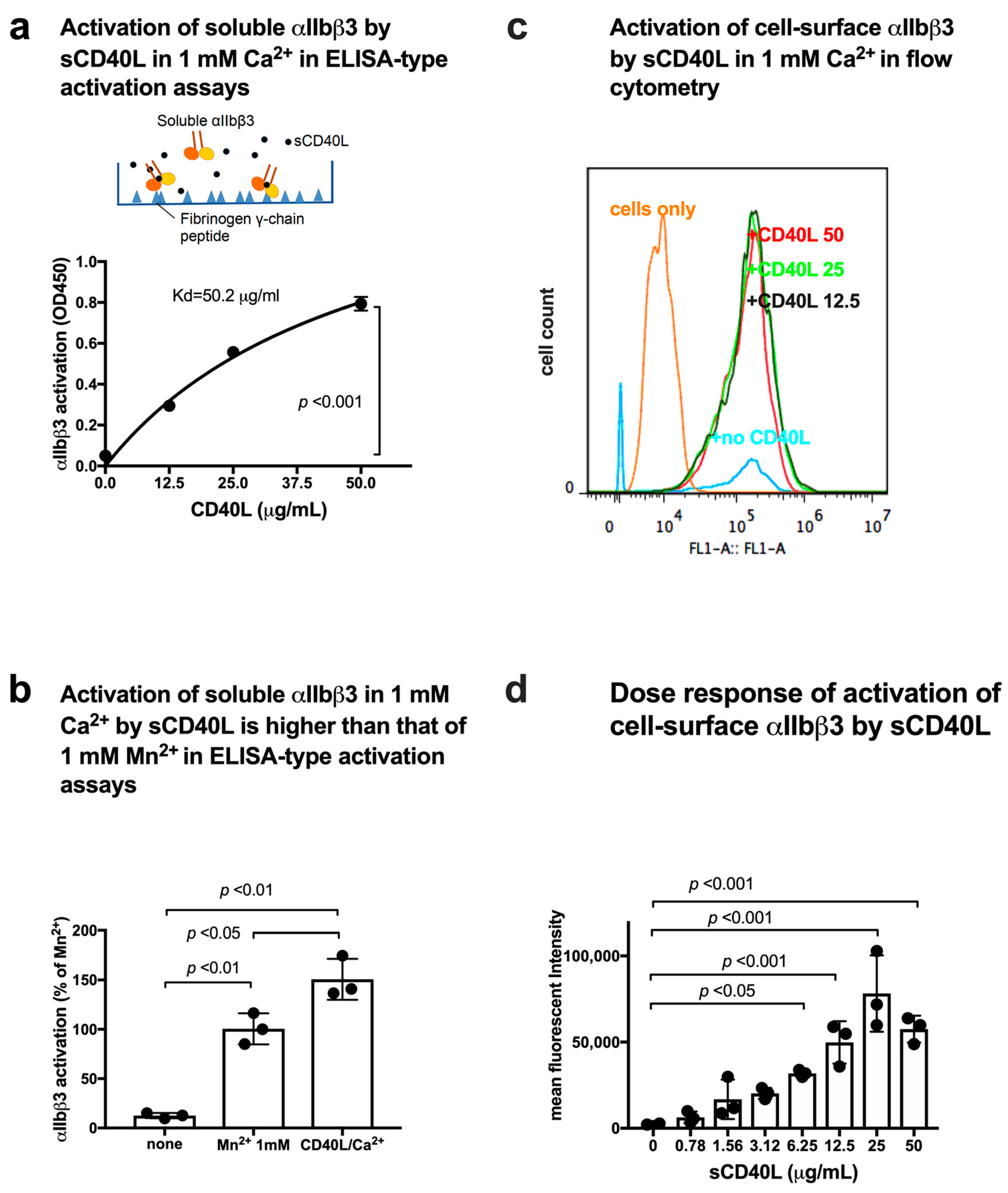
3.3. CD40L Activates Soluble and Cell-Surface Integrin αIIbβ3 in 1 mM Ca2+ by Binding to Site 2
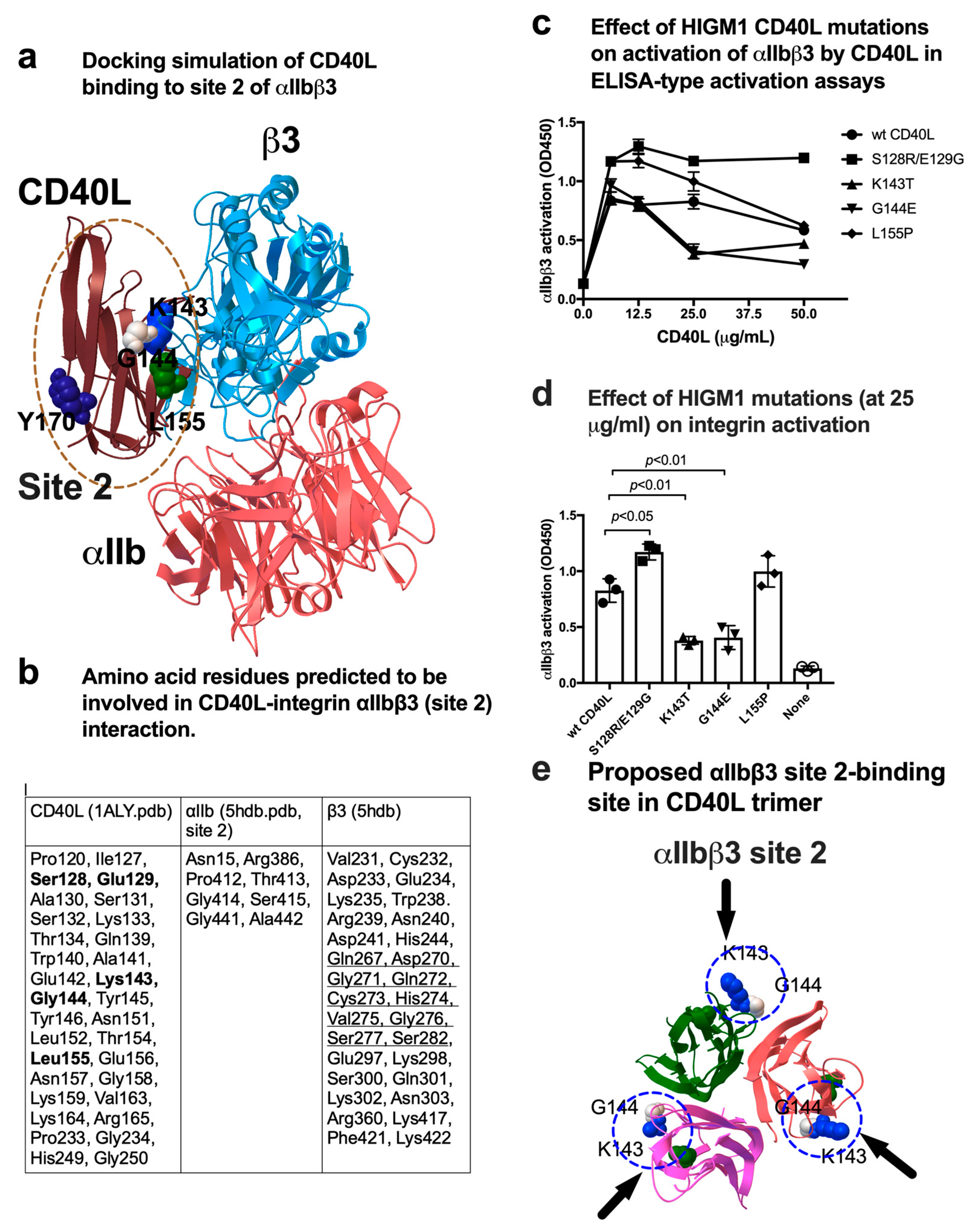
3.4. A Group of HIGM1 Mutations Suppress Activation of αIIbβ3 by CD40L
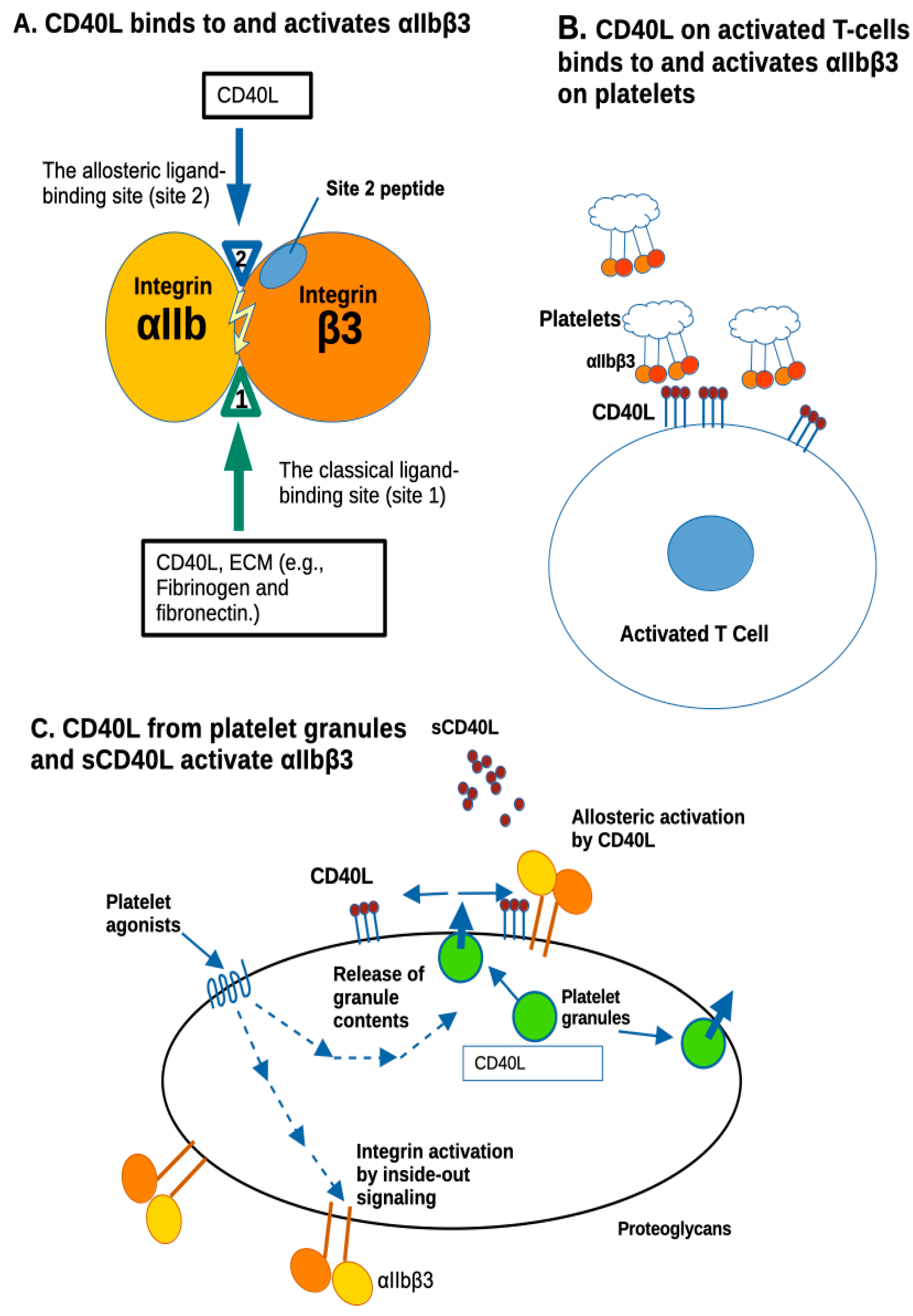
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, G.S.; Salti, S.; Mourad, W. Novel Functions of Integrins as Receptors of CD154: Their Role in Inflammation and Apoptosis. Cells 2022, 11, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, P.; Prasad, K.S.; Denis, C.V.; He, M.; Papalia, J.M.; Hynes, R.O.; Phillips, D.R.; Wagner, D.D. CD40L stabilizes arterial thrombi by a beta3 integrin--dependent mechanism. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, P.; Nannizzi-Alaimo, L.; Prasad, S.K.; Phillips, D.R. Platelet-derived CD40L: The switch-hitting player of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Fiocchi, C. Platelet activation and the CD40/CD40 ligand pathway: Mechanisms and implications for human disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 25, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leveille, C.; Bouillon, M.; Guo, W.; Bolduc, J.; Sharif-Askari, E.; El-Fakhry, Y.; Reyes-Moreno, C.; Lapointe, R.; Merhi, Y.; Wilkins, J.A.; et al. CD40 ligand binds to alpha5beta1 integrin and triggers cell signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5143–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirlik, A.; Maier, C.; Gerdes, N.; MacFarlane, L.; Soosairajah, J.; Bavendiek, U.; Ahrens, I.; Ernst, S.; Bassler, N.; Missiou, A.; et al. CD40 ligand mediates inflammation independently of CD40 by interaction with Mac-1. Circulation 2007, 115, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturaihi, H.; Hassan, G.S.; Al-Zoobi, L.; Salti, S.; Darif, Y.; Yacoub, D.; El Akoum, S.; Oudghiri, M.; Merhi, Y.; Mourad, W. Interaction of CD154 with different receptors and its role in bidirectional signals. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fakhry, Y.; Alturaihi, H.; Yacoub, D.; Liu, L.; Guo, W.; Leveille, C.; Jung, D.; Khzam, L.B.; Merhi, Y.; Wilkins, J.A.; et al. Functional interaction of CD154 protein with alpha5beta1 integrin is totally independent from its binding to alphaIIbbeta3 integrin and CD40 molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18055–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Yu, J.; Shimoda, M.; Takada, Y. Integrin Binding to the Trimeric Interface of CD40L Plays a Critical Role in CD40/CD40L Signaling. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piirila, H.; Valiaho, J.; Vihinen, M. Immunodeficiency mutation databases (IDbases). Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha4beta1 act as coreceptors for fractalkine, and the integrin-binding defective mutant of fractalkine is an antagonist of CX3CR1. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5809–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. The chemokine fractalkine can activate integrins without CX3CR1 through direct binding to a ligand-binding site distinct from the classical RGD-binding site. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Davari, P.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (CXCL12) activates integrins by direct binding to an allosteric ligand-binding site (site 2) of integrins without CXCR4. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.K.; Fujita, M.; Takada, Y. Pro-Inflammatory Chemokines CCL5, CXCL12, and CX3CL1 Bind to and Activate Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 in an Allosteric Manner. Cells 2022, 11, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.S.; Andre, P.; Yan, Y.; Phillips, D.R. The platelet CD40L/GP IIb-IIIa axis in atherothrombotic disease. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2003, 10, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Shimoda, M.; Maverakis, E.; Felding, B.H.; Cheng, R.H.; Takada, Y. Soluble CD40L activates soluble and cell-surface integrins alphavbeta3, alpha5beta1 and alpha4beta1 by binding to the allosteric ligand-binding site (site 2). J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Simon, S.I.; Takada, Y. The C-type lectin domain of CD62P (P-selectin) functions as an integrin ligand. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202201747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, K.; Zhang, X.P.; Medved, L.; Takada, Y. Specific binding of integrin alpha v beta 3 to the fibrinogen gamma and alpha E chain C-terminal domains. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5872–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, T.; Irie, A.; Tokuhira, M.; Takada, Y. Critical residues of integrin alphaIIb subunit for binding of alphaIIbbeta3 (glycoprotein IIb-IIIa) to fibrinogen and ligand-mimetic antibodies (PAC-1, OP-G2, and LJ-CP3). J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18610–18615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieguchi, K.; Fujita, M.; Ma, Z.; Davari, P.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Wang, B.