Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Synergies: Enhancing Soil Properties and Jujube Fruit Quality in Saline–Alkali Orchards of Southern Xinjiang
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis of Soil Properties
2.4. Soil DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.5. Fruit Sampling and Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application Treatments on Soil Physicochemical Properties
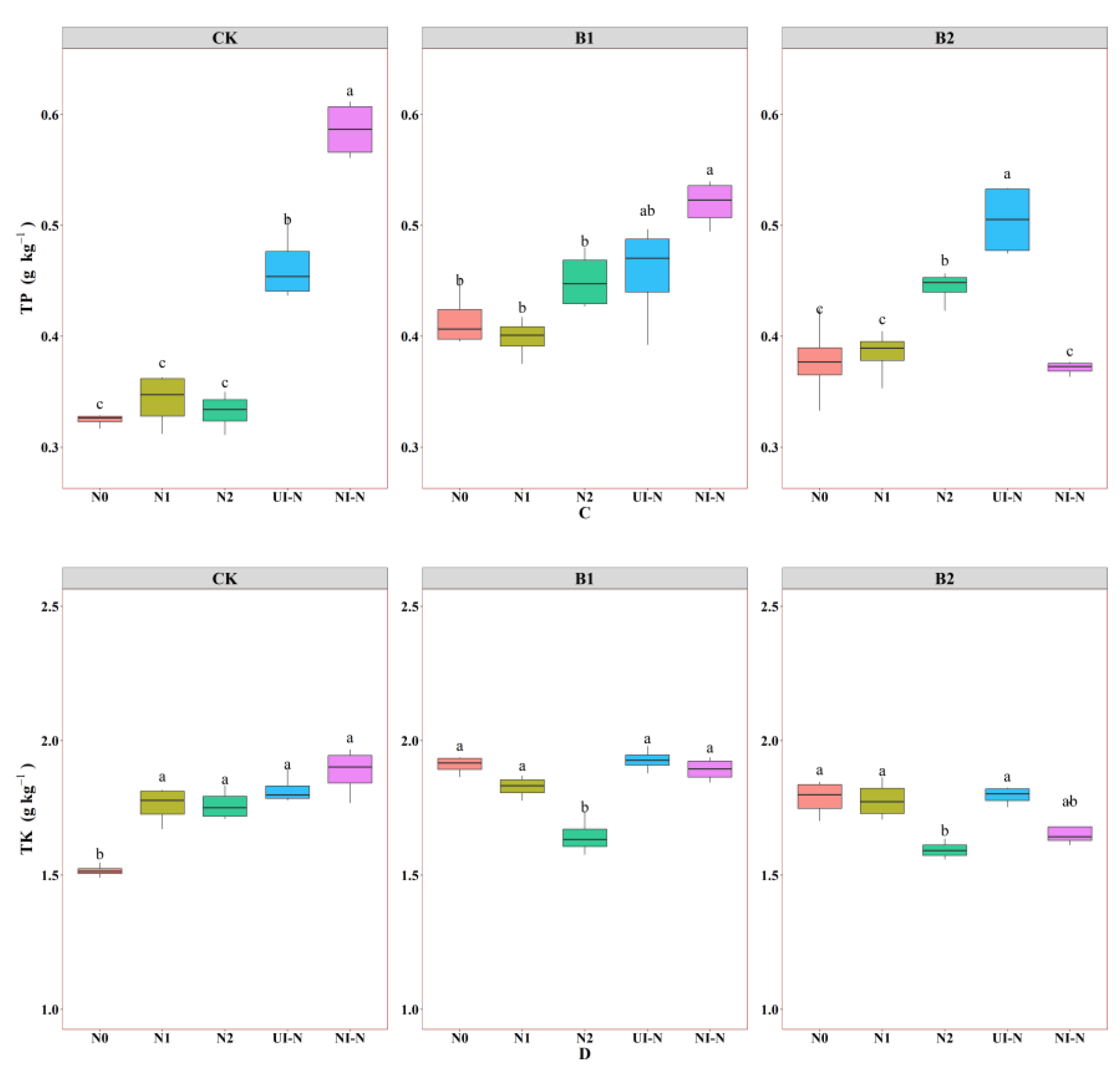
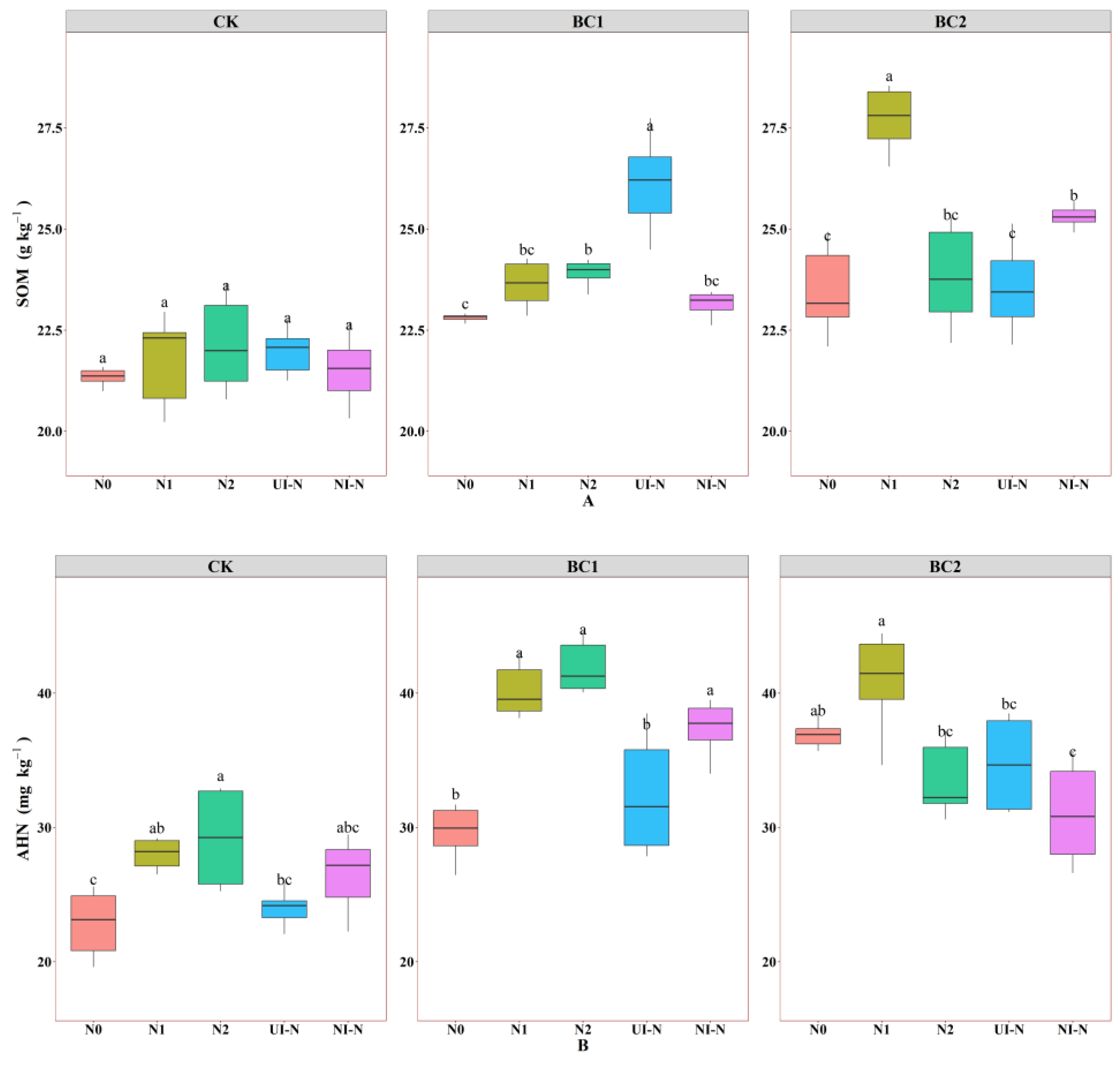
3.1.1. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application Treatments on Soil Total Nutrient Content
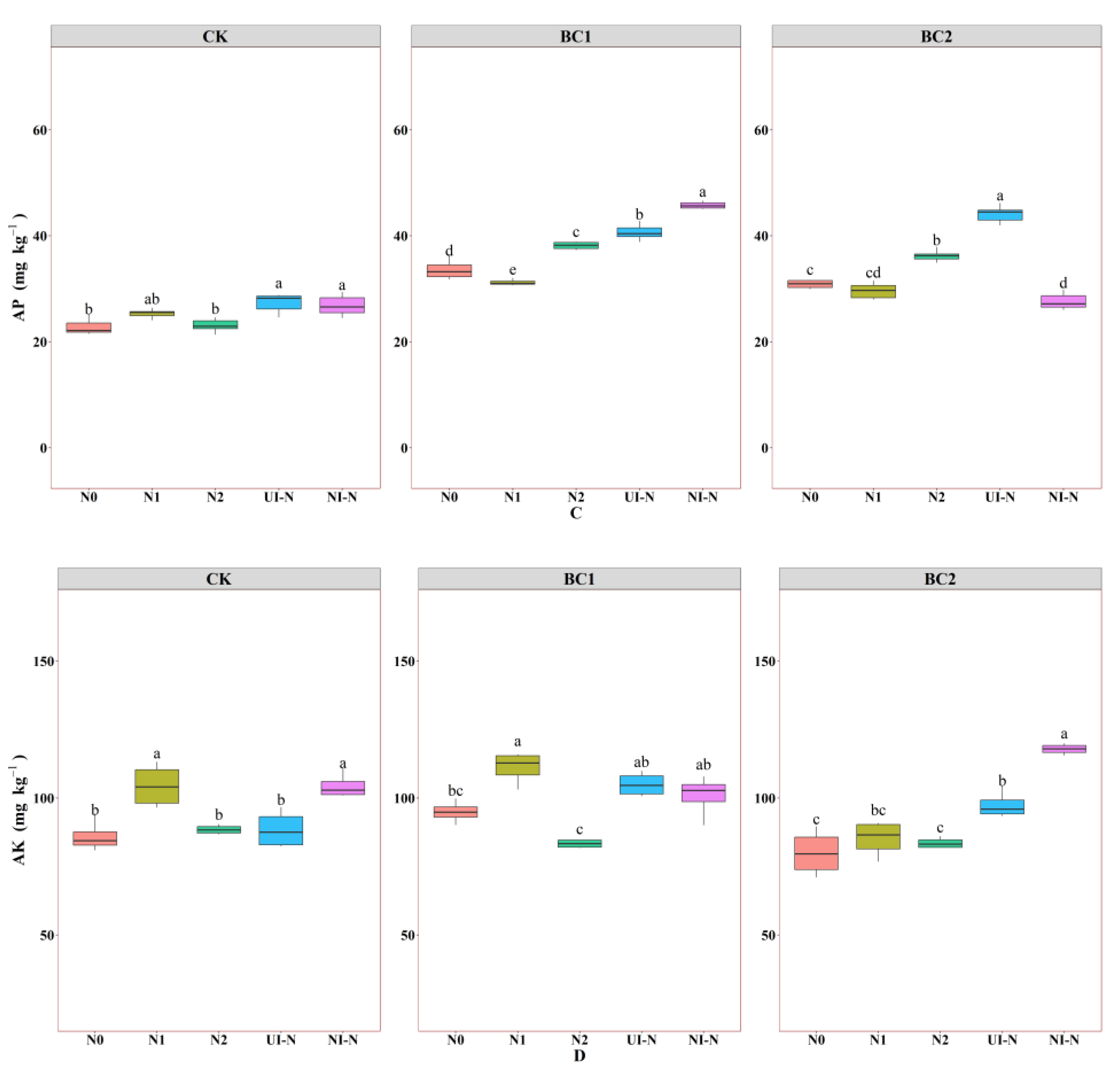
3.1.2. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application Treatments on Soil Available Nutrient Content
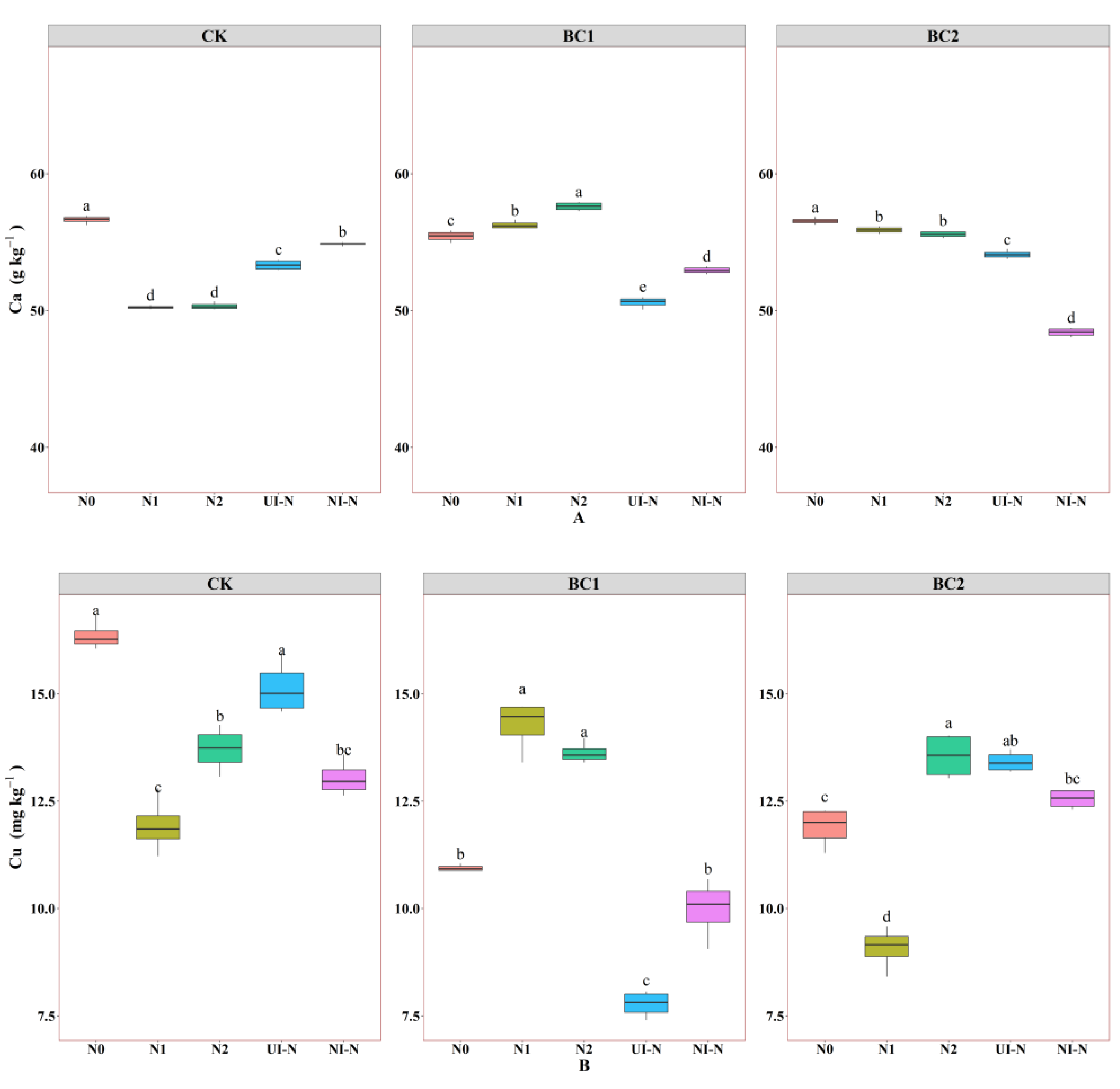
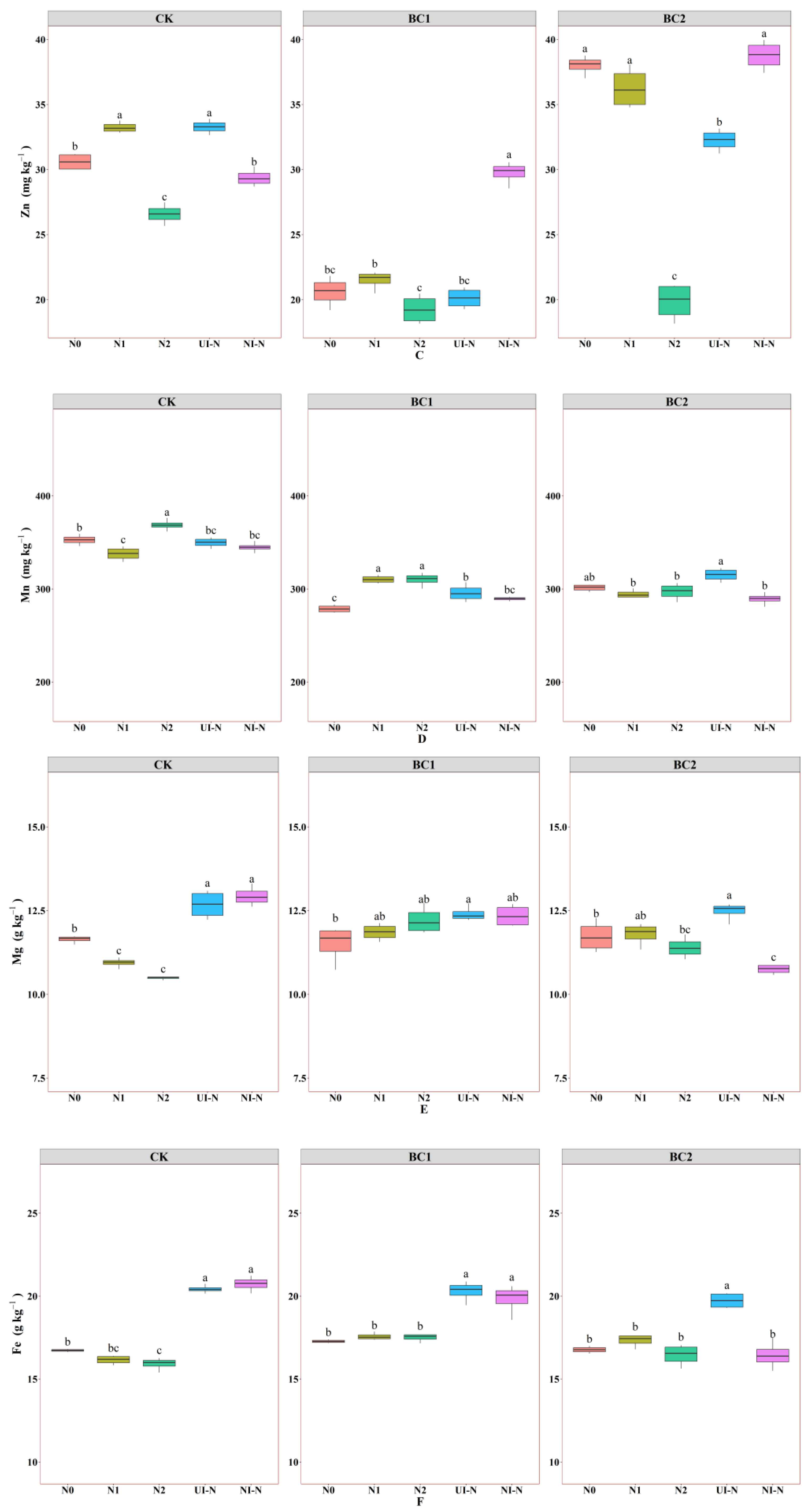
3.1.3. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Micronutrients and Trace Elements
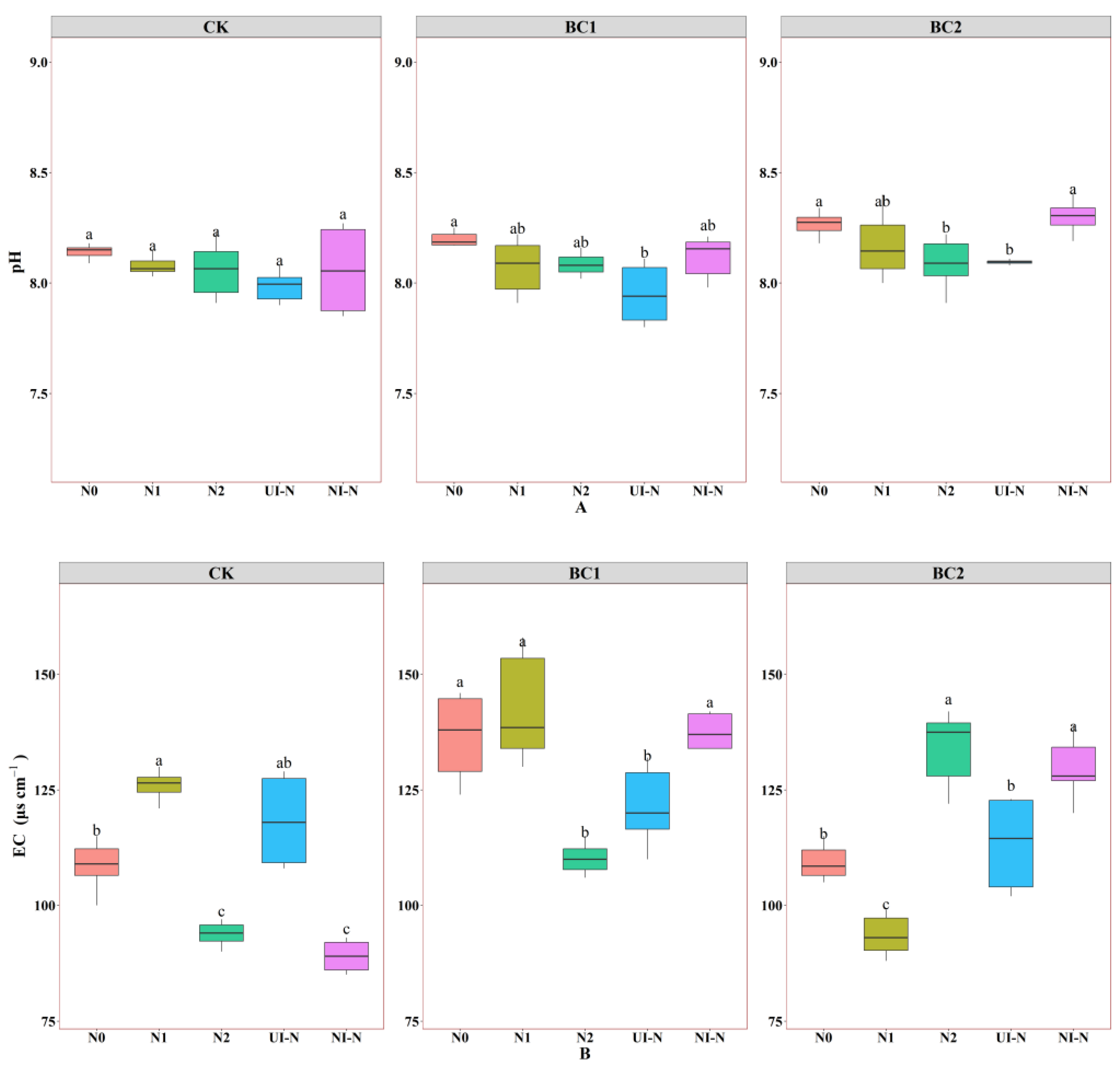
3.1.4. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application on pH and EC
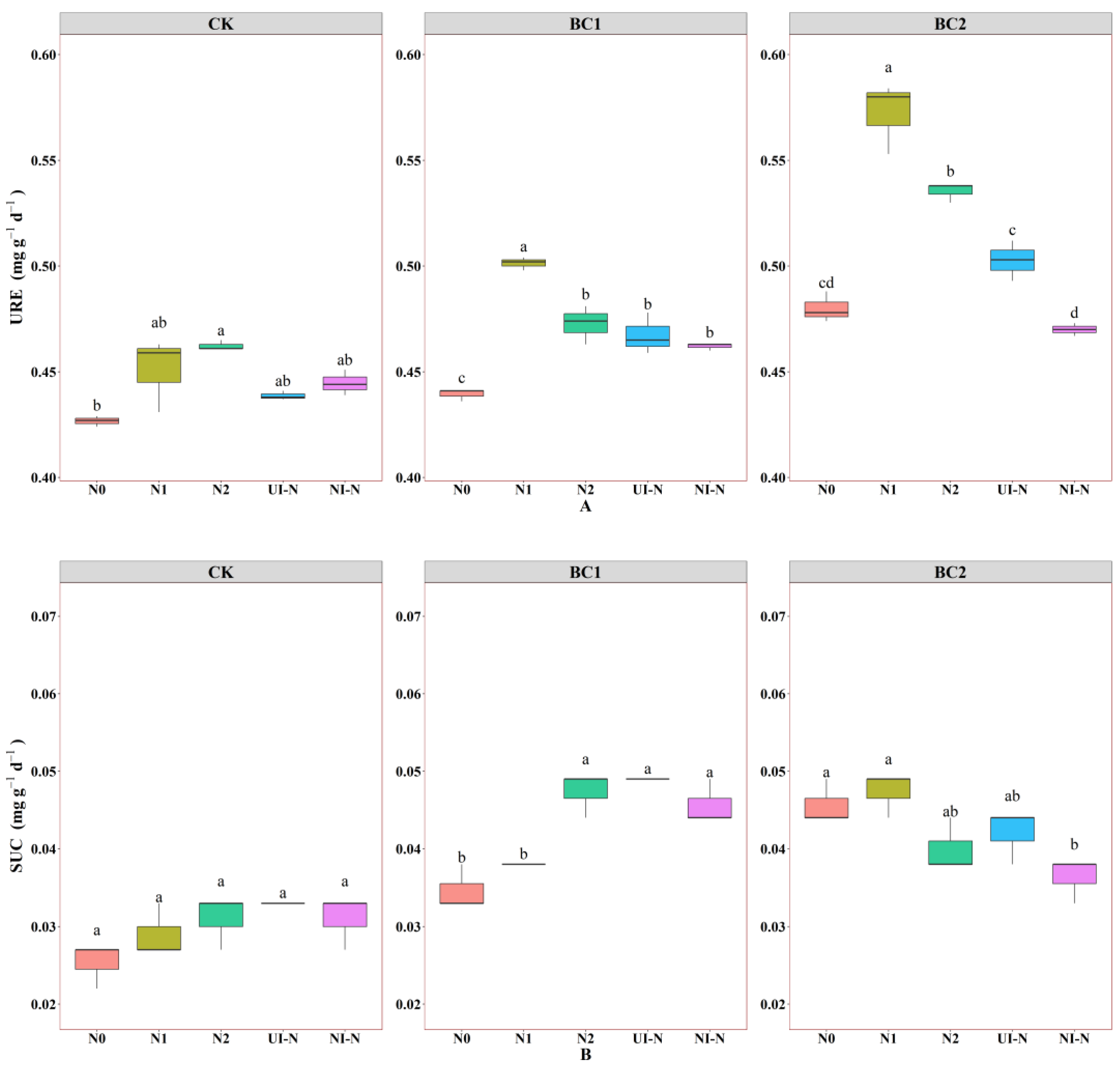
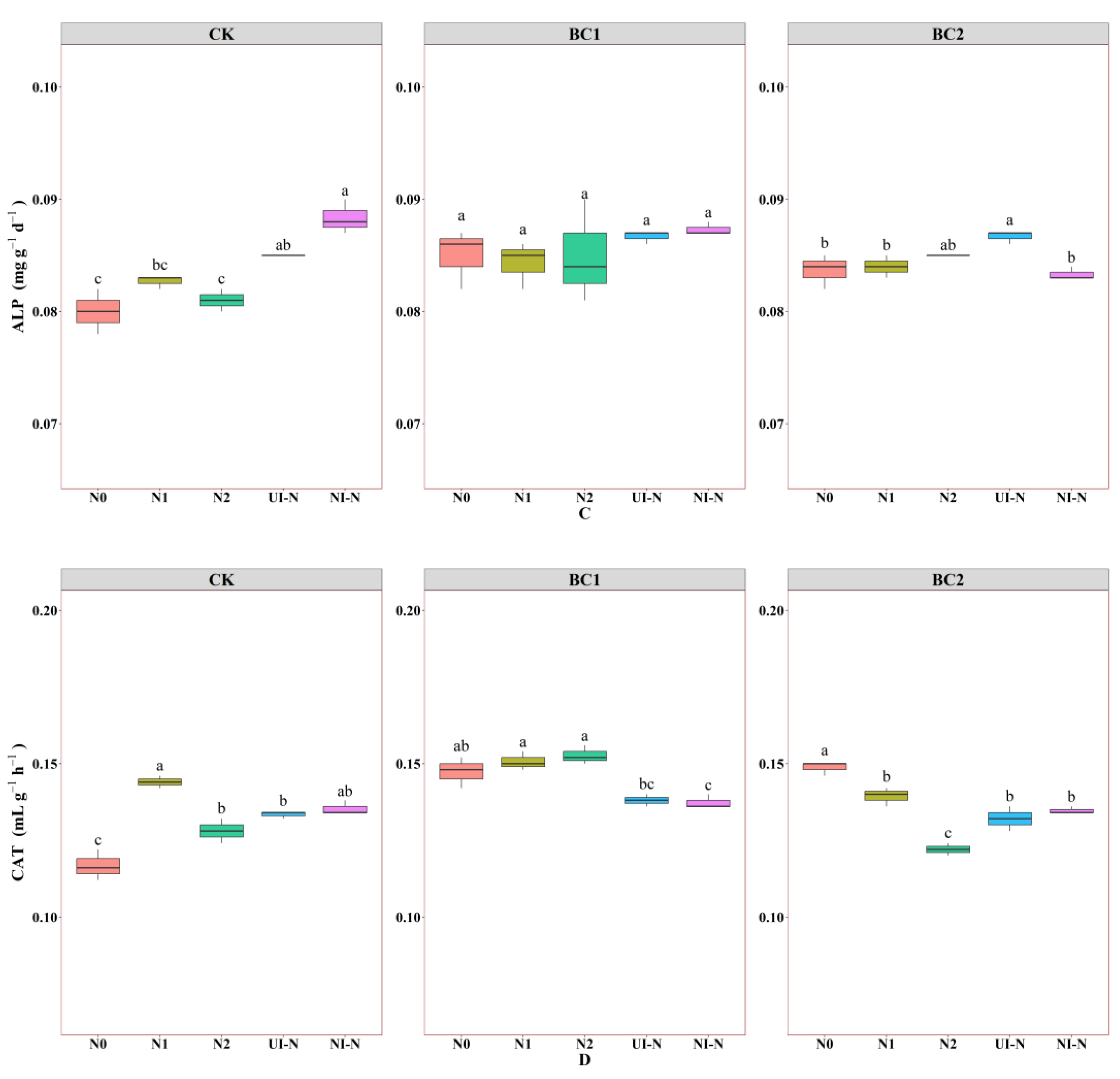
3.2. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Enzyme Activity
3.3. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Microbial Community Architecture
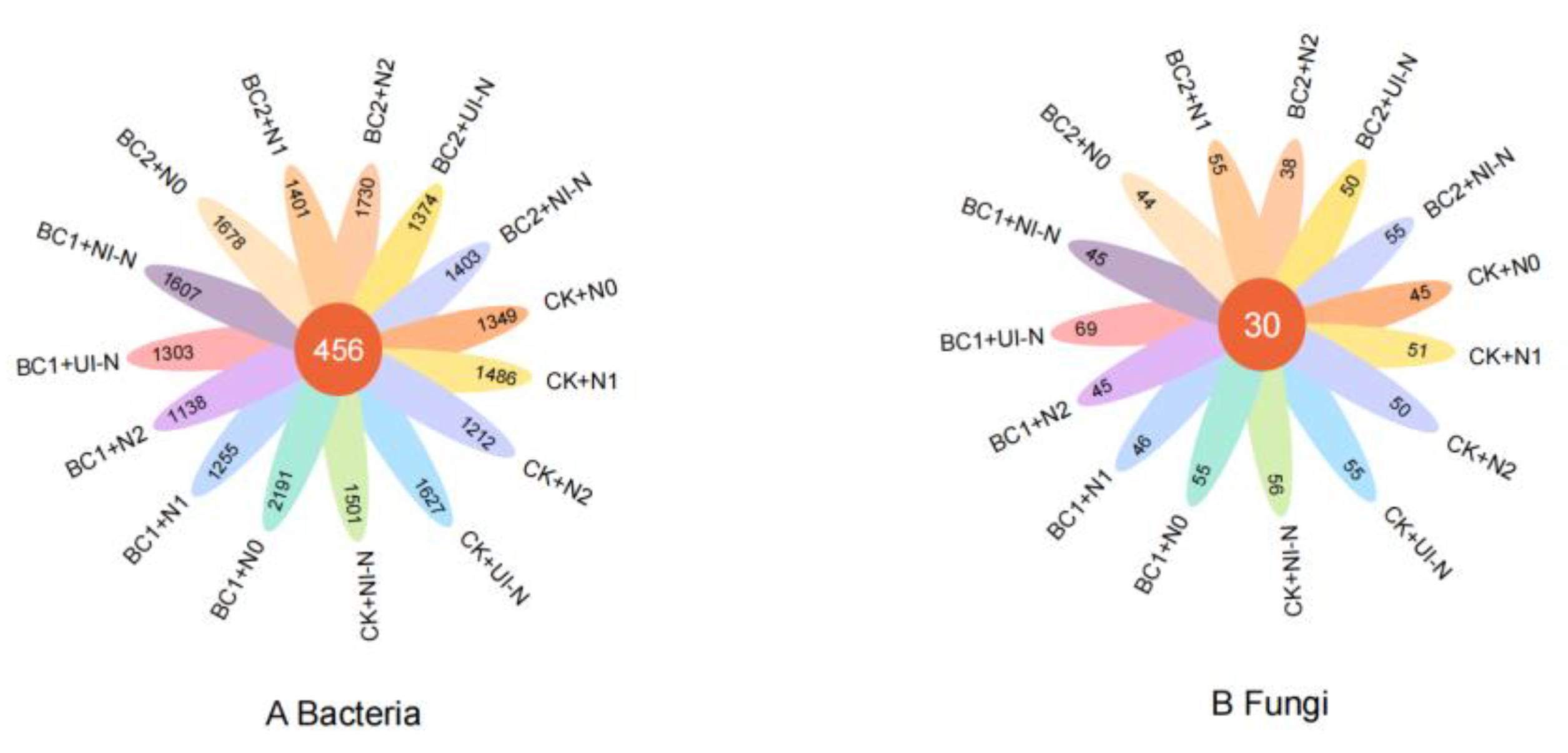
3.3.1. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application on the Abundance of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Microbial Communities
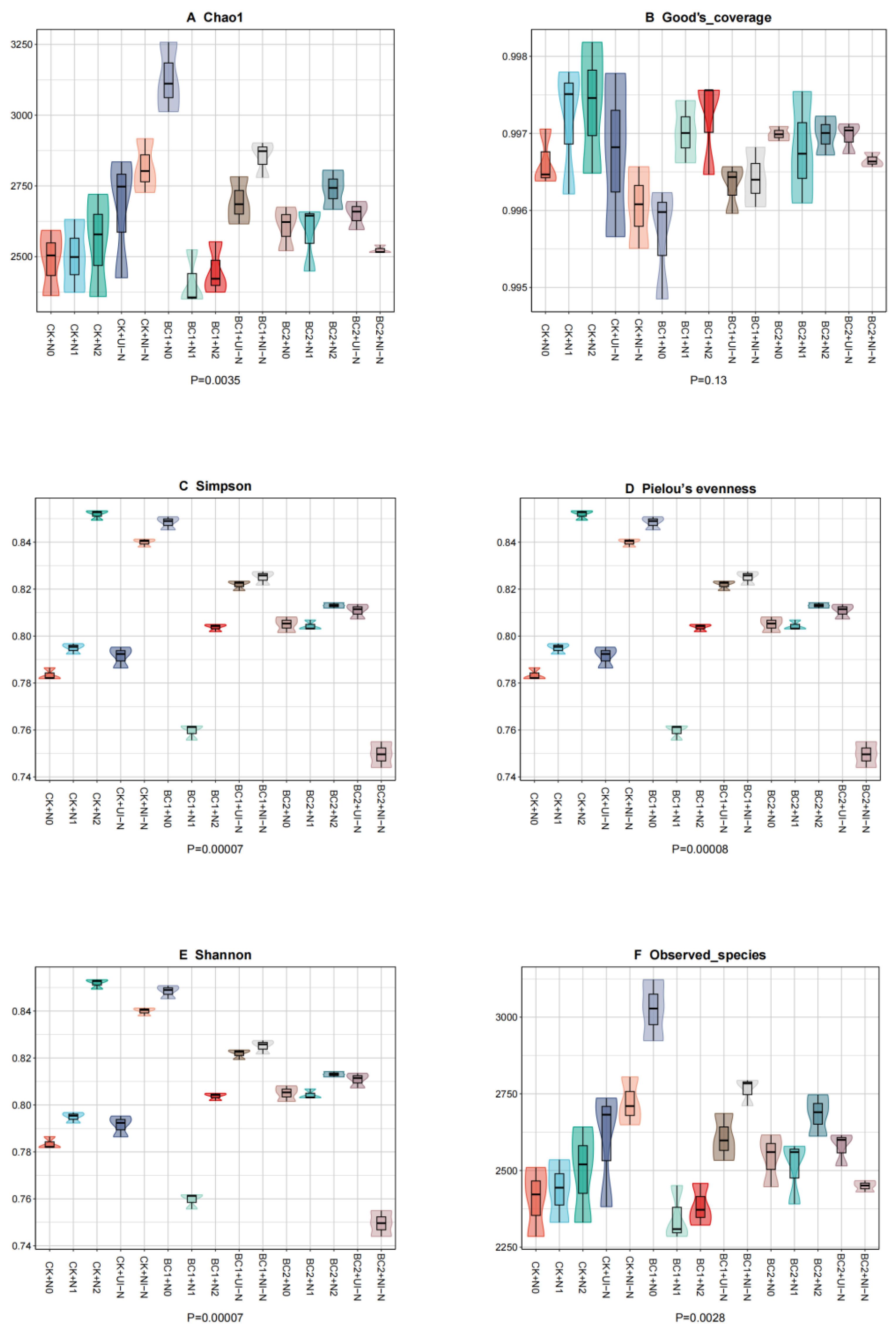
3.3.2. Effects of Different Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Microbial α-Diversity Indices
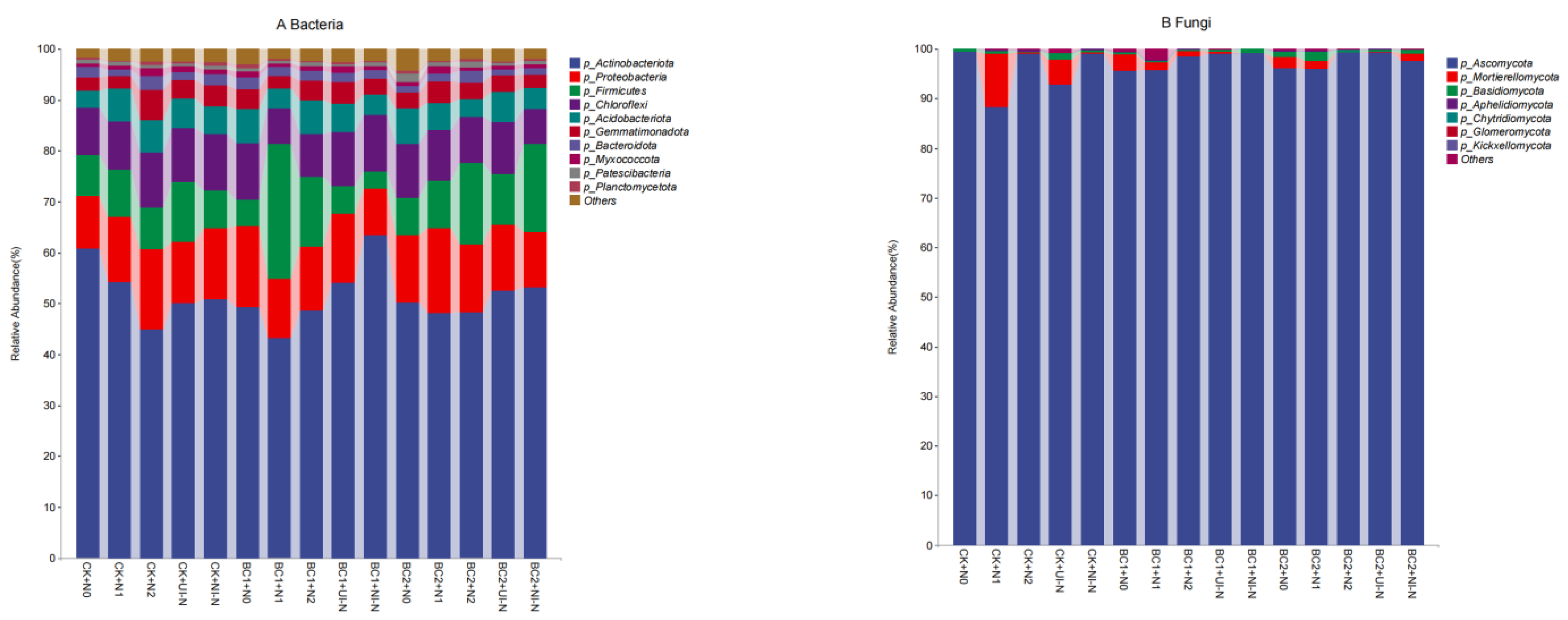
3.3.3. Effects of Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Microbial Community Structure at the Phylum Level
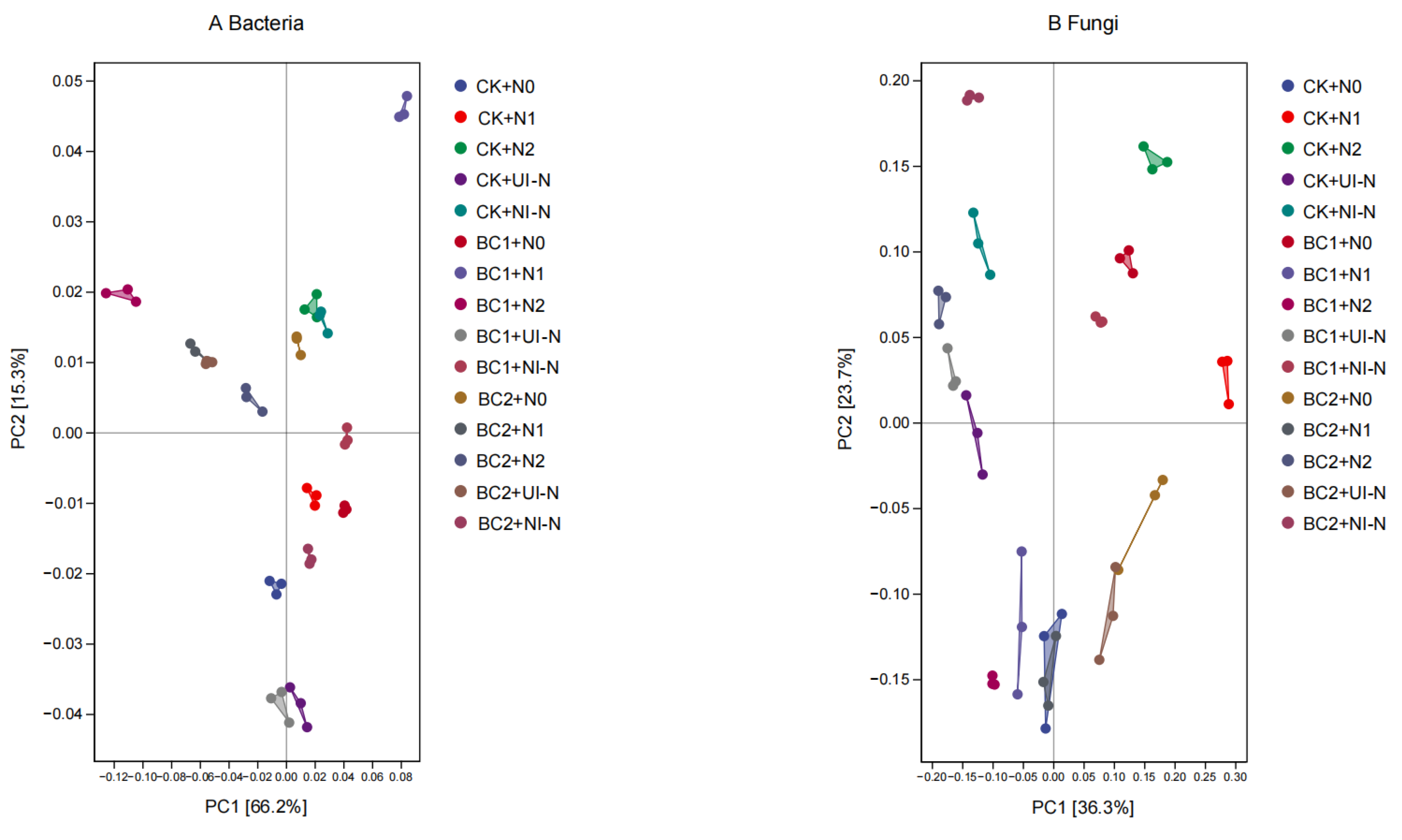
3.3.4. Effects of Different Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Microbial β-Diversity Indices
3.4. Effects of Different Biochar–N Co-Application on the Yield and Fruit Quality of Jujube
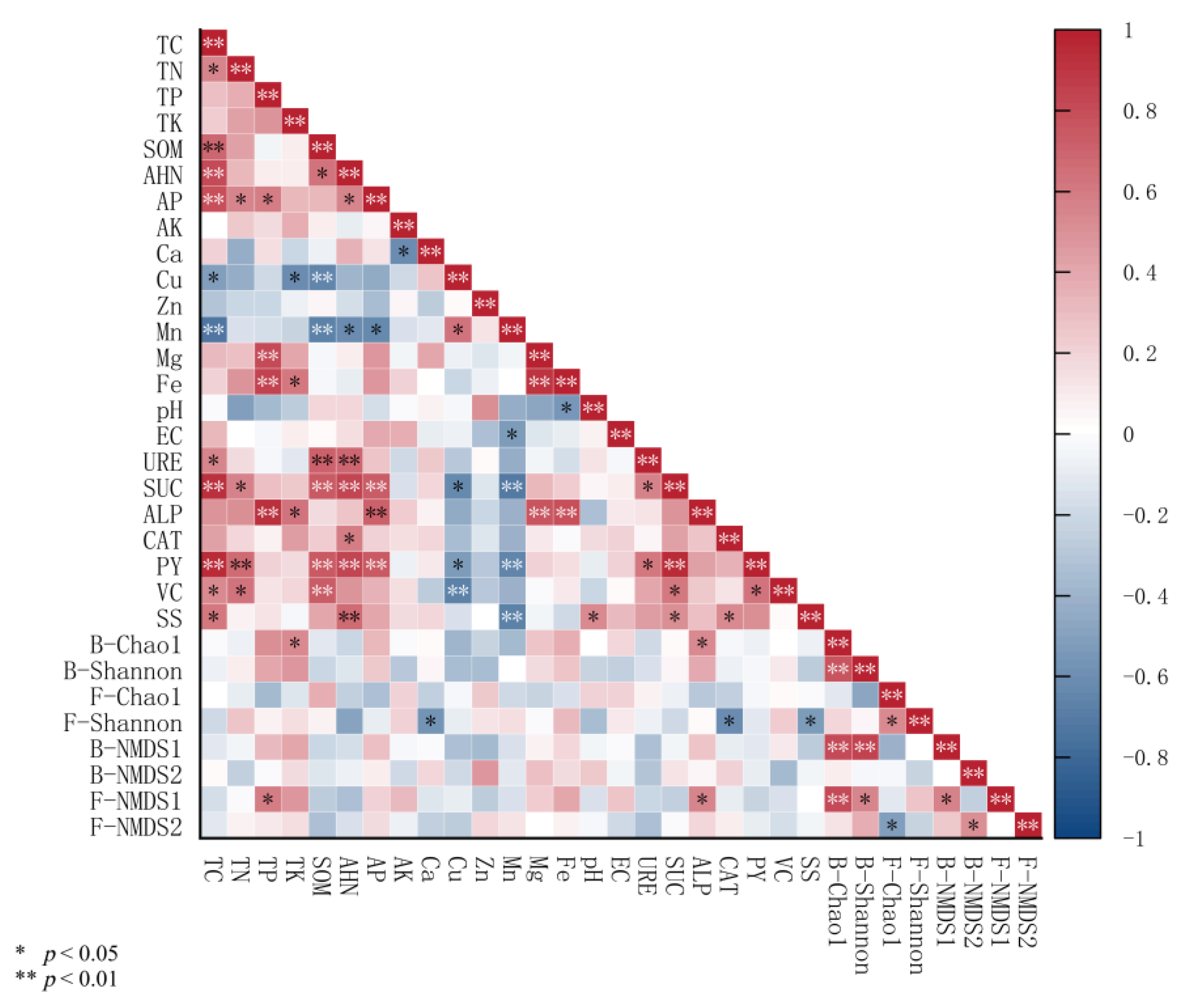
3.5. Correlation Analysis Between Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activities, Microbial Communities, and the Yield and Quality Traits of Jujube Fruits
3.6. Causal Pathways Revealed by Piecewise Structural Equation Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities
4.2. Impacts of Biochar–N Co-Application on Soil Microbial Community Structure
4.3. Impacts of Biochar–N Co-Application on Fruit Yield and Quality Attributes in Jujube
4.4. Synergistic Mechanisms Linking Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activities, and Microbial Communities to Fruit Yield and Quality in Jujube
