Chemical Genetic Screen in Drosophila Germline Uncovers Small Molecule Drugs That Sensitize Stem Cells to Insult-Induced Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly Stocks and Culture Conditions
2.2. Ionizing Radiation Treatment
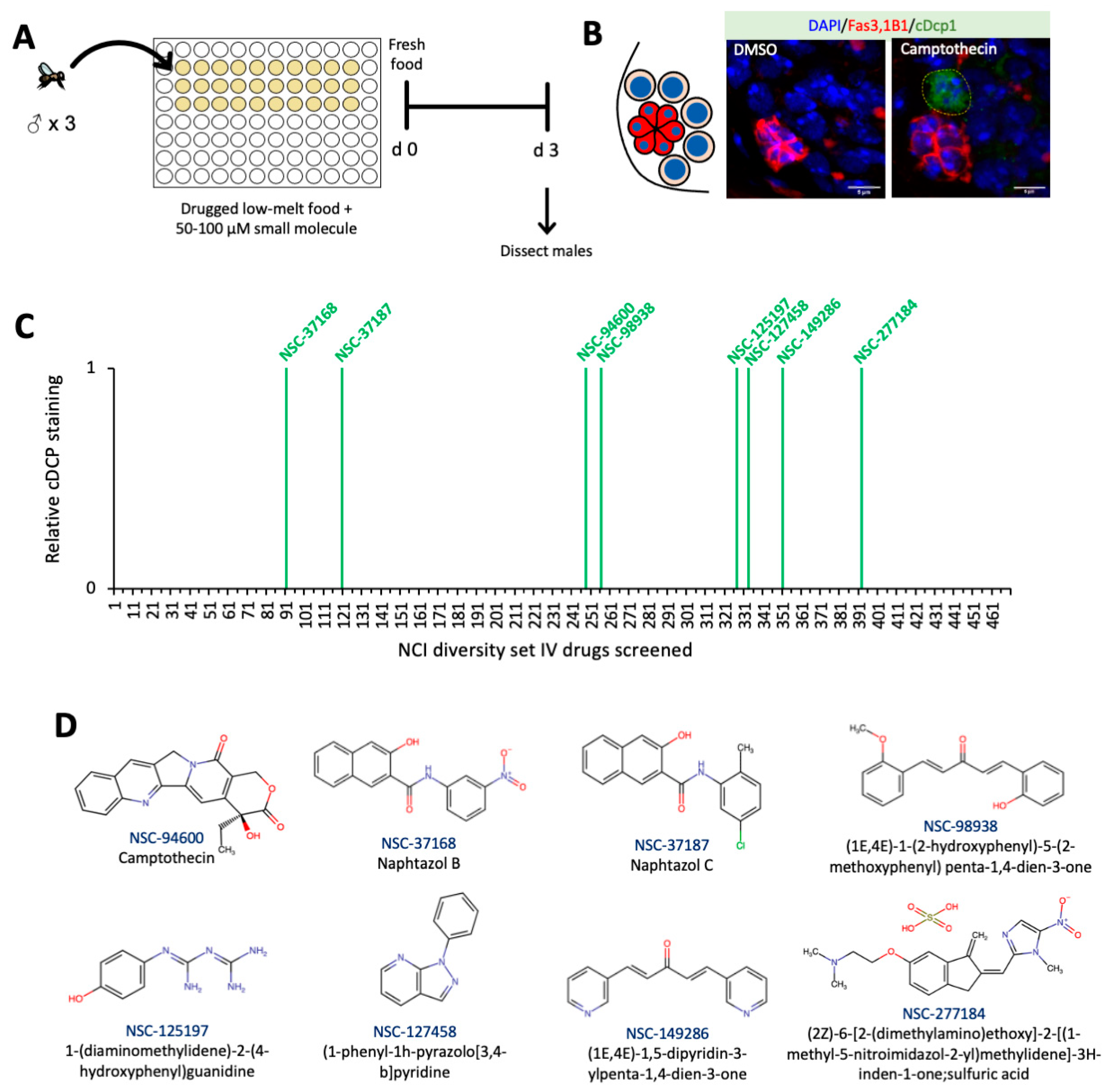
2.3. High-Throughput Screen of Small Molecules in Low-Melt Agarose Fly Food
2.4. Cell Death Screen in Grape Juice
2.5. Mammosphere Formation Assay
2.6. Small Molecule Organismal Viability Assay
2.7. Pathway Analysis in Yeast Paste
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Small Molecule Drug Candidates Predispose GSCs to Apoptosis in The Drosophila Testis
3.2. Small Molecule Drugs Sensitize GSCs to Insult-Induced Apoptosis in The Drosophila Ovary
3.3. Small Molecule Drug Candidates Inhibit Human Breast Cancer Organoid Formation
3.4. Chemical-Genetic Interactions in Drosophila GSCs Suggest Unique Mechanisms between Small Molecules
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pienta, K.J.; Hammarlund, E.U.; Brown, J.S.; Amend, S.R.; Axelrod, R.M. Cancer recurrence and lethality are enabled by enhanced survival and reversible cell cycle arrest of polyaneuploid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020838118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, S.; Hsieh, M.H.; Ng, N.; Sun, F.; Wang, T.; Kasibhatla, S.; Schuller, A.G.; Li, A.G.; Cheng, D.; et al. Targeting Wnt-driven cancer through the inhibition of Porcupine by LGK974. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20224–20229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, N.A.C.; Rodrigues, A.S.D.J.; Rodrigues-Santos, P.; Alves, V.; Gregório, A.C.; Valério-Fernandes, A.; da Silva, L.C.G.; Rosa, M.S.; Moura, V.; Ramalho-Santos, J.; et al. Nucleolin overexpression in breast cancer cell sub-populations with different stem-like phenotype enables targeted intracellular delivery of synergistic drug combination. Biomaterials 2015, 69, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.; Basu, B.; Smith, D.-M.; Gopinathan, A.; Evans, J.; Steward, W.P.; Palmer, D.; Propper, D.; Venugopal, B.; Hategan, M.; et al. A phase I trial of the γ-secretase inhibitor MK-0752 in combination with gemcitabine in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artoni, F.; E Kreipke, R.; Palmeira, O.; Dixon, C.; Goldberg, Z.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Loss of foxo rescues stem cell aging in Drosophila germ line. eLife 2017, 6, e27842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, J.R.; Taslim, T.H.; Hussein, A.M.; Brewer, D.; Liu, S.; Harper, S.; Nguyen, B.; Dang, J.; Chen, A.; Castillo, D.D.; et al. Stem cell quiescence requires PRC2/PRC1-mediated mitochondrial checkpoint. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, K.; Byrnes, L.E.; Yu, K.S.; Park, J.S.; Sneddon, J.B.; Tward, A.D.; Nystul, T.G. A single-cell atlas and lineage analysis of the adult Drosophila ovary. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gancz, D.; Gilboa, L. Insulin and Target of rapamycin signaling orchestrate the development of ovarian niche-stem cell units in Drosophila. Development 2013, 140, 4145–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.; Graham, P.H.; Hao, J.; Ni, J.; Bucci, J.; Cozzi, P.J.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. Acquisition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotypes is associated with activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer radioresistance. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Wulfkuhle, J.; Zhang, H.; Gu, P.; Yang, Y.; Deng, J.; Margolick, J.B.; Liotta, L.A.; Petricoin, E.; Zhang, Y. Activation of the PTEN/mTOR/STAT3 pathway in breast cancer stem-like cells is required for viability and maintenance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16158–16163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzman, M.L.; Neering, S.J.; Upchurch, D.; Grimes, B.; Howard, D.S.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Luger, S.M.; Jordan, C. Nuclear factor-κB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 2001, 98, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, J.M.; Fan, M.; Yang, C.H.; Du, Z.; Sims, M.; Davidoff, A.M.; Pfeffer, L.M. Constitutive Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) and Nuclear Factor κB Signaling in Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells Regulates the Notch Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26167–26176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajasekhar, V.K.; Studer, L.; Gerald, W.; Socci, N.D.; Scher, H.I. Tumour-initiating stem-like cells in human prostate cancer exhibit increased NF-κB signalling. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, A.S. Regulation of cell death and autophagy by IKK and NF-κB: Critical mechanisms in immune function and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G.; Goeddel, D.V.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-κB Antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to Suppress Caspase-8 Activation. Science 1998, 281, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.-L.; McKinsey, T.A.; Liu, L.; Gentry, J.J.; Malim, M.; Ballard, D.W. Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-κB control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10057–10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishnan, P.; A Kahn, D.; Baltimore, D. Anti-apoptotic effect of hyperglycemia can allow survival of potentially autoreactive T cells. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 18, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; E Allen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Yang, W.; Berg, A.; et al. The NFκB inhibitor, SN50, induces differentiation of glioma stem cells and suppresses their oncogenic phenotype. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsubara, S.; Ding, Q.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kuwahata, T.; Tsukasa, K.; Takao, S. mTOR plays critical roles in pancreatic cancer stem cells through specific and stemness-related functions. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, K.Y.; Wang, W.D.; Lin, C.H.; Rastegari, E.; Su, Y.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Liao, Y.F.; Chang, Y.C.; Pi, H.; Yu, B.Y.; et al. Piwi reduction in the aged niche eliminates germline stem cells via Toll-GSK3 signaling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Su, T.T.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Tie-mediated signal from apoptotic cells protects stem cells in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Han, Y.; Song, X.; Do, T.; Yang, Z.; Ni, J.; Xie, T. DNA damage-induced CHK2 activation compromises germline stem cell self-renewal and lineage differentiation. Development 2016, 143, 4312–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engelmann, K.; Shen, H.; Finn, O.J. MCF7 Side Population Cells with Characteristics of Cancer Stem/Progenitor Cells Express the Tumor Antigen MUC1. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Unraveling the roles of CD44/CD24 and ALDH1 as cancer stem cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, M.T.; Spradling, A.C. Male and Female Drosophila Germline Stem Cells: Two Versions of Immortality. Science 2007, 316, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, Y.; de Giorgio, A.; Coombes, C.R.; Stebbing, J.; Castellano, L. Mammosphere Formation Assay from Human Breast Cancer Tissues and Cell Lines. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, e52671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Markstein, M.; Dettorre, S.; Cho, J.; Neumüller, R.A.; Craig-Müller, S.; Perrimon, N. Systematic screen of chemotherapeutics in Drosophila stem cell tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4530–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willoughby, L.F.; Schlosser, T.; Manning, S.; Parisot, J.P.; Street, I.P.; Richardson, H.; Humbert, P.; Brumby, A.M. An in vivo large-scale chemical screening platform using Drosophila for anti-cancer drug discovery. Dis. Model. Mech. 2012, 6, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Sheng, P.; Tu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Geng, H.; Zou, Y.; Di, C.-A.; Yi, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. A two-dimensional π–d conjugated coordination polymer with extremely high electrical conductivity and ambipolar transport behaviour. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pommier, Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: Camptothecins and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulut-Karslioglu, A.; Biechele, S.; Jin, H.; Macrae, T.A.; Hejna, M.; Gertsenstein, M.; Song, J.; Ramalho-Santos, M. Inhibition of mTOR induces a paused pluripotent state. Nature 2016, 540, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y.; Yu, X.; Qiu, J.; Stablewski, A.B.; Zhang, B.; Buck, M.J.; Feng, J. Transient inhibition of mTOR in human pluripotent stem cells enables robust formation of mouse-human chimeric embryos. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz0298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorova, I.I.; Knyazeva, A.R.; Petukhov, A.V.; Aksenov, N.D.; Pospelov, V.A. Resveratrol enhances pluripotency of mouse embryonic stem cells by activating AMPK/Ulk1 pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, B.; Berger, Z.; Vacher, C.; O’Kane, C.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Rapamycin pre-treatment protects against apoptosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, Y.; Bale, J.; Gonen, S.; Shi, D.; Sheffler, W.; Fong, K.K.; Nattermann, U.; Xu, C.; Huang, P.; Ravichandran, R.; et al. Design of a hyperstable 60-subunit protein icosahedron. Nature 2016, 535, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, J.; Gonen, S.; Liu, Y.; Sheffler, W.; Ellis, D.; Thomas, C.; Cascio, D.; Yeates, T.; Gonen, T.; King, N.P.; et al. Accurate design of megadalton-scale two-component icosahedral protein complexes. Science 2016, 353, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Ren, X.; Gowda, A.S.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.-S.; Patel, R.; Wu, H.; Huber-Keener, K.; Yang, J.W.; et al. Interaction of Sirt3 with OGG1 contributes to repair of mitochondrial DNA and protects from apoptotic cell death under oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chevillard, S.; Radicella, J.P.; Levalois, C.; Lebeau, J.; Poupon, M.