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Direct binding of the EGF-like domain of neuregulin-1 to integrins (αvβ3 and α6β4) is involved in neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31388–31398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saegusa, J.; Akakura, N.; Wu, C.Y.; Hoogland, C.; Ma, Z.; Lam, K.S.; Liu, F.T.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Pro-inflammatory secretory phospholipase A2 type IIA binds to integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha4beta1 and induces proliferation of monocytic cells in an integrin-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26107–26115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Wu, C.Y.; Yamaji, S.; Saegusa, J.; Shi, B.; Ma, Z.; Kuwabara, Y.; Lam, K.S.; Isseroff, R.R.; Takada, Y.K.; et al. Direct binding of integrin alphavbeta3 to FGF1 plays a role in FGF1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18066–18075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.P.; Kamata, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Puzon-McLaughlin, W.; Takada, Y. Specific interaction of the recombinant disintegrin-like domain of MDC-15 (metargidin, ADAM-15) with integrin alphavbeta3. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7345–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, H.; May, A.E.; Bultmann, A.; Gawaz, M. ADAM 15 is an adhesion receptor for platelet GPIIb-IIIa and induces platelet activation. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, D.H.; Thiagarajan, P. Binding of recombinant fibrinogen mutants to platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailit, J.; Ruoslahti, E. Regulation of the fibronectin receptor affinity by divalent cations. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 12927–12932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Li, A.; Simonsen, N.; Wilkins, J.A. Integrin activation by dithiothreitol or Mn2+ induces a ligand-occupied conformation and exposure of a novel NH2-terminal regulatory site on the beta1 integrin chain. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7981–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpusas, M.; Hsu, Y.M.; Wang, J.H.; Thompson, J.; Lederman, S.; Chess, L.; Thomas, D. 2 A crystal structure of an extracellular fragment of human CD40 ligand. Structure 1995, 3, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurpf, T.; Springer, T.A. Regulation of integrin affinity on cell surfaces. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4712–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, T.A. Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 activation in Chinese hamster ovary cells and platelets increases clustering rather than affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadokoro, S.; Shattil, S.J.; Eto, K.; Tai, V.; Liddington, R.C.; de Pereda, J.M.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Calderwood, D.A. Talin binding to integrin beta tails: A final common step in integrin activation. Science 2003, 302, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, D.V.; Calderwood, D.A. Regulation of integrin-mediated adhesions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bruhl, M.L.; Stark, K.; Steinhart, A.; Chandraratne, S.; Konrad, I.; Lorenz, M.; Khandoga, A.; Tirniceriu, A.; Coletti, R.; Kollnberger, M.; et al. Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N. Platelet-lymphocyte cross-talk. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzey, B.D.; Schmidt, N.W.; Crist, S.A.; Kresowik, T.P.; Harty, J.T.; Nieswandt, B.; Ratliff, T.L. Platelet-derived CD154 enables T-cell priming and protection against Listeria monocytogenes challenge. Blood 2008, 111, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Hao, L.; Liu, X.; Tan, S.; Song, H.; Ni, H.; Sheng, Z.; Jooss, N.; Liu, X.; Malmstrom, R.E.; et al. Platelets fine-tune effector responses of naive CD4(+) T cells via platelet factor 4-regulated transforming growth factor beta signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, M.; Bergmann, C.B.; Jung, S.; Biberthaler, P.; Heimann, L.; Hanschen, M. Platelets differentially modulate CD4(+) Treg activation via GPIIa/IIIb-, fibrinogen-, and PAR4-dependent pathways. Immunol. Res. 2022, 70, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Geng, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, F.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.Q.; et al. The phosphatase PTEN links platelets with immune regulatory functions of mouse T follicular helper cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannacone, M.; Sitia, G.; Isogawa, M.; Marchese, P.; Castro, M.G.; Lowenstein, P.R.; Chisari, F.V.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Guidotti, L.G. Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced liver damage. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzey, B.D.; Tian, J.; Jensen, R.J.; Swanson, A.K.; Lees, J.R.; Lentz, S.R.; Stein, C.S.; Nieswandt, B.; Wang, Y.; Davidson, B.L.; et al. Platelet-mediated modulation of adaptive immunity. A communication link between innate and adaptive immune compartments. Immunity 2003, 19, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cognasse, F.; Hamzeh-Cognasse, H.; Lafarge, S.; Chavarin, P.; Cogne, M.; Richard, Y.; Garraud, O. Human platelets can activate peripheral blood B cells and increase production of immunoglobulins. Exp. Hematol. 