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suman, J.; Rakshit, A.; Patra, A.; Dutta, A.; Tripathi, V.K.; Mohapatra, K.K.; Tiwari, R.; Krishnamoorthi, S. Enhanced Efficiency N Fertilizers: An Effective Strategy to Improve Use Efficiency and Ecological Sustainability. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 1472–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, W.; Craven, K.D.; Swenson, J.R.; Kataoka, R.; Mahmood, A.; Farias, J.G. Enhancing the Resilience of Agroecosystems Through Improved Rhizosphere Processes: A Strategic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ma, Z.; Chen, R.; Wen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Javed, T.; Li, W.; Wang, Z. Partial organic fertilizer replacing synthetic fertilizer reduces soil salinity, improves photosynthesis, and enhances the water-nitrogen use efficiency of maize (Zea maysl.) in arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 317, 109673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxing, L. The current situation of cultivated land degradation in the western regions of our country and its prevention and control measures. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Guo, Z.; Yang, X.; Su, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Ahmad, I.; Cai, T.; Han, Q. Straw incorporation helps inhibit nitrogen leaching in maize season to increase yield and efficiency in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 211, 105006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, M.; Li, R.; Rasul, F.; Shahzad, S.; Wu, C.; Shao, J.; Huang, G.; Li, R.; Almari, S.; et al. Soil acidification and salinity: The importance of biochar application to agricultural soils. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1206820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.-W.; Ding, J.; Ali, B.; Nawaz, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Ali, A.; Rasheed, A.; Khan, M.N.; Ozdemir, F.A.; Iqbal, R.; et al. Putting Biochar in Action: A Black Gold for Efficient Mitigation of Salinity Stress in Plants. Review and Future Directions. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 31237–31253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W. Reducing ammonia volatilization from paddy field with rice straw derived biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 660, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Yang, H.; Fan, X.; Gao, X.; Tai, J.; Sa, R.; Ge, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q. A microbial ecosystem enhanced by regulating soil carbon and nitrogen balance using biochar and nitrogen fertiliser five years after application. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, S.; Tian, C.; Chen, G.; Luo, N.