Modulation of microRNome by Human Cytomegalovirus and Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection in Human Dermal Fibroblasts: Possible Significance in the Induction of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Human Dermal Fibroblasts
2.2. Virus Strains and Titration
2.3. Virus Infection of Primary Dermal Fibroblasts
2.4. DNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Assay
2.5. RNA Extraction
2.6. miRNA Array Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. HCMV and HHV-6 Infection in Primary Human Dermal Fibroblasts
3.2. Modulation of miRNA Expression in HCMV-Infected Primary Human Dermal Fibroblasts
3.3. Modulation of miRNA Expression in HHV-6A-Infected Primary Human Dermal Fibroblasts
3.4. Pathways Associated with miRNA Expression in HHV-6A-Infected Primary Human Dermal Fibroblasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbloom, J.; Macarak, E.; Piera-Velazquez, S.; Jimenez, S.A. Human Fibrotic Diseases: Current Challenges in Fibrosis Research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1627, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuggioli, D.; Colaci, M.; Cocchiara, E.; Spinella, A.; Lumetti, F.; Ferri, C. From Localized Scleroderma to Systemic Sclerosis: Coexistence or Possible Evolution. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 1284687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, P.; Maslinska, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Lagun, Z.; Malewska, A.; Roszkiewicz, M.; Nitskovich, R.; Szymanska, E.; Walecka, I. Systemic sclerosis—Multidisciplinary disease: Clinical features and treatment. Reumatologia 2019, 57, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, R.; Liakouli, V.; Berardicurti, O.; Ruscitti, P.; Di Benedetto, P.; Carubbi, F.; Guggino, G.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; Ciccia, F.; Triolo, G.; et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: Current and future treatment. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, N.; Hudson, M.; Wang, M.; Gyger, G.; Proudman, S.; Stevens, W.; Nikpour, M.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group; Australian Scleroderma Interest Group; Baron, M. Severe gastrointestinal disease in very early systemic sclerosis is associated with early mortality. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyger, G.; Baron, M. Systemic Sclerosis: Gastrointestinal Disease and Its Management. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 41, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, E.; Battisti, S.; Di Sibio, A.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R.; Liakouli, V.; Ruscitti, P.; Masciocchi, C. Early assessment of sub-clinical cardiac involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc) using delayed enhancement cardiac magnetic resonance (CE-MRI). Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e268–e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, T.G.; Suliman, Y.A.; Li, W.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P. Scleroderma renal crisis and renal involvement in systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeRoy, E.C.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Criteria for the classification of early systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2001, 28, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Murdaca, G.; Contatore, M.; Gulli, R.; Mandich, P.; Puppo, F. Genetic factors and systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulle, A.E.; Diercks, G.F.H.; Feelisch, M.; Mulder, D.J.; van Goor, H. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Development of Systemic Sclerosis Related Vasculopathy. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doridot, L.; Jeljeli, M.; Chene, C.; Batteux, F. Implication of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis via inflammation, autoimmunity and fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcangeletti, M.C.; D’Accolti, M.; Maccari, C.; Soffritti, I.; Conto, F.; Chezzi, C.; Calderaro, A.; Ferri, C.; Caselli, E. Impact of Human Cytomegalovirus and Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection on the Expression of Factors Associated with Cell Fibrosis and Apoptosis: Clues for Implication in Systemic Sclerosis Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcangeletti, M.C.; Maccari, C.; Vescovini, R.; Volpi, R.; Giuggioli, D.; Sighinolfi, G.; De Conto, F.; Chezzi, C.; Calderaro, A.; Ferri, C. A Paradigmatic Interplay between Human Cytomegalovirus and Host Immune System: Possible Involvement of Viral Antigen-Driven CD8+ T Cell Responses in Systemic Sclerosis. Viruses 2018, 10, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, E.; Soffritti, I.; D’Accolti, M.; Bortolotti, D.; Rizzo, R.; Sighinolfi, G.; Giuggioli, D.; Ferri, C. HHV-6A Infection and Systemic Sclerosis: Clues of a Possible Association. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccolo, F.; Drago, F.; Cassina, G.; Fava, A.; Fusetti, L.; Matteoli, B.; Ceccherini-Nelli, L.; Sabbadini, M.G.; Lusso, P.; Parodi, A.; et al. Selective reactivation of human herpesvirus 6 in patients with autoimmune connective tissue diseases. J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccolo, F.; Drago, F.; Paolino, S.; Cassina, G.; Gatto, F.; Fusetti, L.; Matteoli, B.; Zaccaria, E.; Parodi, A.; Lusso, P.; et al. Reactivation of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) infection in patients with connective tissue diseases. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccolo, F.; Fusetti, L.; Ceccherini-Nelli, L. Possible role of human herpesvirus 6 as a trigger of autoimmune disease. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 867389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, S.; Kumar, D.; Rouse, B.T. Herpesviruses: Harmonious Pathogens but Relevant Cofactors in Other Diseases? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Di Luca, D. Molecular biology and clinical associations of Roseoloviruses human herpesvirus 6 and human herpesvirus 7. New Microbiol. 2007, 30, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halenius, A.; Hengel, H. Human cytomegalovirus and autoimmune disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 472978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsotti, S.; Orlandi, M.; Codullo, V.; Di Battista, M.; Lepri, G.; Della Rossa, A.; Guiducci, S. One year in review 2019: Systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 119), 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sinzger, C.; Grefte, A.; Plachter, B.; Gouw, A.S.; The, T.H.; Jahn, G. Fibroblasts, epithelial cells, endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells are major targets of human cytomegalovirus infection in lung and gastrointestinal tissues. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76 Pt 4, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostmans, Y.; Cutolo, M.; Giddelo, C.; Decuman, S.; Melsens, K.; Declercq, H.; Vandecasteele, E.; De Keyser, F.; Distler, O.; Gutermuth, J.; et al. The role of endothelial cells in the vasculopathy of systemic sclerosis: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, C.; Cazzato, M.; Giuggioli, D.; Sebastiani, M.; Magro, C. Systemic sclerosis following human cytomegalovirus infection. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 937–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, C.; Dolcino, M.; Peterlana, D.; Bason, C.; Navone, R.; Tamassia, N.; Beri, R.; Corrocher, R.; Puccetti, A. Antibodies against human cytomegalovirus in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: A gene array approach. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnson, Y.; Amital, H.; Guiducci, S.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Valentini, G.; Barzilai, O.; Maya, R.; Shoenfeld, Y. The role of infections in the immunopathogensis of systemic sclerosis—Evidence from serological studies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marou, E.; Liaskos, C.; Simopoulou, T.; Efthymiou, G.; Dardiotis, E.; Katsiari, C.; Scheper, T.; Meyer, W.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Bogdanos, D.P.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) UL44 and UL57 specific antibody responses in anti-HCMV-positive patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthymiou, G.; Dardiotis, E.; Liaskos, C.; Marou, E.; Scheper, T.; Meyer, W.; Daponte, A.; Daoussis, D.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Bogdanos, D.P.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of antigen-specific antibody responses against human cytomegalovirus in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 207, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardi, C.; Bason, C.; Navone, R.; Millo, E.; Damonte, G.; Corrocher, R.; Puccetti, A. Systemic sclerosis immunoglobulin G autoantibodies bind the human cytomegalovirus late protein UL94 and induce apoptosis in human endothelial cells. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namboodiri, A.M.; Rocca, K.M.; Pandey, J.P. IgG antibodies to human cytomegalovirus late protein UL94 in patients with systemic sclerosis. Autoimmunity 2004, 37, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablashi, D.; Agut, H.; Alvarez-Lafuente, R.; Clark, D.A.; Dewhurst, S.; DiLuca, D.; Flamand, L.; Frenkel, N.; Gallo, R.; Gompels, U.A.; et al. Classification of HHV-6A and HHV-6B as distinct viruses. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, A.; Rotola, A.; Comar, M.; Favilli, F.; Galvan, M.; Tosetti, M.; Campello, C.; Caselli, E.; Alessandri, G.; Grassi, M.; et al. HHV-6 infects human aortic and heart microvascular endothelial cells, increasing their ability to secrete proinflammatory chemokines. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 67, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, A.; Caselli, E.; Fiorentini, S.; Rotola, A.; Prandini, A.; Garrafa, E.; Saba, E.; Alessandri, G.; Cassai, E.; Di Luca, D. U94 of human herpesvirus 6 inhibits in vitro angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20446–20451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger-Rogez, S.; Vidal, E.; Liozon, F.; Denis, F. Primary Sjogren’s syndrome and antibodies to human herpesvirus type 6. Clin. Infect. Dis 1994, 19, 1159–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, G.R.; Sander, C.; Hoffmann, A.; Barth, A.; Koch, B.; Braun, M. Isolation of human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) from patients with collagen vascular diseases. In Vivo 1991, 5, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Lafuente, R.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, B.; de Miguel, S.; Jover, J.A.; Rollin, R.; Loza, E.; Clemente, D.; Lamas, J.R. Potential relationship between herpes viruses and rheumatoid arthritis: Analysis with quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1357–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Lafuente, R.; Martinez, A.; Garcia-Montojo, M.; Mas, A.; De Las Heras, V.; Dominguez-Mozo, M.I.; Maria Del Carmen, C.; Lopez-Cavanillas, M.; Bartolome, M.; Gomez de la Concha, E.; et al. MHC2TA rs4774C and HHV-6A active replication in multiple sclerosis patients. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Zatelli, M.C.; Rizzo, R.; Benedetti, S.; Martorelli, D.; Trasforini, G.; Cassai, E.; degli Uberti, E.C.; Di Luca, D.; Dolcetti, R. Virologic and immunologic evidence supporting an association between HHV-6 and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altorok, N.; Kahaleh, B. Epigenetics and systemic sclerosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altorok, N.; Almeshal, N.; Wang, Y.; Kahaleh, B. Epigenetics, the holy grail in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, T.W.; Mendoza, F.A.; Jimenez, S.A. Role of microRNA in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis tissue fibrosis and vasculopathy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altorok, N.; Wang, Y.; Kahaleh, B. Endothelial dysfunction in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zuo, X.X.; Li, Y.S.; Gao, S.M.; Dai, X.D.; Zhu, H.L.; Luo, H. Integration of microRNA and mRNA expression profiles in the skin of systemic sclerosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Bao, C.; Fu, Q. Corrigendum: Targeting miR-155 to Treat Experimental Scleroderma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Bao, C.; Fu, Q. Targeting miR-155 to Treat Experimental Scleroderma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artlett, C.M.; Sassi-Gaha, S.; Hope, J.L.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Katsikis, P.D. Mir-155 is overexpressed in systemic sclerosis fibroblasts and is required for NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated collagen synthesis during fibrosis. Arthritis Res. Ther 2017, 19, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, N.; Vettori, S.; Maurer, B.; Brock, M.; Pachera, E.; Jungel, A.; Calcagni, M.; Gay, R.E.; Whitfield, M.L.; Distler, J.H.; et al. Downregulation of miR-193b in systemic sclerosis regulates the proliferative vasculopathy by urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, B.; Xiao, X.; Zuo, X. MicroRNA-130b regulates scleroderma fibrosis by targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermuth, P.J.; Li, Z.; Mendoza, F.A.; Jimenez, S.A. Stimulation of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1-Induced Endothelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition and Tissue Fibrosis by Endothelin-1 (ET-1): A Novel Profibrotic Effect of ET-1. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piera-Velazquez, S.; Mendoza, F.A.; Jimenez, S.A. Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EndoMT) in the Pathogenesis of Human Fibrotic Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, S.A.; Piera-Velazquez, S. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in the pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis-associated pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Myth or reality? Matrix Biol. 2016, 51, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasson, C.W.; Abignano, G.; Hermes, H.; Malaab, M.; Ross, R.L.; Jimenez, S.A.; Chang, H.Y.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Del Galdo, F. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR drives EZH2-dependent myofibroblast activation in systemic sclerosis through miRNA 34a-dependent activation of NOTCH. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Shen, D. The mechanism of TGF-beta/miR-155/c-Ski regulates endothelial-mesenchymal transition in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, A.; Suzuki, H.I.; Ueno, T.; Mihira, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Yasuda, T.; Watabe, T.; Mano, H.; Yamada, Y.; Miyazono, K. MicroRNA-31 is a positive modulator of endothelial-mesenchymal transition and associated secretory phenotype induced by TGF-beta. Genes Cells 2016, 21, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Bledsoe, G.; Yang, Z.R.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Kallistatin inhibits TGF-beta-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition by differential regulation of microRNA-21 and eNOS expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 337, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.J.; Tao, J.H.; Mei, B.; Chen, B.; Li, B.Z.; Yang, G.J.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Wang, B.X.; He, Q.; et al. MicroRNA-29: A potential therapeutic target for systemic sclerosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, B.; Stanczyk, J.; Jungel, A.; Akhmetshina, A.; Trenkmann, M.; Brock, M.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Gay, R.E.; Michel, B.A.; Distler, J.H.; et al. MicroRNA-29, a key regulator of collagen expression in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarinejad-Farsangi, S.; Gharibdoost, F.; Farazmand, A.; Kavosi, H.; Jamshidi, A.; Karimizadeh, E.; Noorbakhsh, F.; Mahmoudi, M. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-29a modulate the expression of collagen in dermal fibroblasts of patients with systemic sclerosis. Autoimmunity 2019, 52, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Jinnin, M.; Etoh, M.; Yamane, K.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, K.; Ichihara, A.; Igata, T.; Sakai, K.; Fukushima, S.; et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-196a in the sera and involved skin of localized scleroderma patients. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2014, 24, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, N.; Jinnin, M.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, T.; Makino, K.; Masuguchi, S.; Fukushima, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Fujimoto, M.; et al. TGF-beta-mediated downregulation of microRNA-196a contributes to the constitutive upregulated type I collagen expression in scleroderma dermal fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3323–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, K.; Jinnin, M.; Hirano, A.; Yamane, K.; Eto, M.; Kusano, T.; Honda, N.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, T.; Sakai, K.; et al. The downregulation of microRNA let-7a contributes to the excessive expression of type I collagen in systemic and localized scleroderma. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3905–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, G.; Wasen, C.; Garcia-Bonete, M.J.; Turkkila, M.; Erlandsson, M.C.; Toyra Silfversward, S.; Brisslert, M.; Pullerits, R.; Andersson, K.M.; Katona, G.; et al. Survivin in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.B.; Farashahi Yazd, E.; Gharibdoost, F.; Sheikhha, M.H.; Karimizadeh, E.; Jamshidi, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Overexpression of apoptosis-related protein, survivin, in fibroblasts from patients with systemic sclerosis. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 188, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidi Manesh, P.; Farazmand, A.; Gharibdoost, F.; Vanaki, N.; Mostafaei, S.; Kavosi, H.; Mahmoudi, M.B.; Mahmoudi, M. Downregulation of miR-542-3p Contributes to Apoptosis Resistance in Dermal Fibroblasts from Systemic Sclerosis Patients via Survivin Overexpression. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 18, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlova, A.; Pachera, E.; Maurer, B.; Jungel, A.; Distler, J.H.W.; Kania, G.; Distler, O. Regulation of Fibroblast Apoptosis and Proliferation by MicroRNA-125b in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 2068–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimiyan, H.; Gharibdoost, F.; Aslani, S.; Kavosi, H.; Farsad, F.; Jamshidi, A.; Mahmoudi, M. microRNAs are potentially regulating the survivin gene in PBMCs from systemic sclerosis patients. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piedade, D.; Azevedo-Pereira, J.M. The Role of microRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Herpesvirus Infection. Viruses 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Tian, K.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X. Human cytomegalovirus latent infection alters the expression of cellular and viral microRNA. Gene 2014, 536, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, E.; D’Accolti, M.; Soffritti, I.; Zatelli, M.C.; Rossi, R.; Degli Uberti, E.; Di Luca, D. HHV-6A in vitro infection of thyrocytes and T cells alters the expression of miRNA associated to autoimmune thyroiditis. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, D.; Soffritti, I.; D’Accolti, M.; Gentili, V.; Di Luca, D.; Rizzo, R.; Caselli, E. HHV-6A Infection of Endometrial Epithelial Cells Affects miRNA Expression and Trophoblast Cell Attachment. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 27, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, R.; Soffritti, I.; D’Accolti, M.; Bortolotti, D.; Di Luca, D.; Caselli, E. HHV-6A/6B Infection of NK Cells Modulates the Expression of miRNAs and Transcription Factors Potentially Associated to Impaired NK Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcangeletti, M.C.; De Conto, F.; Ferraglia, F.; Pinardi, F.; Gatti, R.; Orlandini, G.; Calderaro, A.; Motta, F.; Medici, M.C.; Martinelli, M.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus proteins PP65 and IEP72 are targeted to distinct compartments in nuclei and nuclear matrices of infected human embryo fibroblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 90, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, E.; Bracci, A.; Galvan, M.; Boni, M.; Rotola, A.; Bergamini, C.; Cermelli, C.; Dal Monte, P.; Gompels, U.A.; Cassai, E.; et al. Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) U94/REP protein inhibits betaherpesvirus replication. Virology 2006, 346, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Zhou, G.; Soufan, O.; Xia, J. miRNet 2.0: Network-based visual analytics for miRNA functional analysis and systems biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W244–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, J.H.W.; Gyorfi, A.H.; Ramanujam, M.; Whitfield, M.L.; Konigshoff, M.; Lafyatis, R. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardet, A.; Zheng, T.S.; Viney, J.L. Genetic architecture of human fibrotic diseases: Disease risk and disease progression. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, C.; Dovrish, Z.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Amital, H. Do infections facilitate the emergence of systemic sclerosis? Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randone, S.B.; Guiducci, S.; Cerinic, M.M. Systemic sclerosis and infections. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 8, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, H.; Hirose, M.; Kurosawa, G.; Impey, S.; Mikoshiba, K. Time-lapse imaging of microRNA activity reveals the kinetics of microRNA activation in single living cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichholf, B.; Herzog, V.A.; Fasching, N.; Manzenreither, R.A.; Sowemimo, I.; Ameres, S.L. Time-Resolved Small RNA Sequencing Unravels the Molecular Principles of MicroRNA Homeostasis. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 756–768.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotorynski, E. Insights into the kinetics of microRNA biogenesis and turnover. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajihara, I.; Jinnin, M.; Yamane, K.; Makino, T.; Honda, N.; Igata, T.; Masuguchi, S.; Fukushima, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Increased accumulation of extracellular thrombospondin-2 due to low degradation activity stimulates type I collagen expression in scleroderma fibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, M.; Zuo, X. MicroRNAs Regulating Signaling Pathways: Potential Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, R.; Fan, X.; Gu, T.; Zhao, Z.; Chang, D.; Wang, W. MicroRNA array analysis of microRNAs related to systemic scleroderma. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Shinkai, H. Gene expression of types I and III collagen, decorin, matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in skin fibroblasts from patients with systemic sclerosis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1997, 289, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, T.; Jinnin, M.; Yamane, K.; Honda, N.; Makino, K.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, T.; Sakai, K.; Masuguchi, S.; Fukushima, S.; et al. microRNA-92a expression in the sera and dermal fibroblasts increases in patients with scleroderma. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, G.; Roberts, W.N.; Roman, J.; Gangemi, S. A systematic review of overlapping microRNA patterns in systemic sclerosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Suto, A.; Ikeda, K.; Sanayama, Y.; Nakagomi, D.; Iwamoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Kambe, N.; Matsue, H.; Matsumura, R.; et al. Alteration of circulating miRNAs in SSc: miR-30b regulates the expression of PDGF receptor beta. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Qie, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, J.; Jin, Y.; Ding, Z. miR-20a-5p/TGFBR2 Axis Affects Pro-inflammatory Macrophages and Aggravates Liver Fibrosis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. Meta-analysis of differentially expressed microRNAs in systemic sclerosis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerick, M.; Gonzalez-Serna, D.; Carnero-Montoro, E.; Teruel, M.; Acosta-Herrera, M.; Makowska, Z.; Buttgereit, A.; Babaei, S.; Barturen, G.; Lopez-Isac, E.; et al. eQTL analysis in systemic sclerosis identifies new candidate genes associated with multiple aspects of disease pathology. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhou, J.; Xu, D.; Hou, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; et al. MicroRNA-320a: An important regulator in the fibrotic process in interstitial lung disease of systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.P.; Gottardi, C.J. beta-catenin signaling: A novel mediator of fibrosis and potential therapeutic target. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Hou, J.; Xiang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Han, X. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling suppresses myofibroblast differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells and pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piersma, B.; Bank, R.A.; Boersema, M. Signaling in Fibrosis: TGF-beta, WNT, and YAP/TAZ Converge. Front. Med. 2015, 2, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgy, O.; Konigshoff, M. The WNT signaling pathways in wound healing and fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68-69, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, O.; Soliman, H.; Theret, M.; Rossi, F.M.V.; Brandan, E. TGF-beta-driven downregulation of the transcription factor TCF7L2 affects Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in PDGFRalpha(+) fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, F.; Shabaninejad, Z.; Vakili, S.; Derakhshan, M.; Movahedpour, A.; Dabiri, H.; Ghasemi, Y.; Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Nikoozadeh, A.; Savardashtaki, A.; et al. TGF-beta and WNT signaling pathways in cardiac fibrosis: Non-coding RNAs come into focus. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
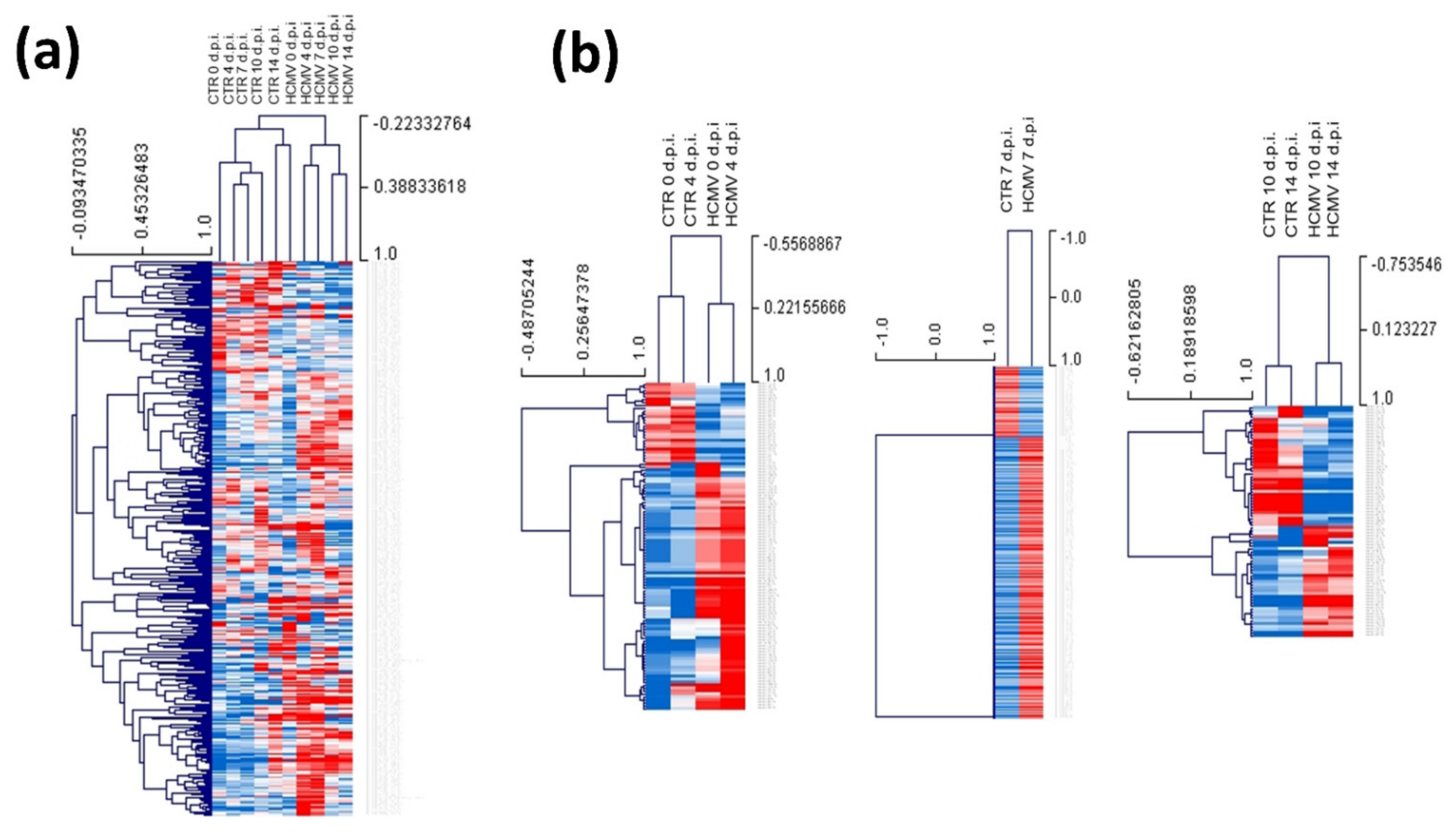
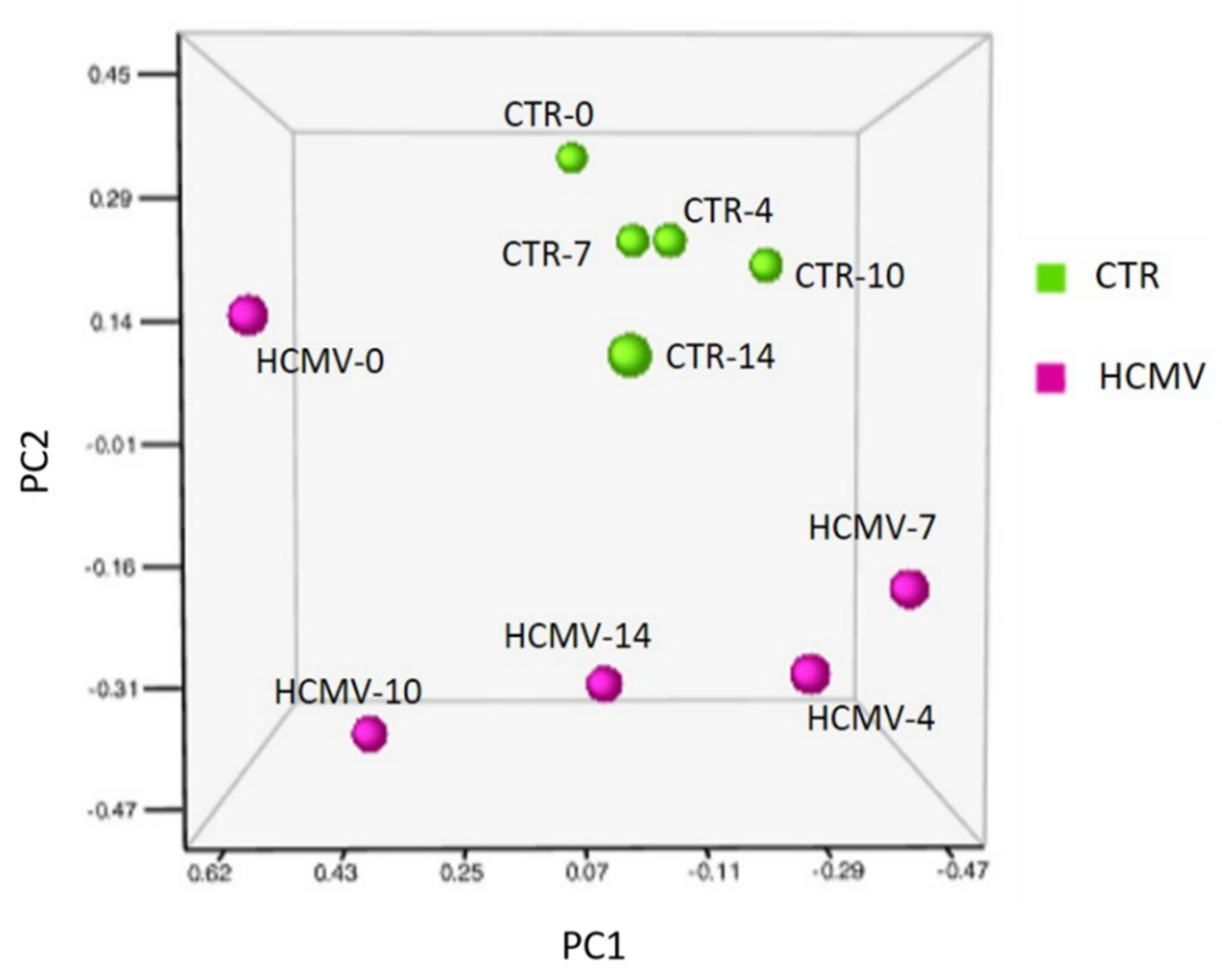
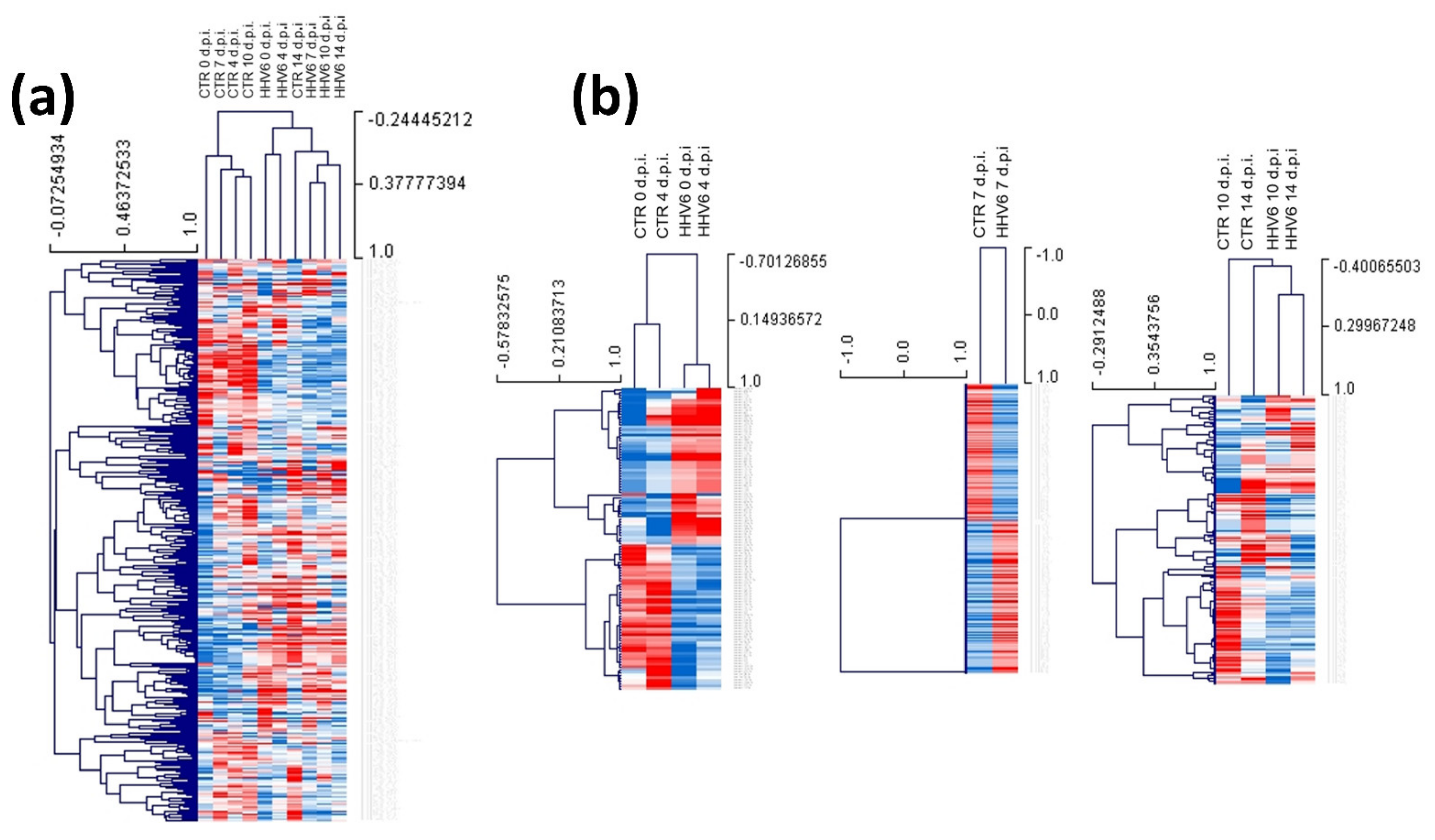


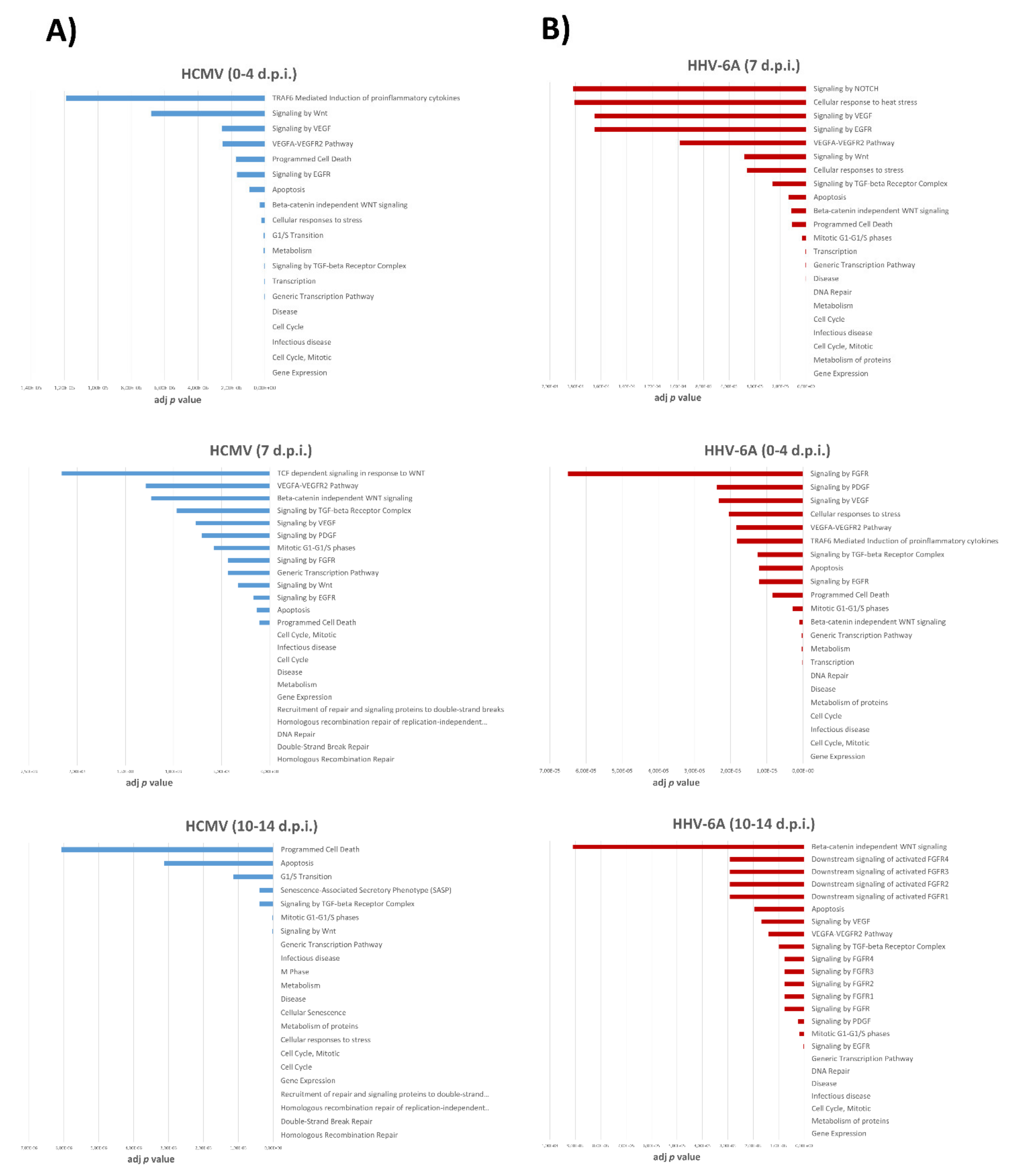
| Times of Infection | HCMV DNA Copies/mL (log10) | HHV-6A DNA Copies/mL (log10) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 days | - | - |
| 4 days | 5.060 ± 0.004 | 5.615 ± 0.006 |
| 7 days | 5.469 ± 0.005 | 5.990 ± 0.004 |
| 10 days | 5.778 ± 0.003 | 5.751 ± 0.001 |
| 14 days | 7.138 ± 0.004 | 4.945 ± 0.006 |
| 0 d.p.i. | 4 d.p.i. | 7 d.p.i. | 10 d.p.i. | 14 d.p.i. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-let-7g (12) | miR-19b (242) | miR-10b (27) | miR-let 7i (8892) | miR-7 (917) |
| miR-15b (1625) | miR-29 (35) | miR-20 (18) | miR-7 (64) | miR-10b (1897) |
| miR-27a (20) | miR-32 (23) | miR-95 (11) | miR-17 (68) | miR-18a (2813) |
| miR-29 (13) | miR-92a (154) | miR-101 (11) | miR-19a (15) | miR-18b (75) |
| miR-33a (11) | miR-95 (20) | miR-124 (25) | miR-19b (11) | miR-19b (61) |