2007, 35, 1376–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zufferey, A.; Speck, E.R.; Machlus, K.R.; Aslam, R.; Guo, L.; McVey, M.J.; Kim, M.; Kapur, R.; Boilard, E.; Italiano, J.E., Jr.; et al. Mature murine megakaryocytes present antigen-MHC class I molecules to T cells and transfer them to platelets. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, K.; Massberg, S. Interplay between inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hottz, E.D.; Azevedo-Quintanilha, I.G.; Palhinha, L.; Teixeira, L.; Barreto, E.A.; Pao, C.R.R.; Righy, C.; Franco, S.; Souza, T.M.L.; Kurtz, P.; et al. Platelet activation and platelet-monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID-19. Blood 2020, 136, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.B.; Fard, S.B.; Ramazi, S.; Atashi, A.; Eslamifar, Z. Thrombosis in COVID-19 infection: Role of platelet activation-mediated immunity. Thromb. J. 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takada, Y.K.; Shimoda, M.; Takada, Y. CD40L Activates Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3 by Binding to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) in a KGD-Independent Manner and HIGM1 Mutations Are Clustered in the Integrin-Binding Sites of CD40L. Cells 2023, 12, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12151977
Takada YK, Shimoda M, Takada Y. CD40L Activates Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3 by Binding to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) in a KGD-Independent Manner and HIGM1 Mutations Are Clustered in the Integrin-Binding Sites of CD40L. Cells. 2023; 12(15):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12151977
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakada, Yoko K., Michiko Shimoda, and Yoshikazu Takada. 2023. "CD40L Activates Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3 by Binding to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) in a KGD-Independent Manner and HIGM1 Mutations Are Clustered in the Integrin-Binding Sites of CD40L" Cells 12, no. 15: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12151977
APA StyleTakada, Y. K., Shimoda, M., & Takada, Y. (2023). CD40L Activates Platelet Integrin αIIbβ3 by Binding to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) in a KGD-Independent Manner and HIGM1 Mutations Are Clustered in the Integrin-Binding Sites of CD40L. Cells, 12(15), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12151977