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Biochar Blended with Nitrogen Fertilizer Promotes Maize Yield by Altering Soil Enzyme Activities and Organic Carbon Content in Black Soil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhu, X.; Song, X. Beneficial Effects of Biochar Application with Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil Nitrogen Retention, Absorption and Utilization in Maize Production. Agronomy 2023, 13, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Atav, V.; Gürbüz, M.A.; Kayalı, E.; Yalınkılıç, E.; Avcı, G.G.; Aydın, B.; Öztürk, O.; Özer, S.; Kıvrak, C.; Başaran, M. Efficient nitrogen use: Deep fertilizer, urease and nitrification inhibitors. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2024, 130, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.J.; Wood, R.H.; Rose, M.T.; Van Zwieten, L. A re-evaluation of the agronomic effectiveness of the nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP and the urease inhibitor NBPT. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Nauman Khan, M.; Luo, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, K.; Rana, M.S.; Hu, L.; Jiang, Y. Compensation of high nitrogen toxicity and nitrogen deficiency with biochar amendment through enhancement of soil fertility and nitrogen use efficiency promoted rice growth and yield. Glob. Chang. Biol. Bioenergy 2021, 13, 1765–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.M.M.; Rais, U.; Sultan, H.; Tahir, A.; Bahadur, S.; Shah, A.; Iqbal, A.; Li, Y.; Khan, M.N.; Nie, L. Residual Effect of Microbial-Inoculated Biochar with Nitrogen on Rice Growth and Salinity Reduction in Paddy Soil. Plants 2024, 13, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Duan, M.; Liu, B. Effects of Biochar Combined with Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction on Rapeseed Yield and Soil Aggregate Stability in Upland of Purple Soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Chang, Z.; Li, Z.; Joseph, J.; Yusuf, A.A.; Luo, X.; Hou, E. Biochar rate-dependent regulation of extended nitrogen supply by modifying stable aggregates-N and microbial responses. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, T.; Condron, L.; Kammann, C.; Müller, C. A Review of Biochar and Soil Nitrogen Dynamics. Agronomy 2013, 3, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, S.D.; Hemes, K.S.; Eichelmann, E.; Szutu, D.J.; Verfaillie, J.G.; Baldocchi, D.D. Effect of Drought-Induced Salinization on Wetland Methane Emissions, Gross Ecosystem Productivity, and Their Interactions. Ecosystems 2019, 23, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, D.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Reduced soil ecosystem multifunctionality is associated with altered complexity of the bacterial-fungal interkingdom network under salinization pressure. Environ. Res. 2025, 269, 120863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algethami, J.S.; Ibrahim, M.; Javed, W.; Alosaimi, E.H.; Irshad, M.K. Efficacy of Fe-BC in enhancing growth, photosynthesis, nutrition, and alleviating the toxicity of Cd and Cr in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): A tool for managing the environment and attaining sustainable agriculture. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasakul, Y.; Aursalung, A.; Thangsiri, S.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Inthachat, W.; Pongwichian, P.; Sasithorn, K.; Suttisansanee, U. Nutritional Compositions, Phenolic Contents and Antioxidant Activities of Rainfed Rice Grown in Different Degrees of Soil Salinity. Foods 2023, 12, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; He, P.; Leenaars, J.G.B.; Schut, A.G.T. Combining production ecology principles with random forest to model potato yield in China. Field Crops Res. 2024, 319, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Sun, W.; Yan, M.; Wu, C. Stage-Dependent Mineral Element Dynamics in ‘Junzao’Jujube: Ionic Homeostasis and Selective Transport Under Graduated Saline-Alkali Stress. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Fu, T.; He, G.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, M.; Lou, F.; He, T. Characteristics of rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial community of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris) grown in Karst area. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1241436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Fu, Y.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, S. Effects of Wheat Tempering with Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water on the Microbiota and Flour Characteristics. Foods 2022, 11, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, L.; Qin, Y.; Lu, B.; Xu, D.; Zhuang, W.; Shu, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Effects of seasonal changes on chlorophyll fluorescence and physiological characteristics in the two Taxus species. Plants 2023, 12, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hussain, A.; Arif, M.; Alkahtani, J.; AlMunqedhi, B.M.; Song, C. Genetic variability for salinity tolerance of tomato (Solanum lycopersicon MILL.) genotypes determined by stress tolerance indices. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2024, 36, 103386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; He, Q.; Hu, T.; Zhang, F. Responses of leaf nitrogen status and leaf area index to water and nitrogen application and their relationship with apple orchard productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ahmed, W.; Ye, C.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Dai, Z.; Khan, K.A.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z. Exploring the effect of different application rates of biochar on the accumulation of nutrients and growth of flue-cured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1225031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Hu, Z.; Wen, G.; Li, S.; Ke, X.; Sun, X.; Tao, M.; Jiang, X. Effects of 3-year biochar application on carbon sequestration, nitrogen retention and nitrate leaching of fluvo-aquic soil profiles in vegetable rotation fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 367, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, S. Influence of Green Manure Rapes Returning and Biochar Application on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Statuts of Newly Built Green Houses. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 2035–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Piao, J.; Miao, S.; Che, W.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Shiraiwa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Taniyoshi, K.; Hua, S.; et al. Long-term effects of biochar one-off application on soil physicochemical properties, salt concentration, nutrient availability, enzyme activity, and rice yield of highly saline-alkali paddy soils: Based on a 6-year field experiment. Biochar 2024, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Liu, Q.; Pan, F.; Yao, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, T.; Zou, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Research Advances in the Impacts of Biochar on the Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Communities of Saline Soils. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Wang, M.; Dong, Y.; He, M.; Dai, X. Effect of Coated Urease/Nitrification Inhibitor Synergistic Urea on Maize Growth and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 5207–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-J.; He, L.-L.; Liu, Y.-X.; Lyu, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Chen, Z.-M.; Chen, J.-Y.; Yang, S.-M. Effects of biochar combined with nitrification/urease inhibitors on soil active nitrogen emissions from subtropical paddy soils. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, K.; Fahad, S.; Jahangir, M.M.R.; Munir, I.; Alam, S.S.; Khan, S.A.; Mian, I.A.; Datta, R.; Saud, S.; Banout, J.; et al. Biochar and urease inhibitor mitigate NH3 and N2O emissions and improve wheat yield in a urea fertilized alkaline soil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Changes of bacterial community compositions after three years of biochar application in a black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, K.; Khan, A.; Sardar, K.; Fahad, S.; Saud, S.; Datta, R.; Danish, S. Effects of the nitrification inhibitor nitrapyrin and mulch on N2O emission and fertilizer use efficiency using 15N tracing techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 757, 143739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liang, X.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Tian, G.; Shi, J. Manure biochar influence upon soil properties, phosphorus distribution and phosphatase activities: A microcosm incubation study. Chemosphere 2015, 142, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Gao, J.; Zhou, B.; Hao, W.; Feng, D.; Sun, X. Effect of biochar on biochemical properties of saline soil and growth of rice. Heliyon 2023, 10, e23859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, H.; Efosa, N.; Oberson, A.; Krause, H.M.; Nägele, H.J.; Frossard, E.; Bünemann, E.K. Nitrogen dynamics after slurry application as affected by anaerobic digestion, biochar and a nitrification inhibitor. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 40, e12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, P.; Li, F.; Xi, J.; Han, Y. Effects of tillage and biochar on soil physiochemical and microbial properties and its linkage with crop yield. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y. The effects of biochar addition on soil physicochemical properties: A review. Catena 2021, 202, 105284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Riaz, M.; Zhang, L.; El-desouki, Z.; Jiang, C. Biochar Induces Changes to Basic Soil Properties and Bacterial Communities of Different Soils to Varying Degrees at 25 mm Rainfall: More Effective on Acidic Soils. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E. Growth of saprotrophic fungi and bacteria in soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N.; Dai, Z.; Xiao, K.; Meng, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Changes in microbial community structure due to biochars generated from different feedstocks and their relationships with soil chemical properties. Geoderma 2014, 226–227, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielak, A.M.; Barreto, C.C.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; van Veen, J.A.; Kuramae, E.E. The Ecology of Acidobacteria: Moving beyond Genes and Genomes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Shen, J.; Luo, Y.; Scheu, S.; Ke, X. Tillage, residue burning and crop rotation alter soil fungal community and water-stable aggregation in arable fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 107, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, N.M.; Clode, P.L.; Abbott, L.K. Microscopy Observations of Habitable Space in Biochar for Colonization by Fungal Hyphae From Soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gong, P.; Shi, Y. Effects of biochar, dual inhibitor, and straw return on maize yield, soil physicochemical properties, and microbial system under fertilization conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1570237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Sun, Q.; Ren, Z.; Xia, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, W. Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper. Open Life Sci. 2024, 19, 20220882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agegnehu, G.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bird, M.I. The role of biochar and biochar-compost in improving soil quality and crop performance: A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Xu, C.-Y.; Tahmasbian, I.; Che, R.