| miR-92a (54) | miR-124 (18) | miR-133 (11) | miR-33a (11) | miR-20 (92) |
| miR-100 (24,209) | miR-143 (16) | miR-143 (43) | miR-92a (83) | miR-26a (14) |
| miR-146b (27) | miR-153 (127) | miR-665 (13) | miR-100 (50,264) | miR-26b (20) |
| miR-153 (32) | miR-181d (11) | miR-124 (15) | miR-92a (167) | |
| miR-188 (17) | miR 196a (18) | miR-126 (50) | miR-124 (219) | |
| miR-190a (20) | miR-487a (47) | miR-139 (48) | miR-126 (299) | |
| miR-219a (11) | miR-545 (11) | miR-140 (14) | miR-132 (14) | |
| miR-381 (113) | miR-573 (24) | miR-143 (58) | miR-146b (12) | |
| miR-544a (47) | miR-1275 (13) | miR-153 (61) | miR-192 (21) | |
| miR-545 (18) | miR-181d (72) | miR-196a (101) | ||
| miR-548a (15) | miR-195 (12) | miR-326 (17) | ||
| miR-590 (162) | miR-204 (33) | miR-363 (654) | ||
| miR-210 (11) | miR-431 (32) | |||
| miR-301b (21) | miR-454 (995) | |||
| miR-338 (11) | miR-483 (11) | |||
| miR-363 (130) | miR-486 (10) | |||
| miR-376a (92) | miR-501 (12) | |||
| miR-483 (18) | miR-551b (285) | |||
| miR-524 (15) | miR-589 (17) | |||
| miR-544a (24) | miR-615 (50) | |||
| miR-551b (50) | miR-744 (234) | |||
| miR-570 (11) | miR-766 (28) | |||
| miR-573 (10) | miR-1275 (187) | |||
| miR-589 (12) | ||||
| miR-590 (16) | ||||
| miR-629 (19) | ||||
| miR-744 (31) | ||||
| miR-1226 (17) | ||||
| miR-1275 (43) |
| 0 d.p.i. | 4 d.p.i. | 7 d.p.i. | 10 d.p.i. | 14 d.p.i. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-let-7a (3541) | miR-let-7a (1105) | miR-let-7a (11) | miR-10a (2266) | miR-10a (326) |
| miR-1 (46) | miR-10a (24) | miR-let-7f (3704) | miR-20b (585) | miR-24 (25) |
| miR-10b (252) | miR-15b (490) | miR-let-7i (5 × 104) | miR-24 (193) | miR-34a (445) |
| miR-24 (114) | miR-18a (16) | miR-15b (9686) | miR-29c (9 × 104) | miR-34c (18) |
| miR-30b (164) | miR-18b (432) | miR-23a (24) | miR-34b (10) | miR-99a (469) |
| miR-124 (64) | miR-20b (137) | miR-24 (34) | miR-99a (662) | miR-103a (89) |
| miR-126 (296) | miR-23a (1 × 105) | miR-30b (29) | miR-100 (54) | miR-122 (32) |
| miR-139 (12) | miR-24 (72) | miR-33a (180) | miR-122 (935) | miR-125b (45) |
| miR-143 (18) | miR-26a (28) | miR-92b (11) | miR-125b (125) | miR-135b (14) |
| miR-193b (347) | miR-27b (3900) | miR-99a (24) | miR-136 (11) | miR-143 (15) |
| miR-200a (20) | miR-33a (42) | miR-122 (80) | miR-193b (484) | miR-148a (47) |
| miR-200b (89) | miR-34b (33) | miR-1254 (12) | miR-196a (63) | miR-181a (156) |
| miR-331 (21) | miR-99a (69) | miR-125b (165) | miR-337 (1681) | miR-199b (26) |
| miR-369 (110) | miR-122 (14) | miR-135b (12) | miR-422a (58) | miR-200b (123) |
| miR-374 (415) | miR-125b (12) | miR-148a (364) | miR-449b (317) | miR-218 (85) |
| miR-422 (29) | miR-126 (309) | miR-181d (167) | miR-454 (15) | miR-302d (42) |
| miR-431 (286) | miR-148a (87) | miR-191 (12) | miR-501 (21) | miR-337 (287) |
| miR-454 (861) | miR-149 (357) | miR-193b (11) | miR-504 (64) | miR-369 (57) |
| miR-486 (82) | miR-181a (49) | miR-196b (21) | miR-542 (51) | miR-449b (18) |
| miR-496 (74) | miR-299 (1928) | miR-337 (1924) | miR-584 (171) | miR-487a (342) |
| miR-548 (2,9 × 106) | miR-337 (1668) | miR-362 (10) | miR-615 (64) | miR-542 (21) |
| miR-585 (1323) | miR-369 (39) | miR-374 (2665) | miR.654 (128) | miR-654 (105) |
| miR-656 (12) | miR-376a (209) | miR-376a (136) | miR-935 (24) | |
| miR-942 (35) | miR-411 (32) | miR-409 (13) | miR-1197 (49) | |
| miR-431 (126) | miR-422a (34) | miR-1303 (45) | ||
| miR-524 (80) | miR-432 (10) | |||
| miR-539 (47) | miR-433 (23) | |||
| miR-541 (37) | miR-450a (11) | |||
| miR-542 (17) | miR-454 (13) | |||
| miR-550a (42) | miR-486 (84) | |||
| miR-584 (209) | miR-487a (329) | |||
| miR-654 (1073) | miR-501 (96) | |||
| miR-665 (28) | miR-504 (115) | |||
| miR-758 (14) | miR-524 (257) | |||
| miR-766 (239) | miR-541 (32) | |||
| miR-889 (191) | miR-542 (355) | |||
| miR-1197 (58) | miR-548k (95) | |||
| miR-1270 (24) | miR-550 (284) | |||
| miR-584 (1195) | ||||
| miR-590 (339) | ||||
| miR-654 (129) | ||||
| miR-889 (513) | ||||
| miR-1197 (139) |
| 0 d.p.i. | 4 d.p.i. | 7 d.p.i. | 10 d.p.i. | 14 d.p.i. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-let-7g (23) | miR-16 (11) | miR-10b (78) | miR-let-7i (7466) | miR-7 (23) |
| miR-15b (878) | miR-19b (191) | miR-17 (77) | miR-7 (31) | miR-15b (2074) |
| miR-17 (93) | miR-24 (12) | miR-29a (11) | miR-16 (19) | miR-18a (429) |
| miR-19a (24) | miR-29 (28) | miR-29 (177) | miR-17 (95) | miR-19b (4333) |
| miR-19b (157) | miR-33a (27) | miR-33b (18) | miR-24 (16) | miR-24 (12) |
| miR-29 (12) | miR-33b (27) | miR-143 (208) | miR-29 (32) | miR-26b (67) |