-F.; Oudard, S.; Dutrillaux, B.; Boiteux, S. Mutations in OGG1, a gene involved in the repair of oxidative DNA damage, are found in human lung and kidney tumours. Oncogene 1998, 16, 3083–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruner, S.D.; Norman, D.P.G.; Verdine, G.L. Structural basis for recognition and repair of the endogenous mutagen 8-oxoguanine in DNA. Nature 2000, 403, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, E.; Seaman, M.; Hedley, D. Relationship between cytoplasmic pH and proliferation during exponential growth and cellular quiescence. Exp. Cell Res. 1987, 172, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donowitz, M.; Li, X. Regulatory Binding Partners and Complexes of NHE3. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 825–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, A. IKKϵ Signaling: Not Just NF-κB. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R588–R590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- House, C.D.; Grajales, V.; Ozaki, M.; Jordan, E.; Wubneh, H.; Kimble, D.C.; James, J.M.; Kim, M.K.; Annunziata, C.M. IΚΚε cooperates with either MEK or non-canonical NF-kB driving growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells in different contexts. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- So, J.Y.; Smolarek, A.K.; Salerno, D.M.; Maehr, H.; Uskokovic, M.; Liu, F.; Suh, N. Targeting CD44-STAT3 Signaling by Gemini Vitamin D Analog Leads to Inhibition of Invasion in Basal-Like Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Stamenkovic, I. Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 9 to the cell surface provides a mechanism for CD44-mediated tumor invasion. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, S.M.; Lyu, Y.L.; Cai, L. NF-κB Affects Proliferation and Invasiveness of Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating CD44 Expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishibashi, J.R.; Keshri, R.; Taslim, T.H.; Brewer, D.K.; Chan, T.C.; Lyons, S.; McManamen, A.M.; Chen, A.; Del Castillo, D.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Chemical Genetic Screen in Drosophila Germline Uncovers Small Molecule Drugs That Sensitize Stem Cells to Insult-Induced Apoptosis. Cells 2021, 10, 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102771
Ishibashi JR, Keshri R, Taslim TH, Brewer DK, Chan TC, Lyons S, McManamen AM, Chen A, Del Castillo D, Ruohola-Baker H. Chemical Genetic Screen in Drosophila Germline Uncovers Small Molecule Drugs That Sensitize Stem Cells to Insult-Induced Apoptosis. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102771
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshibashi, Julien Roy, Riya Keshri, Tommy Henry Taslim, Daniel Kennedy Brewer, Tung Ching Chan, Scott Lyons, Anika Marie McManamen, Ashley Chen, Debra Del Castillo, and Hannele Ruohola-Baker. 2021. "Chemical Genetic Screen in Drosophila Germline Uncovers Small Molecule Drugs That Sensitize Stem Cells to Insult-Induced Apoptosis" Cells 10, no. 10: 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102771
APA StyleIshibashi, J. R., Keshri, R., Taslim, T. H., Brewer, D. K., Chan, T. C., Lyons, S., McManamen, A. M., Chen, A., Del Castillo, D., & Ruohola-Baker, H. (2021). Chemical Genetic Screen in Drosophila Germline Uncovers Small Molecule Drugs That Sensitize Stem Cells to Insult-Induced Apoptosis. Cells, 10(10), 2771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102771