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wallace, H.M.; Bai, S.H. Effects of biochar on soil available inorganic nitrogen: A review and meta-analysis. Geoderma 2017, 288, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, N.A.; Shafiq, F.; Ashraf, M. Ascorbic Acid-A Potential Oxidant Scavenger and Its Role in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 613–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Tong, C.; Hu, K.; Zhou, B.; Xing, S.; Mao, Y. Biochar-fertilizer interaction modifies N-sorption, enzyme activities and microbial functional abundance regulating nitrogen retention in rhizosphere soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y. Biochar stability in soil: Meta-analysis of decomposition and priming effects. Glob. Chang. Biol. Bioenergy 2015, 8, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zong, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J.; Jin, Y.; Zou, J. Response of soil carbon dioxide fluxes, soil organic carbon and microbial biomass carbon to biochar amendment: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. Bioenergy 2015, 8, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.A.; Chen, C.; Jensen, T. Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors Impact on Winter Wheat Fertilizer Timing, Yield, and Protein Content. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Gou, J. Biochar enhances the retention capacity of nitrogen fertilizer and affects the diversity of nitrifying functional microbial communities in karst soil of southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, E.; Thornton, B.; Midwood, A.J.; Osborne, S.M.; Sim, A.; Millard, P. Atmospheric CO2 enrichment and nutrient additions to planted soil increase mineralisation of soil organic matter, but do not alter microbial utilisation of plant- and soil C-sources. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2434–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welutung, P.; Pengthamkeerati, P.; Tawornpruek, S.; Kachenchart, B. Fertilizer Rate and Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors Effects on Soil Inorganic Nitrogen and Sugarcane Yields in Central Thailand. Sugar Tech 2023, 25, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, W.; Li, P.; Shi, P.; Xu, G.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on different potato varieties growth, yield and resources use efficiency in the Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 261, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, K.P.; Harikumar, V.S.; Balakrishna, K.M.; Varghese, T. Inhibitory effect of TiO2 NPs on symbiotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in plant roots. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighe-Neira, R.; Carmora, E.; Recio, G.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Reyes-Diaz, M.; Alberdi, M.; Rengel, Z.; Inostroza-Blancheteau, C. Metallic nanoparticles influence the structure and function of the photosynthetic apparatus in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 130, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Wu, M.; Che, S.; Yuan, S.