| miR-33a (37) | miR-95 (15) | miR-573 (11) | miR-30e (11) | miR-92a (538) |
| miR-92a (140) | miR-101 (12) | miR-615 (14) | miR-33a (26) | miR-126 (53) |
| miR-143 (61) | miR-132 (113) | miR-665 (39) | miR-33b (16) | miR-192 (11) |
| miR-153 (16) | miR-153 (308) | miR-935 (10) | miR-139 (26) | miR-193b (208) |
| miR-196b (27) | miR-181d (22) | miR-1248 (21) | miR-143 (112) | miR-376a (587) |
| miR-363 (10) | miR-363 (17) | miR-1291 (17) | miR-153 (26) | miR-431 (154) |
| miR-374a (10) | miR-381 (11) | miR-1292 (11) | miR-181d (39) | miR-524 (25) |
| miR-381 (160) | miR-504 (14) | miR-1303 (23) | miR-210 (10) | miR-585 (758) |
| miR-524 (77) | miR-542 (14) | miR-376a (63) | miR-589 (47) | |
| miR-544a (22) | miR-573 (14) | miR-544a (37) | miR-615 (174) | |
| miR-550a (19) | miR-590 (16) | miR-548k (15) | miR-629 (41) | |
| miR-573 (23) | miR-625 (11) | miR-550a (24) | miR-744 (28) | |
| miR-590 (10) | miR-629 (10) | miR-573 (60) | miR-766 (37) | |
| miR-605 (11) | miR-665 (14) | miR-585 (32) | miR-935 (11) | |
| miR-1248 (17) | miR-744 (42) | miR-589 (18) | ||
| miR-1290 (12) | miR-708 (11) | miR-590 (11) | ||
| miR-625 (12) | ||||
| miR-628 (22) | ||||
| miR-675 (47) | ||||
| miR-744 (217) | ||||
| miR-1226 (27) | ||||
| miR-1248 (26) | ||||
| miR-1260a (15) |
| 0 d.p.i. | 4 d.p.i. | 7 d.p.i. | 10 d.p.i. | 14 d.p.i. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 (39) | miR-let-7a (317) | miR-let-7a (988) | miR-1 (12) | miR-1 (10) |
| miR-24 (65) | miR-1 (245) | miR-15b (2585) | miR-10a (526) | miR-34a (336) |
| miR-122 (68) | miR-17 (1245) | miR-30b (13) | miR-15b (2076) | miR-103a (92) |
| miR-124 (55) | miR-18 (2 × 104) | miR-33a (58) | miR-20 (136) | miR-122 (16) |
| miR-126 (169) | miR-19 (2289) | miR-92b (551) | miR-26b (33) | miR-148a (30) |
| miR-192 (19) | miR-20 (2458) | miR-122 (21) | miR-122 (217) | miR-190a (42) |
| miR-193b (197) | miR-103a (71) | miR-148a (116) | miR-132 (66) | miR-195 (23) |
| miR-200a (11) | miR-122 (1.2 × 104) | miR-181a (103) | miR-146b (216) | miR-337 (184) |
| miR-200b (75) | miR-124 (1698) | miR-193b (162) | miR-193b (117) | miR-487a (171) |
| miR-323 (16) | miR-126 (2251) | miR-196b (92) | miR-330 (67) | miR-500a (12) |
| miR-340 (341) | miR-139 (1567) | miR-200b (17) | miR-337 (406) | miR-590 (39) |
| miR-422a (25) | miR-148a (298) | miR-323b (12) | miR-454 (294) | miR-1197 (24) |
| miR-431 (162) | miR-148a (2213) | miR-337 (619) | miR-605 (24) | |
| miR-486 (68) | miR-378a (36) | miR-889 (50) | ||
| miR-487a (386) | miR-454 (200) | miR-1303 (11) | ||
| miR-496 (62) | miR-486 (22) | |||
| miR-499a (19) | miR-487a (88) | |||
| miR-548d (2 × 106) | miR-524 (290) | |||
| miR-585 (757) | miR-539 (62) | |||
| miR-889 (292) | miR-541 (10) | |||
| miR-590 (90) | ||||
| miR-889 (137) | ||||
| miR-1197 (18) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soffritti, I.; D’Accolti, M.; Ravegnini, G.; Arcangeletti, M.-C.; Maccari, C.; De Conto, F.; Calderaro, A.; Caselli, E. Modulation of microRNome by Human Cytomegalovirus and Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection in Human Dermal Fibroblasts: Possible Significance in the Induction of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051060
Soffritti I, D’Accolti M, Ravegnini G, Arcangeletti M-C, Maccari C, De Conto F, Calderaro A, Caselli E. Modulation of microRNome by Human Cytomegalovirus and Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection in Human Dermal Fibroblasts: Possible Significance in the Induction of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Cells. 2021; 10(5):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051060
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoffritti, Irene, Maria D’Accolti, Gloria Ravegnini, Maria-Cristina Arcangeletti, Clara Maccari, Flora De Conto, Adriana Calderaro, and Elisabetta Caselli. 2021. "Modulation of microRNome by Human Cytomegalovirus and Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection in Human Dermal Fibroblasts: Possible Significance in the Induction of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis" Cells 10, no. 5: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051060
APA StyleSoffritti, I., D’Accolti, M., Ravegnini, G., Arcangeletti, M.-C., Maccari, C., De Conto, F., Calderaro, A., & Caselli, E. (2021). Modulation of microRNome by Human Cytomegalovirus and Human Herpesvirus 6 Infection in Human Dermal Fibroblasts: Possible Significance in the Induction of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Cells, 10(5), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051060