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Tian, P.; Wu, L.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z. Effects of Continuous Straw Returning on Soil Functional Microorganisms and Microbial Communities. J. Microbiol. 2023, 61, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robin-Soriano, A.; Vincent, B.; Maurice, K.; Battesti, V.; Boukcim, H.; Ducousso, M.; Gros-Balthazard, M. Digging deeper into the impacts of different soil water systems on the date palm root architecture and associated fungal communities. Symbiosis 2025, 95, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | Biochar | Urea | Urease-Inhibited N Fertilizer (45%N) | Nitrification- Inhibited N Fertilizer (45%N) | Superphosphate | Potassium Sulfate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | N0 | 0 | 0 | 150 | 150 | ||
| N1 | 0 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| N2 | 0 | 450 | 150 | 150 | |||
| UI-N | 0 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| NI-N | 0 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| BC1 | N0 | 5000 | 0 | 150 | 150 | ||
| N1 | 5000 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| N2 | 5000 | 450 | 150 | 150 | |||
| UI-N | 5000 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| NI-N | 5000 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| BC2 | N0 | 15,000 | 0 | 150 | 150 | ||
| N1 | 15,000 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| N2 | 15,000 | 450 | 150 | 150 | |||
| UI-N | 15,000 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
| NI-N | 15,000 | 250 | 150 | 150 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y. Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Synergies: Enhancing Soil Properties and Jujube Fruit Quality in Saline–Alkali Orchards of Southern Xinjiang. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092205
Liu H, Ma Y, Wei Y, Wu C, Zhang Y. Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Synergies: Enhancing Soil Properties and Jujube Fruit Quality in Saline–Alkali Orchards of Southern Xinjiang. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092205
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haoyang, Yunqi Ma, Yuxuan Wei, Cuiyun Wu, and Yuyang Zhang. 2025. "Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Synergies: Enhancing Soil Properties and Jujube Fruit Quality in Saline–Alkali Orchards of Southern Xinjiang" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092205
APA StyleLiu, H., Ma, Y., Wei, Y., Wu, C., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Synergies: Enhancing Soil Properties and Jujube Fruit Quality in Saline–Alkali Orchards of Southern Xinjiang. Agronomy, 15(9), 2205. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092205





